GRAAD 12 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
|
|
|
- Bernard Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GR 12 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 12 MEHNIL TEHNOLOGY EXEMPLR 2014 MRKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 18 pages and a 3-page formula sheet. opyright reserved
2 Mechanical Technology 2 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar INSTRUTIONS N INFORMTION 1. Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces provided on the NSWER OOK. 2. Read LL the questions carefully. 3. nswer LL the questions. 4. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. 5. Start EH question on a NEW page. 6. Show LL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places. 7. andidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments. 8. Take the value of gravitational force as 10 m/s ll dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question. 10. formula sheet for your use is attached at the back of this question paper. 11. Write neatly and legibly. 12. Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time. QUESTION ONTENT MRKS TIME (minutes) 1 Multiple-choice questions Safety Tools and Equipment Materials Terminology Joining Methods Forces Maintenance Systems and ontrol Turbines TOTL opyright reserved
3 Mechanical Technology 3 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-HOIE QUESTIONS Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. hoose the answer and write only the letter ( ) next to the question number ( ) in the NSWER OOK, for example What safety measure is applicable to the milling machine in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety ct? o not apply a wrench to revolving work. Guards could be removed when cutting soft material. Make sure the wheel is dressed. Use the machine table as an anvil. (1) 1.2 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the cylinder leakage tester? Use water to remove dust around the spark-plug area. lean the oil-filler cap. o not exceed the prescribed pressure in the cylinder. The tester must be well tightened until no hissing sounds can be heard. (1) 1.3 What is the function of a gas analyser? nalyse inlet gases nalyse oil gases nalyse fuel gases nalyse exhaust gases (1) 1.4 rinell tester is used to test the... of a material. tension elasticity hardness brittleness (1) 1.5 What will be the result when steel is heated in the second phase 2? Grain structure is at its smallest. It will become liquid. It only loses its magnetism. It becomes a stronger magnet. (1) 1.6 Which ONE of the following is a property of pearlite? It is ductile. It is weak. It is malleable. It becomes brittle. (1) opyright reserved
4 Mechanical Technology 4 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 1.7 Identify the type of key shown in FIGURE 1.1. FIGURE 1.1 Square key Gib head key Pratt and Whitney key Woodruff key (1) 1.8 Which milling method is shown in FIGURE 1.2? FIGURE 1.2 own-cut milling Up-cut milling Gang milling Straddle milling (1) 1.9 How are defects shown by applying an X-ray test? efects visible on the weld efects visible on film efects determined by sound efects visible on an oscilloscope screen (1) opyright reserved
5 Mechanical Technology 5 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 1.10 What is the reason for applying a nick-break test on a welded joint? To test the skill of the welder To check the size of the weld To train welders To approve welds and welders to certain standards (1) 1.11 What do you understand by the term stress in materials? Internal force in a material resisting a/an... shearing load. pulling load. compressive load. external load. (1) 1.12 Tensile stress can be defined as an internal force in a material resisting a shearing load. a pulling load a compressive load. any load. (1) 1.13 What do you understand by the term Young's modulus of elasticity? The force value required to produce a unit area in a tensile test specimen The ratio between stress and strain in a metal, provided that the limit of elasticity is not exceeded measurement of the extension or contraction of material due to the load experienced ratio of the deformation because of the application of an external force (1) 1.14 What do you understand by the term viscosity? Resistance of a fluid to... an external load. heat. flow. internal stress. (1) 1.15 SE 20W50 oil is used for engine lubrication. gearbox lubrication. differential lubrication. automatic gearbox lubrication. (1) opyright reserved
6 Mechanical Technology 6 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 1.16 Which ONE of the following statements defines oyle's law? n ideal gas law where,... at constant pressure, the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature at constant volume, the temperature of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure at constant temperature, the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure at constant temperature, the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute pressure (1) 1.17 What is the velocity ratio of the pulley system in FIGURE 1.3 if pulley is the driver? Pulley = river Ø 25 mm Ø 50 mm FIGURE : 1 3 : 1 1 : 2 2 : 1 (1) 1.18 etermine the width of a key if the diameter of the shaft is 60 mm. 15 mm 30 mm 20 mm 6 mm (1) 1.19 What do you understand by the term boost as related to superchargers? The pressure the supercharger makes in the inlet manifold Where the blower is positioned before the carburettor or throttle body The centrifugal force of the air to make compression Where the blower is positioned after the carburettor or throttle body (1) opyright reserved
7 Mechanical Technology 7 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 1.20 Identify the hydro-turbine in FIGURE 1.1. FIGURE 1.1 Francis Pelton Kaplan Turgo (1) [20] QUESTION 2: SFETY 2.1 State FOUR safety measures to be observed while the lathe is in operation after it has been switched on. (4) 2.2 State THREE safety rules to be applied when using the torsion tester. (3) 2.3 State THREE common safety measures to be observed with arc and gas welding. (3) [10] opyright reserved
8 Mechanical Technology 8 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 3: TOOLS N EQUIPMENT 3.1 Mr Jack conducted a compression test on a four-cylinder petrol engine. He found that cylinder two had a lower compression than the other cylinders. State TWO causes for low compression. (2) 3.2 Princess uses the rinell hardness tester to test the hardness of a specimen given to her by the supervisor. FIGURE 3.1 shows the specimen under test. Write down the letters in your NSWER OOK and the correct names of the parts next to the corresponding letters. 3.3 escribe the purpose of the tests below. FIGURE 3.1 (4) Gas analysing test (2) eam-bending test (2) 3.4 Mr Raj did a cylinder leakage test and obtained certain results. State ONE possible result and the fault of the cylinder. (2) [12] opyright reserved
9 Mechanical Technology 9 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 4: MTERILS 4.1 Name ONE property of each of the structures below Ferrite (2) ementite (2) ustenite (2) 4.2 FIGURE 4.1 shows a diagram. nswer the questions that follow E Temperature ,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1,0 1,2 1,4 arbon content % FIGURE What type of diagram is shown in FIGURE 4.1? (2) Write down the letters E in your NSWER OOK and then the correct labels for the diagram next to the corresponding letters. (5) [13] opyright reserved
10 Mechanical Technology 10 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY 5.1 Explain the screw-cutting procedure using the compound-slide method. (7) 5.2 gib head key must be made to fit a 84 mm diameter shaft. alculate the following: The width of the key (2) The thickness of the key (2) The length of the key (2) The thickness of the key at the small end (4) 5.3 State TWO advantages of EH of the following milling operations: Up-cut milling (2) own-cut milling (2) 5.4 gear with 17 teeth has to be machined on a milling machine. alculate the indexing required. (4) 5.5 FIGURE 5.1 shows a milling procedure. nswer the questions that follow. FIGURE Identify the milling process. (2) Write down the letters in your NSWER OOK and the correct names of the parts next to the corresponding letters. (3) [30] opyright reserved
11 Mechanical Technology 11 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 6: JOINING METHOS 6.1 For EH of the following welded joints, identify the defect, state ONE possible cause and ONE preventive action: Gas is trapped in the weld metal. (3) Non-metallic solids are trapped in the weld metal. (3) groove appears in the parent metal, directly along the edges of the weld. (3) 6.2 Name THREE destructive tests exerted onto metals. (3) 6.3 Explain how you will conduct a dye penetration test on a welded joint. (7) 6.4 What does the abbreviation MG/MIGS stand for in terms of welding equipment? (1) 6.5 Name FOUR basic components of a MG/MIGS welding machine. (2) 6.6 State THREE advantages of using a MG/MIGS welding machine. (3) [25] opyright reserved
12 Mechanical Technology 12 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 7: FORES 7.1 efine the concepts below Stress (2) Strain (2) 7.2 Four forces of 9 N, 11 N, 10 N and 8 N as shown in FIGURE 7.1 are acting onto the same point. etermine by means of calculations the equilibrant for the system of forces in FIGURE N 8 N N 10 N FIGURE 7.1 (13) 7.3 compressive force causes internal stress of 16 MPa in a round bar made of an unknown metal. The resistance area of the round bar is 1,26 x 10-3 m 2 and the original length is 80 mm. The force causes the round bar to shorten by 14,4 x 10-3 mm. etermine by means of calculations: The strain in the metal caused by the force (3) The elasticity modulus for this metal (3) opyright reserved
13 Mechanical Technology 13 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 7.4 What does point represent in FIGURE 7.3? E Stress Strain FIGURE 7.3 (1) 7.5 FIGURE 7.4 shows a uniform beam that is supported by two vertical supports, and. uniformly distributed force is exerted on the beam over a distance of 4 m from the left side of the beam. etermine by means of calculations the magnitudes of the reactions in supports and. 150 N/m 400 N 500 N 3 m 1 m 2 m FIGURE 7.4 (6) [30] opyright reserved
14 Mechanical Technology 14 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 8: MINTENNE 8.1 Explain the following properties of oils: Viscosity (1) Pour point (1) 8.2 Mr Sunir owns an old car. He does not keep proper service records of his car. This resulted in his car not being serviced on time, causing the timing chain to become noisy. nswer the questions that follow. E FIGURE Write down the letters E in your NSWER OOK and then the correct labels for the figure next to the corresponding letters. (5) Explain how you would go about replacing the timing chain. (6) 8.3 What does the abbreviation SE stand for regarding oils? (2) [15] opyright reserved
15 Mechanical Technology 15 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS N ONTROL 9.1 FIGURE 9.1 shows a gear drive system. river gear on the shaft of an electric motor has 20 teeth and meshes with gear with 36 teeth on a countershaft. On this countershaft is another driver gear,, with 18 teeth that meshes with gear with 46 teeth on a second countershaft. The second countershaft has a driver gear, E, with 42 teeth that drive gear F with 80 teeth on the output shaft. Electrical motor E ountershaft 42 F 36 ountershaft 18 Output shaft 80 etermine by means of calculations: FIGURE The rotation frequency of the output shaft if the electric motor rotates at r/min (revolutions per minute) (3) The velocity ratio between the input shaft and output shaft (2) 9.2 FIGURE 9.2 shows a belt-drive system. pulley with a diameter of 0,24 m drives a driven pulley with a diameter of 0,36 m. The driver pulley rotates at r/min. T 1 = 200 N and T 2 = 90 N. N N =? r/min N = 0,36 m T 2 N R = r/min R = 0,24 m T 1 FIGURE 9.2 opyright reserved
16 Mechanical Technology 16 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar etermine by means of calculations: The rotation frequency of the driven pulley in r/min (2) The power transmitted (2) The belt speed of the system in metres per second (2) 9.3 hydraulic system is being used to lift a machine part into position. The specifications of the system are diagrammatically represented in FIGURE 9.3. Ø 40 mm 275 N Ø 180 mm Load =? Piston Piston etermine by means of calculations: FIGURE The fluid pressure in the hydraulic system when in equilibrium (3) The load that can be lifted by piston when a force of 275 N is applied to piston (4) 9.4 What do the following abbreviations stand for? S (1) EU (1) 9.5 What is traction control? (2) 9.6 Explain the operation of the central locking system of motor vehicle doors. (3) [25] opyright reserved
17 Mechanical Technology 17 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar QUESTION 10: TURINES 10.1 FIGURE 10.1 shows a water turbine driving a generator. nswer the questions that follow. F E TURINE FIGURE Write down the letters F in your NSWER OOK and then the correct labels for the figure next to the corresponding letters. (6) Explain the operation of the water turbine. (3) 10.2 Many modern motor vehicles make use of superchargers. nswer the questions below State TWO advantages of a supercharger. (2) State ONE disadvantage of a supercharger. (1) 10.3 State TWO advantages of a gas turbine as used in a jet plane. (2) opyright reserved
18 Mechanical Technology 18 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 10.4 large number of trucks make use of turbochargers to enhance their performance. FIGURE 10.2 shows a turbocharger arrangement. Write down the letters F in your NSWER OOK and then the correct labels for the figure next to the corresponding letters. F E FIGURE 10.2 (6) [20] TOTL: 200 opyright reserved
19 Mechanical Technology 1 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 1. ELT RIVES FORMUL SHEET 1.1 πn elt speed = 60 π ( + t ) N 1.2 elt speed = (t = belt thickness) elt mass = area length density ( = thickness width) 1.4 Speed ratio = diameter of diameter of driven pulley driver pulley 1.5 elt length( flat ) = [( + d ) 1,57] + ( 2 centre distance ) 2 π( + d ) ( - d ) 1.6 Open - belt length = + + 2c 2 4c 2 π( + d ) ( + d ) 1.7 rossed-belt length = + + 2c 2 4c 1.8 Power ( P ) = 2 π N T T Ratio of tight side to slack side = T (T1 T2 ) π N Power ( P ) = where T1 = force in the tight side 1.11 T1 Width = permissible tensile force 2. STRESS N STRIN force F 2.1 Stress = or ( σ = ) area 2.2 change in length ( ΔL ) Strain ( ε ) = original length ( L ) stress σ 2.3 Young' s modulus ( E ) = or ( ) strain ε opyright reserved
20 Mechanical Technology 2 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 3. HYRULIS 3.1 Pressure ( P ) = Force ( F ) rea ( ) 3.2 Volume = cross-sectional area stroke length ( l or s ) 3.3 Work done = force distance 4. GER RIVES 4.1 Power ( P ) = 2 π NT Gear ratio = Number of teeth on driven gear Number of teeth on driving gear 4.3 Torque = force radius 4.4 Torque transmitted = gear ratio input torque 4.5 Module ( m ) = Pitch-circle diameter ( P ) Number of teeth ( T ) 4.6 circular Pitch-circle diameter ( P ) = pitch ( P ) number of π teeth ( T ) 4.7 Outside diameter ( O ) = P + 2 module 4.8 ddendum ( a ) = module ( m ) 4.9 edendum ( b ) = 1,157 m or edendum( b ) = 1,25 m 4.10 utting depth ( h ) = 2,157 m or utting depth ( h ) = 2,25 m 4.11 learance ( c ) = 0,157 m or learance ( c ) = 0,25 m 4.12 ircular pitch ( P ) = m π opyright reserved
21 Mechanical Technology 3 E/2014 NS Grade 12 Exemplar 5. PULLEY RIVES 5.1 N 1 1 = N Power ( P ) = 2 π N T Velocity ratio = diameter of diameter of driven pulley driver pulley 5.4 r/min of r/min of driven pulley = driver x diameter of driver diameter of driven pulley pulley 6. KEYWYS diameter of shaft Width of key = 4 diameter of shaft Thickness of key = Length of key = 1,5 x diameter of shaft 6.4 Standard taper for taper key: 1 in 100 or 1 : ININNTI IVIING HE TLE FOR MILLING MHINE Hole circles Side Side Standard change gears 24 x Indexing formula = ( where n = number of n divisions ) opyright reserved
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 12 MEHNIL TEHNOLOGY NOVEMER 2017 MRKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 15 pages and a 4-page formula sheet. Mechanical Technology 2 E/November 2017 INSTRUTIONS
NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 12 MEHNIL TEHNOLOGY NOVEMER 2017 MRKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 15 pages and a 4-page formula sheet. Mechanical Technology 2 E/November 2017 INSTRUTIONS
GRAAD 12 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12
 GR 12 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 12 MEHNIL TEHNOLOGY NOVEMER 2012 MRKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 17 pages and a 5-page formula sheet. opyright reserved Mechanical Technology 2
GR 12 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 12 MEHNIL TEHNOLOGY NOVEMER 2012 MRKS: 200 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 17 pages and a 5-page formula sheet. opyright reserved Mechanical Technology 2
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 11
 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 11 PHYSIL SIENES: PHYSIS (P1) NOVEMER 017 MRKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 15 pages, data sheets and 1 answer sheet. Physical Sciences/P1 E/November 017
NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 11 PHYSIL SIENES: PHYSIS (P1) NOVEMER 017 MRKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours This question paper consists of 15 pages, data sheets and 1 answer sheet. Physical Sciences/P1 E/November 017
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021024) 30 October (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used. This question
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021024) 30 October (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used. This question
University of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 227, 2 nd Semester 2014
 Universit of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 7, nd Semester 04 Semester Test Date: August, 04 Total: 00 Internal eaminer: Duration: hours Mr. Riaan Meeser Instructions:
Universit of Pretoria Department of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering MOW 7, nd Semester 04 Semester Test Date: August, 04 Total: 00 Internal eaminer: Duration: hours Mr. Riaan Meeser Instructions:
Circular motion minutes. 62 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor Page 1 of 22. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks:
 Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
MEMS Project 2 Assignment. Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys
 MEMS 029 Project 2 Assignment Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys Date: February 5, 206 Instructor: Dr. Stephen Ludwick Product Definition Shafts are incredibly important in order
MEMS 029 Project 2 Assignment Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys Date: February 5, 206 Instructor: Dr. Stephen Ludwick Product Definition Shafts are incredibly important in order
ENGINEERING. Unit 3 Principles of mechanical engineering Suite. Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 ENGINEERING Unit 3 Principles of mechanical engineering Y/506/7268 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 3 October 2017 - black lines mark updates ocr.org.uk/engineering
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 ENGINEERING Unit 3 Principles of mechanical engineering Y/506/7268 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 3 October 2017 - black lines mark updates ocr.org.uk/engineering
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
Flexible Mechanical Elements
 lexible Mechanical Elements INTRODUCTION Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar elastic or flexible machine elements are used in conveying systems and in the transmission of power over comparatively long
lexible Mechanical Elements INTRODUCTION Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar elastic or flexible machine elements are used in conveying systems and in the transmission of power over comparatively long
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS. Chapter 6. Torsion
 CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
TIMING PULLEYS & BELTS Timing Belts and Pulleys
 Timing Belts and Pulleys Z e d o1 F U1 v n1 d k1 z 1 a = Centre distance (mm) M B = Acceleration torque (Nm) t B = Acceleration time (s) d = Bore (mm) r = Density (kg/dm 3 ) M = Torque (Nm) n = RPM d k
Timing Belts and Pulleys Z e d o1 F U1 v n1 d k1 z 1 a = Centre distance (mm) M B = Acceleration torque (Nm) t B = Acceleration time (s) d = Bore (mm) r = Density (kg/dm 3 ) M = Torque (Nm) n = RPM d k
R=1/u. May 27, POE FINAL REVIEW.notebook
 POE PART B THURSDAY 6/12 FINAL REVIEW 1. Design Process A problem solving strategy used to develop a solution A) Design Brief written information which contains problem statement, spec s, and constraints.
POE PART B THURSDAY 6/12 FINAL REVIEW 1. Design Process A problem solving strategy used to develop a solution A) Design Brief written information which contains problem statement, spec s, and constraints.
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
Principles Of Engineering. Part A
 Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2007 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Page 1 of 11 Directions: Circle the letter of the response that best
Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2007 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Page 1 of 11 Directions: Circle the letter of the response that best
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
ME Final Exam. PROBLEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) M (x) y. z (neutral axis) beam cross-sec+on. 20 kip ft. 0.2 ft. 10 ft. 0.1 ft.
 ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
Matlab Sheet 2. Arrays
 Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
Matlab Sheet 2 Arrays 1. a. Create the vector x having 50 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10 and ending at 1000. b. Create the vector x having 20 logarithmically spaced values starting at 10
Public Service Commission, West Bengal
 Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
CHAPTER 8 SCREWS, FASTENERS, NONPERMANENT JOINTS
 CHAPTER 8 SCREWS, FASTENERS, NONPERMANENT JOINTS This chapter deals with the design and analysis of nonpermanent fasteners such as bolts, power screws, cap screws, setscrews, eys and pins. 8- Standards
CHAPTER 8 SCREWS, FASTENERS, NONPERMANENT JOINTS This chapter deals with the design and analysis of nonpermanent fasteners such as bolts, power screws, cap screws, setscrews, eys and pins. 8- Standards
Shafts. Fig.(4.1) Dr. Salah Gasim Ahmed YIC 1
 Shafts. Power transmission shafting Continuous mechanical power is usually transmitted along and etween rotating shafts. The transfer etween shafts is accomplished y gears, elts, chains or other similar
Shafts. Power transmission shafting Continuous mechanical power is usually transmitted along and etween rotating shafts. The transfer etween shafts is accomplished y gears, elts, chains or other similar
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
Torsion of shafts with circular symmetry
 orsion of shafts with circular symmetry Introduction Consider a uniform bar which is subject to a torque, eg through the action of two forces F separated by distance d, hence Fd orsion is the resultant
orsion of shafts with circular symmetry Introduction Consider a uniform bar which is subject to a torque, eg through the action of two forces F separated by distance d, hence Fd orsion is the resultant
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
Q.1 a) any six of the following 6x2= 12. i) Define - ( Each term 01 mark)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 3013 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6
 COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
Polyflex JB and Micro-V Belt Drive Selection Procedures
 Polyflex JB and Micro-V Belt Drive Selection Procedures How to Design Polyflex JB and Micro-V Belt Drives Note: The upcoming drive selection and engineering sections provide information for Polyflex JB
Polyflex JB and Micro-V Belt Drive Selection Procedures How to Design Polyflex JB and Micro-V Belt Drives Note: The upcoming drive selection and engineering sections provide information for Polyflex JB
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering 05822/05823/05824/05825 Unit 3: Principles of mechanical engineering Sample Assessment Material Date - Morning/Afternoon Time allowed:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Engineering 05822/05823/05824/05825 Unit 3: Principles of mechanical engineering Sample Assessment Material Date - Morning/Afternoon Time allowed:
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 10
 NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 10 PHYSIL SIENES: PHYSIS (P1) NOVEMER 015 MRKS: 150 TIME: hours This question paper consists of 17 pages and data sheets. Physical Sciences/P1 E/November 015 INSTRUTIONS N INFORMTION
NTIONL SENIOR ERTIFITE GRE 10 PHYSIL SIENES: PHYSIS (P1) NOVEMER 015 MRKS: 150 TIME: hours This question paper consists of 17 pages and data sheets. Physical Sciences/P1 E/November 015 INSTRUTIONS N INFORMTION
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus. Case study
 Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units
 API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units 5 Beam Pump Structure Requirements 5.1 General Requirements for beam pump structures are specified in the following sections. Only loads imposed on the structure
API 11E - Specification for Pumping Units 5 Beam Pump Structure Requirements 5.1 General Requirements for beam pump structures are specified in the following sections. Only loads imposed on the structure
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS).
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS). Lab Director: Coordinating Staff: Mr. Muhammad Farooq (Lecturer) Mr. Liaquat Qureshi (Lab Supervisor)
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS). Lab Director: Coordinating Staff: Mr. Muhammad Farooq (Lecturer) Mr. Liaquat Qureshi (Lab Supervisor)
ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering
 ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Mech. Engineering Objectives Newton s Laws of Motion Free Body Diagram Transmissibility Forces and Moments as vectors Parallel Vectors (addition/subtraction)
ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Mech. Engineering Objectives Newton s Laws of Motion Free Body Diagram Transmissibility Forces and Moments as vectors Parallel Vectors (addition/subtraction)
The problem of transmitting a torque or rotary motion from one plane to another is frequently encountered in machine design.
 CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
 S.3 PHYSICS HOLIDAY WORK Where necessary assume the acceleration due to gravity, g 10ms. 1. 7. 13. 19. 25. 2. 8. 14. 20. 26. 3. 9. 15. 21. 27. 4. 10. 16. 22. 28. 5. 11. 17. 23. 29. 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. SECTION
S.3 PHYSICS HOLIDAY WORK Where necessary assume the acceleration due to gravity, g 10ms. 1. 7. 13. 19. 25. 2. 8. 14. 20. 26. 3. 9. 15. 21. 27. 4. 10. 16. 22. 28. 5. 11. 17. 23. 29. 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. SECTION
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA FURTHER MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 11 - NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - LIFTING MACHINES
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA FURTHER MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 11 - NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - LIFTING MACHINES CONTENT Be able to determine the operating characteristics of lifting
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA FURTHER MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 11 - NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - LIFTING MACHINES CONTENT Be able to determine the operating characteristics of lifting
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s
 D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
PART-A. a. 60 N b. -60 N. c. 30 N d. 120 N. b. How you can get direction of Resultant R when number of forces acting on a particle in plane.
 V.S.. ENGINEERING OLLEGE, KRUR EPRTMENT OF MEHNIL ENGINEERING EMI YER: 2009-2010 (EVEN SEMESTER) ENGINEERING MEHNIS (MEH II SEM) QUESTION NK UNIT I PRT- EM QUESTION NK 1. efine Mechanics 2. What is meant
V.S.. ENGINEERING OLLEGE, KRUR EPRTMENT OF MEHNIL ENGINEERING EMI YER: 2009-2010 (EVEN SEMESTER) ENGINEERING MEHNIS (MEH II SEM) QUESTION NK UNIT I PRT- EM QUESTION NK 1. efine Mechanics 2. What is meant
Mechanical Principles
 Unit 4: Mechanical Principles Unit code: F/601/1450 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learners understanding of an extended range of mechanical principles that underpin the design
Unit 4: Mechanical Principles Unit code: F/601/1450 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learners understanding of an extended range of mechanical principles that underpin the design
Structural Analysis I Chapter 4 - Torsion TORSION
 ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
Sean Carey Tafe No Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test
 Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses
 (Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
(Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
CHAPTER 17 FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HAFTIRMAN
 CHAPTER 17 LEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HATIRMAN lexible Mechanical Elements Belts Roller chains Wire rope lexible shafts lexible Mechanical Elements Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar
CHAPTER 17 LEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HATIRMAN lexible Mechanical Elements Belts Roller chains Wire rope lexible shafts lexible Mechanical Elements Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar
The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties.
 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties. Introduction: Mechanical testing plays an important role
Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties. Introduction: Mechanical testing plays an important role
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
ENT345 Mechanical Components Design
 1) LOAD AND STRESS ANALYSIS i. Principle stress ii. The maximum shear stress iii. The endurance strength of shaft. 1) Problem 3-71 A countershaft carrying two-v belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley
1) LOAD AND STRESS ANALYSIS i. Principle stress ii. The maximum shear stress iii. The endurance strength of shaft. 1) Problem 3-71 A countershaft carrying two-v belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 GE SI CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Torsional Loads on Circular Shafts
GE SI CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Torsional Loads on Circular Shafts
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
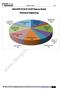 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Shafts Introduction. Shafts 509
 Shafts 509 C H A P T E R 14 Shafts 1. Introduction.. Material Used for Shafts.. Manufacturing of Shafts. 4. Types of Shafts. 5. Standard Sizes of Transmission Shafts. 6. Stresses in Shafts. 7. Maximum
Shafts 509 C H A P T E R 14 Shafts 1. Introduction.. Material Used for Shafts.. Manufacturing of Shafts. 4. Types of Shafts. 5. Standard Sizes of Transmission Shafts. 6. Stresses in Shafts. 7. Maximum
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero.
 When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
4. SHAFTS. A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support
 4. SHAFTS A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support reverse bending (fatigue). Most shafts have circular cross sections, either solid or tubular. The difference between
4. SHAFTS A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support reverse bending (fatigue). Most shafts have circular cross sections, either solid or tubular. The difference between
[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21
![[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21](/thumbs/88/115835122.jpg) [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
[7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians. An Introduction to Solid Mechanics. Is that supposed to bend there?
 High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Overview. Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance
 Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Initial Stress Calculations
 Initial Stress Calculations The following are the initial hand stress calculations conducted during the early stages of the design process. Therefore, some of the material properties as well as dimensions
Initial Stress Calculations The following are the initial hand stress calculations conducted during the early stages of the design process. Therefore, some of the material properties as well as dimensions
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. A grinding wheel is used to sharpen chisels in a school workshop. A chisel is forced against the edge of the grinding wheel so that the tangential force on the wheel is a
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. A grinding wheel is used to sharpen chisels in a school workshop. A chisel is forced against the edge of the grinding wheel so that the tangential force on the wheel is a
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
UNIT D: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS
 1 UNIT D: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 Section 2.0 AN UNDERSTANDING OF MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AND WORK HELPS IN DETERMINING THE EFFICIENCY OF MACHINES. 1 3 MACHINES MAKE WORK EASIER Topic 2.1 4 WHAT WOULD
1 UNIT D: MECHANICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 Section 2.0 AN UNDERSTANDING OF MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AND WORK HELPS IN DETERMINING THE EFFICIENCY OF MACHINES. 1 3 MACHINES MAKE WORK EASIER Topic 2.1 4 WHAT WOULD
Useful Formulas and Calculations
 Drive Design Speed Ratio = rpm (faster) = PD = N rpm (slower) pd n Where: rpm = Revolutions per minute PD = Larger pitch diameter pd = Smaller pitch diameter N = Larger sprocket grooves n = Smaller sprocket
Drive Design Speed Ratio = rpm (faster) = PD = N rpm (slower) pd n Where: rpm = Revolutions per minute PD = Larger pitch diameter pd = Smaller pitch diameter N = Larger sprocket grooves n = Smaller sprocket
Extra Circular Motion Questions
 Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods
 Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010
 NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) PHYSICL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTRY EXMINTION 2010 (10021002) 9 March (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 Suitable mathematical instruments may be used. Non-programmable
NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) PHYSICL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 2 SUPPLEMENTRY EXMINTION 2010 (10021002) 9 March (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 Suitable mathematical instruments may be used. Non-programmable
Principles Of Engineering Final Examination. Part A
 Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2006-07 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Copyright 2006 - Page 1 of 10 Directions: Circle the letter of the
Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2006-07 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Copyright 2006 - Page 1 of 10 Directions: Circle the letter of the
CHAPTER 24 SIMPLE MACHINES
 CHAPTER 24 SIMPLE MACHINES EXERCISE 106, Page 240 1. A simple machine raises a load of 825 N through a distance of 0.3 m. The effort is 250 N and moves through a distance of 3.3 m. Determine: (a) the,
CHAPTER 24 SIMPLE MACHINES EXERCISE 106, Page 240 1. A simple machine raises a load of 825 N through a distance of 0.3 m. The effort is 250 N and moves through a distance of 3.3 m. Determine: (a) the,
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts
 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
AERO 214. Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars
 AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
1 of 7. Law of Sines: Stress = E = G. Deformation due to Temperature: Δ
 NME: ES30 STRENGTH OF MTERILS FINL EXM: FRIDY, MY 1 TH 4PM TO 7PM Closed book. Calculator and writing supplies allowed. Protractor and compass allowed. 180 Minute Time Limit GIVEN FORMULE: Law of Cosines:
NME: ES30 STRENGTH OF MTERILS FINL EXM: FRIDY, MY 1 TH 4PM TO 7PM Closed book. Calculator and writing supplies allowed. Protractor and compass allowed. 180 Minute Time Limit GIVEN FORMULE: Law of Cosines:
 Selection of jack size No. 5 Check again with ball screw jack Type J-B. Yes. Set the hand wheel radius if the screw jack is to be used for manual operation. Yes. Yes. Specification Select temporarily the
Selection of jack size No. 5 Check again with ball screw jack Type J-B. Yes. Set the hand wheel radius if the screw jack is to be used for manual operation. Yes. Yes. Specification Select temporarily the
FME461 Engineering Design II
 FME461 Engineering Design II Dr.Hussein Jama Hussein.jama@uobi.ac.ke Office 414 Lecture: Mon 8am -10am Tutorial Tue 3pm - 5pm 10/1/2013 1 Semester outline Date Week Topics Reference Reading 9 th Sept 1
FME461 Engineering Design II Dr.Hussein Jama Hussein.jama@uobi.ac.ke Office 414 Lecture: Mon 8am -10am Tutorial Tue 3pm - 5pm 10/1/2013 1 Semester outline Date Week Topics Reference Reading 9 th Sept 1
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
Science 7 Unit B: Structures and Forces. Topic 4. Forces, Loads, & Stresses. pp WORKBOOK. Name:
 Science 7 Unit B: Structures and Forces Topic 4 Forces, Loads, & Stresses pp. 305-314 WORKBOOK Name: Every object that provides support is a structure. A structure may be made up of one or more parts,
Science 7 Unit B: Structures and Forces Topic 4 Forces, Loads, & Stresses pp. 305-314 WORKBOOK Name: Every object that provides support is a structure. A structure may be made up of one or more parts,
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL VIA AD SUCCESSORUM
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL VIA AD SUCCESSORUM DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCE GRADE 11 JUNE EXAMINATION PAPER 1 2017 Time: 2 HOURS Total marks: 100 Examiner: Mr R Klein Moderator: Mrs A Fortune INSTRUCTIONS
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL VIA AD SUCCESSORUM DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCE GRADE 11 JUNE EXAMINATION PAPER 1 2017 Time: 2 HOURS Total marks: 100 Examiner: Mr R Klein Moderator: Mrs A Fortune INSTRUCTIONS
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) PHYSICAL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMBER 2009
 NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) PHYSICL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMBER 2009 (10021003) 29 October (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 Non-programmable calculators may be used. Candidates may use drawing instruments.
NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) PHYSICL SCIENCE (First Paper) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMBER 2009 (10021003) 29 October (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 Non-programmable calculators may be used. Candidates may use drawing instruments.
SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS
 SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS Time Allowed:2 Hours Maximum Marks: 300 Attention: 1. Paper consists of Part A (Civil & Structural) Part B (Electrical) and Part C (Mechanical)
SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS Time Allowed:2 Hours Maximum Marks: 300 Attention: 1. Paper consists of Part A (Civil & Structural) Part B (Electrical) and Part C (Mechanical)
Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8
 PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I. Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College. Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY
 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY Two stilt walkers in standing position. All forces acting on each stilt walker balance out; neither
UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY Two stilt walkers in standing position. All forces acting on each stilt walker balance out; neither
