PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79,
|
|
|
- Bertina Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, Ferroelectric poling and converse-piezoelectric-effect-induced strain effects in La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 thin films grown on ferroelectric single-crystal substrates R. K. Zheng, 1, * Y. Jiang, 1 Y. Wang, 1 H. L. W. Chan, 1, C. L. Choy, 1 and H. S. Luo 2 1 Department of Applied Physics and Materials Research Center, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China 2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 218, China Received 1 January 29; revised manuscript received 13 April 29; published 14 May 29 Using ferroelectric.67pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O PbTiO 3 single crystals as substrates, we studied the effects of the ferroelectric poling and the converse piezoelectric effect on the strain state, resistance, insulator-to-metal transition temperature T C, and magnetoresistance MR of La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 LBMO thin films. In situ x-ray diffraction measurements indicate that the ferroelectric poling or the converse piezoelectric effect induces a substantial reduction in the in-plane tensile strain in the LBMO film, giving rise to a decrease in the resistance and an increase in T C. The relative changes of the resistance and T C are proportional to the induced reduction in the in-plane tensile strain xx in the film. The reduction in the in-plane tensile strain leads to opposite effects on MR below and above T C, namely, MR is reduced for T T C while MR is enhanced for T T C.We discuss these strain effects within the framework of the Jahn-Teller JT electron-lattice coupling and phase separation scenario that are relevant to the induced strain. Similar studies on CaMnO 3 thin films, for which there is no JT distortion of MnO 6 octahedra, show that the resistance of the films also decreases when the tensile strain is reduced, indicating that the resistance change arising from the reduction in Mn-O bond length dominates over that arising from the reduction in Mn-O-Mn bond angle. DOI: 1.113/PhysRevB PACS number s : Lx, Gk, Ej, j I. INTRODUCTION In the last decade, much effort has been devoted to colossal magnetoresistance CMR manganite thin films due to their interesting physical properties and possible device applications. A number of experimental studies and theoretical calculations have undoubtedly shown that the substrateinduced strain can drastically influence a variety of properties of manganite thin films, such as the insulator-to-metal transition temperature T C Ref. 1, magnetoresistance MR, 2 magnetic anisotropies, 3 phase separation, 4 and charge/orbital ordering. 5 Therefore, a comprehensive and quantitative study of the intrinsic strain dependence of film properties is very important from both the fundamental and technological viewpoints. Recently, it was reported that an in-plane compressive strain reduces ferromagnetism and T C while a tensile strain enhances ferromagnetism and T C in low-doped La 1 x Ba x MnO 3.5 x.2 thin films. 6,7 These strain effects are different from the usual results observed in other CMR systems, e.g., La.9 Sr.1 MnO 3, where a compressive strain enhances ferromagnetism and T C Ref. 8. Kanki et al. 7 proposed that an increase in charge carrier transfer resulting from the strain-induced modification of Mn-O-Mn networks rather than an increase in charge carrier density is responsible for the strain effect in La 1 x Ba x MnO 3 films. In contrast, Murugavel et al found that, irrespective of whether the substrate-induced strain is compressive or tensile, oxygen nonstoichiometry strongly affects the holedoping level, strain state, and the transport properties of La 1 x Ba x MnO 3 x=.8,.2 films. Orgiani et al. 12 studied the role of oxygen content on the transport properties of La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 LBMO films and found that the oxygen content strongly influences the strain state and transport properties of the films. These results strongly indicate that, in addition to the substrate-induced strain, oxygen content plays a very important role in determining the electrical, magnetic, and structural properties of La 1 x Ba x MnO 3 thin films. Ferroelectric 1 x Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 -xpbtio 3 PMN-xPT single crystals with compositions near the morphotropic phase-boundary region exhibit large remnant ferroelectric polarization =3 35 C/cm 2, low coercive field, and excellent piezoelectric activity d pc/n. 13 PMN-xPT has a perovskite structure with lattice constants a b c 4.2 Å Ref. 13, which are close to those of Pb Zr.52 Ti.48 O 3 a=4.4 Å, c =4.11 Å Ref. 14 and BaTiO 3 a=3.99 Å, c=4.3 Å. 15 Because of the good ferroelectric, piezoelectric, and structural properties of PMN-xPT single crystals, they are very good materials for use as ferroelectrically and piezoelectrically active substrates. Recently, Gangineni et al., 16 Thiele et al., 17,18 and Zheng et al have successfully grown perovskite La 1 x A x MnO 3 A=Ca,Sr thin films on PMN-xPT x.28,.33 substrates, and have demonstrated that the strain state of these films can be reversibly controlled via the converse piezoelectric effect of the substrates. This approach opens the possibility that the intrinsic effects of the substrateinduced strain on the properties of films can be studied without introducing the effects of extrinsic variables, e.g., crystalline quality, disorder, and oxygen nonstoichiometry. In order to attain a detailed and quantitative understanding of the substrate-induced strain effects in La 1 x Ba x MnO 3 films, in this paper, we used ferroelectric.67pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O PbTiO 3 PMN-PT single crystals as substrates and studied the effects of substrate-induced strain on the strain state, resistance, T C, and magnetotransport properties of LBMO films by in situ inducing a strain in the film via the ferroelectric poling or the converse piezo /29/79 17 / The American Physical Society
2 ZHENG et al. Intensity (arb.units) P (µc/cm 2 ) PMN-PT(1) (a) (c) φ (Degree) PMN-PT(2) LBMO(2) (b) LBMO Film φ (Degree) θ (Degree) electric effect. The experimental results indicate that, associated with the ferroelectric poling, the in-plane tensile strain in the film was reduced by.27%, giving rise to a decrease in the resistance in the temperature range from 78 to 325 K and an increase of T C by 12.6 K. At the same time, MR in the ferromagnetic FM state is reduced while MR in the paramagnetic PM state is enhanced. These induced strain effects are found to be closely related to the phase separation and the Jahn-Teller JT electron-lattice coupling linked to the induced reduction in the in-plane tensile strain in the film. II. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS We have grown the PMN-PT single crystals by a modified Bridgman technique. 22 Ferroelectric measurements using a standard Sawyer-Tower circuit driven with 1 Hz sinusoidal pulse electric field showed that the single crystals exhibited a sharp polarization hysteresis loop with a remnant polarization close to 33 C/cm 2 and a coercive field E C close to 2.5 kv/cm inset a of Fig. 1. These crystals were cut into small plates with the plate normal in the 1 crystal direction and polished to a surface roughness less than 1 nm. LBMO films were deposited on the 1 -oriented and polished PMN-PT substrates using dc magnetron sputtering. The deposition was carried out in an argon-oxygen flow with 6% Ar and 4% O 2 at a pressure of 5 Pa, and a substrate temperature of 7 C. After deposition, the films were cooled to room temperature and then postannealed in 1 atm of flowing O 2 at 7 C for 3 min using a rapid thermal processor furnace. Since the lattice constants a b c Å of LBMO bulk material 23 are smaller than those Au V I PMN-PT Au Ground Au 2MΩ resistor (d) FIG. 1. Color online X-ray diffraction pattern of the LBMO/ PMN-PT structure. The inset a shows the polarization electricfield hysteresis loop of the PMN-PT substrate measured at 296 K. The inset b shows a schematic diagram of the LBMO/PMN-PT structure and the electrical measurement circuit. The arrow in the inset b represents the polarization direction. The insets c and d show the XRD scans on the PMN-PT 11 and LBMO 11 reflections, respectively. PMN-PT(3) LBMO(3) dc PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, a b c 4.2 Å of the PMN-PT substrate in unpoled state referred to as, it is estimated that LBMO films grown on PMN-PT substrates would be subjected to an inplane tensile strain. The thicknesses of these films were measured by field-emission scanning electron microscopy to be 65 nm. X-ray diffraction XRD patterns of the PMN-PT substrate and the LBMO film were recorded using a Bruker D8 Discover x-ray diffractometer when a dc electric field E E 1 kv/cm was applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure. The films were highly 1 oriented and no secondary phases were found, as shown in Fig. 1. XRD scans on the PMN-PT 11 and LBMO 11 reflections were also performed. A fourfold symmetry is clearly seen for both the PMN-PT substrate and the LBMO film insets c and d of Fig. 1, respectively, which is an indication of the cube-oncubic epitaxial growth of the LBMO film on the PMN-PT substrate. The resistance of the LBMO films was measured using the electrical measurement circuit shown in the inset b of Fig. 1. A constant current of 5 A was applied to the thin film through the two top-top gold electrodes using a Keithley Model 24 source meter with input resistance 1 G and the voltage difference between the two top-top gold electrodes was measured by a Keithley Model 2 digital multimeter. The PMN-PT substrate was poled by applying a poling field E much larger than E C to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure through the top and bottom gold electrodes using a Keithley Model 6517A electrometer, and the same measurement circuit shown in the inset b of Fig. 1. Note that the top and bottom gold electrodes were always held at low and high potentials, respectively. We point out that the ferroelectric field effect present at the LBMO/PMN-PT interface has a negligible influence on the transport properties since the screening length of the electric field is less than few unit cells, 18,24 which is smaller than the thickness 65 nm of the LBMO films. The resistance of the PMN-PT substrate is estimated to be 5.4 G cm under E=1 kv/cm, obtained by measuring the leakage current in the PMN-PT substrate. Using a Model 76 Lakeshore Hall measurement system, MR of the films was measured when a magnetic field was applied parallel to the film plane. Magnetic measurements were performed with a Model 76 Lakeshore vibrating sample magnetometer. III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 ÕPMN-PT structure 1. Effects of strain induced by ferroelectric substrate poling on the film resistance In order to observe the effects of the strain induced by ferroelectric poling on the strain state and transport properties of the LBMO film, we measured the resistance of the film between the two top-top gold electrodes as a function of the electric field E applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure through the top held at low potential and bottom gold electrodes held at high potential at a fixed temperature of 296 K. Note that the initial polarization state of the PMN-PT substrate was P r and E was increased from to 1 kv/cm
3 FERROELECTRIC POLING AND CONVERSE R/R T=296 K ε xx T=296 K c LBMO (Å) FIG. 2. Color online Relative change of the resistance and the c-axis lattice constant of the LBMO film at 296 K as a function of E applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure. The initial polarization state of the PMN-PT substrate is. The inset shows the in-plane strain xx of the film at 296 K as a function of E applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure. in steps of.21 kv/cm. The relative change of the resistance due to the ferroelectric poling, R/R, is plotted as a function of E in Fig. 2. Here, R/R is defined as R/R= R E R /R, where R E and R are the resistance of the film under an electric field E and zero electric field, respectively. It can be seen that the resistance decreases slightly by.7% for E 2.1 kv/cm, which could be due to the partial poling of the PMN-PT substrate. It is worth noting that the resistance decreases drastically with increasing E from 2.1 to 3 kv/cm and decreases gently with further increase in E. We found that, after the measurements of the resistance as a function of E, the PMN-PT substrate had a piezoelectric coefficient d 33 of 19 pc/n which indicates that the PMN-PT substrate had been poled very well. Moreover, the drastic decrease in the resistance occurs near E 2.5 kv/cm, which is close to the coercive field of the PMN-PT substrate. Therefore, it is reasonable to conclude that the decrease in the resistance induced by the electric field is associated with the ferroelectric poling in the PMN-PT substrate, which could consequently modify the strain state and transport properties of the LBMO film. To clarify this point, we measured the out-of-plane or c-axis lattice constant of the film by in situ measuring the position of LBMO 2 reflection during the application of an electric field E E 1 kv/cm to the LBMO/ PMN-PT structure in steps of 1 kv/cm. Note that the PMN-PT substrate is initially in P r state. In Fig. 2, we show the c-axis lattice constant of the film as a function of E. When the PMN-PT substrate is in state, i.e., E 2 kv/cm, the c-axis lattice constant is about Å. This value is smaller than that i.e., c=3.916 Å of La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 bulk material, 23 indicating that the film is under an out-of-plane compressive zz = 1.71% and an inplane tensile strain. For E 2 kv/cm, the c-axis lattice constant remains almost unchanged with increasing E but increases drastically with increasing E from 2 to 3 kv/cm and then increases monotonously for E 3 kv/cm. For an unpoled ferroelectric material, it is expected that the application PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, of an electric field would induce a nonlinear change in the lattice constants or strain in the material. The observed electric-field-induced nonlinear change in the c-axis lattice constant of the LBMO film is apparently due to the strain induced by the ferroelectric poling in the PMN-PT substrate, giving direct evidence that ferroelectric poling is responsible for the decrease in the resistance of the film. We note that, when E=1 kv/cm is applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure, the c-axis lattice constant increases to 3.87 Å, which is smaller than that of La.7 Ba.3 MnO 3 bulk material, indicating that the film is still under in-plane tensile strain. The in-plane tensile strain xx is related to the out-of-plane compressive strain zz by the expression zz = 2 /1 xx, where is the Poisson s ratio. Using =.5 i.e., volumepreserving distortion for the LBMO film, 25 xx is calculated and plotted as a function of E in the inset of Fig. 2. AsE increases from to 1 kv/cm, xx decreases from.86% to.59%, corresponding to a relative reduction of xx by 31%. The evolution of xx with E is in good agreement with that of the transport behavior, which strongly indicates that the decrease in the resistance is due to the reduction in the in-plane tensile strain induced by the ferroelectric poling. A reduction in the in-plane tensile strain would reduce the tetragonal distortion of the MnO 6 octahedra in the film and hence modify the JT electron-lattice coupling strength. 7,26 29 At E= kv/cm i.e., the PMN-PT substrate is in P r state, the film is subjected to an in-plane tensile strain xx =.86%, implying that the MnO 6 octahedra are compressed along c axis and elongated in the film plane. 29 Such tetragonal distortion of the MnO 6 octahedra would localize the charge carriers due to the JT electron-lattice coupling. At E =1 kv/cm, xx is reduced to.59%, indicating that the tetragonal distortion of the MnO 6 octahedra has been significantly reduced. This would reduce the JT electron-lattice coupling strength, thereby favoring the delocalization and hopping of charge carriers. 7,26,27 2. Effects of strain induced by the converse piezoelectric effect on the film resistance After the PMN-PT substrate had been positively polarized i.e., electric dipole moments in the PMN-PT substrate point toward the LBMO film, referred to as P r, we studied the effects of the strain induced by the converse piezoelectric effect on the strain state, T C, and transport properties of the LBMO film. In Fig. 3, we show the temperature dependence of the resistance for the LBMO film when dc electric fields of, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 1 kv/cm is applied to the LBMO/ PMN-PT structure, respectively. Note that the resistance was measured using the electrical measurement circuit shown in the inset b of Fig. 1. During the measurements the top and bottom gold electrodes were held at low and high potentials, respectively, so that the direction of the electric field is the same as that of the polarization. With increasing E from to 1 kv/cm, the resistance decreases over the entire temperature range, with the decrease being particularly noticeable near T C. We found that, whether the film is in the hightemperature insulating state e.g., 296 K, low-temperature metallic state e.g., 78 K, oratt C i.e., 273 K, the relative change in the resistance R/R at a fixed temperature de
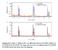
4 ZHENG et al. R (kω) δε xx K K K K -.1 (a) kv/cm 2.5 kv/cm 5 kv/cm 7.5 kv/cm 1 kv/cm R/R T(K) (c) creases linearly with increasing E inset a of Fig. 3. Itis known that, for a ferroelectric material, the strain induced by the converse piezoelectric effect is proportional to the electric field E applied to the material. In situ XRD measurements on the LBMO/PMN-PT structure indicate that both the c-axis lattice constant of the PMN-PT substrate and the LBMO film increases linearly with increasing E not shown here, indicating that the strain induced in the film is due to the converse piezoelectric effect in the PMN-PT substrate Using the expression zz = 2 /1 xx and putting =.5 for the LBMO film, 25 the induced reduction in the in-plane tensile strain xx in comparison with the strain state when E= kv/cm, i.e., xx = xx E xx is calculated and plotted as a function of E in the inset a of Fig. 3. It is clear that xx is linearly dependent on E, thus implying that R/R is proportional to the induced reduction in the in-plane tensile strain xx. The relationship between R/R and xx can be written as R/R=m xx, where m is a constant. We note that, associated with the reduction in the in-plane tensile strain, T C increases linearly with increasing E as shown in the inset b of Fig. 3. Since the reduction in the in-plane tensile strain xx is proportional to E, the relationship between T C and xx can be expressed as T C E =T C p xx, where p is a negative constant and xx has a negative value. Thus, the relationship between T C /T C and xx can be expressed as T C /T C =q xx, where q is a negative constant, so T C /T C is proportional to xx inset c of Fig. 3. The T C - xx coefficient T C /T C / xx is found to be 11.4 here, which implies that a change in the in-plane strain by 1% would induce a 11.4% shift in T C. This is consistent T C /T C R (kω) T C (b). -.1 δε. xx FIG. 3. Color online Temperature dependence of the resistance for the LBMO film when a dc electric field E is applied to the LBMO/PMN-PT structure after the PMN-PT substrate had been polarized to state. The inset a shows the relative change of the resistance, R/R, and the induced reduction in the in-plane tensile strain, xx, of the LBMO film versus E. The inset b shows an expanded view of the temperature dependence of the resistance near T C. The inset c shows T C /T C as a function of xx. R (kω) M(1-4 emu) PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, H=.1 T ZFC T(K) T with the theoretical calculations by Millis et al. 27 who showed that a change in the in-plane biaxial strain by 1% would cause a 1% shift in T C, and thus provides evidence for the important role of the JT electron-lattice coupling linked to substrate-induced strain in the LBMO film. 3. Changes in film magnetoresistance due to strain induced by ferroelectric substrate poling Figure 4 shows the temperature dependence of the resistance for a LBMO film under zero magnetic field and a magnetic field of H=1.2 T when the PMN-PT substrate is in and P r state, respectively. When the PMN-PT substrate is in P r state, the resistance of the film increases with decreasing temperature from 325 K and undergoes an insulator-to-metal transition at T C 26 K. As the magnetic field H increases from to 1.2 T, T C increases from 26 to K and the resistance decreases over the entire temperature range. Associated with the insulator-to-metal transition, the film shows a paramagnetic-to-ferromagnetic phase transition see inset of Fig. 4. As shown in Fig. 4, ath= T, after the PMN-PT substrate has been polarized to P r state, T C increases from 26 to K and the resistance decreases over a wide temperature range from 77 to 325 K. These changes in the transport behavior of the LBMO film induced by ferroelectric poling are qualitatively consistent with those observed in La.75 Ca.25 MnO 3 /PMN-PT Ref. 2, La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 /PMN-PT Ref. 21, and La.85 Ba.15 MnO 3 /PMN-PT Ref. 3 structures. When a field of H=1.2 T is applied, T C increases further to 285 K and the resistance is further reduced. The values of MR at H=1.2 T when the PMN-PT substrate is in P r and P r states were calculated from the data in Fig. 4 and shown in Fig. 5. It is interesting to see that the two MR versus T curves have a crossover near T C, indicating that T C 1.2T T P r 1.2T FIG. 4. Color online Temperature dependence of the resistance for the LBMO film under H= and 1.2 T when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. The inset shows the temperature dependence of the zero-field-cooled magnetization M for the LBMO film when the PMN-PT substrate is in state
5 FERROELECTRIC POLING AND CONVERSE MR H=1.2 T 78 K 235 K 285 K H (T) T(K) MR H=1.2 T K 26 K 335 K H(T) FIG. 5. Color online Temperature dependence of MR MR = R R H /R of the film under H=1.2 T when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. The inset shows MR derived from Fig. 6 as a function of temperature when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively FIG. 6. Color online MR versus H curves at several temperatures for the LBMO film when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, a reduction in the in-plane tensile strain leads to an increase in MR in the PM state but a decrease in MR in the FM state. To confirm this strain effect on MR, we measured MR of the film at various fixed temperatures covering the range from the FM state to the PM state. In Fig. 6, we show MR versus H curves at several temperatures when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. The results clearly indicate that, in comparison with the MR when the PMN-PT substrate is in state, the MR value when the PMN-PT substrate is in state is reduced in the FM state e.g., 78, 155, and 235 K but enhanced in the PM state e.g., 26, 285, and 335 K. We plotted MR at H=1.2 T derived from Fig. 6 for both and states as a function of temperature in the inset of Fig. 5. The two MR versus T curves also show a crossover, consistent with the behavior of the MR shown in Fig. 5. A number of experimental studies and theoretical calculations have shown that the magnetotransport properties of manganite thin films are closely associated with coexisting PM insulating and FM metallic phases, i.e., the phase separation. 1,4,31 33 It is usually observed that MR has a maximum close to T C, where the PM insulating phase and the FM metallic phase coexist and strongly compete with each other. At T C, small external perturbations, e.g., magnetic field, would modify the subtle balance between these two phases, resulting in a large MR. In the high temperature PM insulating state, the PM insulating phase dominates over the FM metallic phase. Thus, the competition between the PM insulating phase and the FM metallic phase for T T C is weaker than that at T C. As discussed above, the reduction in the tensile strain induced by the ferroelectric poling reduces the JT electron-lattice coupling strength, favoring the active hopping of e g electrons. Therefore, the volume fraction of the FM metallic phase would increase at the expense of that of the PM insulating phase, which would enhance MR. In the low temperature FM metallic state, the competition between the PM insulating phase and the FM metallic phase is weaker than that at T C because the volume fraction of the FM metallic phase dominates over the PM insulating phase. Again, the reduction in the JT electron-lattice coupling strength induced by the ferroelectric poling would reinforce the FM metallic state, which would suppress MR. Therefore, if the phase-separation scenario relevant to the strain induced by the ferroelectric poling is taken into account, the opposite effects of the induced strain on the MR in the LBMO film can be reasonably understood. B. CaMnO 3 ÕPMN-PT structure To obtain insight into the effects of induced strain on the Mn-O bond length and/or the Mn-O-Mn bond angle, we studied the effects of strain induced by the ferroelectric poling and the converse piezoelectric effect on the transport properties of CaMnO 3 CMO thin films grown on PMN-PT substrates. CaMnO 3 films were chosen because they do not exhibit JT distortions so the effects of JT electron-lattice coupling on the transport properties can be neglected. XRD measurements indicated that, associated with the switching of the poling state from to, the PMN-PT 2 and CMO 2 reflections shift to lower 2 angles, as shown in the inset a of Fig. 7. As a result, the c-axis lattice constant of the CaMnO 3 film increases from 3.79 to Å, with the latter value still smaller than the lattice constant i.e., Å of the CaMnO 3 bulk material. 34 Assuming a Poisson s ratio of =.5 for the CaMnO 3 film, the in-plane ten
6 ZHENG et al. R (Ω) (b) Intensity (a.u.) θ (Degree) T=296 K R/R PMN-PT (2) (a) T=296 K FIG. 7. Color online Temperature dependence of the resistance for the CaMnO 3 film under H= when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. The inset a shows the XRD patterns for the CaMnO 3 /PMN-PT structure when the PMN-PT substrate is in and states, respectively. The inset b shows the relative change of the resistance, R/R, of the CaMnO 3 film at 296 K as a function of E applied to the CaMnO 3 /PMN-PT structure after the PMN-PT substrate had been polarized to state. CMO (2) PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, sile strain xx is calculated to be reduced from.24% to.13%. As shown in Fig. 7, associated with the decrease in the in-plane tensile strain, the resistance in P r state becomes smaller than that in P r state in the whole temperature range. In order to get a clearer understanding of the strain effects in the CaMnO 3 film, we measured the resistance of the CaMnO 3 film by in situ reducing the in-plane tensile strain in the CaMnO 3 film via the converse piezoelectric effect after the PMN-PT substrate had been polarized to P r state. It can be seen in the inset b of Fig. 7 that the resistance decreases almost linearly with increasing E. Although the relative decrease in the resistance, R/R, is rather small, the results unambiguously show that a reduction in the in-plane tensile strain induced by the converse piezoelectric effect reduces the resistance of the CaMnO 3 film. Since the electronic bandwidth W can be estimated from the Mn-O bond length d and the Mn-O-Mn bond angle by using W sin /2 /d 3.5,a reduction in d would enhance W while a reduction in would reduce W. The effects of the induced strain on the resistance in the CaMnO 3 film demonstrate that the resistance change arising from the reduction in Mn-O bond length dominates over that arising from the reduction in Mn-O-Mn bond angle. We believe that this argument may be extended to the situation in LBMO films. The effect of the reduction in Mn-O bond length on the charge transport may also dominate over that of the reduction in the Mn-O-Mn bond angle in LBMO films. IV. CONCLUSIONS In summary, we examined the effects of substrate-induced strain on the strain state, resistance, and magnetotransport properties of LBMO and CaMnO 3 thin films by in situ modifying strain in the film via the ferroelectric poling or the converse piezoelectric effect. The ferroelectric poling or the converse piezoelectric effect substantially reduces the tensile strain in the film, giving rise to a reduction in the JT electronlattice coupling and thus a large decrease in the resistance and an increase in T C of the LBMO film. Quantitative relationships between the resistance and T C, and the induced strain xx in the LBMO film have been established. The induced strain xx leads to opposite effects on MR below and above T C, i.e., MR for T T C is reduced while MR for T T C is enhanced. We interpreted this behavior within the framework of the phase separation scenario relevant to the electron-lattice coupling linked to the strain induced by the ferroelectric poling. The results on CaMnO 3 film indicate that the strain-induced change of Mn-O bond length plays a more important role than that of Mn-O-Mn bond angle in influencing the transport properties of CaMnO 3 films. A similar scenario is anticipated in LBMO films. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the Hong Kong Research Grants Council under Grant No. CERG PolyU 5122/7E and the Center for Smart Materials of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. *zrk@ustc.edu apahlcha@polyu.edu.hk 1 T. Wu, S. B. Ogale, S. R. Shinde, Amlan Biswas, T. Polletto, R. L. Greene, and T. Venkatesan, J. Appl. Phys. 93, S. I. Khartsev, P. Johnsson, and A. M. Grishin, J. Appl. Phys. 87, F. Tsui, M. C. Smoak, T. K. Nath, and C. B. Eom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, A. Biswas, M. Rajeswari, R. C. Srivastava, T. Venkatesan, R. L. Greene, Q. Lu, A. L. de Lozanne, and A. J. Millis, Phys. Rev. B 63, R. Schmidt, Phys. Rev. B 77, J. Zhang, H. Tanaka, T. Kanki, J. H. Choi, and T. Kawai, Phys. Rev. B 64, T. Kanki, T. Yanagida, B. Vilquin, H. Tanaka, and T. Kawai, Phys. Rev. B 71, X. J. Chen, S. Soltan, H. Zhang, and H.-U. Habermeier, Phys. Rev. B 65, P. Murugavel, T. W. Noh, and J. G. Yoon, J. Appl. Phys. 95, P. Murugavel, J. H. Lee, K. B. Lee, J. H. Park, J. S. Chung, J. G. Yoon, and T. W. Noh, J. Phys. D 35, P. Murugavel, J. H. Lee, J. G. Yoon, T. W. Noh, J.-S. Chung, M. Heu, and S. Yoon, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82,
7 FERROELECTRIC POLING AND CONVERSE 12 P. Orgiani, A. Guarino, C. Aruta, C. Adamo, A. Galdi, A. Yu. Petrov, R. Savo, and L. Maritato, J. Appl. Phys. 11, H. Cao, F. M. Bai, J. F. Li, D. Viehland, G. Y. Xu, H. Hiraka, and G. Shirane, J. Appl. Phys. 97, C. H. Ahn, R. H. Hammond, T. H. Geballe, M. R. Beasley, J.-M. Triscone, M. Decroux, Ø. Fischer, L. Antognazza, and K. Char, Appl. Phys. Lett. 7, M. K. Lee, T. K. Nath, C. B. Eom, M. C. Smoak, and F. Tsui, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, R. B. Gangineni, L. Schultz, C. Thiele, I. Mönch, and K. Dörr, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, C. Thiele, K. Dörr, S. Fähler, L. Schultz, D. C. Meyer, A. A. Levin, and P. Paufler, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, C. Thiele, K. Dörr, O. Bilani, J. Rödel, and L. Schultz, Phys. Rev. B 75, R. K. Zheng, Y. Wang, H. L. W. Chan, C. L. Choy, and H. S. Luo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 9, R. K. Zheng, Y. Wang, J. Wang, K. S. Wong, H. L. W. Chan, C. L. Choy, and H. S. Luo, Phys. Rev. B 74, R. K. Zheng, J. Wang, X. Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, H. L. W. Chan, C. L. Choy, and H. S. Luo, J. Appl. Phys. 99, H. S. Luo, G. S. Xu, H. Q. Xu, P. C. Wang, and Z. W. Yin, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., Part 1 39, P. G. Radaelli, M. Marezio, H. Y. Hwang, and S.-W. Cheong, J. PHYSICAL REVIEW B 79, Solid State Chem. 122, T. Kanki, Y. G. Park, H. Tanaka, and T. Kawai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, Y. F. Lu, J. Klein, C. Höfener, B. Wiedenhorst, J. B. Philipp, F. Herbstritt, A. Marx, L. Alff, and R. Gross, Phys. Rev. B 62, X. J. Chen, H.-U. Habermeier, H. Zhang, G. Gu, M. Varela, J. Santamaria, and C. C. Almasan, Phys. Rev. B 72, A. J. Millis, T. Darling, and A. Migliori, J. Appl. Phys. 83, N. M. Souza-Neto, A. Y. Ramos, H. C. N. Tolentino, E. Favre- Nicolin, and L. Ranno, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, N. M. Souza-Neto, A. Y. Ramos, H. C. N. Tolentino, E. Favre- Nicolin, and L. Ranno, Phys. Rev. B 7, R. K. Zheng, Y. Wang, H. L. W. Chan, C. L. Choy, and H. S. Luo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, S. W. Jin, G. Y. Gao, Z. Z. Yin, Z. Huang, X. Y. Zhou, and W. B. Wu, Phys. Rev. B 75, L. Sudheendra, V. Moshnyaga, and K. Samwer, Contemp. Phys. 48, D. Gillaspie, J. X. Ma, H. Y. Zhai, T. Z. Ward, H. M. Christen, E. W. Plummer, and J. Shen, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 8S Z. Zeng, M. Greenblatt, and M. Croft, Phys. Rev. B 59,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 054108 2007 Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field K. W. Kwok, a M. K. Cheung, H. L. W. Chan, and C. L. Choy Department of Applied Physics
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 054108 2007 Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field K. W. Kwok, a M. K. Cheung, H. L. W. Chan, and C. L. Choy Department of Applied Physics
Intermediate ferroelectric orthorhombic and monoclinic M B phases in [110] electric-field-cooled Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 30%PbTiO 3 crystals
![Intermediate ferroelectric orthorhombic and monoclinic M B phases in [110] electric-field-cooled Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 30%PbTiO 3 crystals Intermediate ferroelectric orthorhombic and monoclinic M B phases in [110] electric-field-cooled Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 30%PbTiO 3 crystals](/thumbs/94/119515660.jpg) Intermediate ferroelectric orthorhombic and monoclinic M B phases in [110] electric-field-cooled Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 30%PbTiO 3 crystals Hu Cao, Feiming Bai, Naigang Wang, Jiefang Li, and D. Viehland
Intermediate ferroelectric orthorhombic and monoclinic M B phases in [110] electric-field-cooled Pb Mg 1/3 Nb 2/3 O 3 30%PbTiO 3 crystals Hu Cao, Feiming Bai, Naigang Wang, Jiefang Li, and D. Viehland
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals
 Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, C.-S. Tu, F.-T. Wang,
Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, C.-S. Tu, F.-T. Wang,
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 3 1 FEBRUARY 2004 Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films K. W. Kwok, a) R. C. W. Tsang,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 3 1 FEBRUARY 2004 Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films K. W. Kwok, a) R. C. W. Tsang,
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Structural Evidence for Strong Coupling between Polarization Rotation and Lattice Strain in Monoclinic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Hui Liu, Jun Chen,*, Longlong Fan, Yang Ren, Lei Hu,
Supporting Information Structural Evidence for Strong Coupling between Polarization Rotation and Lattice Strain in Monoclinic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Hui Liu, Jun Chen,*, Longlong Fan, Yang Ren, Lei Hu,
Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction
 Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction Yang Bai 1,2, Guangping Zheng 1 and Sanqiang Shi 1 1 Department of Mechanical
Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction Yang Bai 1,2, Guangping Zheng 1 and Sanqiang Shi 1 1 Department of Mechanical
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Relaxor characteristics of ferroelectric BaZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 ceramics
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 27, No. 3, 2009 Relaxor characteristics of ferroelectric BaZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 ceramics C. FU 1, 2*, F. PAN 1, W. CAI 1, 2, X. DENG 2, X. LIU 2 1 School of Materials Science
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 27, No. 3, 2009 Relaxor characteristics of ferroelectric BaZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 ceramics C. FU 1, 2*, F. PAN 1, W. CAI 1, 2, X. DENG 2, X. LIU 2 1 School of Materials Science
A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 174415 Anomalous Hall effect of Nd 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films with large magnetoresistance ratio: Evidence of Berry phase effect H. C. Yang Department of Physics, National Taiwan
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
Coaction of strain and polarization effects on tuning the photoinduced resistance changes in La 0.9 Sr 0.1 MnO 3 films
 OFFPRINT Coaction of strain and polarization effects on tuning the photoinduced resistance changes in La 0.9 Sr 0.1 MnO 3 films E. J. Guo, J. Gao and H. B. Lu EPL, 95 (2011) 47006 Please visit the new
OFFPRINT Coaction of strain and polarization effects on tuning the photoinduced resistance changes in La 0.9 Sr 0.1 MnO 3 films E. J. Guo, J. Gao and H. B. Lu EPL, 95 (2011) 47006 Please visit the new
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
Effect of substrate-induced strains on the spontaneous polarization of epitaxial BiFeO 3 thin films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 11, 11415 27 Effect of substrate-induced strains on the spontaneous polarization of epitaxial 3 thin films J. X. Zhang, a Y. L. Li, Y. Wang, Z. K. Liu, and L. Q. Chen Department
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 11, 11415 27 Effect of substrate-induced strains on the spontaneous polarization of epitaxial 3 thin films J. X. Zhang, a Y. L. Li, Y. Wang, Z. K. Liu, and L. Q. Chen Department
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
SEEING Phase Transitions with. Magnetic Force Microscopy. Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin. Alex de Lozanne
 SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in
 Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Flexible Piezoelectric-Induced Pressure Sensors for Static. Measurements Based on Nanowires/Graphene Heterostructures
 Flexible Piezoelectric-Induced Pressure Sensors for Static Measurements Based on Nanowires/Graphene Heterostructures Zefeng Chen,, Zhao Wang,, Xinming Li,*, Yuxuan Lin, Ningqi Luo, Mingzhu Long, Ni Zhao,
Flexible Piezoelectric-Induced Pressure Sensors for Static Measurements Based on Nanowires/Graphene Heterostructures Zefeng Chen,, Zhao Wang,, Xinming Li,*, Yuxuan Lin, Ningqi Luo, Mingzhu Long, Ni Zhao,
Crafting the strain state in epitaxial thin films: A case study of CoFe 2 O 4 films on Pb(Mg,Nb)O 3 -PbTiO 3
 Crafting the strain state in epitaxial thin films: A case study of CoFe 2 O 4 films on Pb(Mg,Nb)O 3 -PbTiO 3 Zhiguang Wang, 1,* Yaojin Wang, 1 Haosu Luo, 2 Jiefang Li, 1 and D. Viehland 1 1 Department
Crafting the strain state in epitaxial thin films: A case study of CoFe 2 O 4 films on Pb(Mg,Nb)O 3 -PbTiO 3 Zhiguang Wang, 1,* Yaojin Wang, 1 Haosu Luo, 2 Jiefang Li, 1 and D. Viehland 1 1 Department
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film
 Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, Volume 108, Issue 4, paper number 044107 High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film T. M. Correia and Q. Zhang*
Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, Volume 108, Issue 4, paper number 044107 High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film T. M. Correia and Q. Zhang*
Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals
 Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals Jae-Hyeon Ko 1 *, Do Han Kim 2, Seiji Kojima 2, D. C. Feng 3 1 Department of Physics, Hallym University,
Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals Jae-Hyeon Ko 1 *, Do Han Kim 2, Seiji Kojima 2, D. C. Feng 3 1 Department of Physics, Hallym University,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 5 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 5 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 5 Oct 2007](/thumbs/72/66315680.jpg) Strain-induced insulator state in La 0.7 Sr 0.3 CoO 3 A. D. Rata 1, A. Herklotz 1, K. Nenkov 1,2, L. Schultz 1, and K. Dörr 1 1 IFW Dresden, Institute for Metallic Materials, Helmholtzstraße 20, 01069
Strain-induced insulator state in La 0.7 Sr 0.3 CoO 3 A. D. Rata 1, A. Herklotz 1, K. Nenkov 1,2, L. Schultz 1, and K. Dörr 1 1 IFW Dresden, Institute for Metallic Materials, Helmholtzstraße 20, 01069
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
I. INTRODUCTION II. SAMPLE PREPARATION JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2001 Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals Hanxing Yu, Venkat Gopalan, Jürgen Sindel,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2001 Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals Hanxing Yu, Venkat Gopalan, Jürgen Sindel,
2 ( º ) Intensity (a.u.) Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure for composition Bi0.75Pb0.25Fe0.7Mn0.05Ti0.25O3. Highresolution
 Intensity (a.u.) Y Obs Y Cal Y Obs - Y Cal Bragg position Cc 20 40 60 80 100 2 ( º ) Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure for composition Bi0.75Pb0.25Fe0.7Mn0.05Ti0.25O3. Highresolution X-ray diffraction
Intensity (a.u.) Y Obs Y Cal Y Obs - Y Cal Bragg position Cc 20 40 60 80 100 2 ( º ) Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure for composition Bi0.75Pb0.25Fe0.7Mn0.05Ti0.25O3. Highresolution X-ray diffraction
Impedance Analysis and Low-Frequency Dispersion Behavior of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 Glass
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 1, January 2010, pp. 462 466 Impedance Analysis and Low-Frequency Dispersion Behavior of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 Glass C. H. Song, M. Kim, S. M. Lee, H. W. Choi
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 1, January 2010, pp. 462 466 Impedance Analysis and Low-Frequency Dispersion Behavior of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 Glass C. H. Song, M. Kim, S. M. Lee, H. W. Choi
Ferroelectric materials contain one or more polar axes along which a spontaneous
 Chapter 3 Ferroelectrics 3.1 Definition and properties Ferroelectric materials contain one or more polar axes along which a spontaneous polarization can be developed below the material s Curie temperature.
Chapter 3 Ferroelectrics 3.1 Definition and properties Ferroelectric materials contain one or more polar axes along which a spontaneous polarization can be developed below the material s Curie temperature.
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Materials 218/UCSB: Phase transitions and polar materials
 Materials 218/UCSB: Phase transitions and polar materials Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) Background: Intrinsic stability of thermodynamic systems (after H. B. Callen, Thermodynamics and an introduction
Materials 218/UCSB: Phase transitions and polar materials Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) Background: Intrinsic stability of thermodynamic systems (after H. B. Callen, Thermodynamics and an introduction
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric Thin Films Consisted of (Na 0.5 Bi 0.5 )TiO 3 and Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-04-24 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 684, pp 307-311 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.684.307 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-04-24 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 684, pp 307-311 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.684.307 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric
Aging effect evolution during ferroelectricferroelectric phase transition: A mechanism study
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Aging effect evolution during ferroelectricferroelectric
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Aging effect evolution during ferroelectricferroelectric
Temperature-dependent phase transitions in Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.93Ti0.07O3 crystal
 Temperature-dependent phase transitions in Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.93Ti0.07O3 crystal Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, Chi-Shun Tu, F. -T. Wang & L. C. Lim This is an Accepted Manuscript of an article published
Temperature-dependent phase transitions in Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.93Ti0.07O3 crystal Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, Chi-Shun Tu, F. -T. Wang & L. C. Lim This is an Accepted Manuscript of an article published
Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method
 Chapter 7 Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method 7-1. Introduction Over the past few decades, various methods for obtaining
Chapter 7 Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method 7-1. Introduction Over the past few decades, various methods for obtaining
Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Physics Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Physics 12-18-2007 Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films Y.
Boise State University ScholarWorks Physics Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Physics 12-18-2007 Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films Y.
Citation JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS (2003),
 Crystallographic characterization o Titlefilms with different Zr/Ti ratio gr magnetron sputtering Author(s) Kanno, I; Kotera, H; Wasa, K; Matsu Takayama, R Citation JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS (2003), Issue
Crystallographic characterization o Titlefilms with different Zr/Ti ratio gr magnetron sputtering Author(s) Kanno, I; Kotera, H; Wasa, K; Matsu Takayama, R Citation JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS (2003), Issue
Poling field versus piezoelectric property for [001] c oriented 91%Pb(Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 )O 3 9%PbTiO 3 single crystals
![Poling field versus piezoelectric property for [001] c oriented 91%Pb(Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 )O 3 9%PbTiO 3 single crystals Poling field versus piezoelectric property for [001] c oriented 91%Pb(Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 )O 3 9%PbTiO 3 single crystals](/thumbs/93/113453013.jpg) J Mater Sci (2011) 46:1839 1843 DOI 10.1007/s10853-010-5009-z Poling field versus piezoelectric property for [001] c oriented 91%Pb(Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 )O 3 9%PbTiO 3 single crystals Yang Xiang Rui Zhang Wenwu
J Mater Sci (2011) 46:1839 1843 DOI 10.1007/s10853-010-5009-z Poling field versus piezoelectric property for [001] c oriented 91%Pb(Zn 1/3 Nb 2/3 )O 3 9%PbTiO 3 single crystals Yang Xiang Rui Zhang Wenwu
Colossal Magnetoresistance Manganites and Related Prototype Devices
 Colossal Magnetoresistance Manganites and Related Prototype Devices Liu Yukuai( 刘愉快 ), Yin Yuewei( 殷月伟 ) *, and Li Xiaoguang( 李晓光 ) * Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, Department
Colossal Magnetoresistance Manganites and Related Prototype Devices Liu Yukuai( 刘愉快 ), Yin Yuewei( 殷月伟 ) *, and Li Xiaoguang( 李晓光 ) * Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, Department
Supplementary Information for. Non-volatile memory based on ferroelectric photovoltaic effect
 Supplementary Information for Non-volatile memory based on ferroelectric photovoltaic effect Rui Guo 1, Lu You 1, Yang Zhou 1, Zhi Shiuh Lim 1, Xi Zou 1, Lang Chen 1, R. Ramesh 2, Junling Wang 1* 1 School
Supplementary Information for Non-volatile memory based on ferroelectric photovoltaic effect Rui Guo 1, Lu You 1, Yang Zhou 1, Zhi Shiuh Lim 1, Xi Zou 1, Lang Chen 1, R. Ramesh 2, Junling Wang 1* 1 School
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition. of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress
 Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light. Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film
 Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology
 Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology MEMS Engineer Forum 2016/5/11 11:50-12:15 Content 1. Introduction 2. Processing 3. Materials Matter Content
Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology MEMS Engineer Forum 2016/5/11 11:50-12:15 Content 1. Introduction 2. Processing 3. Materials Matter Content
Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier
 Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier Yang Zhou, 1 Xi Zou, 1 Lu You, 1 Rui Guo, 1 Zhi Shiuh Lim, 1 Lang Chen, 1 Guoliang Yuan, 2,a) and Junling Wang 1,b) 1 School
Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier Yang Zhou, 1 Xi Zou, 1 Lu You, 1 Rui Guo, 1 Zhi Shiuh Lim, 1 Lang Chen, 1 Guoliang Yuan, 2,a) and Junling Wang 1,b) 1 School
Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers
 15 th Korea-U.S. Forum on Nanotechnology Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers Seung-Hyub Baek Center for Electronic Materials Korea Institute of Science and Technology
15 th Korea-U.S. Forum on Nanotechnology Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers Seung-Hyub Baek Center for Electronic Materials Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics
 Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
X-ray analysis of epitaxial PbTiO 3 thin film grown on an (001) SrTiO 3 substrate by metal organic chemical vapour deposition
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8 (1996) 10185 10194. Printed in the UK X-ray analysis of epitaxial PbTiO 3 thin film grown on an (001) SrTiO 3 substrate by metal organic chemical vapour deposition Li Sun, Yan-Feng
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8 (1996) 10185 10194. Printed in the UK X-ray analysis of epitaxial PbTiO 3 thin film grown on an (001) SrTiO 3 substrate by metal organic chemical vapour deposition Li Sun, Yan-Feng
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions
 Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions B.G. Potter, Jr., B.A. Tuttle, and V. Tikare Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM
Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions B.G. Potter, Jr., B.A. Tuttle, and V. Tikare Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM
Electro-shape-memory effect in Mn-doped BaTiO 3 single crystals and in situ observation of the reversible domain switching
 Materials Science and Engineering A 438 440 (2006) 354 359 Electro-shape-memory effect in Mn-doped BaTiO 3 single crystals and in situ observation of the reversible domain switching L.X. Zhang a,b,c,,x.ren
Materials Science and Engineering A 438 440 (2006) 354 359 Electro-shape-memory effect in Mn-doped BaTiO 3 single crystals and in situ observation of the reversible domain switching L.X. Zhang a,b,c,,x.ren
Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies.
 PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes
 5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Insulating Interlocked Ferroelectric and Structural Antiphase Domain Walls in Multiferroic YMnO 3 T. Choi 1, Y. Horibe 1, H. T. Yi 1,2, Y. J. Choi 1, Weida. Wu 1, and S.-W. Cheong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Insulating Interlocked Ferroelectric and Structural Antiphase Domain Walls in Multiferroic YMnO 3 T. Choi 1, Y. Horibe 1, H. T. Yi 1,2, Y. J. Choi 1, Weida. Wu 1, and S.-W. Cheong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Ferroelectric-field-effect-enhanced electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel junctions Zheng Wen, Chen Li, Di Wu*, Aidong Li and Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures,
Ferroelectric-field-effect-enhanced electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel junctions Zheng Wen, Chen Li, Di Wu*, Aidong Li and Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures,
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates.
 Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5 <= x <= 0.9) manganites
 Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
Title Jahn-Teller effect and stability of the charge-ordered state in La1-xCaxMnO3 (0.5
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 23 Jul 2007](/thumbs/77/75146340.jpg) Polaronic signature in the metallic phase of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films detected by scanning tunneling spectroscopy S. Seiro, Y. Fasano, I. Maggio-Aprile, E. Koller, O. Kuffer, and Ø. Fischer Département
Polaronic signature in the metallic phase of La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films detected by scanning tunneling spectroscopy S. Seiro, Y. Fasano, I. Maggio-Aprile, E. Koller, O. Kuffer, and Ø. Fischer Département
Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers
 Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers W. J. Xu 1, B. Zhang 2, Z. X. Liu 1, Z. Wang 1, W. Li 1, Z. B. Wu 3, R. H. Yu 4 and X. X. Zhang 2* 1 Dept. of Phys. and Institute of Nanoscience & Technology, The
Anomalous Hall Effect in Fe/Gd Bilayers W. J. Xu 1, B. Zhang 2, Z. X. Liu 1, Z. Wang 1, W. Li 1, Z. B. Wu 3, R. H. Yu 4 and X. X. Zhang 2* 1 Dept. of Phys. and Institute of Nanoscience & Technology, The
Adaptive ferroelectric states in systems with low domain wall energy: Tetragonal microdomains
 Adaptive ferroelectric states in systems with low domain wall energy: Tetragonal microdomains Y. M. Jin, Y. U. Wang, A. G. Khachaturyan, J. F. Li, and D. Viehland Citation: Journal of Applied Physics 94,
Adaptive ferroelectric states in systems with low domain wall energy: Tetragonal microdomains Y. M. Jin, Y. U. Wang, A. G. Khachaturyan, J. F. Li, and D. Viehland Citation: Journal of Applied Physics 94,
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces
 Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Applied Surface Science
 Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4293 4297 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Influence of the substrate on ferroelectric
Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4293 4297 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Influence of the substrate on ferroelectric
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics, School of Electrical Engineering,
 Nano-scale oxygen octahedral tilting in 0.90(Bi 1/2 Na 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05(Bi 1/2 K 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05BaTiO 3 lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics,
Nano-scale oxygen octahedral tilting in 0.90(Bi 1/2 Na 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05(Bi 1/2 K 1/2 )TiO 3-0.05BaTiO 3 lead-free perovskite piezoelectric ceramics Cheuk W. Tai * and Y. Lereah Department of Physical Electronics,
Synthesis and Ferroelectric Properties of KNO 3 films
 Synthesis and Ferroelectric Properties of KNO 3 films Shahid Ramay and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar LUMS School of Science and Engineering Friday, August, 20, 2010 Potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) shows ferroelectric
Synthesis and Ferroelectric Properties of KNO 3 films Shahid Ramay and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar LUMS School of Science and Engineering Friday, August, 20, 2010 Potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) shows ferroelectric
Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films
 Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films Tianquan Lü* and Wenwu Cao Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, 83 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films Tianquan Lü* and Wenwu Cao Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, 83 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Structural and electro-optic properties of Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films grown on various substrates using pulsed laser deposition
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 043515 2007 Structural and electro-optic properties of Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films grown on various substrates using pulsed laser deposition D. Y. Wang, a J. Wang, H.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 043515 2007 Structural and electro-optic properties of Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films grown on various substrates using pulsed laser deposition D. Y. Wang, a J. Wang, H.
Ceramic Processing Research
 Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 32~36 (2018) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Dielectric and ferroelectric characteristics of doped BZT-BCT ceramics sintered at
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research. Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 32~36 (2018) J O U R N A L O F Ceramic Processing Research Dielectric and ferroelectric characteristics of doped BZT-BCT ceramics sintered at
Colossal electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor. tunnel diodes for resistive switching memories
 Colossal electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel diodes for resistive switching memories Zheng Wen, Chen Li, Di Wu*, Aidong Li and Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures
Colossal electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel diodes for resistive switching memories Zheng Wen, Chen Li, Di Wu*, Aidong Li and Naiben Ming National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures
Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules
 Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules Metrology, Characterization, Failure Analysis: Data Storage Magnetoresistive (MR) read-write heads Semiconductor Transistors Interconnect Ferroelectric
Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules Metrology, Characterization, Failure Analysis: Data Storage Magnetoresistive (MR) read-write heads Semiconductor Transistors Interconnect Ferroelectric
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 81,
 Electric-field-induced antiferroelectric to ferroelectric phase transition in mechanically confined Pb.99 Nb.2 [(Zr.57 Sn.43 ).94 Ti.6 ].98 O 3 X. Tan, 1, * J. Frederick, 1 C. Ma, 1 E. Aulbach, 2 M. Marsilius,
Electric-field-induced antiferroelectric to ferroelectric phase transition in mechanically confined Pb.99 Nb.2 [(Zr.57 Sn.43 ).94 Ti.6 ].98 O 3 X. Tan, 1, * J. Frederick, 1 C. Ma, 1 E. Aulbach, 2 M. Marsilius,
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information Colossal permittivity with ultralow dielectric loss
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information Colossal permittivity with ultralow dielectric loss
Pulsed laser deposition of PZT and PLZT
 Chapter 3 Pulsed laser deposition of PZT and PLZT A lower growth temperature of PZT films is favored for integration of these films for MEMS application. This chapter gives a detailed account of the work
Chapter 3 Pulsed laser deposition of PZT and PLZT A lower growth temperature of PZT films is favored for integration of these films for MEMS application. This chapter gives a detailed account of the work
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes Hailin Peng 1*, Wenhui Dang 1, Jie Cao 1, Yulin Chen 2,3, Di Wu 1, Wenshan Zheng 1, Hui Li 1, Zhi-Xun Shen 3,4, Zhongfan
Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes Hailin Peng 1*, Wenhui Dang 1, Jie Cao 1, Yulin Chen 2,3, Di Wu 1, Wenshan Zheng 1, Hui Li 1, Zhi-Xun Shen 3,4, Zhongfan
MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications
 MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 26 Dielectric Properties of Ceramic Materials 2 1. Barsoum, Fundamental Ceramics, McGraw-Hill, 2000, pp.513 543 2. Richerson, Modern Ceramic Engineering,
MME 467: Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 26 Dielectric Properties of Ceramic Materials 2 1. Barsoum, Fundamental Ceramics, McGraw-Hill, 2000, pp.513 543 2. Richerson, Modern Ceramic Engineering,
Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum Wells
 Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
Roger Johnson Structure and Dynamics: Displacive phase transition Lecture 9
 9.1. Summary In this Lecture we will consider structural phase transitions characterised by atomic displacements, which result in a low temperature structure that is distorted compared to a higher temperature,
9.1. Summary In this Lecture we will consider structural phase transitions characterised by atomic displacements, which result in a low temperature structure that is distorted compared to a higher temperature,
Trajectory of the anomalous Hall effect towards the quantized state in a ferromagnetic topological insulator
 Trajectory of the anomalous Hall effect towards the quantized state in a ferromagnetic topological insulator J. G. Checkelsky, 1, R. Yoshimi, 1 A. Tsukazaki, 2 K. S. Takahashi, 3 Y. Kozuka, 1 J. Falson,
Trajectory of the anomalous Hall effect towards the quantized state in a ferromagnetic topological insulator J. G. Checkelsky, 1, R. Yoshimi, 1 A. Tsukazaki, 2 K. S. Takahashi, 3 Y. Kozuka, 1 J. Falson,
Flexible Asymmetrical Solid-state Supercapacitors Based on Laboratory Filter Paper
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Flexible Asymmetrical Solid-state Supercapacitors Based on Laboratory Filter Paper Leicong Zhang,,,# Pengli Zhu,,,#, * Fengrui Zhou, Wenjin Zeng, Haibo Su, Gang Li, Jihua Gao, Rong
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Flexible Asymmetrical Solid-state Supercapacitors Based on Laboratory Filter Paper Leicong Zhang,,,# Pengli Zhu,,,#, * Fengrui Zhou, Wenjin Zeng, Haibo Su, Gang Li, Jihua Gao, Rong
Evidence for Jahn-Teller Polarons*
 Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, S. 263-269 (1997) by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München 1997 Giant Oxygen-Isotope Shift of the Ferromagnetic Transition Temperature in the Colossal Magnetoresistive
