Neural Network Representation of Tensor Network and Chiral States
|
|
|
- Blaze Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neural Network Representation of Tensor Network and Chiral States Yichen Huang ( 黄溢辰 ) 1 and Joel E. Moore 2 1 Institute for Quantum Information and Matter California Institute of Technology 2 Department of Physics University of California, Berkeley KITS Workshop on Machine Learning and Many-Body Physics July 6, 2017
2 Background In machine learning, neural network is the most widely used method. It is a variational approach in that the learning process is to perform optimization over the parameters in the neural network. Types of neural network: feedforward neural network, convolutional neural network, (restricted) Boltzmann machine, etc. Recently, Carleo and Troyer simulated quantum many-body systems with a variational approach based on restricted Boltzmann machines. The most popular variational approach in the study of many-body physics is based on tensor network states. It is important to compare and understand the connection between the representational power of neural versus tensor network states.
3 Boltzmann machine (BM) {s 1,s 2,...,s V + H } {±1} ( V + H ) e V + H j=1 h j s j V + H j,k=1 w jk s j s k {s 1, s 2,..., s V } V = {v 1, v 2,... v V } is the set of visible units carrying classical Ising variables s 1, s 2,... s V. H = {h 1, h 2,... h H } is the set of hidden units carrying s V +1, s V +2,..., s V + H. Figure taken from wiki/boltzmann_machine
4 Locality {s 1,s 2,...,s V + H } {±1} ( V + H ) e V + H j=1 h j s j V + H j,k=1 w jk s j s k {s 1, s 2,..., s V } A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a BM such that w jk = 0 for any edge that connects a visible unit j V with a hidden unit k V + 1. A (restricted) Boltzmann machine is local if there are only short-range connections. Figure taken from Deng et al. PRX 7, , 2017.
5 References and related work G. Carleo and M. Troyer. Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks. Science 355, 602, 2017.
6 References and related work G. Carleo and M. Troyer. Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks. Science 355, 602, D.-L. Deng, X. Li, and S. Das Sarma. Exact machine learning topological states. arxiv: ; Quantum entanglement in neural network states. Phys. Rev. X 7, , J. Chen, S. Cheng, H. Xie, L. Wang, and T. Xiang. On the equivalence of restricted Boltzmann machines and tensor network states. arxiv: X. Gao and L.-M. Duan. Efficient representation of quantum many-body states with deep neural networks. arxiv: Y. Huang and J. E. Moore. Neural network representation of tensor network and chiral states. arxiv:
7 Motivations We study the representational power of Boltzmann machines. In terms of representational power, how are neural network states compared with tensor network states? Do all tensor network states have neural network representations? How much computational time does it take to convert a tensor network state into a neural network state? How much space does such a neural network representation occupy? Can we find a physically interesting class of states, which have neural network representations, but are hard (or even impossible) to describe using tensor networks?
8 Neural and tensor network representations We provide a polynomial-time algorithm that constructs a (local) neural network representation for any (local) tensor network state. 1 The construction is almost optimal: the number of parameters in the neural network representation is almost linear in the number of nonzero parameters in the tensor network representation. 1 See X. Gao and L.-M. Duan, arxiv: for a similar result. 2 N. Le Roux and Y. Bengio. Neural Comput. 20, 1631, 2008.
9 Neural and tensor network representations We provide a polynomial-time algorithm that constructs a (local) neural network representation for any (local) tensor network state. 1 The construction is almost optimal: the number of parameters in the neural network representation is almost linear in the number of nonzero parameters in the tensor network representation. Example: Any n-qubit matrix product state of bond dimension D has a local neural network representation with 2nD 2 hidden units and 4nD 2 log 2 D parameters. 1 See X. Gao and L.-M. Duan, arxiv: for a similar result. 2 N. Le Roux and Y. Bengio. Neural Comput. 20, 1631, 2008.
10 Neural and tensor network representations We provide a polynomial-time algorithm that constructs a (local) neural network representation for any (local) tensor network state. 1 The construction is almost optimal: the number of parameters in the neural network representation is almost linear in the number of nonzero parameters in the tensor network representation. Example: Any n-qubit matrix product state of bond dimension D has a local neural network representation with 2nD 2 hidden units and 4nD 2 log 2 D parameters. Using the universal approximation theorem, we convert every tensor in the network to a RBM. Then, we contract these RBMs in the same way as the tensors are contracted. Universal approximation theorem 2 : Any tensor M can be arbitrarily well approximated by a RBM, provided that the number of hidden units is the number of nonzero elements in M. 1 See X. Gao and L.-M. Duan, arxiv: for a similar result. 2 N. Le Roux and Y. Bengio. Neural Comput. 20, 1631, 2008.
11 Tensor network representation of chiral states Early attempts did not impose locality 3 or just target at expectation values of local observables rather than the wave function. 4 Recent progress 5 shows that local tensor networks can describe chiral topological states, but the examples there are all gapless. Dubail and Read s no-go theorem: For any chiral local free-fermion tensor network state, any local parent Hamiltonian is gapless. 3 Z.-C. Gu, F. Verstraete, and X.-G. Wen. arxiv: B. Beri and N. R. Cooper. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, , T. B. Wahl, H.-H. Tu, N. Schuch, and J. I. Cirac. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, , 2013; J. Dubail and N. Read. Phys. Rev. B 92, , 2015.
12 Tensor network representation of chiral states Early attempts did not impose locality 3 or just target at expectation values of local observables rather than the wave function. 4 Recent progress 5 shows that local tensor networks can describe chiral topological states, but the examples there are all gapless. Dubail and Read s no-go theorem: For any chiral local free-fermion tensor network state, any local parent Hamiltonian is gapless. It seems difficult to obtain a local tensor network representation for gapped chiral topological states. This is an open problem in the community. 3 Z.-C. Gu, F. Verstraete, and X.-G. Wen. arxiv: B. Beri and N. R. Cooper. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, , T. B. Wahl, H.-H. Tu, N. Schuch, and J. I. Cirac. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, , 2013; J. Dubail and N. Read. Phys. Rev. B 92, , 2015.
13 Fermionic neural network states ( dξ V +1 dξ V +2 dξ V + H e V + H j,k=1 w jk ξ j ξ k ) 0 V = {v 1, v 2,... v V } is the set of visible units carrying Grassmann numbers ξ 1, ξ 2,... ξ V. H = {h 1, h 2,... h H } is the set of hidden units carrying ξ V +1, ξ V +2,..., ξ V + H. We identify ξ 1, ξ 2,... ξ V with c 1, c 2,..., c V. Locality in fermionic BMs can be defined in the same way as in spin systems.
14 p + ip superconductor H = x Z 2 (c x+ i c x + c x+ j c x + c x+ i c x + ic x+ j c x + h.c.) 2µ x Z 2 c x c x = BZ d kh k, H k = k c k c k + k c k c k + 2M k c k c k k = sin k x + i sin k y, M k = cos k x + cos k y µ E k = 2 k 2 + M BZ, g.s. = e d 2 k k c c E k 2M k k k 0 k This model represents topological superconductors with opposite chirality for 2 < µ < 0 and 0 < µ < 2, respectively.
15 Neural network representation of chiral states Approximate representations are acceptable, and we have to work with a finite system size in order to rigorously quantify the error of the approximation and the succinctness of the representation. Example: A gapped ground state in a chain of n spins can be approximated (in the sense of 99% fidelity) by a matrix product state with bond dimension 2Õ(log3/4 n). 6 6 I. Arad, A. Kitaev, Z. Landau, and U. Vazirani. arxiv:
16 Neural network representation of chiral states Approximate representations are acceptable, and we have to work with a finite system size in order to rigorously quantify the error of the approximation and the succinctness of the representation. Example: A gapped ground state in a chain of n spins can be approximated (in the sense of 99% fidelity) by a matrix product state with bond dimension 2Õ(log3/4 n). 6 On a square lattice of size n n, we construct a O(log n)-local neural network state n.n.s. with one visible and one hidden unit per site such that n.n.s g.s. > 1 1/ poly n. The same result can be established for the ground state of any translationally invariant gapped free-fermion systems. 6 I. Arad, A. Kitaev, Z. Landau, and U. Vazirani. arxiv:
17 Summary We provide a polynomial-time algorithm that constructs a (local) neural network representation for any (local) tensor network state. The construction is almost optimal in the sense that the number of parameters in the neural network representation is almost linear in the number of nonzero parameters in the tensor network representation.
18 Summary We provide a polynomial-time algorithm that constructs a (local) neural network representation for any (local) tensor network state. The construction is almost optimal in the sense that the number of parameters in the neural network representation is almost linear in the number of nonzero parameters in the tensor network representation. Despite the difficulty of representing (gapped) chiral topological states with local tensor networks, we construct a quasi-local neural network representation for a chiral p-wave superconductor. This is an explicit and physically interesting example that neural network states may go beyond tensor network states.
19 Outlook Numerical study of chiral topological order with neural network states. 7 The parton approach may allow us to construct quasi-local neural network representation for strongly interacting chiral topological states (e.g., the fractional quantum Hall state). What is the representational power of neural network states based on RBM? 7 I. Glasser et al. The geometry of neural network states, string-bond states and chiral topological order. preceding talk in this workshop.
Tensor network vs Machine learning. Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS
 Tensor network vs Machine learning Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS physichengsong@iphy.ac.cn Outline Tensor network in a nutshell TN concepts in machine learning TN methods in machine learning Outline Tensor
Tensor network vs Machine learning Song Cheng ( 程嵩 ) IOP, CAS physichengsong@iphy.ac.cn Outline Tensor network in a nutshell TN concepts in machine learning TN methods in machine learning Outline Tensor
Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks
 Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks Iris Cong Soonwon Choi Mikhail D. Lukin arxiv:1810.03787 Berkeley Quantum Information Seminar October 16 th, 2018 Why quantum machine learning? Machine learning: interpret
Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks Iris Cong Soonwon Choi Mikhail D. Lukin arxiv:1810.03787 Berkeley Quantum Information Seminar October 16 th, 2018 Why quantum machine learning? Machine learning: interpret
Fermionic topological quantum states as tensor networks
 order in topological quantum states as Jens Eisert, Freie Universität Berlin Joint work with Carolin Wille and Oliver Buerschaper Symmetry, topology, and quantum phases of matter: From to physical realizations,
order in topological quantum states as Jens Eisert, Freie Universität Berlin Joint work with Carolin Wille and Oliver Buerschaper Symmetry, topology, and quantum phases of matter: From to physical realizations,
A Video from Google DeepMind.
 A Video from Google DeepMind http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v518/n7540/fig_tab/nature14236_sv2.html Can machine learning teach us cluster updates? Lei Wang Institute of Physics, CAS https://wangleiphy.github.io
A Video from Google DeepMind http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v518/n7540/fig_tab/nature14236_sv2.html Can machine learning teach us cluster updates? Lei Wang Institute of Physics, CAS https://wangleiphy.github.io
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Jan 2017 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Jan 2017](/thumbs/92/108771472.jpg) Efficient Representation of Quantum Many-body States with Deep Neural Networks Xun Gao 1 and Lu-Ming Duan 1, 2 1 Center for Quantum Information, IIIS, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, PR China 2 Department
Efficient Representation of Quantum Many-body States with Deep Neural Networks Xun Gao 1 and Lu-Ming Duan 1, 2 1 Center for Quantum Information, IIIS, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, PR China 2 Department
Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications
 Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications Frank Verstraete Ghent University and University of Vienna Nick Bultinck, Jutho Haegeman, Michael Marien Burak Sahinoglu, Dominic Williamson Ignacio
Matrix Product Operators: Algebras and Applications Frank Verstraete Ghent University and University of Vienna Nick Bultinck, Jutho Haegeman, Michael Marien Burak Sahinoglu, Dominic Williamson Ignacio
arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 26 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 26 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [hep-th] 26 Sep 2017](/thumbs/93/113646333.jpg) Eigenstate entanglement in the Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev model arxiv:709.0960v [hep-th] 6 Sep 07 Yichen Huang ( 黄溢辰 ) Institute for Quantum Information and Matter, California Institute of Technology Pasadena,
Eigenstate entanglement in the Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev model arxiv:709.0960v [hep-th] 6 Sep 07 Yichen Huang ( 黄溢辰 ) Institute for Quantum Information and Matter, California Institute of Technology Pasadena,
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems
 Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Topological Phases in One Dimension
 Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
Rigorous free fermion entanglement renormalization from wavelets
 Computational Complexity and High Energy Physics August 1st, 2017 Rigorous free fermion entanglement renormalization from wavelets arxiv: 1707.06243 Jutho Haegeman Ghent University in collaboration with:
Computational Complexity and High Energy Physics August 1st, 2017 Rigorous free fermion entanglement renormalization from wavelets arxiv: 1707.06243 Jutho Haegeman Ghent University in collaboration with:
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect
 Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Machine Learning with Tensor Networks
 Machine Learning with Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 Beijing Jun 2017 Machine learning has physics in its DNA # " # #
Machine Learning with Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 Beijing Jun 2017 Machine learning has physics in its DNA # " # #
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks
 Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 RIKEN AICS - Mar 2017 Collaboration with David
Machine Learning with Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks E.M. Stoudenmire and David J. Schwab Advances in Neural Information Processing 29 arxiv:1605.05775 RIKEN AICS - Mar 2017 Collaboration with David
Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity. Itai Arad
 1 18 / Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Itai Arad Centre of Quantum Technologies National University of Singapore QIP 2015 2 18 / Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity condensed matter physics QHC complexity theory
1 18 / Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity Itai Arad Centre of Quantum Technologies National University of Singapore QIP 2015 2 18 / Quantum Hamiltonian Complexity condensed matter physics QHC complexity theory
Universal Topological Phase of 2D Stabilizer Codes
 H. Bombin, G. Duclos-Cianci, D. Poulin arxiv:1103.4606 H. Bombin arxiv:1107.2707 Universal Topological Phase of 2D Stabilizer Codes Héctor Bombín Perimeter Institute collaborators David Poulin Guillaume
H. Bombin, G. Duclos-Cianci, D. Poulin arxiv:1103.4606 H. Bombin arxiv:1107.2707 Universal Topological Phase of 2D Stabilizer Codes Héctor Bombín Perimeter Institute collaborators David Poulin Guillaume
Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity. Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM
 Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM Influence of quantum information Easy Hard (at present) Easy Hard (at present)!! QI-inspired classical, e.g. tensor networks
Quantum Fields, Gravity, and Complexity Brian Swingle UMD WIP w/ Isaac Kim, IBM Influence of quantum information Easy Hard (at present) Easy Hard (at present)!! QI-inspired classical, e.g. tensor networks
Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems
 Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems Lecture 1 Norbert Schuch California Institute of Technology Institute for Quantum Information Quantum Information and Quantum Many-Body Systems Aim: Understand
Quantum Information and Quantum Many-body Systems Lecture 1 Norbert Schuch California Institute of Technology Institute for Quantum Information Quantum Information and Quantum Many-Body Systems Aim: Understand
Fermionic tensor networks
 Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETH Zurich Bosons vs Fermions P. Corboz and G. Vidal, Phys. Rev. B 80, 165129 (2009) : fermionic 2D MERA P. Corboz, R. Orus,
Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, ETH Zurich Bosons vs Fermions P. Corboz and G. Vidal, Phys. Rev. B 80, 165129 (2009) : fermionic 2D MERA P. Corboz, R. Orus,
Storage of Quantum Information in Topological Systems with Majorana Fermions
 Storage of Quantum Information in Topological Systems with Majorana Fermions Leonardo Mazza Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa Mainz September 26th, 2013 Leonardo Mazza (SNS) Storage of Information & Majorana
Storage of Quantum Information in Topological Systems with Majorana Fermions Leonardo Mazza Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa Mainz September 26th, 2013 Leonardo Mazza (SNS) Storage of Information & Majorana
Local Algorithms for 1D Quantum Systems
 Local Algorithms for 1D Quantum Systems I. Arad, Z. Landau, U. Vazirani, T. Vidick I. Arad, Z. Landau, U. Vazirani, T. Vidick () Local Algorithms for 1D Quantum Systems 1 / 14 Many-body physics Are physical
Local Algorithms for 1D Quantum Systems I. Arad, Z. Landau, U. Vazirani, T. Vidick I. Arad, Z. Landau, U. Vazirani, T. Vidick () Local Algorithms for 1D Quantum Systems 1 / 14 Many-body physics Are physical
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE
 SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL TOPOLOGICAL, AND GAPLESS NON-FERMI-LIQUID PHASE ANDREAS W.W. LUDWIG (UC-Santa Barbara) work done in collaboration with: Bela Bauer (Microsoft Station-Q, Santa
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications
 Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems
 CENTRE FOR QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE AND CLARENDON LABORATORY UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems Stephen Clark LXXT[[[GSQPEFS\EGYOEGXMZMXMIWUYERXYQGSYVWI
CENTRE FOR QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE AND CLARENDON LABORATORY UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD Tensor network simulations of strongly correlated quantum systems Stephen Clark LXXT[[[GSQPEFS\EGYOEGXMZMXMIWUYERXYQGSYVWI
Cenke Xu. Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem 许岑珂
 Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases
 The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases - anomaly-free and chiral fermions Juven Wang, Xiao-Gang Wen (arxiv:1307.7480, arxiv:140?.????) MIT/Perimeter Inst. 2014 @ APS March A Lattice
The uses of Instantons for classifying Topological Phases - anomaly-free and chiral fermions Juven Wang, Xiao-Gang Wen (arxiv:1307.7480, arxiv:140?.????) MIT/Perimeter Inst. 2014 @ APS March A Lattice
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization
 Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer
 Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer Martin Schwarz, Kristan Temme, Frank Verstraete University of Vienna, Faculty of Physics, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090 Vienna, Austria Toby Cubitt,
Preparing Projected Entangled Pair States on a Quantum Computer Martin Schwarz, Kristan Temme, Frank Verstraete University of Vienna, Faculty of Physics, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090 Vienna, Austria Toby Cubitt,
Accelerated Monte Carlo simulations with restricted Boltzmann machines
 Accelerated simulations with restricted Boltzmann machines Li Huang 1 Lei Wang 2 1 China Academy of Engineering Physics 2 Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences July 6, 2017 Machine Learning
Accelerated simulations with restricted Boltzmann machines Li Huang 1 Lei Wang 2 1 China Academy of Engineering Physics 2 Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences July 6, 2017 Machine Learning
Composite Dirac liquids
 Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
team Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber
 title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation
 Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation Thomas Quella University of Cologne Presentation given on 18 Feb 2016 at the Benasque Workshop Entanglement in Strongly
Chiral Haldane-SPT phases of SU(N) quantum spin chains in the adjoint representation Thomas Quella University of Cologne Presentation given on 18 Feb 2016 at the Benasque Workshop Entanglement in Strongly
Entanglement in Topological Phases
 Entanglement in Topological Phases Dylan Liu August 31, 2012 Abstract In this report, the research conducted on entanglement in topological phases is detailed and summarized. This includes background developed
Entanglement in Topological Phases Dylan Liu August 31, 2012 Abstract In this report, the research conducted on entanglement in topological phases is detailed and summarized. This includes background developed
Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks
 Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks Albert H. Werner QMath University of Copenhagen Together with: C. Cedzic, T. Geib, F. A. Grünbaum, C. Stahl, L. Velazques, R. F. Werner Phase classification
Topological classification of 1D symmetric quantum walks Albert H. Werner QMath University of Copenhagen Together with: C. Cedzic, T. Geib, F. A. Grünbaum, C. Stahl, L. Velazques, R. F. Werner Phase classification
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ 2 Topological Insulator
 Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Time Reversal Invariant Ζ Topological Insulator D Bloch Hamiltonians subject to the T constraint 1 ( ) ΘH Θ = H( ) with Θ = 1 are classified by a Ζ topological invariant (ν =,1) Understand via Bul-Boundary
Exploring Topological Phases With Quantum Walks
 Exploring Topological Phases With Quantum Walks Tk Takuya Kitagawa, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner Eugene Demler Harvard University References: PRA 82:33429 and PRB 82:235114 (2010) Collaboration with A. White
Exploring Topological Phases With Quantum Walks Tk Takuya Kitagawa, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner Eugene Demler Harvard University References: PRA 82:33429 and PRB 82:235114 (2010) Collaboration with A. White
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models
 Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d
 Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d Román Orús University of Mainz (Germany) K. Zapp, RO, Phys. Rev. D 95, 114508 (2017) Goal of this
Tensor network simulation of QED on infinite lattices: learning from (1 + 1)d, and prospects for (2 + 1)d Román Orús University of Mainz (Germany) K. Zapp, RO, Phys. Rev. D 95, 114508 (2017) Goal of this
Markov Chains for Tensor Network States
 Sofyan Iblisdir University of Barcelona September 2013 arxiv 1309.4880 Outline Main issue discussed here: how to find good tensor network states? The optimal state problem Markov chains Multiplicative
Sofyan Iblisdir University of Barcelona September 2013 arxiv 1309.4880 Outline Main issue discussed here: how to find good tensor network states? The optimal state problem Markov chains Multiplicative
Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium
 Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Solvay Workshop on Quantum Simulation ULB, Brussels, 18 February 2019 Max McGinley
Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Solvay Workshop on Quantum Simulation ULB, Brussels, 18 February 2019 Max McGinley
Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang
 Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang Institute of Physics/Institute of Theoretical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Physical Background: characteristic energy scales
Renormalization of Tensor- Network States Tao Xiang Institute of Physics/Institute of Theoretical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Physical Background: characteristic energy scales
Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory
 Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory Robert Koenig (TUM) and Volkher B. Scholz (Ghent University) based on arxiv:1509.07414 and 1601.00470 (published
Matrix product approximations to multipoint functions in two-dimensional conformal field theory Robert Koenig (TUM) and Volkher B. Scholz (Ghent University) based on arxiv:1509.07414 and 1601.00470 (published
Basics of quantum computing and some recent results. Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) min
 Basics of quantum computing and some recent results Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) 50+10 min Outline 1. Basics of quantum computing circuit model, classically simulatable/unsimulatable, quantum
Basics of quantum computing and some recent results Tomoyuki Morimae YITP Kyoto University) 50+10 min Outline 1. Basics of quantum computing circuit model, classically simulatable/unsimulatable, quantum
Fermionic tensor networks
 Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, ETH Zurich / EPF Lausanne, Switzerland Collaborators: University of Queensland: Guifre Vidal, Roman Orus, Glen Evenbly, Jacob Jordan University of Vienna: Frank
Fermionic tensor networks Philippe Corboz, ETH Zurich / EPF Lausanne, Switzerland Collaborators: University of Queensland: Guifre Vidal, Roman Orus, Glen Evenbly, Jacob Jordan University of Vienna: Frank
Lecture 3: Tensor Product Ansatz
 Lecture 3: Tensor Product nsatz Graduate Lectures Dr Gunnar Möller Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge slide credits: Philippe Corboz (ETH / msterdam) January 2014 Cavendish Laboratory Part I:
Lecture 3: Tensor Product nsatz Graduate Lectures Dr Gunnar Möller Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge slide credits: Philippe Corboz (ETH / msterdam) January 2014 Cavendish Laboratory Part I:
3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase
 Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
News on tensor network algorithms
 News on tensor network algorithms Román Orús Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) December 6th 2018 S. S. Jahromi, RO, M. Kargarian, A. Langari, PRB 97, 115162 (2018) S. S. Jahromi, RO, PRB 98,
News on tensor network algorithms Román Orús Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) December 6th 2018 S. S. Jahromi, RO, M. Kargarian, A. Langari, PRB 97, 115162 (2018) S. S. Jahromi, RO, PRB 98,
4 Matrix product states
 Physics 3b Lecture 5 Caltech, 05//7 4 Matrix product states Matrix product state (MPS) is a highly useful tool in the study of interacting quantum systems in one dimension, both analytically and numerically.
Physics 3b Lecture 5 Caltech, 05//7 4 Matrix product states Matrix product state (MPS) is a highly useful tool in the study of interacting quantum systems in one dimension, both analytically and numerically.
Defects in topologically ordered states. Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014
 Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Classical Monte Carlo Simulations
 Classical Monte Carlo Simulations Hyejin Ju April 17, 2012 1 Introduction Why do we need numerics? One of the main goals of condensed matter is to compute expectation values O = 1 Z Tr{O e βĥ} (1) and
Classical Monte Carlo Simulations Hyejin Ju April 17, 2012 1 Introduction Why do we need numerics? One of the main goals of condensed matter is to compute expectation values O = 1 Z Tr{O e βĥ} (1) and
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
3.14. The model of Haldane on a honeycomb lattice
 4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
Bell-like non-locality from Majorana end-states
 Bell-like non-locality from Majorana end-states Alessandro Romito with Yuval Gefen (WIS) 07.09.2016, Daejeon, Workshop on Anderson Localiation in Topological Insulators Outline Topological superconductors
Bell-like non-locality from Majorana end-states Alessandro Romito with Yuval Gefen (WIS) 07.09.2016, Daejeon, Workshop on Anderson Localiation in Topological Insulators Outline Topological superconductors
Machine learning quantum phases of matter
 Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Cornell, May 2017 Simon Trebst University of Cologne Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer
Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer School on Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Materials Cornell, May 2017 Simon Trebst University of Cologne Machine learning quantum phases of matter Summer
Topology driven quantum phase transitions
 Topology driven quantum phase transitions Dresden July 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q UC Santa Barbara Charlotte Gils Alexei Kitaev Andreas Ludwig Matthias Troyer Zhenghan Wang Topological quantum
Topology driven quantum phase transitions Dresden July 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q UC Santa Barbara Charlotte Gils Alexei Kitaev Andreas Ludwig Matthias Troyer Zhenghan Wang Topological quantum
Plaquette Renormalized Tensor Network States: Application to Frustrated Systems
 Workshop on QIS and QMP, Dec 20, 2009 Plaquette Renormalized Tensor Network States: Application to Frustrated Systems Ying-Jer Kao and Center for Quantum Science and Engineering Hsin-Chih Hsiao, Ji-Feng
Workshop on QIS and QMP, Dec 20, 2009 Plaquette Renormalized Tensor Network States: Application to Frustrated Systems Ying-Jer Kao and Center for Quantum Science and Engineering Hsin-Chih Hsiao, Ji-Feng
MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions
 MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions Eddy Ardonne Hans Hansson Jonas Kjäll Jérôme Dubail Maria Hermanns Nicolas Regnault GAQHE-Köln 2015-12-17 Outline Short review of matrix product states
MPS formulation of quasi-particle wave functions Eddy Ardonne Hans Hansson Jonas Kjäll Jérôme Dubail Maria Hermanns Nicolas Regnault GAQHE-Köln 2015-12-17 Outline Short review of matrix product states
Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems
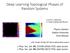 Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems 2017/6/5 Osaka Univ. in Deep Learning and Physics Physics division Sophia University Tomi Ohtsuki with Tomoki Ohtsuki, NTT data mathemahcal systems J.
Deep Learning Topological Phases of Random Systems 2017/6/5 Osaka Univ. in Deep Learning and Physics Physics division Sophia University Tomi Ohtsuki with Tomoki Ohtsuki, NTT data mathemahcal systems J.
Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors
 Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors Anton Akhmerov with Carlo Beenakker, Jan Dahlhaus, Fabian Hassler, and Michael Wimmer New J. Phys. 13, 053016 (2011) and arxiv:1105.0315 Superconductor
Detecting and using Majorana fermions in superconductors Anton Akhmerov with Carlo Beenakker, Jan Dahlhaus, Fabian Hassler, and Michael Wimmer New J. Phys. 13, 053016 (2011) and arxiv:1105.0315 Superconductor
Constructing Landau Formalism for Topological Order: Spin Chains and Ladders
 Constructing Landau Formalism for Topological Order: Spin Chains and Ladders Gennady Y. Chitov Laurentian University Sudbury, Canada Talk at Washington University in St. Louis, October 20, 2016 Collaborators:
Constructing Landau Formalism for Topological Order: Spin Chains and Ladders Gennady Y. Chitov Laurentian University Sudbury, Canada Talk at Washington University in St. Louis, October 20, 2016 Collaborators:
Topological insulator (TI)
 Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals
 2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains
 16 th December 2015 Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains Matilda Peruzzo Fermions (I) Quantum many-body theory: Fermions Bosons Fermions (II) Properties Pauli exclusion principle Fermions (II)
16 th December 2015 Majorana Fermions in Superconducting Chains Matilda Peruzzo Fermions (I) Quantum many-body theory: Fermions Bosons Fermions (II) Properties Pauli exclusion principle Fermions (II)
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
Frustration and Area law
 Frustration and Area law When the frustration goes odd S. M. Giampaolo Institut Ruder Bošković, Zagreb, Croatia Workshop: Exactly Solvable Quantum Chains Natal 18-29 June 2018 Coauthors F. Franchini Institut
Frustration and Area law When the frustration goes odd S. M. Giampaolo Institut Ruder Bošković, Zagreb, Croatia Workshop: Exactly Solvable Quantum Chains Natal 18-29 June 2018 Coauthors F. Franchini Institut
Nematicity and quantum paramagnetism in FeSe
 Nematicity and quantum paramagnetism in FeSe Fa Wang 1,, Steven A. Kivelson 3 & Dung-Hai Lee 4,5, 1 International Center for Quantum Materials, School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.
Nematicity and quantum paramagnetism in FeSe Fa Wang 1,, Steven A. Kivelson 3 & Dung-Hai Lee 4,5, 1 International Center for Quantum Materials, School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.
Fidelity susceptibility and long-range correlation in the Kitaev honeycomb model
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 78, 4 8 Fidelity susceptibility and long-range correlation in the Kitaev honeycomb model Shuo Yang,, Shi-Jian Gu,, * Chang-Pu Sun, and Hai-Qing Lin Department of Physics and ITP, The
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 78, 4 8 Fidelity susceptibility and long-range correlation in the Kitaev honeycomb model Shuo Yang,, Shi-Jian Gu,, * Chang-Pu Sun, and Hai-Qing Lin Department of Physics and ITP, The
Tensor network renormalization
 Coogee'15 Sydney Quantum Information Theory Workshop Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal In collaboration with GLEN EVENBLY IQIM Caltech UC Irvine Quantum Mechanics 1920-1930 Niels Bohr Albert
Coogee'15 Sydney Quantum Information Theory Workshop Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal In collaboration with GLEN EVENBLY IQIM Caltech UC Irvine Quantum Mechanics 1920-1930 Niels Bohr Albert
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond
 Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More
 Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More Román Orús Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz (Germany)! School on computational methods in quantum materials Jouvence,
Introduction to Tensor Networks: PEPS, Fermions, and More Román Orús Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz (Germany)! School on computational methods in quantum materials Jouvence,
Tensor network renormalization
 Walter Burke Institute for Theoretical Physics INAUGURAL CELEBRATION AND SYMPOSIUM Caltech, Feb 23-24, 2015 Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal Sherman Fairchild Prize Postdoctoral Fellow (2003-2005)
Walter Burke Institute for Theoretical Physics INAUGURAL CELEBRATION AND SYMPOSIUM Caltech, Feb 23-24, 2015 Tensor network renormalization Guifre Vidal Sherman Fairchild Prize Postdoctoral Fellow (2003-2005)
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases
 SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
A new perspective on long range SU(N) spin models
 A new perspective on long range SU(N) spin models Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Lie Theory and Mathematical Physics Centre de Recherches Mathématiques (CRM), Montreal Based on work with
A new perspective on long range SU(N) spin models Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Lie Theory and Mathematical Physics Centre de Recherches Mathématiques (CRM), Montreal Based on work with
Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect
 Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) with L. Georgiev (Sofia), G. Zemba (Buenos Aires), G. Viola (Florence) Outline Incompressible Hall fluids:
Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) with L. Georgiev (Sofia), G. Zemba (Buenos Aires), G. Viola (Florence) Outline Incompressible Hall fluids:
Simulation of Quantum Many-Body Systems
 Numerical Quantum Simulation of Matteo Rizzi - KOMET 337 - JGU Mainz Vorstellung der Arbeitsgruppen WS 14-15 QMBS: An interdisciplinary topic entanglement structure of relevant states anyons for q-memory
Numerical Quantum Simulation of Matteo Rizzi - KOMET 337 - JGU Mainz Vorstellung der Arbeitsgruppen WS 14-15 QMBS: An interdisciplinary topic entanglement structure of relevant states anyons for q-memory
Lecture notes on topological insulators
 Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan Dated: May 8, 07 I. D p-wave SUPERCONDUCTOR Here we study p-wave SC in D
Lecture notes on topological insulators Ming-Che Chang Department of Physics, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan Dated: May 8, 07 I. D p-wave SUPERCONDUCTOR Here we study p-wave SC in D
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators
 Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases
 Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Quantum simulation with string-bond states: Joining PEPS and Monte Carlo
 Quantum simulation with string-bond states: Joining PEPS and Monte Carlo N. Schuch 1, A. Sfondrini 1,2, F. Mezzacapo 1, J. Cerrillo 1,3, M. Wolf 1,4, F. Verstraete 5, I. Cirac 1 1 Max-Planck-Institute
Quantum simulation with string-bond states: Joining PEPS and Monte Carlo N. Schuch 1, A. Sfondrini 1,2, F. Mezzacapo 1, J. Cerrillo 1,3, M. Wolf 1,4, F. Verstraete 5, I. Cirac 1 1 Max-Planck-Institute
Loop optimization for tensor network renormalization
 Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan June, 6 Loop optimization for tensor network renormalization Shuo Yang! Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Canada Zheng-Cheng
Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Japan June, 6 Loop optimization for tensor network renormalization Shuo Yang! Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Canada Zheng-Cheng
Topology of electronic bands and Topological Order
 Topology of electronic bands and Topological Order R. Shankar The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai TIFR, 26 th April, 2011 Outline IQHE and the Chern Invariant Topological insulators and the
Topology of electronic bands and Topological Order R. Shankar The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai TIFR, 26 th April, 2011 Outline IQHE and the Chern Invariant Topological insulators and the
The computational difficulty of finding MPS ground states
 The computational difficulty of finding MPS ground states Norbert Schuch 1, Ignacio Cirac 1, and Frank Verstraete 2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Quantum Optics, Garching, Germany 2 University of Vienna,
The computational difficulty of finding MPS ground states Norbert Schuch 1, Ignacio Cirac 1, and Frank Verstraete 2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Quantum Optics, Garching, Germany 2 University of Vienna,
Topological order of a two-dimensional toric code
 University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Seminar I a, 1st year, 2nd cycle Topological order of a two-dimensional toric code Author: Lenart Zadnik Advisor: Doc. Dr. Marko Žnidarič June
University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Seminar I a, 1st year, 2nd cycle Topological order of a two-dimensional toric code Author: Lenart Zadnik Advisor: Doc. Dr. Marko Žnidarič June
Simulation of Quantum Many-Body Systems
 Numerical Quantum Simulation of Matteo Rizzi - KOMET 7 - JGU Mainz Vorstellung der Arbeitsgruppen WS 15-16 recent developments in control of quantum objects (e.g., cold atoms, trapped ions) General Framework
Numerical Quantum Simulation of Matteo Rizzi - KOMET 7 - JGU Mainz Vorstellung der Arbeitsgruppen WS 15-16 recent developments in control of quantum objects (e.g., cold atoms, trapped ions) General Framework
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter Quantum Hall effect: bulk and edge Effective field
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter Quantum Hall effect: bulk and edge Effective field
It from Qubit Summer School
 It from Qubit Summer School July 27 th, 2016 Tensor Networks Guifre Vidal NSERC Wednesday 27 th 9AM ecture Tensor Networks 2:30PM Problem session 5PM Focus ecture MARKUS HAURU MERA: a tensor network for
It from Qubit Summer School July 27 th, 2016 Tensor Networks Guifre Vidal NSERC Wednesday 27 th 9AM ecture Tensor Networks 2:30PM Problem session 5PM Focus ecture MARKUS HAURU MERA: a tensor network for
From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order
 From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order Arxiv: 1201.3757, to appear in PRL. B.M. Terhal, F. Hassler, D.P. DiVincenzo IQI, RWTH Aachen We are looking for PhD students or postdocs for theoretical research
From Majorana Fermions to Topological Order Arxiv: 1201.3757, to appear in PRL. B.M. Terhal, F. Hassler, D.P. DiVincenzo IQI, RWTH Aachen We are looking for PhD students or postdocs for theoretical research
Experimental reconstruction of the Berry curvature in a topological Bloch band
 Experimental reconstruction of the Berry curvature in a topological Bloch band Christof Weitenberg Workshop Geometry and Quantum Dynamics Natal 29.10.2015 arxiv:1509.05763 (2015) Topological Insulators
Experimental reconstruction of the Berry curvature in a topological Bloch band Christof Weitenberg Workshop Geometry and Quantum Dynamics Natal 29.10.2015 arxiv:1509.05763 (2015) Topological Insulators
Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1
 1 Davis, January 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard Werner
1 Davis, January 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard Werner
Condensed Matter Physics in the City London, June 20, 2012
 Entanglement, holography, and the quantum phases of matter Condensed Matter Physics in the City London, June 20, 2012 Lecture at the 100th anniversary Solvay conference, Theory of the Quantum World arxiv:1203.4565
Entanglement, holography, and the quantum phases of matter Condensed Matter Physics in the City London, June 20, 2012 Lecture at the 100th anniversary Solvay conference, Theory of the Quantum World arxiv:1203.4565
Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order
 Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order Juven Wang (MIT/Perimeter Inst.) - and Xiao-Gang Wen Mar 15, 2013 @ PI arxiv.org/abs/1212.4863 Lattice model: Toric Code and String-net Flux Insertion What is?
Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order Juven Wang (MIT/Perimeter Inst.) - and Xiao-Gang Wen Mar 15, 2013 @ PI arxiv.org/abs/1212.4863 Lattice model: Toric Code and String-net Flux Insertion What is?
Topological Kondo Insulators!
 Topological Kondo Insulators! Maxim Dzero, University of Maryland Collaborators: Kai Sun, University of Maryland Victor Galitski, University of Maryland Piers Coleman, Rutgers University Main idea Kondo
Topological Kondo Insulators! Maxim Dzero, University of Maryland Collaborators: Kai Sun, University of Maryland Victor Galitski, University of Maryland Piers Coleman, Rutgers University Main idea Kondo
Quantum Phase Transitions
 1 Davis, September 19, 2011 Quantum Phase Transitions A VIGRE 1 Research Focus Group, Fall 2011 Spring 2012 Bruno Nachtergaele See the RFG webpage for more information: http://wwwmathucdavisedu/~bxn/rfg_quantum_
1 Davis, September 19, 2011 Quantum Phase Transitions A VIGRE 1 Research Focus Group, Fall 2011 Spring 2012 Bruno Nachtergaele See the RFG webpage for more information: http://wwwmathucdavisedu/~bxn/rfg_quantum_
Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1
 1 FRG2011, Harvard, May 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard
1 FRG2011, Harvard, May 19, 2011 Frustration-free Ground States of Quantum Spin Systems 1 Bruno Nachtergaele (UC Davis) based on joint work with Sven Bachmann, Spyridon Michalakis, Robert Sims, and Reinhard
Multichannel Majorana Wires
 Multichannel Majorana Wires Piet Brouwer Frascati, 2014 Dahlem Center for Complex Quantum Systems Physics Department Inanc Adagideli Freie Universität Berlin Mathias Duckheim Dganit Meidan Graham Kells
Multichannel Majorana Wires Piet Brouwer Frascati, 2014 Dahlem Center for Complex Quantum Systems Physics Department Inanc Adagideli Freie Universität Berlin Mathias Duckheim Dganit Meidan Graham Kells
Accelerating QMC on quantum computers. Matthias Troyer
 Accelerating QMC on quantum computers Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers Richard P. Feynman Department of Physics, California
Accelerating QMC on quantum computers Matthias Troyer International Journal of Theoretical Physics, VoL 21, Nos. 6/7, 1982 Simulating Physics with Computers Richard P. Feynman Department of Physics, California
Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini
 New Frontiers in Theoretical Physics XXXIV Convegno Nazionale di Fisica Teorica - Cortona Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini Collaborators:
New Frontiers in Theoretical Physics XXXIV Convegno Nazionale di Fisica Teorica - Cortona Universal Quantum Simulator, Local Convertibility and Edge States in Many-Body Systems Fabio Franchini Collaborators:
