Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions
|
|
|
- Arleen Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple to count the number of taxa, but there are actually quite a few complications Measuring Diversity Diversity was revisited with a more quantitative approach in the late 1970s and 1980s The number of described species had increased ~25 times, providing much more data for analysis New analyses Phillips, 1860
2 Measuring Diversity Jack Sepkoski spent 15 years compiling a database to produce the classic diversity curve Phanerozoic Diversity The Sepkoski curve revealed a number of interesting patterns in the history of animal diversity Ordovician Radiation Paleozoic Plateau Meso-Cenozoic Diversification Cambrian Explosion Sepkoski wanted to analyze fossil record for patterns Are there groups of taxa with coherent diversity trends? # Families per class Time Intervals Coherent Patterns? Classes A B C Used factor analysis to extract variables that explain variation in original data set
3 Factors are termed evolutionary faunas Primarily controlled by changes in the diversity of four groups Brachiopods w/ hinged shells Evolutionary Faunas Sepkoski grouped clades into evolutionary faunas based on the times during which they were most diverse EFs are not coherent biological units, but rather are composed of different taxa that happen to share similar diversity patterns
4 Bias and Diversity Patterns How closely does this curve actually match the true history of Phanerozoic biodiversity? What if fossil preservation or the extent of sedimentary rocks was lower in the past?
5 Rock Volume Bias There is a broad correspondence between diversity and the exposed area of sedimentary rocks More sampling = more taxa! Rock Volume Bias Changes in diversity correlate strongly with changes in the number of named geological formations (in the USA) # Formations Diversity Pull of the Recent Because the living fauna is so well known, the ranges of many taxa are artificially pulled to the Recent Diversity Diversity is inflated in younger time intervals Time
6 Standardization with the Paleobiology Database Standardization with the Paleobiology Database 1. Sampling standardization accounts for variable rock area 2. Excluding unlithified sediments (Neogene) compensates for Pull of the Recent No Paleozoic Plateau Cenozoic only slight more diverse than Paleozoic Mass Extinctions Raup, Sepkoski, and others realized that extinction and origination rates could be calculated from diversity compilations Five major mass extinctions have been recognized: Late Ordovician, Late Devonian, End-Permian, End-Triassic, End-Cretaceous
7 Ecological Effects In addition to reduced diversity and taxonomic losses, mass extinctions alter community and/or ecosystem structure Ecological impacts not always predictable from taxonomic severity Were mass extinctions gradual or abrupt? Signor-Lipps Effect Because of the imperfect fossil record we never find the true last occurrence of a species Tempo of Extinction Extinctions are smeared backwards and appear to be more gradual than they were K-Pg ammonite ranges with confidence intervals abrupt extinction
8 Abrupt Extinction End Cretaceous Abrupt Extinction End Permian Timing: Very abrupt (<<100 kyr) single event just before P/T boundary Gradual Extinction Late Devonian Timing: At least three major events in the Givetian, Frasnian, and Famennian stages Hangenberg Event Kellwasser Event Taghanic Event Kellwasser event was the most severe and virtually eliminated stromatoporoid reef ecosystems
9 Post-Extinction Recovery Biotic recovery after extinction can be divided into survival and recovery phases Survival phase: 1) Possible dead zone 2) Early crisis interval with extinction survivors and disaster taxa 3) Later interval with opportunists + some Lazarus taxa Recovery phase: 1) Reappearance of many Lazarus taxa 2) More rapid diversity increase, radiation of new lineages Disaster Taxa Specific type of opportunistic organisms that expand to become abundant in a wider range of habitats after a biotic crisis Early Triassic disaster taxa: Lingulid Brachiopods Microbes Post-Extinction Recovery Post-extinction communities often exhibit signs of stress 1. Fewer individuals, dominance by opportunists or disaster taxa 2. Increase in generalists (deposit feeders, etc.) 3. Reduction in body size Typically lasts <500 ka
10 Delayed Early Triassic Recovery 4-5 Myr long Reduced bioturbation and tiering, plus disaster taxa and opportunists Causes of Extinctions End-Cretaceous: Largest impact of the Phanerozoic (180 km-diameter Chicxulub crater) Contributions from environmental stress from Deccan trap volcanism? Kill curve to predict impact-caused extinction But Chicxulub is only impact associated with extinction Impacts and Extinctions Manicouagan, 214 Ma
11 Flood Basalt Volcanism Mass extinctions occurred during times of major flood basalt eruptions Flood Basalt Volcanism Three largest flood basalts associated with three largest extinctions, but no correlation beyond that level CAMP was probably larger than Siberian Traps, but P/T extinction is much more severe than T/J Siberian Traps P/T extinction CAMP T/J extinction Importance of Target Rock Chicxulub hit carbonate platform with abundant sulfates Siberian traps erupted into West Siberian high-sulfur coal basin Additional CO2, SO2 (+other toxic chemicals) more important than actual impact or volcanism
12 Volcanism (effects of reducing molecules like SO 2 ) leads to anoxia + euxinia (H 2 S) in surface ocean, ocean acidification Kellwasser Event: Frasnian Taghanic Event: Givetian Devonian extinctions also coincide with marine anoxia May actually be triggered by land plant evolution, not by flood basalt volcanism Climate cooling also hypothesized for Devonian crises (Hangenberg Event) Late Ordovician Glaciation Timing: Two short-lived events in the latest Ordovician Probable Cause: Climate change, short-lived Hirnantian glaciation Contrasts with extreme climate warming, caused by flood basalt eruptions, during T/J and probably P/T extinctions Hirnantia fauna
13 Extinction Causes Extinction Late Ordovician Late Devonian Climate Change? COOLING / WARMING Anoxia? Large Igneous Province? COOLING YES?? Impact? End Permian WARMING YES YES End Triassic WARMING YES YES End Cretaceous Yes? YES Diversity / Extinction Summary 1. Cenozoic diversity is greater than in the Paleozoic, but not as much as previously thought 2. Diversity compilations allow recognition of five major mass extinctions and many smaller extinction events 3. The Big Five had differing taxonomic and ecological consequences (but why is not clear) 4. Only the end Cretaceous was associated with an impact, but the correlations between anoxia and extinctions, and large igneous provinces and extinctions, are strong
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Taxonomic diversity of skeletonized marine animal families during the Phanerozoic Spindle diagram of family diversification/extinction PNAS 1994. 91:6758-6763. Background
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences
 Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Mass Extinctions &Their Consequences Microevolution and macroevolution Microevolution: evolution occurring within populations p Adaptive and neutral changes in allele frequencies Macroevolution: evolution
Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape. David J. Bottjer University of Southern California
 Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape David J. Bottjer University of Southern California Permian-Triassic Mass Extinction A profoundly important event in the history of Earth and the Solar System.
Update on Permian-Triassic Extinction Landscape David J. Bottjer University of Southern California Permian-Triassic Mass Extinction A profoundly important event in the history of Earth and the Solar System.
Body Fossils Trace Fossils
 Evolution, Phanerozoic Life and Mass Extinctions Hilde Schwartz hschwartz@pmc.ucsc.edu Body Fossils Trace Fossils FOSSILIZED Living bone Calcium hydroxyapatite Ca 10 (PO4) 6 (OH OH,Cl,F,CO CO 3 ) 2 Fossil
Evolution, Phanerozoic Life and Mass Extinctions Hilde Schwartz hschwartz@pmc.ucsc.edu Body Fossils Trace Fossils FOSSILIZED Living bone Calcium hydroxyapatite Ca 10 (PO4) 6 (OH OH,Cl,F,CO CO 3 ) 2 Fossil
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The History of Life on Earth
 8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
The Evolution of Biological Diversity. All living organisms are descended from an ancestor that arose between 3 and 4 billion years ago.
 The Evolution of Biological Diversity All living organisms are descended from an ancestor that arose between 3 and 4 billion years ago. The diversity of life on earth currently includes some 5 to 50 million
The Evolution of Biological Diversity All living organisms are descended from an ancestor that arose between 3 and 4 billion years ago. The diversity of life on earth currently includes some 5 to 50 million
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
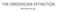 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Biodiversity Through Earth History. What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events?
 Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts...
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
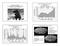 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life
 Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION. α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate
 EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
EXTINCTION CALCULATING RATES OF ORIGINATION AND EXTINCTION α = origination rate Ω = extinction rate 1 SPECIES AND GENERA EXTINCTION CURVES INDICATE THAT MOST SPECIES ONLY PERSIST FOR A FEW MILLION YEARS.
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
Causes of Extinction
 Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
How volcanic eruptions caused Earth s greatest mass extinction
 How volcanic eruptions caused Earth s greatest mass extinction and what that tells us about its future David Bond, University of Hull European Geosciences Union, Tuesday 10 th April, 2018 1 So, what is
How volcanic eruptions caused Earth s greatest mass extinction and what that tells us about its future David Bond, University of Hull European Geosciences Union, Tuesday 10 th April, 2018 1 So, what is
IX Life on Earth.
 IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
GO ON. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1.
 d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life
 Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name:
 Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Deccan Traps eruptions
 Wright State University From the SelectedWorks of Rebecca Teed May 9, 2016 The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Deccan Traps eruptions Rebecca Teed This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Wright State University From the SelectedWorks of Rebecca Teed May 9, 2016 The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Deccan Traps eruptions Rebecca Teed This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Please take out your fill-in notes again, and we will continue learning about extinct creatures.
 Today s Topic Evolution: Extinction Learning Goal: SWBAT explain why creatures go extinct from Earth, and why some recently-extinct creatures have gone extinct. Please take out your fill-in notes again,
Today s Topic Evolution: Extinction Learning Goal: SWBAT explain why creatures go extinct from Earth, and why some recently-extinct creatures have gone extinct. Please take out your fill-in notes again,
Patterns of extinction and biodiversity in the fossil record
 Patterns of extinction and biodiversity in the fossil record Ricard V. Solé and Mark Newman Santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, Santa Fe, NM 87501 Life has existed on the Earth for more than three
Patterns of extinction and biodiversity in the fossil record Ricard V. Solé and Mark Newman Santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, Santa Fe, NM 87501 Life has existed on the Earth for more than three
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Geologic Time. Geologic Events
 Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time.
 Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Where did all the dinosaurs go?
 Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions
 Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions Kyle Gray & Alexa Sedlacek Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences University of Northern Iowa Mass Extinctions
Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions Kyle Gray & Alexa Sedlacek Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences University of Northern Iowa Mass Extinctions
I know that dinosaurs were not very big at the time of the end Triassic extinction, but this graphic from the National Science Foundation website
 I know that dinosaurs were not very big at the time of the end Triassic extinction, but this graphic from the National Science Foundation website sets the theme of mass extinction by fissure volcanism.
I know that dinosaurs were not very big at the time of the end Triassic extinction, but this graphic from the National Science Foundation website sets the theme of mass extinction by fissure volcanism.
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Moving plate tectonics to the next level of detail
 Moving plate tectonics to the next level of detail by understanding how plate tectonics controls sudden global warming, slow incremental global cooling, air temperatures, ocean temperatures, ocean acidification,
Moving plate tectonics to the next level of detail by understanding how plate tectonics controls sudden global warming, slow incremental global cooling, air temperatures, ocean temperatures, ocean acidification,
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record
 1 G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record Approaches: Rarefaction Logarithmic Decay Model How many species might have been alive in the past? What percentage are fossilized? How many skeletonized
1 G331: The Nature and Adequacy of the Fossil Record Approaches: Rarefaction Logarithmic Decay Model How many species might have been alive in the past? What percentage are fossilized? How many skeletonized
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
GEOLOGY - GL4 INTERPRETING THE GEOLOGICAL RECORD
 Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE A level 1214/01 GEOLOGY - GL4 INTERPRETING THE GEOLOGICAL RECORD A.M. MONDAY, 21 June 2010 2 hours Section A 1. 2. 3. 15 15 15 1214 01 01 4. 15 Section
Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE A level 1214/01 GEOLOGY - GL4 INTERPRETING THE GEOLOGICAL RECORD A.M. MONDAY, 21 June 2010 2 hours Section A 1. 2. 3. 15 15 15 1214 01 01 4. 15 Section
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
A brief history of the Earth!
 A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
Fossils Biology 2 Thursday, January 31, 2013
 Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Ecology. Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation
 Ecology Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation Population Ecology: Population Growth Models Population Limiting Factors Population growth models Logistic
Ecology Part 4. Populations Part 5. Communities Part 6. Biodiversity and Conservation Population Ecology: Population Growth Models Population Limiting Factors Population growth models Logistic
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation
 DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation from ancient times to the 1600s, where time was thought of at all, it was supposed either continuous & 'circular' or of rather short duration either way, the
DEEP TIME it's discovery and interpretation from ancient times to the 1600s, where time was thought of at all, it was supposed either continuous & 'circular' or of rather short duration either way, the
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
The Fossil Record. CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163
 The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Earth and Space Science Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
251 Million years. 299 Million years. 318 Million years. 359 Million years
 The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Use Target Reading Skills
 The Geologic Time Scale (pp. 286 297) This section tells why the geologic time scale is used to show Earth s history, and what the organisms were like and the major events that happened in the different
The Geologic Time Scale (pp. 286 297) This section tells why the geologic time scale is used to show Earth s history, and what the organisms were like and the major events that happened in the different
Time. How we achieved a modern sense of time. Yearly Calendars are Ancient
 Time How we achieved a modern sense of time. Yearly Calendars are Ancient Stonehenge is 2000+ BC and indicates that ancient cultures counted days and knew precisely the repeat cycle of the seasons. 1 Renaissance
Time How we achieved a modern sense of time. Yearly Calendars are Ancient Stonehenge is 2000+ BC and indicates that ancient cultures counted days and knew precisely the repeat cycle of the seasons. 1 Renaissance
GY 112: Earth History
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 31: Mesozoic Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Overview A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 31: Mesozoic Tectonics Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Overview A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR GEOLOGY 103, TEST 1 The correct answers are listed at the bottom (no peeking!). These questions are to give you an idea of the type of questions that will be asked. They are not a
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Geologic Time. What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils?
 Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origins and extinctions
 Origins and extinctions Michael J. Benton (University of Bristol) Bright Horizons 10 Sunday, October 2 nd, 2011 History of Life on Earth The origin of life, followed by a whirlwind tour of the past 4.6
Origins and extinctions Michael J. Benton (University of Bristol) Bright Horizons 10 Sunday, October 2 nd, 2011 History of Life on Earth The origin of life, followed by a whirlwind tour of the past 4.6
Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions.
 Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions. 1. Animals colonized the land during the Devonian period. This was during the era and the eon. Paleozoic; Phanerozoic 2. The mother of all mass extinctions occurred
Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions. 1. Animals colonized the land during the Devonian period. This was during the era and the eon. Paleozoic; Phanerozoic 2. The mother of all mass extinctions occurred
Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is:
 DDA1 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics PS 100 Chapter 28 Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is: A. Average density of the earth is greater than the density of the crust.
DDA1 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics PS 100 Chapter 28 Review participation point: The evidence for a fluid outer core is: A. Average density of the earth is greater than the density of the crust.
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale
 History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
TREATISE ONLINE Number 9
 TREATISE ONLINE Number 9 Part E, Revised, Volume 4, Chapter 11A: Diversity Trends of the Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea Colin W. Stearn 2010 Lawrence, Kansas, USA ISSN 2153-4012 paleo.ku.edu/treatiseonline
TREATISE ONLINE Number 9 Part E, Revised, Volume 4, Chapter 11A: Diversity Trends of the Paleozoic Stromatoporoidea Colin W. Stearn 2010 Lawrence, Kansas, USA ISSN 2153-4012 paleo.ku.edu/treatiseonline
GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Overview
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Overview Lecture Goals: A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary developments C) Paleogeography and key
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Mesozoic Overview Lecture Goals: A) The end of the Paleozoic B) Mesozoic time frame and evolutionary developments C) Paleogeography and key
Patterns of Evolution: A. Mass Extinctions. B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution. E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium
 : A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
: A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
Question #1: What are some ways that you think the climate may have changed in the area where you live over the past million years?
 Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Figure 65: Reservoir in a steady state condition where the input flux is equal to the output flux and the reservoir size remains constant.
 7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
Genus-level versus species-level extinction rates
 Acta Geologica Polonica, Vol. 66 (2016), No. 3, pp. 261 265 DOI: 10.1515/agp-2016-0012 Genus-level versus species-level extinction rates JERZY TRAMMER Faculty of Geology, University of Warsaw, ul. Żwirki
Acta Geologica Polonica, Vol. 66 (2016), No. 3, pp. 261 265 DOI: 10.1515/agp-2016-0012 Genus-level versus species-level extinction rates JERZY TRAMMER Faculty of Geology, University of Warsaw, ul. Żwirki
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32. Paleoclimate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries
 ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
This talk is available at Plate tectonics controls global climate change by determining
 This talk is available at https://youtu.be/0e1oioze-9e Plate tectonics controls global climate change by determining the frequency of major explosive, subductionrelated volcanic eruptions causing incremental
This talk is available at https://youtu.be/0e1oioze-9e Plate tectonics controls global climate change by determining the frequency of major explosive, subductionrelated volcanic eruptions causing incremental
Extinctions & Climate Change Student Activity. Diagram interpretation and using research data
 Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans. Oceans and Life. How Old is Earth? The Solar System? Oceans are the birthplace of life.
 Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans Oceans and Life Oceans are the birthplace of life. Life metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli Metabolism use of energy stored in ambient chemicals Reproduction
Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans Oceans and Life Oceans are the birthplace of life. Life metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli Metabolism use of energy stored in ambient chemicals Reproduction
What is the Earth s time scale?
 Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Geologic Time Test Study Guide
 Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
PTYS 214 Fall Announcements. Materials from last week moved to web page. Midterm #4 next Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE. Dr. Bertolotti
 CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity. Monday, May 16, 16
 Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity Earth is home to a tremendous diversity of species Ecosystem diversity- the variety of ecosystems within a given region. Species diversity- the variety of species in
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity Earth is home to a tremendous diversity of species Ecosystem diversity- the variety of ecosystems within a given region. Species diversity- the variety of species in
