Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks
|
|
|
- Diana Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks Iris Cong Soonwon Choi Mikhail D. Lukin arxiv: Berkeley Quantum Information Seminar October 16 th, 2018
2 Why quantum machine learning?
3 Machine learning: interpret and process large amounts of data Genomics Unmanned Vehicle Image recognition = Cat = Dog Quantum physics: many- body interactionsà extremely large complexity Quantum chemistry Quantum phases of matter Near- term quantum computers/ quantum simulators /J Cluster Model: QCNN Phase Diagram (N = 135 Spins) /J 0 0 h2 /J h1 /J Machine learning 0.5 Quantum many- body physics Exciting!
4 Û <latexit sha1_base64="hp+6lruf2d3tzaldqaqqvekmxyw=">aaab2xicbzdnsgmxfixv1l86vq1rn8eiucozbnqpuhfzwbzco5rm5k4bmskmyr2hdh0bf25efc93vo3pz0jbdwq+zknivscullqubn9ebwd3b/+gfugfnfzjk9nmo2fz0gjsilzl5jnmfpxu2cvjcp8lgzylffbj6f0i77+gstlxtzqrmmr4wmtuck7o6oyaraadlmw2ivxdc9yanb+gss7kddujxa0dhefbucunsafw7g9liwuxuz7ggupnm7rrtrxzzi6dk7a0n+5oykv394ukz9bostjdzdhn7ga2mp/lbiwlt1eldvesarh6kc0vo5wtdmajnchizrxwyasblykjn1yqa8z3hysbg29d77odbu3wmya6nmmfxeein3ahd9cblghi4bxevyn35n2suqp569lo4i+8zx84xio4</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="xib49up2d+brvzmhgzmrab82ohw=">aaab7nicbvbns8naej3ur1q/qh69lbbbu0m86lhoxwmf0xbaudbbtbt0swm7eyge/ggvhhtx6u/x5r9x2+agrq8ghu/nmdmvtkuw6lrftmvjc2t7p7pb29s/odyqh590tjjpxn2wyet3qmq4fir7kfdyxqo5jupju+h0bu53n7g2ilgpmkc8iolyiugwilbqdiyuc382rdfcprsawsdesrpqoj2sfw1gcctirpbjakzfc1mmcqprmmlntufmeerzli5531jfy26cynhujfxyzusirntssbbq74mcxsbkcwg7y4ots+rnxf+8fobrtvailwbifvsuijjjmchz38liam5q5pzqpow9lbaj1zshtahmq/bwx14nnaum5za9b7frui3jqmiznmmlehanlbihnvjayarp8apvtuq8oo/ox7k14pqzp/ahzucpec2pog==</latexit> Machine Learning and Quantum Physics (Classical) Machine learning to study quantum physics Quantum machines to perform classical or quantum computation Neural network Carleo and Troyer, Science (2017) Carrasquilla and Melko, N. Phys. (2017) Quantum circuits and many others Tensor networks Quantum speedup? supremacy? Input state ψ Farhi and Neven (2018) Gao, Zhang, Duan (2017) Glasser et al., PRX (2018)
5 Machine Learning and Quantum Physics Many open questions: Why/how does quantum machine learning work? Concrete circuit models suitable for near- term implementation? Relationship to quantum many- body physics? Relationship with quantum information theory? Goal of our work
6 Main Contributions Concrete and efficient circuit model for quantum classification problems Good connection to existing ML techniques Application: Quantum Phase Recognition Theoretical Explanation: RG Flow, MERA, Quantum Error Correction 1.5 ConvolutionPooling Fully Connected h 2 /J h 1 /J Cluster Model: QCNN Phase Diagram (N = 135 Spins)
7 Overview Review of (Classical) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks Application to quantum phase recognition Example: 1D symmetry- protected topological (SPT) phase Theoretical explanation: RG flow using MERA + quantum error correction Summary and Outlook
8 Review of (Classical) CNN Particular class of deep, feed- forward neural network Input Output
9 Review of (Classical) CNN A structured network multiple layers of image processing Example (simplified): = Cat Dog Convolution Pooling Fully connected Convolution layers Pooling layers Fully connected y %,' = w * x %,' + w - x %.,' + w / x %,'.- + w 0 x %.-,'.-
10 Review of (Classical) CNN Many ImageNet Competition Winners! GoogLeNet (2014) ResNet (2015) And many others
11 Learning Procedure for (Classical) CNN Gradient- based supervised learning Training data: labeled {(x i, y i )} Common error functions Initialize to random weights Update w to w = w η w E, η = learning rate
12 Overview Review of (Classical) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks (QCNNs) Application to quantum phase recognition Example: 1D symmetry- protected topological (SPT) phase Theoretical explanation: RG flow using MERA + quantum error correction Summary and Outlook
13 <latexit sha1_base64="hp+6lruf2d3tzaldqaqqvekmxyw=">aaab2xicbzdnsgmxfixv1l86vq1rn8eiucozbnqpuhfzwbzco5rm5k4bmskmyr2hdh0bf25efc93vo3pz0jbdwq+zknivscullqubn9ebwd3b/+gfugfnfzjk9nmo2fz0gjsilzl5jnmfpxu2cvjcp8lgzylffbj6f0i77+gstlxtzqrmmr4wmtuck7o6oyaraadlmw2ivxdc9yanb+gss7kddujxa0dhefbucunsafw7g9liwuxuz7ggupnm7rrtrxzzi6dk7a0n+5oykv394ukz9bostjdzdhn7ga2mp/lbiwlt1eldvesarh6kc0vo5wtdmajnchizrxwyasblykjn1yqa8z3hysbg29d77odbu3wmya6nmmfxeein3ahd9cblghi4bxevyn35n2suqp569lo4i+8zx84xio4</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="xib49up2d+brvzmhgzmrab82ohw=">aaab7nicbvbns8naej3ur1q/qh69lbbbu0m86lhoxwmf0xbaudbbtbt0swm7eyge/ggvhhtx6u/x5r9x2+agrq8ghu/nmdmvtkuw6lrftmvjc2t7p7pb29s/odyqh590tjjpxn2wyet3qmq4fir7kfdyxqo5jupju+h0bu53n7g2ilgpmkc8iolyiugwilbqdiyuc382rdfcprsawsdesrpqoj2sfw1gcctirpbjakzfc1mmcqprmmlntufmeerzli5531jfy26cynhujfxyzusirntssbbq74mcxsbkcwg7y4ots+rnxf+8fobrtvailwbifvsuijjjmchz38liam5q5pzqpow9lbaj1zshtahmq/bwx14nnaum5za9b7frui3jqmiznmmlehanlbihnvjayarp8apvtuq8oo/ox7k14pqzp/ahzucpec2pog==</latexit> Prior Works: Generic Quantum Circuit Farhi and Neven, 2018 Problems: Too many parameters Subject to overfitting (Quantum or classical) Input state ψ Û Need all- to- all connectivity Lack of physical intuition? Impose CNN structure
14 Quantum CNN Architecture Same types of layers: 1. Convolution Local unitaries, trans. inv., 1D, 2D, 3D 2. Pooling Reduce system size Final unitary depends on meas. outcomes 3. Fully connected Non- local measurement E.g. for quantum phase recognition: string operator measurement Convolution Pooling Fully Connected
15 Learning Procedure for Quantum CNN Parameterize unitariesin convolution, pooling, and fully- connected layers Initialize to random unitaries Similar gradient- based learning
16 Overview Review of (Classical) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks Application to quantum phase recognition Example: 1D symmetry- protected topological (SPT) phase Theoretical explanation: RG flow using MERA + quantum error correction Summary and Outlook
17 Application: Quantum Phase Recognition Problem: Given quantum many-body system in (unknown) ground state ψ 2, does ψ 2 belong to a particular quantum phase P? Direct analog of image classification, but intrinsically quantum problem Claim: Quantum CNN is very efficient in quantum phase recognition ψ 2 ConvolutionPooling Fully Connected if ψ 2 P if ψ 2 P
18 Example: 1D ZXZ Model (G = Z 2 Z 2 SPT) Z / Z / symmetry: X: ; = % ;=;> X: %, and X:? = %?@@ X: % When h - = h / = 0, g.s. = 1D cluster state (stabilizer code) When h / = 0, exactly solvable by Jordan- Wigner Simple example à good analytical guess for QCNN circuit, demonstrate learning later h / /J Our target phase Contains 1D AKLT ground state SPT (Z 2 Z 2 ) Anti- ferromagnetic Paramagnetic h - /J * Phase diagram is obtained from idmrg with bond dimension 150.
19 Example: 1D ZXZ Model (G = Z 2 Z 2 SPT) Quantum CNN Circuit: System size reduction L L/3 Repeat depth d & Fully connected layer X " " " Pooling "!! " "!! " "! "! " P L = L * Convolution " " " " " " " " " " C C if ψ 2 SPT if ψ 2 SPT
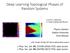
20 Example: 1D ZXZ Model (G = Z 2 Z 2 SPT) Results of numerical simulation: h2/j Paramagnetic SPT <X> Fixed h 2 = 0: <X> Fixed h 1 = 0: Fixed h 1 = 0.5J: h 2 /J Antiferromagnetic h 1 /J * Phase diagram is obtained from idmrg with bond dimension 150. Ground states are obtained from DMRG with bond dimension D plot: N = 45 spins (depth 2), 1D curves: N = 135 spins h 1 /J <X> h 2 /J
21 Why does it work? Multiscale Entanglement Renormalization Ansatz (MERA) + Quantum Error Correction QCNN MERA = (MERA) = QEC (QCNN) Circuit simulation of RG flow
22 Multiscale Entanglement Renormalization Ansatz (MERA) Variational ansatz for many- body wavefunction Efficient description of: Gapped ground states Critical systems Depth d L = 2 d Many interesting physical systems Quantum CNN has very similar structure!
23 Why does it work? QCNN MERA = (MERA) = QEC (QCNN) Key differences: Opposite direction MERA circuit is only defined for ancillas = 0> Measurement does not always give 0>!
24 Û <latexit sha1_base64="hp+6lruf2d3tzaldqaqqvekmxyw=">aaab2xicbzdnsgmxfixv1l86vq1rn8eiucozbnqpuhfzwbzco5rm5k4bmskmyr2hdh0bf25efc93vo3pz0jbdwq+zknivscullqubn9ebwd3b/+gfugfnfzjk9nmo2fz0gjsilzl5jnmfpxu2cvjcp8lgzylffbj6f0i77+gstlxtzqrmmr4wmtuck7o6oyaraadlmw2ivxdc9yanb+gss7kddujxa0dhefbucunsafw7g9liwuxuz7ggupnm7rrtrxzzi6dk7a0n+5oykv394ukz9bostjdzdhn7ga2mp/lbiwlt1eldvesarh6kc0vo5wtdmajnchizrxwyasblykjn1yqa8z3hysbg29d77odbu3wmya6nmmfxeein3ahd9cblghi4bxevyn35n2suqp569lo4i+8zx84xio4</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="xib49up2d+brvzmhgzmrab82ohw=">aaab7nicbvbns8naej3ur1q/qh69lbbbu0m86lhoxwmf0xbaudbbtbt0swm7eyge/ggvhhtx6u/x5r9x2+agrq8ghu/nmdmvtkuw6lrftmvjc2t7p7pb29s/odyqh590tjjpxn2wyet3qmq4fir7kfdyxqo5jupju+h0bu53n7g2ilgpmkc8iolyiugwilbqdiyuc382rdfcprsawsdesrpqoj2sfw1gcctirpbjakzfc1mmcqprmmlntufmeerzli5531jfy26cynhujfxyzusirntssbbq74mcxsbkcwg7y4ots+rnxf+8fobrtvailwbifvsuijjjmchz38liam5q5pzqpow9lbaj1zshtahmq/bwx14nnaum5za9b7frui3jqmiznmmlehanlbihnvjayarp8apvtuq8oo/ox7k14pqzp/ahzucpec2pog==</latexit> Why does it work? Good starting point! MERA representation of ψ * à QCNN circuit to exactly recognize ψ * with deterministic intermediate measurement outcomes. ψ * QCNN but NOT sufficient for quantum phase recognition. Phase P ψ * Some other phase ψ ψ * Ideally, a single QCNN should recognize ALL ψ in the same phase P. Key idea: use quantum error correction to induce flow.
25 Why does it work? Idea: Treat perturbations terms as quantum errors Example: RG fixed point = Quantum code Error perturbations This construction is generic: includes all 1D SPT, 2D string- net models
26 Why does it work? (cluster state) Quantum CNN for Z 2 Z 2 SPT phase = MERA for ψ * + QEC ψ * (L) N ψ * (L/0) N 0000!! " "!! " "!! Paramagnetic ψ (L) N ψ (L/0) N ψ (L/0) N Quantum error correction Repeat d times " " " " " " " h / /J ψ * ψ ψ Anti- ferromagnetic SPT h - /J Measure string order parameter for ψ *
27 Example: 1D ZXZ Model (G = Z 2 Z 2 SPT) RG flow in our example (N = 135 spins):
28 Why does it work? (alternative explanation using string order parameters) Identifying an SPT phase = Detecting a string order parameter U S Example: Z 2 Z 2 SPT S %' = Z % X %.- X %.0 X 'V- Z ' Spin chain Problem: away from RG fixed point ξ S %' = O 1 Zξ Y QCNN: use more than one string operator
29 Û <latexit sha1_base64="hp+6lruf2d3tzaldqaqqvekmxyw=">aaab2xicbzdnsgmxfixv1l86vq1rn8eiucozbnqpuhfzwbzco5rm5k4bmskmyr2hdh0bf25efc93vo3pz0jbdwq+zknivscullqubn9ebwd3b/+gfugfnfzjk9nmo2fz0gjsilzl5jnmfpxu2cvjcp8lgzylffbj6f0i77+gstlxtzqrmmr4wmtuck7o6oyaraadlmw2ivxdc9yanb+gss7kddujxa0dhefbucunsafw7g9liwuxuz7ggupnm7rrtrxzzi6dk7a0n+5oykv394ukz9bostjdzdhn7ga2mp/lbiwlt1eldvesarh6kc0vo5wtdmajnchizrxwyasblykjn1yqa8z3hysbg29d77odbu3wmya6nmmfxeein3ahd9cblghi4bxevyn35n2suqp569lo4i+8zx84xio4</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="v8saqttxyshnlvcclpscskjc46i=">aaab43icbzdnsgmxfixv1l9aq1a3bojfcfvm3ohscooygtmk7vdupjk2njmzkjtcgfoqblwo4ju5821mfxbaeidwcu5c7j1xrqql3//2klvbo7t71f3aqf3w6lhxuu/yrdbchdxtmxmk0qoltqhjkhjpurgyxkp048ndpo8+c2nlph9pmosoxzgwierizur2x0hlobs0mn7lx4htqrccjqzuhjs++somf6nqxbva2wv8nkisdumuxkzwl6ziku9wjhoonabcruvi3bm7cm6qjzlxrxnbul9fljhao01jdznfgtv1bg7+l/uksm6iuuq8ikh58qokuiwynt+ddaurnntuaxij3aymj9egj9dqzzuqrk+8cz2rvuc3ggcfqnag53ajavzdldxdg0lgmiexein3l/devy9lxrvv1dsp/jh3+qnkly5n</latexit> <latexit sha1_base64="xib49up2d+brvzmhgzmrab82ohw=">aaab7nicbvbns8naej3ur1q/qh69lbbbu0m86lhoxwmf0xbaudbbtbt0swm7eyge/ggvhhtx6u/x5r9x2+agrq8ghu/nmdmvtkuw6lrftmvjc2t7p7pb29s/odyqh590tjjpxn2wyet3qmq4fir7kfdyxqo5jupju+h0bu53n7g2ilgpmkc8iolyiugwilbqdiyuc382rdfcprsawsdesrpqoj2sfw1gcctirpbjakzfc1mmcqprmmlntufmeerzli5531jfy26cynhujfxyzusirntssbbq74mcxsbkcwg7y4ots+rnxf+8fobrtvailwbifvsuijjjmchz38liam5q5pzqpow9lbaj1zshtahmq/bwx14nnaum5za9b7frui3jqmiznmmlehanlbihnvjayarp8apvtuq8oo/ox7k14pqzp/ahzucpec2pog==</latexit> Why does it work? (alternative explanation using string order parameters) ψ S %' Heisenberg picture ψ U [ S %' U ψ ) ) C - ψ U [ Z %V- X % Z %.- U ψ +C / +C 0 +C ] +C^ Exponentially many, long string operators!
30 Training: Example Circuit structure: N = 15 spins (depth 1) for simulations XV V 2 V 1 X F V 2 V 1 XV XV V 2 XV XV V 1 3U 4 3U 4 U 3 U U 3 U U 2 U 2 U 2 FC XV P C 4 C 3 C 2 Initialize all unitaries to random values U 1 U 1 C 1 Train along h 2 = 0 (solvable by JW) Paramagnetic Gradient descent: h2/j SPT Antiferromagnetic h 1 /J 0-0.1
31 Training: Example Observation: training on 1D, JW- solvable set can still produce the correct 2D phase diagram Demonstrates how QCNN structure avoids overfitting Paramagnetic h2/j SPT Antiferromagnetic h 1 /J
32 Training: General Cases More generally: training = expanding QEC threshold ψ QCNN Training Efficiency: reduced # of parameters (O(log(N)) instead of O(exp(N)) Target phase boundary Fixed point QEC threshold
33 General Recipe - QCNN for quantum phase recognition Step 1: Given a quantum phase construct a MPS representation of a RG fixed point and its MERA circuit Schuch et al, PRB 84, (2011) ψ * = (isometric form) MERA isometry = Step 2: Construct its parent Hamiltonian H = % h % with h %, h ' = 0. Step 3: Design quantum error correction code based on Stabilizers from h %. Code space from Step 4: Construct QCNN ansatz based on Step 3. Step 5: Optimize QCNN via learningprocedures.
34 Generic Construction of QCNN Circuit (High- level outline; in progress) Goal: Given quantum phase P classified by its RG fixed point, construct quantum CNN circuit to best recognize states in P Step 1: Construct tensor network representation of RG fixed point ψ * = (isometric form) Schuch et al, PRB 84, (2011) Step 2: Construct parent Hamiltonian of this tensor network (nearest- neighbor commuting terms): H = % h % with h %,h ' = 0.
35 Generic Construction of QCNN Circuit (High- level outline; in progress) Step 3: Design quantum error correction code with (generalized) stabilizers which are the h %. The code space forms the ground state space Step 4: Construct quantum CNN circuit based on Step 3 Step 5: Optimize quantum CNN based on learning procedures
36 Overview Review of (Classical) CNN Quantum CNN: Architecture and Learning Procedure Application: quantum phase recognition Example: 1D cluster state Theoretical explanation: RG flow using MERA + quantum error correction Summary and Outlook
37 Summary Concrete architecture, learning proposal for quantum classification Application to quantum phase recognition: 1D SPT phase (Z 2 Z 2 ) Theoretical explanation: QCNN MERA + QEC RG flow Paramagnetic Fully Connected h2/j SPT Convolution Pooling Antiferromagnetic h 1 /J
38 Other Results and Outlook 2D Quantum CNN circuit: toric code, string- net Efficient training procedures inspired by machine learning Gapless phases (e.g. spin liquids), holographic codes Application: fault- tolerant computation Experimental realizations e.g. trapped ions, Rydberg atoms, superconducting circuits
39 Thanks!
40 Backup Slides
41 Heisenberg Picture: Topological Measurement... X X X X X X X X X Measured operator = Z H H H H H H H H Z Z Z Z Z Z X Z = sum of exponentially many string operators Detects presence of edge modes! Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H X X X X X X X X X Z...
42 Heisenberg Picture: Topological... Measurement... X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Z H H H H H H H H Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H Z Z Z Z Z Z Z X = Z X Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H X X X X X X X X X Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H X X X X X X X X X Z......
43 Heisenberg Picture: Topological... Measurement... X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Z H H H H H H H H Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H X = XZ X XZ Z Z Z Z Z Z Z H H H H H H H H X X X X X X X X X Z H H H H H H H H X X X X X X X X X......
44 Conclusion: Heisenberg Picture: Topological Measurement Measured operator is sum of exponentially many string operators Measures probability for all Majorana modes to be topologically connected à 1 in the SPT phase, 0 in the trivial phase...
Neural Network Representation of Tensor Network and Chiral States
 Neural Network Representation of Tensor Network and Chiral States Yichen Huang ( 黄溢辰 ) 1 and Joel E. Moore 2 1 Institute for Quantum Information and Matter California Institute of Technology 2 Department
Neural Network Representation of Tensor Network and Chiral States Yichen Huang ( 黄溢辰 ) 1 and Joel E. Moore 2 1 Institute for Quantum Information and Matter California Institute of Technology 2 Department
3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase
 Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
4 Matrix product states
 Physics 3b Lecture 5 Caltech, 05//7 4 Matrix product states Matrix product state (MPS) is a highly useful tool in the study of interacting quantum systems in one dimension, both analytically and numerically.
Physics 3b Lecture 5 Caltech, 05//7 4 Matrix product states Matrix product state (MPS) is a highly useful tool in the study of interacting quantum systems in one dimension, both analytically and numerically.
Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks
 Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 RIKEN AICS - Mar 2017 Collaboration with David
Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 RIKEN AICS - Mar 2017 Collaboration with David
Tensor network vs Machine learning. Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS
 Tensor network vs Machine learning Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS physichengsong@iphy.ac.cn Outline Tensor network in a nutshell TN concepts in machine learning TN methods in machine learning Outline Tensor
Tensor network vs Machine learning Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS physichengsong@iphy.ac.cn Outline Tensor network in a nutshell TN concepts in machine learning TN methods in machine learning Outline Tensor
Introduction to tensor network state -- concept and algorithm. Z. Y. Xie ( 谢志远 ) ITP, Beijing
 Introduction to tensor network state -- concept and algorithm Z. Y. Xie ( 谢志远 ) 2018.10.29 ITP, Beijing Outline Illusion of complexity of Hilbert space Matrix product state (MPS) as lowly-entangled state
Introduction to tensor network state -- concept and algorithm Z. Y. Xie ( 谢志远 ) 2018.10.29 ITP, Beijing Outline Illusion of complexity of Hilbert space Matrix product state (MPS) as lowly-entangled state
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications
 Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Machine Learning with Tensor Networks
 Machine Learning with Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 Beijing Jun 2017 Machine learning has physics in its DNA # " # #
Machine Learning with Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 Beijing Jun 2017 Machine learning has physics in its DNA # " # #
Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1
 1 Davis, January 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard Werner
1 Davis, January 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard Werner
Fermionic tensor networks
 Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETH Zurich Bosons vs Fermions P. Corboz and G. Vidal, Phys. Rev. B 80, 165129 (2009) : fermionic 2D MERA P. Corboz, R. Orus,
Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETH Zurich Bosons vs Fermions P. Corboz and G. Vidal, Phys. Rev. B 80, 165129 (2009) : fermionic 2D MERA P. Corboz, R. Orus,
Holographic Geometries from Tensor Network States
 Holographic Geometries from Tensor Network States J. Molina-Vilaplana 1 1 Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena Perspectives on Quantum Many-Body Entanglement, Mainz, Sep 2013 1 Introduction & Motivation
Holographic Geometries from Tensor Network States J. Molina-Vilaplana 1 1 Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena Perspectives on Quantum Many-Body Entanglement, Mainz, Sep 2013 1 Introduction & Motivation
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems
 Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation
 Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation Thomas Quella University of Cologne Presentation given on 18 Feb 2016 at the Benasque Workshop Entanglement in Strongly
Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation Thomas Quella University of Cologne Presentation given on 18 Feb 2016 at the Benasque Workshop Entanglement in Strongly
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More
 Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More Román Orús Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz (Germany)! School on computational methods in quantum materials Jouvence,
Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More Román Orús Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz (Germany)! School on computational methods in quantum materials Jouvence,
It from Qubit Summer School
 It from Qubit Summer School July 27 th, 2016 Tensor Networks Guifre Vidal NSERC Wednesday 27 th 9AM ecture Tensor Networks 2:30PM Problem session 5PM Focus ecture MARKUS HAURU MERA: a tensor network for
It from Qubit Summer School July 27 th, 2016 Tensor Networks Guifre Vidal NSERC Wednesday 27 th 9AM ecture Tensor Networks 2:30PM Problem session 5PM Focus ecture MARKUS HAURU MERA: a tensor network for
Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems
 10sor network workshop @Kashiwanoha Future Center May 14 (Thu.), 2015 Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems NIMS U. Tokyo Shintaro Takayoshi Collaboration with A. Tanaka (NIMS)
10sor network workshop @Kashiwanoha Future Center May 14 (Thu.), 2015 Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems NIMS U. Tokyo Shintaro Takayoshi Collaboration with A. Tanaka (NIMS)
Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1
 1 FRG2011, Harvard, May 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard
1 FRG2011, Harvard, May 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard
Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses about the label (Top-5 error) No Bounding Box
 ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
Machine learning quantum phases of matter
 Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Cornell, May 2017 Simon Trebst University of Cologne Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer
Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Cornell, May 2017 Simon Trebst University of Cologne Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer
Basics of quantum computing and some recent results. Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) min
 Basics of quantum computing and some recent results Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) 50+10 min Outline 1. Basics of quantum computing circuit model, classically simulatable/unsimulatable, quantum
Basics of quantum computing and some recent results Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) 50+10 min Outline 1. Basics of quantum computing circuit model, classically simulatable/unsimulatable, quantum
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 31 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 31 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 31 Oct 2013](/thumbs/93/112286981.jpg) Quantum Criticality with the Multi-scale Entanglement Renormalization Ansatz arxiv:1109.5334v2 [quant-ph] 31 Oct 2013 G. Evenbly 1 and G. Vidal 2 1 The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland 4072,
Quantum Criticality with the Multi-scale Entanglement Renormalization Ansatz arxiv:1109.5334v2 [quant-ph] 31 Oct 2013 G. Evenbly 1 and G. Vidal 2 1 The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland 4072,
Disentangling Topological Insulators by Tensor Networks
 Disentangling Topological Insulators by Tensor Networks Shinsei Ryu Univ. of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Collaborators: Ali Mollabashi (IPM Tehran) Masahiro Nozaki (Kyoto) Tadashi Takayanagi (Kyoto) Xueda
Disentangling Topological Insulators by Tensor Networks Shinsei Ryu Univ. of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Collaborators: Ali Mollabashi (IPM Tehran) Masahiro Nozaki (Kyoto) Tadashi Takayanagi (Kyoto) Xueda
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases
 Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
News on tensor network algorithms
 News on tensor network algorithms Román Orús Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) December 6th 2018 S. S. Jahromi, RO, M. Kargarian, A. Langari, PRB 97, 115162 (2018) S. S. Jahromi, RO, PRB 98,
News on tensor network algorithms Román Orús Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) December 6th 2018 S. S. Jahromi, RO, M. Kargarian, A. Langari, PRB 97, 115162 (2018) S. S. Jahromi, RO, PRB 98,
Topological Phases in One Dimension
 Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect
 Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
CSE446: Neural Networks Spring Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer
 CSE446: Neural Networks Spring 2017 Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer Human Neurons Switching time ~ 0.001 second Number of neurons 10 10 Connections per neuron 10 4-5 Scene
CSE446: Neural Networks Spring 2017 Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer Human Neurons Switching time ~ 0.001 second Number of neurons 10 10 Connections per neuron 10 4-5 Scene
The density matrix renormalization group and tensor network methods
 The density matrix renormalization group and tensor network methods Outline Steve White Exploiting the low entanglement of ground states Matrix product states and DMRG 1D 2D Tensor network states Some
The density matrix renormalization group and tensor network methods Outline Steve White Exploiting the low entanglement of ground states Matrix product states and DMRG 1D 2D Tensor network states Some
Z2 topological phase in quantum antiferromagnets. Masaki Oshikawa. ISSP, University of Tokyo
 Z2 topological phase in quantum antiferromagnets Masaki Oshikawa ISSP, University of Tokyo RVB spin liquid 4 spins on a square: Groundstate is exactly + ) singlet pair a.k.a. valence bond So, the groundstate
Z2 topological phase in quantum antiferromagnets Masaki Oshikawa ISSP, University of Tokyo RVB spin liquid 4 spins on a square: Groundstate is exactly + ) singlet pair a.k.a. valence bond So, the groundstate
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Nov 2013
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Nov 2013 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Nov 2013](/thumbs/82/87025724.jpg) Symmetry Protected Quantum State Renormalization Ching-Yu Huang, Xie Chen, and Feng-Li Lin 3 Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme, 087 Dresden, Germany Department of Physics, University of
Symmetry Protected Quantum State Renormalization Ching-Yu Huang, Xie Chen, and Feng-Li Lin 3 Max-Planck-Institut für Physik komplexer Systeme, 087 Dresden, Germany Department of Physics, University of
Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini
 New Frontiers in Theoretical Physics XXXIV Convegno Nazionale di Fisica Teorica - Cortona Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini Collaborators:
New Frontiers in Theoretical Physics XXXIV Convegno Nazionale di Fisica Teorica - Cortona Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini Collaborators:
Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications
 Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications Frank Verstraete Ghent University and University of Vienna Nick Bultinck, Jutho Haegeman, Michael Marien Burak Sahinoglu, Dominic Williamson Ignacio
Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications Frank Verstraete Ghent University and University of Vienna Nick Bultinck, Jutho Haegeman, Michael Marien Burak Sahinoglu, Dominic Williamson Ignacio
/21. Tsuneya Yoshida. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami 2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1. Kyoto Univ.
 2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1 /21 Tsuneya Yoshida Kyoto Univ. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami T.Y., Satoshi Fujimoto, and Norio Kawakami Phys. Rev. B 85, 125113 (2012) Outline 2 /21
2013/6/07 (EQPCM) 1 /21 Tsuneya Yoshida Kyoto Univ. Collaborators: Robert Peters, Satoshi Fujimoto, and N. Kawakami T.Y., Satoshi Fujimoto, and Norio Kawakami Phys. Rev. B 85, 125113 (2012) Outline 2 /21
Fermionic topological quantum states as tensor networks
 order in topological quantum states as Jens Eisert, Freie Universität Berlin Joint work with Carolin Wille and Oliver Buerschaper Symmetry, topology, and quantum phases of matter: From to physical realizations,
order in topological quantum states as Jens Eisert, Freie Universität Berlin Joint work with Carolin Wille and Oliver Buerschaper Symmetry, topology, and quantum phases of matter: From to physical realizations,
Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks
 Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks Albert H. Werner QMath University of Copenhagen Together with: C. Cedzic, T. Geib, F. A. Grünbaum, C. Stahl, L. Velazques, R. F. Werner Phase classification
Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks Albert H. Werner QMath University of Copenhagen Together with: C. Cedzic, T. Geib, F. A. Grünbaum, C. Stahl, L. Velazques, R. F. Werner Phase classification
Entanglement spectrum and Matrix Product States
 Entanglement spectrum and Matrix Product States Frank Verstraete J. Haegeman, D. Draxler, B. Pirvu, V. Stojevic, V. Zauner, I. Pizorn I. Cirac (MPQ), T. Osborne (Hannover), N. Schuch (Aachen) Outline Valence
Entanglement spectrum and Matrix Product States Frank Verstraete J. Haegeman, D. Draxler, B. Pirvu, V. Stojevic, V. Zauner, I. Pizorn I. Cirac (MPQ), T. Osborne (Hannover), N. Schuch (Aachen) Outline Valence
arxiv: v4 [quant-ph] 13 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v4 [quant-ph] 13 Mar 2013 arxiv: v4 [quant-ph] 13 Mar 2013](/thumbs/75/72057259.jpg) Deep learning and the renormalization group arxiv:1301.3124v4 [quant-ph] 13 Mar 2013 Cédric Bény Institut für Theoretische Physik Leibniz Universität Hannover Appelstraße 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany cedric.beny@gmail.com
Deep learning and the renormalization group arxiv:1301.3124v4 [quant-ph] 13 Mar 2013 Cédric Bény Institut für Theoretische Physik Leibniz Universität Hannover Appelstraße 2, 30167 Hannover, Germany cedric.beny@gmail.com
Quantum Phase Transitions
 1 Davis, September 19, 2011 Quantum Phase Transitions A VIGRE 1 Research Focus Group, Fall 2011 Spring 2012 Bruno Nachtergaele See the RFG webpage for more information: http://wwwmathucdavisedu/~bxn/rfg_quantum_
1 Davis, September 19, 2011 Quantum Phase Transitions A VIGRE 1 Research Focus Group, Fall 2011 Spring 2012 Bruno Nachtergaele See the RFG webpage for more information: http://wwwmathucdavisedu/~bxn/rfg_quantum_
Golden chain of strongly interacting Rydberg atoms
 Golden chain of strongly interacting Rydberg atoms Hosho Katsura (Gakushuin Univ.) Acknowledgment: Igor Lesanovsky (MUARC/Nottingham Univ. I. Lesanovsky & H.K., [arxiv:1204.0903] Outline 1. Introduction
Golden chain of strongly interacting Rydberg atoms Hosho Katsura (Gakushuin Univ.) Acknowledgment: Igor Lesanovsky (MUARC/Nottingham Univ. I. Lesanovsky & H.K., [arxiv:1204.0903] Outline 1. Introduction
Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d
 Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d Román Orús University of Mainz (Germany) K. Zapp, RO, Phys. Rev. D 95, 114508 (2017) Goal of this
Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d Román Orús University of Mainz (Germany) K. Zapp, RO, Phys. Rev. D 95, 114508 (2017) Goal of this
Noise-resilient quantum circuits
 Noise-resilient quantum circuits Isaac H. Kim IBM T. J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, NY Oct 10th, 2017 arxiv:1703.02093, arxiv:1703.00032, arxiv:17??.?????(w. Brian Swingle) Why don t we have
Noise-resilient quantum circuits Isaac H. Kim IBM T. J. Watson Research Center Yorktown Heights, NY Oct 10th, 2017 arxiv:1703.02093, arxiv:1703.00032, arxiv:17??.?????(w. Brian Swingle) Why don t we have
Matrix Product States
 Matrix Product States Ian McCulloch University of Queensland Centre for Engineered Quantum Systems 28 August 2017 Hilbert space (Hilbert) space is big. Really big. You just won t believe how vastly, hugely,
Matrix Product States Ian McCulloch University of Queensland Centre for Engineered Quantum Systems 28 August 2017 Hilbert space (Hilbert) space is big. Really big. You just won t believe how vastly, hugely,
Neural Networks. Single-layer neural network. CSE 446: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington March 10, /9/17
 3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
Markov Chains for Tensor Network States
 Sofyan Iblisdir University of Barcelona September 2013 arxiv 1309.4880 Outline Main issue discussed here: how to find good tensor network states? The optimal state problem Markov chains Multiplicative
Sofyan Iblisdir University of Barcelona September 2013 arxiv 1309.4880 Outline Main issue discussed here: how to find good tensor network states? The optimal state problem Markov chains Multiplicative
Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer
 Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer Martin Schwarz, Kristan Temme, Frank Verstraete University of Vienna, Faculty of Physics, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090 Vienna, Austria Toby Cubitt,
Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer Martin Schwarz, Kristan Temme, Frank Verstraete University of Vienna, Faculty of Physics, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090 Vienna, Austria Toby Cubitt,
Haldane phase and magnetic end-states in 1D topological Kondo insulators. Alejandro M. Lobos Instituto de Fisica Rosario (IFIR) - CONICET- Argentina
 Haldane phase and magnetic end-states in 1D topological Kondo insulators Alejandro M. Lobos Instituto de Fisica Rosario (IFIR) - CONICET- Argentina Workshop on Next Generation Quantum Materials ICTP-SAIFR,
Haldane phase and magnetic end-states in 1D topological Kondo insulators Alejandro M. Lobos Instituto de Fisica Rosario (IFIR) - CONICET- Argentina Workshop on Next Generation Quantum Materials ICTP-SAIFR,
Neural Networks. Intro to AI Bert Huang Virginia Tech
 Neural Networks Intro to AI Bert Huang Virginia Tech Outline Biological inspiration for artificial neural networks Linear vs. nonlinear functions Learning with neural networks: back propagation https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/neuron#/media/file:chemical_synapse_schema_cropped.jpg
Neural Networks Intro to AI Bert Huang Virginia Tech Outline Biological inspiration for artificial neural networks Linear vs. nonlinear functions Learning with neural networks: back propagation https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/neuron#/media/file:chemical_synapse_schema_cropped.jpg
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I
 Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
Convolutional Neural Networks
 Convolutional Neural Networks Books» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ Books http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/.org/ reviews» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/linear_algebra.html» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/prob.html»
Convolutional Neural Networks Books» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ Books http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/.org/ reviews» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/linear_algebra.html» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/prob.html»
Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems
 CENTRE FOR QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE AND CLARENDON LABORATORY UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems Stephen Clark LXXT[[[GSQPEFS\EGYOEGXMZMXMIWUYERXYQGSYVWI
CENTRE FOR QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE AND CLARENDON LABORATORY UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems Stephen Clark LXXT[[[GSQPEFS\EGYOEGXMZMXMIWUYERXYQGSYVWI
Binary Convolutional Neural Network on RRAM
 Binary Convolutional Neural Network on RRAM Tianqi Tang, Lixue Xia, Boxun Li, Yu Wang, Huazhong Yang Dept. of E.E, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList) Tsinghua
Binary Convolutional Neural Network on RRAM Tianqi Tang, Lixue Xia, Boxun Li, Yu Wang, Huazhong Yang Dept. of E.E, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList) Tsinghua
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models
 Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics. Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL
 Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
 TOPOLOGY + LOCALIZATION: QUANTUM COHERENCE IN HOT MATTER Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:1307.4092 (to appear in Nature Comm.) Thanks to David Huse for inspiring discussions Yasaman Bahri (Berkeley)
TOPOLOGY + LOCALIZATION: QUANTUM COHERENCE IN HOT MATTER Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:1307.4092 (to appear in Nature Comm.) Thanks to David Huse for inspiring discussions Yasaman Bahri (Berkeley)
Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems
 Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems Lecture 1 Norbert Schuch California Institute of Technology Institute for Quantum Information Quantum Information and Quantum Many-Body Systems Aim: Understand
Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems Lecture 1 Norbert Schuch California Institute of Technology Institute for Quantum Information Quantum Information and Quantum Many-Body Systems Aim: Understand
From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order
 From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order Arxiv: 1201.3757, to appear in PRL. B.M. Terhal, F. Hassler, D.P. DiVincenzo IQI, RWTH Aachen We are looking for PhD students or postdocs for theoretical research
From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order Arxiv: 1201.3757, to appear in PRL. B.M. Terhal, F. Hassler, D.P. DiVincenzo IQI, RWTH Aachen We are looking for PhD students or postdocs for theoretical research
Least Mean Squares Regression
 Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture Overview Linear classifiers What functions do linear classifiers express? Least Squares Method
Least Mean Squares Regression Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Lecture Overview Linear classifiers What functions do linear classifiers express? Least Squares Method
An overview of deep learning methods for genomics
 An overview of deep learning methods for genomics Matthew Ploenzke STAT115/215/BIO/BIST282 Harvard University April 19, 218 1 Snapshot 1. Brief introduction to convolutional neural networks What is deep
An overview of deep learning methods for genomics Matthew Ploenzke STAT115/215/BIO/BIST282 Harvard University April 19, 218 1 Snapshot 1. Brief introduction to convolutional neural networks What is deep
Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity. Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM
 Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM Influence of quantum information Easy Hard (at present) Easy Hard (at present)!! QI-inspired classical, e.g. tensor networks
Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM Influence of quantum information Easy Hard (at present) Easy Hard (at present)!! QI-inspired classical, e.g. tensor networks
Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems
 Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems 2017/6/5 Osaka Univ. in Deep Learning and Physics Physics division Sophia University Tomi Ohtsuki with Tomoki Ohtsuki, NTT data mathemahcal systems J.
Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems 2017/6/5 Osaka Univ. in Deep Learning and Physics Physics division Sophia University Tomi Ohtsuki with Tomoki Ohtsuki, NTT data mathemahcal systems J.
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE
 SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
Fermionic tensor networks
 Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, ETH Zurich / EPF Lausanne, Switzerland Collaborators: University of Queensland: Guifre Vidal, Roman Orus, Glen Evenbly, Jacob Jordan University of Vienna: Frank
Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, ETH Zurich / EPF Lausanne, Switzerland Collaborators: University of Queensland: Guifre Vidal, Roman Orus, Glen Evenbly, Jacob Jordan University of Vienna: Frank
Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains
 16 th December 2015 Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains Matilda Peruzzo Fermions (I) Quantum many-body theory: Fermions Bosons Fermions (II) Properties Pauli exclusion principle Fermions (II)
16 th December 2015 Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains Matilda Peruzzo Fermions (I) Quantum many-body theory: Fermions Bosons Fermions (II) Properties Pauli exclusion principle Fermions (II)
Topological Phases of the Spin-1/2 Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic Alternating Heisenberg Chain with Frustrated Next-Nearest-Neighbour Interaction
 Topological Phases of the Spin-1/2 Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic Alternating Heisenberg Chain with Frustrated Next-Nearest-Neighbour Interaction Kazuo Hida (Saitama University) Ken ichi Takano (Toyota
Topological Phases of the Spin-1/2 Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic Alternating Heisenberg Chain with Frustrated Next-Nearest-Neighbour Interaction Kazuo Hida (Saitama University) Ken ichi Takano (Toyota
August 28, 2016 (Sunday)
 August 28, 2016 (Sunday) 09:00-10: 30 The Theory of Statistical Comparison with Applications in Quantum Information Science....... 1 Francesco Buscemi (Nagoya University) 10:50-12:20 Introduction to measurement-based
August 28, 2016 (Sunday) 09:00-10: 30 The Theory of Statistical Comparison with Applications in Quantum Information Science....... 1 Francesco Buscemi (Nagoya University) 10:50-12:20 Introduction to measurement-based
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Neural Networks Varun Chandola x x 5 Input Outline Contents February 2, 207 Extending Perceptrons 2 Multi Layered Perceptrons 2 2. Generalizing to Multiple Labels.................
Introduction to Machine Learning Neural Networks Varun Chandola x x 5 Input Outline Contents February 2, 207 Extending Perceptrons 2 Multi Layered Perceptrons 2 2. Generalizing to Multiple Labels.................
Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 UVA CS 6316 / CS 4501-004 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning Jack Lanchantin Dr. Yanjun Qi 1 Neurons 1-Layer Neural Network Multi-layer Neural Network Loss Functions
UVA CS 6316 / CS 4501-004 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning Jack Lanchantin Dr. Yanjun Qi 1 Neurons 1-Layer Neural Network Multi-layer Neural Network Loss Functions
Accelerating QMC on quantum computers. Matthias Troyer
 Accelerating QMC on quantum computers Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers Richard P. Feynman Department of Physics, California
Accelerating QMC on quantum computers Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers Richard P. Feynman Department of Physics, California
LOCAL RECOVERY MAPS AS DUCT TAPE FOR MANY BODY SYSTEMS
 LOCAL RECOVERY MAPS AS DUCT TAPE FOR MANY BODY SYSTEMS Michael J. Kastoryano November 14 2016, QuSoft Amsterdam CONTENTS Local recovery maps Exact recovery and approximate recovery Local recovery for many
LOCAL RECOVERY MAPS AS DUCT TAPE FOR MANY BODY SYSTEMS Michael J. Kastoryano November 14 2016, QuSoft Amsterdam CONTENTS Local recovery maps Exact recovery and approximate recovery Local recovery for many
Introduction to Deep Learning
 Introduction to Deep Learning A. G. Schwing & S. Fidler University of Toronto, 2015 A. G. Schwing & S. Fidler (UofT) CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 2015 1 / 39 Outline 1 Universality of Neural Networks
Introduction to Deep Learning A. G. Schwing & S. Fidler University of Toronto, 2015 A. G. Schwing & S. Fidler (UofT) CSC420: Intro to Image Understanding 2015 1 / 39 Outline 1 Universality of Neural Networks
Deep learning quantum matter
 Deep learning quantum matter Machine-learning approaches to the quantum many-body problem Joaquín E. Drut & Andrew C. Loheac University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill SAS, September 2018 Outline Why
Deep learning quantum matter Machine-learning approaches to the quantum many-body problem Joaquín E. Drut & Andrew C. Loheac University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill SAS, September 2018 Outline Why
Lab 5: 16 th April Exercises on Neural Networks
 Lab 5: 16 th April 01 Exercises on Neural Networks 1. What are the values of weights w 0, w 1, and w for the perceptron whose decision surface is illustrated in the figure? Assume the surface crosses the
Lab 5: 16 th April 01 Exercises on Neural Networks 1. What are the values of weights w 0, w 1, and w for the perceptron whose decision surface is illustrated in the figure? Assume the surface crosses the
Chiral spin liquids. Bela Bauer
 Chiral spin liquids Bela Bauer Based on work with: Lukasz Cinco & Guifre Vidal (Perimeter Institute) Andreas Ludwig & Brendan Keller (UCSB) Simon Trebst (U Cologne) Michele Dolfi (ETH Zurich) Nature Communications
Chiral spin liquids Bela Bauer Based on work with: Lukasz Cinco & Guifre Vidal (Perimeter Institute) Andreas Ludwig & Brendan Keller (UCSB) Simon Trebst (U Cologne) Michele Dolfi (ETH Zurich) Nature Communications
Tensor network renormalization
 Coogee'15 Sydney Quantum Information Theory Workshop Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal In collaboration with GLEN EVENBLY IQIM Caltech UC Irvine Quantum Mechanics 1920-1930 Niels Bohr Albert
Coogee'15 Sydney Quantum Information Theory Workshop Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal In collaboration with GLEN EVENBLY IQIM Caltech UC Irvine Quantum Mechanics 1920-1930 Niels Bohr Albert
Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
 Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Zhisheng Zhong Feburary 2nd, 2018 Zhisheng Zhong Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Feburary 2nd, 2018 1 / 55 Outline 1 Introduction of Convolution Motivation
Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Zhisheng Zhong Feburary 2nd, 2018 Zhisheng Zhong Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Feburary 2nd, 2018 1 / 55 Outline 1 Introduction of Convolution Motivation
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Sep 2015](/thumbs/78/77924120.jpg) Gapped boundaries, group cohomology and fault-tolerant logical gates NSF-KITP-15-096 Beni Yoshida Walter Burke Institute for Theoretical Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California
Gapped boundaries, group cohomology and fault-tolerant logical gates NSF-KITP-15-096 Beni Yoshida Walter Burke Institute for Theoretical Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California
Topological order from quantum loops and nets
 Topological order from quantum loops and nets Paul Fendley It has proved to be quite tricky to T -invariant spin models whose quasiparticles are non-abelian anyons. 1 Here I ll describe the simplest (so
Topological order from quantum loops and nets Paul Fendley It has proved to be quite tricky to T -invariant spin models whose quasiparticles are non-abelian anyons. 1 Here I ll describe the simplest (so
Introduction to the Renormalization Group
 Introduction to the Renormalization Group Gregory Petropoulos University of Colorado Boulder March 4, 2015 1 / 17 Summary Flavor of Statistical Physics Universality / Critical Exponents Ising Model Renormalization
Introduction to the Renormalization Group Gregory Petropoulos University of Colorado Boulder March 4, 2015 1 / 17 Summary Flavor of Statistical Physics Universality / Critical Exponents Ising Model Renormalization
Supersymmetry breaking and Nambu-Goldstone fermions in lattice models
 YKIS2016@YITP (2016/6/15) Supersymmetry breaking and Nambu-Goldstone fermions in lattice models Hosho Katsura (Department of Physics, UTokyo) Collaborators: Yu Nakayama (IPMU Rikkyo) Noriaki Sannomiya
YKIS2016@YITP (2016/6/15) Supersymmetry breaking and Nambu-Goldstone fermions in lattice models Hosho Katsura (Department of Physics, UTokyo) Collaborators: Yu Nakayama (IPMU Rikkyo) Noriaki Sannomiya
Deep Learning. Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) Ali Ghodsi. October 30, Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, Deep Learning
 Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) University of Waterloo October 30, 2015 Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, by Bengio, Goodfellow, and Aaron Courville, 2015 Convolutional Networks Convolutional
Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) University of Waterloo October 30, 2015 Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, by Bengio, Goodfellow, and Aaron Courville, 2015 Convolutional Networks Convolutional
Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory
 Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory Robert Koenig (TUM) and Volkher B. Scholz (Ghent University) based on arxiv:1509.07414 and 1601.00470 (published
Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory Robert Koenig (TUM) and Volkher B. Scholz (Ghent University) based on arxiv:1509.07414 and 1601.00470 (published
2015 Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials. Program Overview
 Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Program Overview Each talk to be 45min with 15min Q&A. Monday 8/3 8:00AM Registration & Breakfast 9:00-9:10 Welcoming Remarks 9:10-10:10 Eugene Demler Harvard University
Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Program Overview Each talk to be 45min with 15min Q&A. Monday 8/3 8:00AM Registration & Breakfast 9:00-9:10 Welcoming Remarks 9:10-10:10 Eugene Demler Harvard University
Kaviti Sai Saurab. October 23,2014. IIT Kanpur. Kaviti Sai Saurab (UCLA) Quantum methods in ML October 23, / 8
 A review of Quantum Algorithms for Nearest-Neighbor Methods for Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Nathan Wiebe,Ashish Kapoor,Krysta M. Svore Jan.2014 Kaviti Sai Saurab IIT Kanpur October 23,2014 Kaviti
A review of Quantum Algorithms for Nearest-Neighbor Methods for Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Nathan Wiebe,Ashish Kapoor,Krysta M. Svore Jan.2014 Kaviti Sai Saurab IIT Kanpur October 23,2014 Kaviti
Quantum Algorithms for Many-Body Systems: A chemistry and materials science perspective. Matthias Troyer
 Quantum Algorithms for Many-Body Systems: A chemistry and materials science perspective Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers
Quantum Algorithms for Many-Body Systems: A chemistry and materials science perspective Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers
Real-Space RG for dynamics of random spin chains and many-body localization
 Low-dimensional quantum gases out of equilibrium, Minneapolis, May 2012 Real-Space RG for dynamics of random spin chains and many-body localization Ehud Altman, Weizmann Institute of Science See: Ronen
Low-dimensional quantum gases out of equilibrium, Minneapolis, May 2012 Real-Space RG for dynamics of random spin chains and many-body localization Ehud Altman, Weizmann Institute of Science See: Ronen
Understanding Topological Order with PEPS. David Pérez-García Autrans Summer School 2016
 Understanding Topological Order with PEPS David Pérez-García Autrans Summer School 2016 Outlook 1. An introduc
Understanding Topological Order with PEPS David Pérez-García Autrans Summer School 2016 Outlook 1. An introduc
Multilayer Neural Networks
 Multilayer Neural Networks Multilayer Neural Networks Discriminant function flexibility NON-Linear But with sets of linear parameters at each layer Provably general function approximators for sufficient
Multilayer Neural Networks Multilayer Neural Networks Discriminant function flexibility NON-Linear But with sets of linear parameters at each layer Provably general function approximators for sufficient
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Neural networks Daniel Hennes 21.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Logistic regression Neural networks Perceptron
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Neural networks Daniel Hennes 21.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Logistic regression Neural networks Perceptron
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point
 Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Real-Space Renormalization Group (RSRG) Approach to Quantum Spin Lattice Systems
 WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 49 54, 011. ISBN 978-80-7378-186-6 MATFYZPRESS Real-Space Renormalization Group (RSRG) Approach to Quantum Spin Lattice Systems A. S. Serov and G. V.
WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 49 54, 011. ISBN 978-80-7378-186-6 MATFYZPRESS Real-Space Renormalization Group (RSRG) Approach to Quantum Spin Lattice Systems A. S. Serov and G. V.
Holographic Branching and Entanglement Renormalization
 KITP, December 7 th 2010 Holographic Branching and Entanglement Renormalization Glen Evenbly Guifre Vidal Tensor Network Methods (DMRG, PEPS, TERG, MERA) Potentially offer general formalism to efficiently
KITP, December 7 th 2010 Holographic Branching and Entanglement Renormalization Glen Evenbly Guifre Vidal Tensor Network Methods (DMRG, PEPS, TERG, MERA) Potentially offer general formalism to efficiently
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond
 Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop , Fall 2018 Lecture 4
 Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions
 MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions Eddy Ardonne Hans Hansson Jonas Kjäll Jérôme Dubail Maria Hermanns Nicolas Regnault GAQHE-Köln 2015-12-17 Outline Short review of matrix product states
MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions Eddy Ardonne Hans Hansson Jonas Kjäll Jérôme Dubail Maria Hermanns Nicolas Regnault GAQHE-Köln 2015-12-17 Outline Short review of matrix product states
Artificial Neural Networks D B M G. Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino. Elena Baralis. Politecnico di Torino
 Artificial Neural Networks Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Elena Baralis Politecnico di Torino Artificial Neural Networks Inspired to the structure of the human brain Neurons as
Artificial Neural Networks Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Elena Baralis Politecnico di Torino Artificial Neural Networks Inspired to the structure of the human brain Neurons as
Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang
 Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang Institute of Physics/Institute of Theoretical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Physical Background: characteristic energy scales
Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang Institute of Physics/Institute of Theoretical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Physical Background: characteristic energy scales
Revealing fermionic quantum criticality from new Monte Carlo techniques. Zi Yang Meng ( 孟子杨 )
 Revealing fermionic quantum criticality from new Monte Carlo techniques Zi Yang Meng ( 孟子杨 ) http://ziyangmeng.iphy.ac.cn Collaborators and References Xiao Yan Xu Zi Hong Liu Chuang Chen Gao Pei Pan Yang
Revealing fermionic quantum criticality from new Monte Carlo techniques Zi Yang Meng ( 孟子杨 ) http://ziyangmeng.iphy.ac.cn Collaborators and References Xiao Yan Xu Zi Hong Liu Chuang Chen Gao Pei Pan Yang

 CSE446: Neural Networks Winter 2015 Luke Ze
CSE446: Neural Networks Winter 2015 Luke Ze