Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop. View of the Rocking Stone at Cludders Rocks looking east to Widdop Reservoir.
|
|
|
- Chad Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop View of the Rocking Stone at Cludders Rocks looking east to Widdop Reservoir.
2 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop 2 Cludders Rocks Local Geological Site is an area of the high Pennines on Widdop Moor (SD ) about 9 kilometres north-west of Hebden Bridge, West Yorkshire, as shown on the map below. The site covers a small area of exposed rock crags, known as The Cludders or Cludders Rocks and the steep slope below them, called Cludders Slack, down to the edge of Widdop Reservoir to the north. There is access to Widdop Reservoir from a minor road between Hebden Bridge and Burnley over the moors. From the road there are panoramic views across moorland. The height of the crags above Cludders Slack is about 375m, descending to about 320m at reservoir level. The slope below the crags is littered with large slipped blocks of sandstone. The existing car park at the Widdop Reservoir dam is an excellent point from which to observe Cludders Rocks. The track along the south side of Widdop Reservoir gives access to Cludders Rocks at the top of the slope, but also continues onwards towards Burnley as Gorple Gate and Gorple Road. The track is also part of the Pennine Bridleway network so can be used by horse-riders as well as walkers. The crags and the boulders on the slope are used by climbers. The name Cludders Rocks or The Cludders, is given to the 25m high natural crags at the top of the slope to the south-east of Widdop Reservoir. The Local Geological Site also includes the Cludders Slack slope below the crags down to the waterside, which is steep and has many slipped boulders, some of enormous size. The rocks underlying the area are sandstones and mudstones of Upper Carboniferous (Namurian) age. The crags at the top of the slope are made of a gritstone. This is a tough sandstone with massive beds, broken up by prominent vertical joints and bedding planes which have been heavily weathered. The blocks of sandstone appear to balance on top of the blocks below, as shown in the photo of the Rocking Stone on page 1. Widdop Reservoir The Watershed Landscape Project Area Railways and stations Pennine Way Pennine Bridleway Cludders Rocks from the car park at Widdop Dam.
3 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop 3 Beneath the gritstones are beds of dark grey or black mudstones (shales) which are made from clay particles and siltstones, which are made of very fine quartz grains. Both these rocks are prone to weathering into small flakes and thus being washed down the slope. The concave slope near the reservoir results from the down-slope movement of fine clay, silt and sand particles. However, it is difficult to see these rock particles, as they are covered by sandstone blocks and slope wash. The boulders which make up the dramatic landscape of Cludders Slack are large blocks of Lower Kinderscout Grit from the Cludders Rocks which have slipped down the mudstone slopes. Bedrock geology The rocks forming this area of the Pennines are Upper Carboniferous in age, so they date from about 310 million years ago, from that section of the Upper Carboniferous period which is called the Namurian stage. The rock type which forms the Cludders Rocks themselves is the Lower Kinderscout Grit, which is a gritstone with coarse, angular sand grains. It often contains bands of rounded white pebbles of quartz, which have been deposited by currents in the rivers in which most of the Namurian gritstones formed. The Lower Kinderscout Grit forms the top of the slope as shown in the section below. Below this gritstone lies a thick layer of mudstones and siltstones called the Hebden Formation. This forms the steep lower slopes of the hillside. Mudstones were deposited in the lakes or marshes of the Upper Carboniferous delta, away from the main river channels. Close-up of Lower Kinderscout Grit on Cludders Rocks, showing rounded quartz pebbles, set amongst coarse, angular sand grains. Lower Kinderscout Grit Cludders Rocks Hebden Formation mudstones and siltstones Cludders Slack Cross-section to show the geology of Cludders Rocks and Cludders Slack. Fallen boulders down slope Widdop Reservoir At the end of the Carboniferous period, the Pennines were formed when two tectonic plates collided across central Europe. This caused the uplift of the Pennines in a north-south trending fold, with limbs dipping to east and west as shown in the diagram. Widdop Moors lie across the crest of the anticline so the rocks are largely horizontal in this area. However, the beds of gritstone and mudstone in the Widdop area dip very gently to the south-east. WEST Lancashire Widdop Moors Millstone Grit Yorkshire The Pennine Anticline Coal Measures EAST The features of Cludders Rocks, with their huge blocks of rock, are defined by the bedding planes and joints in the sandstone. The near horizontal bedding planes are well-spaced and the near vertical joints are also several metres apart. Carboniferous Limestone
4 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop 4 Weathered joint Scree slopes under rock exposures are also characteristic of cold areas because freeze-thaw action occurred on many days of the year as temperatures fluctuated around 0 C. The bedding planes and joints in the sandstones and mudstones were forced open by expanding ice-crystals, loosening the rocks which would fall to form scree slopes. The scree slopes below the crags of the Cludders are stable now because vegetation has been able to grow around them and prevent further movement downslope. Cross bedding at an angle to the bedding planes Bedding plane The ice sheet which moved down the west side of the Pennines during the last glacial event, which was at its maximum about 17,000 years ago, reached close to the Pennine watershed, only a few kilometres to the west of Widdop. The evidence for this is shown by the glacial till (clay and boulders dropped as the ice melted) recorded in the Burnley, Nelson and Colne areas. Glacial till is shown on the British Geological Survey Sheet 76 Rochdale at high levels on the west side of the Pennines. Features of the Kinderscout Grits at Cludders Rocks. Weathering takes place preferentially along these natural breaks, thus breaking the rock into large blocks. The rocks also include a feature called cross-bedding which develops at a gentle angle to the horizontal bedding planes, as a result of strong currents in large river channels which flowed across the Carboniferous delta. This is shown in the photo above. Landslipping The boulders, which have slid down the slope from the gritstone crags onto the mudstones of the lower slopes, probably moved shortly after the end of the last glacial event, about 12,000 years ago. During this time of intensely cold conditions, the rocks and subsoil would have been frozen for much of the year and only melted during the summers. Summer meltwater would have lubricated the subsoil which allowed large blocks to creep slowly downslope. Boulders lying on the slope below the crags at Cludders Rocks.
5 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop 5 However, it is clear that ice did not move over the 400m col at Widdop Cross, about 2km west of Widdop Reservoir, although glacial till is recorded just to the west of this point. There is no evidence for glacial deposits in the Widdop valley. Both the 1875 Geological Survey Memoir of the Burnley Coalfield and the recent remapping in 2008 (see references on page 6) do not record any glacial deposits in this area. Archaeology As with other upland areas of the Pennines there is considerable archaeological interest in the area around Widdop Reservoir. Flint finds have been discovered by local enthusiasts along the reservoir edges over the years. This includes Mesolithic, Neolithic and Bronze Age material and demonstrates a continuity of activity in the immediate vicinity, although the nature of that activity is not clear. The flint microliths are thought to be armatures or components of the arrow type found in the early Mesolithic. The Cludders Rocks are probably significant for early Mesolithic archaeology since they are an ideal spot for a hunting stand to observe passing game animals. However, no prehistoric occupation can be demonstrated and the best that can be claimed is that the area was utilised either for hunting or other seasonal activities. Of great significance is a standing stone about 1m high called The Notch, probably late Neolithic or early Bronze Age. This can be found about 500m east of Widdop dam adjacent to the road (SE ). There are also a number of other stones found to the east along the same contour. The whole Widdop area itself is significant as an access route through the Pennines into the main Calder Valley during the prehistoric and medieval periods. There are remnants of causey paving (for packhorses) visible in the bottom of the reservoir when it is drained. At a later time there was a farm located to the west of Cludders Rocks which could possibly date back to the late medieval period.
6 Rocks and Landscapes of Cludders Rocks, Widdop 6 Acknowledgements Dave Shepherd and Frank Jolley for help with the archaeology section Simon Firth of Yorkshire Water Hugh Firman of Calderdale Countryside Services Photos Alison Tymon References Aitkenhead, N, Barclay, W J, Brandon, A, Chadwick, R A, Chisholm, J I, Cooper, A H, and Johnson, E W, 2002, British Regional Geology: the Pennines and adjacent areas, British Geological Survey Crofts, R G, Hough, E, and Northmore, K J, 2010, Geology of the Rochdale district a brief explanation of the geological map 1:50,000 Sheet 76 Rochdale Hull, E, Dakyns, J R, Tiddeman, R H, Ward, J C, Gunn, W, and De Rance, C E, 1875, Geology of the Burnley Coalfield, Memoirs of the Geological Survey Wright, W B, Sherlock, R L, Wray, D A, and Tonks, L H, 1927, The Geology of the Rossendale Anticline, Memoirs of the Geological Survey Useful websites Useful maps OS map 1:50,000 Landranger 103 Blackburn and Burnley OS map 1:25,000 Explorer OL 21 South Pennines British Geological Survey :50,000 Clitheroe Sheet 68 British Geological Survey :50,000 Rochdale Sheet 76 Written by Alison Tymon West Yorkshire Geology Trust West Yorkshire Geology Trust (WYGT) is part of a national network of voluntary groups which are actively conserving important geological features. These sites include rocky crags, active or disused quarries, railway cuttings and stream beds. Important sites are called Local Geological Sites (LGS) and there are about 80 in the county. West Yorkshire Geology Trust aims to encourage public enjoyment of rocks, fossils and landscapes and link geological features with the local industrial heritage. WYGT also maintains a database of Local Geological Sites and encourages landowners and managers to participate in good site practice and management. This leaflet has been produced with support from the Watershed Landscape Project, a three year Heritage Lottery Funded project managed by Pennine Prospects to enhance and conserve the South Pennine upland landscape and its heritage, whilst improving access for all. The aims of the project are to protect the internationally important natural and historic features of this special landscape and to encourage greater understanding and enjoyment of the area so that it is further valued and protected. The project has been telling the fascinating stories of the moors by offering opportunities to get involved in local heritage projects, delivering moorland conservation initiatives, developing resources to help people explore the landscape, hosting exciting events and activities, and working with artists and writers on an original creative arts programme. For more information about the Watershed Landscape Project please visit
Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax. A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries.
 Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries. Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax 2 Ogden Clough Local Geological Site
Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries. Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax 2 Ogden Clough Local Geological Site
Rocks and Landscapes of Gorpley Clough, Todmorden
 Rocks and Landscapes of Gorpley Clough, Todmorden Rocks and Landscapes of Gorpley Clough, Todmorden 2 Gorpley Clough, near Todmorden, West Yorkshire (SD 914 233) is a very attractive, steep-sided valley,
Rocks and Landscapes of Gorpley Clough, Todmorden Rocks and Landscapes of Gorpley Clough, Todmorden 2 Gorpley Clough, near Todmorden, West Yorkshire (SD 914 233) is a very attractive, steep-sided valley,
Rocks and Landscapes of Todmorden Moor
 Rocks and Landscapes of Todmorden Moor Rocks and Landscapes of Todmorden Moor 2 Todmorden Moor is an upland plateau moor with an altitude of about 350 to 400m, reaching a high point of 441m at Carr and
Rocks and Landscapes of Todmorden Moor Rocks and Landscapes of Todmorden Moor 2 Todmorden Moor is an upland plateau moor with an altitude of about 350 to 400m, reaching a high point of 441m at Carr and
GEOLOGY OF TODMORDEN MOOR 2 BACKGROUND
 GEOLOGY OF TODMORDEN MOOR 2 BACKGROUND 1) THE CARBONIFEROUS SERIES OF ROCKS The rocks of the Todmorden district are of the Carboniferous Series and were first laid down in an ancient sea, which covered
GEOLOGY OF TODMORDEN MOOR 2 BACKGROUND 1) THE CARBONIFEROUS SERIES OF ROCKS The rocks of the Todmorden district are of the Carboniferous Series and were first laid down in an ancient sea, which covered
Rocks and Landscapes of Marsden
 Rocks and Landscapes of Marsden Rocks and Landscapes of Marsden 2 The rocks which form the landscape around Marsden, West Yorkshire, were formed during the late Carboniferous period, about 315 million
Rocks and Landscapes of Marsden Rocks and Landscapes of Marsden 2 The rocks which form the landscape around Marsden, West Yorkshire, were formed during the late Carboniferous period, about 315 million
Rocks and Landscapes of Penistone Hill, Haworth
 Rocks and Landscapes of Penistone Hill, Haworth Rocks and Landscapes of Penistone Hill, Haworth 2 Geological Trail A rocks and landscapes trail booklet for Penistone Hill is available from Haworth Visitor
Rocks and Landscapes of Penistone Hill, Haworth Rocks and Landscapes of Penistone Hill, Haworth 2 Geological Trail A rocks and landscapes trail booklet for Penistone Hill is available from Haworth Visitor
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
PROMISED LAND STATE PARK PIKE COUNTY ANCIENT RIVERS AND AGES OF ICE
 PENNSYLVANIA TRAIL OF GEOLOGY PARK GUIDE 18 PROMISED LAND STATE PARK PIKE COUNTY ANCIENT RIVERS AND AGES OF ICE Promised Land State Park is located on a broad upland surface known as the Pocono Plateau.
PENNSYLVANIA TRAIL OF GEOLOGY PARK GUIDE 18 PROMISED LAND STATE PARK PIKE COUNTY ANCIENT RIVERS AND AGES OF ICE Promised Land State Park is located on a broad upland surface known as the Pocono Plateau.
Todmorden Wind Farm Geotechnical Site Investigations, Calderdale, West Yorkshire
 Todmorden Wind Farm Geotechnical Site Investigations, Calderdale, West Yorkshire Archaeological Watching Brief Report Oxford Archaeology North March 2013 I and H Brown Issue No: 2012-13/1370 OA North Job
Todmorden Wind Farm Geotechnical Site Investigations, Calderdale, West Yorkshire Archaeological Watching Brief Report Oxford Archaeology North March 2013 I and H Brown Issue No: 2012-13/1370 OA North Job
Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream as it enters a lake. At which points along the stream are erosion and deposition dominant?
 1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
=%REPORT RECONNAISSANCE OF CHISHOLM LAKE PROSPECT. October 25, 1977
 =%REPORT ON FIELD RECONNAISSANCE OF CHISHOLM LAKE PROSPECT October 25, 1977 Bruce D. Vincent Imperial Oil Limited, Minerals - Coal, CALGARY, ALBERTA CHISHOLM LAKE PROSPECT Introduction The Chisholm Lake
=%REPORT ON FIELD RECONNAISSANCE OF CHISHOLM LAKE PROSPECT October 25, 1977 Bruce D. Vincent Imperial Oil Limited, Minerals - Coal, CALGARY, ALBERTA CHISHOLM LAKE PROSPECT Introduction The Chisholm Lake
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
The River Otter: A Field Guide to the. Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB)
 The River Otter: A Field Guide to the Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB) Produced by The Palaeolithic Rivers of South-West Britain Project and the National Ice
The River Otter: A Field Guide to the Palaeolithic Landscape Picture of Otter Valley taken by Laura Basell (PRoSWeB) Produced by The Palaeolithic Rivers of South-West Britain Project and the National Ice
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Warwickshire Geological Conservation Group
 Warwickshire Geological Conservation Group Site No: 97 Geological Formations Warwickshire Local Geological Site Kenilworth Cutting (Coventry Road) Kenilworth Formation (Permian) Criteria Form p 2 Description
Warwickshire Geological Conservation Group Site No: 97 Geological Formations Warwickshire Local Geological Site Kenilworth Cutting (Coventry Road) Kenilworth Formation (Permian) Criteria Form p 2 Description
Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016
 Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016 1 Introduction The Nidderdale Iron-Age group and its forerunners have been investigating
Excavations at Clocken Syke Farm, Dairy Lane,Dacre By Nidderdale Iron-age Archaeology community group 2015 and 2016 1 Introduction The Nidderdale Iron-Age group and its forerunners have been investigating
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
Wonder as you Wander up the Carding Mill Valley
 Wonder as you Wander up the Carding Mill Valley Spot clues to the 600 million year old history of the Long Mynd. Consider how the Earth has evolved since the rock you are walking over first formed. Welcome
Wonder as you Wander up the Carding Mill Valley Spot clues to the 600 million year old history of the Long Mynd. Consider how the Earth has evolved since the rock you are walking over first formed. Welcome
EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE
 EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE Weathering Together, weathering and erosion work continuously to wear down the material on Earth s surface. weathering process that breaks down rock and other substances of Earth
EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE Weathering Together, weathering and erosion work continuously to wear down the material on Earth s surface. weathering process that breaks down rock and other substances of Earth
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore BEDRO CK For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore BEDRO CK For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
Cape Breton Island Mineral Inventory Studies: A Sandstone Quarry Development Opportunity at Graham River (NTS 11F/14), Inverness County
 Report of Activities 2001 23 Cape Breton Island Mineral Inventory Studies: A Sandstone Quarry Development Opportunity at Graham River (NTS 11F/14), Inverness County G. J. DeMont and J. E. Hawken Compilation
Report of Activities 2001 23 Cape Breton Island Mineral Inventory Studies: A Sandstone Quarry Development Opportunity at Graham River (NTS 11F/14), Inverness County G. J. DeMont and J. E. Hawken Compilation
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16
 Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
Lowland Glaciation North Wales
 Lowland Glaciation North Wales Background Although there have been many glaciations and advances in ice, the most significant for this are was the Dimlington Stadial which was a period of glacial advance
Lowland Glaciation North Wales Background Although there have been many glaciations and advances in ice, the most significant for this are was the Dimlington Stadial which was a period of glacial advance
KRIS wsbssm. IBHiiilll
 KRIS wsbssm IBHiiilll Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2012 with funding from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign http://archive.org/details/engineeringaspec34ekbl STATE OF ILLINOIS HENRY HORNER,
KRIS wsbssm IBHiiilll Digitized by the Internet Archive in 2012 with funding from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign http://archive.org/details/engineeringaspec34ekbl STATE OF ILLINOIS HENRY HORNER,
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
The Geology of Two Lights State Park. Cape Elizabeth, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2002 Cape Elizabeth, Maine 43 33 33.48 N, 70 12 13.32 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV and Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2002 Cape Elizabeth, Maine 43 33 33.48 N, 70 12 13.32 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV and Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1
Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification Video (Mr. White s website) Questions (Pg.
 Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
1. The diagram below shows the stump of a tree whose root grew into a small crack in bedrock and split the rock apart.
 1. The diagram below shows the stump of a tree whose root grew into a small crack in bedrock and split the rock apart. 4. Which process involves either a physical or chemical breakdown of earth materials?
1. The diagram below shows the stump of a tree whose root grew into a small crack in bedrock and split the rock apart. 4. Which process involves either a physical or chemical breakdown of earth materials?
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, Lobster Lake, Maine. Text by Robert G. Marvinney. Maine Geological Survey
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, 1998 Lobster Lake, Maine 45 o 51 7.91 N, 69 o 30 53.88 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Introduction
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, 1998 Lobster Lake, Maine 45 o 51 7.91 N, 69 o 30 53.88 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Introduction
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Be able to understand the processes which occurred during the last ice age.
 Glaciation Learning Intentions Be able to understand the processes which occurred during the last ice age. Be able to describe and explain the formation of features formed during glacial periods. 1 Water
Glaciation Learning Intentions Be able to understand the processes which occurred during the last ice age. Be able to describe and explain the formation of features formed during glacial periods. 1 Water
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p ) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 WEATHERING
 Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
Unit 3 Review - Surface Processes
 Unit 3 Review - Surface Processes 1. Why is the surface of Mercury covered with meteor impact craters, while Earth s surface has relatively few craters? A) Mercury is larger than Earth, so it gets hit
Unit 3 Review - Surface Processes 1. Why is the surface of Mercury covered with meteor impact craters, while Earth s surface has relatively few craters? A) Mercury is larger than Earth, so it gets hit
Earth processes are dynamic actions that occur both on
 29 Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition R EA D I N G Earth processes are dynamic actions that occur both on the earth s surface and inside the earth. Any process that breaks down earth material, such as
29 Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition R EA D I N G Earth processes are dynamic actions that occur both on the earth s surface and inside the earth. Any process that breaks down earth material, such as
1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow.
 1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow. Which cross section best represents the shape of the river bottom at
1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow. Which cross section best represents the shape of the river bottom at
A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities April, 1998 A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine 44 45 3.21 N, 70 32 50.24 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities April, 1998 A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine 44 45 3.21 N, 70 32 50.24 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry
The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! S R Curd, R Downie, P C Logan, P Holley Heritage Oil plc *
 A Bird in the Hand! EXTENDED ABSTRACT The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! Heritage Oil plc * The Kingfisher Field lies on Uganda s western border beneath Lake Albert, situated in the western
A Bird in the Hand! EXTENDED ABSTRACT The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! Heritage Oil plc * The Kingfisher Field lies on Uganda s western border beneath Lake Albert, situated in the western
QUINTETTE COAL LIMITED 1979 EXPLORATION ASSESSMENT REPORT
 QUINTETTE COAL LIMITED 1979 EXPLORATION ASSESSMENT REPORT JANUARY 1980 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Geological Mapping 1.2 Field Camp 2.0 Geology 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Stratigraphy 2.3 Structure
QUINTETTE COAL LIMITED 1979 EXPLORATION ASSESSMENT REPORT JANUARY 1980 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Geological Mapping 1.2 Field Camp 2.0 Geology 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Stratigraphy 2.3 Structure
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Day 3 Weathering and Erosion.notebook. October 02, Section 7.2. Erosion and Deposition. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
The Niagara Escarpment extends from western New York, through the GTA all the way up to Manitoulin Island and into Michigan and Wisconsin.
 is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
3 Erosion and Deposition by Ice
 CHAPTER 12 3 Erosion and Deposition by Ice SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are glaciers? How do
CHAPTER 12 3 Erosion and Deposition by Ice SECTION Agents of Erosion and Deposition BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are glaciers? How do
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis
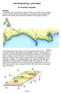 Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Match up the pictures and key terms
 Match up the pictures and key terms 1 Plucking Striations 3 Roche Mountonnees 2 Chatter Marks 4 What is the difference between plucking and abrasion? Glacial Processes Erosion, Weathering and Deposition
Match up the pictures and key terms 1 Plucking Striations 3 Roche Mountonnees 2 Chatter Marks 4 What is the difference between plucking and abrasion? Glacial Processes Erosion, Weathering and Deposition
Field Meeting Report: Coniston, led by Derek Leviston 18 th May 1986
 ISSN 1750-855X (Print) ISSN 1750-8568 (Online) Field Meeting Report: Coniston, led by Derek Leviston 18 th May 1986 Les Dolamore 1 DOLAMORE, L. (1987). Field Meeting Report: Carrock Fell, led by Derek
ISSN 1750-855X (Print) ISSN 1750-8568 (Online) Field Meeting Report: Coniston, led by Derek Leviston 18 th May 1986 Les Dolamore 1 DOLAMORE, L. (1987). Field Meeting Report: Carrock Fell, led by Derek
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition The breakdown of rocks at or near the Earth s Surface. Physical Chemical - The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without chemical change. - Dominant in moist /cold conditions
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition The breakdown of rocks at or near the Earth s Surface. Physical Chemical - The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without chemical change. - Dominant in moist /cold conditions
Clyde River Landslide
 Clyde River Landslide Department of Geology, Perkins Hall, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 Abstract: This paper investigates a landslide on the Clyde River in Newport, Vermont. The landslide
Clyde River Landslide Department of Geology, Perkins Hall, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 Abstract: This paper investigates a landslide on the Clyde River in Newport, Vermont. The landslide
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
1. Erosion by Running Water Most powerful cause of erosion
 I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Rocks and Weathering
 Rocks and Weathering The Effects of Weathering The process of mountain building thrusts rock up to Earth s surface. Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface.
Rocks and Weathering The Effects of Weathering The process of mountain building thrusts rock up to Earth s surface. Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface.
1. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows the generalized bedrock of a part of western New York State.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows the generalized bedrock of a part of western New York State. 3. The table below describes the deposits that an observer saw while
1. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows the generalized bedrock of a part of western New York State. 3. The table below describes the deposits that an observer saw while
Name: Which rock layers appear to be most resistant to weathering? A) A, C, and E B) B and D
 Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR
 Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, ME
 Geologic Site of the Month May, 2013 Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, Maine 44 o 25 59.18"N, 68 o 56 37.11"W Text and photos by Woodrow B. Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation &
Geologic Site of the Month May, 2013 Glacial Geology of Moose Point State Park, Maine 44 o 25 59.18"N, 68 o 56 37.11"W Text and photos by Woodrow B. Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation &
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Allagash Falls Geology
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2005 46 o 57 0.13"N, 69 o 7 59.15"W Text by Robert Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Photos by Kyle Marvinney Introduction The
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2005 46 o 57 0.13"N, 69 o 7 59.15"W Text by Robert Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Photos by Kyle Marvinney Introduction The
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 7 Glaciers, Desert, and Wind 7.1 Glaciers Types of Glaciers A glacier is a thick ice mass that forms above the snowline over hundreds or thousands of
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 7 Glaciers, Desert, and Wind 7.1 Glaciers Types of Glaciers A glacier is a thick ice mass that forms above the snowline over hundreds or thousands of
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
Bell Ringer. Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants.
 Bell Ringer Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants. 5.3 Mass Movements Triggers of Mass Movements The transfer of rock and soil downslope due to gravity is
Bell Ringer Are soil and dirt the same material? In your explanation be sure to talk about plants. 5.3 Mass Movements Triggers of Mass Movements The transfer of rock and soil downslope due to gravity is
HW #2 Landscape Travel from A to B 12,
 HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
Think about the landforms where you live. How do you think they have changed over time? How do you think they will change in the future?
 reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
Geography Knowledge Organiser: What is a Geographer?
 Geography Knowledge Organiser: What is a Geographer? KPI 7.1.1 Locate and name the continents and oceans of the world, identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom
Geography Knowledge Organiser: What is a Geographer? KPI 7.1.1 Locate and name the continents and oceans of the world, identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom
June 9, R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western Region PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON
 PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED MARTIN RIVER BRIDGE MILE 306.7 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY Submitted by : R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED MARTIN RIVER BRIDGE MILE 306.7 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY Submitted by : R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Pratice Surface Processes Test
 1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
Bowen s Chemical Stability Series
 Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
core mantle crust the center of the Earth the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock
 core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
Earth and Space Science. Semester 2 Review, Part 2
 Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
3.0 GEOLOGY AND HYDROGEOLOGY
 3.0 GEOLOGY AND HYDROGEOLOGY 3.1 Methodology The Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) publication Geology of South Cork was consulted to establish the nature of the bedrock lithology and Quaternary sediments.
3.0 GEOLOGY AND HYDROGEOLOGY 3.1 Methodology The Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) publication Geology of South Cork was consulted to establish the nature of the bedrock lithology and Quaternary sediments.
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 6. Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
The Agents of Erosion
 The Agents of Erosion 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. Ice California Science Project 1 1. Erosion and Deposition Erosion is the physical removal and transport of material by mobile agents such
The Agents of Erosion 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. Ice California Science Project 1 1. Erosion and Deposition Erosion is the physical removal and transport of material by mobile agents such
Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock
 Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Weathering and Erosion Wherever rock is exposed at Earth s surface, it is continuously being broken down by weathering a set of physical and chemical processes
Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Weathering and Erosion Wherever rock is exposed at Earth s surface, it is continuously being broken down by weathering a set of physical and chemical processes
Urban fieldwork the stories from materials, colours, lines and shapes Find out the stories told by materials used in building and for decoration
 Urban fieldwork the stories from materials, colours, lines and shapes Find out the stories told by materials used in building and for decoration When you look at the stones used for buildings and in parks
Urban fieldwork the stories from materials, colours, lines and shapes Find out the stories told by materials used in building and for decoration When you look at the stones used for buildings and in parks
NAME: GEL 109 Final Winter 2010
 GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
The Welsh Borderland. Geologically recent surface deposits. The Welsh Borderland
 The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed. Y11 Changing landscapes of the UK
 Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed Small particles that have been transported and deposited in layers, such as sandstone; or from the remains of plants and animals e.g. chalk. Pressure
Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed Small particles that have been transported and deposited in layers, such as sandstone; or from the remains of plants and animals e.g. chalk. Pressure
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland
 Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland Abstract The Waterbury Dam was completed in October 1938 as a method of flood control in the Winooski Valley. The construction began in April1935
Waterbury Dam Disturbance Mike Fitzgerald Devin Rowland Abstract The Waterbury Dam was completed in October 1938 as a method of flood control in the Winooski Valley. The construction began in April1935
The boulder was most likely moved to this location by A) glacial ice B) prevailing wind C) streamfiow D) volcanic action
 1. Which rock material was most likely transported to its present location by a glacier? A) rounded sand grains found in a river delta B) rounded grains found in a sand dune C) residual soil found on a
1. Which rock material was most likely transported to its present location by a glacier? A) rounded sand grains found in a river delta B) rounded grains found in a sand dune C) residual soil found on a
Page 1. Weathering & Erosion by Mass Wasting Pre-Test. Name:
 Weathering & Erosion by Mass Wasting Pre-Test 3048-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) As a particle of sediment in a stream breaks into several smaller pieces, the rate of weathering of the sediment will A) increase
Weathering & Erosion by Mass Wasting Pre-Test 3048-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) As a particle of sediment in a stream breaks into several smaller pieces, the rate of weathering of the sediment will A) increase
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
LAB - Rock Classification
 NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
The Hillsvale Vein System, Hants County
 Report of Activities 2004 39 The Hillsvale Vein System, Hants County R. J. Horne, R. R. Stea and D. J. Kontak Introduction A number of previously undocumented, beddingparallel quartz veins were discovered
Report of Activities 2004 39 The Hillsvale Vein System, Hants County R. J. Horne, R. R. Stea and D. J. Kontak Introduction A number of previously undocumented, beddingparallel quartz veins were discovered
Grade 5 Hands on Science Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
 Grade 5 Hands on Science Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Objective: To demonstrate and investigate the effect of weathering, water and wind erosion and the subsequent deposition into landforms. Background:
Grade 5 Hands on Science Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Objective: To demonstrate and investigate the effect of weathering, water and wind erosion and the subsequent deposition into landforms. Background:
What is a map? Understanding your map needs
 What is a map? A map is simply a drawing or picture of a landscape or location. Maps usually show the landscape as it would be seen from above, looking directly down. As well as showing the landscape of
What is a map? A map is simply a drawing or picture of a landscape or location. Maps usually show the landscape as it would be seen from above, looking directly down. As well as showing the landscape of
A model of the Ipswich Urban area, geological mapping in 3D.
 A model of the Ipswich Urban area, geological mapping in 3D. Steve Mathers British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottingham E-mail sjma@bgs.ac.uk Background Over the last ten years the British Geological
A model of the Ipswich Urban area, geological mapping in 3D. Steve Mathers British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottingham E-mail sjma@bgs.ac.uk Background Over the last ten years the British Geological
Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation
 Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
Glacial Erosion Polished on front side Glacial striations (scratches) on top
 St Mary s Cemetery Glacial Erosion Polished on front side Glacial striations (scratches) on top Weathering Water channel in the rock mechanical weathering Some rocks eroding faster than others mechanical
St Mary s Cemetery Glacial Erosion Polished on front side Glacial striations (scratches) on top Weathering Water channel in the rock mechanical weathering Some rocks eroding faster than others mechanical
Wearing Down Landforms
 Wearing Down Landforms Denudation Denudation has also been called gradation. It is the Natural loss of soil and rock debris, blown away by wind or washed away by running water, laying bare the rock below.
Wearing Down Landforms Denudation Denudation has also been called gradation. It is the Natural loss of soil and rock debris, blown away by wind or washed away by running water, laying bare the rock below.
