Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Anne Replumaz
|
|
|
- Julia Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Great Earthquakes: Observa1ons and modeling Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Anne Replumaz 1
2 Great Earthquakes, Great Faults cu<ng Asia in blocks? linked to con1nental subduc1on? ~ 80% energy released By M>7 2
3 con8nental plate- tectonics model block geometry deduced from fault geometry Inferring Indian and Asian slabs So= Tibet model Focus on rheology of the lower crust Inferring a wide indian slab Meyer et al., 1998 Tapponnier et al., 2001 Beaumont et al., 2001, 2004 Clark& Royden, 2000 Vanderhaeghe et al.,
4 Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Upper crust ü fault rate and offset ü 2D tectonics reconstruc7on Lithosphere ü slabs in global tomography ü 3D lithospheric reconstruc7on Dynamics of processes ü Numerical models of upper plate deforma7on due to slab breakoff ü Analogue models of upper plate collisional subduc7on
5 Deforma8on of the upper crust DeterminaOon fault rate and offset in SouthEast Tibet XianShuiHe Fault Red River Fault Using thermochronology Using morphotectonics 5
6 N Replumaz et al., 2001 Red River fault dextral offset of the drainage network: 25 km 6
7 Total dextral offset 25 km / Ac1va1on of RRF 5Ma => mean Pliocene rate 5 mm/yr Tectonic inversion at the SouthEast extremity of the fault in the Tonkin Gulf using seismic lines dated at 5 Ma Replumaz et al.,
8 LRHE ~4500m Gongga Shan 7556m
9 rapid exhuma1on started at ~9 Ma at a rate of ~1.85 km/myr Zhang et al., 2017
10 XFS ac1ve since ~9 Ma + total offset of ~62 km average slip rate of the XFS is ~7 mm/yr Zhang et al., 2017
11 Tectonics Reconstruc8on Replumaz &Tapponnier, / rigid mooon of blocks constrain by fault rate and offset Red River Fault 25km 5Ma 2/ restauraoon of block cononuity and change the fault network 11
12 tectonics reconstruc8on: upper crust evolu8on using the great displacements documented along the Great faults how to accomodate these great displacement at the lithospheric scale? 12 Replumaz & Tapponnier, 2003
13 Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Upper crust ü fault rate and offset ü 2D tectonics reconstruc7on Lithosphere ü slabs in global tomography ü 3D lithospheric reconstruc7on Dynamics of processes ü Numerical models of upper plate deforma7on due to slab breakoff ü Analogue models of upper plate collisional subduc7on
14 Coupling tectonics of Asia and geodynamics : formaoon of Tibetan plateau 14 e.g. Patriat &Achache, 1984
15 Asian slab Dipping southward deepest intracon7nental seismicity in the world, 2 on- going con7nental subduc7ons with opposite vergence A B North South HK B Indian slab Dipping northward P wave global tomographic model (Villasenor et al., 2003) Negredo et al., 2007 A e.g. Chatelain et al. (1980), Sippl et al. (2015) Kufner et al. (2016) 15
16 Several slabs successive subduc8on events Replumaz et al., 2010,
17 Deeper posi1ve anomaly Older subduc1on event OCB breakoff ~45Ma India resumes subduc1on 40-30Ma second breakoff 25-15Ma Shallower posi1ve anomaly Younger subduc1on event
18 2D tectonics reconstruc8on + global tomography 3D lithospheric reconstruc8on Con8nental plate- tectonics model Valid but not so simple So= Tibet model Tapponnier et al., 2001 Vanderhaeghe et al., 2012
19 Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Upper crust ü fault rate and offset ü 2D tectonics reconstruc7on Lithosphere ü slabs in global tomography ü 3D lithospheric reconstruc7on Dynamics of processes ü Numerical models of upper plate deforma7on due to slab breakoff ü Analogue models of upper plate collisional subduc7on
20 Numerical models of upper plate deformation due to subduction of continental plate attached to oceanic plate Par1cle- in- cell finite element method, Underworld (Moresi et al., 2003; Stegman et al., 2006) 3 plates viscoplas1c rheology u =0 p = g =2 II < Y = C 0 + µp II Y Density contrast Capitanio and Replumaz, 2013 Under incompressibility approxima1ons force balance governed by : conserva1on of mass, and momentum equa1ons.
21 Subduc7on of con7nental lithosphere aoer OCB breakoff? Breakoff imposed at the Ocean-Continent Boundary by reducing locally the plate s plastic limit COMPLETE PARTIAL Capitanio & Replumaz,
22 The complete breakoff preserves the poloidal mantle flow in the center of the slab dragging the con1nental plate in the mantle Except at the slab edge, where indenta1on of the upper plate occurs
23 Stress in the upper plate due to slab breakoff (top view) No breakoff partial breakoff complete breakoff shearing at the margin stress in the upper plate localised along a stress belt at an angle with the trench of 45 ±5 result of stress coupling gradients at the trench Capitanio & Replumaz,
24 Far field forces > ridge push Oceanic Subduction stress coupling gradient at the trench spontaneous slab breakoff? Continent Subduction Slab Break-Off at OCB Oceanic Trench Retreat Continental margin advance Capitanio, Replumaz and Riel, 2015
25 Viscosity Time Upper Plate Cont. Subduction Oc. Subduction Oceanic subduc1on before collision But no rupture in the upper plate, and no asian con7nental subduc7on ~50 Ma OCB Slab Breakoff & Indenta1on Ma Indenta1on & Extrusion Ma Capitanio, Replumaz and Riel, 2015 Far field forces > ridge push
26 subduc8on of Asian con8nental lithosphere? Lithosphere: silicone pusy visco- elas1c materials, quasi- Newtonian at experimental strain rates Indenter η= 4.9 x 104 Pa*s D = 1411 kg/m3 mantle: glucose syrup Newtonian fluid Density D = 1428 kg/m3 viscosity η=22 Pa*s Far field forces = piston scale factor for length of about (upper mantle 11cm in model, 660 km in nature) scale for time (1 minute = 0.55 Myr) Scale for velocity (piston 0.54 cm/min = 5.7 cm/yr) t model /t nature = (Δρ h / η l ) nature / (Δρ h /η l ) model U model /U nature = t nature / t model L model /L nature
27 Replumaz, Funiciello, Reitano, Faccenna, Balon Geology, 2016 indenter subducts pushed by the piston and pulled by the dense oceanic slab Indenter con1nental slab reaches 2/3 of the box overturns backwall con1nental slab Not arached to any dense slab steep but not ver1cal reaches 1/3 of the box
28 14-18% Convergence (100%) absorbed by: Subduc7on ~ 40% Indenter (20-25%) backwall plate (14-18%) Thickening ~ 60% Indenter (17-24%) Backwall plate (16-18%) Upper plate (23%) 20-25%
29 counter- intui7ve subduc7on not driven by posi7ve slab pull mantle kinema7cs and dynamics? 29
30 Tectonics horizontal forces wide cell with mostly horizontal component of mo1on Advec1ng passively the back wall slab 30
31 Tectonics horizontal forces Strong horizontal component of mo1on Mantle push 31
32 rigid con1nental lithosphere subducts in a collision context the slab pull is not the driving force tectonic forces, mostly horizontal, generated by the mo7on of the piston are the driving forces The term subduc1on is not describing adequately this process collisional subduc8on Replumaz, et al., Geology, 2016
33 Link between the Great Faults of Asia, con7nental plate tectonics and con7nental subduc7on Coupling 2D tectonics reconstruc7on, using fault rate and offset, and posi7on of slabs in global tomography 3D tectonics reconstruc7on, showing importance of con7nental subduc7on of both Indian and Asian lithospheres during the collision mantle kinema7cs and dynamics associated with such counter- intui7ve subduc7on not driven by posi7ve slab pull? Tectonics horizontal forces con7nental plate tectonics dynamically sustainable 33
34 Ques8ons?
35
36
37 Upper Plate Extrusion & Indentation Tectonics Slab Break-off Slab Break-off & Increasing external forces CONT. OCEANIC CONT. OCEANIC CONT. OCEANIC F RP F F 2) Far-field Forces à Trench Advance Continental Subduction Margin advance a.k.a. Indentation and Hampered Oceanic Trench Retreat (when large F F )
38 Slab Break-off Slab Break-off & Increasing external forces CONT. OCEANIC CONT. OCEANIC CONT. OCEANIC Thinning Thickening Far-field Forces necessary for sufficient Trench Advance Generating Indentation and thickening Of the upper plate similar to Tibet
39
40 Experiment 2: 2 oceans backwall slab : twice the length observed in the experiment 1.
41 Upper plate ρ = 1397 kg/m3 Experiment 3: upper plate easily deformable upper plate spreads laterally no indenter subduc1on backwall slab similar Upper plate ρ = 967 kg/m3
Marine Geophysics. Plate tectonics. Dept. of Marine Sciences, Ocean College, Zhejiang University. Nov. 8, 2016
 Marine Geophysics Plate tectonics 何小波 Dept. of Marine Sciences, Ocean College, Zhejiang University Nov. 8, 2016 Ocean College (ZJU) Plate tectonics xbhe@zju.edu.cn 1 / 1 Mantle flow and Plate tectonics
Marine Geophysics Plate tectonics 何小波 Dept. of Marine Sciences, Ocean College, Zhejiang University Nov. 8, 2016 Ocean College (ZJU) Plate tectonics xbhe@zju.edu.cn 1 / 1 Mantle flow and Plate tectonics
Forces That Shape Earth. How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle?
 Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Tectonics and Convection
 Tectonics and Convection 1. Historical introduction 2. Surface kinematics 3. Subduction dynamics 4. Subduction dynamics in their ecosystems 5. A world tour of horizontal tectonics 6. Going vertical: Dynamic
Tectonics and Convection 1. Historical introduction 2. Surface kinematics 3. Subduction dynamics 4. Subduction dynamics in their ecosystems 5. A world tour of horizontal tectonics 6. Going vertical: Dynamic
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions. Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions
 Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
Shape Earth. Plate Boundaries. Building. Building
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Section 2: How Mountains Form
 Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Section 2: How Mountains Form Preview Objectives Mountain Ranges and Systems Plate Tectonics and Mountains Types of Mountains Objectives Identify the types of plate collisions that form mountains. Identify
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea)
 Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
Continental Margin Geology of Korea : Review and constraints on the opening of the East Sea (Japan Sea) Han-Joon Kim Marine Satellite & Observation Tech. Korea Ocean Research and Development Institute
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults
 The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? What are Plates? The Earth s crust and upper
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? What are Plates? The Earth s crust and upper
The continental lithosphere
 Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Plate Tectonics Notes
 Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Strike-Slip Faults. ! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.
 Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
11/14/17. Con;nental DriB Continents have slowly moved over geologic time
 GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) #23 - Grand Unifica;on Theory (s) Con;nental DriB Continents have slowly moved over geologic time Sea-floor Spreading Ocean crust forms at oceanic ridges, moves away from there,
GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) #23 - Grand Unifica;on Theory (s) Con;nental DriB Continents have slowly moved over geologic time Sea-floor Spreading Ocean crust forms at oceanic ridges, moves away from there,
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics. Question
 OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
OCN 201 Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics Question What was wrong from Wegener s theory of continental drift? A. The continents were once all connected in a single supercontinent B. The continents
Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides
 Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides Pete Betts - School of Earth, Atmosphere, and environment, Monash University Louis Moresi Department of Earth Sciences,
Geodynamics of congested subduction zones - implications for evolution of the Tasmanides Pete Betts - School of Earth, Atmosphere, and environment, Monash University Louis Moresi Department of Earth Sciences,
Chapter. Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc.
 Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
Journal of Control Science and Engineering 1 (2015) 40-47 doi: 10.17265/2328-2231/2015.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Deformation of Mild Steel Plate with Linear Cracks due to Horizontal Compression Mitsuru
OCN 201: Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics I
 OCN 201: Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics I Revival of Continental Drift Theory Kiyoo Wadati (1935) speculated that earthquakes and volcanoes may be associated with continental drift. Hugo Benioff
OCN 201: Seafloor Spreading and Plate Tectonics I Revival of Continental Drift Theory Kiyoo Wadati (1935) speculated that earthquakes and volcanoes may be associated with continental drift. Hugo Benioff
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Layer Composition Thickness State of Matter
 Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
Surface changes caused by erosion and sedimentation were treated by solving: (2)
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
What Are Tectonic Plates?
 Plate Tectonics The theory that the Earth s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more large and small plates that move relative to one another as they ride on top of hotter, more mobile material.
Plate Tectonics The theory that the Earth s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more large and small plates that move relative to one another as they ride on top of hotter, more mobile material.
GEO- DEEP9300 Lithosphere and Asthenosphere: Composi;on and Evolu;on Kaiming Wang
 Con$nental lithosphere and evolu$on GEO- DEEP9300 Lithosphere and Asthenosphere: Composi;on and Evolu;on Kaiming Wang 1. Con$nental lithosphere Con$nental lithosphere houses the oldest and thickest regions
Con$nental lithosphere and evolu$on GEO- DEEP9300 Lithosphere and Asthenosphere: Composi;on and Evolu;on Kaiming Wang 1. Con$nental lithosphere Con$nental lithosphere houses the oldest and thickest regions
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Agree or Disagree? 1. The Earth if made up of 4 different layers. 2. The crust (where we live) can be made of either less dense continental crust or the more
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Agree or Disagree? 1. The Earth if made up of 4 different layers. 2. The crust (where we live) can be made of either less dense continental crust or the more
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11
 Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Plate Tectonics on a Plane. Observations related to plate tectonics " " Plate tectonic theory types of plate boundaries!
 Plate Tectonics on a Plane Scripps Inst. Of Oceanography" Observations related to plate tectonics " Ocean and continent topography, hypsometry, and crustal thickness. Global seismicity, Benioff zones,
Plate Tectonics on a Plane Scripps Inst. Of Oceanography" Observations related to plate tectonics " Ocean and continent topography, hypsometry, and crustal thickness. Global seismicity, Benioff zones,
The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru
 Chapter 7 The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru Abstract Flat subduction near Peru occurs only where the thickened crust of
Chapter 7 The importance of the South-American plate motion and the Nazca Ridge subduction on flat subduction below South Peru Abstract Flat subduction near Peru occurs only where the thickened crust of
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
 Newly formed rock from rising magma rises above sea floor and forms mountain ranges known as midocean ridges. Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
Newly formed rock from rising magma rises above sea floor and forms mountain ranges known as midocean ridges. Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is a rift valley that forms when the plates separate.
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Thermal-Mechanical Behavior of Oceanic Transform Faults
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Thermal-Mechanical Behavior of Oceanic Transform Faults COMSOL Conference - Boston, Massachusetts October 2008 Emily C. Roland - MIT/WHOI Joint Program Mark
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Thermal-Mechanical Behavior of Oceanic Transform Faults COMSOL Conference - Boston, Massachusetts October 2008 Emily C. Roland - MIT/WHOI Joint Program Mark
Plate Tectonics. I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move
 Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Orocline and syntaxes formation during subduction and collision
 TECTONICS, VOL. 32, 1529 1546, doi:10.1002/tect.20087, 2013 Orocline and syntaxes formation during subduction and collision Flora Bajolet, 1,2 Anne Replumaz, 3,4 and Romain Lainé 3,4 Received 23 December
TECTONICS, VOL. 32, 1529 1546, doi:10.1002/tect.20087, 2013 Orocline and syntaxes formation during subduction and collision Flora Bajolet, 1,2 Anne Replumaz, 3,4 and Romain Lainé 3,4 Received 23 December
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Plate Tectonics Comic Book Pg s 9-13
 Plate Tectonics Comic Book Pg s 9-13 Your Comic Book should include the following on each page: Your CHARACTER thoroughly explaining the concept for the page DRAWINGS for each of the topics A brief EXPLANATION
Plate Tectonics Comic Book Pg s 9-13 Your Comic Book should include the following on each page: Your CHARACTER thoroughly explaining the concept for the page DRAWINGS for each of the topics A brief EXPLANATION
RESTLESS EARTH - CHAPTER 4
 RESTLESS EARTH - CHAPTER 4 continental crust - Composition is similar to granite and forms the continents and the areas of shallow seabed. oceanic crust - Composition similar to basalt. It is thinner,
RESTLESS EARTH - CHAPTER 4 continental crust - Composition is similar to granite and forms the continents and the areas of shallow seabed. oceanic crust - Composition similar to basalt. It is thinner,
Plate Tectonics. How do the plates move?
 Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
Plate Tectonics How do the plates move? Continental Drift Hypothesis In 1915, Alfred Wegener s hypothesis about Continental Drift couldn t explain the forces that could move continents. Wegener wasn t
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Plate Tectonics. What is a theory? What is a fact? In science, a theory is an explana4on, with evidence, that can be tested.
 What is a theory? Plate Tectonics In science, a theory is an explana4on, with evidence, that can be tested. What is a fact? Informa4on that cannot be argued. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The theory
What is a theory? Plate Tectonics In science, a theory is an explana4on, with evidence, that can be tested. What is a fact? Informa4on that cannot be argued. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The theory
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES
 CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES Plate boundaries initially viewed as narrow Now recognize that many plate boundaries - especially continental - are deformation zones up to 1000 km wide, with motion spread
CONTINENTAL PLATE BOUNDARY ZONES Plate boundaries initially viewed as narrow Now recognize that many plate boundaries - especially continental - are deformation zones up to 1000 km wide, with motion spread
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches. Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes
 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Global Problems in Geology Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches Orogenic Belts Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes Development of Continental
Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Global Problems in Geology Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches Orogenic Belts Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes Development of Continental
FORCES ON EARTH. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
FORCES ON EARTH An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. GEOLOGY Geologists scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth Geologists
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID: GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics. The Theory of Plate Tectonics. The Plate Tectonics Theory. 62 Plate Tectonics Reading Essentials
 CHAPTER 4 LESSON 3 Tectonics The Theory of Tectonics Key Concepts What is the theory of plate tectonics? What are the three types of plate boundaries? Why do tectonic plates move? What do you think? Read
CHAPTER 4 LESSON 3 Tectonics The Theory of Tectonics Key Concepts What is the theory of plate tectonics? What are the three types of plate boundaries? Why do tectonic plates move? What do you think? Read
1. List the 3 main layers of Earth from the most dense to the least dense.
 1. List the 3 main layers of Earth from the most dense to the least dense. 2. List the 6 layers of earth based on their physical properties from the least dense to the most dense. 3. The thinnest layer
1. List the 3 main layers of Earth from the most dense to the least dense. 2. List the 6 layers of earth based on their physical properties from the least dense to the most dense. 3. The thinnest layer
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS. asthenosphere uplift continental drift. known as. tectonic plates move. object. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry. Planetary Surfaces
 Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Gravity Tectonics Volcanism Atmosphere Water Winds Chemistry Planetary Surfaces Gravity & Rotation Polar flattening caused by rotation is the largest deviation from a sphere for a planet sized object (as
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Important information from Chapter 1
 Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
 Sedimentary Basin Analysis http://eqsun.geo.arizona.edu/geo5xx/geos517/ Sedimentary basins can be classified based on the type of plate motions (divergent, convergent), type of the lithosphere, distance
Sedimentary Basin Analysis http://eqsun.geo.arizona.edu/geo5xx/geos517/ Sedimentary basins can be classified based on the type of plate motions (divergent, convergent), type of the lithosphere, distance
PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes
 PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes Review Earth s Interior Ch 1. Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth s interior: Direct evidence from rocks drilled from deep inside Earth
PLATE TECTONICS Chapter 4 Notes Review Earth s Interior Ch 1. Geologists have used two main types of evidence to learn about Earth s interior: Direct evidence from rocks drilled from deep inside Earth
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
10/29/13. Plate Boundaries. 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past)
 Plate Boundaries 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past) 1 Remember the plates are in motion. When plates move, they can either: A) converge (collide)
Plate Boundaries 3 types of plate boundaries: Divergent (divide) Convergent (collide) Transform (slide past) 1 Remember the plates are in motion. When plates move, they can either: A) converge (collide)
GCSE Geology Plate Tectonics: Features and Processes
 GCSE Geology Plate Tectonics: Features and Processes A) DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES: 1. O-O Divergence, Example: The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Iceland The North American and Eurasian Plates are moving away from each
GCSE Geology Plate Tectonics: Features and Processes A) DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES: 1. O-O Divergence, Example: The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Iceland The North American and Eurasian Plates are moving away from each
Plate tectonics. Chapter Slab pull. Dynamics of the Mantle and Lithosphere
 Chapter 6 In a number of aspects the Earth s mantle can be regarded as a fluid that shows simple fluid-dynamical behavior. or instance, the mantle of the Earth is probably showing a form of convection.
Chapter 6 In a number of aspects the Earth s mantle can be regarded as a fluid that shows simple fluid-dynamical behavior. or instance, the mantle of the Earth is probably showing a form of convection.
Chapter 5 Notes: Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 5 Notes: Plate Tectonics Earth s Interior Scientists learn about the interior of Earth in 2 ways o Direct Method Rock Samples Drilling Caves o Indirect Method Seismic Waves Speed of waves and paths
Chapter 5 Notes: Plate Tectonics Earth s Interior Scientists learn about the interior of Earth in 2 ways o Direct Method Rock Samples Drilling Caves o Indirect Method Seismic Waves Speed of waves and paths
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Theory of Plate Tectonics The Theory of Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics is the theory that the Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere. The plates
Theory of Plate Tectonics The Theory of Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics is the theory that the Earth's lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere. The plates
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Plate tectonics - 3. Homework 1: Due Monday. Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics. EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System.
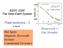 2500 EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System Plate tectonics - 3 17 Sep 08 Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics Depth (m) 6000 0 9 36 100 155 Homework 1: Due Monday Review: Fracture zone
2500 EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System Plate tectonics - 3 17 Sep 08 Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics Depth (m) 6000 0 9 36 100 155 Homework 1: Due Monday Review: Fracture zone
Earth. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth.
 Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth. Spheroid: with a longer major
Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth. Spheroid: with a longer major
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
Earth s Magnetic Field Differential Rotation between the inner core and the outer core.
 Geology 15 Lecture 7 Schedule: Hazard Update: Review Lecture 6 Activity 2 cont: Plate Boundaries and Their Motions Cover Material/Objectives Plate Tectonics (continued) Earth s Structure Evidence for Continental
Geology 15 Lecture 7 Schedule: Hazard Update: Review Lecture 6 Activity 2 cont: Plate Boundaries and Their Motions Cover Material/Objectives Plate Tectonics (continued) Earth s Structure Evidence for Continental
Plate Tectonics. Chapter 5
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 5 Earth s Interior Scientists learn about the interior of Earth in 2 ways Direct Method Rock Samples Drilling Caves Earth s Interior Indirect Method Seismic Waves Speed of waves
Plate Tectonics Chapter 5 Earth s Interior Scientists learn about the interior of Earth in 2 ways Direct Method Rock Samples Drilling Caves Earth s Interior Indirect Method Seismic Waves Speed of waves
Plaattektoniek en Mickey Mouse: de bewegingen van de Aarde en de geologie van Marokko. G. Bertotti - TUDelft
 Plaattektoniek en Mickey Mouse: de bewegingen van de Aarde en de geologie van Marokko G. Bertotti - TUDelft Moving continents Continent with matching boundaries Same fauna in different continents Similar
Plaattektoniek en Mickey Mouse: de bewegingen van de Aarde en de geologie van Marokko G. Bertotti - TUDelft Moving continents Continent with matching boundaries Same fauna in different continents Similar
Lithospheric plates. Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Tectonic processes
 1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
1. What is Wegener s theory of continental drift? 2. What were the 4 evidences supporting his theory? 3. Why wasn t Wegener s theory excepted?
 Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Earth s Interior. Theory of Tectonics. Tectonics & Landforms. Vocabulary
 Vocabulary Earth s Interior Theory of Tectonics Tectonics & Landforms Earthquake Volcano 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
Vocabulary Earth s Interior Theory of Tectonics Tectonics & Landforms Earthquake Volcano 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500
The influence of short wavelength variations in viscosity on subduction dynamics
 1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy
 There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
Bell Ringer 5 Minutes. Click Picture to Start Timing
 Plate Tectonics SC.7.E.6.5: Explore the scien6fic theory of plate tectonics by describing how the movement of Earth s crustal plates causes both slow and rapid changes in Earth s surface, including volcanic
Plate Tectonics SC.7.E.6.5: Explore the scien6fic theory of plate tectonics by describing how the movement of Earth s crustal plates causes both slow and rapid changes in Earth s surface, including volcanic
Unit 4 Lesson 7 Mountain Building
 Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
Indiana Standards 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in the mantle cause lithospheric plates to move causing fast changes like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and slow changes like creation of mountains
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics?
 What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust.
 1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and
 Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
12/3/2014. Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7. Continental drift: an idea before its time
 Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Continental drift: an idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed
Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Continental drift: an idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries
 Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
Plate Tectonics IDEA THAT EARTH S SURFACE IS BROKEN INTO PLATES THAT MOVE AROUND. Fault = fracture in the crust where the movement has occurred
 Warm-up #14 A mountain range found 100 meters above sea level is measured to be 1,000 meters high from its tallest peak. From the top, the first 500 meters are incredibly steep. After this point, the mountain
Warm-up #14 A mountain range found 100 meters above sea level is measured to be 1,000 meters high from its tallest peak. From the top, the first 500 meters are incredibly steep. After this point, the mountain
Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit II: The Plate Boundaries (Topic 11A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts) Plate Boundaries We will now discuss
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit II: The Plate Boundaries (Topic 11A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit II: Plate Boundaries (3.5 pts) Plate Boundaries We will now discuss
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics
 Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics Indiana Standards 7.2.1 Describe how the earth is a layered structure composed of lithospheric plates, a mantle and a dense core. 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Plate Tectonics Indiana Standards 7.2.1 Describe how the earth is a layered structure composed of lithospheric plates, a mantle and a dense core. 7.2.4 Explain how convection currents in
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
The Theory of Continental Drift. Continental Drift Discovery
 The Theory of Continental Drift Continental Drift Discovery The World ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Found evidence for PANGAEA and proposed the theory of continental drift. Continental Drift
The Theory of Continental Drift Continental Drift Discovery The World ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL DRIFT Found evidence for PANGAEA and proposed the theory of continental drift. Continental Drift
