New downhole technologies helped develop horizontal thin sand
|
|
|
- Georgia Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reprinted from: June 2005 issue, pgs Used with permission. DRILLING AND COMPLETION TECHNOLOGY SPECIAL FOCUS New downhole technologies helped develop horizontal thin sand Completion of Well Ewan-YH with a 1,200-ft horizontal borehole in a 6-ft sand in Niger Delta, Nigeria, proved success of new downhole drilling technologies and reservoir management techniques. Kenneth D. Kelsch and Bayo Oguntona, ChevronTexaco, and Parvez Butt and Elise Ingebrigtsen, Schlumberger New drilling and formation evaluation technologies and reservoir management techniques enabled a horizontal well to be placed successfully within a thin hydrocarbon sand having structural dip and stratigraphic uncertainty, making it feasible to develop and produce reserves that have been unattainable both technically and economically. The Ewan-YH, Ewan field, Niger Delta, Nigeria, achieved its objective with a 1,200-ft horizontal well drilled through the thin, productive BXX sand using enhanced drilling technology, geosteering techniques and reservoir management. The well s initial production was 1,600 bopd, exceeding expectations by 33%. Integration of logging while drilling (LWD) resistivity and resistivity images and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements as well as a new rotary steerable system (RSS) enabled the well to successfully land and be geosteered in a 6-ft stratigraphic thick sand, and be geostopped at optimum drainhole length that met productivity targets. Incorporating these technologies in the bottomhole assembly (BHA) and transmitting and obtaining the information in real time has had a significant impact on drilling and completion decisions, regarding well placement, that impact productivity and overall well economics in Niger Delta. Specifically, the Ewan-YH horizontal well, its planning, execution and results will be discussed herein. SETTING OBJECTIVES, ASSESSING GEOLOGIC RISKS The process of drilling horizontal wells in Chevron Nigeria Ltd. (CNL) is generally executed in three main phases: planning, execution and post-job. Upfront planning by a multifunctional team for well placement determination, uncertainty management/technology, and tool selection are key. Execution of landing and lateral placement, and length requires maximum flexibility and accuracy from tools and the team. The post-job reporting phase typically comprises an after action review critical to learning from both mistakes and success- Fig. 1. A top structure map of the BXX sand, Ewan field, shows planned well, Ewan- YH, and its surrounding offsets. The drainhole section was planned along strike to reduce risk of drilling out of the sand.
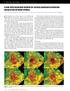
2 es, and bringing each well experience to subsequent wells. The objective of the Ewan-YH was to place a horizontal well within a 6-ft thin sand and drill an optimal lateral length that would meet hydrocarbon deliverability requirements. Specifically, the plan called for targeting and landing within the 6-ft BXX sand and, after setting casing, drilling a 1,200-ft long horizontal lateral with 90E 2E inclination within the sand. While offset wells provided both structural and stratigraphic control around the field, some structural uncertainties regarding target depth were present in the seismic mapping, Fig. 1. Key to reducing structural risk was use of near-bit LWD azimuthal resistivity. The well also presented stratigraphic risk as a result of shaliness within the reservoir; and the target sand decreased in both reservoir thickness and sand quality toward the west and SSW direction. Therefore, LWD NMR was added to evaluate the permeability both in the pilot hole and the drainhole section. To help reduce the possibility of exiting the sand, the drain was planned along its strike, which reduced structural uncertainty and helped achieve generally flat dip. While better reservoir quality was expected near the fault, lack of nearby well control coupled with high structural dip limited the ability to target the drain hole along strike of the NW trending fault. The team optimally placed Ewan-YH between two wells, where one supported placement of the toe while the other defined a zone of likely poor productivity. Fig. 2. NMR log of Ewan pilot hole shows up to 1 Darcy permeability and 15% FFV in the target sand, the basis for drilling a horizontal well. Acquired by an induction tool, the resistivity indicates a polarization effect when the well crossed bed boundaries. UTILIZING NOVEL FORMATION EVALUATION TECHNOLOGIES To drill the Ewan-YH, the BHA for the 6-in. drainhole section was optimized to reduce geological risks. It was recommended to use the Schlumberger geovi- SION* downhole MWD/LWD imaging services for at-the-bit resistivity, near-bit azimuthal button resistivity and azimuthal resistivity images to geosteer the well within the thin sand. The provision* NMR tool was also used to obtain NMR measurements for calculating effective porosity and permeability, and analyzing drainhole productivity while drilling. This allowed geostopping the drainhole length at the optimum total depth (TD) to achieve productivity targets. The azimuthal resistivity tool provides a laterolog type resistivity-at-thebit (GVR) and a high-resolution ring resistivity with a 7-in. depth of investigation. Three azimuthally focused 1-in. diameter buttons longitudinally spaced along the tool s axis provide shallow, medium and deep depths of investigation of about 1, 3 and 5 in., respectively, for quantifying invasion profiles. These measurements are essential for interpreting and steering horizontal wells in complex reservoirs like Ewan where either the structural or stratigraphic risk (or both) is significant. In addition to the five resistivity measurements, the tool also acquires azimuthal gamma ray data, radial and lateral shock records, and temperature measurements. As the GVR tool operates in conductive water-based mud systems, the team ensured that proper salinity was achieved to improve its resistivity measurements. While drilling the Ewan-YH well, the deep button images and up and down resistivity, ring and bit resistivities as well as gamma ray up and down were transmitted while drilling with 6 bps mudpulse telemetry. Though the ROP exceeded 100 ft/hr (90 ft/hr ROP average), the resolution of the LWD logs were good to excellent. High ROP, coupled with RSS use, kept the average borehole size to 8.6 in., which helped prepare for the completion phase of the well. Resistivity-at-bit was used to restrict the well within the target sand while the real-time deep-button image and azimuthal resistivity aided in steering through the thin sand. The resistivity images were used continuously while drilling for dip interpretation, with subsequent trajectory adjustments made to place the well within the most productive sand. Along with the images, up and down deep resistivity measurements also enabled the geosteering team to stay in the sweet spot of the heterogeneous sandstone reservoir.
3 Concurrent to resistivity data acquisition, permeability was estimated from the LWD NMR log, which was used to compute hydrocarbon producibility as a basis for determining optimal drill length. NMR technology provides critical reservoir parameters like effective porosity and permeability in real time which traditional LWD tools cannot measure. The LWD NMR tool can be placed anywhere in the BHA with no detrimental effects to drilling operations. Highly programmable and extremely flexible, the tool s acquisition modes allow a wide range of future acquisition sequence development. Typically, a multiple wait-time acquisition sequence is used. However, a fast, about 100 ft/hr ROP was expected for the Ewan-YH well, so a pulse sequence designed with a single longer initial wait-time of 12.5 seconds was used to completely polarize the oil productive intervals. Six bits per second data transmission was programed into the mudpulse telemetry tool for providing high quality real-time data despite the drillstring s five tools and their large concurrent data transmissions. Update rate for all variables was 41 sec, enabling good real-time data at the expected ROPs. PILOT WELL DRILLING, GEOSTEERING LANDING The pilot hole was planned to evaluate reservoir thickness, permeability and placement of the well s heel position. The plan for the drainhole section was adjusted to place it along formation strike (62E in NE direction). Previous sensitivity analysis on reservoir thickness, permeability and drainhole length run by engineering determined that a 5-ft thick target with a 1,200-ft lateral drainhole section was needed to meet productivity requirements. Upon entering the objective sand in the pilot hole, gamma ray decreased to 75 GAPI, resistivity increased to 8-10 ohmm and the neutron porosity and density overlapped, showing that the objective sand was sufficiently thick with a 5-ft true vertical depth (TVD). NMR data in the pilot hole indicated up to 800-mD permeabilities midway through the sand, Fig. 2. While total porosity was about 25, the free fluid porosity was only The early T2 arrivals indicated some shaliness, whereas the cleanest sand was found in the middle. The data confirmed that both permeability and thickness were sufficient to place a drain hole that would meet productivity targets. Landing can be one of the most difficult aspects in horizontal drilling. The Ewan-YH heel position was targeted about 30 m away from the pilot well. The section above the target sand consisted mainly of shale, with no specific sand markers. The target sand was 3.2-ft TVD deeper than the pilot hole, so the landing also had to be deeper (by 3 ft) to position the heel midway through the sand. In past CNL examples, the team would go farther to attempt landing the well at 89E or 90E. During the landing, it was evident that the soft formation would result in drilling out the bottom of the thin sand when attempting to increase dogleg severity. The landing BHA assembly for the 12¼-in. hole was heavier and had to push against the formation for directional drilling changes. Upon entering the sand, the ability to increase inclination to achieve 90E inclination had diminished. The team decided to stop at 88E inclination, case and change-out the drilling assembly to drill the 8½-in. lateral using alternate directional drilling technology. DRAINHOLE GEOSTEERING WITH RSS/LWD TECHNOLOGIES As a result of the landing difficulties, the team decided to use an enhanced RSS system from Schlumberger, along with the GVR and LWD-NMR tools, for geosteering and later geostopping the Ewan-YH horizontal well. The Power- Drive Xceed* RSS has a steering assembly that continuously orients the tilted bit shaft to control drilling direction and borehole dogleg severity, also referred to as point-the-bit technology. In soft formations, the RSS is capable of developing dogleg severity as high as 8 ft/100 ft. The RSS tool does not push against the Fig. 3. While drilling Ewan-YH, up and down resistivity was used for geosteering within the sand, together with dip interpretation from the r
4 borehole to build angle, making it more effective in steering unconsolidated formations. This was the case in the Ewan target sand, where hole angle was in fact built with minimal dependence on the borehole for deflection. Xceed RSS is a fully rotating tool with no stationary external parts, which reduces the risk of sticking the pipe assembly. Moreover, penetration rates are improved because there are no stationary components to create friction, which reduces efficiency and anchors the BHA in the hole. While the tool looks and acts very much like a conventional drilling motor, it has the ability to adjust azimuth and inclination of the bit. After drilling out of casing, hole inclination dropped to 87.5E from casing and back reaming. As such, the dogleg severity was increased to 4 to 4.5. During the first 100-ft of lateral drilling, bit inclination was 90E, at which point geosteering via the GVR was initiated. Early on, the resistivity image showed downward progress stratigraphically in the sand, while button resistivity images indicated a calculated apparent up dip of 0.5E along the wellbore. Also, the NMR log showed poorer quality reservoir with early T2 arrivals, indicating silty sand having less free fluid volume. Therefore, it was decided to build to 91E to climb back up toward the middle of the sand. Drilling ahead, the well climbed midway to cleaner sand. The sample description indicated that sand content increased to 90% 100% from 40%; sand grain size went from fine to medium; and resistivity measurements ranged between 9 and 12 ohms. However, after 25 ft within the clean sand, up resistivity decreased, indicating drilling was progressing upward. Dip interpretation from the resistivity image showed that the apparent dip was flattening out, so it was decided to level off at 90E inclination. Permeability estimates showed that the silty sand in the lower part had less than 100 md permeabilities, but the middle lobe had higher permeabilities ranging from 300 md to 1 Darcy. The FFVs increased when the well again approached the middle of the sand. Drilling on, resistivity images showed that the well was progressing along the top of the sand. The apparent dip had dropped to 1E down dip, so the inclination was decreased even more to 88.5E to drop down midway to cleaner sand. The apparent dip sustained at about 1.5E for the rest of the well and the inclination was maintained between 87E and 88E to follow the sand down dip. Here, permeabilities ranged from medium (200 to 300 md) to high (300 md up to 1 Darcy). However, in the heel of the well, or the first 200 ft, real-time productivity analysis using LWD-NMR images indicated poorer reservoir quality having low permeabilities (less than 100 md), which prior reservoir simulation estimates showed was not sufficiently productive. Therefore, an additional 200 ft of drainhole section was extended from the planned TD, geosteered within medium to high permeability sand. The TD was declared after 1,400 ft of lateral section had been drilled from the landing point within the sand, Fig. 3. The well achieved its objective with 1,200 ft of productive sand. During drilling of the 1,400-ft lateral section, a total of 15 adjustments called by geosteering staff were made. After 20 min., the change would be realized by geosteering staff via differences in tool read-out at the rig and geosteering work area. Average ROP was about 90 ft/hr, which was high in comparison to past CNL laterals drilled. However, GVR measurements provided the team with confidence to quickly and successfully navigate through the thin sand and complete the lateral section. The high ROP also prevented the ability of the BHA to produce washouts that can affect well completion, the Ewan-YH well having an average 8.6-in. diameter. GVR tool use limited completion type and equipment, so the Concentric Annual Production System (CAPS) was deployed in the well. Ewan field is known to produce sand when a wellbore first produces water. Consequently, sand control was deemed critical for this well s production success. While the initial production estimate was 1,200 bopd, the actual IP was 1,600 bopd after bringing the well on production, exceeding expectations by 33%. Future tests will verify sustained well productivity. OVERVIEW AND FUTURE OUTLOOK The Ewan-YH well shows that it is feasible technically and economically to develop thinner sand targets through use of enhanced drilling technology, geosteering techniques and reservoir management. Attractive economic results were achieved for the well. More importantly, there are huge economic implications to CNL in light of its vast reserve potential in thin sand development. Lessons learned from Ewan-YH provide the beginning of a road map on how to reclassify CNL s P2 and P3 reserves to P1 and increase its production. While near-bit azimuthal resistivity and images generated with the geovi- SION downhole MWD/LWD imaging services were essential for steering Ewan- YH within thin target sand, calculating dips and adjusting trajectory continuously, the provision LWD NMR tool proved vital for evaluating reservoir quality and estimating permeability in the shaly sand reservoir. Another case study, not included in this article, but discussed fully in the acknowledged SPE Paper No , used LWD NMR information to optimize a horizontal sidetrack in a highly permeable section of a reservoir that was also very thin. The Meji-4XH well, Meji field, offshore Nigeria, used the LWD NMR tool in both the pilot hole and the wellbore, which demonstrated that the horizontal section was placed generally within the most productive sand, or sweet spot, of high permeability and high free fluid, with production rates exceeding 2,200 bopd. This well illustrated that NMR acquisition using the LWD tool delivered near wireline quality data at ROP in excess of 200 ft/hr. This novel approach discussed in this article, combining best reservoir management practices with enhanced drilling technology and geosteering techniques using flexible LWD tools are key to future development of thin hydrocarbon reservoirs in the Niger Delta and around the world. WO *Mark of Schlumberger ACKNOWLEDGMENT This article is a condensed version of SPE Paper No , Thin sand development made possible through enhanced geosteering and reservoir planning with while-drilling resistivity and NMR Logs: Example from Niger Delta, Oguntona, J.A., Kelsch, K., Osman, K., ChevronTexaco, and Ingebrigtsen, E., Butt, P., Saha, S., Schlumberger. The authors would like to thank the Chevron Nigeria Ltd. and Nigeria National Petroleum Corp. for granting permission to publish the paper.
5 THE AUTHORS Kenneth D. Kelsch is a staff earth scientist for Chevron Nigeria Ltd. within a production asset team in Lagos, Nigeria. He has more than 15 years work experience within strikeslip and extensional tectonic environments such as Central Sumatra Indonesia basin, Los Angeles basin and Niger Delta. He has mentored staff within structural analysis and full field development processes, and has assisted in teaching ChevronTexaco s compressional/extensional tectonic workshops. Mr. Kelsch has a BS in geology/geophysics from the University of California, and an MS in geology/ geophysics from California State University. Bayo Oguntona, a reservoir engineer for Chevron Overseas Petroleum, Lagos, Nigeria, has more than 15 years experience in: field development planning, optimization and implementation, full field/ reservoir simulation model development, and economic evaluation and justification of proposed capital projects. He has mentored staff; provided engineering support for exploration opportunities; evaluated and supported computer needs; and worked with drilling, facilities and operations to plan and implement development and operations strategies. Mr. Oguntona has a BS in mechanical engineering from the University of Ilorin, Nigeria, and an MS in petroleum engineering from Stanford University. Parvez Butt, manager of the Schlumberger dedicated client center in ChevronTexaco Nigeria, at the time of this article, is responsible for wireline and LWD log interpretation. His primary focus is interpretation/development of new real-time answer products from LWD services, with his areas of technical expertise including advanced formation evaluation with LWD services, geosteering, horizontal well placement and drainhole length optimization using real-time ADN images and real-time LWD services. Mr. Butt has an MS in geophysics from University of Islamabad, Pakistan. Elise Ingebrigtsen was well placement team leader, Drilling & Measurement, Schlumberger, Nigeria, at the time of this article. With experience including Norwegian and Nigerian regions, her primary focuses are well placement and MWD/LWD log interpretation; and areas of technical expertise include well planning, structural geology and advanced formation evaluation. Ms. Ingebrigtsen has an MS in petroleum geology from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, and has conducted university studies in Arctic geology at Svalbard, Spitsbergen. Article copyright 2005 by Gulf Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
geovision Resistivity imaging for productive drilling
 geovision Resistivity imaging for productive drilling geovision Resistivity imaging while drilling helps position wells in the best place in the reservoir in less time. Real-time resistivity measurements
geovision Resistivity imaging for productive drilling geovision Resistivity imaging while drilling helps position wells in the best place in the reservoir in less time. Real-time resistivity measurements
MicroScope. Resistivity- and imagingwhile-drilling
 MicroScope Resistivity- and imagingwhile-drilling service MicroScope Magnify your reservoir Multidepth laterolog resistivity Multidepth borehole images Mud resistivity Azimuthal gamma ray Bit resistivity
MicroScope Resistivity- and imagingwhile-drilling service MicroScope Magnify your reservoir Multidepth laterolog resistivity Multidepth borehole images Mud resistivity Azimuthal gamma ray Bit resistivity
X,800. X,850 ft. X,900 ft. X,950 ft. X,000 ft. GeoSphere. Reservoir Mapping-While-Drilling Service
 X,800 X,850 ft X,900 ft X,950 ft X,000 ft GeoSphere Reservoir Mapping-While-Drilling Service Discover reservoir mapping-while-drilling...... and reveal subsurface beddings and fluid contacts at the reservoir
X,800 X,850 ft X,900 ft X,950 ft X,000 ft GeoSphere Reservoir Mapping-While-Drilling Service Discover reservoir mapping-while-drilling...... and reveal subsurface beddings and fluid contacts at the reservoir
Advances in Geosteering
 Advances in Geosteering SMART4D While Drilling Geosteering Marcellus Case Study Joint Presentation: Feb 27 th 2014, Houston, TX Rocky Mottahedeh, P.Geol. P.Eng. EOW Report University_31_18_2H Advances
Advances in Geosteering SMART4D While Drilling Geosteering Marcellus Case Study Joint Presentation: Feb 27 th 2014, Houston, TX Rocky Mottahedeh, P.Geol. P.Eng. EOW Report University_31_18_2H Advances
Precise well placement in the Cygnus gas field. Ian Dredge ENGIE E&P UK Limited
 Precise well placement in the Cygnus gas field Ian Dredge ENGIE E&P UK Limited Executive summary The Lower Leman reservoir in the Cygnus gas field is highly layered with low vertical permeability The use
Precise well placement in the Cygnus gas field Ian Dredge ENGIE E&P UK Limited Executive summary The Lower Leman reservoir in the Cygnus gas field is highly layered with low vertical permeability The use
Downhole Navigation for Oil & Gas Drilling
 Downhole Navigation for Oil & Gas Drilling Martin E. Poitzsch Research Director, Sensor Physics Schlumberger-Doll Research, Cambridge, MA A Division of Schlumberger Ltd. Outline Importance of Accurate
Downhole Navigation for Oil & Gas Drilling Martin E. Poitzsch Research Director, Sensor Physics Schlumberger-Doll Research, Cambridge, MA A Division of Schlumberger Ltd. Outline Importance of Accurate
DEVEX Moving in the Right Direction; Realising Upside Potential in a Mature Field Using Real Time 3D Geo-Steering Technology
 DEVEX 2010 Moving in the Right Direction; Realising Upside Potential in a Mature Field Using Real Time 3D Geo-Steering Technology Authors: Lisa Chisholm, Chevron Upstream Europe David Holbrough, Baker
DEVEX 2010 Moving in the Right Direction; Realising Upside Potential in a Mature Field Using Real Time 3D Geo-Steering Technology Authors: Lisa Chisholm, Chevron Upstream Europe David Holbrough, Baker
Directional Drilling. History
 Directional Drilling Directional drilling is the science of deviating a well bore along a planned course to a subsurface target whose location is a given lateral distance and direction from the vertical.
Directional Drilling Directional drilling is the science of deviating a well bore along a planned course to a subsurface target whose location is a given lateral distance and direction from the vertical.
Heterogeneity Type Porosity. Connected Conductive Spot. Fracture Connected. Conductive Spot. Isolated Conductive Spot. Matrix.
 Porosity Histogram Porosity Contribution 1.3.3.3 Connected 9.8 ohm.m U R D 9 18 7. 5.25 4.38 3.5 2.63 1.75 48 Heterogeneity Distribution Image Orientation, L U 27 36.4.3 X,X72.5 Depth, ft.3 1 Isolated.3
Porosity Histogram Porosity Contribution 1.3.3.3 Connected 9.8 ohm.m U R D 9 18 7. 5.25 4.38 3.5 2.63 1.75 48 Heterogeneity Distribution Image Orientation, L U 27 36.4.3 X,X72.5 Depth, ft.3 1 Isolated.3
Predicting the path ahead
 Predicting the path ahead Horizontal drilling has become a routine procedure in many parts of the world and is particularly popular in the Middle East. Despite increasing familiarity with the techniques,
Predicting the path ahead Horizontal drilling has become a routine procedure in many parts of the world and is particularly popular in the Middle East. Despite increasing familiarity with the techniques,
SELECTED PAPERS AND PUBLICATIONS
 SELECTED PAPERS AND PUBLICATIONS SPE 153580: Milestone in Production Using Proactive Azimuthal Deep- Resistivity Sensor Combined with Advanced Geosteering Techniques: Tarapoa Block, Ecuador. Alex Guevara,
SELECTED PAPERS AND PUBLICATIONS SPE 153580: Milestone in Production Using Proactive Azimuthal Deep- Resistivity Sensor Combined with Advanced Geosteering Techniques: Tarapoa Block, Ecuador. Alex Guevara,
Introduction to Formation Evaluation Abiodun Matthew Amao
 Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
Introduction to Formation Evaluation By Abiodun Matthew Amao Monday, September 09, 2013 Well Logging PGE 492 1 Lecture Outline What is formation evaluation? Why do we evaluate formation? What do we evaluate?
1st SPWLA India Regional Conference Formation Evaluation in Horizontal Wells
 GOING BEYOND GEOMETRICAL DRILLING : A REVIEW OF THE CONTRIBUTION OF LWD MEASUREMENTS TO THE IMPROVEMENT OF WELL PLACEMENT. Jacques R. Tabanou, Jean Michel Denichou, Jack Horkowitz, Dzevat Omeragic, John
GOING BEYOND GEOMETRICAL DRILLING : A REVIEW OF THE CONTRIBUTION OF LWD MEASUREMENTS TO THE IMPROVEMENT OF WELL PLACEMENT. Jacques R. Tabanou, Jean Michel Denichou, Jack Horkowitz, Dzevat Omeragic, John
The Deployment of an Azimuthal Resistivity Tool for Geosteering - A Case Study from the Foinaven Field (North Sea)*
 The Deployment of an Azimuthal Resistivity Tool for Geosteering - A Case Study from the Foinaven Field (North Sea)* Martin Bedrock 1 and Darren Moody 1 Search and Discovery Article #40540 (2010) Posted
The Deployment of an Azimuthal Resistivity Tool for Geosteering - A Case Study from the Foinaven Field (North Sea)* Martin Bedrock 1 and Darren Moody 1 Search and Discovery Article #40540 (2010) Posted
Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics COPYRIGHT. Introduction to Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics
 Learning Objectives Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics Introduction to Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
Learning Objectives Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics Introduction to Petrophysical Data and Open Hole Logging Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
SPWLA-INDIA 3rd Annual Logging Symposium, Mumbai, India Nov 25-26, 2011
 GEOSTEERING TECHNOLOGY SHOWS THE NEW DIRECTION FOR MAJOR PRODUCTION ENHANCEMENT IN WESTERN ONSHORE, INDIA: AN EXCEPTIONAL SUCCESS-STORY FROM ONGC AHMEDABAD ASSET Arvind Vilasrao Sapkal*, Chandan Jyoti
GEOSTEERING TECHNOLOGY SHOWS THE NEW DIRECTION FOR MAJOR PRODUCTION ENHANCEMENT IN WESTERN ONSHORE, INDIA: AN EXCEPTIONAL SUCCESS-STORY FROM ONGC AHMEDABAD ASSET Arvind Vilasrao Sapkal*, Chandan Jyoti
Multi-target wells: a new concept to improve well economics
 Multi-target wells: a new concept to improve well economics OMV AG, Vienna, Austria ABSTRACT: The Vienna Basin is a sedimentary basin more than 10 km in thickness and composed of more than a dozen hydrocarbon
Multi-target wells: a new concept to improve well economics OMV AG, Vienna, Austria ABSTRACT: The Vienna Basin is a sedimentary basin more than 10 km in thickness and composed of more than a dozen hydrocarbon
Abstract. 1. Introduction. Geophysics Engineer-Schlumberger 2. M.Sc. Petroleum-PEMEX 3,4 Geologists-PEMEX
 IBP3018 MINIMIZING DRILLING RISKS FOR EXPLORATION WELL IN DEEP WATER USING SEISMIC WHILE DRILLING TECHNOLOGY Sanchez Adrian 1, Mora Alfonso 2 Aguilera Leonardo 3, Gaitan Rito 4 Copyright 2010, Brazilian
IBP3018 MINIMIZING DRILLING RISKS FOR EXPLORATION WELL IN DEEP WATER USING SEISMIC WHILE DRILLING TECHNOLOGY Sanchez Adrian 1, Mora Alfonso 2 Aguilera Leonardo 3, Gaitan Rito 4 Copyright 2010, Brazilian
Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model
 IPTC 16575 Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model Chuck Peng, John Dai and Sherman Yang, Schlumberger WesternGeco Copyright 2013, International
IPTC 16575 Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model Chuck Peng, John Dai and Sherman Yang, Schlumberger WesternGeco Copyright 2013, International
GEOSTEERING SERVICES. Geosteering Technologies develops the software for geosteering in real-time and provides technical support in this areas.
 Компания «Геонавигационные Технологии» занимается производством программного обеспечения для сопровождения наклоннонаправленного бурения скважин, а также оказывает консультационные услуги в данной области.
Компания «Геонавигационные Технологии» занимается производством программного обеспечения для сопровождения наклоннонаправленного бурения скважин, а также оказывает консультационные услуги в данной области.
New MWD, LWD Services Help Drillers Keep Bit In Formation s Sweet Spot
 NOVEMBER 2013 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry New MWD, LWD Services Help Drillers Keep Bit In Formation s Sweet Spot By Randy Brown, Les Honeyman,
NOVEMBER 2013 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry New MWD, LWD Services Help Drillers Keep Bit In Formation s Sweet Spot By Randy Brown, Les Honeyman,
M.M.Panigrahi*, S.R.Meena, Rudal Singh, B.C.Sethy, R.D.Chourasiya, S.K.Verma. ONGC Ltd., India; Pallav Chakraborty, Schlumberger, India Geomarket.
 P - 35 Improved Hydrocarbon Recovery from Carbonate Reservoir of Mumbai High North Field by Geological Steering Based on Real Time LWD (Logging While Drilling) Data- A Case Study. M.M.Panigrahi*, S.R.Meena,
P - 35 Improved Hydrocarbon Recovery from Carbonate Reservoir of Mumbai High North Field by Geological Steering Based on Real Time LWD (Logging While Drilling) Data- A Case Study. M.M.Panigrahi*, S.R.Meena,
Drillworks. DecisionSpace Geomechanics DATA SHEET
 DATA SHEET Drillworks overview DecisionSpace Geomechanics Key features Pre-drill, real-time, and post-drill analyses are all easily performed in one application using the latest data from across the field
DATA SHEET Drillworks overview DecisionSpace Geomechanics Key features Pre-drill, real-time, and post-drill analyses are all easily performed in one application using the latest data from across the field
N121: Modern Petrophysical Well Log Interpretation
 Summary This course presents the principles and methods associated with the petrophysical interpretation of openand cased-hole wireline and LWD well logs. Open-hole topics covered include the use of log
Summary This course presents the principles and methods associated with the petrophysical interpretation of openand cased-hole wireline and LWD well logs. Open-hole topics covered include the use of log
Corporate Houston, TX... (713)
 Allied Wireline Services and Horizontal Wireline Services are proud to announce that we are now one company, dedicated to providing you the highest value wireline services and built on the commitment to
Allied Wireline Services and Horizontal Wireline Services are proud to announce that we are now one company, dedicated to providing you the highest value wireline services and built on the commitment to
Surface and Wellbore Positioning Errors and the Impact on Subsurface Error Models and Reservoir Estimates
 Surface and Wellbore Positioning Errors and the Impact on Subsurface Error Models and Reservoir Estimates Ed Stockhausen 1 43 rd General Meeting March 4 th, 2016 Speaker Information Ed Stockhausen Horizontal
Surface and Wellbore Positioning Errors and the Impact on Subsurface Error Models and Reservoir Estimates Ed Stockhausen 1 43 rd General Meeting March 4 th, 2016 Speaker Information Ed Stockhausen Horizontal
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS
 NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
NOTICE CONCERNING COPYRIGHT RESTRICTIONS This document may contain copyrighted materials. These materials have been made available for use in research, teaching, and private study, but may not be used
True 3D measurements for enhanced reservoir quantification. Rt Scanner
 True 3D measurements for enhanced reservoir quantification Rt Scanner Rt Scanner measurements in three dimensions at multiple depths of investigation (DOIs) quantify even low-resistivity laminated pay
True 3D measurements for enhanced reservoir quantification Rt Scanner Rt Scanner measurements in three dimensions at multiple depths of investigation (DOIs) quantify even low-resistivity laminated pay
Wellsite Consulting Services Diversified Well Logging LLC. All Rights Reserved.
 Wellsite Consulting Services We are CUSTOMER FOCUSED: We seek to exceed customer expectations by providing solutions that improve their drilling, completions, and production economics OUR CORE VALUES DEFINE
Wellsite Consulting Services We are CUSTOMER FOCUSED: We seek to exceed customer expectations by providing solutions that improve their drilling, completions, and production economics OUR CORE VALUES DEFINE
Optimizing Drilling Performance by Wellbore Stability and Pore-Pressure Evaluation in Deepwater Exploration T. Klimentos, Schlumberger
 IPTC 10933 Optimizing Drilling Performance by Wellbore Stability and Pore-Pressure Evaluation in Deepwater Exploration T. Klimentos, Schlumberger Copyright 2005, International Petroleum Technology Conference
IPTC 10933 Optimizing Drilling Performance by Wellbore Stability and Pore-Pressure Evaluation in Deepwater Exploration T. Klimentos, Schlumberger Copyright 2005, International Petroleum Technology Conference
Horizontal well Development strategy
 Horizontal well Development strategy Pakawas Mangkang Team Member Yoseph Partono Stephan Otero Duangdao Chutanukarn Warin Lobtong Suarporn Ketpreechasawat B8/32 Asset, Thailand Chiangmai, 11 th Nov-13
Horizontal well Development strategy Pakawas Mangkang Team Member Yoseph Partono Stephan Otero Duangdao Chutanukarn Warin Lobtong Suarporn Ketpreechasawat B8/32 Asset, Thailand Chiangmai, 11 th Nov-13
Rotary Steerable System Technology Case Studies in the Canadian Foothills: A Challenging Drilling Environment
 AADE-07-NTCE-71 Rotary Steerable System Technology Case Studies in the Canadian Foothills: A Challenging Drilling Environment Essam Adly, Schlumberger Copyright 2007, AADE This paper was prepared for presentation
AADE-07-NTCE-71 Rotary Steerable System Technology Case Studies in the Canadian Foothills: A Challenging Drilling Environment Essam Adly, Schlumberger Copyright 2007, AADE This paper was prepared for presentation
Formation Resistivity Measurements Through Casing In The Wells of Bombay Offshore Basin
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 101-105 Formation Resistivity Measurements Through Casing In The Wells of Bombay Offshore Basin B. V. Jacob, Naresh Kumar,
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 101-105 Formation Resistivity Measurements Through Casing In The Wells of Bombay Offshore Basin B. V. Jacob, Naresh Kumar,
Identified a possible new offset location where the customer is currently exploring drill options.
 GroundMetrics was hired to conduct a Full-Field Resistivity Survey for an oil and gas producer that needed to make crucial decisions to drive profitability at the location. The results saved them hundreds
GroundMetrics was hired to conduct a Full-Field Resistivity Survey for an oil and gas producer that needed to make crucial decisions to drive profitability at the location. The results saved them hundreds
GEOSTEERING Scope of work, project management and geosteering scenarios
 GEOSTEERING Scope of work, project management and geosteering scenarios Chinook Consulting Services Office: 403 242 1522 742 Memorial Drive NW Calgary, Alberta T2N 3C7 reports@chinookconsulting.ca www.chinookconsulting.ca
GEOSTEERING Scope of work, project management and geosteering scenarios Chinook Consulting Services Office: 403 242 1522 742 Memorial Drive NW Calgary, Alberta T2N 3C7 reports@chinookconsulting.ca www.chinookconsulting.ca
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs
 Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
Advances in Elemental Spectroscopy Logging: A Cased Hole Application Offshore West Africa
 Journal of Geography and Geology; Vol. 9, No. 4; 2017 ISSN 1916-9779 E-ISSN 1916-9787 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Advances in Elemental Spectroscopy Logging: A Cased Hole Application
Journal of Geography and Geology; Vol. 9, No. 4; 2017 ISSN 1916-9779 E-ISSN 1916-9787 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Advances in Elemental Spectroscopy Logging: A Cased Hole Application
INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS
 BY: MUHAMMAD ZAHID INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS 1- SPONTANEOUS POTENTIAL (SP) The Spontaneous potential survey, (sp) was one of the first measurements, which was carried out, in a well bore. The SP log
BY: MUHAMMAD ZAHID INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS 1- SPONTANEOUS POTENTIAL (SP) The Spontaneous potential survey, (sp) was one of the first measurements, which was carried out, in a well bore. The SP log
ACCURATE HORIZONTAL WELL PLACEMENT THROUGH EVALUATION OF MULTIPLE LWD IMAGES WITH GEOLOGICAL MODELING.
 ACCURATE HORIZONTAL WELL PLACEMENT THROUGH EVALUATION OF MULTIPLE LWD IMAGES WITH GEOLOGICAL MODELING. Mark Bacciarelli, Giorgio Nardi; Baker Hughes INTEQ, A. A. Al-Hajari, and S. Ma, Saudi Aramco Copyright
ACCURATE HORIZONTAL WELL PLACEMENT THROUGH EVALUATION OF MULTIPLE LWD IMAGES WITH GEOLOGICAL MODELING. Mark Bacciarelli, Giorgio Nardi; Baker Hughes INTEQ, A. A. Al-Hajari, and S. Ma, Saudi Aramco Copyright
Cornish Institute of Engineers Conference th October 2013
 Wellbore Stability and Real Time Drilling Optimisation: Delivered Worldwide from Cornwall Sarah Marks Cornish Institute of Engineers Conference 2013 11 th October 2013 GeoScience Limited, Falmouth Business
Wellbore Stability and Real Time Drilling Optimisation: Delivered Worldwide from Cornwall Sarah Marks Cornish Institute of Engineers Conference 2013 11 th October 2013 GeoScience Limited, Falmouth Business
Horizontal Drilling Pilot In a Shallow Heavy Oil Reservoir in Northwestern Romania. Authors: John Lavelle, Amin Yaghoobi
 Horizontal Drilling Pilot In a Shallow Heavy Oil Reservoir in Northwestern Romania Authors: John Lavelle, Amin Yaghoobi About Suplac Oil Field Discovered 1958 Oil Density 960 kg/m3 (16 API) Viscosity 2300
Horizontal Drilling Pilot In a Shallow Heavy Oil Reservoir in Northwestern Romania Authors: John Lavelle, Amin Yaghoobi About Suplac Oil Field Discovered 1958 Oil Density 960 kg/m3 (16 API) Viscosity 2300
Somenath Kar*, Krishnendu Ghosh*, Arnab Ghosh*, Koushik Sikdar*, Udit Kumar Guru*, Priyanka Bhattacharya*, K.M Sundaram**, G M Chavan**
 P-419 Summary Characterizing the Clay Particle distribution in Deepwater Channel Levee Complex using Borehole Micro Image and Multi Triaxial Induction Measurement: A Case Studies from Eastern Offshore
P-419 Summary Characterizing the Clay Particle distribution in Deepwater Channel Levee Complex using Borehole Micro Image and Multi Triaxial Induction Measurement: A Case Studies from Eastern Offshore
An Integrated Approach to Volume of Shale Analysis: Niger Delta Example, Orire Field
 World Applied Sciences Journal 7 (4): 448-452, 2009 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2009 An Integrated Approach to Volume of Shale Analysis: Niger Delta Example, Orire Field 1 1 2 L. Adeoti, E.A. Ayolabi
World Applied Sciences Journal 7 (4): 448-452, 2009 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2009 An Integrated Approach to Volume of Shale Analysis: Niger Delta Example, Orire Field 1 1 2 L. Adeoti, E.A. Ayolabi
Exploring and Drilling for Oil and Gas. Prepared by Tom Sheeran
 Exploring and Drilling for Oil and Gas What are Oil and Gas? Oil and Gas are substances found within the earth s crust. They are thought to come from decomposed plant and animal matter. Scientists believe
Exploring and Drilling for Oil and Gas What are Oil and Gas? Oil and Gas are substances found within the earth s crust. They are thought to come from decomposed plant and animal matter. Scientists believe
Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAMWORK DELIVERS OUTSTANDING KRECHBA HORIZONTAL WELL PERFORMANCE
 6 JOURNEES SCIENTIFIQUES ET TECHNIQUES Hôtel Hilton, 20 to 22 june 2004, Algiers, Algeria MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAMWORK DELIVERS OUTSTANDING KRECHBA HORIZONTAL WELL PERFORMANCE FOSTER, L. AIDOO, A. TOURQUI,
6 JOURNEES SCIENTIFIQUES ET TECHNIQUES Hôtel Hilton, 20 to 22 june 2004, Algiers, Algeria MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAMWORK DELIVERS OUTSTANDING KRECHBA HORIZONTAL WELL PERFORMANCE FOSTER, L. AIDOO, A. TOURQUI,
Shale gas developments: enabled by technology
 Shale gas developments: enabled by technology Andrew Jennings * reviews some exploration and development technologies employed by Schlumberger that have supported the economic production of shale gas in
Shale gas developments: enabled by technology Andrew Jennings * reviews some exploration and development technologies employed by Schlumberger that have supported the economic production of shale gas in
AADE 2009NTCE DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF HIGH DOGLEG ROTARY STEERABLE SYSTEM
 2009 NATIONAL TECHNICAL CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION, NEW ORLEANS, LOUISIANA AADE 2009NTCE-14-06 DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF HIGH DOGLEG ROTARY STEERABLE SYSTEM AUTHOR(S) & AFFILIATIONS: SONNY BRYAN, JOE COX,
2009 NATIONAL TECHNICAL CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION, NEW ORLEANS, LOUISIANA AADE 2009NTCE-14-06 DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF HIGH DOGLEG ROTARY STEERABLE SYSTEM AUTHOR(S) & AFFILIATIONS: SONNY BRYAN, JOE COX,
P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd.
 1. Synopsis: P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd. UK offshore Licence P1488 was awarded to OMV, Dana Petroleum and Rocksource in the 24 th Licence Round on the 24 th of January 2007 as a frontier
1. Synopsis: P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd. UK offshore Licence P1488 was awarded to OMV, Dana Petroleum and Rocksource in the 24 th Licence Round on the 24 th of January 2007 as a frontier
OTC OTC PP. Abstract
 OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
Antelope Hills Directionally Drilled Water Well. Theresa Jehn-Dellaport Jehn Water Consultants, Inc.
 Antelope Hills Directionally Drilled Water Well Theresa Jehn-Dellaport Directional Well Applications Deep Bedrock Aquifers Proven Oil field technology Initial Analysis indicates up to 4 times the production
Antelope Hills Directionally Drilled Water Well Theresa Jehn-Dellaport Directional Well Applications Deep Bedrock Aquifers Proven Oil field technology Initial Analysis indicates up to 4 times the production
Formation Evaluation: Logs and cores
 These powerpoint files were produced for the Earth History class at the Free University Berlin, Department of Geological Sciences The copyright for texts, graphical elements, and images lies with C. Heubeck,
These powerpoint files were produced for the Earth History class at the Free University Berlin, Department of Geological Sciences The copyright for texts, graphical elements, and images lies with C. Heubeck,
Improved Petrophysical Analysis in Horizontal Wells: From Log Modeling Through Formation Evaluation to Reducing Model Uncertainty A Case Study
 SPE 164881 Improved Petrophysical Analysis in Horizontal Wells: From Log Modeling Through Formation Evaluation to Reducing Model Uncertainty A Case Study A. Valdisturlo, M. Mele, Eni e&p. D. Maggs SPE,
SPE 164881 Improved Petrophysical Analysis in Horizontal Wells: From Log Modeling Through Formation Evaluation to Reducing Model Uncertainty A Case Study A. Valdisturlo, M. Mele, Eni e&p. D. Maggs SPE,
Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges
 Haynesville Shale Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges Solving challenges. conservative estimates show 168 trillion cubic feet of natural gas Haynesville formation The Haynesville shale
Haynesville Shale Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges Solving challenges. conservative estimates show 168 trillion cubic feet of natural gas Haynesville formation The Haynesville shale
The State of the Industry of Drillbit Geomechanics
 The State of the Industry of Drillbit Geomechanics Value Proposition of Drillbit Geomechanics In Situ Rock Properties Along All Wells allows Operators to Optimize Completion Designs Improved completion
The State of the Industry of Drillbit Geomechanics Value Proposition of Drillbit Geomechanics In Situ Rock Properties Along All Wells allows Operators to Optimize Completion Designs Improved completion
Cracking the carbonate code
 Cracking the carbonate code Carbonate reservoirs are the most complex reservoirs in existence, and the Middle East is the place to find them. The complexity and unpredictability of carbonates has frequently
Cracking the carbonate code Carbonate reservoirs are the most complex reservoirs in existence, and the Middle East is the place to find them. The complexity and unpredictability of carbonates has frequently
Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole Data over Umoru Field, Niger Delta-Nigeria
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, 179-183 doi:10.4236/ijg.2011.22019 Published Online May 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole
International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, 179-183 doi:10.4236/ijg.2011.22019 Published Online May 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole
F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin
 The Role of 4D Seismic Interpretation and Dynamic Modelling in the Successful Drilling of a Late Stage Development Well in the West Brae Field, North Sea F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin Introduction
The Role of 4D Seismic Interpretation and Dynamic Modelling in the Successful Drilling of a Late Stage Development Well in the West Brae Field, North Sea F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin Introduction
Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production
 Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Dr. R. Giri Prasad 1 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Petroleum Engineering, Aditya Engineering College, hod_pt@aec.edu.in I. INTRODUCTION
Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Dr. R. Giri Prasad 1 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Petroleum Engineering, Aditya Engineering College, hod_pt@aec.edu.in I. INTRODUCTION
Characterization of Fractures from Borehole Images. Sandeep Mukherjee- Halliburton
 Characterization of Fractures from Borehole Images Sandeep Mukherjee- Halliburton Summary Characterization of fractures is an important aspect of formation evaluation. Fractures, when present could alter
Characterization of Fractures from Borehole Images Sandeep Mukherjee- Halliburton Summary Characterization of fractures is an important aspect of formation evaluation. Fractures, when present could alter
IPTC Abstract. Introduction
 IPTC 14538 Doubling a Marginal Field's Reserves by Understanding the Application of "Enabling" Technology Ong Tee Suan, Newfield Exploration; Mark Lambert, Newfield Sarawak Malaysia Inc; Barry Goodin,
IPTC 14538 Doubling a Marginal Field's Reserves by Understanding the Application of "Enabling" Technology Ong Tee Suan, Newfield Exploration; Mark Lambert, Newfield Sarawak Malaysia Inc; Barry Goodin,
Relinquishment Report
 Relinquishment Report Licence P1403 Block 13/22d Chevron North Sea Limited Korean National Oil Company Chevron North Sea Limited December 2009 1 SYNOPSIS... 3 2 INTRODUCTION. 3 2.1 Licence Terms.. 3 2.2
Relinquishment Report Licence P1403 Block 13/22d Chevron North Sea Limited Korean National Oil Company Chevron North Sea Limited December 2009 1 SYNOPSIS... 3 2 INTRODUCTION. 3 2.1 Licence Terms.. 3 2.2
Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford shale
 Originally appeared in World Oil JULY 2017 issue, pgs 53-57. Posted with permission. SHALETECH REPORT / INNOVATIONS AND TECHNIQUES Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford
Originally appeared in World Oil JULY 2017 issue, pgs 53-57. Posted with permission. SHALETECH REPORT / INNOVATIONS AND TECHNIQUES Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford
NAPE 2011 Lagos, Nigeria 28 November-2 December 2011 Extended Abstract
 T: +44 191 334 2191 E: info@ikonscience.com W: www.ikonscience.com Pore Pressure Prediction in the Niger Delta NAPE 2011 Lagos, Nigeria 28 November-2 December 2011 Extended Abstract PORE PRESSURE PREDICTION
T: +44 191 334 2191 E: info@ikonscience.com W: www.ikonscience.com Pore Pressure Prediction in the Niger Delta NAPE 2011 Lagos, Nigeria 28 November-2 December 2011 Extended Abstract PORE PRESSURE PREDICTION
1 General introduction
 1 General introduction 1.1 Oil well drilling system Oil and other hydrocarbons are the primary source of global energy. However, the exploration of these hydrocarbons presents a myriad of challenges resulting
1 General introduction 1.1 Oil well drilling system Oil and other hydrocarbons are the primary source of global energy. However, the exploration of these hydrocarbons presents a myriad of challenges resulting
Pore Pressure Prediction and Distribution in Arthit Field, North Malay Basin, Gulf of Thailand
 Pore Pressure Prediction and Distribution in Arthit Field, North Malay Basin, Gulf of Thailand Nutthaphon Ketklao Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
Pore Pressure Prediction and Distribution in Arthit Field, North Malay Basin, Gulf of Thailand Nutthaphon Ketklao Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn
Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling
 Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling Drilling Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling The term drilling indicates the whole complex of operations necessary to construct wells of circular section applying
Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling Drilling Introduction to Oil&Gas Well Drilling The term drilling indicates the whole complex of operations necessary to construct wells of circular section applying
The Maule Field: An Economic Small Field Development
 AUSTRALIA ARGENTINA CANADA EGYPT NORTH SEA U.S. CENTRAL U.S. GULF The Maule Field: An Economic Small Field Development J. Pyle*, K. Koster, G. Barker and P. Rose Introduction 2 Eocene penetrations with
AUSTRALIA ARGENTINA CANADA EGYPT NORTH SEA U.S. CENTRAL U.S. GULF The Maule Field: An Economic Small Field Development J. Pyle*, K. Koster, G. Barker and P. Rose Introduction 2 Eocene penetrations with
Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques.
 ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil ASA, N-4035 Stavanger, Norway Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques. Summary By the use of 3D seismic data,
ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil ASA, N-4035 Stavanger, Norway Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques. Summary By the use of 3D seismic data,
J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science)
 29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
More Than Painting The Line: Optimizing Asset Value With Wellbore Placement
 More Than Painting The Line: Optimizing Asset Value With Wellbore Placement Marc Willerth VP of Survey Technologies, MagVAR Marc.Willerth@magvar.com May 22nd, 2018 Slide 1 Asset Optimization: Longer Laterals
More Than Painting The Line: Optimizing Asset Value With Wellbore Placement Marc Willerth VP of Survey Technologies, MagVAR Marc.Willerth@magvar.com May 22nd, 2018 Slide 1 Asset Optimization: Longer Laterals
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Fundamentals Of Petroleum Engineering FORMATION EVALUATION
 Fundamentals Of Petroleum Engineering FORMATION EVALUATION Mohd Fauzi Hamid Wan Rosli Wan Sulaiman Department of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum & Renewable Engineering Universiti Technologi
Fundamentals Of Petroleum Engineering FORMATION EVALUATION Mohd Fauzi Hamid Wan Rosli Wan Sulaiman Department of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum & Renewable Engineering Universiti Technologi
The Evolution of Drilling Techniques at the Camden Gas Project. Chris Holmes and Jon Black AGL 27 th June 2007
 The Evolution of Drilling Techniques at the Camden Gas Project Chris Holmes and Jon Black AGL 27 th June 2007 1 Camden Gas Project Status AGL acquired operatorship from Sydney Gas February 2006 106 production
The Evolution of Drilling Techniques at the Camden Gas Project Chris Holmes and Jon Black AGL 27 th June 2007 1 Camden Gas Project Status AGL acquired operatorship from Sydney Gas February 2006 106 production
Geohazards have a direct impact on the drilling and
 SPECIAL Geohazards SECTION: G e o h a z a r d s A new, fully integrated method for seismic geohazard prediction ahead of the bit while drilling CENGIZ ESMERSOY, ARTURO RAMIREZ, SHARON TEEBENNY, YANGJUN
SPECIAL Geohazards SECTION: G e o h a z a r d s A new, fully integrated method for seismic geohazard prediction ahead of the bit while drilling CENGIZ ESMERSOY, ARTURO RAMIREZ, SHARON TEEBENNY, YANGJUN
Rocsol D-Series Technology
 Rocsol D-Series Technology D-ROCK October 25, 2017 Rocsol Technologies Inc. Challenges of Horizontal Well Logging Conventional logging and rock mechanical testing are expensive (logging cost and rig time)
Rocsol D-Series Technology D-ROCK October 25, 2017 Rocsol Technologies Inc. Challenges of Horizontal Well Logging Conventional logging and rock mechanical testing are expensive (logging cost and rig time)
Fluids, Hole Cleaning and Tripping Optimization
 Fluids, Hole Cleaning and Tripping Optimization Overview Hole cleaning in highly deviated wells is probably one of the most misunderstood concepts. Primarily, relying on Plastic Viscosity and Yield Point
Fluids, Hole Cleaning and Tripping Optimization Overview Hole cleaning in highly deviated wells is probably one of the most misunderstood concepts. Primarily, relying on Plastic Viscosity and Yield Point
Main Challenges and Uncertainties for Oil Production from Turbidite Reservoirs in Deep Water Campos Basin, Brazil*
 Main Challenges and Uncertainties for Oil Production from Turbidite Reservoirs in Deep Water Campos Basin, Brazil* Carlos H. Bruhn 1, Antonio Pinto 1, and Paulo R. Johann 1 Search and Discovery Article
Main Challenges and Uncertainties for Oil Production from Turbidite Reservoirs in Deep Water Campos Basin, Brazil* Carlos H. Bruhn 1, Antonio Pinto 1, and Paulo R. Johann 1 Search and Discovery Article
P026 Outcrop-based reservoir modeling of a naturally fractured siliciclastic CO 2 sequestration site, Svalbard, Arctic Norway
 P026 Outcrop-based reservoir modeling of a naturally fractured siliciclastic CO 2 sequestration site, Svalbard, Arctic Norway K. Senger (University of Bergen / CIPR), K. Ogata* (University Centre in Svalbard),
P026 Outcrop-based reservoir modeling of a naturally fractured siliciclastic CO 2 sequestration site, Svalbard, Arctic Norway K. Senger (University of Bergen / CIPR), K. Ogata* (University Centre in Svalbard),
Well Logging. Salam Al Rbeawi 2011
 Well Logging Salam Al Rbeawi 2011 Well Logging: Is a technique used for formation evaluation to determine the size of the reservoir and the amount of oil and gas in place. The following parameters can
Well Logging Salam Al Rbeawi 2011 Well Logging: Is a technique used for formation evaluation to determine the size of the reservoir and the amount of oil and gas in place. The following parameters can
EMEKA M. ILOGHALU, NNAMDI AZIKIWE UNIVERSITY, AWKA, NIGERIA.
 Automatic classification of lithofacies and interpretation of depositional environment using Neural Networks Technique - A Novel Computer-Based methodology for 3-D reservoir geological modelling and exploration
Automatic classification of lithofacies and interpretation of depositional environment using Neural Networks Technique - A Novel Computer-Based methodology for 3-D reservoir geological modelling and exploration
GeoSteering
 GeoSteering GeoSteering Significance The geosteering uses real-time geological parameters to clarify various uncertainties and effectively control the landing and direction of the well trajectory, and
GeoSteering GeoSteering Significance The geosteering uses real-time geological parameters to clarify various uncertainties and effectively control the landing and direction of the well trajectory, and
Introduction Geology
 Introduction The Wild Horse Anticline is located in the prolific Bighorn Basin of Wyoming about 5 miles northeast of the town of Basin. This structure demonstrates excellent fourway closure encompassing
Introduction The Wild Horse Anticline is located in the prolific Bighorn Basin of Wyoming about 5 miles northeast of the town of Basin. This structure demonstrates excellent fourway closure encompassing
Shale Development and Hydraulic Fracturing or Frac ing (Fracking) What is it?
 P E T R O L E U M E N G I N E E R I N G D E P A R T M E N T Shale Development and Hydraulic Fracturing or Frac ing (Fracking) What is it? Dr. Will Fleckenstein, PE Colorado School of Mines 1 Who is involved
P E T R O L E U M E N G I N E E R I N G D E P A R T M E N T Shale Development and Hydraulic Fracturing or Frac ing (Fracking) What is it? Dr. Will Fleckenstein, PE Colorado School of Mines 1 Who is involved
Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
 Introduction to Oil and Gas Production Steven Marzuola ATA Energy Conference May 4-6, 2007 Houston Texas Introduction Dope, Joints, Tripping Strippers Casing, Tubing, Liner API - American Petroleum Institute
Introduction to Oil and Gas Production Steven Marzuola ATA Energy Conference May 4-6, 2007 Houston Texas Introduction Dope, Joints, Tripping Strippers Casing, Tubing, Liner API - American Petroleum Institute
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT. 6.1 Introduction. 6.2 Overburden Pressures
 6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
6. THE BOREHOLE ENVIRONMENT 6.1 Introduction Wireline logging has a single clearly defined purpose: to give accurate and representative data on the physical properties of the rock formations and fluids
DESIGN OF AN ULTRA-SPEED LAB-SCALE DRILLING RIG FOR SIMULATION OF HIGH SPEED DRILLING OPERATIONS IN HARD ROCKS. *V. Rasouli, B.
 DESIGN OF AN ULTRA-SPEED LAB-SCALE DRILLING RIG FOR SIMULATION OF HIGH SPEED DRILLING OPERATIONS IN HARD ROCKS *V. Rasouli, B. Evans Department of Petroleum Engineering, Curtin University ARRC Building,
DESIGN OF AN ULTRA-SPEED LAB-SCALE DRILLING RIG FOR SIMULATION OF HIGH SPEED DRILLING OPERATIONS IN HARD ROCKS *V. Rasouli, B. Evans Department of Petroleum Engineering, Curtin University ARRC Building,
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA
 FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA 1 Obioha C, ²Adiela U. P and ³*Egesi N 1,3 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, University of Port Harcourt,
FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA 1 Obioha C, ²Adiela U. P and ³*Egesi N 1,3 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, University of Port Harcourt,
The Stratigraphic Trap in the Benchamas Field Pattani Basin, Gulf of Thailand
 The Stratigraphic Trap in the Benchamas Field Pattani Basin, Gulf of Thailand Jurairat Buangam Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
The Stratigraphic Trap in the Benchamas Field Pattani Basin, Gulf of Thailand Jurairat Buangam Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Applications of Borehole Imaging to Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production
 Applications of Borehole Imaging to Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Instructor: Philippe MONTAGGION / NExT, Schlumberger Title: Petroleum Geology Consultant Specialty: Borehole Imaging, Petroleum
Applications of Borehole Imaging to Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Instructor: Philippe MONTAGGION / NExT, Schlumberger Title: Petroleum Geology Consultant Specialty: Borehole Imaging, Petroleum
Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir Sands (OML 60) from Wire-line Logs, Niger Delta, Nigeria. EKINE, A. S.
 JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at wwwbiolineorgbr/ja J Appl Sci Environ Manage December, 2009 Vol 13(4) 81-85 Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir
JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at wwwbiolineorgbr/ja J Appl Sci Environ Manage December, 2009 Vol 13(4) 81-85 Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir
Constrained Fault Construction
 Constrained Fault Construction Providing realistic interpretations of faults is critical in hydrocarbon and mineral exploration. Faults can act as conduits or barriers to subsurface fluid migration and
Constrained Fault Construction Providing realistic interpretations of faults is critical in hydrocarbon and mineral exploration. Faults can act as conduits or barriers to subsurface fluid migration and
PETROPHYSICAL EVALUATION CORE COPYRIGHT. Petrophysical Evaluation Approach and Shaly Sands Evaluation. By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
 PETROPHYSICAL EVALUATION CORE Petrophysical Evaluation Approach and Shaly Sands Evaluation LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Discuss how to approach a petrophysical evaluation
PETROPHYSICAL EVALUATION CORE Petrophysical Evaluation Approach and Shaly Sands Evaluation LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Discuss how to approach a petrophysical evaluation
Sperry Drilling New LWD Technology. Mike Dautel Petrophysics Manager Asia Pacific
 Sperry Drilling New LWD Technology Mike Dautel Petrophysics Manager Asia Pacific Complete LWD Formation Evaluation Azimuthal Gamma Ray Directional Sensors Multi-Depth Resistivity Imaging Azimuthal Density
Sperry Drilling New LWD Technology Mike Dautel Petrophysics Manager Asia Pacific Complete LWD Formation Evaluation Azimuthal Gamma Ray Directional Sensors Multi-Depth Resistivity Imaging Azimuthal Density
Relinquishment Report for Licence Number P1356, Block 48/8c March 2008
 Relinquishment Report for Licence Number P1356, Block 48/8c March 2008 Table of Contents 1.0 Header...3 2.0 Synopsis...3 3.0 Exploration Activities...4 4.0 Prospectivity Analysis...11 5.0 Conclusions...12
Relinquishment Report for Licence Number P1356, Block 48/8c March 2008 Table of Contents 1.0 Header...3 2.0 Synopsis...3 3.0 Exploration Activities...4 4.0 Prospectivity Analysis...11 5.0 Conclusions...12
Neutron Log. Introduction
 Neutron Log Introduction This summary focuses on the basic interactions between the tool s signal and measured information, that help characterize the formation. It is not intended to be a comprehensive
Neutron Log Introduction This summary focuses on the basic interactions between the tool s signal and measured information, that help characterize the formation. It is not intended to be a comprehensive
MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS COPYRIGHT. Coring Operations Basics. By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS Coring Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Understand why cores are justified and who needs core data
LEARNING OBJECTIVES MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS Coring Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Understand why cores are justified and who needs core data
Licence P1368: Relinquishment Report (end of 2 nd term) Hurricane Exploration PLC
 Licence P1368: Relinquishment Report (end of 2 nd term) Hurricane Exploration PLC March 2012 1. Header Licence Number: P1368 Licence Round: 23 rd Licence Type: Frontier Block Numbers: 202/4, 202/5, 204/30,
Licence P1368: Relinquishment Report (end of 2 nd term) Hurricane Exploration PLC March 2012 1. Header Licence Number: P1368 Licence Round: 23 rd Licence Type: Frontier Block Numbers: 202/4, 202/5, 204/30,
COPYRIGHT PETROSKILLS LLC
 RESISTIVITY LOGGING TOOLS AND INTERPRETATION CORE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Resistivity Logging Tools By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Explain the tool physics and applications of resistivity
RESISTIVITY LOGGING TOOLS AND INTERPRETATION CORE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Resistivity Logging Tools By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Explain the tool physics and applications of resistivity
