PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05
|
|
|
- Charity Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHASE DIAGRAM AND MAGNETOCALORIC EFFECTS IN Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 Anil Aryal 1, Abdiel Quetz 1, Sudip Pandey 1, Michael Eubank 1, Tapas Samanta 2, Igor Dubenko 1, Shane Stadler 2, and Naushad Ali 1 1 Department of Physics, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL USA 2 Department of Physics & Astronomy, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA USA I. ABSTRACT: The structural and magnetic properties of the Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 system (for x = 0, 0.035, 0.070, 0.105) have been studied by x-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and magnetization measurements. A change in crystal structure from orthorhombic to hexagonal was observed in the XRD data at chromium concentrations of x = 0.035, 0.070, and The values of the cell parameters and volume of the unit cell for orthorhombic and hexagonal phase were determined. It was found that the partial substitution of Ni for Cr in Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 results in a first order magnetostructural transition from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic (FM) at T M = 132 K for x = A FM to paramagnetic second order transition has been observed at T C = 204 K. A magnetic entropy change of S M = 4.5 J/kg K for ΔH = 5T was observed in the vicinity of T C and T M for x = The values of the latent heat (L = 2.2 J/g) and corresponding total entropy changes (ΔS T = 16 J/kg K) have been determined from DSC measurements. A concentration-dependent phase diagram of transition temperatures has been constructed using the magnetic and DSC data.
2 II. INTRODUCTION Materials that undergo magnetostructural transitions have been actively studied in recent years. Some of the MnNiGe-based intermetallic compounds undergo temperature-induced magnetostructural phase transitions (MST). The MST is responsible for many observed multifunctional properties in these materials such as magnetocaloric effects (MCE), magnetoresistance, magnetostriction, and magnetic shape memory [1-5]. By changing intrinsic and extrinsic parameters (such as chemical composition, crystal structure, applied magnetic field, temperature, and pressure), the MST can be controlled, which in turn influences the material s multifunctional properties. Such materials are of great importance for their possible practical application. The stoichiometric alloy MnNiGe has a helical antiferromagnetic (AF) structure below the Neel temperature (T N ~ 370 K) with a TiNiSi-type orthorhombic structure (Pnma space group). Upon increasing the temperature it undergoes a first order structural transition (FOT) at T = 470 K from an orthorhombic TiNiSi-type crystal structure to a hexagonal Ni 2 In type (P6 3 /mmc space group), with both phases being paramagnetic [6]. Recently it has been observed that, by changing the stoichiometry and chemical composition of the parent MnNiGe compound, the first order structural transition temperature (FOT) can be altered. In some MnNiGe-based off-stoichiometric compounds, shifting the FOT below the Curie temperature results in a magnetostructural transition [7-11]. The concentration of valence electrons per atom (e/a), interatomic distance, and degree of hexagonal distortion (c/a ratio) are the major factors that control the phase transition. It has been reported that the structural stability of these compounds at low temperature are greatly affected by Mn-Mn separation (i.e., by the volume expansion of unit cell) [7, 8, 12]. In this work, we present the results of our studies on the fractional substitution of Ni by Cr in the Ni 1-
3 xcr x MnGe 1.05 system (for x = 0, 0.035, 0.070, and 0.105) and investigate the magnetostructural phase transition and magnetocaloric effects (MCEs), and construct a phase diagram of transition temperature as a function of concentration (x) and e/a ratio. III. EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES The off-stoichiometric Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 samples with 0 < x < were arc-melted in an ultra-high purity argon atmosphere using 99.99% purity elements. The compounds were annealed in high vacuum ( 10 5 torr) for 48 hours at 850 o C. An X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation was implemented to measure the room temperature X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, and the Rietveld profile refinement method was employed within the FULLPROF program to obtain the lattice constants of the samples. The magnetization measurements were obtained in a temperature interval of 5 to 380 K in magnetic fields up to 5 T using a superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer (SQUID by Quantum Design). The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements were obtained using a DSC 8000 instrument (with a ramp rate of 20 K/min during heating and cooling) in the temperature range of K. The latent heat (L) was estimated from the endothermic peak of the heat flow curves using L = T f dq T s dt dt, where dq is the change of heat flow with respect to temperature, dt and T s and T f are the initial and final temperatures of the magnetostructural phase transitions on heating, respectively. IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The room temperature XRD patterns of Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (x= 0, 0.035, 0.070, 0.105) are shown in Figure 1. The parent compound, NiMnGe, has an orthorhombic TiNiSi- type structure at room temperature. Samples with higher chromium content (x = 0.035, 0.070, and 0.105) exhibit a hexagonal Ni 2- In type structure. It has been reported that doping the stoichiometric compound with foreign atoms of different size can induce a chemical
4 pressure with a similar effect as the application of an external mechanical pressure [13]. It was observed that an increase in Cr concentration results in an increase of lattice parameters of the hexagonal phase, resulting in the expansion of cell volume (see table 1). Thus the increase in lattice parameters and cell volume is due to the substitution of the larger ionic radius Cr (R = Å) for smaller Ni (1.246 Å), acting like negative chemical pressure, increasing the Mn Mn distance. It has been found from band structure calculations that the free energy of the low temperature phase depends on the degree of hexagonal distortion (c/a) [14]. In the case of x = 0.035, 0.070,and compounds, as c/a ratio decreases, the free energy is minimized, and the high temperature phase becomes stable at low temperature. Thus, the increase in cell volume of high temperature hexagonal phase results in stability loss of low temperature phase. The temperature dependence of the magnetization M(T) of Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (for x= 0.105) on heating and cooling under a field of 100 Oe is shown in Figure 2. The sample with higher Cr concentration (x = 0.105) shows two successive magnetic phase transitions. In the low temperature region, weak magnetization is observed that corresponds to the non-collinear AF state with a TiNiSi-type orthorhombic structure. The observation is consistent with stoichiometric MnNiGe [6]. On increasing the temperature, a jump-like increase in magnetization is observed at T M = 132 K with a thermal hysteresis of about 14 K. This lowtemperature transition corresponds to a first order magnetostructure transition (MST) from non-collinear AF orthorhombic phase to non-collinear ferromagnetic (FM) hexagonal phase. Further heating results a second order transition (SOT) from non-collinear FM to paramagnetic (PM) Ni 2 In-type structure at T C = 204 K. Figure 3 shows the DSC heat flow curves for Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (x= 0, 0.035, 0.070, 0.105) on heating and cooling cycles. Large endothermic and exothermic peaks were observed during heating and cooling cycles. For the compound with x = 0.105, two peaks
5 were observed. The first peak at 142 K corresponds to the crystallographic transition and second peak at 204 K is expected to be related to the magnetic phase transition. The observed thermal hysteresis of 17 K confirms the first order nature of the transition. The values of latent heat (L) and the corresponding total entropy changes (ΔS T ) were found to be 2.2 J/g and 16 J/KgK respectively in the vicinity of MST. The result from DSC experiment is consistent with the first order magnetostructural transition from AF orthorhombic phase to FM hexagonal phase seen in the magnetization measurements. The isothermal magnetization M(H) curves for the sample x = were measured around the transition temperature (T M ) in a magnetic fields up to 50 koe (Figure 4). At temperatures near T M, a change in magnetization was observed which resembles the noncollinear ferromagnetic nature. Considering the magnetization curve M(H), it can be inferred that the low-temperature transitions are from noncollinear AF to noncollinear FM. The magnetic entropy changes (ΔS M ) in the vicinity of the magnetostructural transition temperature for different magnetic fields (ΔH) are shown in Figure 5. The magnetic entropy changes (ΔS M ) were calculated using the Maxwell relation, ( S/ H) T = ( M/ T) H, from the magnetization isotherms measured at different temperatures [15]. An inverse MCE has been observed in the vicinity of T M (see Figure 5), which is due to the jump-like change of magnetization (see Figure 2) corresponding to the first-order magnetostructural transition from orthorhombic AF to hexagonal FM phases. Using DSC and magnetic data, a concentration-dependent phase diagram as a function of concentration (x) and e/a ratio has been constructed (Figure 6). With the chromium concentration x = 0.070, a triple-point was observed near the critical temperature of 210 K. A first order structural transformation and the second order magnetic phase transitions coincide to produce a first order magnetostructural transformation around the critical temperature. For x < 0.070, magnetic transitions from AF to PM states were observed with negligible change in
6 magnetization. For x > 0.070, magnetostructural transitions between an AF, orthorhombic TiNiSi-type state to a FM hexagonal Ni 2 In-type state were observed, followed by a magnetic transition from a FM to PM state. From Figure 6 it is concluded that with the increase in chromium concentration, the e/a ratio decreases, resulting in a decrease in the phase transition temperature. V. CONCLUSION The magnetostructural phase transitions and MCEs in off-stoichiometric NiMnGe 1.05 alloys have been studied, and a concentration-dependent phase diagram has been constructed for this system. The experimental results show that increasing the Cr concentration results a decrease of T M. As T M decreases below T C, a magnetostructural transition from an AF state to FM state was observed, followed by a jump in magnetization. Large positive and negative values of magnetic entropy changes were observed near T M and T C, respectively. Acknowledgements: Work at Southern Illinois University was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences (BES) under Award No. DE-FG02-06ER Work at Louisiana State University was supported by DOE, Office of Science, BES under Award No. DE-FG02-13ER46946
7 References: [1] A. O. Pecharsky, K. A. Gschneidner, Jr, and V. K. Pecharsky, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4722 (2003). [2] O. Tegus, E. Bruck, K. H. J. Buschow, and F. R. de Boer, Nature (London) 415, 150 (2002). [3] T. Krenke, E. Duman, M. Acet, E. F. Wassermann, X. Moya, L. Mañosa, and A. Planes, Nat. Mater. 4, 450 (2005). [4] S. Y. Yu, Z. H. Liu, G. D. Liu, J. L. Chen, Z. X. Cao, G. H. Wu, B. Zhang, and X. X. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, (2006). [5] R. Kainuma, Y. Imano, W. Ito, Y. Sutou, H. Morito, S. Okamoto, O. Kitakami, K. Oikawa, A. Fujita, T. Kanomata, and K. Ishida, Nature (London) 439, 957 (2006). [6] W. Bazela, A. Szytuła, T. Todorovic, Z. Tomkowicz, and A. Zieba, Phys. Status Solidi A 38, 721 (1976). [7] C. L. Zhang, D. H.Wang, Q. Q. Cao, Z. D. Han, H. C. Xuan, and Y. W. Du, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, (2008). [8] C. Zhang, D. Wang, Q. Cao, S. Ma, H. Xuan, and Y. Du, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43, (2010). [9] Z. C. Liang, W. D. Hui, C. Jian, W. T. Zhi, X. G. Xi, and Z. Chun, Chin. Phys. B 20, (2011). [10] E. Liu, Y. Du, J. Chen, W. Wang, H. Zhang, and G. Wu, IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 4041 (2011). [11] A. Quetz, B. Muchharla, T. Samanta, I. Dubenko, S. Talapatra, S. Stadler, N. Ali, J. Appl. Phys A922 (2014) [12] J. T. Wang, D. S. Wang, C. F. Chen, O. Nashima, T. Kanomata, H. Mizuseki, and Y. Kawazoe, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, (2006). [13] Lyubina J, Nenkov K, Schultz L and Gutfleisch O 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett [14] A. Ayuela, J. Enkovaara, K. Ullako, R.M. Neiminen, J. Phys. Comdens. Matter 11, 2017 (1999). [15] K. A. Gschneidner, Jr., V. K. Pecharsky, and A. O. Tsokol, Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 1479 (2005)
8 Tables Table1: Cell parameters of Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 at room temperature. Chromium concentration (x) a (Å) c (Å) Volume of unit cell (Å) 3 c/a Figure captions Figure 1. The room temperature XRD patterns of Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (x = 0, 0.035,0.070, and 0.105). Figure 2. The temperature dependence of the magnetization M(T) of Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (x = 0.105) on heating and cooling under the field of 100 Oe. Figure 3. DSC heat flow curves for Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 on heating and cooling cycles. Figure 4. The isothermal magnetization M(H) curves for the sample with x = Figure 5. The magnetic entropy changes as a function of temperature for Ni 1-x Cr x MnGe 1.05 (x=0.105) at different applied fields around T M and T C Figure 6. The phase diagram of transition temperatures as a function of concentration (x) and e/a ratio.
9
10
11
12
13
14
Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds with 0 x 0.5
 Vol 16 No 12, December 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(12)/3848-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds
Vol 16 No 12, December 2007 c 2007 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2007/16(12)/3848-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy changes of La 1 x Pr x Fe 11.5 Si 1.5 compounds
Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in HoCoSi
 Materials Letters 113, 195 (2013) Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in ocosi Sachin Gupta and K.G. Suresh * Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India Abstract
Materials Letters 113, 195 (2013) Observation of giant magnetocaloric effect in ocosi Sachin Gupta and K.G. Suresh * Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India Abstract
Ti substitution for Mn in MnCoGe - The magnetism of Mn0.9Ti0.1CoGe
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 213 Ti substitution for Mn in MnCoGe - The magnetism of Mn.9Ti.1CoGe
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 213 Ti substitution for Mn in MnCoGe - The magnetism of Mn.9Ti.1CoGe
Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6 by the addition of boron
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant La0.8Ce0.2Fe11.4Si1.6
Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in layered NdMn1.9Ti0.1Si2
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 214 Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in layered
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 214 Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in layered
Wide temperature span of entropy change in first-order metamagnetic MnCo 1-x Fe x Si
 Wide temperature span of entropy change in first-order metamagnetic MnCo 1-x Fe x Si J H Xu 1, W Y Yang 1, Q H Du 1, Y H Xia 1, X M Liu 2, H L Du 1, J B Yang 1, C S Wang 1, J Z Han 1, S Q Liu 1, Y Zhang
Wide temperature span of entropy change in first-order metamagnetic MnCo 1-x Fe x Si J H Xu 1, W Y Yang 1, Q H Du 1, Y H Xia 1, X M Liu 2, H L Du 1, J B Yang 1, C S Wang 1, J Z Han 1, S Q Liu 1, Y Zhang
Large magnetic entropy change near room temperature in antipervoskite SnCMn 3
 Large magnetic entropy change near room temperature in antipervoskite SnCMn 3 B. S. Wang, 1 P. Tong, 1,2(a) Y. P. Sun, 1(b) X. Luo, 1 X. B. Zhu, 1 G. Li, 1 X. D. Zhu, 1 S. B. Zhang, 1 Z. R. Yang, 1 W.
Large magnetic entropy change near room temperature in antipervoskite SnCMn 3 B. S. Wang, 1 P. Tong, 1,2(a) Y. P. Sun, 1(b) X. Luo, 1 X. B. Zhu, 1 G. Li, 1 X. D. Zhu, 1 S. B. Zhang, 1 Z. R. Yang, 1 W.
The magnetocaloric effect and critical behaviour of the Mn0.94Ti0.06CoGe alloy
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 The magnetocaloric effect and critical behaviour
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 The magnetocaloric effect and critical behaviour
Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi
 Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi Sachin Gupta and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India
Correlations among magnetic, magnetocaloric and magneto-transport properties in HoNiSi Sachin Gupta and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai-400076, India
SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy
 SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy Review December 2013 Vol.56 No.12: 2302 2311 85th Anniversary for the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences doi: 10.1007/s11433-013-5357-1 Effects
SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy Review December 2013 Vol.56 No.12: 2302 2311 85th Anniversary for the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences doi: 10.1007/s11433-013-5357-1 Effects
Magnetocaloric-Transport Properties Correlation in La 0.8 Ca 0.2 MnO 3 -Doped Manganites
 J Supercond Nov Magn 17 3:391 395 DOI 1.17/s1948-17-4139-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Magnetocaloric-Transport Properties Correlation in La.8 Ca. MnO 3 -Doped Manganites R. Skini 1 M. Khlifi E. Dhahri E. K. Hlil 3
J Supercond Nov Magn 17 3:391 395 DOI 1.17/s1948-17-4139-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Magnetocaloric-Transport Properties Correlation in La.8 Ca. MnO 3 -Doped Manganites R. Skini 1 M. Khlifi E. Dhahri E. K. Hlil 3
Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds
 Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds Niraj K. Singh, S. Agarwal, and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India-400076 R.
Anomalous magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ho Ni,Fe 2 compounds Niraj K. Singh, S. Agarwal, and K. G. Suresh* Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India-400076 R.
Structure and magnetic transition of LaFe 13 x Si x compounds
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15 (2003) 7385 7394 PII: S0953-8984(03)65192-1 Structure and magnetic transition of LaFe 13 x Si x compounds
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15 (2003) 7385 7394 PII: S0953-8984(03)65192-1 Structure and magnetic transition of LaFe 13 x Si x compounds
1-2-1, Sengen, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 19 Mar 2014
![1-2-1, Sengen, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 19 Mar 2014 1-2-1, Sengen, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 19 Mar 2014](/thumbs/92/107905969.jpg) A generalized magnetic refrigeration scheme Ryo Tamura,,a) Takahisa Ohno,,b) and Hideaki Kitazawa,c) ) International Center for Young Scientists, National Institute for Materials Science, --, Sengen, Tsukuba,
A generalized magnetic refrigeration scheme Ryo Tamura,,a) Takahisa Ohno,,b) and Hideaki Kitazawa,c) ) International Center for Young Scientists, National Institute for Materials Science, --, Sengen, Tsukuba,
Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La 0.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ) 0.3 CoO 3 System
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
PACS numbers: Sg, Eh, q, Fj, Kz Keywords: Magnetocaloric Effects, Magnetostriction, Metamagnetic transition
 The influence of hydrostatic pressure on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of DyRu Si Ahmad Us Saleheen, 1, a) Tapas Samanta, 1 Mojammel Khan, 1 Philip W. Adams, 1 David P. Young, 1 Igor Dubenko,
The influence of hydrostatic pressure on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of DyRu Si Ahmad Us Saleheen, 1, a) Tapas Samanta, 1 Mojammel Khan, 1 Philip W. Adams, 1 David P. Young, 1 Igor Dubenko,
Technology, 100 Pingleyuan, Chaoyang District, Beijing , China
 Temperature, magnetic field, and pressure dependence of the crystal and magnetic structures of the magnetocaloric compound Mn 1.1 Fe 0.9 (P 0.8 Ge 0.2 ) D. M. Liu 1, Q. Z. Huang 2, M. Yue 1, J. W. Lynn
Temperature, magnetic field, and pressure dependence of the crystal and magnetic structures of the magnetocaloric compound Mn 1.1 Fe 0.9 (P 0.8 Ge 0.2 ) D. M. Liu 1, Q. Z. Huang 2, M. Yue 1, J. W. Lynn
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2. Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1. Germany.
 Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetic Transition in the Kondo Lattice System CeRhSn 2 Z. Hossain 1, L.C. Gupta 2 and C. Geibel 1 1 Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, 01187 Dresden, Germany. 2
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
The spike in the relation between entropy change and temperature in LaFe Si 1.17 compound
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 3 (8) 1879 1883 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm The spike in the relation between entropy change and temperature in LaFe 11.83 Si 1.17 compound Hong-wei Zhang a,,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 3 (8) 1879 1883 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm The spike in the relation between entropy change and temperature in LaFe 11.83 Si 1.17 compound Hong-wei Zhang a,,
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic
 Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Recent progress in exploring magnetocaloric materials
 Recent progress in exploring magnetocaloric materials B. G. Shen,* J. R. Sun, F. X. Hu, H. W. Zhang, and Z. H. Cheng State Key Laboratory for Magnetism, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Recent progress in exploring magnetocaloric materials B. G. Shen,* J. R. Sun, F. X. Hu, H. W. Zhang, and Z. H. Cheng State Key Laboratory for Magnetism, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Doping-induced valence change in Yb 5 Ge 4 x (Sb, Ga) x : (x 1)
 Hyperfine Interact (2012) 208:59 63 DOI 10.1007/s10751-011-0415-4 Doping-induced valence change in Yb 5 Ge 4 x (Sb, Ga) x : (x 1) D. H. Ryan N. R. Lee-Hone J. M. Cadogan Published online: 26 October 2011
Hyperfine Interact (2012) 208:59 63 DOI 10.1007/s10751-011-0415-4 Doping-induced valence change in Yb 5 Ge 4 x (Sb, Ga) x : (x 1) D. H. Ryan N. R. Lee-Hone J. M. Cadogan Published online: 26 October 2011
Magnetic structure of Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 2 and Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 1.9 M 0.1 (M = Ga, Cu)
 Magnetic structure of Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 2 and Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 1.9 M 0.1 (M = Ga, Cu) E Palacios 1, J A Rodríguez-Velamazán 1,2, G F Wang 1, R Burriel 1, G Cuello 2 and J Rodríguez-Carvajal 2 1 Instituto de Ciencia
Magnetic structure of Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 2 and Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 1.9 M 0.1 (M = Ga, Cu) E Palacios 1, J A Rodríguez-Velamazán 1,2, G F Wang 1, R Burriel 1, G Cuello 2 and J Rodríguez-Carvajal 2 1 Instituto de Ciencia
Magnetoresistance and its relation to magnetization in Ni50Mn35Sn15 shape-memory epitaxial films
 Magnetoresistance and its relation to magnetization in Ni50Mn35Sn15 shape-memory epitaxial films J. Dubowik, K. Załski, I. Gościańska, H. Głowiński, and A. Ehresmann Citation: Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 162403
Magnetoresistance and its relation to magnetization in Ni50Mn35Sn15 shape-memory epitaxial films J. Dubowik, K. Załski, I. Gościańska, H. Głowiński, and A. Ehresmann Citation: Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 162403
Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge
![Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge Fe Co Si. Fe Co Si. Ref. p. 59] d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb Alloys and compounds with Ge](/thumbs/72/66917236.jpg) Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
Ref. p. 59] 1.5. 3d elements and C, Si, Ge, Sn or Pb 7 1.75 1.50 Co Si 0.8 0. 3.50 3.5 Co Si 0.8 0. H cr Magnetic field H [koe] 1.5 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.5 C C IF "A" P Frequency ωγ / e [koe] 3.00.75.50.5.00
Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 299 (2006) 255 259 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process Wei Zhang a, Zhengnan
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 299 (2006) 255 259 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Magnetism and Hall effect of the Heusler alloy Co 2 ZrSn synthesized by melt-spinning process Wei Zhang a, Zhengnan
Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe
 Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe B.M. Sondezi-Mhlungu, A.M. Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg,P.O. Box 524, Auckland Park, 2006,South Africa
Critical behavior near the ferromagnetic Curie phase transition in CeCuGe B.M. Sondezi-Mhlungu, A.M. Strydom Physics Department, University of Johannesburg,P.O. Box 524, Auckland Park, 2006,South Africa
Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of NdMn2 xtixsi2 compounds
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of NdMn2
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of NdMn2
Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature
![Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature](/thumbs/82/86626971.jpg) Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (24), No. (1), (2001) 33 Structural Study of [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Ba 0.25 ) MnO 3 ] and [Nd 0.5 (Ca 0.25 Sr 0.25 )MnO 3 ] Perovskites at Room Temperature F. F. Hanna Faculty of Petroleum
Large exchange bias after zero-field cooling from an unmagnetized state
 Large exchange bias after zero-field cooling from an unmagnetized state B. M. Wang, 1 Y. Liu, 1,* P. Ren, 2 B. Xia, 2 K. B. Ruan, 2 J. B. Yi, 3 J. Ding, 3 X. G. Li, 4 and L. Wang 2, 1 School of Mechanical
Large exchange bias after zero-field cooling from an unmagnetized state B. M. Wang, 1 Y. Liu, 1,* P. Ren, 2 B. Xia, 2 K. B. Ruan, 2 J. B. Yi, 3 J. Ding, 3 X. G. Li, 4 and L. Wang 2, 1 School of Mechanical
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LaNiSn
 Philips J. Res. 39, 77-81, 1984 R1082 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF by J. L. C. DAAMS and K. H. J. BUSCHOW Philips Research boratories, 5600 JA Eindhoven, The Netherlands Abstract The crystal structure of the
Philips J. Res. 39, 77-81, 1984 R1082 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF by J. L. C. DAAMS and K. H. J. BUSCHOW Philips Research boratories, 5600 JA Eindhoven, The Netherlands Abstract The crystal structure of the
Superconductivity in oxygen-annealed FeTe 1-x S x single crystal
 Superconductivity in oxygen-annealed FeTe 1-x S x single crystal Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Keita Deguchi 1,2,3, Yasuna Kawasaki 1,2,3, Toshinori Ozaki 1,2, Masanori Nagao 4, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,2, Takahide
Superconductivity in oxygen-annealed FeTe 1-x S x single crystal Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Keita Deguchi 1,2,3, Yasuna Kawasaki 1,2,3, Toshinori Ozaki 1,2, Masanori Nagao 4, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,2, Takahide
Analysis and modeling of magnetocaloric effect near magnetic phase transition temperature
 Analysis and modeling of magnetocaloric effect near magnetic phase transition temperature Mohamed alli, F. Allab, Cédric Dupuis, Daniel Fruchart, Damien Gignoux, Afef Kedous-Lebouc,. M. Fournier,. P. Yonnet
Analysis and modeling of magnetocaloric effect near magnetic phase transition temperature Mohamed alli, F. Allab, Cédric Dupuis, Daniel Fruchart, Damien Gignoux, Afef Kedous-Lebouc,. M. Fournier,. P. Yonnet
Magnetocaloric properties of LaFe13xyCoxSiy and commercial grade Gd
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 8, 9 Magnetocaloric properties of LaFe3xyCoxSiy and commercial grade Bjørk, Rasmus; Bahl, Christian; Katter, M. Published in: Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Mar 8, 9 Magnetocaloric properties of LaFe3xyCoxSiy and commercial grade Bjørk, Rasmus; Bahl, Christian; Katter, M. Published in: Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
Preparation, structure evolution, and magnetocaloric effects of MnFe(PGe) compounds
 Preparation, structure evolution, and magnetocaloric effects of MnFe(PGe) compounds Ming Yue 1,a), Hongguo Zhang 1, Danmin Liu 2, and Jiuxing Zhang 1 1. College of Materials Science andengineering, Beijing
Preparation, structure evolution, and magnetocaloric effects of MnFe(PGe) compounds Ming Yue 1,a), Hongguo Zhang 1, Danmin Liu 2, and Jiuxing Zhang 1 1. College of Materials Science andengineering, Beijing
The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+±
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 38, NO. 2-II APRIL 2000 The Chemical Control of Superconductivity in Bi 2 Sr 2 (Ca 1 x Y x )Cu 2 O 8+± R. S. Liu 1, I. J. Hsu 1, J. M. Chen 2, and R. G. Liu 2 1 Department
Magnetism and the magnetocaloric effect in PrMn1. 6Fe0. 4Ge2
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Magnetism and the magnetocaloric effect in Mn1. 6Fe0.
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2013 Magnetism and the magnetocaloric effect in Mn1. 6Fe0.
Magnetic and thermal properties of Er75Dy25 single crystals
 Ames Laboratory Publications Ames Laboratory 1-18-211 Magnetic and thermal properties of Er75Dy25 single crystals Mahmud Khan Iowa State University, muk@ualberta.ca Deborah L. Schlagel Iowa State University,
Ames Laboratory Publications Ames Laboratory 1-18-211 Magnetic and thermal properties of Er75Dy25 single crystals Mahmud Khan Iowa State University, muk@ualberta.ca Deborah L. Schlagel Iowa State University,
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
On the derivation of the magnetocaloric properties in ferrimagnetic spinel. Mn 3 O 4. Abstract
 On the derivation of the magnetocaloric properties in ferrimagnetic spinel Mn 3 O 4 Subhash Thota, Francois Guillou, Vincent Hardy, Alexandre Wahl and Wilfrid Prellier* Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS UMR 6508,
On the derivation of the magnetocaloric properties in ferrimagnetic spinel Mn 3 O 4 Subhash Thota, Francois Guillou, Vincent Hardy, Alexandre Wahl and Wilfrid Prellier* Laboratoire CRISMAT, CNRS UMR 6508,
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles
 Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
Research Highlights. Salient results from our group. Mixed phosphides in Sn-P and Sn-Mn-P systems
 Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
Research Highlights Dilute magnetic semiconductors and Spintronics Spintronics is a branch of electronics emerged from the dilute magnetic semiconductor in an aspect of utilization of the spin in addition
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3463 Giant and reversible extrinsic magnetocaloric effects in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films due to strain X. Moya 1, L. E. Hueso 2,3, F. Maccherozzi 4, A. I. Tovstolytkin 5, D. I. Podyalovskii
DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3463 Giant and reversible extrinsic magnetocaloric effects in La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films due to strain X. Moya 1, L. E. Hueso 2,3, F. Maccherozzi 4, A. I. Tovstolytkin 5, D. I. Podyalovskii
Spin Transition and Structural Transformation in a
 Supporting Information for Spin Transition and Structural Transformation in a Mononuclear Cobalt(II) Complex Ying Guo, Xiu-Long Yang, Rong-Jia Wei, Lan-Sun Zheng, and Jun Tao* State Key Laboratory of Physical
Supporting Information for Spin Transition and Structural Transformation in a Mononuclear Cobalt(II) Complex Ying Guo, Xiu-Long Yang, Rong-Jia Wei, Lan-Sun Zheng, and Jun Tao* State Key Laboratory of Physical
Magnetic Properties of the Mn 5 Si 3 Compound
 Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the National Conference on Neutron Scattering and the Complementary Methods in the Investigations of the Condensed Phases, Chlewiska 2007 Magnetic
Vol. 113 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 Proceedings of the National Conference on Neutron Scattering and the Complementary Methods in the Investigations of the Condensed Phases, Chlewiska 2007 Magnetic
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran *
 Magnetic behavior of bulk and fine particles of RCr 2 Si 2 C (R= La, Ce) compounds: Possible magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran * Tata Institute of Fundamental
Magnetic behavior of bulk and fine particles of RCr 2 Si 2 C (R= La, Ce) compounds: Possible magnetic ordering from Cr K. Mukherjee, Kartik K Iyer and E.V. Sampathkumaran * Tata Institute of Fundamental
Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2008 Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3 V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2008 Effect of randomness on anomalous Hall coefficient in antiferromagnet U 2 PdGa 3 V. H. TRAN * Institute of Low Temperature and Structure Research, Polish
Direct observation of magnetocaloric effect by differential thermal analysis: influence of experimental parameters
 1 Direct observation of magnetocaloric effect by differential thermal analysis: influence of experimental parameters Yamila Rotstein Habarnau a,b, Pablo Bergamasco a,b, Joaquin Sacanell a, Gabriela Leyva
1 Direct observation of magnetocaloric effect by differential thermal analysis: influence of experimental parameters Yamila Rotstein Habarnau a,b, Pablo Bergamasco a,b, Joaquin Sacanell a, Gabriela Leyva
Experimental and theoretical investigations on magnetic and related properties of ErRuSi
 Experimental and theoretical investigations on magnetic and related properties of ErRuSi Sachin Gupta, 1 A. Das, 2 K. G. Suresh, 1,* A. Hoser 3, Yu.V. Knyazev, 4 Yu. I. Kuz'min, 4 and A. V. Lukoyanov 4,5
Experimental and theoretical investigations on magnetic and related properties of ErRuSi Sachin Gupta, 1 A. Das, 2 K. G. Suresh, 1,* A. Hoser 3, Yu.V. Knyazev, 4 Yu. I. Kuz'min, 4 and A. V. Lukoyanov 4,5
Keywords: superconductivity, Fe-based superconductivity, FeTe, alcohol, wine
 Superconductivity in FeTe1-xSx induced by alcohol Keita Deguchi 1,2,3, Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Toshinori Ozaki 1,3, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,3, Takahide Yamaguchi 1,3 and Yoshihiko Takano 1,2,3 1. National
Superconductivity in FeTe1-xSx induced by alcohol Keita Deguchi 1,2,3, Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Toshinori Ozaki 1,3, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,3, Takahide Yamaguchi 1,3 and Yoshihiko Takano 1,2,3 1. National
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Tuning phase transitions and magnetocaloric properties of novel materials for magnetic refrigeration
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2012 Tuning phase transitions and magnetocaloric properties of novel materials
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2012 Tuning phase transitions and magnetocaloric properties of novel materials
Magnetic transitions and the magnetocaloric effect in the Pr 1-xYxMn2Ge2 system
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 14 Magnetic transitions and the magnetocaloric effect in the
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 14 Magnetic transitions and the magnetocaloric effect in the
materials for magnetic refrigeration
 materials for magnetic refrigeration Ekkes Brück Introduction Magnetic cooling Giant magnetocaloric effect Outlook Review: E. Brück, Magnetic refrigeration near room temperature, Handbook of magnetic materials
materials for magnetic refrigeration Ekkes Brück Introduction Magnetic cooling Giant magnetocaloric effect Outlook Review: E. Brück, Magnetic refrigeration near room temperature, Handbook of magnetic materials
A Comparative Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Gd 5 Ge 4 and Gd 5 Si 4 Compounds
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 62 (2014) 903 908 Vol. 62, No. 6, December 1, 2014 A Comparative Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Gd 5 Ge 4 and Gd 5 Si 4 Compounds Z. Momeni Larimi, 1, A. Amirabadizadeh,
Commun. Theor. Phys. 62 (2014) 903 908 Vol. 62, No. 6, December 1, 2014 A Comparative Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Gd 5 Ge 4 and Gd 5 Si 4 Compounds Z. Momeni Larimi, 1, A. Amirabadizadeh,
Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, 1/AF Bidhannagar, Calcutta , India
 Supplementary information for Coexistence of topological Dirac fermions on the surface and three-dimensional Dirac cone state in the bulk of ZrTe 5 single crystal Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute
Supplementary information for Coexistence of topological Dirac fermions on the surface and three-dimensional Dirac cone state in the bulk of ZrTe 5 single crystal Arnab Pariari & Prabhat Mandal Saha Institute
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1: Structure and composition of Teflon tape. (a) XRD spectra of original Teflon tape and Teflon tape subjected to annealing at 150 o C under Ar atmosphere.
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1: Structure and composition of Teflon tape. (a) XRD spectra of original Teflon tape and Teflon tape subjected to annealing at 150 o C under Ar atmosphere.
Analysis of the Magnetocaloric Effect in Heusler Alloys: Study of Ni 50 CoMn 36 Sn 13 by Calorimetric Techniques
 Entropy 2015, 17, 1236-1252; doi:10.3390/e17031236 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Analysis of the Magnetocaloric Effect in Heusler Alloys: Study of Ni 50 CoMn 36
Entropy 2015, 17, 1236-1252; doi:10.3390/e17031236 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Analysis of the Magnetocaloric Effect in Heusler Alloys: Study of Ni 50 CoMn 36
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
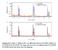 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Mixed Magnetism for Refrigeration and Energy Conversion Dung, Nguyen H.; Ou, Zhi Qiang; Caron, Luana; Zhang, Lian; Cam Thanh, Dinh T.; Wijs, Gilles A. de; Groot, Rob A. de; Buschow,
University of Groningen Mixed Magnetism for Refrigeration and Energy Conversion Dung, Nguyen H.; Ou, Zhi Qiang; Caron, Luana; Zhang, Lian; Cam Thanh, Dinh T.; Wijs, Gilles A. de; Groot, Rob A. de; Buschow,
Structural and magnetic properties of Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles
 *E-mail: shailuphy@gmail.com Abstract: We report room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM),
*E-mail: shailuphy@gmail.com Abstract: We report room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped CeO 2 nanoparticles using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM),
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials
 Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanoparticles of Superconducting materials Shipra, A. Gomathi, A. Sundaresan* and C. N. R. Rao* Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit and Department of Science and
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds
 Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
We have investigated the effect of atomic substitutions in the FeSe system, which
 Substitution Effects on FeSe Superconductor Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Fumiaki Tomioka 1,3, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,3, Takahide Yamaguchi 1,3 and Yoshihiko Takano 1,2,3 1 National Institute for Materials Science,
Substitution Effects on FeSe Superconductor Yoshikazu Mizuguchi 1,2,3, Fumiaki Tomioka 1,3, Shunsuke Tsuda 1,3, Takahide Yamaguchi 1,3 and Yoshihiko Takano 1,2,3 1 National Institute for Materials Science,
Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 53, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 1996-I Anisotropic magnetic properties of TbNi 2 B 2 C single crystals C. V. Tomy, L. A. Afalfiz, M. R. Lees, J. M. Martin, and D. McK. Paul Department of
Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction
 Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction Yang Bai 1,2, Guangping Zheng 1 and Sanqiang Shi 1 1 Department of Mechanical
Direct measurement of giant electrocaloric effect in BaTiO 3 multilayer thick film structure beyond theoretical prediction Yang Bai 1,2, Guangping Zheng 1 and Sanqiang Shi 1 1 Department of Mechanical
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based
 Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Magnetic Order versus superconductivity in the Iron-based layered La(O 1-x F x )FeAs systems Clarina de la Cruz 1,2, Q. Huang 3, J. W. Lynn 3, Jiying Li 3,4, W. Ratcliff II 3, J. L. Zarestky 5, H. A. Mook
Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi
 Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi Junyi Ge, Shixun Cao, Jincang Zhang Department of Physics,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200444, China We successfully
Superconductivity in nickel-based compound GdONiBi and hole doped Gd 0.9 Sr 0.1 ONiBi Junyi Ge, Shixun Cao, Jincang Zhang Department of Physics,Shanghai University,Shanghai 200444, China We successfully
T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike
 Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
Resistive superconducting transition and effects of atmospheric exposure in the intercalation superconductor A x (A = Li, Na) T. Hatakeda, T. Noji, S. Hosono, T. Kawamata, M. Kato, and Y. Koike Department
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY May 10, 2009 Department of Physics Advanced Materials 7.5 ECTS. Magnetic Cooling. Erik Wallin.
 UMEÅ UNIVERSIY May 10, 2009 Department of Physics Advanced Materials 7.5 ECS Magnetic Cooling Erwa0002@student.umu.se Supervisor: Andreas Sandström Abstract he magnetocaloric effect works by changing the
UMEÅ UNIVERSIY May 10, 2009 Department of Physics Advanced Materials 7.5 ECS Magnetic Cooling Erwa0002@student.umu.se Supervisor: Andreas Sandström Abstract he magnetocaloric effect works by changing the
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5
 Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
Field-Temperature Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Phases in Ludvigites Ni 3-x Mn x BO 5 L. N. Bezmaternykh, E. M. Kolesnikova*, E. V. Eremin, S. N. Sofronova, N. V. Volkov, and M. S. Molokeev Kirensky Institute
Pathways for tailoring the magnetostructural response of FeRh-based compounds. A Dissertation. Radhika Barua. The Department of Chemical Engineering
 Pathways for tailoring the magnetostructural response of FeRh-based compounds A Dissertation By Radhika Barua To The Department of Chemical Engineering In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the
Pathways for tailoring the magnetostructural response of FeRh-based compounds A Dissertation By Radhika Barua To The Department of Chemical Engineering In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Specific Heat of MCE materials
 Specific Heat of MCE materials Van der Waals-Zeeman Institute, University of Amsterdam Jacques C. P. Klaasse Measurement and interpretation of specific-heat data around magnetic transitions Presentation
Specific Heat of MCE materials Van der Waals-Zeeman Institute, University of Amsterdam Jacques C. P. Klaasse Measurement and interpretation of specific-heat data around magnetic transitions Presentation
Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 122, No. 6, November 2010, pp. 807 811. Indian Academy of Sciences. Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden Popper (RP) type phase LaSr 2 MnCrO 7 DEVINDER SINGH* and RAJINDER SINGH
Structure, crystal fields, magnetic interactions, and heavy-fermion behavior in Ce 1 x La x 3 Al
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 9 1 MARCH 1997-I Structure, crystal fields, magnetic interactions, and heavy-fermion behavior in Ce 1 x La x 3 Al Y. Y. Chen and Y. D. Yao Institute of Physics, Academia
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 9 1 MARCH 1997-I Structure, crystal fields, magnetic interactions, and heavy-fermion behavior in Ce 1 x La x 3 Al Y. Y. Chen and Y. D. Yao Institute of Physics, Academia
alkaline-metal-ethylenediamine-intercalated superconductors A x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 (A = Li, Na) with T c = 45 K
 Synthesis and post-annealing effects of alkaline-metal-ethylenediamine-intercalated superconductors A x (C N Fe -z Se (A = Li, Na) with T c = K Takashi Noji, Takehiro Hatakeda, Shohei Hosono, Takayuki
Synthesis and post-annealing effects of alkaline-metal-ethylenediamine-intercalated superconductors A x (C N Fe -z Se (A = Li, Na) with T c = K Takashi Noji, Takehiro Hatakeda, Shohei Hosono, Takayuki
Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x
 Vol. 46 No. 4 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) August 2003 Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x HAO Shiqiang ( ) 1 & CHEN Nanxian ( ) 1,2 1. Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Vol. 46 No. 4 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) August 2003 Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x HAO Shiqiang ( ) 1 & CHEN Nanxian ( ) 1,2 1. Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Synthesis, crystal structure and physical properties of quasi-one-dimensional ACr 3 As 3 (A = Rb, Cs)
 Synthesis, crystal structure and physical properties of quasi-one-dimensional ACr 3 As 3 (A = Rb, Cs) Zhang-Tu Tang 1,3, Jin-Ke Bao 1,3, Liu Yi 1,3, Hua Bai 1,3, Hao Jiang 1,3, Hui-Fei Zhai 1,3, Chun-Mu
Synthesis, crystal structure and physical properties of quasi-one-dimensional ACr 3 As 3 (A = Rb, Cs) Zhang-Tu Tang 1,3, Jin-Ke Bao 1,3, Liu Yi 1,3, Hua Bai 1,3, Hao Jiang 1,3, Hui-Fei Zhai 1,3, Chun-Mu
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Apr 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Apr 2012](/thumbs/73/68870198.jpg) arxiv:118.1291v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Apr 212 Anisotropic magnetic properties and superzone gap formation in single crystal Pranab Kumar Das, Neeraj Kumar, R. Kulkarni, S. K. Dhar and A. Thamizhavel Department
arxiv:118.1291v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Apr 212 Anisotropic magnetic properties and superzone gap formation in single crystal Pranab Kumar Das, Neeraj Kumar, R. Kulkarni, S. K. Dhar and A. Thamizhavel Department
Supporting Information (Online Material) for
 Supporting Information (Online Material) for Five-Fold Ordering in High-Pressure Perovskites RMn 3 O 6 (R = Gd-Tm and Y) Lei Zhang,, Yoshitaka Matsushita, Kazunari Yamaura,, Alexei A. Belik, *, Research
Supporting Information (Online Material) for Five-Fold Ordering in High-Pressure Perovskites RMn 3 O 6 (R = Gd-Tm and Y) Lei Zhang,, Yoshitaka Matsushita, Kazunari Yamaura,, Alexei A. Belik, *, Research
Heterometallic Strategy to Achieve Large Magnetocaloric Effect. in Polymeric 3d Complexes
 . This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for Heterometallic Strategy to Achieve Large Magnetocaloric Effect in Polymeric 3d Complexes Jiong-Peng Zhao, a,b Song-De Han,
. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for Heterometallic Strategy to Achieve Large Magnetocaloric Effect in Polymeric 3d Complexes Jiong-Peng Zhao, a,b Song-De Han,
No. 3 An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in MFM results, it is suggested that the PS in LSMO is not a charge seg
 Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Constraints on the Adiabatic Temperature Change in Magnetocaloric Materials
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 05, 2018 Constraints on the Adiabatic Temperature Change in Magnetocaloric Materials Nielsen, Kaspar Kirstein; Bahl, Christian; Smith, Anders Published in: Physical
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 05, 2018 Constraints on the Adiabatic Temperature Change in Magnetocaloric Materials Nielsen, Kaspar Kirstein; Bahl, Christian; Smith, Anders Published in: Physical
Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation
 NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
NTC, Taiwen Aug. 31, 212 Neutron Powder Diffraction Theory and Instrumentation Qingzhen Huang (qing.huang@nist.gov) NIST Center for Neutron Research (www.ncnr.nist.gov) Definitions E: energy; k: wave vector;
Coexistence of Ferromagnetic and Glassy States in Mechanically Milled GdAl 2
 Coexistence of Ferromagnetic and Glassy States in Mechanically Milled GdAl 2 C. Stark and P.M. Shand Physics Department University of Northern Iowa Cedar Falls, Iowa 50614-0150 USA T.M. Pekarek Department
Coexistence of Ferromagnetic and Glassy States in Mechanically Milled GdAl 2 C. Stark and P.M. Shand Physics Department University of Northern Iowa Cedar Falls, Iowa 50614-0150 USA T.M. Pekarek Department
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China. To whom correspondence should be addressed :
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 NaBaM III Q 3 (M III = Al, Ga; Q = S, Se): First quaternary chalcogenides with the isolated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 NaBaM III Q 3 (M III = Al, Ga; Q = S, Se): First quaternary chalcogenides with the isolated
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):2606-2610 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Preparation and characterization of double perovskit
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):2606-2610 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Preparation and characterization of double perovskit
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Ag@Pd Satellites-Fe 3 O 4 Core Nanocomposite as Efficient and Reusable Hydrogenation Catalysts Kun Jiang, a Han-Xuan Zhang, a Yao-Yue Yang a, Robert Mothes, b
Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Ag@Pd Satellites-Fe 3 O 4 Core Nanocomposite as Efficient and Reusable Hydrogenation Catalysts Kun Jiang, a Han-Xuan Zhang, a Yao-Yue Yang a, Robert Mothes, b
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 9 Dec 2015](/thumbs/87/97379003.jpg) : A Model Molecular-Field Helical Heisenberg Antiferromagnet N. S. Sangeetha, Abhishek Pandey, and D. C. Johnston Ames Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
: A Model Molecular-Field Helical Heisenberg Antiferromagnet N. S. Sangeetha, Abhishek Pandey, and D. C. Johnston Ames Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Supporting Information for. Remarkably high temperature spin transition exhibited by two new metal-organic frameworks
 Supporting Information for Remarkably high temperature spin transition exhibited by two new metal-organic frameworks Xin Bao, a Peng-Hu Guo, a Wei Liu, a Jiri Tucek, b Wei-Xiong Zhang, a Ji-Dong Leng,
Supporting Information for Remarkably high temperature spin transition exhibited by two new metal-organic frameworks Xin Bao, a Peng-Hu Guo, a Wei Liu, a Jiri Tucek, b Wei-Xiong Zhang, a Ji-Dong Leng,
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K
 New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
New Li-Ethylenediamine-Intercalated Superconductor Li x (C 2 H 8 N 2 ) y Fe 2-z Se 2 with T c = 45 K Takehiro Hatakeda, Takashi Noji, Takayuki Kawamata, Masatsune Kato, and Yoji Koike Department of Applied
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
