DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 1 - PYROCLASTIC TERMINOLOGY. The volcaniclastic terminology used in this paper largely follows that of Fisher
|
|
|
- Jasper Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DATA REPOSITORY ITEM 1 - PYROCLASTIC TERMINOLOGY The volcaniclastic terminology used in this paper largely follows that of Fisher and Schmincke (1984) and Heiken and Wohletz (1985). A deposit made of >75% pyroclasts with pyroclasts <2 mm in size is referred to as ash (or tuff, if consolidated); if the pyroclasts are 2-64 mm, they are referred to as lapilli (lapillistone); and if the pyroclasts are >64 mm, they are referred to as blocks (breccia). Mixtures are referred to as lapilli tuff or tuff breccia. The term "pyroclastic flow" refers to a highly-concentrated pyroclastic density current composed entirely of freshly-erupted pyroclastic debris (e.g. glass shards, crystals, pumice and rock fragments); sensu strictu the fluid phase is hot gases, but since the temperature of emplacement can rarely be determined in ancient settings, we use the term sensu lato, i.e., regardless of emplacement temperature. Pyroclastic flow deposits are predominantly massive (i.e. nonstratified) and poorly sorted (Freundt et al., 2000). Evidence for hot emplacement may include welding (at very high temperatures ~500 C), carbonized wood fragments, occurence of columnar jointing (not discernable in drill core), or occurence of perliticly fractured clasts suggesting quenching of glass in situ. Welding must be documented as sintering of shards recognizable in thin section by petrographic or scanning electron microscopes, and must not be confused with pumice flattening, which can occur diagenetically (Kokelaar and Busby, 1992). Subaqueous pyroclastic flow deposits are the subaqueous equivalent of subaerial pyroclastic flow deposits (Fiske, 1963; Fiske and Matsuda, 1964; Gibson et al., 2000).
2 Several workers have proposed that the term "subaqueous pyroclastic flow" be applied only to hot, gas-supported density currents (Cas and Wright 1987, 1991; Stix, 1991; McPhie et al., 1993); subaqueous water-supported pyroclastic flows were termed "volcaniclastic mass flows". This distinction cannot be applied to most ancient pyroclastic flow deposits, where one can rarely prove whether the flow was above or below 100 C at deposition (Busby-Spera, 1986; Gibson et al, 2000). Furthermore, this nomenclature does not attempt to seperate eruptive-fed density currents from those stemming from much later resedimentation (Kano, 1996). I agree with Gibson et al. (2000) that the nomenclature of Cas and Wright (1991) masks the origin of subaqueous pyroclastic flows as the direct product of an eruption. Most volcanic eruptions on Earth take place under water, and it is important to name their products accordingly where they are recognized. A deposit that is predominantly massive (i.e. lacking traction structures), nongraded, nonsorted, thick, and composed entirely of fresh pyroclastic debris is highly likely to be the direct result of an eruption (i.e it is a primary deposit), whether or not one can determine temperature of emplacement. A more complete discussion of terminology will be warranted only when the nature of submarine pyroclastic volcanology is better understood (Fiske et al., 1998). Meanwhile, a clear statement of useage of terms is all that is needed. Pyroclastic flows may be classified according to the degree of vesiculation shown by essential fragments (Wright et al., 1981; Heiken and Wohletz, 1985). The term "ignimbrite" is used for pumiceous, ash-rich pyroclastic flow deposits, which may or may not be welded; some other workers use the term "ash-flow tuff" for these instead (Freundt et al., 2000). In this paper, we use the term "ignimbrite" for the deposits of pumiceous
3 pyroclastic flows. Ignimbrites result from explosive eruptions and are commonly fed by collapse of Plinian eruption columns. Block-and-ash flow deposits, in contrast, are composed of nonvesicular to poorly vesicular juvenile lithic to glassy fragments in an ash matrix. They commonly result from gravitational or explosive collapse of silicic lava domes (Fisher and Heiken, 1982; Fink and Anderson, 2000). Less commonly, block-andash flows form by collapse of Vulcanian eruption columns of intermediate composition (Freundt et al., 2000). The components (i.e. glass shards, crystals, etc) of dominantly massive pyroclastic flow deposits may also be present in more stratified or cross-stratified, better sorted deposits that may show grading or partial Bouma sequences. These are referred to here as tuff turbidites, and were probably transported by high density or low density turbidity currents with interstitial water. Finally, subaqueous fallout tuffs are accumulations of pyroclastic material that settled through water; sorting and stratification are greatly accentuated by this settling process (Fisher, 1964). Autoclastic fragments are defined as those resulting from "mechanical friction or gaseous explosion during movement of lava, or gravity crumbling of spines and domes" (p. 89, Fisher and Scmincke, 1984). Autobreccias are coarse, dominantly "stony" (nonglassy) aggregates with minimal fine-grained debris, and they may form substantial proportions of lavas (Macdonald, 1972). Rittman (1962) introduced the term "hyaloclastite" for rocks composed of glass produced by nonexplosive spalling and granulation of pillow rinds, but the term has since been expanded to include all vitroclastic (i.e. glassy) tephra produced by the interaction of water and hot magma or lava (Fisher and Schmincke, 1984). Thus, hydroclastic
4 processes have been defined as those causing breakup of magma by interaction with external water, including explosive comminution and nonexplosive granulation. Other workers, in contrast, restrict the term "hyaloclastite" to non-explosive or midly explosive granulation of volcanic glass due to quenching (thermal shock) on contact with water (Heiken and Wohletz, 1985; Yamagishi, 1987). These and other workers distinguish hyalotuffs from hyaloclastites on the basis of greater inferred explosivity (Honnorez and Kirst, 1975). REFERENCES Busby-Spera, C. J., 1986, Depositional features of rhyolitic and andesitic volcaniclastic rocks of the Mineral King submarine caldera complex, Sierra Nevada, California: Jour. Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 27, p Cas, R.A.F., and Wright, J.V., Volcanic Successions: Modern and Ancient: London: Allen and Unwin, Cas, R.A.F., and Wright, J.V., 1991, Subaquoeus pyroclastic flows and ignimbrites: an assessment: Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 53, p Fink, J.H., and Anderson, S.W., 2000, Lava domes and coulees: in, H. Sigurdsson, (ed), Encyclopoedia of Volcanoes: Academic Press, San Diego, p Fisher, R.V., 1964, Maximum size, median diameter, and sorting of tephra: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 69, p Fisher, R.V., 1964, Maximum size, median diameter, and sorting of tephra: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 69, p Fisher, R.V., and Schmincke, H.-U., 1984, Pyroclastic Rocks; Springer-Verlag, New York, 472 pp. Fiske, R.S., 1963, Subaqueous pyroclastic flows in the Ohanapecosh Formation, Washington. Geological Society of America Bulletin, v. 74, p Fiske, R.S.., and Matsuda, T., 1964, Submarine equivalents of ash flows in the Tokiwa formation, Japan. American Journal of Science v. 262, p Fiske, R.S., Cashman, K.V., Shibata, A., and Watanabe, K., 1998, Tephra dispersal from Myojinsho, Japan, during its shallowe submarine eruptions of : Interpretations based on a new bathymetric map: Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 59, p
5 Freundt, A., Wilson, C.J.N., and Carey, S.N., 2000, Ignimbrites and block-an-ash flow deposits: in, H. Sigurdsson, (ed), Encyclopoedia of Volcanoes: Academic Press, San Diego, p Gibson, H.L., Morton, R.L., and Hudak, G.J., 2000, Submarine volcanic processes, deposits and environments favorable for the location of volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits, in, C.T. Barrie and M. D. Hannington (eds), Volcanic-Associated Massive Sulfide Deposits: Processes and Examples in Modern and Ancient Settings: Reviews in Economic Geology, v. 8, p Heiken, G., and Wohletz, K., 1985, Volcanic Ash: University of California Press, Berkeley, California, 246 pp. Honnorez, J., and Kirst, P., 1975, Submarine basaltic volcanism: morphometric parameters for discriminating hyaloclastites from hyalotuffs: Bulletin Volcanologique, v. 34-3, p Kano, K., 1996, A Miocene coarse volcaniclastic mass-flow deposit in the Shimane Peninsula, SW Japan: product of a deep submarine eruption? Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 58, p Kokelaar, B. P., and Busby C. J., 1992, Subaqueous explosive eruption and welding of pyroclastic deposits: Science, Full Article, v. 257, p Macdonald, G.A., 1972, Volcanoes. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Emglewood Cliffs, N.J., 510 pp. McPhie, J., Doyle, M., Allen, R., 1993, Volcanic Textures: a Guide to the Interpretation of Textures in Volcanic Rocks: Tasmania: Pongrats. Rittman, A., 1962, Volcanoes and their activity. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 305 pp. Stix, J., 1991, Subaqeous, intermediate to silicic-composition explosive volcanism: a review. Earth Science Review, v. 31, p Wright, J.V., Self, S. and Fisher, R.V., 1981, Towards a facies model for ignimbriteforming eruptions. In: S Self and RSJ Sparks (Eds) Tephra Studies. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp Yamagishi, H., 1987, Studies on the Neogene subaqueous lavas and hyaloclastites in Soutwest Hokkaido: Report of the Geolgical Survey of Hokkaido, no. 59, 117 pp.
TRANSPORT AND EMPLACEMENT OF IGNIMBRITES AND RESEDIMENTED VOLCANICLASTICS FROM GUTÂI MTS., EASTERN CARPATHIANS, ROMANIA
 STUDIA UNIVERSITATIS BABEŞ-BOLYAI, GEOLOGIA, XLIX, 1, 2004, 65-73 TRANSPORT AND EMPLACEMENT OF IGNIMBRITES AND RESEDIMENTED VOLCANICLASTICS FROM GUTÂI MTS., EASTERN CARPATHIANS, ROMANIA ALEXANDRINA FÜLÖP
STUDIA UNIVERSITATIS BABEŞ-BOLYAI, GEOLOGIA, XLIX, 1, 2004, 65-73 TRANSPORT AND EMPLACEMENT OF IGNIMBRITES AND RESEDIMENTED VOLCANICLASTICS FROM GUTÂI MTS., EASTERN CARPATHIANS, ROMANIA ALEXANDRINA FÜLÖP
WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS. Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel
 WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS mechanisms hot magma/ hot rock + water pyroclasts + steam rapid expansion of gas fragmentation of magma + wall rock external
WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS mechanisms hot magma/ hot rock + water pyroclasts + steam rapid expansion of gas fragmentation of magma + wall rock external
The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform
 The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform Charity J. Southworth Indiana University, 2012 Abstract The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff that was created 760,000 years
The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform Charity J. Southworth Indiana University, 2012 Abstract The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff that was created 760,000 years
Calderas. Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera m. 500 m. 5 km. (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003)
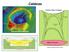 Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
Volcanic Plumes. JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
 Volcanic Plumes R. S. J. SPARKS University of Bristol, UK M. I. BURSIK State University of New York, USA S. N. CAREY University of Rhode Island, USA J. S. GILBERT Lancaster University, UK L. S. GLAZE NASA/Goddard
Volcanic Plumes R. S. J. SPARKS University of Bristol, UK M. I. BURSIK State University of New York, USA S. N. CAREY University of Rhode Island, USA J. S. GILBERT Lancaster University, UK L. S. GLAZE NASA/Goddard
Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits
 Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits EAS 458 Volcanology Introduction We have seen that physics is useful in understanding volcanic processes, but physical models must be constrained by and
Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits EAS 458 Volcanology Introduction We have seen that physics is useful in understanding volcanic processes, but physical models must be constrained by and
Engineering Geology. Igneous rocks. Hussien Al - deeky
 Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption
 The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption Eyal Goldmann Division of Natural Sciences, El Camino College, Torrance, CA, 90506 Prepared for Geology 1 at El Camino College Fall 2009 1 1. Introduction
The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption Eyal Goldmann Division of Natural Sciences, El Camino College, Torrance, CA, 90506 Prepared for Geology 1 at El Camino College Fall 2009 1 1. Introduction
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism
 Find the Face Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism Ocean Ridges Continental Rifts Subduction Zones: Continental Oceanic Back Arc Basins Hot Spots Plumes Cinder Cones Composite Volcanoes Shield VolcanoesCinder
Find the Face Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism Ocean Ridges Continental Rifts Subduction Zones: Continental Oceanic Back Arc Basins Hot Spots Plumes Cinder Cones Composite Volcanoes Shield VolcanoesCinder
GEOS 606 Physical Volcanology GEOS 606 CRN credits
 GEOS 606 Physical Volcanology GEOS 606 CRN 74060 3 credits September 1th December 17 th, 2011 Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays MWF 10:30-11:30 Irving 208 and Elvey 101 Dr. Jonathan Dehn office: WRRB 108G,
GEOS 606 Physical Volcanology GEOS 606 CRN 74060 3 credits September 1th December 17 th, 2011 Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays MWF 10:30-11:30 Irving 208 and Elvey 101 Dr. Jonathan Dehn office: WRRB 108G,
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways.
 A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
A Rock is A group of minerals that have been put together in several different ways. Depending on how they are put together, rocks are classified as: 1. Sedimentary 2. Igneous 3. Metamorphic Sedimentary
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Alison M. Raos. Jocelyn McPhie. Centre for Ore Deposit Research and the School of Earth Sciences, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia
 The Submarine Record of a Large-Scale Explosive Eruption in the Vanuatu arc: ~1 Ma Efaté Pumice Formation Alison M. Raos Centre for Ore Deposit Research and the School of Earth Sciences, University of
The Submarine Record of a Large-Scale Explosive Eruption in the Vanuatu arc: ~1 Ma Efaté Pumice Formation Alison M. Raos Centre for Ore Deposit Research and the School of Earth Sciences, University of
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Physical Volcanology. Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg
 55 Physical Volcanology Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg Structure: Introduction Reology and deformation of magma and lava Eruption processes and types Volcano forms Emplacement of lava flows,
55 Physical Volcanology Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg Structure: Introduction Reology and deformation of magma and lava Eruption processes and types Volcano forms Emplacement of lava flows,
Subaerial Felsic Lava Flows and Domes
 Subaerial Felsic Lava Flows and Domes Occurrence Alone or in linear and arcuate chains up to 20 km long Margins of calderas or volcanic depressions. Feeder occupies synvolcanic fault (ring fracture). Extrusion
Subaerial Felsic Lava Flows and Domes Occurrence Alone or in linear and arcuate chains up to 20 km long Margins of calderas or volcanic depressions. Feeder occupies synvolcanic fault (ring fracture). Extrusion
Data Repository Item 1
 GSA DR 2006031 Burgisser, p. 1 Data Repository Item 1 of Burgisser, A., and Gardner. J., Using Hydraulic Equivalence to Discriminate Transport Processes of Volcanic Flows This Electronic Supplement contains
GSA DR 2006031 Burgisser, p. 1 Data Repository Item 1 of Burgisser, A., and Gardner. J., Using Hydraulic Equivalence to Discriminate Transport Processes of Volcanic Flows This Electronic Supplement contains
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks
 Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Physical Volcanology. Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg. Recommended literature
 55 Physical Volcanology Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg Structure: Introduction Reology and deformation of magma and lava Eruption processes and types Volcano forms Emplacement of lava flows,
55 Physical Volcanology Christoph Breitkreuz, TU Bergakademie Freiberg Structure: Introduction Reology and deformation of magma and lava Eruption processes and types Volcano forms Emplacement of lava flows,
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks
 321 Lab 8 Instructor: L. Porritt - 1 - Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Identify fine-grained
321 Lab 8 Instructor: L. Porritt - 1 - Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Identify fine-grained
Weak to extremely powerful
 Hydrovolcanism Thus there is a continuum between magmatic and hydrovolcanic processes And thus between subaerial and subaqueous volcanism-hydrovolcanic processes active in both environments Continuum represent
Hydrovolcanism Thus there is a continuum between magmatic and hydrovolcanic processes And thus between subaerial and subaqueous volcanism-hydrovolcanic processes active in both environments Continuum represent
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS ROCK CLASSIFICATION LAB 2 HANDOUT Sources: University of Washington, Texas A&M University, University of Southern Alabama What is an igneous rock (a
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism. Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes:
 Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism November 1, 2011 Mary Tardona GG 711 Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes: Typically, three main stages: Pre shield Shield Post shield Sometimes followed by: Rejuvenation Stage GG
Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism November 1, 2011 Mary Tardona GG 711 Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes: Typically, three main stages: Pre shield Shield Post shield Sometimes followed by: Rejuvenation Stage GG
Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera. Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its
 Rachael Fleck Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its predecessor occurred nearly 760,000 thousand years ago. This
Rachael Fleck Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its predecessor occurred nearly 760,000 thousand years ago. This
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks. Calc-alkali Volcanics. Fabric. Petrography. Compositional Classification. Petrography. Processes.
 Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
Volcanoes. volcanic hazards. Image courtesy of USGS.
 Volcanoes volcanic hazards Volcanic hazards Pyroclastic flows and surges Pyroclastic flows and surges PYROCLAST: all solid fragments ejected from volcanoes PYROCLASTIC FLOW: A flow of hot gas and volcanic
Volcanoes volcanic hazards Volcanic hazards Pyroclastic flows and surges Pyroclastic flows and surges PYROCLAST: all solid fragments ejected from volcanoes PYROCLASTIC FLOW: A flow of hot gas and volcanic
Geological Society, London, Special Publications 1984; v. 16; p Submarine volcaniclastic rocks. alerting service
 Geological Society, London, Special Publications Submarine volcaniclastic rocks Richard V. Fisher Geological Society, London, Special Publications 1984; v. 16; p. 5-27 doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.1984.016.01.02
Geological Society, London, Special Publications Submarine volcaniclastic rocks Richard V. Fisher Geological Society, London, Special Publications 1984; v. 16; p. 5-27 doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.1984.016.01.02
1/31/2013 BASALTIC BASALTIC ANDESITIC RHYOLITIC
 Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Sedimentary Geology 220 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Sedimentary Geology
 Sedimentary Geology 220 (2009) 227 242 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Sedimentary Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sedgeo Sedimentation and welding processes of dilute pyroclastic
Sedimentary Geology 220 (2009) 227 242 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Sedimentary Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sedgeo Sedimentation and welding processes of dilute pyroclastic
Scarpati Claudio and Perrotta Annamaria
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012292 Supplemental Information Scarpati Claudio (email:claudio.scarpati@unina.it) and Perrotta Annamaria Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Napoli Federico II Erosional
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012292 Supplemental Information Scarpati Claudio (email:claudio.scarpati@unina.it) and Perrotta Annamaria Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Napoli Federico II Erosional
From Punchbowl to Panum: Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain
 From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
Subaqueous Volcanism
 Find the Face Subaqueous Volcanism Submarine Lavas Most abundant surficial igneous rocks on earth Form in: 1) Mid-ocean ridges- 1-2 km thick 2) Back arc basins 3) Island Arcs 4) Hot Spots 5) Hypabasal
Find the Face Subaqueous Volcanism Submarine Lavas Most abundant surficial igneous rocks on earth Form in: 1) Mid-ocean ridges- 1-2 km thick 2) Back arc basins 3) Island Arcs 4) Hot Spots 5) Hypabasal
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Available online at Research paper. Received 11 March 2007; accepted 9 November 2007
 VOLGEO-03805; No of Pages 19 ARTICLE IN PRESS Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research xx (2008) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores Research paper
VOLGEO-03805; No of Pages 19 ARTICLE IN PRESS Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research xx (2008) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores Research paper
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5
 Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
Geology 101 Name Reading Guide for Chapters 1, 4, and 5 The purpose of the Reading Guides is to help you sort out the most important ideas in the text. I recommend answering the questions as you read the
GEOLOGY OF THE DO27 PIPE: A PYROCLASTIC KIMBERLITE IN THE LAC DE GRAS PROVINCE, NWT, CANADA
 GEOLOGY OF THE DO27 PIPE: A PYROCLASTIC KIMBERLITE IN THE LAC DE GRAS PROVINCE, NWT, CANADA Margaret Harder 1, Casey Hetman 2, Barbara Scott Smith 3, and Jennifer Pell 1 1 Peregrine Diamonds Ltd. 2 Mineral
GEOLOGY OF THE DO27 PIPE: A PYROCLASTIC KIMBERLITE IN THE LAC DE GRAS PROVINCE, NWT, CANADA Margaret Harder 1, Casey Hetman 2, Barbara Scott Smith 3, and Jennifer Pell 1 1 Peregrine Diamonds Ltd. 2 Mineral
Chapter 5 9/10/2011. Introduction. Volcanoes and Volcanism. Volcanism. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Introduction Chapter 5 Volcanism is the eruption of magma, and associated gases at the surface. Some magma erupts explosively as pyroclastic (fire-broken) rock and other erupts as lava flows. Volcanoes
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11. International PAPER WORKING TESTING. (Presented DISCUSSION. 2.1 presented. this working. paper, some.
 International Civil Aviation Organization IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11 WORKING PAPER INTERNATIONAL VOLCANIC ASH TASK FORCE (IVATF) SECOND MEETING Montréal, 11 to 15 July 2011 Agenda Item 2: Report of the Science
International Civil Aviation Organization IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11 WORKING PAPER INTERNATIONAL VOLCANIC ASH TASK FORCE (IVATF) SECOND MEETING Montréal, 11 to 15 July 2011 Agenda Item 2: Report of the Science
Student Name: College: Grade:
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
A Synopsis of the Krakatau 1883 Eruption: The Story Told by The Deposits
 A Synopsis of the Krakatau 1883 Eruption: The Story Told by The Deposits By Dr. Charles W. Mandeville American Museum of Natural History Dr. Steve Carey Dr. Haraldur Sigurdsson, both at Univ. Rhode Island,
A Synopsis of the Krakatau 1883 Eruption: The Story Told by The Deposits By Dr. Charles W. Mandeville American Museum of Natural History Dr. Steve Carey Dr. Haraldur Sigurdsson, both at Univ. Rhode Island,
Volcanic Mass Flow Processes and Deposits
 Volcanic Mass Flow Processes and Deposits Smith and Lowe, 1991 Lahars=hyperconcentrated (flood) flow (HFF) and debris flow Note ideal HFF deposit has normal grading, parallel bedding, better sorting Ideal
Volcanic Mass Flow Processes and Deposits Smith and Lowe, 1991 Lahars=hyperconcentrated (flood) flow (HFF) and debris flow Note ideal HFF deposit has normal grading, parallel bedding, better sorting Ideal
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
JAPEX s 60 Years Experience Exploring Volcanic Reservoirs in Japan*
 Click to view oral presentation (3.00 MB) JAPEX s 60 Years Experience Exploring Volcanic Reservoirs in Japan* Kentaro Takeda 1 and Yasuo Yamada 2 Search and Discovery Article #70297 (2017)** Posted October
Click to view oral presentation (3.00 MB) JAPEX s 60 Years Experience Exploring Volcanic Reservoirs in Japan* Kentaro Takeda 1 and Yasuo Yamada 2 Search and Discovery Article #70297 (2017)** Posted October
Chapter 5 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions
 Chapter 5 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 5 The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions The Wrath of Vulcan: Volcanic Eruptions Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 3 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
CHAPTER ROCK WERE FORMED
 HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
HOW CHAPTER 5 ROCK WERE FORMED 1 I. Modern geology- 1795 A. James Hutton- 1. uniformitarianism- "the present is the key to the past" a. b. the geologic processes now at work were also active in the past
Notes Week 1 Engineering Geology Problems
 Notes Week 1 Engineering Geology Problems The Big Three of Engineering Geology 1. Will the ground bear the weight? (i.e. Subsurface materials? Rock or soft soil and sediment? Differential settlement?)
Notes Week 1 Engineering Geology Problems The Big Three of Engineering Geology 1. Will the ground bear the weight? (i.e. Subsurface materials? Rock or soft soil and sediment? Differential settlement?)
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann
 17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
GEOLOGY OF THE VICTOR KIMBERLITE, ATTAWAPISKAT, NORTHERN ONTARIO, CANADA: CROSS-CUTTING AND NESTED CRATERS
 GEOLOGY OF THE VICTOR KIMBERLITE, ATTAWAPISKAT, NORTHERN ONTARIO, CANADA: CROSS-CUTTING AND NESTED CRATERS Kimberley Webb 1, Barbara Scott Smith 2, Joanne Paul 3 and Casey Hetman 1 1 De Beers Canada Kimberlite
GEOLOGY OF THE VICTOR KIMBERLITE, ATTAWAPISKAT, NORTHERN ONTARIO, CANADA: CROSS-CUTTING AND NESTED CRATERS Kimberley Webb 1, Barbara Scott Smith 2, Joanne Paul 3 and Casey Hetman 1 1 De Beers Canada Kimberlite
Title: Role of Magma-Water Interaction in Very Large Explosive Eruptions
 LA-UR - 93-3699 II Title: Role of Magma-Water Interaction in Very Large Explosive Eruptions _ "g_ Author(s): Greg A. Valentine _" Submittedto: International Seminar on Physics of Vapor Explosions Tomakomai,
LA-UR - 93-3699 II Title: Role of Magma-Water Interaction in Very Large Explosive Eruptions _ "g_ Author(s): Greg A. Valentine _" Submittedto: International Seminar on Physics of Vapor Explosions Tomakomai,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening.
 Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
Chapter 9 Volcano an opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt and the landform that develops around this opening. 3 Conditions Allow Magma to Form: Decrease in pressure
Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p )
 READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 2 (Rocks) PSCI 131 18/WI 70 pts NAME DUE: Monday, January 29 Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p. 34-43) 1. What is magma? 2. Extrusive igneous rocks form at the Earth s, and intrusive
READING QUESTIONS: Chapter 2 (Rocks) PSCI 131 18/WI 70 pts NAME DUE: Monday, January 29 Igneous Rocks: Formed by Fire (p. 34-43) 1. What is magma? 2. Extrusive igneous rocks form at the Earth s, and intrusive
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
VOLCANOES. {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows!
 Name: Tymesha B, Manny U, Malaika R VOLCANOES {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows! --Jimmy Buffett Part 1 Volcanic History of New Jersey Use
Name: Tymesha B, Manny U, Malaika R VOLCANOES {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows! --Jimmy Buffett Part 1 Volcanic History of New Jersey Use
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Quiz Five (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 10: Intrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) Pyro-what? (air fall volcanic rocks) 2)
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds
 Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds Project Representative Takehiro Koyaguchi Authors Yujiro Suzuki Takehiro Koyaguchi Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo
Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds Project Representative Takehiro Koyaguchi Authors Yujiro Suzuki Takehiro Koyaguchi Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Thursday, October 4 th
 Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter
 A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter Rocks are classified by how they are formed, their composition, and texture Rocks change over time through the rock
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Facies architecture of a continental, below-wave-base. volcaniclastic basin: the Ohanapecosh Formation, Ancestral
 1 of 53 1 2 3 Facies architecture of a continental, below-wave-base volcaniclastic basin: the Ohanapecosh Formation, Ancestral Cascades arc (Washington, USA) 4 5 6 7 Martin Jutzeler 1, J. McPhie 1, and
1 of 53 1 2 3 Facies architecture of a continental, below-wave-base volcaniclastic basin: the Ohanapecosh Formation, Ancestral Cascades arc (Washington, USA) 4 5 6 7 Martin Jutzeler 1, J. McPhie 1, and
Eruptive origins of a lacustrine pyroclastic succession: insights from the middle Huka Falls Formation, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand
 New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics ISSN: 0028-8306 (Print) 1175-8791 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnzg20 Eruptive origins of a lacustrine pyroclastic succession:
New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics ISSN: 0028-8306 (Print) 1175-8791 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnzg20 Eruptive origins of a lacustrine pyroclastic succession:
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
View of an intact oceanic arc, from surficial to mesozonal levels: Cretaceous Alisitos arc, Baja California
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 149 (2006) 1 46 www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores View of an intact oceanic arc, from surficial to mesozonal levels: Cretaceous Alisitos arc, Baja California
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 149 (2006) 1 46 www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores View of an intact oceanic arc, from surficial to mesozonal levels: Cretaceous Alisitos arc, Baja California
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
To get you thinking What natural process is responsible for the appearance of these rocks? Rocks and the Rock Cycle Bell Ringer Name the 3 types of rock. Is one type of rock able to change into a different
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
I m good. Thank you.
 I m good. Thank you. The Rock Cycle Ag Earth Science Chapter 3.1 A natural occurring, inorganic crystalline material with a unique chemical composition. mineral A consolidated mixture of minerals rock
I m good. Thank you. The Rock Cycle Ag Earth Science Chapter 3.1 A natural occurring, inorganic crystalline material with a unique chemical composition. mineral A consolidated mixture of minerals rock
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle
 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS
 LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
