Size differences of the post-anoxia, biotic recovery brachiopod, Dyoros sp., in Hughes Creek Shale (Carboniferous), Richardson County, Nebraska.
|
|
|
- Clemence Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Size differences of the post-anoxia, biotic recovery brachiopod, Dyoros sp., in Hughes Creek Shale (Carboniferous), Richardson County, Nebraska. Daryl Johnson and Rex Hanger Dept. of Geography & Geology University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Whitewater, WI Abstract. Two localities of the Carboniferous Hughes Creek Shale in southeastern Nebraska contain both fossiliferous limestones and shales, as well as black shales interpreted as being deposited under anoxic conditions in ancient oceans. Fossils within strata above the anoxic layers represent life that had recovered from a local killing event. Examining the killing/recovery patterns on expanded, regional scales is made difficult due to the relative lack of good exposures between outcrops. Previous miscorrelations have occurred for the Hughes Creek Shale in two established collecting localities separated by only a few kilometers. Specimens of the brachiopod fossil, Dyoros sp., abundant at both localities were compared using the size frequency distributions of their length measurements. Null hypotheses of the equality of the medians and equality of the overall distributions were not able to be rejected, adding support to the current accepted interpretation of correlation for the two localities, allowing for future use of both for examining killing/recovery of life on expanded geographic scale. Introduction The Hughes Creek Shale of southeastern Nebraska is a Carboniferous Period (~ million years ago) rock unit that has been interpreted to contain evidence of several intervals of anoxia, or low/no oxygen in the oceans in which they were originally deposited. The anoxic episodes are shown as black-colored shales that are devoid of fossil remains. For the Hughes Creek Shale the anoxic episodes were regional in scale probably covering only several 100km 2. Even so, they are a good, small-scale model for the larger (global?) existence of anoxia during mass extinction events, such as at the end of the Permian Period (~250 million years ago), while the normal limestones and shales deposited above them (and containing fossils) indicate how life and environments recover afterwards.
2 Before testing any hypotheses of mass extinction and recovery, it is necessary to show that rocks in geographically separated locations can be correlated, or shown to be coeval. Locality 5 of Pabian and Diffendal (2003) is assumed to be correlative to their Locality 10, but they correctly note that it was only a few years before thought to be from a different formation, and several million years younger (Holterhoff and Pabian, 1990). Correlative rock units in this study are assumed to contain fossils with the same size characteristics. In order to test a hypothesis that Localities 5 and 10 are correlative, the size frequency distributions of one of the most distinctive and well-preserved species, the brachiopod Dyoros sp., were statistically compared. Significance for Astrobiology Anoxic events as preserved in the stratigraphic record on Earth are related to space science via the interdisciplinary sciences of Astrobiology and Exobiology. The current guidelines for NASA-supported studies of this type are the Astrobiology Roadmap (Des Marais et al., 2008). This paper addresses GOAL4 Understand how life on Earth and its planetary environment have co-evolved through geological time. Investigate the evolving relationships between Earth and its biota by integrating evidence from the geosciences and biosciences that shows how life evolved, responded to environmental change, and modified environmental conditions on a planetary scale. Objective 4.3 within GOAL 4 is to investigate the effects of extraterrestrial and terrestrial events upon the biosphere, with research based on the fossil record of life and its activities. Evidence of the timeliness of such studies is the fact that a complete session, entitled, Oxygen and Evolution: Looking to the Past was devoted to anoxic black rocks and their associated fossils in the most recent Astrobiology Science Conference 2012 (NASA, 2012). Location Carboniferous age rocks are sporadically exposed in road and stream cuts throughout southeastern Nebraska. Localities 5 and 10 (Figure 1) are both road cut exposures of the Carboniferous rocks in Richardson County, Nebraska, separated by approximately 10 miles of geographic distance. The land cover between the two localities is mostly agricultural, making exact correlations, and even formation identification, difficult.
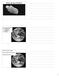
3 Figure 1 Locality map of Carboniferous localities in southeastern Nebraska (adapted from Pabian and Diffendal, 2003). Localities 5 and 10 are indicated with arrows. Methods Specimens of Dyoros sp. were collected in the field using both surface collection and bulk sampling methods. These have been shown previously to be an efficient method of maximizing species richness and biomass values. Both localities (5 and 10 of Pabian and Diffendal, 2003) were sampled for equal duration over relatively equal surface areas. In addition, the field collections were supplemented by previously collected specimens from the same sampling localities now deposited in the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater Invertebrate Paleontology collections. All Dyoros sp. specimens (N=103 from Loc. 5; N=257 from Loc. 10) were identified, sorted from the other taxa, counted, and measured for length and width (Figure 2) using digital calipers.
4 Figure 2 Ventral view of Dyoros sp. from the Hughes Creek Shale. White bar indicates the standardized length measurement for all individuals. For the individual shown, length = 12.73mm. All statistical analyses were performed using the software package, PAST (Hammer et al., 2001). Measurements of the length of unbroken specimens were log-transformed as is standard in biometric analyses (Zelditch et al., 2012) and tested for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Mann-Whitney U and Kruskal-Wallis tests were used to test hypotheses of equality of medians, and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to test a hypothesis of equality of distributions for the two sampling localities. Results Though both the distributions for Localities 5 and 10 appear normally distributed (Figure 3), Shapiro-Wilk tests for their normal distribution are rejected for Locality 5, p(normal) = 3.009e - 05 ; but not for Locality 10, p(normal) = Since at least one of the distributions is not normal, non-parametric statistical tests were used for further testing.
5 Figure 3 Size frequency distributions for log-transformed mm length measurements (x-axis) of Dyoros sp. at Locality 5 (right) and Locality 10 (left). Both the Mann-Whitney U and the Kruskal-Wallis are used with non-normal distributions tests for a null hypothesis that two samples are taken from populations with equal medians. Values greater than 0.05 would fail to reject such hypotheses, and thus one could not say that the medians of the two distributions had different medians. Both the Mann-Whitney (p= ) and the Kruskal-Wallis (p=0.0521) fail to reject the null hypothesis. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov can test a null hypothesis of equality of overall distributions for nonnormal data. For a null hypothesis that the two samples are taken from populations with equal distributions, p values greater than 0.05 will fail to reject, and one could say that the two samples had different distributions. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov (p=0.1563) thus fails to reject the null hypothesis. Discussion and Conclusions Body size is an important population characteristic for all marine animals, but especially so for suspension feeding organisms, such as the brachiopod Dyoros sp., because the size of the body has a direct effect on the availability of food particles moving around an obstructive skeleton (Humphries, 2007). In general, larger body sizes can be viewed as a positive factor in feeding, with increased size meaning increased size of flow (and thus, food) vortices shed around a suspension feeding organism. If the ambient environment were different in the original seas existing at Localities 5 and 10, such as would be expected if the two localities were not coeval,
6 then the expectation would be that this should be reflected in different body size distributions between localities for populations of the same species, like Dyoros sp. At the community level, body size distribution has proven useful in describing variation both within and between modern (Robson et al., 2005) and ancient (Payne, 2005) communities. The relative body size distributions of any member species may control the species composition and relative abundances, influencing community function. Again, if Localities 5 and 10 were not coeval, then the expected, different body size distributions of suspension feeding species like Dyoros sp. would produce cascading effects throughout numerous species of the communities, which are simply not observed for Localities 5 and 10. The failure to reject null hypotheses of the equality of medians (Mann-Whitney and Kruskal- Wallis tests) and equality of distributions (Kolomogorov-Smirnov test) supports the correlation of Localities 5 and 10 of the Hughes Creek Shale. This then fails to reject an informal hypothesis that the two localities preserve coeval beds of strata. The rejection of the earlier interpretation of Holterhoff and Pabian (1990) by Pabian and Diffendal (2003) is supported by the evidence presented here. Confident that Localities 5 and 10 are indeed coeval, they can both be used in aggregate to examine the recovery of marine fauna after recovery after a small-scale anoxic event covering at minimum, the ~10 mile distance between them. Both localities are highly fossiliferous, and their summed diversities and body size distributions for all taxa, including Dyoros sp., as shown here, add to their robustness as an astrobiologic model for the extinction and recovery of taxa during larger-scale extinctions. Bibliography Des Marais, D., J. A. Nuth, III, L. Allamandola, A. P. Boss, J. D. Farmer, T. M. Hoehler, B. M. Jakosky, V. S. Meadows, A. Pohorille, B. Runnegar and A. M. Sporman The NASA Astrobiology Roadmap. Astrobiology, 8(4): Hammer, O., Harper, D. A. T. and Ryan, P. D PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologica Electronica, 4(1): 1-9. Holterhoff, P. and R. K. Pabian Paleoenvironmental implications of a pyritized molluscan fauna from the Bennett Shale Member, Red Eagle Formation (Lower Permian), Richardson County, Nebraska. The Compass, 67(1): Humphries, S Body size and suspension feeding, Pp , In Hildrew, A., D. G. Raffaelli and R. Edmonds-Brown (eds.), Body Size: The Structure and Function of Aquatic Ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
7 NASA Pabian, R. K. and R. F. Diffendal, Jr Late Pennsylvanian and earliest Permian cyclic sedimentation and paleoecology in southeastern Nebraska. In Niemi, T. (ed.) Geologic Field Trips in the Greater Kansas City area. Missouri Geological Survey, Special Publication, pp Payne, J. L Evolutionary dynamics of gastropod size across the end-permian extinction and through the Triassic recovery interval. Paleobiology, 31(2): Robson, B. J., L. A. Barmuta and P. G. Fairweather Methodological and conceptual issues in the search for a relationship between animal body-size distributions and benthic habitat architecture. Marine and Freshwater Research, 56: Zelditch, M., D. Swiderski and H. D. Sheets Geometric Morphometrics for Biologists; A Primer. Second Edition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 478pp.
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas
 Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions
 Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois
 Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois Primary objectives for this fieldtrip 1) Collect and identify the fossils of the Racine Reef Complex. 2) Discuss procedures for collecting fossil
Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois Primary objectives for this fieldtrip 1) Collect and identify the fossils of the Racine Reef Complex. 2) Discuss procedures for collecting fossil
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Geologic Time. Geologic Events
 Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
GEOLOGICAL AGE OF ROCKS. Absolute geological age
 GEOLOGICAL AGE OF ROCKS Absolute geological age The pioneer of nuclear physics discovered at the turn of centuries that atoms of certain elements, the radioactive ones, spontaneously disintegrate to form
GEOLOGICAL AGE OF ROCKS Absolute geological age The pioneer of nuclear physics discovered at the turn of centuries that atoms of certain elements, the radioactive ones, spontaneously disintegrate to form
Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape. David J. Bottjer University of Southern California
 Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape David J. Bottjer University of Southern California Permian-Triassic Mass Extinction A profoundly important event in the history of Earth and the Solar System.
Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape David J. Bottjer University of Southern California Permian-Triassic Mass Extinction A profoundly important event in the history of Earth and the Solar System.
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Dating the age of the Earth
 Dating the age of the Earth What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D. 10000 years Discuss this with your neighbor: How do we know the age of the Earth?
Dating the age of the Earth What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D. 10000 years Discuss this with your neighbor: How do we know the age of the Earth?
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Tanyard Creek Virtual Field Trip
 Tanyard Creek Virtual Field Trip NorthWest Arkansas Community College s GEOL 1114 Hybrid Instructor Dr. Wendi J. Williams Student Team Members Cynthia Brantley Cassie Harris Jonathan Mooney David Selby
Tanyard Creek Virtual Field Trip NorthWest Arkansas Community College s GEOL 1114 Hybrid Instructor Dr. Wendi J. Williams Student Team Members Cynthia Brantley Cassie Harris Jonathan Mooney David Selby
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon
 Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
The terrestrial rock record
 The terrestrial rock record Stratigraphy, vertebrate biostratigraphy and phylogenetics The Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary at Hell Creek, Montana. Hell Creek Fm. lower, Tullock Fm. upper. (P. David Polly,
The terrestrial rock record Stratigraphy, vertebrate biostratigraphy and phylogenetics The Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary at Hell Creek, Montana. Hell Creek Fm. lower, Tullock Fm. upper. (P. David Polly,
MOR SEAWAY TEACHERS. A CHANGING LANDSCAPE Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
Regents Earth Science
 Regents Earth Science Earth s History Name Section Rock Correlation Lab Lab# Introduction: The Cayuga Lake Basin contains one of the scenic Finger Lakes of central New York State. During the Devonian Period,
Regents Earth Science Earth s History Name Section Rock Correlation Lab Lab# Introduction: The Cayuga Lake Basin contains one of the scenic Finger Lakes of central New York State. During the Devonian Period,
G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record
 1 G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record Approaches: Rarefaction Logarithmic Decay Model How many species might have been alive in the past? What percentage are fossilized? How many skeletonized
1 G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record Approaches: Rarefaction Logarithmic Decay Model How many species might have been alive in the past? What percentage are fossilized? How many skeletonized
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Depositional Environments. Depositional Environments
 Depositional Environments Geographic area in which sediment is deposited Characterized by a combination of geological process & environmental conditions Depositional Environments Geological processes:
Depositional Environments Geographic area in which sediment is deposited Characterized by a combination of geological process & environmental conditions Depositional Environments Geological processes:
Date: TEN UNIT. Earth. History. and
 Name: Date: UNIT TEN Geologic Time and Earth History *Dedicated to: Name: Date: ABSTRACTT AND RATIONALE The Earth is very old 4.5 billion years or more according to scientific estimates. Most of the evidence
Name: Date: UNIT TEN Geologic Time and Earth History *Dedicated to: Name: Date: ABSTRACTT AND RATIONALE The Earth is very old 4.5 billion years or more according to scientific estimates. Most of the evidence
Age Dating and the Oceans
 Age Dating and the Oceans 1. Age dating of geologic materials reveals (a) the age of the Earth, and (b) how long oceans have been on Earth. 2. Relative dating of fossils from the seafloor allows us to
Age Dating and the Oceans 1. Age dating of geologic materials reveals (a) the age of the Earth, and (b) how long oceans have been on Earth. 2. Relative dating of fossils from the seafloor allows us to
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities
 Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life
 Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Ordovician. System. Cambrian. System
 443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
Plan of Development Mountain Valley Pipeline Project. APPENDIX P Plan for Unanticipated Discovery of Paleontological Resources
 APPENDIX P Plan for Unanticipated Discovery of Paleontological Resources Appendix P Plan for Unanticipated Discovery of Paleontological Resources Prepared by: TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1
APPENDIX P Plan for Unanticipated Discovery of Paleontological Resources Appendix P Plan for Unanticipated Discovery of Paleontological Resources Prepared by: TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 245 Exam 1 12 February 2008 1. Use the following list of fossil taxa to answer parts a through g below. (2 pts each) 2 Aegyptopithecus Australopithecus africanus Diacronis
Fossils and Geology of Litzsinger Road Ecology Center
 Fossils and Geology of Litzsinger Road Ecology Center Table of Content Key Terms 1 Key Terms 2 What you need to know Geologic Map of Missouri Geologic Time Chart More of what you need to know Digital map
Fossils and Geology of Litzsinger Road Ecology Center Table of Content Key Terms 1 Key Terms 2 What you need to know Geologic Map of Missouri Geologic Time Chart More of what you need to know Digital map
PERSISTENT PREDATOR-PREY DYNAMICS REVEALED BY MASS EXTINCTION.
 1 Supporting Information Appendix for PERSISTENT PREDATOR-PREY DYNAMICS REVEALED BY MASS EXTINCTION. Lauren Cole Sallan, Thomas W. Kammer, William I. Ausich, Lewis A. Cook 1 2 Illustration - A Viséan Euramerican
1 Supporting Information Appendix for PERSISTENT PREDATOR-PREY DYNAMICS REVEALED BY MASS EXTINCTION. Lauren Cole Sallan, Thomas W. Kammer, William I. Ausich, Lewis A. Cook 1 2 Illustration - A Viséan Euramerican
GCE A level 1214/01 GEOLOGY GL4 Interpreting the Geological Record
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1214/01 GEOLOGY GL4 Interpreting the Geological Record P.M. MONDAY, 6 June 2016 2 hours S16-1214-01 For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1214/01 GEOLOGY GL4 Interpreting the Geological Record P.M. MONDAY, 6 June 2016 2 hours S16-1214-01 For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Adjustments to Life in Air
 1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY
 PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils
 Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils Appendix 1 Brachiopods Cephalopods Brachiopods (brack'-i-oh-pods) are a group of marine animals with two shells. They all have an upper and lower shell. The
Illustrations of Selected Ordovician fossils Appendix 1 Brachiopods Cephalopods Brachiopods (brack'-i-oh-pods) are a group of marine animals with two shells. They all have an upper and lower shell. The
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
Geology Merit Badge Workbook
 Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
Merit Badge Workbook This workbook can help you but you still need to read the merit badge pamphlet. This Workbook can help you organize your thoughts as you prepare to meet with your merit badge counselor.
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
TIME LINE OF LIFE. Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference. 1. Review the eras represented on the Clock of Eras:
 TIME LINE OF LIFE Material Time Line of Life Working Time Line of Life Clock of Eras Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference Elastic strip for Clock of Eras Presentation 1: Overview 1. Review
TIME LINE OF LIFE Material Time Line of Life Working Time Line of Life Clock of Eras Strip for Clock of Eras representing the circumference Elastic strip for Clock of Eras Presentation 1: Overview 1. Review
Proterozoic Life and Environments
 Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
Proterozoic Life and Environments (or: 3 billion years in 70 minutes) Cambrian Explosion Origin of Life Great Oxygenation Event Origin of Life Early Life Localities >2.5 Ga Named localities: >3.2 Ga Isua
Shield was above sea-level during the Cambrian and provided the sediment for the basins.
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED GCE GEOLOGY Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate F795 * OCE / 2 6692* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED GCE GEOLOGY Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate F795 * OCE / 2 6692* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Other Materials Required:
1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B.
 Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit A.M. TUESDAY, 13 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 17 2. 14 Mark Awarded 1211 010001
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit A.M. TUESDAY, 13 May 2014 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 17 2. 14 Mark Awarded 1211 010001
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Geological History of the Grand Canyon
 Geological History of the Grand Canyon For a copy of this assignment, print a copy of this web page. The Project Your job is to write a short paper that describes the geological history of the Grand Canyon
Geological History of the Grand Canyon For a copy of this assignment, print a copy of this web page. The Project Your job is to write a short paper that describes the geological history of the Grand Canyon
DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation
 DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation from ancient times to the 1600s, where time was thought of at all, it was supposed either continuous & 'circular' or of rather short duration either way, the
DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation from ancient times to the 1600s, where time was thought of at all, it was supposed either continuous & 'circular' or of rather short duration either way, the
Pee Dee Explorer. Science Standards
 Science Standards About Pee Dee Explorer What does it mean when someone says they are from the "Pee Dee" of South Carolina? A place is bigger than its physical geography. A "sense of place" weaves together
Science Standards About Pee Dee Explorer What does it mean when someone says they are from the "Pee Dee" of South Carolina? A place is bigger than its physical geography. A "sense of place" weaves together
The Problem of the Welden, Sycamore and Lower Caney in the Eastern Arbuckle Mountains
 120 PROC. OF THE OKLA. ACAD. OF SCI. FOR 1958 The Problem of the Welden, Sycamore and Lower Caney in the Eastern Arbuckle Mountains STEVE C. CHAMPLIN, University of Oklahoma, Norman This paper is a preliminary
120 PROC. OF THE OKLA. ACAD. OF SCI. FOR 1958 The Problem of the Welden, Sycamore and Lower Caney in the Eastern Arbuckle Mountains STEVE C. CHAMPLIN, University of Oklahoma, Norman This paper is a preliminary
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time. Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic
 Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
Jack Sepkoski s Three Great Evolutionary Faunas: Diversity of marine families through time Soft bodied fauna Revolutions in the History of Life In the Phanerozoic Modern fauna Cambrian fauna Paleozoic
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
FY 2013 Annual Technical Report for NCRDS State Cooperative Program
 FY 2013 Annual Technical Report for NCRDS State Cooperative Program SUBSURFACE GAS-SHALE SAMPLES OF THE UPPER DEVONIAN AND LOWER MISSISSIPPIAN WOODFORD SHALE, PERMIAN BASIN, WEST TEXAS AND SOUTHEASTERN
FY 2013 Annual Technical Report for NCRDS State Cooperative Program SUBSURFACE GAS-SHALE SAMPLES OF THE UPPER DEVONIAN AND LOWER MISSISSIPPIAN WOODFORD SHALE, PERMIAN BASIN, WEST TEXAS AND SOUTHEASTERN
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Geologic Time. What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils?
 Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Lab 2 Geological Time and Fossil Samples
 Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 2 Geological Time and Fossil Samples This lab has two components: understanding geological time scales and choosing fossil samples from the IU Paleontology
Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Lab 2 Geological Time and Fossil Samples This lab has two components: understanding geological time scales and choosing fossil samples from the IU Paleontology
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Laboratory 7 Geologic Time
 (Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
(Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
Chapter 15. The Late Paleozoic World
 Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY
 WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
WHO'S ON FIRST? A RELATIVE DATING ACTIVITY MARSHA BARBER and DIANA SCHEIDLE BARTOS INTRODUCTION PALEONTOLOGY, AND in particular the study of dinosaurs, is an exciting topic to people of all ages. Although
Core Curriculum Course Proposal Cover Sheet
 Department Chemistry and Geosciences College Science and Technology Department Head Dr. Arthur Low Core Curriculum Course Proposal Cover Sheet Course Prefix & Number GEOL 106-4 Course Title Historical
Department Chemistry and Geosciences College Science and Technology Department Head Dr. Arthur Low Core Curriculum Course Proposal Cover Sheet Course Prefix & Number GEOL 106-4 Course Title Historical
5 Year B.S/M.S. Program in Geological Sciences and Marine Geosciences
 Geological Sciences 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES Dept. Code: GSC Geological Sciences Geological Sciences is concerned with Planet Earth, its origin, evolution, structure, internal and surface processes, mineral
Geological Sciences 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES Dept. Code: GSC Geological Sciences Geological Sciences is concerned with Planet Earth, its origin, evolution, structure, internal and surface processes, mineral
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION. α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate
 EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
1. Identify this organism (it is 1mm in diameter) 2. The shell or of this organism is made of 3. How do these one-celled organism feed? 4.
 Fossil Test 2 1. Identify this organism (it is 1mm in diameter) 2. The shell or of this organism is made of 3. How do these one-celled organism feed? 4. Describe the biological and geological importance
Fossil Test 2 1. Identify this organism (it is 1mm in diameter) 2. The shell or of this organism is made of 3. How do these one-celled organism feed? 4. Describe the biological and geological importance
454/01 GEOLOGY GL4 EXTENSION GEOLOGY. P.M. FRIDAY, 14 June (2 Hours)
 WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Education Advanced CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Uwch 454/01 GEOLOGY GL4 EXTENSION GEOLOGY P.M. FRIDAY, 14 June 2002 (2
WELSH JOINT EDUCATION COMMITTEE General Certificate of Education Advanced CYD-BWYLLGOR ADDYSG CYMRU Tystysgrif Addysg Gyffredinol Uwch 454/01 GEOLOGY GL4 EXTENSION GEOLOGY P.M. FRIDAY, 14 June 2002 (2
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
First, an supershort History of the Earth by Eon
 HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
HISTORY OF LIFE WRITTEN IN THE ROCKS (geological record): notice how at first no life, very simple if for billions of years, complex life only recently 600 mya In these chapters, two primary themes: History
Objectives. Vocabulary. Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch.
 The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
BOY SCOUTS GEOLOGY MERIT BADGE
 Requirements highlighted in yellow will be covered at the club show. Merit Badge Counselors will be on-hand. Please bring your own paperwork. Children under 12 and scouts in uniform are admitted to the
Requirements highlighted in yellow will be covered at the club show. Merit Badge Counselors will be on-hand. Please bring your own paperwork. Children under 12 and scouts in uniform are admitted to the
Geology and Natural Resources
 Geology and Natural Resources Brought to you by: Western Michigan University Department of Geosciences and The Michigan Geological Repository for Research and Education s K-12 Outreach Program Core Kids
Geology and Natural Resources Brought to you by: Western Michigan University Department of Geosciences and The Michigan Geological Repository for Research and Education s K-12 Outreach Program Core Kids
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania
 Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE
 GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmar.edu For the maps accompanying
GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmar.edu For the maps accompanying
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Different Coloration of Devonian Shales
 The JUNIATA JOURNAL of GEOLOGY, 1, 1-6 (2014) Original Article Different Coloration of Devonian Shales Garrett Lavelle Shale is a sedimentary rock that develops in a deep marine environment. The coloration
The JUNIATA JOURNAL of GEOLOGY, 1, 1-6 (2014) Original Article Different Coloration of Devonian Shales Garrett Lavelle Shale is a sedimentary rock that develops in a deep marine environment. The coloration
Deep Time: How Old Is Old?
 Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Geologic Time: Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point. How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know?
 Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Michelle M. Casey, Erin E. Saupe, and Bruce S. Lieberman
 The Biogeography of Sluggish Evolution: The Impact of Geographic Range Size on Extinction Selectivity in Pennsylvanian Brachiopods of The North American Midcontinent Michelle M. Casey, Erin E. Saupe, and
The Biogeography of Sluggish Evolution: The Impact of Geographic Range Size on Extinction Selectivity in Pennsylvanian Brachiopods of The North American Midcontinent Michelle M. Casey, Erin E. Saupe, and
Life on Earth Topic Test
 Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
Life on Earth Topic Test Multiple Choice Questions Select the best alternative and indicate your response on the answer sheet. (1 mark each) 1. The list below contains common substances that exist in Earth
Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community Population Organism
 Ecology ecology - The study of living things and how they relate to their environment Levels of Organization in Ecology organism lowest level one living thing population collection of organisms of the
Ecology ecology - The study of living things and how they relate to their environment Levels of Organization in Ecology organism lowest level one living thing population collection of organisms of the
Page 1. Name:
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Structural Features and Fracture Orientation similarities between outcrops of the Ridgeley Sandstone
 The JUNIATA JOURNAL of GEOLOGY, 1, 1-8 (2014) Original article Structural Features and Fracture Orientation similarities between outcrops of the Ridgeley Sandstone Robert W. Baronner Two outcrops of the
The JUNIATA JOURNAL of GEOLOGY, 1, 1-8 (2014) Original article Structural Features and Fracture Orientation similarities between outcrops of the Ridgeley Sandstone Robert W. Baronner Two outcrops of the
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments
 Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
