Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
|
|
|
- Angelina Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The crystalline structure, anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR), and magnetization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (LSMO/STO) superlattices grown by an rf sputtering system are systematically analyzed to study the spin polarization of manganite at interfaces. A perfectly epitaxial growth with sharp interfaces between LSMO and STO layers is confirmed by the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image and the x-ray diffraction. The presence of positive low-temperature AMR in LSMO/STO superlattices with thinner LSMO layers or thicker STO layers implies that two bands of majority and minority character contribute to the transport properties, leading to a reduced spin polarization. Furthermore, the magnetization of superlattices follows the T 3/2 law at low temperatures and decays more quickly as the thickness ratio d STO /d LSMO increases, corresponding to a reduced exchange coupling. The results clearly show that the spin polarization is strongly correlated with the influence of interface-induced strain on the structure. PACS numbers: Gk, d, Cn 1
2 Manganites of the type R 1-x A x MnO 3 (R = rare earth, A = Ca, Sr, Ba, and Pb) are considered to be half-metallic and therefore ideal candidates for the use in spin-electronic devices. Recently, a tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio of more than 1800% at 4 K for La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 /La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 trilayer junctions was obtained, 2 leading to an inferred electrode spin polarization of at least 95%. However the reported low-field magnetoresistance for these manganite-based devices decreases rapidly with increased temperature, and even vanishes at temperatures well below the Curie temperature of bulk manganites. It is generally believed that tunneling is a mechanism occurring near the electrode/barrier interface, and the TMR is dominated by charge carriers near the interface boundary. 3, 4 In particular, the rapid decrease of the spin polarization at interfaces with increasing temperature would thus limit the application of the half-metallic materials for spin-electronics devices. That points to an important issue in the physics of their interface properties. Ferromagnetic manganite-insulator superlattices, containing many interfaces of interest, offer the possibility to probe the properties of ultrathin manganite layers and the interface magnetism. Up to now, several groups have reported on the fundamental properties of La 1-x A x MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (A= Ca, Sr, and Ba) superlattices. 5-9 For example, Sahana et al. 5 and Dörr et al. 6 have studied the magnetic and transport properties of 2
3 La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (LSMO/STO) superlattices. They observed the suppression in both T C and magnetization accompanying an increase of resistivity as the thickness of LSMO layers decreases. An enhanced high-field magnetoresistance implicated in the magnetically disordered interfaces for La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /STO superlattices was reported by Jo et al. 7 Various magneto-transport properties of manganite-insulator superlattices have been attributed to the strain effect, 8 or interlayer coupling. 9 However, for the ferromagnetic manganite-based superlattices, surprisingly few studies have so far been made on the central problem of the spin polarization in ultrathin manganite layers. This is a key issue for the fabrication of any spin-electronic device composed of manganite/insulator tunneling interfaces. In this paper we report on the anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) and the low-temperature magnetization of LSMO/STO superlattices grown on (001) LaAlO 3 substrates. The AMR, being a property determined by the contributions of majority and minority current, can offer information on the spin-dependent band structure. 10 On the other hand, the temperature-dependent magnetization of ferromagnetic superlattices will reflect the temperature dependence of spin polarization near the interfaces. A reduced-spin polarization and a rapidly decreased magnetization with an increase of temperature for superlattices with thinner LSMO layers or thicker STO layers are reported and discussed. 3
4 LSMO/STO superlattices grown on (001) LaAlO 3 substrate were prepared in an rf magnetron sputtering system as previously described. 11 A buffer STO layer of 60 nm in thickness was deposited prior to the growth of LSMO/STO superlattices to diminish the substrate-induced strain. LSMO and STO layers were alternatively deposited at 700 o C in 300-mTorr sputtering gas (Ar and O 2, 3:7) until the desired thickness of a superlattice was reached. Sharp interfaces and uniformly continuous layers in superlattices were confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The epitaxial growth of superlattices was characterized by an x-ray θ-2θ diffractometer using Cu-K α radiations. For transport measurements, films were photo-lithographically patterned to a 100-µm long by 50-µm wide bridge. The resistivities and magnetizations of superlattices were measured by the standard four-terminal method, and by a superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer, respectively. Figure 1 is a high-resolution cross-sectional TEM lattice image of a LSMO/STO superlattice denoted by (76/56) 12 in [010] direction, where the numbers in parentheses correspond respectively to the thicknesses of LSMO and STO layers, and the subscript denotes the total repeated number of bilayers. This figure shows a perfectly epitaxial growth with sharp interfaces between LSMO and STO within less than 1 nm. Furthermore, the TEM analysis shows that the superlattice maintains the 4
5 in-plane crystal coherency at the interfaces with an in-plane lattice constant of Å, which ranges just between the lattice constant of 3.79 Å for the LaAlO 3 and the pseudocubic lattice constant of Å for bulk LSMO. 12 This indicates that the LSMO and STO (a axis = Å) layers are in an in-plane compressive stress state due to a smaller lattice constant of substrate. 8 Normally along the film there can be seen a slightly incoherent growth with out-of-plane lattice constants of and Å in LSMO and STO layers, respectively. This corresponds to an elongation of the c axis by Å for LSMO and a negligible c-axis strain in STO layers. The presented TEM image shows a more clearly coherent hetrostructure with sharp interfaces than that reported on LSMO/STO superlattices grown by pulsed laser deposition. 6 It also demonstrates that high-quality perovskite superlattices can be achieved by a lower-cost sputtering technique. Figure 2(a) shows the x-ray θ-2θ diffraction spectra in the region near the (002) peak for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices. Clearly, the 2θ position of the (002) peak, which corresponds to the out-of-plane lattice constant, is dependent on the layer thickness in LSMO/STO superlattices, indicating a variation of out-of-plane strain among these superlattices. The observed average c-axis lattice constant of Å for the (76/56) 12 superlattice is close to that seen in the TEM image. For the (142/82) 6 and (76/147) 12 superlattices, the determined average c-axis lattice constants are Å and Å respectively. 5
6 To put it briefly, for a superlattice with thicker STO layers or thinner LSMO layers, an enhanced c-axis lattice was observed. This feature is similar to that observed in LSMO/STO superlattices grown on STO substrates. 5 Figure 2(b) shows the x-ray scan for sample (76/147) 12, in which only the (001) and (002) diffraction peaks of film were observed, also indicating that the film has growth that is oriented along the c-axis. Furthermore, the in-plane orientation of the superlattices has been studied by the x-ray Φ-scanning on the orthorhombic (332) LSMO diffraction peak. The inset of Fig. 2(b) gives a typical pattern for (76/56) 12 superlattice. As can be seen, the fourfold symmetry of this pattern clearly indicates the in-plane epitaxial structure. In Fig. 2(a), the presence of the satellite peaks on both sides of the main peak (002) confirms that a periodic structure in the superlattices has been achieved. The modulation wavelength, Λ = d LSMO + d STO, where d LSMO and d STO are the thickness of the LSMO and STO layers respectively, can be calculated from the separation of two successive peaks (i and i +1) using the equation: Λ = (λ/2)[1/(sinθ i - sinθ i+1 )], where λ is the x-ray wavelength (λ = Å). The modulation wavelength Λ = 128 Å obtained from the x-ray data for (76/56) 12 superlattice is in close agreement with that of 132 Å observed in the TEM image. Figure 3 shows the zero-field resistivities ρ as a function of temperature for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices and the LSMO film. The inset of Fig. 3 illustrates 6
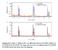
7 the temperature dependence of the magnetoresistance ratio, defined as MR(7 T) = [ρ(h = 7 T) ρ(h = 0)]/ρ(H = 7 T), for the corresponding samples. It can be seen that with decreasing d LSMO or increasing d STO, the value of ρ increases, and ρ reveals a metallic state at low temperatures for all superlattices. Also visible in the inset of Fig. 3 is that a maximum MR(7 T) value occurs near the Curie temperature for all the superlattices and the 800-Å LSMO film. The maximum MR values for LSMO/STO superlattices occurring at temperatures K are in the range of 37 38%, which is slightly smaller than that of 41% at 352 K for the LSMO film. Figure 4 shows the temperature dependence of AMR for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices. The AMR is defined as AMR(7 T) = MR(7 T) // - MR(7 T), where MR(7 T) // and MR(7 T) denote the longitudinal (H // the electric current) and transverse (H the electric current) magnetoresistance ratio, respectively. Here the data were obtained with currents along crystal [100] direction, and magnetic fields applied in the film plane to eliminate the demagnetization effect. It can be observed that the AMR behavior is markedly different among the superlattices with different thicknesses of LSMO or STO layers. For example, the AMR of (76/56) 12 superlattice shows a negative value of -2% at low temperatures that gradually diminishes at higher temperatures; whereas the AMR for (76/147) 12 superlattice, a sample with thicker STO layers, shows a positive value of 3.4% at low temperatures. It is found that the 7
8 low-temperature AMR value increases gradually and changes to a positive value for superlattices with thinner LSMO layers or thicker STO layers. The top inset of Fig. 4 shows the AMR behavior of the 800-Å LSMO film for comparison. One can find that the AMR of LSMO film at low temperatures is very low, around -0.06%, then gradually drops to the lowest point of -8.9% at the highest temperature measured. This presents a very similar feature compared to that of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films observed by Ziese, 10 but a quit different behavior from that of the superlattices studied. The excess negative AMR near T C for high-quality manganite films has been suggested to be related to the inhomogeneous magnetic state. 13 Moreover, contrary to the high-quality epitaxial films, the AMR, being highest at low temperatures with no clear peak near T C, was also observed in a polycrystalline La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 film. 10 Since the grain-boundary or interface-scattering resistance is isotropic and will be canceled in the calculation of the AMR, the anisotropic transport properties have been suggested to be related to the local lattice distortions of the Mn-O bonds. 13 Thus, the AMR reflects an intrinsic transport property and is related to the crystalline structure. This gives a good account for the variegated AMR behaviors observed in the LSMO/STO superlattices. It must be recalled here that a variation of out-of-plane strain can be deduced from the x-ray results, as previously mentioned. Turning now to concentrate on the low-temperature AMR features of LSMO/STO superlattices, Ziese 8
9 has recently analyzed the AMR behaviors of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 and Fe 3 O 4 films within the two-current model and an atomic d-state calculation. 10 For the La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 film, in which a negative AMR was observed, he pointed out a weak influence of a minority spin band. Additionally, based on the observation of a positive AMR in the Fe 3 O 4 film, it was suggested that at least two bands of majority and minority character contribute to the transport properties of Fe 3 O 4, leading to its lower spin polarization. The same is true of the presented case for LSMO/STO superlattices. The presence of positive AMR in LSMO/STO superlattices with thinner LSMO layers or thicker STO layers implies a reduced spin polarization occurring in them. The lower inset of Fig. 4 shows the hysteretic AMR curve associated with the normalized magnetization M/M(H = 5 kg) of the (76/82) 12 superlattices performed at 5 K. It can be seen that the AMR remains nearly constant as the magnetization saturates, while an anomalous AMR behavior appears at low fields. Considering that the magnetization is not fully aligned in the low-field region, the low-field AMR is supposed to contain an extrinsic contribution originating from the grain-boundary or interface magnetization anisotropy. 14 The nearly field-independent AMR observed in the high-field region also indicates that the Lorentz force effect is suppressed in the LSMO/STO superlattices with increasing the spacer layer thickness. It is known the Lorentz force bends the trajectory of the carriers and then contributes a positive MR at high fields for the 9
10 transverse configuration. If the Lorentz mechanism dominates the AMR at high fields, it may be expected that the AMR value will be negative and decrease with increasing fields according to the definition of AMR = MR // - MR. In fact, a marked Lorentz-force-like contribution is observed only on the high-field AMR of the LSMO film (not shown). The results give evidence that the AMR behavior is controllable by the artificial superlattices. To explore the temperature dependence of spin polarization P(T), a convenient method is to study the temperature dependence of magnetization M(T). 15, 16 The measurement of M(T) on LSMO/STO superlattices is supposed to reflect the P(T) over the ultrathin LSMO layers. The M(T), being proportional to P(T), should follow the T 3/2 law according to M(T)/M(0) = 1- CT 3/2 = 1- kc bulk T 3/2, where C bulk is the constant describing the decrease of the bulk magnetization due to thermal excitation of the spin wave, and k = 2 for the ideal surface case. 17 Figures 5(a) and 5(b) show the normalized magnetization M/M(5 K) measured with H = 500 G as a function of T 3/2 for two series of superlattices with varied thicknesses of STO layers and LSMO layers respectively. It can be seen that the M(T) follows the T 3/2 law at temperatures below 140 K for all the superlattices and the LSMO film. It can also be seen that the M(T) of superlattices decays more quickly with increasing temperature, corresponding to a fast decay of P(T), as the STO layers become thicker or the LSMO layers become thinner. 10
11 It is found that the value of constant C increases with an increase of d STO /d LSMO ratio, as shown in the inset of Fig. 5(a). Taking k = 1 for the LSMO film, the parameter k of superlattices also shows a monotonous increase with an increase of d STO /d LSMO ratio, as seen in the inset of Fig. 5(b). The presented values of k, in the range of , are comparable to those in the range of derived from the P(T) of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 TMR devices. 16 It is noteworthy that the parameter k can be a measure of the exchange coupling J on a path perpendicular to the interfaces. 15 According to Mathon, 18 the value of k = 3.0 for the (76/147) 12 superlattice corresponds to J /J 0.3, where J is the exchange interaction in the bulk. It is known that a reduced exchange coupling should not completely separate the majority carrier conduction band from the minority band, leading to an incomplete polarization of the carriers. 19 This result is consistent with the inference from the AMR properties previously discussed. In summary, high-quality LSMO/STO superlattices have been grown in an rf sputtering system, and characterized by the TEM image, x-ray diffraction, and resistive measurement. These superlattices offer a good opportunity to probe the properties of ultrathin manganite layers and the interface magnetism. According to Ziese, 10 the presence of positive low-temperature AMR in LSMO/STO superlattices with thinner LSMO layers or thicker STO layers implies that at least two bands, of 11
12 majority and minority character, contribute to the transport properties, leading to a reduced spin polarization. Furthermore, the M(T) of superlattices follows the T 3/2 law at low temperatures and decays more quickly as the d STO /d LSMO ratio increases. The results clearly show that the spin polarization is strongly correlated with the influence of interface-induced strain on the structure. The interface-induced strain must be taken into account in the fabrications of TMR devices based on doped manganites. The author thanks the National Science Council of the Republic of China for financial support under Grant Nos. NSC M and NSC AT. This work was also partially supported by Da-Yeh University under Grant No. ORD
13 References 1. E. D. Wollan and W. C. Köhler, Phys. Rev. 100, 5643 (1955). 2. M. Bowen, M. Bibes, A. Barthélémy, J.-P. Contour, A. Anane, Y. Lemaître, and A. Fert, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 233(2003). 3. J. H. Park, E. Vescovo, H. J. Kim, C. Kwon, R. Ramesh, and T. Venkatesan, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1953(1998). 4. Jagadeesh S. Moodera, Janusz Nowak, and Rene J. M. van de Veerdonk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2941(1998). 5. M. Sahana, T. Walter, K. Dörr, K.-H. Müller, D. Eckert, and K. Brand, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 6834 (2001). 6. K. Dörr, T. Walter, M. Sahana, K.-H. Müller, K. Nenkov, K. Brand, and L. Schultz, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 6973 (2001). 7. Moon-Ho Jo, Neil D. Mathur, Jan E. Evetts, Mark G. Blamire Manuel Bibes, and Josep Fontcuberta, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3689 (1999). 8. Yafeng Lu, J. Klein, C. Höfener, B. Wiedenhorst, J. B. Philipp, F. Herbstritt, A. Marx, L. Alff, and R. Gross, Phys. Rev. B 62, (2000). 9. M. Izumi, Y. Ogimoto, Y. Okimoto, T. Manako, P. Ahmet, K. Nakajima, T. Chikyow, M. Kawasaki, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 64, (2001). 10. M. Ziese, Phys. Rev. B 62, 1044 (2000); M. Ziese and S. P. Sena, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10, 2727 (1998). 11. L. M. Wang, H. H. Sung, B. T. Su, H. C. Yang, and H. E. Horng, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 4236 (2000). 12. Michael C. Martin, G. Shirane, Y. Endoh, K. Hirota, Y. Moritomo, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 53, (1996). 13. V. S. Amaral, A. A. C. S. Lourenco, J. P. Araújo, P. B. Tavares, E. Alves, J. B. Sousa, J. M. Vieira, M. F. da Silva, and J. C. Soares, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 211, 1 (2000). 14. R. Mathieu, P. Svedlindh, R. A. Chakalov, and Z. G. Ivanov, Phys. Rev. B 62, 3333 (2000). 15. D. Mauri, D. Scholl, H. C. Siegmann, and E. Kay, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 758 (1988). 13
14 16. V. Garcia, M. Bibes, A. Barthélémy, M. Bowen, E. Jacquet, J.-P. Contour, and A. Fert, Rev. B 69, (2004). 17. D. Mills and A. Maradudin, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 28, 1855 (1967). 18. J. Mathon, Physica B 149, 31 (1988). 19. H. Y. Hwang, S-W. Cheong, N. P. Ong, and B. Batlogg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2041 (1996). 14
15 Figure captions Figure 1. High-resolution cross-sectional TEM lattice image of a LSMO/STO superlattice. Figure 2. (a) X-ray θ-2θ diffraction spectra in the region near the (002) peak for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices. The satellite peaks are indicated by star symbols. (b) Wide-range x-ray scan for the (76/147) 12 superlattice. The inset shows its x-ray φ-scanning on the orthorhombic (332) LSMO diffraction peak. Figure 3. Zero-field resistivities ρ as a function of temperature for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices and the LSMO film. The inset illustrates the temperature dependence of magnetoresistance ratio for corresponding samples. Figure 4. Temperature dependence of AMR for a series of LSMO/STO superlattices. Top inset: the AMR behavior of the 800-Å LSMO film for comparison. Lower inset: the hysteretic AMR curve associated with the normalized magnetization M/M(5 kg) of the (76/82) 12 superlattices performed at 5 K. Figure 5. Normalized magnetization M/M(5 K) measured with H = 500 G as a function of T 3/2 for (a) a series of superlattices with varied thicknesses of 15
16 STO layers and (b) a series of superlattices with varied thicknesses of LSMO layers. Inset of (a): the value of constant C as a function of d STO /d LSMO ratio. Inset of (b): the parameter k as a function of d STO /d LSMO ratio. The dashed lines are for the purpose of guiding the eye. 16
17 Fig Å 56 Å 50 Å 17
18 Fig. 2 Intensity (arb. units) 2 θ (degree) a. (142 / 82) 6 b. (76 / 56) 12 c. (76 / 82 ) 12 d. (76 / 147) 12 a b c d (002) LSMO/ STO superlattices LaAlO 3 (002) (a) Intensity (arb. units) (76 / 147) Φ (degree) (001) LaAlO 3 (001) Intensity (002) LaAlO 3 (002) (b) θ (degree) 18
19 Fig (76 / 147) 12 (76 / 82) 12 ρ (10-3 Ω cm) (76 / 56) 12 (142 / 82) 6 LSMO (800 Å ) MR(7 T) % T (K) T (K) 19
20 Fig. 4 AMR (%) AMR (%) a b c d AMR (%) H (G) (76 /82) LSMO (800 Å) T (K) M/M(5 kg) -1.0 a. (76 / 147) 12 b. (76 / 82 ) 12 c. (142 / 82 ) 6 d. (76 / 56 ) T (K) 20
21 Fig. 5 M/M(5 K) M/M(5 K) T 1.5 (K 1.5 ) (76 / 56) 12 (76 / 82) 12 (76 / 147) 12 LSMO (800 Å ) d STO / d LSMO LSMO (800 Å) 3 C (10-5 K -1.5 ) T (K) 200 H = 500 G (142 / 82) 6 (92 / 82) 8 (76 /82) 12 d STO / d LSMO LSMO (800 Å) k H = 500 G T 1.5 (K 1.5 ) (a) (b) 21
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
with micrometer wide atomic terraces
 Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor. (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction
 Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES. J. M. De Teresa
 MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
P. Khatua IIT Kanpur. D. Temple MCNC, Electronic Technologies. A. K. Majumdar, S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata
 The scaling law and its universality in the anomalous Hall effect of giant magnetoresistive Fe/Cr multilayers A. K. Majumdar S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata & Department of Physics
The scaling law and its universality in the anomalous Hall effect of giant magnetoresistive Fe/Cr multilayers A. K. Majumdar S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata & Department of Physics
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3. Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and
 Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Orientation dependence of the Schottky barrier height for
 Orientation dependence of the Schottky barrier height for La 0.6 Sr 0.4 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 heterojunctions M. Minohara 1, Y. Furukawa 2, R. Yasuhara 2, H. Kumigashira 2,3,4,a), and M. Oshima 1,2,3,4 1 Graduate
Orientation dependence of the Schottky barrier height for La 0.6 Sr 0.4 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 heterojunctions M. Minohara 1, Y. Furukawa 2, R. Yasuhara 2, H. Kumigashira 2,3,4,a), and M. Oshima 1,2,3,4 1 Graduate
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.
![Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998. Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.](/thumbs/90/104152266.jpg) Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function
 Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES IN Co/Pt MULTILAYERS WITH PERPENDICULAR MAGNETIC ANISOTROPY
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 19, Nos. 15, 16 & 17 (2005) 2562-2567 World Scientific Publishing Company World Scientific V www.worldscientific.com ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 19, Nos. 15, 16 & 17 (2005) 2562-2567 World Scientific Publishing Company World Scientific V www.worldscientific.com ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films on SrTiO 3 and CaTiO 3 buffered Si substrates: structural, static, and dynamic magnetic properties
 J Nanopart Res (2011) 13:5669 5675 DOI 10.1007/s11051-011-0334-y SPECIAL ISSUE: NANOSTRUCTURED MATERIALS 2010 La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films on SrTiO 3 and CaTiO 3 buffered Si substrates: structural, static,
J Nanopart Res (2011) 13:5669 5675 DOI 10.1007/s11051-011-0334-y SPECIAL ISSUE: NANOSTRUCTURED MATERIALS 2010 La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films on SrTiO 3 and CaTiO 3 buffered Si substrates: structural, static,
Mesoscopic Spintronics
 Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 1 Today s Topics 1.1 History of Spintronics 1.2 Fudamentals in Spintronics Spin-dependent transport GMR and TMR effect Spin injection
Mesoscopic Spintronics Taro WAKAMURA (Université Paris-Sud) Lecture 1 Today s Topics 1.1 History of Spintronics 1.2 Fudamentals in Spintronics Spin-dependent transport GMR and TMR effect Spin injection
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
TEMPERATURE DEPENDENCE OF TUNNEL MAGNETORESISTANCE OF IrMn BASED MTJ
 MOLECULAR PHYSICS REPORTS 40 (2004) 192-199 TEMPERATURE DEPENDENCE OF TUNNEL MAGNETORESISTANCE OF IrMn BASED MTJ P. WIŚNIOWSKI 1, T. STOBIECKI 1, M. CZAPKIEWICZ, J. WRONA 1, M. RAMS 2, C. G. KIM 3, M.
MOLECULAR PHYSICS REPORTS 40 (2004) 192-199 TEMPERATURE DEPENDENCE OF TUNNEL MAGNETORESISTANCE OF IrMn BASED MTJ P. WIŚNIOWSKI 1, T. STOBIECKI 1, M. CZAPKIEWICZ, J. WRONA 1, M. RAMS 2, C. G. KIM 3, M.
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders
 Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Magnetic anisotropy of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 nanopowders I. Radelytskyi (1), P. Dłużewski (1), V. Dyakonov (1 and 2), P. Aleshkevych (1), W. Kowalski (1), P. Jarocki (1), H. Szymczak (1) ((1) Institute of
Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
Extraordinary Hall effect in Fe-Cr giant magnetoresistive multilayers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 68, 144405 2003 Extraordinary Hall effect in Fe-Cr giant magnetoresistive multilayers P. Khatua and A. K. Majumdar* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 208016,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 68, 144405 2003 Extraordinary Hall effect in Fe-Cr giant magnetoresistive multilayers P. Khatua and A. K. Majumdar* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 208016,
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces
 Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers
 Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers W. J. Xu 1, B. Zhang 2, Z. X. Liu 1, Z. Wang 1, W. Li 1, Z. B. Wu 3, R. H. Yu 4 and X. X. Zhang 2* 1 Dept. of Phys. and Institute of Nanoscience & Technology, The
Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers W. J. Xu 1, B. Zhang 2, Z. X. Liu 1, Z. Wang 1, W. Li 1, Z. B. Wu 3, R. H. Yu 4 and X. X. Zhang 2* 1 Dept. of Phys. and Institute of Nanoscience & Technology, The
of Spontaneous and field-induced
 Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
Magneto-Optics of Spontaneous and field-induced induced Vortices in twinned YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ /La 1-x Sr x MnO 3 bilayers Superconductivity Group (Politecnico di Torino): Roberto Gerbaldo, Gianluca Ghigo,
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers
 Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2 artificial lattices by polarized neutron reflection
 Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 -
 Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
FIG. 1: (Supplementary Figure 1: Large-field Hall data) (a) AHE (blue) and longitudinal
 FIG. 1: (Supplementary Figure 1: Large-field Hall data) (a) AHE (blue) and longitudinal MR (red) of device A at T =2 K and V G - V G 0 = 100 V. Bold blue line is linear fit to large field Hall data (larger
FIG. 1: (Supplementary Figure 1: Large-field Hall data) (a) AHE (blue) and longitudinal MR (red) of device A at T =2 K and V G - V G 0 = 100 V. Bold blue line is linear fit to large field Hall data (larger
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics
 La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics Investigation on fundamental issues and applications Umberto Scotti di Uccio DiMSAT, Università di Cassino CNR Coherentia Napoli MR (%) 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-50 0 50 µ
La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 - based Spintronics Investigation on fundamental issues and applications Umberto Scotti di Uccio DiMSAT, Università di Cassino CNR Coherentia Napoli MR (%) 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-50 0 50 µ
Thickness-induced anomalous angular-dependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO 3
 Received: 27 June 2017 Accepted: 15 December 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thickness-induced anomalous angular-dependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO
Received: 27 June 2017 Accepted: 15 December 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15402 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thickness-induced anomalous angular-dependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves
 Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+±
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
Holcomb Group Capabilities
 Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008](/thumbs/88/117898456.jpg) Current induced resistance change of magnetic tunnel junctions with ultra-thin MgO tunnel barriers Patryk Krzysteczko, 1, Xinli Kou, 2 Karsten Rott, 1 Andy Thomas, 1 and Günter Reiss 1 1 Bielefeld University,
Current induced resistance change of magnetic tunnel junctions with ultra-thin MgO tunnel barriers Patryk Krzysteczko, 1, Xinli Kou, 2 Karsten Rott, 1 Andy Thomas, 1 and Günter Reiss 1 1 Bielefeld University,
Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics
 Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics Ulrike Lüders 1,2, Agnès Barthélémy 3 *, Manuel Bibes 4, Karim Bouzehouane 3, Stéphane Fusil 5, Eric Jacquet 3, Jean-Pierre Contour
Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics Ulrike Lüders 1,2, Agnès Barthélémy 3 *, Manuel Bibes 4, Karim Bouzehouane 3, Stéphane Fusil 5, Eric Jacquet 3, Jean-Pierre Contour
Spin-dependent tunneling through high-k LaAlO 3. J.-L. Maurice, E. Jacquet, K. Bouzehouane, J.-P. Contour and A. Barthélémy.
 Spin-dependent tunneling through high-k LaAlO 3 V. Garcia Institut des NanoSciences de Paris, Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7, CNRS UMR 7588, 140 rue de Lourmel 75015 Paris, France and Unité Mixte de Physique
Spin-dependent tunneling through high-k LaAlO 3 V. Garcia Institut des NanoSciences de Paris, Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7, CNRS UMR 7588, 140 rue de Lourmel 75015 Paris, France and Unité Mixte de Physique
Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface
 Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2. Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1. Germany.
 Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Superconductivity Induced Transparency
 Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
Superconductivity Induced Transparency Coskun Kocabas In this paper I will discuss the effect of the superconducting phase transition on the optical properties of the superconductors. Firstly I will give
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions
 Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
doi: /PhysRevLett
 doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
doi: 1.113/PhysRevLett.9.17 PRL 9, 17 (7) 5 JANUARY 7 Optical Control of the Magnetic Anisotropy of Ferromagnetic Bilayered Manganites S. Tomimoto, 1 M. Matsubara, 1 T. Ogasawara, 1 H. Okamoto, 1, T. Kimura,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002](/thumbs/75/71660699.jpg) Low frequency 1/ f noise in doped manganite grain-boundary junctions J. B. Philipp, L. Alff, A. Marx, and R. Gross Walther-Meissner-Institut, Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Walter-Meissner-Straße
Low frequency 1/ f noise in doped manganite grain-boundary junctions J. B. Philipp, L. Alff, A. Marx, and R. Gross Walther-Meissner-Institut, Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Walter-Meissner-Straße
When transition metals are incorporated into a certain site of the BiT, some of BiT-LaTMO 3
 Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
From Hall Effect to TMR
 From Hall Effect to TMR 1 Abstract This paper compares the century old Hall effect technology to xmr technologies, specifically TMR (Tunnel Magneto-Resistance) from Crocus Technology. It covers the various
From Hall Effect to TMR 1 Abstract This paper compares the century old Hall effect technology to xmr technologies, specifically TMR (Tunnel Magneto-Resistance) from Crocus Technology. It covers the various
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La 0:8 Sr 0:2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb Heterojunction at Low Temperature
 Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 1, 25, pp. 7367 7371 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La :8 Sr :2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Vol. 44, No. 1, 25, pp. 7367 7371 #25 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Photocarrier Injection and Current Voltage Characteristics of La :8 Sr :2 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 :Nb
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE-
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 001 Materials Research Society MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS M. Hehn, O. Lenoble, D. Lacour and A. Schuhl Laboratoire de Physique
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 001 Materials Research Society MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS M. Hehn, O. Lenoble, D. Lacour and A. Schuhl Laboratoire de Physique
Spatial Symmetry of Superconducting Gap in YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ Obtained from Femtosecond Spectroscopy
 Spatial Symmetry of Superconducting Gap in YBa Cu 3 O 7-δ Obtained from Femtosecond Spectroscopy C. W. Luo, M. H. Chen, S. P. Chen, K. H. Wu, J. Y. Juang, J.-Y. Lin, T. M. Uen and Y. S. Gou Department
Spatial Symmetry of Superconducting Gap in YBa Cu 3 O 7-δ Obtained from Femtosecond Spectroscopy C. W. Luo, M. H. Chen, S. P. Chen, K. H. Wu, J. Y. Juang, J.-Y. Lin, T. M. Uen and Y. S. Gou Department
Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum Wells
 Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 23 Aug 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 23 Aug 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 23 Aug 2005](/thumbs/73/69527740.jpg) Spin-polarized tunneling spectroscopy in tunnel junctions with half-metallic electrodes arxiv:cond-mat/58548v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 3 Aug 5 M. Bowen, 1 A. Barthélémy, 1, M. Bibes, 1 E. Jacquet, 1 J.-P.
Spin-polarized tunneling spectroscopy in tunnel junctions with half-metallic electrodes arxiv:cond-mat/58548v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 3 Aug 5 M. Bowen, 1 A. Barthélémy, 1, M. Bibes, 1 E. Jacquet, 1 J.-P.
ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS
 ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS Peter C Riedi School of Physics and Astronomy, University of St. Andrews, Fife, Scotland KY16 9SS, UK (pcr@st-and.ac.uk) INTRODUCTION This talk will introduce
ELECTRON MAGNETIC RESONANCE OF MANGANESE COMPOUNDS Peter C Riedi School of Physics and Astronomy, University of St. Andrews, Fife, Scotland KY16 9SS, UK (pcr@st-and.ac.uk) INTRODUCTION This talk will introduce
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 73, 39 47, 2007 MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR C.-J. Wu Department of Applied Physics National University of Kaohsiung
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 73, 39 47, 2007 MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR C.-J. Wu Department of Applied Physics National University of Kaohsiung
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Sep 2013](/thumbs/71/65996707.jpg) Interlayer Diffusion of Nuclear Spin Polarization in ν = 2/3 Quantum Hall States arxiv:1309.5185v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Sep 2013 Minh-Hai Nguyen, 1, Shibun Tsuda, 1 Daiju Terasawa, 2 Akira Fukuda, 2
Interlayer Diffusion of Nuclear Spin Polarization in ν = 2/3 Quantum Hall States arxiv:1309.5185v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Sep 2013 Minh-Hai Nguyen, 1, Shibun Tsuda, 1 Daiju Terasawa, 2 Akira Fukuda, 2
Italian School of Magnetism
 Spintronics I 1. Introduction 3. Mott paradigm: two currents model 4. Giant MagnetoResistance: story and basic principles 5. Semiclassical model for CIP GMR Italian School of Magnetism Prof. Riccardo Bertacco
Spintronics I 1. Introduction 3. Mott paradigm: two currents model 4. Giant MagnetoResistance: story and basic principles 5. Semiclassical model for CIP GMR Italian School of Magnetism Prof. Riccardo Bertacco
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene
 Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007](/thumbs/93/118034102.jpg) Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices
 Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
BF 3 -doped polyaniline: A novel conducting polymer
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 1 journal of July 2006 physics pp. 135 139 BF 3 -doped polyaniline: A novel conducting polymer DEBANGSHU CHAUDHURI and D D SARMA Solid State and Structural
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 1 journal of July 2006 physics pp. 135 139 BF 3 -doped polyaniline: A novel conducting polymer DEBANGSHU CHAUDHURI and D D SARMA Solid State and Structural
Magnetic bubblecade memory based on chiral domain walls
 Magnetic bubblecade memory based on chiral domain walls Kyoung-Woong Moon, Duck-Ho Kim, Sang-Cheol Yoo, Soong-Geun Je, Byong Sun Chun, Wondong Kim, Byoung-Chul Min, Chanyong Hwang & Sug-Bong Choe 1. Sample
Magnetic bubblecade memory based on chiral domain walls Kyoung-Woong Moon, Duck-Ho Kim, Sang-Cheol Yoo, Soong-Geun Je, Byong Sun Chun, Wondong Kim, Byoung-Chul Min, Chanyong Hwang & Sug-Bong Choe 1. Sample
Giant Magnetoresistance
 Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED TEM RHEED
 Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
Some pictures are taken from the UvA-VU Master Course: Advanced Solid State Physics by Anne de Visser (University of Amsterdam), Solid State Course
 Some pictures are taken from the UvA-VU Master Course: Advanced Solid State Physics by Anne de Visser (University of Amsterdam), Solid State Course by Mark Jarrel (Cincinnati University), from Ibach and
Some pictures are taken from the UvA-VU Master Course: Advanced Solid State Physics by Anne de Visser (University of Amsterdam), Solid State Course by Mark Jarrel (Cincinnati University), from Ibach and
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
EXCHANGE COUPLING IN MAGNETIC MULTILAYERS GROWN ON IRON WHISKERS (INVITED)
 EXCHANGE COUPLING IN MAGNETIC MULTILAYERS GROWN ON IRON WHISKERS (INVITED) J. Unguris, R. J. Celotta, D. A. Tulchinsky, and D. T. Pierce Electron Physics Group, National Institute of Standards and Technology,
EXCHANGE COUPLING IN MAGNETIC MULTILAYERS GROWN ON IRON WHISKERS (INVITED) J. Unguris, R. J. Celotta, D. A. Tulchinsky, and D. T. Pierce Electron Physics Group, National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Probing Tunnel Barrier Shape and Its Effects on Inversed Tunneling Magnetoresistance at High Bias
 Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 33, No. 11, 2004 Special Issue Paper Probing Tunnel Barrier Shape and Its Effects on Inversed Tunneling Magnetoresistance at High Bias WEN-TING SHENG, 1,2 W.G. WANG,
Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 33, No. 11, 2004 Special Issue Paper Probing Tunnel Barrier Shape and Its Effects on Inversed Tunneling Magnetoresistance at High Bias WEN-TING SHENG, 1,2 W.G. WANG,
HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
The Initial Process of Photoinduced Phase Transition in an Organic Electron-Lattice Correlated System using 10-fs Pulse
 The Initial Process of Photoinduced Phase Transition in an Organic Electron-Lattice Correlated System using 1-fs Pulse S. Koshihara, K. Onda, Y. Matsubara, T. Ishikawa, Y. Okimoto, T. Hiramatsu, G. Saito,
The Initial Process of Photoinduced Phase Transition in an Organic Electron-Lattice Correlated System using 1-fs Pulse S. Koshihara, K. Onda, Y. Matsubara, T. Ishikawa, Y. Okimoto, T. Hiramatsu, G. Saito,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
Interface magnetism and spin wave scattering in ferromagnet-insulator-ferromagnet tunnel junctions Moodera, J.S.; Nowak, J.; van de Veerdonk, R.J.M.
 Interface magnetism and spin wave scattering in ferromagnet-insulator-ferromagnet tunnel junctions Moodera, J.S.; Nowak, J.; van de Veerdonk, R.J.M. Published in: Physical Review Letters DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2941
Interface magnetism and spin wave scattering in ferromagnet-insulator-ferromagnet tunnel junctions Moodera, J.S.; Nowak, J.; van de Veerdonk, R.J.M. Published in: Physical Review Letters DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2941
Nanoxide electronics
 Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
