Design and Key Structure Analysis of the Building Tile Making Machine
|
|
|
- Brice Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Abstract Design and Key Structure Analysis of the Building Tile Making Machine Hui Guo, Shijiao Sun Shandong University of Science and Technology, QingDao 66590, China. Based on the existing tile making equipment has a poor degree of mechanical integration and there are some problems with the stability of key structures,taking a new type of building tile making machine as the object of study,the main problems in the design of its structural parameters are determined,the mathematical model is used to analyze the physical characteristics of key structures,on this basis,the stability analysis of each key structure is carried out according to the principle of reliability interference,the analysis proves that the structure of this new type of building tile making machine is reasonable,and simulation experiments were conducted to determine its reliability, the research methods and results can provide theoretical guidance for lean design of key parts of building tile equipment. Keywords The building tile making machine;tile making;physical characteristics;simulation analysis. 1. Introduction The traditional tile process mainly depends on artificial, complicated links, long production cycle, this backward process can not meet the rapid, high-quality industrial and market requirements, followed by the rapid development of tile industry technology and equipment, but the degree of integration is currently in the primary stage of tile equipment is not high, and the key structure in the work the process is easy to interfere with each other for tile effect of efficiency and quality, and even the failure[1-4]. The research on tile making equipment in China mostly focuses on structure and function design, ignoring the influence of key structure on its production reliability, and the existence of short service life. [9-10]. At present, the research and analysis of the tile equipment and its key structure are relatively rare. Therefore, it is of great significance to study and analyze the equipment of the tile making. In view of the above problems, designed a new type of building tile machine structure, with the main function of mud conveying, tile molding, tile delivery of three parts, the main part is conveying mud mud with grasping and conveying belt longitudinal dip into the mud; the key is tile molding molding; key tile conveying is tile crawling and discharging mechanism, structure of figure 1. Fig.1 Structural Diagram of the Building Tile Making Machine From the implementation of the mechanical integration into mud to link, significantly reduces the labor intensity and production cycle, analyzed the main parameters of the structure function design, the stress and the key influencing factors of the key structure using mathematical model is analyzed, 148
2 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: based on the simulation analysis of its key structure using finite element analysis software, and explores the design of stability and rationality, reliability of the production was verified by experiments. Study on tile equipment is the high technology to transform traditional industry model, on behalf of the manufacturing technology of [9] gangwa advanced industry.. The Main Problems to be Determined in the Design of the Structural Parameters of the Building Tile integrated Machine.1 Determination of Main Problems of Slime Slab Grasping Unit The adsorption force sucker is a key to the success or failure of grasping movements, effective absorption area A suction force is equal to the vacuum sucker sucker for p times, to provide sufficient adsorption force the design adopts multi suction side by side adsorption way of mud, according to the actual shape of the design layout as shown in Figure D Fig. Sketch Map of Arrangement of Suction Cups The vacuum p in the suction cup can be determined by the following formula: 8mgh p t 4 mg a nd The lifting height of the design is h=50mm, the lifting time is t=0.3s, the suction disc diameter is D=40mm, the quality of the billet is m=3kg, the number of sucker is n=1, the safety rate a=5 is taken into the upper form: then, the magnitude of the adsorption force is determined.. Determination of Main Problems in the Conveying Unit of Mud Billet The transportation of billet is carried out by longitudinal feeding of the billet inclined angle, the inclination angle is 16 degrees ~18 degrees, the lifting height is 90mm, the belt speed is 0~.7m/s, and the length of the billet is 370mm. Considering the overload and other reasons, the belt width 480mm is designed, the 55mm width is reserved on both sides, the diameter of the belt roller is 60mm, and the length is 500mm. In order to accurately enter the platform after throwing the belt, it is necessary to analyze the throwing speed V of the billet. The influencing factors include throwing speed and horizontal angle a, gravity acceleration g and movement time t, and establish the motion model shown in Figure 3. Fig.3 The Model of the Mud Slab When the dip angle is a and the drop point is A point, V needs to be satisfied: 1 v t sin a gt v t cos a When the dip angle is a and the drop point is B point, V needs to be satisfied: 1 v t sin a gt v t cos a 0.39
3 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Determination of Main Problems of Tile Forming Unit The speed increasing cylinder is the driving element of compression molding. The main design size is set up: the diameter of the piston rod increasing chamber is d0=45mm, the inner diameter of the cylinder is D=160mm, the diameter of the piston rod is d=150mm, and the oil cylinder stroke is S=400mm. The key to the forming of the tile is that the lifting force of the cylinder should meet the load requirement, and the calculation formula of the lifting force when the cylinder rises is as follows: F P ( D d / 4 t ) The range of the working pressure of P is 15~0MPa, the range was Ft lifting force is 36.5~48kN, a known load of the ascension is about 1.5kN, much more than the lifting load, meet the load requirements..4 Determination of Main Problems of tile Conveying Unit The key to tile transportation is the body grasping mechanism. The layout and parameter setting of suction cups are the same as those of the billet grasping mechanism. The difference is that the tile billet is grabbed by adjustable double row suction cups to grab the tile blank, and the double row suction cups grabbed by the billet are fixed. 3. Analysis of the Physical Characteristics of Key Structures 3.1 Analysis of Absorptive Capacity of Sucker In the process of sucking the slime, the reset spring is always in the compressed state, and the slime grasping mechanism is reset under the push and pull of the compression spring. The reduction process is a reciprocating linear motion, and the acceleration is larger. The mud billet may fall off from the friction force of the sucker because of the speed change. The reset model is shown in Figure 4. Fig.4 esetting Model of the Gripping Mechanism Speed change is the key factor [10] of slime reliability. Therefore, it is necessary to study the frictional force requirement of reciprocating linear motion to calculate the maximum acceleration Amax of clay movement. The calculation formula is as follows: a max nd p 1 4m In the formula, M is the quality of the mud billet; it is the static friction coefficient of the sucker, 0.61 of the mu; the n is the number of the sucker; the D1 is the diameter of the sucker, and the P is the vacuum degree in the suction cup. 3. The Force Analysis of the Scratch Arm The grabbing arm is the key structural part of the billet conveying and tile conveying unit. For the cantilever structure, its lateral spacing is L, which is affected by the whole grasping mechanism's self weight and the conveying cylinder pressure of the billet. The force analysis diagram is shown in Figure 5. The basic mechanical model is established, and the rotation function in the vertical direction is expressed as X. The maximum displacement function in the vertical direction of the grabbing arm arm beam is U (x). Then the expression of the shear lag warping displacement function U (x) of the grabbing arm arm beam is: ( b y) u( x) L( y, z) U( x) ( M s0 zs( y)) U( x) ( y) 1 s, 0 y b. b 1 150
4 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: In the formula, x, y, Z coordinates for the grasping arm beam tile transverse and longitudinal and vertical direction; L (y, z) as the shape function of warping function; Ms0 bending moment, decided by the formula A da 0, and its value is:ms0= (4h1tb)/(3A); to grasp the tile arm width; arm sx bending radius is the radius of curvature; P, -b ρ z qz M 0 M 1 y L G 1 x Fig.5 Stress Analysis Diagram of the Tile-Grabbing Arm Considering the effect of twist angle deformation and shear lag effect on [11-1], the size of positive stress produced by the brachial arm beam structure is as follows: The size of shear stress is: u x) sx E E ( M x ( ' S 0 ZS ( y)) U ( x u( x) d ( y) s sx G G zu ( x) y dy ( b y) ( y) 1, 0 y b s ; A is the area of the cross section of the brachial arm, and the young's b modulus is E, and the G is the shear modulus. The bending moment of the total vertical direction is: M y EI The corresponding positive stress size is as follows: ' ' ( ) EI U y sy ' za [ Ez( ) E( M s0 ) ' z( y) U ] [( / ) z] da, I z M z y da sy ( / ) ( ( )). A s0 s I y 3.3 Natural Frequency Analysis of Mould Press Molded frame is the key structure of tile molding, pump motor and the frame body is fixedly connected with the rigid molding, easy to cause the motor vibration molded frame frame structure to avoid resonance, resonance caused by the deformation of the frame body natural frequency analysis[. Molded frame body by vibration influence is the largest part of the top three side position, for the calculation of the resonance frequency of the frame body, the frame body can be molded as a simplified frequency frequency calculation sheet model shown in Figure 6, to establish the neutral surface sheet as shown in the coordinate system, C, D, H said is in the process of vibration plate deformation in X, y, z direction. z h d c a h o x b Fig. 6 Model Diagram of the Sheet In the process of vibration, the displacement occurs in the direction of X. Based on the dynamic balance, the differential equation of free vibration on the X direction of thin plate is established. y 151
5 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: w w w w D( ) h( ) x x y y t The form of general solution is set by separating the variable: w( x, y, t) W( x, y) T( t) mx nx W ( x, y ) Amn sin sin m1 n1 a b For a thin plate with fixed constraints on the edge, the maximum potential energy produced by the deformation is as follows: The maximum kinetic energy is: U D ( w ) max w Kmax mw dxdy The whole vibration process establishes the following equilibrium equations according to the law of conservation of energy: Umax Kmax, Thus the value of the natural frequency W of the plate in the vibration process is solved. dxdy 4. Simulation Analysis of Key Structure eliability 4.1 Simulation Analysis of eset Acceleration For the verification process will not change speed of mud reduction resulted in the decline of the reliability of sorption problem, using AMESim on the mud reset mechanism simulation analysis, according to the actual condition of variable settings, set the mass 8.5Kg, viscous friction coefficient of N/ (m/s), 0.N 0.17N, static friction, sliding friction coefficient of elastic spring reset, 650N/m, initial compression the amount of 40mm, 10-5s, 10s simulation, simulation time. The simulation results are shown in Figure 7. From the graph, we can see that the maximum velocity of mud motion is 0.34m/s, the maximum acceleration is 1.04m/s, and the speed and acceleration are decreasing alternation, which satisfies the simple harmonic motion rule of spring under sliding friction. The results show that the maximum acceleration of the mud billet is less than the maximum allowable acceleration of the reposition of the mud billet. Therefore, the adsorption reliability of the mud billet meets the required requirements. Fig.7 The Acceleration Curve of the eset Velocity 4. Structural Mechanics Simulation Analysis of Scratch Arm Catch the tile arm as the cantilever beam structure, the weight in the grab mechanism and tile billet conveying cylinder pressure will produce under the influence of local stress and strain, so it is necessary to grasp the tile arm structure static analysis to ensure its reliability, in order to avoid catching tile arm grab and other institutions contact interference, should also guarantee the catch w arm end deformation is less than 8mm. The analysis results are shown in figure 8. 15
6 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: (a)total Deformation Cloud Diagram of the Tile-Grabbing Arm (b)equivalent Stress Cloud Diagram of the the Tile-Grabbing Arm Fig. 8 Static Analysis esults of the the Tile-Grabbing Arm From the equivalent stress distribution results, the maximum stress appears in the fixed constraint and cantilever junction value is MPa, far less than the material yield strength Q35, meet the design requirements of strength; from the total deformation nephogram results, the maximum deformation position in the distal end of the cantilever, the maximum deformation is mm, less than the allowable deformation 8mm, so grab a structure that does not produce interference. Through the analysis results, it is known that the design reliability of the grab arm meets the work requirements. 4.3 Model Simulation Analysis of Mould Pressure Frame The results of the four - order modal vibration analysis of the moulded frame are shown in Figure 9. (a)one Order Vibration Pattern Nephogram (b) Two Order Vibration Pattern Nephogram 153
7 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: (c) Three Order Vibration Pattern Nephogram (d) Tour Order Vibration Pattern Nephogram Fig.9 Modal Analysis esults of the the Mould Frame The analysis results from the analysis of images: (1) the maximum deformation of the frame in three modes, the maximum total deformation is less than allowable deformation 10mm institutions; () the frame body deformation is mainly modal cylinder mounted bracket portion in the upper part of the frame body, the deformation of the molding mode the accuracy of impact; (3) a frame frequency is 67.77Hz, the excitation frequency of pump motor is 15~5Hz, so the motor vibration will not cause strong resonance molded frame. In a comprehensive analysis, the design reliability of the mould press meets the requirements, and the influence on the precision of molding is in the expected range. 4.4 Fatigue Analysis of Cylinder Cylinder Cylinder cylinders are subjected to cyclic fluctuating load of oil pressure during operation, and work continuously for 4 hours. In order to ensure effective and stable molding work, it is necessary to analyze the fatigue characteristics of cylinder's cyclic load. Figure.10 Life (Lifetime) Nephogram Fig. 10 is the fatigue life chart. The life equivalent cloud chart obtained from the fatigue analysis indicates the working cycle times of the fatigue failure to the cylinder under the action of cylinder pressure. The fatigue life of the cylinder is minimum 107 times, which exceeds the design life value and meets the design requirements. 154
8 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: Fig.11 Damage Nephogram Figure 11 is the structure cloud of fatigue damage. Fatigue damage cloud contour line refers to the ratio between design life and service life. From the graph, we can see that the maximum ratio of fatigue damage is 0.864, that is, where fatigue strength is the weakest, and its design life is still less than that of usable life, which indicates that there will be no fatigue failure of cylinder or crack during design life range. 5. Experimental Analysis To catch tile experiments by the arm, shown in Figure 1, up to 400 times the confidence interval in number (two black curve) became smaller and the fluctuation is slow, this means that the number of simulations can fully reflect the characteristics of the subjects, the experimental data to summarize the actual building reliability of tile development pilot period grab after work. The maximum values of deformation appear before the 100 times of simulation, and then tend to be gentle. The maximum deformation is not 4mm, and the final stability is 1.5mm, which is smaller than the allowable form variable 8mm. This indicates that there will be no interference when the stress and variable shape are too large in the long term working condition of the grabbing arm, which will affect the normal operation of the whole machine, and it has high reliability. Fig. 1 Simulation Experimental Data Graph of the Tile-Grabbing Arm Figure 13 is the oil cylinder fatigue sensitivity characteristic curve. According to the data in the chart, when the load change range is less than 135%, the service life meets the design requirement of 8.64 *106 times. This shows that the oil cylinder will not have too large deformation, meet the requirements of long-term work and have high reliability. Fig.13 Fatigue Sensitivity Curve 155
9 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No ISSN: In the tile production line workshop, the four workstations are placed in the building tile machine, and the blank pieces are processed and transported. Building clay all-in-one under the actual working condition of continuous work week, set up the confidence level of 0.95 for reliability test, data statistics show that: the strength reliability of 0.94, the stiffness reliability is 0.96, it shows that the clay machine has high reliability. 6. Conclusion The design of a new type of building tile machine has greatly improved the mechanical integration level of the tile equipment, reduced the manual operation strength, and realized the breakthrough and improvement of the machine making equipment. The main parameters in the design are analyzed, and the structure design is completed. Analysis and study of its key structure stability, in combination with mud reset dynamics analysis, grasp the mechanics model of the arm and moulded body vibration frequency characteristic, the simulation of mud slab reduction and movement characteristics, verify chuck can reliably, sucking mud slab; The structural mechanics analysis of the grasping arm was completed, and the deformation amount of the grasping arm was verified. The modal analysis of the prestress is carried out to verify that there is no strong resonance with the motor. Then the fatigue strength analysis of cylinder cylinder under pulsation load is carried out to verify that the life of cylinder cylinder can meet the design requirements, and the fatigue failure will not occur. Through simulation experiment, the analysis of experimental data shows all the key structure and the whole machine has high reliability, the new construction system all-in-one structure stability can be guaranteed and the structure optimization design needs further research and analysis. eferences [1] W. Shihe:Found and analysis on the development situation of China's construction industry in 016.Construction daily of china, (008). [] S. J. Xun:Adapting to the new normal is the Keynote of the 13th five-year plan.china's National Conditions and Strength.015,6(4):0-. [3] L.D.Cong,X.Y.Ming:Development status and Prospect of roof tile in China.New building materials.005,(11):3-7. [4] Kayacan E,Ulutas B,Kaynak: Grey system theory based models in time series prediction.espert Systems with Applications,010, 37(): [5] Z..Chuan:eview and Prospect of brick and tile machinery in China.Brick & Tile World.006,9(08):8-11. [6] Kayacan E, Ulutas B, Kaynak O:Grey system theory based models in time series prediction[j].espert Systems with Applications, 010, 37(): [7] S.H.Wen:Development trend of brick and tile machinery equipment in China[J]. Brick & Tile World.011,10(0): [8] Z.Haien:Three bottlenecks of brick and tile equipment development[j].brick & Tile World.016,5(08): [9] Z. Gang: Non-&D Innovation Activities and Performance:An Empirical Study Based on SMEs in Zhejiang Province[].Zhejiang:Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Global Manufacturing and China(GMC'13). 013: 9. [10] Z.L.Gan,S.J.Zheng:Dynamic Analysis on PT1300 Type Palletizing obot Containing Closed-loop[J].Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology.013,3(0):
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
1618. Dynamic characteristics analysis and optimization for lateral plates of the vibration screen
 1618. Dynamic characteristics analysis and optimization for lateral plates of the vibration screen Ning Zhou Key Laboratory of Digital Medical Engineering of Hebei Province, College of Electronic and Information
1618. Dynamic characteristics analysis and optimization for lateral plates of the vibration screen Ning Zhou Key Laboratory of Digital Medical Engineering of Hebei Province, College of Electronic and Information
C7047. PART A Answer all questions, each carries 5 marks.
 7047 Reg No.: Total Pages: 3 Name: Max. Marks: 100 PJ DUL KLM TEHNOLOGIL UNIVERSITY FIRST SEMESTER.TEH DEGREE EXMINTION, DEEMER 2017 ourse ode: E100 ourse Name: ENGINEERING MEHNIS PRT nswer all questions,
7047 Reg No.: Total Pages: 3 Name: Max. Marks: 100 PJ DUL KLM TEHNOLOGIL UNIVERSITY FIRST SEMESTER.TEH DEGREE EXMINTION, DEEMER 2017 ourse ode: E100 ourse Name: ENGINEERING MEHNIS PRT nswer all questions,
UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS)
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
4. SHAFTS. A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support
 4. SHAFTS A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support reverse bending (fatigue). Most shafts have circular cross sections, either solid or tubular. The difference between
4. SHAFTS A shaft is an element used to transmit power and torque, and it can support reverse bending (fatigue). Most shafts have circular cross sections, either solid or tubular. The difference between
two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS
 APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
KNIFE EDGE FLAT ROLLER
 EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Calculation and analysis of internal force of piles excavation supporting. based on differential equation. Wei Wang
 International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 016) Calculation and analysis of internal force of piles excavation supporting based on differential equation Wei Wang School of Prospecting
International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 016) Calculation and analysis of internal force of piles excavation supporting based on differential equation Wei Wang School of Prospecting
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian
 Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 22, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
ME Final Exam. PROBLEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) M (x) y. z (neutral axis) beam cross-sec+on. 20 kip ft. 0.2 ft. 10 ft. 0.1 ft.
 ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral. mechanism under the vibration environment
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements
 A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
Design and analysis of a pneumatic test system for shock response spectrum
 Design and analysis of a pneumatic test system for shock response spectrum Yan Tingfei 1, Xiang Shuhong 2, Shen Zhiqiang 3, Zhang Jungang 4, Liu Mo 5 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Beijing Institute of Spacecraft Environment
Design and analysis of a pneumatic test system for shock response spectrum Yan Tingfei 1, Xiang Shuhong 2, Shen Zhiqiang 3, Zhang Jungang 4, Liu Mo 5 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Beijing Institute of Spacecraft Environment
DESIGN AND APPLICATION
 III. 3.1 INTRODUCTION. From the foregoing sections on contact theory and material properties we can make a list of what properties an ideal contact material would possess. (1) High electrical conductivity
III. 3.1 INTRODUCTION. From the foregoing sections on contact theory and material properties we can make a list of what properties an ideal contact material would possess. (1) High electrical conductivity
Simulation of process of hot pilgrim rolling
 Simulation of process of hot pilgrim rolling YURY B. CHECHULIN, Doctor of Engineering Science, Professor EVGENY U. RASKATOV, Doctor of Engineering Science, Professor YURY A. POPOV, post-graduate student
Simulation of process of hot pilgrim rolling YURY B. CHECHULIN, Doctor of Engineering Science, Professor EVGENY U. RASKATOV, Doctor of Engineering Science, Professor YURY A. POPOV, post-graduate student
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS).
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS). Lab Director: Coordinating Staff: Mr. Muhammad Farooq (Lecturer) Mr. Liaquat Qureshi (Lab Supervisor)
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENIGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY LAHORE (KSK CAMPUS). Lab Director: Coordinating Staff: Mr. Muhammad Farooq (Lecturer) Mr. Liaquat Qureshi (Lab Supervisor)
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
Dynamic behavior of turbine foundation considering full interaction among facility, structure and soil
 Dynamic behavior of turbine foundation considering full interaction among facility, structure and soil Fang Ming Scholl of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, China Wang Tao Institute of
Dynamic behavior of turbine foundation considering full interaction among facility, structure and soil Fang Ming Scholl of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, China Wang Tao Institute of
SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS
 CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil
CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame
 Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame Ketan Gajanan Nalawade 1, Ashish Sabu 2, Baskar P 3 School of Mechanical and building science, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamil
Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame Ketan Gajanan Nalawade 1, Ashish Sabu 2, Baskar P 3 School of Mechanical and building science, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamil
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
142. Determination of reduced mass and stiffness of flexural vibrating cantilever beam
 142. Determination of reduced mass and stiffness of flexural vibrating cantilever beam Tamerlan Omarov 1, Kuralay Tulegenova 2, Yerulan Bekenov 3, Gulnara Abdraimova 4, Algazy Zhauyt 5, Muslimzhan Ibadullayev
142. Determination of reduced mass and stiffness of flexural vibrating cantilever beam Tamerlan Omarov 1, Kuralay Tulegenova 2, Yerulan Bekenov 3, Gulnara Abdraimova 4, Algazy Zhauyt 5, Muslimzhan Ibadullayev
The basic dynamic load rating C is a statistical number and it is based on 90% of the bearings surviving 50 km of travel carrying the full load.
 Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Technical data Load Rating & Life Under normal conditions, the linear rail system can be damaged by metal fatigue as the result of repeated stress. The repeated stress causes flaking of the raceways and
Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a, PeiWei Ni1,b, Ye Zhang1,c and MingXiao Dong1,2,d
 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2016) Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a,
2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2016) Investigation into the Self-loosening Trend of Bolt Joints on the Tower Crane ShengChun Wang1,a,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Physics *P44923A0128* Pearson Edexcel P44923A. Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go. International Advanced Level
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Physics Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go Centre Number Candidate Number Tuesday 19 May 2015 Morning Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Physics Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go Centre Number Candidate Number Tuesday 19 May 2015 Morning Time:
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability:
 UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
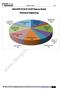 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee
 Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
PHYA2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Mechanics, Materials and Waves. (JUN11PHYA201) WMP/Jun11/PHYA2 PMT
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics A Unit 2 For this paper you must have: l a pencil and a ruler l a calculator l a Data
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics A Unit 2 For this paper you must have: l a pencil and a ruler l a calculator l a Data
Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production
 Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production Ganush V. I. National metallurgical academe of Ukraine Ostroverhov N. P., Sultan A. V., Dzichkovky
Investigation of basic elements loading and tension of heavy hydraulic presses for metallurgical production Ganush V. I. National metallurgical academe of Ukraine Ostroverhov N. P., Sultan A. V., Dzichkovky
Sean Carey Tafe No Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test
 Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
Chapter 13. Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 13 Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law F s = - k x F s is the spring force k is the spring constant It is a measure of the stiffness of the spring A large k indicates a stiff spring and a small
Chapter 13 Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law F s = - k x F s is the spring force k is the spring constant It is a measure of the stiffness of the spring A large k indicates a stiff spring and a small
MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP 1) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter (1)
 sr. no. MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP ) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter VSAQ () SA-I (2) SA-II (3) Value based (4) LA(5) Total 70 Physical world and measurement 3 2 Kinematics 2 3,3 5 3 Laws of motion
sr. no. MODEL PAPER CLASS XI PHYSICS (GROUP ) BLUEPRINT Name of chapter VSAQ () SA-I (2) SA-II (3) Value based (4) LA(5) Total 70 Physical world and measurement 3 2 Kinematics 2 3,3 5 3 Laws of motion
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump
 An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
Design of Beams (Unit - 8)
 Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Structure Design and Modal Analysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives
 Structure Design and Modal nalysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives Yiqiang Jiang, Li Hou, Yunxia You, Jingyu Zhang School of Manufacturing Science and Engineering Sichuan University Chengdu, Sichuan,China
Structure Design and Modal nalysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives Yiqiang Jiang, Li Hou, Yunxia You, Jingyu Zhang School of Manufacturing Science and Engineering Sichuan University Chengdu, Sichuan,China
(Refer Slide Time: 1: 19)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition
 Computers in Railways XIII 745 CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition L. Li & Y. Luo Railway and Urban Mass Transit Research Institute, Tongji University, China
Computers in Railways XIII 745 CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition L. Li & Y. Luo Railway and Urban Mass Transit Research Institute, Tongji University, China
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
Strength Study of Spiral Flexure Spring of Stirling Cryocooler
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
PSD Analysis and Optimization of 2500hp Shale Gas Fracturing Truck Chassis Frame
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 533-538 533 Open Access PSD Analysis and Optimization of 2500hp Shale Gas Fracturing Truck Chassis
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 533-538 533 Open Access PSD Analysis and Optimization of 2500hp Shale Gas Fracturing Truck Chassis
Dept of ECE, SCMS Cochin
 B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
Motion Analysis and Optimization Design of Back Support Mechanism Based on Pose Adjustment
 American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 2018; 3(3): 47-53 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajetm doi: 10.11648/j.ajetm.20180303.12 ISSN: 2575-1948 (Print); ISSN: 2575-1441 (Online)
American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 2018; 3(3): 47-53 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajetm doi: 10.11648/j.ajetm.20180303.12 ISSN: 2575-1948 (Print); ISSN: 2575-1441 (Online)
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE
 TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis
 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1
 ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
93. Study on the vibration characteristics of structural of hydrocyclone based on fluid structure interaction
 93. Study on the vibration characteristics of structural of hydrocyclone based on fluid structure interaction Sen Li 1, Chunhong Dong 2, Zunce Wang 3, Yan Xu 4, Yuejuan Yan 5, Daoli Zhai 6 College of Mechanical
93. Study on the vibration characteristics of structural of hydrocyclone based on fluid structure interaction Sen Li 1, Chunhong Dong 2, Zunce Wang 3, Yan Xu 4, Yuejuan Yan 5, Daoli Zhai 6 College of Mechanical
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Mechanics of Materials
 Mechanics of Materials Notation: a = acceleration = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) SD = allowable stress design d = diameter of a hole = calculus symbol for differentiation e = change
Mechanics of Materials Notation: a = acceleration = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) SD = allowable stress design d = diameter of a hole = calculus symbol for differentiation e = change
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Fatigue Crack Analysis on the Bracket of Sanding Nozzle of CRH5 EMU Bogie
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 577-583 Published Online May 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.35071 Fatigue Crack Analysis on the
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2015, 3, 577-583 Published Online May 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.35071 Fatigue Crack Analysis on the
Module 3 : Equilibrium of rods and plates Lecture 15 : Torsion of rods. The Lecture Contains: Torsion of Rods. Torsional Energy
 The Lecture Contains: Torsion of Rods Torsional Energy This lecture is adopted from the following book 1. Theory of Elasticity, 3 rd edition by Landau and Lifshitz. Course of Theoretical Physics, vol-7
The Lecture Contains: Torsion of Rods Torsional Energy This lecture is adopted from the following book 1. Theory of Elasticity, 3 rd edition by Landau and Lifshitz. Course of Theoretical Physics, vol-7
MODELING INITIAL VELOCITY PROFILES FOR CONTINUOUS FREE-VIBRATING BEAMS USING DISTRIBUTED IMPULSE LOADING
 VOL. 1, NO. 9, MAY 17 ISSN 1819-668 6-17 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. MODELING INITIAL VELOCITY PROFILES FOR CONTINUOUS FREE-VIBRATING BEAMS USING DISTRIBUTED IMPULSE
VOL. 1, NO. 9, MAY 17 ISSN 1819-668 6-17 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. MODELING INITIAL VELOCITY PROFILES FOR CONTINUOUS FREE-VIBRATING BEAMS USING DISTRIBUTED IMPULSE
Equilibrium of a Particle
 ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM
 8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM Jungong Ma, Xiaoye Qi, Juan Chen BeiHang University,Beijing,China jgma@buaa.edu.cn;qixiaoye@buaa.edu.cn;sunchenjuan@hotmail.com
8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM Jungong Ma, Xiaoye Qi, Juan Chen BeiHang University,Beijing,China jgma@buaa.edu.cn;qixiaoye@buaa.edu.cn;sunchenjuan@hotmail.com
Problem d d d B C E D. 0.8d. Additional lecturebook examples 29 ME 323
 Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
Problem 9.1 Two beam segments, AC and CD, are connected together at C by a frictionless pin. Segment CD is cantilevered from a rigid support at D, and segment AC has a roller support at A. a) Determine
5. STRESS CONCENTRATIONS. and strains in shafts apply only to solid and hollow circular shafts while they are in the
 5. STRESS CONCENTRATIONS So far in this thesis, most of the formulas we have seen to calculate the stresses and strains in shafts apply only to solid and hollow circular shafts while they are in the elastic
5. STRESS CONCENTRATIONS So far in this thesis, most of the formulas we have seen to calculate the stresses and strains in shafts apply only to solid and hollow circular shafts while they are in the elastic
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1
 Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Linear graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
3. BEAMS: STRAIN, STRESS, DEFLECTIONS
 3. BEAMS: STRAIN, STRESS, DEFLECTIONS The beam, or flexural member, is frequently encountered in structures and machines, and its elementary stress analysis constitutes one of the more interesting facets
3. BEAMS: STRAIN, STRESS, DEFLECTIONS The beam, or flexural member, is frequently encountered in structures and machines, and its elementary stress analysis constitutes one of the more interesting facets
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever
 Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS
 61 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS 4.1 INTRODUCTION The analysis of cantilever beams of small dimensions taking into the effect of fringing fields is studied and
61 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS 4.1 INTRODUCTION The analysis of cantilever beams of small dimensions taking into the effect of fringing fields is studied and
Analysis of Shear Lag Effect of Box Beam under Dead Load
 Analysis of Shear Lag Effect of Box Beam under Dead Load Qi Wang 1, a, Hongsheng Qiu 2, b 1 School of transportation, Wuhan University of Technology, 430063, Wuhan Hubei China 2 School of transportation,
Analysis of Shear Lag Effect of Box Beam under Dead Load Qi Wang 1, a, Hongsheng Qiu 2, b 1 School of transportation, Wuhan University of Technology, 430063, Wuhan Hubei China 2 School of transportation,
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity
 2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
1 Static Plastic Behaviour of Beams
 1 Static Plastic Behaviour of Beams 1.1 Introduction Many ductile materials which are used in engineering practice have a considerable reserve capacity beyond the initial yield condition. The uniaxial
1 Static Plastic Behaviour of Beams 1.1 Introduction Many ductile materials which are used in engineering practice have a considerable reserve capacity beyond the initial yield condition. The uniaxial
1859. Forced transverse vibration analysis of a Rayleigh double-beam system with a Pasternak middle layer subjected to compressive axial load
 1859. Forced transverse vibration analysis of a Rayleigh double-beam system with a Pasternak middle layer subjected to compressive axial load Nader Mohammadi 1, Mehrdad Nasirshoaibi 2 Department of Mechanical
1859. Forced transverse vibration analysis of a Rayleigh double-beam system with a Pasternak middle layer subjected to compressive axial load Nader Mohammadi 1, Mehrdad Nasirshoaibi 2 Department of Mechanical
Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design
 Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design Elmer E. Marx, Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities Michael Keever, California Department
Seismic Pushover Analysis Using AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design Elmer E. Marx, Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities Michael Keever, California Department
