The Assessment of Sediment Quality in Northport Based on the Index Analysis Approach
|
|
|
- Alban Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
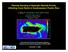
1 The Assessment of Sediment Quality in Northport Based on the Index Analysis Approach Belin.Tavakoly Sany*, Aishah. Salleh, Abdul Halim.Sulaiman, and Ghazaleh. Monazami Tehrani Abstract The coastal sediments of North Port of Malaysia was monitored from Nov to Oct to assess spatial distribution of heavy metals As, Cu, Cd, Cr, Hg, Ni, Zn and Pb. Sediment samples were collected from 6 stations.the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and the enrichment factor (EF) were considered to assess sediment contamination degree based on background values. The results show that the concentrations of some metals, such as As, Cd and Hg were significantly higher than the background values. This is considered a critical environmental issue for this region. Spatial distribution maps of heavy metals would aid in the identification of pollution sources and vulnerable Stations. Keywords Heavy metals, Sediment Quality, North Port, Malaysia I.INTRODUCTION ARINE sediments are sensitive media for monitoring Mcontaminants in aquatic ecosystems The bottom sediments are a reservoir for heavy metals and therefore deserve special Consideration in the planning and design of aquatic pollution research studies [1, 2]. According to Caeiro et al [2] the concentration of metal contaminants can be classified into three types which are (i) contamination indiceswhich Compare the contaminants with the clean or polluted stations measured elsewhere; (ii) Background enrichments indices- which compare the results for the contaminants with the baseline or background levels and (iii) ecological risk indices- which compare the results for the contaminants with Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQG). *Seyedeh Belin. Tavakoly Sany is PhD student in the Institute of Biological Sciences University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia (corresponding author to provide phone: ; (belintavakoli332@gmail.com). Professor Datin Dr Aishah Salleh is with the Institute of biological sciences University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur,Malaysia;( aishahsalleh@um.edu.my). Professor Abdul Halim Sulaiman is with the Institute of biological sciences University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia ( halim@yahoo.com). Ghazaleh. Monazami Tehrani is PhD student in the Institute of Biological Sciences University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia ( ghazaltehrani@yahoo.com). These indexes are providing comprehensive assessment of environmental quality, planning and management for local and regional researchers [3]. Heavy metal contamination in sediment is a critical factor for evaluating potential environment effects because of the associated bio-toxicity, high environmental stability and high occurrence of bioaccumulation in the food chain[3, 4]. More studies indicated that in the aquatic environment, the minor quantities of some metals such as: copper, zinc, iron, manganese and nickel are essential for biological systems to function, but their excessive concentration can be toxic to living organisms. Other metals such as cadmium, mercury, arsenic and lead are non-essential, and therefore have toxic effects on living organisms [5]. Northport is strategically located midway on the West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia overlooking the world's busiest waterway, the Straits of Malacca. It is in the Free Commercial Zone of Port Klang, in the state of Selangor. It is further complemented by Malaysia's premier business township, the Klang Valley and is only 60 kilometers away from the federal capital, Kuala Lumpur. The main objectives of this research are; (1) to provide basic data of heavy metals concentration and compare these data with geochemical background value to assess impacts of the industrial and economic activities in the Northport (2) To use different types of indices to evaluate the sediment quality based on the heavy metal contamination. With regard to the importance of the Northport as an international shipping route, and ecological habitat, it is necessary to evaluate environmental properties in order to control pollution occurrence and protect living organisms. II. MATERIAL AND METHODS A. Study area From November 2009 to October 2010, sediment samples were collected two times in year, from 6 stations where located along transects parallel to the berths line with three different distances (Fig 1). Sediments were collected in triplicate from surface of sediments by Petersen Grab sampler. Surface sediments were chosen for this study as this layer controls the exchange of metals between sediment and water. 99
2 in sediment samples that is divided by the ratio of metal background to the normalising elements [13]. Fig.1 Location of stations in the North Port B. Sampling and Experimental analysis Sediment grain size was determined using a multiwavelength particle size analyzer (model LS ), and results were divided into sand ( >64 μm), silt (2 μm <size < 64 μm) and clay (<2 μm) fractions for the determination of heavy metals in the contaminated soil [6, 7]. Total organic carbon (TOC) was measured in surface sediment by using a Perkin- Elmer 2400 carbon hydrogen nitrogen sulfur (CHNS) elemental analyzer at a 950 C combustion temperature [6, 7]. Dried samples were sieved through a 2mm sieve, after that About 2g of the sediment to be used for metal analysis was treated with 2ml of48% hydrofluoric acid (HF) and 2ml of 65% nitric acid3 (HNO ), heated to dryness, and allowed to cool. 0.5g of 99.99%on boric acid was added to the cooled solution and the resulting suspensions was centrifuged. The decanted solution from the centrifugal operation was filtered using Whatman No. 40 filter-paper and the volume made up to 50 ml with demonized water for measurement of total concentration of heavy metals. Plasma mass spectrometry (ICP/MS) was used to analyze the following suite of metals: preparation procedure described above for the metal analyses is the same as the one adopted in[6]. The indexes used in this research were Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geo-accumulation Index (Igeo). The Geo-accumulation Index (Igeo) introduced by Muller are also used to assess metal pollution in sediments. It is expressed as in Eq. 1, and [8] [9] [10]. Igeo = Log2 (Cn/1.5Bn) (1) Where Cn is heavy metal concentration in sediment of study area, Bn is the geochemical background value; 1.5 is the background matrix correction in factor due to lithogenic effects. The contamination level was classified in 6 scale: Igeo 0= unpolluted, Igeo < 1= unpolluted to moderately polluted,1 < Igeo 2 = moderately polluted, Igeo 2 < Igeo 3 = moderately to strongly polluted, Igeo 3 < Igeo 4 = strongly polluted, Igeo 4 < Igeo 5 = strongly to very strongly polluted. Igeo > 5 = very strongly polluted[11, 12]. EF is estimated based on the concentration ratio of measured heavy metals to normalising elements (Al, Fe, Cs, Rb, Li, Si) (2) According to the enrichment factor, sediment is classified into groups by river, estuary and coastal environments. EF 2 indicates that metal contamination might be entirely from natural sources, an EF value of 2 5 indicates that a moderate portion of heavy metals originated from an anthropogenic source or non-natural process, an EF of 5 20 indicates that a significant portion are from anthropogenic sources, an EF of 20 to 40 indicates that a high portion of contamination is derived from anthropogenic sources, and an EF > 40 indicates an extremely high portion of contamination. [7, 14] Statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and SPSS 17 software. To statistically evaluate the data, Kendall s tau-b correlation analysis and the two-way ANOVA test (level of significant is 0.05) were employed to understand the relationship between heavy metals in sediment and other parameters. Geo-statistical analysis was performed using Surfer 8 software (GPS value of stations) based on geospatial methods to better understand contaminant pathways and to provide a comprehensive contour map of the spatial distribution of contaminants over a large area. III. RESULT AND DISCUSSION Analysis of sediment grain size demonstrated that finegrained sediment (<64 µm) predominated at almost all stations ( %). The maximum of fine fractions were measured at stations close to the mangrove line According to the Two- Way ANOVA, there is significant differences (p< 0.05, df= 21, f=8.82, sig=.00) between distribution of fine grained sediment at different stations and stations 3 and 6 were not homogenous to other stations. Several factors affected grain size variation in marine system, such as sediment transportation and sedimentary process [15, 16]. In this study, areas with high percentage of fine sediment were found near the mangrove forest. This may be due to the land-based runoff and sedimentary process of mangrove forests. Several studies showed that mangrove forests can increase the suspended solid deposition by decreasing the water dynamic energy and provide enough time for deposition of fine grain sediment [17-21]. The TOC content of sediment ranged between and its concentrations were significantly different at different stations (p< 0.05, df= 21, f=10.10, sig=.00). The distribution of TOC follows the same pattern as fine-grained sediment in North Port with high concentrations at stations 3 and 6 (along the mangrove line) and the lower concentration at stations 2 and 5. the correlation analysis showed the high relation between the TOC and fine-grained sediment in study area(r= 0.716). Several research showed that TOC concentration increase when the mean grain size decreased because the fine particle size, particularly the clay colloid, has a high tendency to adsorb TOC [22]. According to Fig. 2, In North Port, the distribution of As, Cr, Hg, and Zn generally showed a bimodal pattern that varied from a high to low concentration from north to south and exhibited a high trend 100
3 to the east (along the berth line). The high concentration of Cu and Pb also occurred in the east direction and to the northwest. These areas are adjoining to land runoff and industrial outlets, which can directly release organic and inorganic pollutants. The distribution Cd showed the highest trend in the western part of the strait with the mangrove forest, which had the same distribution pattern of TOC and finegrained sediment. The distribution Cd showed the same pattern with fine particle sized sediments and TOC distribution. The highest concentration occurred in the western part of strait and along the mangrove forest fringes, which was related to the higher concentration of TOC and fine grain size in mangrove sediment. In this study, there was a significant correlation (0.4<r. P<0.01) between fine particle size and the following metals: Cd (0.406), Cu (0.447) and TOC (0.716). The results indicate that these metals were better enriched in finer particles compared to the sand particles; therefore, high concentrations were estimated around the mangrove line. The distribution of Ni was unique because it was high along the mangrove coastline. Generally, the lowest concentration of metals (except for As) was found close to the stations 2 and 5 in North Port. This may be due to the strong water currents which decrease the chemical reactions between metals and sediments. Moreover, these stations had substrates with a high percentage of sand grain sized sediments compared to other stations. TABLE I AVERAGE AND STANDARD DIVISION (SD) OF HEAVY METALS CONCENTRATIONS (µg/g) AND PERCENTAGE OF TOC AND FINE PARTICLE SIZ IN SURFACE SEDIMENT DURING SAMPLING PERIODS Stations As Cu Cd Cr Ni Pb Hg Zn TOC Fine particle
4 ecological indexes. According to the Geo-accumulation Index, Zn, Cu, Cr and Ni elements are unpolluted, Pb is moderately polluted, As and Hg elements are highely polluted and Cd element is very highly polluted. The enrichment factor (EF) was also applied to evaluate sediment quality in surface sediments. The EF value of Zn, Ni, Cr and Cu were between 2< EF <5, indicating that the sediment of North Port had moderate anthropogenic inputs of these heavy metals. There were significant enrichment of Pb, As, Hg and Cd in sediments, which suggests that a significant proportion of these metals were from anthropogenic sources exception Cd that was highly derived from anthropogenic sourced. According to these results heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of North Port was attributed human activities (anthropogenic) and its sediments were considered to be polluted with Cd, As and Hg. TABLE.II ECOLOGICAL INDEX VALUE, AVERAGE CONCENTRATION OF METALS AND THEIR BACKGROUND VALUE Metal Metals concentration Heavy metal Background value in present study Igeo Index Enrichment Factor As Cu Cd Cr Ni Pb Hg Zn FIG. 2 DISTRIBUTION OF HEAVY METALS IN NORTH PORT According to the Table 2, the average concentration of As, Cd, Pb and Hg are significantly higher than their background concentration in the North port while other metals are lower than background value. This implies that heavy metals are originated from many sources such as runoff due to rainfall and anthropogenic activities in the study area. These sources cause disturbance in environment and change geochemical concentrations ratio of metals and increase metals concentration from their background value. Generally more research stated that, when geochemical metals concentration suffered from disturbance due to potential change in environmental, the relative concentration ratio of metals goes beyond their background levels in sediment [23, 24]. Moreover table 2 shows the sediment quality according IV. CONCLUSION The extent of pollution was clarified by the use of the spatial distribution map and geo-statistical index to assess the degree of contamination of surface sediments at spatial scales. This data revealed that the geo-statistical index of sediments is in a pristine state with respect to metal contamination, except for Cd, As and Hg. Furthermore the concentration of Cd, As and Hg were significantly greater the background value. Therefore these metals can be considered as serious threat to biological communities and human health. In summary, the present study has provides basic data for the first time in North Port which is useful for long-term monitoring of heavy metal pollution in future. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors gratitude goes to support of University Malaya Research Grunt (UMRG) with project number RG083-10SUS and University Malaya Postgraduate Research Grant (PPP). REFERENCES [1] Borja, A., et al., Classifying ecological quality and integrity of estuaries.in: Wolanski, E., McLusky, D. (Eds.),. Chapter 1.9 within the Treatiseon Estuarine and Coastal Science. Elsevier, [2] U.S. EPA.Sediment quality guidelines. Draft report. EPA Region V Chicago IL,
5 [3] Pan, K. and W.X. Wang, Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Science of the total environment, [4] Caeiro, S., et al., Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: An index analysis approach. Ecological Indicators, (2): p [5] Burger, J. and M. Gochfeld, Metal levels in eggs of common terns (Sterna hirundo) in New Jersey: temporal trends from 1971 to Environmental Research, (3): p [6] Nobi, E., et al., Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of different coastal ecosystems of Andaman Islands, India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, (2): p [7] Cressie, N., The origins of kriging. Mathematical Geology, (3): p [8] Vallejuelo, S.F.-O.d., et al., Risk assessment of trace elements in sediments: The case of the estuary of the Nerbioi Ibaizabal River (Basque Country). Journal of Hazardous Materials 2010(181): p [9] Sinex, S. and G. Helz, Regional geochemistry of trace elements in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Environmental Geology, (6): p [10] Singh, A.K., S.I. Hasnain, and D.K. Banerjee, Grain Size and Geochemical Portioning of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Damodar River- A Tributary of the Lower Ganga, India. Environmental Geology, 2003(39): p [11] Loska, K., et al., Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, (1): p [12] Leorri, E., et al., Geochemical and microfaunal proxies to assess environmental quality conditions during the recovery process of a heavily polluted estuary: The Bilbao estuary case (N. Spain). Science of the total environment, (1): p [13] Rule, J.H., Assessment of trace element geochemistry of Hampton Roads Harbor and lower Chesapeake Bay area sediments. Environmental Geology, (4): p [14] Sparks, T., Statistics in Ecotoxicology2000: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, England, pp: [15] He, Z., et al., Variation characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the south Yellow Sea surface sediments. Environmental monitoring and assessment, (1): p [16] Qin, Y.S., Y.Y. Zhao, and L.R. Chen, the geography southern yellow sea. Beijing marine, 1989: p [17] Woodroffe, C., Mangrove sediments and geomorphology. Tropical mangrove ecosystems, 1992: p [18] Wolanski, E., Y. Mazda, and P. Ridd, Mangrove hydrodynamics. Tropical mangrove ecosystems, 1992: p [19] Furukawa, K., E. Wolanski, and H. Mueller, Currents and sediment transport in mangrove forests. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, (3): p [20] Kathiresan, K., How do mangrove forests induce sedimentation? Revista de biologia tropical, (2): p [21] Cunha-Lignon, M., et al., Mangrove forests and sedimentary processes on the south coast of São Paulo State (Brazil). J. coast. Res., (Special). [22] He, Z., et al., Variation characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the south Yellow Sea surface sediments. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 157(1), [23] Wang, China cracks down on heavy metal pollution. China Daily. Availableat: [24] Wells, P.G., et al., Rapid toxicity assessment and biomonitoring of marine contaminants--exploiting the potential of rapid biomarker assays and microscale toxicity tests. Marine Pollution Bulletin, (10): p
Assessment at mid-black Sea coast of Turkey for recovery valuable heavy metals from sediments
 European Water 58: 173-177, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Assessment at mid-black Sea coast of Turkey for recovery valuable heavy metals from sediments A. Şimşek * and G. Bakan Department of Environmental
European Water 58: 173-177, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Assessment at mid-black Sea coast of Turkey for recovery valuable heavy metals from sediments A. Şimşek * and G. Bakan Department of Environmental
Assessment of Sediment Quality According To Heavy Metal Status in the West Port of Malaysia
 Assessment of Sediment Quality According To Heavy Metal Status in the West Port of Malaysia B.Tavakoly Sany, A.H.Sulaiman, GH. Monazami and A. Salleh Abstract eight heavy metals (Cu, Cr, Zn, Hg, Pb, Cd,
Assessment of Sediment Quality According To Heavy Metal Status in the West Port of Malaysia B.Tavakoly Sany, A.H.Sulaiman, GH. Monazami and A. Salleh Abstract eight heavy metals (Cu, Cr, Zn, Hg, Pb, Cd,
Distribution and Contamination of Heavy Metal in the Coastal Sediments of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia
 Water Air Soil Pollut (2013) 224:1476 DOI 10.1007/s11270-013-1476-6 Distribution and Contamination of Heavy Metal in the Coastal Sediments of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia Seyedeh Belin Tavakoly Sany
Water Air Soil Pollut (2013) 224:1476 DOI 10.1007/s11270-013-1476-6 Distribution and Contamination of Heavy Metal in the Coastal Sediments of Port Klang, Selangor, Malaysia Seyedeh Belin Tavakoly Sany
Spatial and Temporal distribution of metals in sediments of a tropical lagoon, SW coast of India: Environmental Indicators ABSTRACT
 Spatial and Temporal distribution of metals in sediments of a tropical lagoon, SW coast of India: Environmental Indicators C.P. Priju 1 and A.C. Narayana 2 * 1 Department of Marine Geology & Geophysics
Spatial and Temporal distribution of metals in sediments of a tropical lagoon, SW coast of India: Environmental Indicators C.P. Priju 1 and A.C. Narayana 2 * 1 Department of Marine Geology & Geophysics
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
THE EFFECT OF SEDIMENT GRAIN SIZE ON HEAVY METAL CONTENT*
 Water resources and wetlands, Editors: Petre Gâştescu, William Lewis Jr., Petre Breţcan Conference Proceedings, 14-16 September 2012, Tulcea - Romania ISBN: 978-606-605-038-8 THE EFFECT OF SEDIMENT GRAIN
Water resources and wetlands, Editors: Petre Gâştescu, William Lewis Jr., Petre Breţcan Conference Proceedings, 14-16 September 2012, Tulcea - Romania ISBN: 978-606-605-038-8 THE EFFECT OF SEDIMENT GRAIN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 4, No 5, Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 4, No 5, 2014 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4402 Distribution and Seasonal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 4, No 5, 2014 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4402 Distribution and Seasonal
Current issues in establishing geochemical background of trace elements
 Geochemistry and the Environment Division Institute of Chemistry Jan Kochanowski University in Kielce Current issues in establishing geochemical background of trace elements Agnieszka Gałuszka & Zdzisław
Geochemistry and the Environment Division Institute of Chemistry Jan Kochanowski University in Kielce Current issues in establishing geochemical background of trace elements Agnieszka Gałuszka & Zdzisław
UPSTREAM-DOWNSTREAM CONTAMINATION GRADIENT OF THE FLUVIAL URBAN SYSTEM IN CHENNAI (Tamil Nadu, India)
 UPSTREAM-DOWNSTREAM CONTAMINATION GRADIENT OF THE FLUVIAL URBAN SYSTEM IN CHENNAI (Tamil Nadu, India) Saravanan S.P. a,b, Desmet. M. a, Ambujam N.K. b, Thenmozhi D. b, Manikandabharath K. b, Rukkumany
UPSTREAM-DOWNSTREAM CONTAMINATION GRADIENT OF THE FLUVIAL URBAN SYSTEM IN CHENNAI (Tamil Nadu, India) Saravanan S.P. a,b, Desmet. M. a, Ambujam N.K. b, Thenmozhi D. b, Manikandabharath K. b, Rukkumany
Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City To cite this article: Daiwen Zhu et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Pollution in Maozhou River in Shenzhen City To cite this article: Daiwen Zhu et al 2018 IOP
Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania
 Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania Introduction Summary In 2003 Lithuanian Ministry of Transport initiated the preparation of feasibility
Environmental impact assessment study of the new offshore dumping sites for Šventoji port in Lithuania Introduction Summary In 2003 Lithuanian Ministry of Transport initiated the preparation of feasibility
Degree of Pollution in Water and Sediments of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in Valsequillo Dam, Puebla City, México
 2014 3 rd International Conference on Geological and Environmental Sciences IPCBEE vol. 73 (2014) (2014) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2014. V73. 10 Degree of Pollution in Water and Sediments
2014 3 rd International Conference on Geological and Environmental Sciences IPCBEE vol. 73 (2014) (2014) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2014. V73. 10 Degree of Pollution in Water and Sediments
Assess the Potential for Accumulation of Toxic Trace Elements in Biota near Burton Island Ash Disposal Site Indian River Bay, Delaware
 Assess the Potential for Accumulation of Toxic Trace Elements in Biota near Burton Island Ash Disposal Site Indian River Bay, Delaware Gerhardt Riedel Ph.D. Smithsonian Environmental Research Center Bartholomew
Assess the Potential for Accumulation of Toxic Trace Elements in Biota near Burton Island Ash Disposal Site Indian River Bay, Delaware Gerhardt Riedel Ph.D. Smithsonian Environmental Research Center Bartholomew
Heavy Metals in Water and Bottom Sediments of Odessa Region of the Black Sea
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 5 (2015) 51-58 doi: 10.17265/2159-5879/2015.02.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING Heavy Metals in Water and Bottom Sediments of Odessa Region of the Black Sea Sergey Yevgenevich
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 5 (2015) 51-58 doi: 10.17265/2159-5879/2015.02.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING Heavy Metals in Water and Bottom Sediments of Odessa Region of the Black Sea Sergey Yevgenevich
Possible causes of sediment dynamics and mixing in western Baltic Sea basins
 Tauber, F. (2012), BSH, BSBD Possible causes of sediment dynamics and mixing in western Baltic Sea basins Dennis Bunke Thomas Leipe, Matthias Moros & Helge W. Arz dennis.bunke@io-warnemuende.de Tauber,
Tauber, F. (2012), BSH, BSBD Possible causes of sediment dynamics and mixing in western Baltic Sea basins Dennis Bunke Thomas Leipe, Matthias Moros & Helge W. Arz dennis.bunke@io-warnemuende.de Tauber,
EVALUATION OF MIGRATION OF HEAVY METAL CONTAINING SEDIMENT RESULTING FROM WATER EROSION USING A GEO- INFORMATION MODEL
 EVALUATION OF MIGRATION OF HEAVY METAL CONTAINING SEDIMENT RESULTING FROM WATER EROSION USING A GEO- INFORMATION MODEL János Tamás, Elza Kovács University of Debrecen, Centre of Agricultural Sciences Department
EVALUATION OF MIGRATION OF HEAVY METAL CONTAINING SEDIMENT RESULTING FROM WATER EROSION USING A GEO- INFORMATION MODEL János Tamás, Elza Kovács University of Debrecen, Centre of Agricultural Sciences Department
Environmental Implications A Case Study
 Grain Size Variations and Its Environmental Implications A Case Study DR PURANDARA BEKAL SCIENTIST, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY HARD ROCK REGIONAL CENTER HANUMAN NAGAR BELGAUM, KARNATAKA Particle Transport
Grain Size Variations and Its Environmental Implications A Case Study DR PURANDARA BEKAL SCIENTIST, NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY HARD ROCK REGIONAL CENTER HANUMAN NAGAR BELGAUM, KARNATAKA Particle Transport
Sediment characteristics of Beaver Lake and implications for remediation; A Pilot Project.
 Sediment characteristics of Beaver Lake and implications for remediation; A Pilot Project. Delphine Faugeraux Leah Bendell A report to the Stanley Park Ecological Society. September 15 th 2011. Abstract
Sediment characteristics of Beaver Lake and implications for remediation; A Pilot Project. Delphine Faugeraux Leah Bendell A report to the Stanley Park Ecological Society. September 15 th 2011. Abstract
Prof. Dr. Biljana Škrbić, Jelena Živančev
 5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
Spatial distribution and mobility of trace metals in sediments of the Krka River estuary (Adriatic Sea, Croatia)
 Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 4, SPLIT, CROATIA (2017) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Spatial distribution
Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime EDITION 4, SPLIT, CROATIA (2017) Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference Disponible en ligne http://www.paralia.fr Available online Spatial distribution
Dynamic preservation of the coastline
 Dynamic preservation of the coastline Content Introduction The Dutch coastal defence by dynamic processes Data collection Management of the sand resources Growing importance of marine sand and gravel resources
Dynamic preservation of the coastline Content Introduction The Dutch coastal defence by dynamic processes Data collection Management of the sand resources Growing importance of marine sand and gravel resources
Determination of Some Trace Elements in Marine Sediment using ICP-MS and XRF (A Comparative Study)
 Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2013, Vol. 29, No. (2): Pg. 645-653 Determination
Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2013, Vol. 29, No. (2): Pg. 645-653 Determination
FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE, DEHRADUN
 PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
Trace Metals in Macroalgae from the Qatari Coastal Water
 J. KAU: Mar. Sri., vol. 5, pp. 13-24 (1414A.H./1994 A.D.) Trace Metals in Macroalgae from the Qatari Coastal Water * MOHAMED A. EL SAYED and MOHAMED M. DORGHAM National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries,
J. KAU: Mar. Sri., vol. 5, pp. 13-24 (1414A.H./1994 A.D.) Trace Metals in Macroalgae from the Qatari Coastal Water * MOHAMED A. EL SAYED and MOHAMED M. DORGHAM National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries,
DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS
 EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF AQUATIC RESEARCH 1687-4285 VOL. 32 NO. 1, 2006: 12-21 DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS KH. M. EL-MOSELHY National Institute
EGYPTIAN JOURNAL OF AQUATIC RESEARCH 1687-4285 VOL. 32 NO. 1, 2006: 12-21 DISTRIBUTION OF VANADIUM IN BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM THE MARINE COASTAL AREA OF THE EGYPTIAN SEAS KH. M. EL-MOSELHY National Institute
Stickney Avenue Depositional Zone (SADZ) Investigation
 The Ottawa River: A Report to the Community Stickney Avenue Depositional Zone (SADZ) Investigation May 22, 2007 Presented by: Scott Bell, P.E., BCEE (LimnoTech) Kelly Bensman (Hull & Associates) SADZ Location
The Ottawa River: A Report to the Community Stickney Avenue Depositional Zone (SADZ) Investigation May 22, 2007 Presented by: Scott Bell, P.E., BCEE (LimnoTech) Kelly Bensman (Hull & Associates) SADZ Location
Reexamining the Relationship of Beryllium-7 Adsorption to Grain Size in the York River, Virginia
 Reexamining the Relationship of Beryllium-7 Adsorption to Grain Size in the York River, Virginia A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science in Geology
Reexamining the Relationship of Beryllium-7 Adsorption to Grain Size in the York River, Virginia A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science in Geology
Study on Characteristics of Sediment and Sedimentation Rate at Sungai Lembing, Kuantan, Pahang
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 5 ( ) 8 9 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology, MUCET Part - Civil and Chemical Engineering Study on Characteristics
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 5 ( ) 8 9 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology, MUCET Part - Civil and Chemical Engineering Study on Characteristics
SEA BOTTOM MORPHOLOGY AND SEDIMENT DISTRIBUTION OF KUALA BESAR KELANTAN RIVER DELTA AND ITS OFFSHORE AREAS
 BORNEO SCIENCE 35: SEPTEMBER 2014 SEA BOTTOM MORPHOLOGY AND SEDIMENT DISTRIBUTION OF KUALA BESAR KELANTAN RIVER DELTA AND ITS OFFSHORE AREAS Nurul Afifah Mohd Radzir* 1, Che Aziz Ali 1, Kamal Roslan Mohamed
BORNEO SCIENCE 35: SEPTEMBER 2014 SEA BOTTOM MORPHOLOGY AND SEDIMENT DISTRIBUTION OF KUALA BESAR KELANTAN RIVER DELTA AND ITS OFFSHORE AREAS Nurul Afifah Mohd Radzir* 1, Che Aziz Ali 1, Kamal Roslan Mohamed
An Investigative Study on Heavy Metal Content in Sediment of Bellandur Lake, Bengaluru
 An Investigative Study on Heavy Metal Content in Sediment of Bellandur Lake, Bengaluru Anoop Toolahalli 1, Dr. K. M. Sham Sundar 2 1MTech student, Department of Civil Engineering, U B D T College of Engineering,
An Investigative Study on Heavy Metal Content in Sediment of Bellandur Lake, Bengaluru Anoop Toolahalli 1, Dr. K. M. Sham Sundar 2 1MTech student, Department of Civil Engineering, U B D T College of Engineering,
Results of a Sediment Survey in the Near Offshore Waters of the Proposed Quarry Site in the Vicinity of Whites Cove, Digby Neck, Nova Scotia
 Results of a Sediment Survey in the Near Offshore Waters of the Proposed Quarry Site in the Vicinity of Whites Cove, Digby Neck, Nova Scotia Prepared for Paul G. Buxton P.O. Box 98 Annapolis Royal, Nova
Results of a Sediment Survey in the Near Offshore Waters of the Proposed Quarry Site in the Vicinity of Whites Cove, Digby Neck, Nova Scotia Prepared for Paul G. Buxton P.O. Box 98 Annapolis Royal, Nova
ASSESSMENT OF GODAVARI ESTUARINE MANGROVE ECOSYSTEM THROUGH TRACE METAL STUDIES
 ASSESSMENT OF GODAVARI ESTUARINE MANGROVE ECOSYSTEM THROUGH TRACE METAL STUDIES A. K. Ray, S. C. Tripathy, S. Patra & V. V. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography, Regional Centre, 176, Lawson s Bay
ASSESSMENT OF GODAVARI ESTUARINE MANGROVE ECOSYSTEM THROUGH TRACE METAL STUDIES A. K. Ray, S. C. Tripathy, S. Patra & V. V. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography, Regional Centre, 176, Lawson s Bay
Grain size distribution of surface sediment. Mineralogy of different sediment fractions. Geochemistry of surface sediment fine fraction
 TRACE ELEMENT N DFFERENT MARNE SEDMENT FRACTONS OF THE GULF OF TUNS: CENTRAL MEDTERRANEAN SEA Noureddine Zaaboub1*, Walid Oueslati2, Saadi Abdeljaoued2, F. Javier Huertas3, Alberto López-Galindo3 1 National
TRACE ELEMENT N DFFERENT MARNE SEDMENT FRACTONS OF THE GULF OF TUNS: CENTRAL MEDTERRANEAN SEA Noureddine Zaaboub1*, Walid Oueslati2, Saadi Abdeljaoued2, F. Javier Huertas3, Alberto López-Galindo3 1 National
Metals Sediment Study in Lower Newport Bay (Post-dredging) Final Report
 Metals Sediment Study in Lower Newport Bay (Post-dredging) Final Report by Orange County Coastkeeper and Linda M. Candelaria, PhD for the Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board March 2014 Page
Metals Sediment Study in Lower Newport Bay (Post-dredging) Final Report by Orange County Coastkeeper and Linda M. Candelaria, PhD for the Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board March 2014 Page
River bank erosion risk potential with regards to soil erodibility
 River Basin Management VII 289 River bank erosion risk potential with regards to soil erodibility Z. A. Roslan 1, Y. Naimah 1 & Z. A. Roseli 2 1 Infrastructure University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Humid
River Basin Management VII 289 River bank erosion risk potential with regards to soil erodibility Z. A. Roslan 1, Y. Naimah 1 & Z. A. Roseli 2 1 Infrastructure University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Humid
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT OF CONTAMINATED FLUVIAL SEDIMENTS EROSION RISK AND ECOLOGICAL HAZARD
 COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT OF CONTAMINATED FLUVIAL SEDIMENTS EROSION RISK AND ECOLOGICAL HAZARD INGO HAAG, ULRICH KERN and BERNHARD WESTRICH Institut für Wasserbau, Universität Stuttgart, 70550 Stuttgart,
COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT OF CONTAMINATED FLUVIAL SEDIMENTS EROSION RISK AND ECOLOGICAL HAZARD INGO HAAG, ULRICH KERN and BERNHARD WESTRICH Institut für Wasserbau, Universität Stuttgart, 70550 Stuttgart,
Sediment Sampling Protocols
 Sediment Sampling Protocols February 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Sediment Sampling in Large and
Sediment Sampling Protocols February 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Sediment Sampling in Large and
The Baltic Soil Survey
 The Baltic Soil Survey C. Reimann, U. Siewers, T. Tarvainen, L. Bityukova, J. Erikson, A. Gilucis, V. Gregorauskiene, V. Lukashev, N. Matinian & A. Pasieczna PROJECT AIM: create a comparable database
The Baltic Soil Survey C. Reimann, U. Siewers, T. Tarvainen, L. Bityukova, J. Erikson, A. Gilucis, V. Gregorauskiene, V. Lukashev, N. Matinian & A. Pasieczna PROJECT AIM: create a comparable database
GEMAS: A European scale geochemical atlas for environmental management and mineral exploration
 GEMAS PROJECT GEMAS: A European scale geochemical atlas for environmental management and mineral exploration Clemens Reimann 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth 2007: Eurometaux contacts EuroGeoSurveys:
GEMAS PROJECT GEMAS: A European scale geochemical atlas for environmental management and mineral exploration Clemens Reimann 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth 2007: Eurometaux contacts EuroGeoSurveys:
Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk of Mercury in Sediments of Kaohsiung River Mouth, Taiwan
 Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk of Mercury in Sediments of Kaohsiung River Mouth, Taiwan Chiu-Wen Chen, Chih-Feng Chen, and Cheng-Di Dong Abstract The distribution, enrichment, and potential
Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk of Mercury in Sediments of Kaohsiung River Mouth, Taiwan Chiu-Wen Chen, Chih-Feng Chen, and Cheng-Di Dong Abstract The distribution, enrichment, and potential
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT
 DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
Aim and objectives Components of vulnerability National Coastal Vulnerability Assessment 2
 ASSESSING THE UTILITY OF GEOMORPHIC SENSITIVITY MAPPING ON THE ILLAWARRA COAST Pamela Abuodha, Christina Baker, Chris Sharples, Darren Skene and Colin Woodroffe Geoquest Research Centre, University of
ASSESSING THE UTILITY OF GEOMORPHIC SENSITIVITY MAPPING ON THE ILLAWARRA COAST Pamela Abuodha, Christina Baker, Chris Sharples, Darren Skene and Colin Woodroffe Geoquest Research Centre, University of
Copper Contamination in the Sediments of Love River Mouth, Taiwan
 Copper Contamination in the Sediments of Love River Mouth, Taiwan Chiu-Wen Chen, Chih-Feng Chen, and Cheng-Di Dong Abstract This study was conducted using the data collected at the mouth of Love River
Copper Contamination in the Sediments of Love River Mouth, Taiwan Chiu-Wen Chen, Chih-Feng Chen, and Cheng-Di Dong Abstract This study was conducted using the data collected at the mouth of Love River
STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY
 . CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
. CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
ICP/MS Multi-Element Standards
 Standards Ultra Pure Matrix Special Packaging Traceability to National Reference Materials AccuStandard s ICP/MS Standards are formulated to meet the needs of this very special instrument. As matrix effect
Standards Ultra Pure Matrix Special Packaging Traceability to National Reference Materials AccuStandard s ICP/MS Standards are formulated to meet the needs of this very special instrument. As matrix effect
Geochemical Study of Coastal Sediments In uenced by River-Transported Pollution: Southern Evoikos Gulf, Greece
 PII: S0025-326X(99)00174-5 Marine Pollution Bulletin Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 77±82, 2000 Ó 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0025-326X/00 $ - see front matter Geochemical
PII: S0025-326X(99)00174-5 Marine Pollution Bulletin Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 77±82, 2000 Ó 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0025-326X/00 $ - see front matter Geochemical
Supporting Information Appendix. Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for more than a century
 Supporting Information Appendix for article published in PNAS P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1011915108 Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for
Supporting Information Appendix for article published in PNAS P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1011915108 Arsenic pollution of groundwater in Vietnam exacerbated by deep aquifer exploitation for
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE
 Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE Current PA Guidance Many guidance documents apply expected pollutant removals based on literature. However, typically presented
Shirley E. Clark, Ph.D., P.E., D. WRE Robert E. Pitt, Ph.D., P.E., BCEE, D. WRE Current PA Guidance Many guidance documents apply expected pollutant removals based on literature. However, typically presented
EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment
 EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 8(1) (2015) 133-143 Genotoxicity
EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 8(1) (2015) 133-143 Genotoxicity
REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER
 REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1399 COLLEGE : DAYANANDA SAGAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH :
REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS USING COMBINATION OF ADSORBENTS - A CASE STUDY USING INDUSTRIAL WASTE WATER PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1399 COLLEGE : DAYANANDA SAGAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE BRANCH :
Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution in the Sediments of Euphrates River, Iraq
 Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 12, 4, 1009-1023 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.12.412117 Published Online December 12 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution
Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 12, 4, 1009-1023 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.12.412117 Published Online December 12 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution
2008 POST-TSUNAMI FIELD SURVEY REPORT
 2008 POST-TSUNAMI FIELD SURVEY REPORT FIELD SURVEY ON ASSESSMENT OF TSUNAMI LONGTERM EFFECTS AND PILOT PALEOTSUNAMI SURVEY 29.01 0 NIRAN CHAIMANEE, WITOLD SZCZUCIŃSKI, PASSKORN KUNTHASAP, WISUT CHOTIKASATHIEN
2008 POST-TSUNAMI FIELD SURVEY REPORT FIELD SURVEY ON ASSESSMENT OF TSUNAMI LONGTERM EFFECTS AND PILOT PALEOTSUNAMI SURVEY 29.01 0 NIRAN CHAIMANEE, WITOLD SZCZUCIŃSKI, PASSKORN KUNTHASAP, WISUT CHOTIKASATHIEN
Pyrite in acid sulfate soils: transformation and inhibition of its oxidation by application of natural materials
 Symposium no. 28 Paper no. 97 Presentation: oral Pyrite in acid sulfate soils: transformation and inhibition of its oxidation by application of natural materials SHAMSHUDDIN Jusop and SARWANI Muhrizal
Symposium no. 28 Paper no. 97 Presentation: oral Pyrite in acid sulfate soils: transformation and inhibition of its oxidation by application of natural materials SHAMSHUDDIN Jusop and SARWANI Muhrizal
2015 Toxicity Testing of BEAR CREEK SEDIMENT
 2015 Toxicity Testing of BEAR CREEK SEDIMENT Sparrows Point Meeting Sollers Pt / Dundalk Public Library DECEMBER 16TH, 2015 LANCE YONKOS / SHARON HARTZELL PAST INVESTIGATIONS: 2004 Reported toxicity in
2015 Toxicity Testing of BEAR CREEK SEDIMENT Sparrows Point Meeting Sollers Pt / Dundalk Public Library DECEMBER 16TH, 2015 LANCE YONKOS / SHARON HARTZELL PAST INVESTIGATIONS: 2004 Reported toxicity in
Integrated GIS based approach in mapping the groundwater potential zones in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia
 Integrated GIS based approach in mapping the groundwater potential zones in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia Zulherry Isnain and Juhari Mat Akhir Faculty of Science and Natural Resources, Universiti Malaysia
Integrated GIS based approach in mapping the groundwater potential zones in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia Zulherry Isnain and Juhari Mat Akhir Faculty of Science and Natural Resources, Universiti Malaysia
Diffuse Pollution Conference, Dublin 2003 EFFECT OF SALINITY ON HEAVY METALS MIGRATION AMONG DISSOLVED AND SOLID PHASES IN ESTUARY SEDIMENT
 Diffuse Pollution Conference, Dublin 23 EFFECT OF SALINITY ON HEAVY METALS MIGRATION AMONG DISSOLVED AND SOLID PHASES IN ESTUARY SEDIMENT *TsaiL. J. 1, Yu.C. 1, Ho S.T. 2, Chang J. S. 1, Wu T. S. 1 1 Department
Diffuse Pollution Conference, Dublin 23 EFFECT OF SALINITY ON HEAVY METALS MIGRATION AMONG DISSOLVED AND SOLID PHASES IN ESTUARY SEDIMENT *TsaiL. J. 1, Yu.C. 1, Ho S.T. 2, Chang J. S. 1, Wu T. S. 1 1 Department
(São Paulo, Brazil) Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares - IPEN/CNEN-SP, Caixa Postal 11049, Pinheiros, São Paulo, Brasil 2
 Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 249, No. 1 (2001) 257 261 210Pb and 137 Cs geochronologies in the Cananeia-Iguape Estuary (São Paulo, Brazil) R. T. Saito, 1 R. C. L. Figueira, 2
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 249, No. 1 (2001) 257 261 210Pb and 137 Cs geochronologies in the Cananeia-Iguape Estuary (São Paulo, Brazil) R. T. Saito, 1 R. C. L. Figueira, 2
Available online Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2018, 5(2): Research Article
 Available online www.jsaer.com, 2018, 5(2):342-351 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Application of geo-accumulation index (I-geo) for assessment the sediments contamination with heavy
Available online www.jsaer.com, 2018, 5(2):342-351 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Application of geo-accumulation index (I-geo) for assessment the sediments contamination with heavy
Metal fluxes from a sea deposit site for mine tailings
 Metal fluxes from a sea deposit site for mine tailings Morten T. Schaanning, Kuria Ndungu, Sigurd Øxnevad, Hilde C. Trannum Norwegian Institute for Water Research (NIVA) NRC Project ES32333 New knowledge
Metal fluxes from a sea deposit site for mine tailings Morten T. Schaanning, Kuria Ndungu, Sigurd Øxnevad, Hilde C. Trannum Norwegian Institute for Water Research (NIVA) NRC Project ES32333 New knowledge
The Preliminary Investigation on The Dredged Marine Sediment of Kuala Perlis as A Potential Brick Material
 2012 2nd International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment Management IPCBEE vol. 42 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V42. 6 The Preliminary Investigation on The
2012 2nd International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment Management IPCBEE vol. 42 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V42. 6 The Preliminary Investigation on The
Comprehensive Evaluation of Trace Metal Distribution and Pollution index in the Sediments of Coastal areas of Sindh, Pakistan
 IAAST ONLINE ISSN 2277-1565 PRINT ISSN 0976-4828 CODEN: IAASCA International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology IAAST; Vol 4 [3] September 2013: 01-08 2012 Society of Education, India [ISO9001:
IAAST ONLINE ISSN 2277-1565 PRINT ISSN 0976-4828 CODEN: IAASCA International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology IAAST; Vol 4 [3] September 2013: 01-08 2012 Society of Education, India [ISO9001:
ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
 ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS ANALYSIS Identification and Quantification CHEMICAL The Analyte: A Discrete Chemical Species or A Collection of Related Chemical Species (i.e., An Aggregate) ENVIRONMENTAL
ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS ANALYSIS Identification and Quantification CHEMICAL The Analyte: A Discrete Chemical Species or A Collection of Related Chemical Species (i.e., An Aggregate) ENVIRONMENTAL
Characterization of Sand Formation from a Crude Oilfield
 This work by IJARBEST is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Available at https://www.ijarbest.com Characterization of Sand Formation from a Crude Oilfield 1 A. Sivasakthi,
This work by IJARBEST is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Available at https://www.ijarbest.com Characterization of Sand Formation from a Crude Oilfield 1 A. Sivasakthi,
Akvaplan-niva rapport
 Grunnlagsundersøkelse på Snøhvit og Område C i Barentshavet, 2003 Akvaplan-niva rapport APN-411.2785-1 Introduction Statoil and Norsk Hydro commissioned Akvaplan-niva AS to perform baseline surveys at
Grunnlagsundersøkelse på Snøhvit og Område C i Barentshavet, 2003 Akvaplan-niva rapport APN-411.2785-1 Introduction Statoil and Norsk Hydro commissioned Akvaplan-niva AS to perform baseline surveys at
Salmon Aquaculture Environmental Monitoring Data Report. Results of Sampling Program for Year Clayton Rd., RR #1 Sidney, BC V8L 5P6
 Salmon Aquaculture Environmental Monitoring Data Report Results of Sampling Program for Year 2002 by Cindy Wright 1, Bernie Taekema 2, Brenda Burd 1, and Eric McGreer 2 1 Ecostat Research Ltd. 1040 Clayton
Salmon Aquaculture Environmental Monitoring Data Report Results of Sampling Program for Year 2002 by Cindy Wright 1, Bernie Taekema 2, Brenda Burd 1, and Eric McGreer 2 1 Ecostat Research Ltd. 1040 Clayton
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy
 Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Hiroshi Onodera Application & Research Center, JEOL Ltd. Introduction um, PBB and PBDE) are subject to usage restrictions in Europe.
Analysis of Cadmium (Cd) in Plastic Using X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Hiroshi Onodera Application & Research Center, JEOL Ltd. Introduction um, PBB and PBDE) are subject to usage restrictions in Europe.
Screening of Algae Material as a Filter for Heavy Metals in Drinking Water
 1 Screening of Algae Material as a Filter for Heavy Metals in Drinking Water 2 ABSTRACT Calcium alginate beads generated from alginic acid sodium salt from brown algae were 3 used to explore the adsorption
1 Screening of Algae Material as a Filter for Heavy Metals in Drinking Water 2 ABSTRACT Calcium alginate beads generated from alginic acid sodium salt from brown algae were 3 used to explore the adsorption
Trace metal contamination of soils and sediments in the Port Kembla area, New South Wales, Australia
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2009 Trace metal contamination of soils and sediments in the Port Kembla area, New South
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2009 Trace metal contamination of soils and sediments in the Port Kembla area, New South
GUAMA RIVER AND GUAJARA BAY, BELEM - AMAZON REGION
 2007 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2007 Santos, SP, Brazil, September 30 to October 5, 2007 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-02-1 210 Pb GEOCHRONOLOGY
2007 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2007 Santos, SP, Brazil, September 30 to October 5, 2007 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-02-1 210 Pb GEOCHRONOLOGY
Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (Germany)
 Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (Germany) C r u i s e R e p o r t r/v "Poseidon" Cruise No. P 475 This report based on preliminary data and results Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde
Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (Germany) C r u i s e R e p o r t r/v "Poseidon" Cruise No. P 475 This report based on preliminary data and results Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde
LI Yong (1,2), FRIELINGHAUS Monika (1), BORK Hans-Rudolf (1), WU Shuxia (2), ZHU Yongyi (2)
 Scientific registration n : Symposium n : 31 Presentation : poster Spatial patterns of soil redistribution and sediment delivery in hilly landscapes of the Loess Plateau Motifs spaciaux de zones d'érosion
Scientific registration n : Symposium n : 31 Presentation : poster Spatial patterns of soil redistribution and sediment delivery in hilly landscapes of the Loess Plateau Motifs spaciaux de zones d'érosion
Risk Assessment of Trace Element Pollution in Gymea Bay, NSW, Australia
 Risk Assessment of Trace Element Pollution in Gymea Bay, NSW, Australia Yasir M. Alyazichi, Brian G. Jones, Errol McLean, Hamd N. Altalyan, Ali K. M. Al-Nasrawi Abstract The main purpose of this study
Risk Assessment of Trace Element Pollution in Gymea Bay, NSW, Australia Yasir M. Alyazichi, Brian G. Jones, Errol McLean, Hamd N. Altalyan, Ali K. M. Al-Nasrawi Abstract The main purpose of this study
Supporting Information for. Spatiotemporal Trends of Elemental Carbon and Char/Soot Ratios in
 1 2 3 4 Supporting Information for Spatiotemporal Trends of Elemental Carbon and Char/Soot Ratios in Five Sediment Cores from Eastern China Marginal Seas: Indicators of Anthropogenic Activities and Transport
1 2 3 4 Supporting Information for Spatiotemporal Trends of Elemental Carbon and Char/Soot Ratios in Five Sediment Cores from Eastern China Marginal Seas: Indicators of Anthropogenic Activities and Transport
This table connects the content provided by Education Perfect to the NSW Syllabus.
 Education Perfect Geography provides teachers with a wide range of quality, engaging and innovative content to drive positive student learning outcomes. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house
Education Perfect Geography provides teachers with a wide range of quality, engaging and innovative content to drive positive student learning outcomes. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house
15 Mineral Resources
 15 Mineral Resources Overview of Chapter 15 Introduction to Minerals Environmental Impact Associated with Minerals An International Perspective Increasing the Supply of Minerals Using Substitution and
15 Mineral Resources Overview of Chapter 15 Introduction to Minerals Environmental Impact Associated with Minerals An International Perspective Increasing the Supply of Minerals Using Substitution and
Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids
 Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids Geochemical methods for evaluating whether metals and metalloids are from geogenic versus anthropogenic sources 1 Definitions Geogenic from natural geological
Geogenic versus Anthropogenic Metals and Metalloids Geochemical methods for evaluating whether metals and metalloids are from geogenic versus anthropogenic sources 1 Definitions Geogenic from natural geological
The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and
 The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and physical properties. REEs along with certain other trace
The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and physical properties. REEs along with certain other trace
INVESTIGATING THE IMPACT OF FLOW CONDITIONS ON METAL CONTENTS IN NILE BED SEDIMENTS
 INVESTIGATING THE IMPACT OF FLOW CONDITIONS ON METAL CONTENTS IN NILE BED SEDIMENTS Mohsen M. Yousry 1, Mahmoud T. Heikal 2, Amal El-Sherbini 3 and Talaat A. Salem 4 1 Researcher, Water Quality Department,
INVESTIGATING THE IMPACT OF FLOW CONDITIONS ON METAL CONTENTS IN NILE BED SEDIMENTS Mohsen M. Yousry 1, Mahmoud T. Heikal 2, Amal El-Sherbini 3 and Talaat A. Salem 4 1 Researcher, Water Quality Department,
Ambient Air Sampling Program First Quarter 2016 Report Sudbury, Ontario. Submitted to:
 First Quarter 2016 Report Sudbury, Ontario Submitted to: Vale Canada Limited Submitted by: Amec Foster Wheeler Environment & Infrastructure 131 Fielding Road Lively, Ontario P3Y 1L7 9 Amec Foster Wheeler
First Quarter 2016 Report Sudbury, Ontario Submitted to: Vale Canada Limited Submitted by: Amec Foster Wheeler Environment & Infrastructure 131 Fielding Road Lively, Ontario P3Y 1L7 9 Amec Foster Wheeler
DETECTION OF GROUNDWATER POLLUTION USING RESISTIVITY IMAGING AT SERI PETALING LANDFILL, MALAYSIA
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 8 2000 DETECTION OF GROUNDWATER
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 8 2000 DETECTION OF GROUNDWATER
Geochemical Assessment of Trace Metal Distribution and Contamination in the Surface Sediments of the Coast of Okinawa Island, Japan
 Environment and Pollution; Vol. 6, No. 1; 2017 ISSN 1927-0909 E-ISSN 1927-0917 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Geochemical Assessment of Trace Metal Distribution and Contamination
Environment and Pollution; Vol. 6, No. 1; 2017 ISSN 1927-0909 E-ISSN 1927-0917 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Geochemical Assessment of Trace Metal Distribution and Contamination
Altitude influence of elemental distribution in grass from Rila mountain. Dr. E. Nikolova, Dr. A. Artinyan, S. Nikolova INRNE - BAS XRF Laboratory
 Altitude influence of elemental distribution in grass from Rila mountain Dr. E. Nikolova, Dr. A. Artinyan, S. Nikolova INRNE - BAS XRF Laboratory I. Introduction The application of modern instrumental
Altitude influence of elemental distribution in grass from Rila mountain Dr. E. Nikolova, Dr. A. Artinyan, S. Nikolova INRNE - BAS XRF Laboratory I. Introduction The application of modern instrumental
Contamination of peat and moss samples 190 km from the Flin Flon Cu-Zn smelter, Canada: implications for exploration.
 Contamination of peat and moss samples 19 km from the Flin Flon Cu-Zn smelter, Canada: implications for exploration. Paul Polito, Kurt Kyser, Dave Lawie, Steve Cooke, Chris Oates Location of the Harmin
Contamination of peat and moss samples 19 km from the Flin Flon Cu-Zn smelter, Canada: implications for exploration. Paul Polito, Kurt Kyser, Dave Lawie, Steve Cooke, Chris Oates Location of the Harmin
The river basin-coastal zone continuum: heavy metal contents in stream and marine sediments, NW Aegean Sea (EUROCAT Project)
 The river basin-coastal zone continuum: heavy metal contents in stream and marine sediments, NW Aegean Sea (EUROCAT Project) Aristomenis P. Karageorgis 1, Nikolaos P. Nikolaidis 2 1 Institute of Oceanography,
The river basin-coastal zone continuum: heavy metal contents in stream and marine sediments, NW Aegean Sea (EUROCAT Project) Aristomenis P. Karageorgis 1, Nikolaos P. Nikolaidis 2 1 Institute of Oceanography,
Remote Sensing of Episodic Rainfall Events Affecting Coral Reefs in Southwestern Puerto Rico
 Remote Sensing of Episodic Rainfall Events Affecting Coral Reefs in Southwestern Puerto Rico Y. Detrés, R. Armstrong, E. Otero and R. García yasmin@cacique.uprm.edu University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez
Remote Sensing of Episodic Rainfall Events Affecting Coral Reefs in Southwestern Puerto Rico Y. Detrés, R. Armstrong, E. Otero and R. García yasmin@cacique.uprm.edu University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez
Optimal acid digestion for multi-element analysis of different waste matrices
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 06, 2018 Optimal acid digestion for multi-element analysis of different waste matrices Götze, Ramona; Astrup, Thomas Fruergaard Publication date: 2014 Document Version
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 06, 2018 Optimal acid digestion for multi-element analysis of different waste matrices Götze, Ramona; Astrup, Thomas Fruergaard Publication date: 2014 Document Version
Background Field program information Examples of measurements Wind validation for synthetic modeling effort
 Background Field program information Examples of measurements Wind validation for synthetic modeling effort How do complex fine-scale structure and processes in coastal waters dominated by pulsed-river
Background Field program information Examples of measurements Wind validation for synthetic modeling effort How do complex fine-scale structure and processes in coastal waters dominated by pulsed-river
Phase I System Characterization: Year 2 Study Plans
 Phase I System Characterization: Year 2 Study Plans Year I Physical and Biological Data Sets Quarterly Storm Sampling Four storm events with 8 sample stations at bridges Monthly Baseline Characterization
Phase I System Characterization: Year 2 Study Plans Year I Physical and Biological Data Sets Quarterly Storm Sampling Four storm events with 8 sample stations at bridges Monthly Baseline Characterization
INTRODUCTION. Climate
 INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
INTRODUCTION Climate Landslides are serious natural disasters in many parts of the world. Since the past 30 years, rainfall triggered landslides and debris flows had been one of the natural disasters of
Types of Wetlands. Tidal Systems
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems 1 COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands 2 Tidal Estuarine Wetland 3 Definition and Formation of Estuaries Estuary: : partially
Subtidal permanently flooded with tidal water. Irregularly exposed surface exposed by tides less often than daily
 Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Types of Wetlands Tidal Systems COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS Tidal Salt Marshes Tidal Freshwater Marshes Mangrove Wetlands Tidal Estuarine Wetland 1 Definition and Formation of Estuaries u Estuary : partially
Graphite Block Acid Digestion System ODLAB
 Graphite Block Acid Digestion System Table of contents 1. company introduction and product development background 2. Hot Plate and Graphite Block Acid Digestion and Microwave Digestion comparison 1 2 3
Graphite Block Acid Digestion System Table of contents 1. company introduction and product development background 2. Hot Plate and Graphite Block Acid Digestion and Microwave Digestion comparison 1 2 3
Assessment of heavy metals contamination in the Nile River water and adjacent sediments: A case study from Khartoum City and Nile River State, Sudan
 Assessment of heavy metals contamination in the Nile River water and adjacent sediments: A case study from Khartoum City and Nile River State, Sudan Magboul M. Sulieman a, *, Jamal T. Elfaki b, Mutwakil
Assessment of heavy metals contamination in the Nile River water and adjacent sediments: A case study from Khartoum City and Nile River State, Sudan Magboul M. Sulieman a, *, Jamal T. Elfaki b, Mutwakil
Trace metals geochemical background in soil in the Suape Port and Industrial Complex, Pernambuco Brazil
 The Sustainable City IX, Vol. 2 1721 Trace metals geochemical background in soil in the Suape Port and Industrial Complex, Pernambuco Brazil E. Santos de Lima & A. de Souza Moraes Centro de Tecnologia
The Sustainable City IX, Vol. 2 1721 Trace metals geochemical background in soil in the Suape Port and Industrial Complex, Pernambuco Brazil E. Santos de Lima & A. de Souza Moraes Centro de Tecnologia
Watershed concepts for community environmental planning
 Purpose and Objectives Watershed concepts for community environmental planning Dale Bruns, Wilkes University USDA Rural GIS Consortium May 2007 Provide background on basic concepts in watershed, stream,
Purpose and Objectives Watershed concepts for community environmental planning Dale Bruns, Wilkes University USDA Rural GIS Consortium May 2007 Provide background on basic concepts in watershed, stream,
Environmental Resources Management
 Figure 1: Concentration of Metals and Metalloid (Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, As; mean +SD) in sediment samples collected from Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry Monitoring for CMP 1 in January 2014. Figure 2: Concentration
Figure 1: Concentration of Metals and Metalloid (Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, As; mean +SD) in sediment samples collected from Pit Specific Sediment Chemistry Monitoring for CMP 1 in January 2014. Figure 2: Concentration
Trace elements. Geochemistry-Usually those with crustal abundance of < 100 ppm or ug/g or less
 The last assignment is for you to pick a paper discussing the biogeochemical cycling of a trace metal. You should provide some introduction to the metal you have chosen. You must discuss the movement or
The last assignment is for you to pick a paper discussing the biogeochemical cycling of a trace metal. You should provide some introduction to the metal you have chosen. You must discuss the movement or
Historical changes of heavy metals content and sequential extraction in a sediment core from the Gorgan Bay, Southeastern Caspian Sea
 Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 37(3), September 2008, pp. 267-272 Historical changes of heavy metals content and sequential extraction in a sediment core from the Gorgan Bay, Southeastern Caspian
Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 37(3), September 2008, pp. 267-272 Historical changes of heavy metals content and sequential extraction in a sediment core from the Gorgan Bay, Southeastern Caspian
