1. Main features of the long-term seismic hazard map of the territory of Armenia
|
|
|
- Martina Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
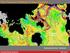
1 RELATION BETWEEN THE COMPOSITION, STRUCTURE, EVOLUTION OF EARTH CRUST AND SEISMIC ZONATION OF THE TERRITORY OF ARMENIA A. V. Harutyunyan 1 and H. M. Petrosyan 2 ABSTRACT In the last decades a numerous publications on the Lesser Caucasus seismicity had been published, and the new long-term seismic hazard map of the territory of Armenia had been compiled, and the new geological and geophysical factual data on crust deep structure had been obtained as well as the detailed geological maps by the ophiolite belts of Armenia had been compiled. The elastic and density properties of the rocks on high termobaric parameters had been investigated, based on which the numerous geological and geophysical profiles had been interpreted. The petrographic section and crust evolution were introduced. In the article, the innovative 3-dimensional block-scheme of the crust in the territory of Armenia was presented based on the comparison of the above-mentioned and other materials was presented, and defined that the most seismically active zones are coincided with ophiolite belts. Suggestion has been made that the seismic activity is stipulated by the protrusive permanent intrusion of serpentinized masses into the upper horizons as well as dehydration of the rocks at the different depths of the ophiolite belts. The ultimate objective of the research is the correct and in-time evaluation of the seismic hazard in the territory of Armenia [15]. Introduction The Lesser Caucasus is located in the northern-eastern part of Anatolia -Caucasus-Iran region. The peculiar feature of the territory of Armenia is the complicated tectonic composition: availability of deep faults and ophiolite structures, volcanity and seimicity etc. Many facts regarding the tectonic structure and composition, location of deep faults, mechanism of geological structure formation, volcanity had been obtained through complex geological and geophysical investigations provided in recent years. However, some problems concerning the crust deep structure and composition, seismicity, fluid regime and evolution of the crust, in general, remain arguing yet. Results of the geophysical research obtained through different methods were often indefinitely interpreted. Aiming at raising of interpretation exactness the seismic properties and density of the rocks have been investigated at the laboratory of experimental tectonics of the SEUA in the conditions which were modeling the termodynamic media of the deep structure of the Earth. Such investigations for different areas of the world are carried out at the labs of high temperatures and pressures in the developed countries (USA, England, Japan, Russia, Switzerland France and Germany). 1. Main features of the long-term seismic hazard map of the territory of Armenia In 1998 the Armenian National Survey for Seismic Protection (Armenian NSSP) under the leadership of Prof. S. Balassanian, had developed the probabilistic map of general seismic zonation (scale: 1: ) [7, 17]. The data-set included the maps as follows: density of earthquake epicenters in time and magnitudes, parameters of earthquake sources mechanisms, isoseists of strong earthquakes, seismic violations and active faults, zones of possible earthquake, modern vertical drifts, tectonic, geological and topographic maps as well as accelerograms of strong earthquakes, unified national seismic catalogue. 1 Associate professor, State Engineering University of Armenia, Yerevan City, 0009, Armenia, avhk@seua.am 2 PhD, Armenian National Survey for Seismic Protection, Yerevan City, 0054, Armenia, hrachikp@yahoo.com
2 The clearing house of the knowledge included analysis of seismic regime, creation of 3-dimensional physical and geological model of the crust, and creation of the dynamic physical and geological models of the crust based on the newest materials of the modern movements of the crust using seismic, geological and geostructural data. The research has resulted in the map with four seismic hazard zones: a=0.2g, 0.3g, 0.4g and 0.5g (Fig. 1) with 90% probability of the value non-exceeding. Two zones of the most seismic hazard (a=0.5g) are defined. Figure 1. The long-term seismic hazard map of the territory of Armenia, compiled by the Armenian NSSP in Analysis of the geological and geophysical data and research results on high temperature and pressure parameters A vast amount of geological and geophysical research had been fulfilled in recent decades in Armenia. Most significant results of geological and geophysical research had been accounted and interpreted for developments of the authors [3-6]. The heterogeneity of the crust had been defined through seismic investigations [9, 13]: availability of highspeed (4-6km and 22-35km) and low-speed (5-13km and 35-50km) layers, lenticular low-speed and highplastic structures had been defined rightly at the source zone of the Spitak earthquake. The gravitation minimums at the toe of the crust had been defined in some regions of Armenia basing on gravimetric data, and the author guess that it was connected with media incompaction. The geo-electrical section, as MTS revealed, had shown the availability of high-conductivity layer (5 Om.m) at the depths of 35-50km. It should be noted that in some zones the conductivity had decreased up to Om.m. The diapiric structure has emerged from the high-conductivity layer in the northern area of the Yerevan-city and raised from the toe of the crust up to the depths of 8-10km from the surface of the earth. High conductivity of the lower layers of the crust may be stipulated either by semi-melted condition of material or by availability of hydrated rocks.
3 Estimation of temperature had revealed that the geo-isothermal line of C within Hoktemberyan basin (Vedi ophiolite belt) is at the level of Moho border. The temperature of C is observed at the Moho border in Ijevan trough [11]. The temperature of C [12] is observed at the depth of 6km in the northern part of Yerevan where the diapiric structure is revealed at the depth of 8-10km. The thermal flow is absent here and so there is no semi-melted material available, and the high conductivity is stipulated by hydration of the rocks at the depths mentioned. The availability of the lenticular low-speed and density, and high-plastic and high-conductivity structures at the toe of the crust, especially beneath the source zone of the Spitak earthquake at the depths of 35-50km is non-arguable fact. The deep structure, composition and evolution of the crust in the territory of Armenia were provided basing on the research results of the rocks at high temperature and pressure and other geological and geophysical data [2-6] (Fig.2). Figure 2. Structure, composition and evolution of the crust in the territory of Armenia [3] 1-water; 2-sedimentary layer; 3- weakly meta-morphized complex of the sedimentary layers; 4- metamorphized complex of Pre-Cambrian and Lower Paleozoic (granite layer-g); 5- volcanogenic layer; 6- gabbro-diorite layer (B1); 7- gabbro layer (B2); 8- amphibolite and serpentine layer (B3); 9- serpentinized layer; 10- ultra-basites (upper mantle); 11- volcanic apparatus; 12- collision volcanites of ophiolites; 13- granite intrusion; 14- cover structures; 15- domain structures of hydrocarbons; 16- faults; 17- hypocenter of the Spitak 1988 Earthquake; TC- microplate of Southern Caucasus, L - Lock's massiv, S- Sevan ophiolite zone, TM-Tsaghkunyats massiv, CA- Central Armenian microplate, V- Vedi ophiolite zone, SA- South- Armenian microplate. According to petrophysical section the above mentioned lenticular bodies in the toe of the crust are wholly matched the hydrated rocks such as serpentinites, serpentinized ultrabazites and amphibolites. Petrological research leaded to the conclusion that in the central Armenia andesite-bazalts are re-melted products of gabbro-amphibolites at the depths of 30-40km [8]. Up to seismic parameters the high speed gabbroide layer is appeared above the serpentinized and amphibolized layers. Relatively low speed rocks of gabbro-diorite composition are laid above gabbroide layer. Pre-Cambrian metamorphized complex is forming the granite layer above which the sidementary and volcanogenic deposits of Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic are appeared.
4 3. On ophiolite structures formation mechanisms of the territory of Armenia The principal structural elements of the crust within the territory of Armenia are appeared to be Sevan and Vedi ophiolite zones which had been studied in detail including interrelation of rocks comprising ophiolite triad, composition of melange, contact behavior of oceanic blocks of crust and containing rocks, and petrography and chemical composition, etc [1, 10, 16]. The geological maps of the ophiolite structures of different scales have been compiled (Fig.3). Figure 3. The schematic map of the ophiolite belts location of the territory of Armenia [1] The problem of ophiolite zones' formation in the territory of Armenia is not yet solved in spite of extensive and long study [3, 4]. The results obtained highlighted yet some aspects of the problem. Those structures are controlled by deep faults and are appeared to be the protrusive intrusions. The petrophysical section and evolution of the crust in the territory of Armenia provided it is evident that the low density, high plastic serpentinized layer located at the toe of the crust is crucial for the formation of the ophiolite zones. Those rocks had been protrusively intruding into upper horizons of the crust along the deep ruptures involving the blocks of different sizes from the layers laid above. The volcanites are the secant bodies in the ophiolite belts presented by rocks of alkaline medium and rarely acid composition. 4. The results of comparative analysis of the materials Comparing the maps of seismic zonation and location of the ophiolite belts, and petrography the innovative block diagram of the crust of the territory of Armenia has been created (Fig.4).
5 Figure 4. Block diagram of the crust of the territory of Armenia The full coincidence of both most seismic hazardous zones and both ophiolite zones is noted. As to interrelation of the deep processes and seismicity the following should be mentioned: 1. The zones of the highest seismicity (a= g) are coincided with the zones of ophiolite structures and deep faults whereas the comparatively low seismicity (a= g) is noted in other regions including volcanogenic central trough of Armenia. 2. According to the model of crust evolution the ophiolite structures are formed due to permanent protrusive intrusion of serpentinized masses from the toe of the crust (35-50km) into upper horizons. It is natural to assume that the permanent intrusion of serpentinized massess through fault zones has drastically occurred accompanying with seismic shakings. 3. The process of protrusive intrusion of serpeninized masses encourage the development of deep faults and is accompanying with them. 4. Uneven distribution of the deep tectonic strengths within ophiolite structures may cause the dehydration of serpentinized masses and amphibolites and formation of magmatic and seismic sources. The dehydration is accompanying with the release of the energy and drastic change of the size of the rocks (up to 30%). Those processes may be accompanied with seismic shakings. Conclusion Comparing the results of research fulfilled in last decades in three directions: deep structure, ophiolites and seismic zonation one could admit that the main reason of seismic processes may be the protrusive intrusion of serpentinized masses into upper horizons of the crust. The process of dehydration of serpentinized masses may accompany the general process of seismigenic phenomena. It may be assumed that those processes permanently occur nowadays as well.
6 Acknowledgement The authors are sincerely grateful to Ms Armenuhi Abrahamyan and Ms Lilit Sargsyan from the Armenian NSSP and Mr Sargis Grigoryan and Mr Enok Abazyan, post-graduates of SEUA for assistance in preparing the materials and compiling of the article. References 1. Abovyan S.V., 1981, Maphite and ultra maphite intrusive complexes of the ophiolite belts of Armenian SSR, AS publishers, Yerevan (in Russian). 2. Harutyunyan A.V.,1975, Research on elastic properties and density of basites and ultra basites of the ophiolite belts of Armenia on high pressure (up to 20Kb), dissertation for PhD, USSR AS, Institute of Physics of the Earth, Moscow (in Russian). 3. Harutyunyan A.V., 1992, On petrography section of upper lithosphere of the territory of Armenia, Annali of AS of Armenia, 92, N4 (in Russian). 4. Harutyunyan A.V., 1998, On structure and composition of the crust of Lesser Caucasus and formation of deep ophiolite underthrusts, Geology and Prospecting, Annali of HEI, N2, Russian Federation, (in Russian). 5. Aslanyan A.T., Volarovich M. P., Harutyunyan A.V., Levikin A.I., 1975, On structure, composition and plastic characteristics of the crust and upper mantle in the territory of Armenia, Annali of AS of Armenian SSR, 61, N3 (in Russian). 6. Aslanyan A.T., Harutyunyan A.V., 1988, On the problem of deep structure of the ophiolite zones of the Lesser Caucasus, Annali of HEI, Armenian SSR, Earth Sciences, N5 (in Russian). 7. Balassanian S.Yu., Nazaretyan S.N., Amirbekyan V.S., 2004, Seismic protection and its organization, Eldorado Publishers, Gyumri (in Russian). 8. Genshaft Yu.S. et al,1982, Ksenolites and magacrystals in the lava of the Gegam upland (Armenia), Physical and chemical investigations of deep magmatic products, Nauka publishera, Moscow (in Russian) 9. Goritovskaya I.V., Study of deep structure of Armenia through nearby earthquakes recorded by the Zemlya stations, Geological fields and seismicity, Nauka publishers, Moscow (in Russian) 10. Knipper A.L., 1975, Oceanic crust and the structure of Alpine folded region, Nauka, Moscow (in Russian) 11. Mirijanyan R.T., 1979, Prognostic evaluation of the temperature in deep crust layers in the territory of the Armenian SSR, Annali of AS of Armenian SSR, Series Earth Sciences (in Russian) 12. Mirijanyan R.T., Vardanyan K.S. 1985, Rock temperature change in depth in the territory of the Armenian SSR, Annali of AS of Armenian SSR, Series Earth Sciences (in Russian) 13. Mikhaltsev A.V., et al. 1990, Deep geophysical research in seismically hazardous zones, Earth interior prospecting and preservation (in Russian) 14. Hovhanisyan Sh. S., 1977, Crust structure of the territory of Armenia, Annali of AS of Armenian SSR, Series Earth Sciences (in Russian) 15. Petrosyan H. 2004, Testing and prediction of earthquakes, 157pp 16. Satian M.A., 1984, Ophiolite troughs of Mezotetis, Armenian SSR AS publishers, Yerevan 17. Balassanian S., 1999, Seismic Hazard assessment for the Caucasus test area, Annali di Geofisica, 42, N6.
ACTIVE FAULTS AND PICULIARITES OF SEISMICITY AND FAULT BEHAVIOR OF THE TERRITORY OF ARMENIA
 ACTIVE FAULTS AND PICULIARITES OF SEISMICITY AND FAULT BEHAVIOR OF THE TERRITORY OF ARMENIA RAFAYEL HARUTYUNYAN HEAD OF GEOLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WESTERN SURWEY FOR SEISMIC PROTECTIN, MES ARMENIA ASHKHEN TOVMASYAN
ACTIVE FAULTS AND PICULIARITES OF SEISMICITY AND FAULT BEHAVIOR OF THE TERRITORY OF ARMENIA RAFAYEL HARUTYUNYAN HEAD OF GEOLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WESTERN SURWEY FOR SEISMIC PROTECTIN, MES ARMENIA ASHKHEN TOVMASYAN
GEOTHERMAL FEATURES OF ARMENIA: A COUNTRY UPDATE
 GEOTHERMAL FEATURES OF ARMENIA: A COUNTRY UPDATE Moushegh Badalyan Institute of Geophysics and Engineering Seismology of the National Academy of Science of Armenia, 5 Leningradian St., Giumri, 377501,
GEOTHERMAL FEATURES OF ARMENIA: A COUNTRY UPDATE Moushegh Badalyan Institute of Geophysics and Engineering Seismology of the National Academy of Science of Armenia, 5 Leningradian St., Giumri, 377501,
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Disaster Risk Reduction in Survey for Seismic Protection of MES
 Survey for Seismic Protection Ministry of Emergency Situations of Republic of Armenia Disaster Risk Reduction in Survey for Seismic Protection of MES Syuzanna Kakoyan Leading specialist at the Department
Survey for Seismic Protection Ministry of Emergency Situations of Republic of Armenia Disaster Risk Reduction in Survey for Seismic Protection of MES Syuzanna Kakoyan Leading specialist at the Department
Modern geodynamic model of the Arctic Ocean
 Modern geodynamic model of the Arctic Ocean O. Petrov, N. Sobolev, A. Morozov, G. Grikurov, S. Shokalsky, S. Kashubin, E. Petrov Vienna, April 2012 Atlas of Geological Maps of the Circumpolar Arctic Magnetic
Modern geodynamic model of the Arctic Ocean O. Petrov, N. Sobolev, A. Morozov, G. Grikurov, S. Shokalsky, S. Kashubin, E. Petrov Vienna, April 2012 Atlas of Geological Maps of the Circumpolar Arctic Magnetic
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms
 Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Mountain Building. Mountain Building
 Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Earthquake = vibration of the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Seismic Waves Focus = the place within the Earth where the rock breaks, producing an earthquake.
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Earthquake = vibration of the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Seismic Waves Focus = the place within the Earth where the rock breaks, producing an earthquake.
Geology 15 West Valley College. Exam IV: Sierra Nevada
 Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System. The Structure of the Earth. Temperature 3000º ºC. Mantle
 The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
GEOLOGY CURRICULUM. Unit 1: Introduction to Geology
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Current Seismic Hazard Assessment and Creation of Early Warning System in the Republic of Armenia
 Current Seismic Hazard Assessment and Creation of Early Warning System in the Republic of Armenia Dr. Alvaro Antonyan, Dr. Valeri Arzumanyan National Survey for Seismic Protection Agency (NSSP) Ministry
Current Seismic Hazard Assessment and Creation of Early Warning System in the Republic of Armenia Dr. Alvaro Antonyan, Dr. Valeri Arzumanyan National Survey for Seismic Protection Agency (NSSP) Ministry
Required Materials Plummer, C., Physical geology. Columbus, OH: McGraw Hill Higher Education
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
P105 Particularities of Astrakhan Gas Field Deep Structure Resulting from Microseismic Sounding Technique Application
 P105 Particularities of Astrakhan Gas Field Deep Structure Resulting from Microseismic Sounding Technique Application A.V. Gorbatikov* (Institute of Physics of the Earth, Rus.Acad.Sci.), M.Y. Stepanova
P105 Particularities of Astrakhan Gas Field Deep Structure Resulting from Microseismic Sounding Technique Application A.V. Gorbatikov* (Institute of Physics of the Earth, Rus.Acad.Sci.), M.Y. Stepanova
LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP
 OBJECTIVES: LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP 1) to develop your powers of observation, especially of geological phenomena; 2) to identify the rocks exposed at Trinidad Beach; 3) to reconstruct some of
OBJECTIVES: LAB 6: TRINIDAD BEACH FIELD TRIP 1) to develop your powers of observation, especially of geological phenomena; 2) to identify the rocks exposed at Trinidad Beach; 3) to reconstruct some of
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
The Sea of Okhotsk crust from deep seismic sounding data
 RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES, VOL. 6, NO. 1, PAGES 1 14, FEBRUARY 2004 The Sea of Okhotsk crust from deep seismic sounding data V. B. Piip Moscow State University, Moscow A. G. Rodnikov Geophysical
RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF EARTH SCIENCES, VOL. 6, NO. 1, PAGES 1 14, FEBRUARY 2004 The Sea of Okhotsk crust from deep seismic sounding data V. B. Piip Moscow State University, Moscow A. G. Rodnikov Geophysical
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20
 Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
CONTENT. A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction. B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence
 Name Earth Science Date Period TOPIC THE DYNAMIC EARTH CONTENT A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence C. Theory of Plate Tectonics
Name Earth Science Date Period TOPIC THE DYNAMIC EARTH CONTENT A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence C. Theory of Plate Tectonics
Name Class Date. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. mesosphere
 Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006
 Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006 Convergent boundaries are characterized by consumption of oceaninc crust in subduction zones, with attendant arc volcanism, metamorphism and uplift.
Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006 Convergent boundaries are characterized by consumption of oceaninc crust in subduction zones, with attendant arc volcanism, metamorphism and uplift.
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Science 2015 Earth Science. Study Guide
 Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Earthquakes in Canada
 Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
Earthquakes in Canada Maurice Lamontagne, Ph.D., ing. Geological Survey of Canada Natural Resources Canada 1 What is an Earthquake? P S P S P PS 2 2 Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger
GO ON. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1.
 d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
Internal Layers of the Earth
 Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Physical Geology Lab. Teacher Check (show your screen to your teacher) Part ONE: Dynamic Earth. Continents Over Time.
 Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Chino Valley Unified School District High School Course Description
 CONTACTS 1. School/District Information: School/District: Chino Valley Unified School District Street Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Phone: (909) 628-1201 Web Site: chino.k12.ca.us 2. Course
CONTACTS 1. School/District Information: School/District: Chino Valley Unified School District Street Address: 5130 Riverside Dr., Chino, CA 91710 Phone: (909) 628-1201 Web Site: chino.k12.ca.us 2. Course
Chapter 3. Geology & Tectonics
 Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
Chapter 3 Geology & Tectonics 3.1 Geology The general geological features of Indonesia are shown in Figure 3.1. The basement formation is metamorphic and it is intruded with plutonic formations. They are
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Grand Unifying Theory of everything... for the Geosciences, at least!
 Plate Tectonics: Grand Unifying Theory of everything... for the Geosciences, at least! The Earth s lithosphere, composed of Oceanic and continental crust, is broken up into pieces that move and interact
Plate Tectonics: Grand Unifying Theory of everything... for the Geosciences, at least! The Earth s lithosphere, composed of Oceanic and continental crust, is broken up into pieces that move and interact
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide
 Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
MOBILE-PERMEABLE ZONES IN THE BASEMENT OF THE NORTH-EASTERN BALTIC SHIELD AND CONDITIONS OF THEIR LOCATION
 Valentina T. FILATOVA 1 M 6 MOBILE-PERMEABLE ZONES IN THE BASEMENT OF THE NORTH-EASTERN BALTIC SHIELD AND CONDITIONS OF THEIR LOCATION 1 Geological Institute, Kola Science Center of the Russian Academy
Valentina T. FILATOVA 1 M 6 MOBILE-PERMEABLE ZONES IN THE BASEMENT OF THE NORTH-EASTERN BALTIC SHIELD AND CONDITIONS OF THEIR LOCATION 1 Geological Institute, Kola Science Center of the Russian Academy
Heat Flow in the Caspian Black Sea Region and its Tectonic Implications*
 Heat Flow in the Caspian Black Sea Region and its Tectonic Implications* R. I. Kutas 1 Search and Discovery Article #50400 (2011) Posted April 25, 2011 *Adapted from extended abstract prepared for presentation
Heat Flow in the Caspian Black Sea Region and its Tectonic Implications* R. I. Kutas 1 Search and Discovery Article #50400 (2011) Posted April 25, 2011 *Adapted from extended abstract prepared for presentation
History of Earth. Chapter 9: HISTORY OF EARTH. The Solar System. Early Earth: A Giant Impact! Early Earth. Formation of the Solar System
 Chapter 9: HISTORY OF EARTH The Essential Earth, 2 nd Edition Thomas H. Jordan & John Grotzinger History of Earth Earth is 4.56 Billion Years Old Earth has experienced a rich and diverse history that we
Chapter 9: HISTORY OF EARTH The Essential Earth, 2 nd Edition Thomas H. Jordan & John Grotzinger History of Earth Earth is 4.56 Billion Years Old Earth has experienced a rich and diverse history that we
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
24th Seismic Research Review Nuclear Explosion Monitoring: Innovation and Integration
 REFINEMENT OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENT LOCATION IN NORTHERN EURASIA USING 3-D CRUSTAL AND UPPER MANTLE VELOCITY MODEL Russian Federation/United States Calibration Working Group 1 Sponsored by Defense Threat
REFINEMENT OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENT LOCATION IN NORTHERN EURASIA USING 3-D CRUSTAL AND UPPER MANTLE VELOCITY MODEL Russian Federation/United States Calibration Working Group 1 Sponsored by Defense Threat
Name Class Date. Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One)
 Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017
 LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Multi-Messenger Astronomy This
LIGO sees binary neutron star merger on August 17, 2017 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Multi-Messenger Astronomy This
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis
 Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April
 TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate
TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate
Fig Stable Platforms. Canadian Shield. Folded Mountain Belts. The Canadian Shield is typical. Sedimentary rock covering a shield.
 The Interior of the Earth PS 100 Chapter 27 When the gravitation constant G was determined so was the density of the earth. It is 5.5g/cc. Granite is 2.7 Mountain Belt Shield Stable Platform Canadian Shield
The Interior of the Earth PS 100 Chapter 27 When the gravitation constant G was determined so was the density of the earth. It is 5.5g/cc. Granite is 2.7 Mountain Belt Shield Stable Platform Canadian Shield
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION
 CHAPER 3 EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION 3-1 General Geology of the Surrounding Area (1) General geology and ore deposits in Mongolia Geographically, Mongolia is a country located between Russia to the
CHAPER 3 EXISTING GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION 3-1 General Geology of the Surrounding Area (1) General geology and ore deposits in Mongolia Geographically, Mongolia is a country located between Russia to the
SEDIMENTARY BASINS Red Sea Coast of Egypt. by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour
 SEDIMENTARY BASINS Red Sea Coast of Egypt by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour Sedimentary basins Sedimentary basins are, in a very broad sense, all those areas in which sediments can accumulate to considerable
SEDIMENTARY BASINS Red Sea Coast of Egypt by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour Sedimentary basins Sedimentary basins are, in a very broad sense, all those areas in which sediments can accumulate to considerable
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction 10/15/2014. The Agents of Metamorphism. Metamorphism. and Metamorphic Rocks
 Introduction Metamorphism The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
Introduction Metamorphism The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić *** N.B. The material presented in these lectures is from the principal textbooks, other books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from
LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić *** N.B. The material presented in these lectures is from the principal textbooks, other books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Physical Geology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Physical Geology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Science Course Number GLG 101 (SUN# 1101) Title Physical Geology Credits 4 Developed by David Morris Lecture/Lab
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Physical Geology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Science Course Number GLG 101 (SUN# 1101) Title Physical Geology Credits 4 Developed by David Morris Lecture/Lab
GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES OF ARMENIA
 GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES OF ARMENIA Roger Henneberger 1, David Cooksley 2 and John Hallberg 2 1 GeothermEx, Inc., 5221 Central Avenue, Suite 201, Richmond, California 94804 USA 2 Burns and Roe Enterprises,
GEOTHERMAL RESOURCES OF ARMENIA Roger Henneberger 1, David Cooksley 2 and John Hallberg 2 1 GeothermEx, Inc., 5221 Central Avenue, Suite 201, Richmond, California 94804 USA 2 Burns and Roe Enterprises,
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Mid Term II Study Guide
 (1) 10 pts. Use the seismographs below, along with the travel time plot for California, and the location map for seismographs in this region to do the following: a. Determine the origin time for the earthquake
(1) 10 pts. Use the seismographs below, along with the travel time plot for California, and the location map for seismographs in this region to do the following: a. Determine the origin time for the earthquake
7 Sedimentation and tectonics at a mid- Ordovician to Silurian active margin
 80 Mountain Building in Scotland 7 Sedimentation and tectonics at a mid- Ordovician to Silurian active margin 7.1 Introduction In mid-ordovician to Silurian times, the Grampian mountains underwent exhumation,
80 Mountain Building in Scotland 7 Sedimentation and tectonics at a mid- Ordovician to Silurian active margin 7.1 Introduction In mid-ordovician to Silurian times, the Grampian mountains underwent exhumation,
EARTHQUAKES. Similar to sound, seismic waves can be generated by natural and artificial movements.
 EARTHQUAKES In general terms, an earthquake occurs usually when mechanical energy transmitted from the earth s core by the mantle is released and it reaches the solid cold crust, and tends to propagate
EARTHQUAKES In general terms, an earthquake occurs usually when mechanical energy transmitted from the earth s core by the mantle is released and it reaches the solid cold crust, and tends to propagate
Earthquakes. Pt Reyes Station 1906
 Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Unit Topics. Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes
 The Dynamic Earth Unit Topics Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes Topic 1: Earth s Interior Essential Question:
The Dynamic Earth Unit Topics Topic 1: Earth s Interior Topic 2: Continental Drift Topic 3: Crustal Activity Topic 4: Crustal Boundaries Topic 5: Earthquakes Topic 1: Earth s Interior Essential Question:
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX. Course: Physical Geology Department: _Physical Science. Study the text and lecture material
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: Physical Geology Department: _Physical Science Physical Geology This course is intended to acquaint students with the physical structure of the Earth, the nature
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: Physical Geology Department: _Physical Science Physical Geology This course is intended to acquaint students with the physical structure of the Earth, the nature
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES GENERAL SUBJECTS. GEODESY and GRAVITY
 COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
Chapter 8 10/19/2012. Introduction. Metamorphism. and Metamorphic Rocks. Introduction. Introduction. The Agents of Metamorphism
 Chapter 8 Metamorphism Introduction Metamorphism - The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks During
Chapter 8 Metamorphism Introduction Metamorphism - The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks During
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
GLG101: What-To-Know List
 Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
2/13/17. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination
 A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
MODELING OF MENTAWAI SUBDUCTION ZONE BASED ON GRAVITY DATA
 MODELING OF MENTAWAI SUBDUCTION ZONE BASED ON GRAVITY DATA I. M. Fairayanti 1, Irham, MN 2, H. Danusaputro 3 1,2,3 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Mathematics, Diponegoro University, Semarang
MODELING OF MENTAWAI SUBDUCTION ZONE BASED ON GRAVITY DATA I. M. Fairayanti 1, Irham, MN 2, H. Danusaputro 3 1,2,3 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and Mathematics, Diponegoro University, Semarang
GEOLOGY. What is geology?
 GEOLOGY What is geology? It is essentially the study of the earth and it s dynamic processes. Features and processes of rocks, the earth s interior and surface. Structure of the Earth Made up of three
GEOLOGY What is geology? It is essentially the study of the earth and it s dynamic processes. Features and processes of rocks, the earth s interior and surface. Structure of the Earth Made up of three
SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA
 SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA Hovhannes Khangeldyan Head of National Crisis Management Center Rescue Service Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Armenia Tokyo, 2016 ARMENIA: GEOGRAPHICAL
SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT IN ARMENIA Hovhannes Khangeldyan Head of National Crisis Management Center Rescue Service Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Armenia Tokyo, 2016 ARMENIA: GEOGRAPHICAL
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
 Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
Overview of the Seismic Source Characterization for the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station Scott Lindvall SSC TI Team Lead Palo Verde SSC SSHAC Level 3 Project Tuesday, March 19, 2013 1 Questions from
Earthquake. What is it? Can we predict it?
 Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY STRUCTURES OF SOUTHERN TUSCANY GEOTHERMAL AREAS, ITALY
 Proceedings 24* NZ Geothermal Workshop 2002 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY STRUCTURES OF SOUTHERN TUSCANY GEOTHERMAL AREAS, ITALY A. MANZELLA CNR- Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources, Pisa, Italy SUMMARY-
Proceedings 24* NZ Geothermal Workshop 2002 ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY STRUCTURES OF SOUTHERN TUSCANY GEOTHERMAL AREAS, ITALY A. MANZELLA CNR- Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources, Pisa, Italy SUMMARY-
An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone. Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29
 An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29 Outline General Introduction Formation history Structure from seismic study geochemical features
An Introduction of Aleutian Subduction Zone Chuanmao Yang, Hong Yang, Meng Zhang, Wenzhong Wang 2016/04/29 Outline General Introduction Formation history Structure from seismic study geochemical features
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand
 The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
The Tectonic Setting of New Zealand we are here Subduction-driven tectonics The New Zealand continent Papua New Guinea Australia 3,000,000 sq km micro-continent back-arc basin trench volcanism faults accretionary
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
GENERAL GEOLOGY Fall Chapter 18: The Sea Floor. Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli
 GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
Lecture 4.1 Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE
 crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
crustal structure experiment beneath Wairarapa - Wellington area: results from SAHKE Tim Stern and SAHKE team* * VUW, GNS, University of Southern California, University of Tokyo(Japan) SAHKE = Seismic
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
DYNAMIC CRUST AND THE EARTH S INTERIOR
 Name DYNAMIC CRUST AND THE EARTH S INTERIOR Regents Earth Science I EARTHQUAKES Earthquake Any natural shaking of the Earth caused by displacement of rock. Terms: (1) Focus- The point within the crust
Name DYNAMIC CRUST AND THE EARTH S INTERIOR Regents Earth Science I EARTHQUAKES Earthquake Any natural shaking of the Earth caused by displacement of rock. Terms: (1) Focus- The point within the crust
Term 1 final review ES
 Name: Date: 1. t what approximate altitude in the atmosphere can stratospheric ozone be found?. 10 km. 30 km. 70 km D. 100 km 2. What percentage of Earth s history represents human existence?. less than
Name: Date: 1. t what approximate altitude in the atmosphere can stratospheric ozone be found?. 10 km. 30 km. 70 km D. 100 km 2. What percentage of Earth s history represents human existence?. less than
EDIMENTARY BASINS. What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour
 EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Yanbu University College. General Studies Department. PHSC001 Course. Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions
 Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Using a pencil, complete the following practice questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Using a pencil, complete the following practice questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you
Perspectives of oil and gas presence in prejurassic sediments on the example of one West Siberian deposit
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Perspectives of oil and gas presence in prejurassic sediments on the example of one West Siberian deposit To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Perspectives of oil and gas presence in prejurassic sediments on the example of one West Siberian deposit To cite this article:
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group
 White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group A submarine landslide team of The Japanese planning group for Geohazard science at IODP* *Kiichiro
White paper for Geohazard (Submarine landslides and mass movements) at INVEST09 from Japanese research group A submarine landslide team of The Japanese planning group for Geohazard science at IODP* *Kiichiro
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8. Elastic rebound. Earthquakes. Earthquakes 11/19/2014.
 and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
