Creation Answers. In this issue...! Craters and Noah s Flood! Climate Change and. Who does this newsletter? Extinctions! ICR Opens Dallas Office
|
|
|
- Anthony Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Creation Answers Creation Education Materials, P.O. Box , Irving, TX Who does this newsletter? This newsletter is produced by Wayne Spencer on a Quarterly basis. Its purpose is to bring creation research within the reach of Christians and provide up-todate reliable information on creation issues. Wayne Spencer is a creation author and former teacher who has presented papers at the International Conference on Creationism and has published in various creation publications, such as the Creation Research Society Quarterly, Creation Ex Nihilo, TJ, and Origins (from the Biblical Creation Society, UK). This newsletter is meant to help people plug into creation resources and get informed about creation and evolution. It is provided free of charge on request. Using the free Adobe Acrobat Reader is necessary for viewing the newsletter. There are no restrictions in copying this newsletter or passing it on to others. To request to be placed on the list, send a request to Wayne at wayne@creationanswers.net. More information on Wayne Spencer s education and publications can be found on the creationanswers.net web site. You ll also find many other resources. In this issue...! Craters and Noah s Flood! Climate Change and Extinctions! ICR Opens Dallas Office A Personal Note from Wayne Spencer The Thousands Not Billions conference in Dallas was a great success. I wish that everyone getting this newsletter would have an opportunity to attend such a conference. The results of the RATE research project on radioisotope dating methods give Christians reason to have great confidence in Scripture. I would recommend the Thousands Not Billions books and videos and the RATE Premier Conference DVD set as well. This issue contains an article summarizing information published in several papers and articles that I have written. Some of these papers are available from my website. The article below addresses how we can understand the issue of impacts from space from a young age creation perspective. This newsletter is slightly late because of pressing matters that have demanded my time and attention. One was the Thousands Not Billions conference September 30th. The other was the death of my Mother, Alma Spencer. My Mother was 92 when she went to be with the Lord. She had lived a long life and was a good Christian example to the family. She raised three kids during the great depression in the 1930's and saw many changes in technology in her lifetime. To my Mother, there was no origins controversy, because she just believed the Bible. My mother never seemed to understand evolution when I tried to explain it to her. It was just too foreign to her Biblical mind set. Perhaps that is how we all should be. Wayne Spencer, M.S., Physics 1
2 Craters and Noah s Flood by Wayne Spencer Some think that eventually civilization as we know it will meet its end from a giant impact from space. For some years now scientists have been tracking small asteroids that come near the Earth. This is done in the hope of having warning if an object could strike the Earth. We know from Scripture that this is not how the world will end. But, this does not mean that impacts have not occurred or could not occur on Earth in the future. How do we understand the issue of impacts from space from a young age creation perspective? This is a question I have given significant thought. This article will summarize some information on this from my own technical papers. Much has been learned in recent years about the remnants of craters on Earth. There are about 170 known impact craters on the Earth today. More are being considered all the time as possible additions to this list. It is obvious that our Moon and many other objects in our solar system have many craters. In the evolutionary view of our solar system, many craters are said to have formed billions of years ago shortly after the solar system formed. Also, some impacts would have happened at random at other times. We know that comets and asteroids can undergo collisions occasionally. Comet SL- 9 was seen colliding with Jupiter in Some asteroids, between Mars and Jupiter, look roughly like a dumbbell because two asteroids collided and stuck together. Impacts on Earth are also believed by many scientists to be the cause of the extinction of the dinosaurs. The Alvarez Hypothesis For years now, the concept accepted by the scientific community on why the dinosaurs went extinct is that a large impact occurred. This is often called the Alvarez Hypothesis, after the scientists that proposed it. There is a site just off the coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico where there is a buried structure that may be an impact crater. It was argued for some years that this impact was large enough to cause the extinction of all dinosaurs at the end of the age of Earth history known as the Mesozoic Era, which is believed to be 65 million years ago. Then in recent years more study of this structure, called Chixulub, showed it to be a smaller crater than was initially thought. This has made it difficult for scientists believing the Alvarez Hypothesis to make a case that global extinctions could be caused by one impact. Thus, today, there are a variety of ideas put forward to explain the extinction of the dinosaurs. A few evolutionist scientists suggest volcanic eruptions, instead of an impact or impacts, caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. Some other scientists have tried to argue that it was not just one impact but several impacts occurring simultaneously in various locations around the world that did it. Evolutionists themselves have debated and argued about how an impact or impacts would kill the dinosaurs. First, why would only dinosaurs be killed by an impact? Impacts would kill in a fairly indiscriminate manner; they would not kill only dinosaurs. Second, the effects of an impact do not last very long. The initial blast and surface effects last less than an hour. But dust and ash can be ejected high into the stratosphere by a large impact. It is believed this could cause what has sometimes been called impact winter. The dust from vaporized rock would block some of the sunlight and lower the temperature felt at the Earth s surface. There are a variety of other possible effects of a large impact, but they are not global, but only local effects that would be limited in area. (Examples would include acid rain or forest fires.) Impacts into the ocean would vaporize both water and ocean sediments. It is the effects of this 2
3 ejecta in the atmosphere that would last longest, of all the effects of an impact. Yet all the atmospheric effects would be over in a few months, after the dust has had time to fall to the surface. It is unlikely that the dust put into the atmosphere would cause global extinctions of just dinosaurs. Many animals could survive such conditions and because plants could recover from it, some dinosaurs could recover from it as well. In fact, the fossil record does show some dinosaur fossils later than the end of the Mesozoic. The Bible and Dinosaurs An impact from space is thus not a good explanation for what made the dinosaurs die out. A Biblical view of Earth history however provides a logical explanation. Biblically, dinosaurs are treated as just another group of animals. After Noah s Flood, there would have been climate changes and there is scientific evidence that an ice age followed the Flood. The book of Job in the Old Testament makes reference to ice as well, which may allude to the ice age. The climate changes after the Flood provide a good explanation for something that could cause dinosaurs to die because of harsh weather, lack of food, etc. Yet, it allows for the possibility that a few dinosaurs could survive in a few remote places. There have occasionally been reports throughout history of people seeing or encountering animals that could have been reptiles like dinosaurs. Some of these reports may be exaggerations or not accurate, but some could be true. There are even a few evolutionists who believe there are a few extinct reptiles like dinosaurs alive in remote jungles today. Earth Craters The term crater does not always refer to something formed by an impact from space. Sometimes volcanoes are said to form craters. A round depression or whole in rock can be formed from a variety of geological processes. Thus, a volcanic explanation needs to be ruled out before calling something an impact crater. On an object like our Moon, because there is currently no volcanic activity, craters can normally be assumed to be from impacts. The impact origin of lunar craters has also been confirmed in other ways from our study of the Moon. On Earth, impact craters are often hard to find and sometimes hard to recognize. On Earth many craters have been buried, melted, moved, or otherwise modified by various geological processes. But, scientists have found some reliable indicators of impacts craters on Earth. First, there are special minerals called shocked quartz, or other shocked minerals like stishovite, and coesite that are good indicators of an impact. These are good indicators because they can only form at very extreme pressures, pressures even much greater than inside volcanoes. So, when these minerals are found at the surface it has to be from a high speed impact. Another type of rock that is a good indicator of impact is what s called a shatter cone. A shatter cone is an interesting thing that the heat and pressure of an impact can do to rock. It makes the rock fracture in the form of a cone and the rock takes on an internal structure that is like having cones inside of cones. Shatter cones are found near some large craters. There are other clues that point to something being an impact crater or the remnant of a crater. Craters tend to take on certain shapes if they have not been modified too much by geological processes following the impact. So, the shape of the crater bowl structure, its proportions and other characteristics can suggest its an impact. There are also sometimes predictable amounts of melted rock or breccia in the floor of the crater or around it. Breccia is a type of rock that is made up of many fragments of broken rock (and sometimes fossils) that get mixed together and buried in a muddy cement like material. 3
4 There can also be small objects that suggest something is an impact. Meteorites can suggest an impact but meteorites are not always found near craters. Meteorites are objects that fall from space and remain intact long enough to hit the Earth s surface. Small meteorites fall through Earth s atmosphere every day, and more of them fall at certain times of the year, called meteor showers. These showers are times when Earth crosses the orbits of certain comets. Meteorites are recognized mainly by their unique composition and the fact that they have been severely heated in passing through the atmosphere. Meteorites have higher amounts of certain metals than many Earth rocks, such as nickel and some rare metals. Tektites are very small objects that sometimes are evidence of an impact. Tektites are often a few millimeters in size and can come from either volcanic eruptions or impacts. They are essentially small bits of mineral or metal that have been melted and ejected into the atmosphere. Then they cool off and fall to the surface again and often get mixed with sediments. There are certain places around the Earth known as tektite strewn fields, where tektites are known to be common. Some tektites have shock minerals in them and have a composition similar to meteorites. Even if the crater has been destroyed there can be tektites and other evidence of the material ejected from an impact crater. When craters are found throughout many sedimentary rock layers that were formed by Noah s Flood, this suggests that impacts were occurring during the Flood. It does leave much research that needs to be done to unravel clues that Earth crater sites give us about how the Flood took place. Two craters I have written about are the Sudbury crater in Ontario and the Chesapeake Bay crater in Chesapeake Bay, Virginia. The Sudbury crater is very interesting. It is located in rock classified as Precambrian; this rock would have an evolutionary age of 1.85 billion years. Sudbury is known as a location where various metals such as zinc and copper are mined. These metals are present because of how the impact made hot water from below the Earth s crust able to come near the surface through deep fractures, bringing dissolved metals with it. The Sudbury crater is covered by over a mile of various sedimentary and other rock layers. The Sudbury structure is one of the largest craterremnants on Earth. Some of it has been destroyed but originally it would have been about 220 km in diameter. Some of the materials on top of it require that it was under water after it formed. The Sudbury impact thus must have taken place early in the Flood or perhaps near the beginning of the event. Another important Earth crater is located under Chesapeake Bay, Virginia. Unlike the well-known crater in Arizona, the Chesapeake Bay crater is buried and not visible from the surface. It is also a large one, being over 50 miles in diameter. In the evolutionary time scale it would be dated at 35.5 million years. Michael Oard and myself wrote about this crater in the Creation Research Society Quarterly (Dec. 2004). You could fit two states of Rhode Island in the area encompassed by this crater. This crater appears to have formed during Noah s Flood, probably while waters were running off the continent. Under the Chesapeake crater are igneous and metamorphic rocks that could be either from creation or the Flood. Then there are some thick sedimentary rock layers that were present prior to the impact. Some of these are limestones, which have to form under water. Then there is a thick layer of breccia that fills the crater called the Exmore Breccia with other thinner sedimentary layers on top of it. The Exmore layer contains a wide variety of materials including marine fossils, wood and gravel from the continent, pollen, and boulders up to 30 feet in size. The Chesapeake Bay impact occurred in water 4
5 and a large tsunami would have been generated by it. It would also have vaporized large amounts of water. The Flood may provide the best explanation for why the breccia is only found along the Virginia coastline and not all over Virginia. Strong currents were probably rushing off the continent as the impact occurred. This would have caused the crater to fill up with a variety of sediments containing both marine material and continental material. Michael Oard and myself argue that this impact would be placed in the mid-to-late Flood time frame. Some creationists might take the view that it would actually be post- Flood. But at any rate the evidence can be accounted for in a Biblical approach to Earth history. Creationists still debate where the objects came from that would have produced Earth s craters. I have leaned toward the view that most of the craters formed during and after the Flood. I suspect there was some kind of event that led to widespread impacts on many objects in the solar system around the time of the Flood. Other creation scientists may prefer to say some craters formed during the creation week or after mankind s Fall into sin, then there were more around the time of the Flood. There may be a number of possibilities for how this may have happened. As Christians we do not have to accept billions of years (which compromises Biblical inerrancy regarding times and dates) to deal honestly with the facts of science. There are always options other than the naturalistic evolutionary ideas. Old age evolutionary ideas actually make a number of things about the solar system hard to explain. We can rationally accept the Biblical time scale for both the Earth and the solar system. Creation scientists continue to discuss and debate these issues. As so much is being learned about the solar system, this is an exciting time to be a creationist. Climate Change and Extinctions Evolutionary scientists struggle explaining extinctions in Earth history. The extinction of the dinosaurs is not the only extinction mystery to evolutionists. Evolutionary Earth scientists believe in many ice ages throughout Earth history (creation scientists generally believe in just one ice age following Noah s Flood). Evolutionists try to argue that the extinction of various animals could correspond to either the beginning or the end of an ice age. What evidence is there to make such an argument? There is a great deal of research on ice cores which measure oxygen isotopes from glaciers. The oxygen isotope data is believed to indicate variations in annual temperatures. But evolutionists do not take account of the many effects possible from a global Flood and its aftermath. Creationists can explain the ice cores better than evolutionists. Studies of ice cores in recent years have pointed to rapid climate changes. Evolutionists have difficulty explaining such rapid changes in their long age time scale. From an evolutionary perspective, there is not an adequate mechanism to support the significant rapid changes in climate. But, from a creationist perspective, there are a number of possibilities for explaining such changes. They are just what would be expected as consequences of a global Flood. In a creationist perspective of Earth history, the ice age could generate thick ice layers from the climate effects of the post-flood period. Volcanoes were a key factor in the ice age as well. These eruptions after the Flood could explain some of the ice core data in a time frame much shorter than the long periods of time supposed by evolutionists. Layers that are often interpreted as annual seasonal deposition in the ice are better explained as changes due to storm surges and varying amounts of volcanic dust and ash in the atmosphere. For more information on Noah s Flood and how it would cause an ice age, see the 5
6 September 2005 issue of the Creation Answers newsletter (available on the creationanswers.net web site). Also, there are a number of books and articles in creation publications from Michael Oard and Larry Vardiman that address these issues in detail. They have done most of the original research on ice age climate issues. ICR Opens Dallas Office The Institute for Creation Research (ICR) has a new presence in Dallas, Texas. The Thousands Not Billions conference of September 30 th in Dallas corresponded with an Open House event for ICR s new Dallas office. Called the Henry M. Morris Center for Christian Leadership, the office will mark a new chapter in ICR s ministry. The Dallas office will house a small group of staff that will focus on ICR s internet ministries and reaching Christian leaders. The Morris Center has reproduced the office of the late Henry M. Morris. It also has space for offices and at least one classroom. ICR has plans to offer a new web-based course for Christian leaders on creationism. Henry Morris III, son of the late Henry M. Morris, lives in the Dallas area and will be the Director of the Dallas office. The address to the Morris center is 1806 Royal Lane, Dallas, TX Below are two pictures from the new Morris center in Dallas. The first is the outside of the building and the other is a mural seen when you walk in the lobby. 6
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
5/3/17. Extinction of the Dinosaurs. Extinction of Dinosaurs - Causes. #40 Meteorite Impacts III - Dinosaur Extinction, Future Risk, Mitigation
 Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Grade 1.) 2.) 3.) 3.7 (EVOLUTION & EXTINCTION) HISTORY OF THE EARTH CATALYST
 SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 12: The Mesozoic Dies
 Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition Test Bank Chapter 03 - Near-Earth Objects
 Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
Where do they come from?
 Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
Question #1: What are some ways that you think the climate may have changed in the area where you live over the past million years?
 Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Creation vs. Evolution
 Creation vs. Evolution The Biblical Creation Model 1. Special Creation of all things by God in six solar days. 2. The Curse on all things because of sin. All things are dying. 3. The global Flood of Noah
Creation vs. Evolution The Biblical Creation Model 1. Special Creation of all things by God in six solar days. 2. The Curse on all things because of sin. All things are dying. 3. The global Flood of Noah
Causes of Extinction
 Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE
 INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
The History of Life on Earth
 8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
Unit 10 Lesson 2 What Was Ancient Earth Like? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
NOTES 1. Fossils. The BIG Idea Rocks, fossils, and other types of natural evidence tell Earth s story.
 Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Teacher Background. Impact! Down to Earth KS 3&4
 Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice. Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto
 Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
Biodiversity Through Earth History. What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events?
 Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes
 3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins
 9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins About Earth: Earth was formed about 4.6 billion years ago! The first life on earth appeared about 4 billion years ago Life started out as small, single-celled organisms
9.1- Earth Forms and Life Begins About Earth: Earth was formed about 4.6 billion years ago! The first life on earth appeared about 4 billion years ago Life started out as small, single-celled organisms
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5
 College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
What Happened to the Dinosaurs?
 A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
August 20, EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines th Street Golden, CO Dear EPICS 1 Teams,
 Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
1. What is the definition of uniformitarianism? 2. What is the definition of organic? 4. What is the definition of inorganic?
 Earth Science Unit 3- History of the Earth Knowledge Packet Learning Target 3B: Have you ever thought about the history of the Earth? No, well you should have because it s pretty cool. Things like mountain
Earth Science Unit 3- History of the Earth Knowledge Packet Learning Target 3B: Have you ever thought about the history of the Earth? No, well you should have because it s pretty cool. Things like mountain
Name Test Date Hour. forms that lived only during certain periods. abundant and widespread geographically. changes to the surface of Earth.
 Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#3 - Notebook Earth s History LEARNING TARGETS I can explain the lack of evidence about the Precambrian Time. I can describe possible causes for the mass extinction in
Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#3 - Notebook Earth s History LEARNING TARGETS I can explain the lack of evidence about the Precambrian Time. I can describe possible causes for the mass extinction in
GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler
 When Worlds Collide GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. Introduction This talk is about impacts between objects
When Worlds Collide GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. Introduction This talk is about impacts between objects
The Cycling of Matter. Day 1
 The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
GLY August, Ms. Nelda Breedt. Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth.
 Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy
 Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Asteroids: Introduction
 Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Where did all the dinosaurs go?
 Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Resources for Treasure Hunt In Earth s Attic Try This!
 Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past
 FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science. Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. Problem: What caused the huge ocean waves?
 Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More
 12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8
 The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Moon. Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon
 The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
Mystery of odd Wisconsin rock formations solved
 Mystery of odd Wisconsin rock formations solved Juliet Williams,ÊAssociated Press April 27, 2004CRATER0427 ROCK ELM, WIS. -- The muddy brown hills and rolling farmland at first look like typical Wisconsin.
Mystery of odd Wisconsin rock formations solved Juliet Williams,ÊAssociated Press April 27, 2004CRATER0427 ROCK ELM, WIS. -- The muddy brown hills and rolling farmland at first look like typical Wisconsin.
Good Day everyone! Today is Wednesday 10/4/17
 Good Day everyone! Today is Wednesday 10/4/17 Agenda: 1. Warm Up 2. Video: Intro to the Geologic Time Scale 3. Notes: Geologic Time Scale a. How the Geologic Time Scale is Organized b. Principle of Uniformitarianism
Good Day everyone! Today is Wednesday 10/4/17 Agenda: 1. Warm Up 2. Video: Intro to the Geologic Time Scale 3. Notes: Geologic Time Scale a. How the Geologic Time Scale is Organized b. Principle of Uniformitarianism
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle
 Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit?
 Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth
 The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
Chapter 1: Earth as a System
 Chapter 1: Earth as a System Science is: Any system of knowledge which tries to observe, identify, understand and describe the nature of the Universe in whole or part. Science explains and predicts the
Chapter 1: Earth as a System Science is: Any system of knowledge which tries to observe, identify, understand and describe the nature of the Universe in whole or part. Science explains and predicts the
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide
 Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center
 Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center Section 1: Introduction 1. What percentage of the Earth cannot be accessed by humans? 99% 2. True or False: It would be easier to invent something to travel to the
Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center Section 1: Introduction 1. What percentage of the Earth cannot be accessed by humans? 99% 2. True or False: It would be easier to invent something to travel to the
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
-Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher
 -Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher Formation Overview All explanations as to how the solar system was formed are only
-Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher Formation Overview All explanations as to how the solar system was formed are only
Scales Jacques Swartz
 Scales Jacques Swartz One way or another, all the events you can recall have an order to them. Or maybe it s more accurate to say: You can give order to your own history any way you like. You can think
Scales Jacques Swartz One way or another, all the events you can recall have an order to them. Or maybe it s more accurate to say: You can give order to your own history any way you like. You can think
Do Now: Vocabulary: Objectives. Vocabulary: 1/5/2016. Wegener? (Can they move?) the idea that continents have moved over time?
 Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Chapter 3 Checkpoint 3.1 Checkpoint 3.2 Venn Diagram: Planets versus Asteroids Checkpoint 3.3 Asteroid Crashes the Moon?
 Chapter 3 Checkpoint 3.1 Which characteristics are true of both planets and asteroids? a) They are approximately spherical in shape. b) There are thousands of examples. c) They formed 1 to 2 billion years
Chapter 3 Checkpoint 3.1 Which characteristics are true of both planets and asteroids? a) They are approximately spherical in shape. b) There are thousands of examples. c) They formed 1 to 2 billion years
National Science Standards Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8
 Unifying Concepts and Processes Geology Geologic Changes The Dynamic Earth Water and Water Systems National Science Standards Systems, order, and organization Evidence, models, and explanation Change,
Unifying Concepts and Processes Geology Geologic Changes The Dynamic Earth Water and Water Systems National Science Standards Systems, order, and organization Evidence, models, and explanation Change,
Section 1: How Did Life Begin? Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth. Section 2: The Age of Earth
 Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Chapter 19: History of Life on Earth Section 1: How Did Life Begin? I. The Basic Chemicals of Life A. 1920s B. Earth s early oceans contained large amounts of organic molecules C. Molecules formed spontaneously
Astronomy 3. Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
 Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Introduction to Landform Study Chapter 13
 Introduction to Landform Study Chapter 13 Geomorphology The study of the characteristics, origin, and development of landforms 58 million square miles of land 7 continents Wide latitudinal range and environmental
Introduction to Landform Study Chapter 13 Geomorphology The study of the characteristics, origin, and development of landforms 58 million square miles of land 7 continents Wide latitudinal range and environmental
GCSE ready intervention tasks
 7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
Introduction. Background
 Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
I. Introduction: II. Background:
 I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
How the Earth was formed
 How the Earth was formed Short Answer: (2 points a piece) 1) Who was the man that stated the Earth was 6000 yrs old? 2) Hutton determined that this age was incorrect, what lead him to a much later date?
How the Earth was formed Short Answer: (2 points a piece) 1) Who was the man that stated the Earth was 6000 yrs old? 2) Hutton determined that this age was incorrect, what lead him to a much later date?
STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Non-fiction: Deep-Sea Detectives
 Non-fiction: Deep-Sea Detectives Deep-Sea Detectives A couple of years ago, a volcano erupted more than 8,000 feet underwater. Today, researchers 500 miles off the coast of Mexico are getting a close look
Non-fiction: Deep-Sea Detectives Deep-Sea Detectives A couple of years ago, a volcano erupted more than 8,000 feet underwater. Today, researchers 500 miles off the coast of Mexico are getting a close look
GO ON. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1.
 d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
Terrestrial Planetary Atmospheres
 Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
Earth. Physical Properties of Earth kg. Average Density g/cm 2. Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s o C to 50 o C. Surface Temperature
 Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32. Paleoclimate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
B. Phylogeny and Systematics:
 Tracing Phylogeny A. Fossils: Some fossils form as is weathered and eroded from the land and carried by rivers to seas and where the particles settle to the bottom. Deposits pile up and the older sediments
Tracing Phylogeny A. Fossils: Some fossils form as is weathered and eroded from the land and carried by rivers to seas and where the particles settle to the bottom. Deposits pile up and the older sediments
Back to the Big Question
 5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
ADVENTURES IN WATER DEVELOPED BY LOUISVILLE WATER COMPANY
 ADVENTURES IN WATER DEVELOPED BY LOUISVILLE WATER COMPANY Tunneling for Water explains the science behind a first-of-its-kind project in the world! Louisville Water Company is the first water utility
ADVENTURES IN WATER DEVELOPED BY LOUISVILLE WATER COMPANY Tunneling for Water explains the science behind a first-of-its-kind project in the world! Louisville Water Company is the first water utility
Vocabulary and Section Summary B
 The Study of Earth s History After you finish reading the section, try this puzzle! Use the clues given to fill in the blanks below. Then, copy the numbered letters into the corresponding boxes below to
The Study of Earth s History After you finish reading the section, try this puzzle! Use the clues given to fill in the blanks below. Then, copy the numbered letters into the corresponding boxes below to
(continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
What is Earth Science? Earth science is the branch of science dealing with the constitution of the earth and its atmosphere.
 What is Earth Science? Earth science is the branch of science dealing with the constitution of the earth and its atmosphere. 1 2 The Branches of Earth Science Major Astronomy (celestial objects, space,
What is Earth Science? Earth science is the branch of science dealing with the constitution of the earth and its atmosphere. 1 2 The Branches of Earth Science Major Astronomy (celestial objects, space,
Guided Notes Geologic History
 Guided Notes Geologic History Relative Age Sequence of Events Correlation Techniques Volcanic Ash Markers Index Fossils Geologic Time Scale Evolution Radioactive Dating 9) How has Earth changed over time?
Guided Notes Geologic History Relative Age Sequence of Events Correlation Techniques Volcanic Ash Markers Index Fossils Geologic Time Scale Evolution Radioactive Dating 9) How has Earth changed over time?
Fossils. Who studies fossils? How do fossils form? Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of living things.
 Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
The Scope of Earth Science
 Earth science Earth Science The Scope of Earth Science The field of Earth Science can be broken into four major areas of specialization: astronomy, meteorology, geology, and oceanography. 1. Astronomy
Earth science Earth Science The Scope of Earth Science The field of Earth Science can be broken into four major areas of specialization: astronomy, meteorology, geology, and oceanography. 1. Astronomy
Geologic History Unit Notes. Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent
 Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
Activity 1-2: Origin of the Earth
 Earth Science 11 Name: Block: Activity 1-2: Origin of the Earth Read the following passage, and then answer the questions at the end: Where Earth Science Begins: The Solar System Where shall the study
Earth Science 11 Name: Block: Activity 1-2: Origin of the Earth Read the following passage, and then answer the questions at the end: Where Earth Science Begins: The Solar System Where shall the study
SU230R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
 Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Hayes SU230R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA OUR SOLAR SYSTEM Fast Facts & Dazzling Data Our Solar System This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc.,
Lecture 20. Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p )
 Lecture 20 Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p.158-170) end of last ice-age; begin civilization beginning of modern era of ice-ages asteroid
Lecture 20 Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p.158-170) end of last ice-age; begin civilization beginning of modern era of ice-ages asteroid
Earth & Space. Learning Target:
 Earth & Space Learning Target: Most of the cycles and patterns of motion between the Earth and sun are predictable. You understand this when you know: 1) 1 Revolution of the Earth takes approximately 365
Earth & Space Learning Target: Most of the cycles and patterns of motion between the Earth and sun are predictable. You understand this when you know: 1) 1 Revolution of the Earth takes approximately 365
NARRATOR: Welcome to Astronomy Behind the Headlines, a podcast by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific.
 ASTRONOMY BEHIND THE HEADLINES A podcast for Informal Science Educators from the Astronomical Society of the Pacific with guest Dr. Peter Jenniskens of the SETI Institute Written by Carolyn Collins Petersen
ASTRONOMY BEHIND THE HEADLINES A podcast for Informal Science Educators from the Astronomical Society of the Pacific with guest Dr. Peter Jenniskens of the SETI Institute Written by Carolyn Collins Petersen
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts. Chapter 12 Review Clickers
 Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Review Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets: Their Natures, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroids a) are rocky and small typically the size of a grain of rice or
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
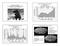 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
2nd Grade Changing of Earth
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Weathering and Erosion
 Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered how it was shaped? The geologic features that help define the world are still being shaped by the natural processes of weathering, erosion, and
Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered how it was shaped? The geologic features that help define the world are still being shaped by the natural processes of weathering, erosion, and
