TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April
|
|
|
- Rosanna Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate tectonics recorded in the geological record: a journey to the verticals (including Augustus Love Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30 17:00, Room G11 TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7, The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, TS8.1/NH4.6/SM2.2, Active Tectonics and the Earthquake Cycle (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, Room B1 TS9.5, Advances in paleostress/strain reconstructions in tectonic studies : methods, applications, perspectives, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate tectonics recorded in the geological record: a journey to the verticals (including Augustus Love Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30 17:00, Room G11 SM4.2/GD8.5/TS9.10, Seismic imaging and tomography: theory and practice (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B5 TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7, The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, TS8.1/NH4.6/SM2.2, Active Tectonics and the Earthquake Cycle (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, Room B1 TS9.5, Advances in paleostress/strain reconstructions in tectonic studies : methods, applications, perspectives, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 PSD4.12, TS8.3/G6.5/NH4.7/SM5.7 - Seismotectonics and crustal deformation in Africa, 12:15 13:00, Room B4 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate tectonics recorded in the geological record: a journey to the verticals (including Augustus Love Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30 17:00, Room G11 GMPV9/GD2.13/TS11.8, Evolution of the lithospheric mantle: a petrological and geochemical perspective from the non-cratonic mantle xenoliths and orogenic peridotites (co-organized), 13:30 15:00, Room G6 SM2.1/GD2.7/NH5.8/TS8.4, Large Earthquake and Tsunami Activity (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 SM4.2/GD8.5/TS9.10, Seismic imaging and tomography: theory and practice (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B5 TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7, The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, TS8.1/NH4.6/SM2.2, Active Tectonics and the Earthquake Cycle (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, Room B1 TS10.4, Lessons on tectonic processes from the Caledonides, 13:30 15:00, Room B13 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate tectonics recorded in the geological record: a journey to the verticals (including Augustus Love Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30 17:00, Room G11 SM2.1/GD2.7/NH5.8/TS8.4, Large Earthquake and Tsunami Activity (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 SM4.2/GD8.5/TS9.10, Seismic imaging and tomography: theory and practice (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B5 Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 1
2 Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 2 TS4.8/GM3.8, TOPO-EUROPE: Coupled deep earth - surface processes, and their role in shaping Europe's topography (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, TS8.3/G6.5/NH4.7/SM5.7, Seismotectonics and crustal deformation in Africa (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room B1 TS10.5/GMPV41, Structural, metamorphic and magmatic evolution of the margin of Baltica and Laurentia and other Mesoproterozoic orogens (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room B13 Tuesday, 09 April TU1, 08:30 10:00 TS3.1/EMRP4.2, Fluid-rock interaction, deformation mechanisms and microstructural development in shear zones (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1 TU2, 10:30 12:00 TUL, 12:15 13:15 TU3, 13:30 15:00 TS6.3, Tectonics and lithospheric structure of the Indo-Eurasia collision zone, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS9.4/G5.4/GMPV47/NH2.6, Crustal faulting and deformation processes observed by InSAR, pixel offsets, GPS, and modelling techniques (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, ERE2.2/TS1.2, Field methods and analysis of field data for CO2 geological storage (co-organized), 10:30 12:00, Room G12 PSD8.12, GD4.1/SM5.4/TS5.5 - Evolution of passive margins and adjacent continents with emphasis on the North and South Atlantic, 10:30 11:15, Room R7 PSD14.2, GMPV30/NH2.2/TS3.5 - The mechanics of volcanic and sub-volcanic systems: modelling, experiments and field observations, 11:30 12:15, Room B7 TS3.1/EMRP4.2, Fluid-rock interaction, deformation mechanisms and microstructural development in shear zones (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1 TS6.3, Tectonics and lithospheric structure of the Indo-Eurasia collision zone, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS9.4/G5.4/GMPV47/NH2.6, Crustal faulting and deformation processes observed by InSAR, pixel offsets, GPS, and modelling techniques (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, PSD2.3, ERE2.2/TS1.2 - Field methods and analysis of field data for CO2 geological storage, 12:15 13:00, Room R5 PSD4.8, TS6.1 - The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 12:15 13:00, Room B7 GD4.1/SM5.4/TS5.5, Evolution of passive margins and adjacent continents with emphasis on the North and South Atlantic (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G13 GMPV30/NH2.2/TS3.5, The mechanics of volcanic and sub-volcanic systems: modelling, experiments and field observations (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G6 SM4.2/GD8.5/TS9.10, Seismic imaging and tomography: theory and practice (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room PICO Spot 4 TS9.1/GD8.2, Recent advances in analogue and numerical modeling of tectonic processes (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1
3 TU4, 15:30 17:00 WE1, 08:30 10:00 WE2, 10:30 12:00 TS9.4/G5.4/GMPV47/NH2.6, Crustal faulting and deformation processes observed by InSAR, pixel offsets, GPS, and modelling techniques (co-organized), 08:30 15:00, TS10.1/GD3.9, Geodynamics of the Western Mediterranean and Northwest Africa (co-organized), 13:30 15:00, Room B13 G3.1/CR3.9/GD1.4/TS1.5, Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Mantle Viscosity and Ice Sheet Fluctuations (co-organized), 15:30 17:15, Room R13 GD4.1/SM5.4/TS5.5, Evolution of passive margins and adjacent continents with emphasis on the North and South Atlantic (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G13 GMPV30/NH2.2/TS3.5, The mechanics of volcanic and sub-volcanic systems: modelling, experiments and field observations (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G6 PSD4.13, TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7 - The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes, 16:30 17:15, Room B7 SM4.2/GD8.5/TS9.10, Seismic imaging and tomography: theory and practice (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room PICO Spot 4 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 15:30 17:00, TS9.1/GD8.2, Recent advances in analogue and numerical modeling of tectonic processes (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1 Wednesday, 10 April GMPV36/TS3.4, Volcanoes: Tectonics, Deformation, Geodesy (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G6 TS4.1/GM3.5/SSP3.8, Tectonics, sedimentation and surface processes: from the erosional engine to basin deposition (jointly sponsored by the Geological Society of London and the Geological Society of America) (co-organized), 08:30 10:00, Room B1 TS5.3/SM5.6, Tectonics and seismicity of continental extension zones (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 08:30 17:00, EMRP1.4/SM4.9/TS2.8, Mechanical heterogeneity and their transient evolution along fault zones (co-organized), 10:30 12:00, Room B3 GMPV36/TS3.4, Volcanoes: Tectonics, Deformation, Geodesy (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G6 PSD4.7, TS4.1/GM3.5/SSP3.8 - Tectonics, sedimentation and surface processes: from the erosional engine to basin deposition (jointly sponsored by the Geological Society of London and the Geological Society of America), 10:30 11:15, Room B7 PSD8.19, GD1.2/EMRP4.1/GMPV12/SM6.5/TS Anisotropy and small-scale heterogeneity in the Solid Earth: Observations, models and implications, 10:30 11:15, Room R12 TS2.5/GD2.8, Fluids-rocks-tectonics interactions in basins and orogens, and feed-back with geodynamics (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B1 TS5.3/SM5.6, Tectonics and seismicity of continental extension zones (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 08:30 17:00, Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 3
4 Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 4 WEL, 12:15 13:15 PSD2.4, ERE3.1/TS3.6 - Structural interpretation and evolution of mineral systems from geological, geochemical and geophysical data, 12:15 13:00, Room R7 WE3, 13:30 15:00 WE4, 15:30 17:00 TH1, 08:30 10:00 EMRP1.3, Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling and physical properties: implications for natural hazards (co-listed), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 GD1.2/EMRP4.1/GMPV12/SM6.5/TS11.5, Anisotropy and small-scale heterogeneity in the Solid Earth: Observations, models and implications (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G10 SM1.1, Open Session on Seismology (including Beno Gutenberg Medal Lecture) (co-listed), 13:30 15:00, Room B5 TS2.5/GD2.8, Fluids-rocks-tectonics interactions in basins and orogens, and feed-back with geodynamics (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B1 TS5.2/GD4.4, From the East African Rift through Afar to the Gulf of Aden: insights into rift basins, oceanic propagators, and mature ridges and rifted margins evolution (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B13 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 08:30 17:00, EMRP1.3, Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling and physical properties: implications for natural hazards (co-listed), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 ERE3.1/TS3.6, Structural interpretation and evolution of mineral systems from geological, geochemical and geophysical data (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room G12 GD1.2/EMRP4.1/GMPV12/SM6.5/TS11.5, Anisotropy and small-scale heterogeneity in the Solid Earth: Observations, models and implications (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G10 GD4.2/GMPV27/SM5.1/TS5.6, Mid-ocean ridge processes and their consequences: a discussion on melting, hydrothermalism and dynamics at ocean spreading centers (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room G11 SM4.4/TS9.9, Active seismic investigations of the Earth's crust (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room B5 TS2.5/GD2.8, Fluids-rocks-tectonics interactions in basins and orogens, and feed-back with geodynamics (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room B1 TS5.2/GD4.4, From the East African Rift through Afar to the Gulf of Aden: insights into rift basins, oceanic propagators, and mature ridges and rifted margins evolution (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B13 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 08:30 17:00, Thursday, 11 April GD2.5/GMPV10/TS9.8, Long-term rheological behavior of the lithosphere inferred from observations and models at laboratory and geological time and spatial scales (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G10 SM6.3/GD2.11/GMPV26/TS11.6, Moho (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B5 SSP3.3, Limnogeology - reading the geological record of lakes (sponsored by the IAS) (co-listed), 08:30 10:00, Room B11 TS2.3/ERE5.5, Faulted and fractured reservoirs: structure and uncertainty, mechanics, reactions and flow (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS6.7/GMPV19, Orogeny, continental growth and magmatism across Eurasia (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1
5 TH2, 10:30 12:00 TH3, 13:30 15:00 TH4, 15:30 17:00 GD2.5/GMPV10/TS9.8, Long-term rheological behavior of the lithosphere inferred from observations and models at laboratory and geological time and spatial scales (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G10 SM6.3/GD2.11/GMPV26/TS11.6, Moho (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B5 TS2.3/ERE5.5, Faulted and fractured reservoirs: structure and uncertainty, mechanics, reactions and flow (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B13 TS6.7/GMPV19, Orogeny, continental growth and magmatism across Eurasia (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1 GD8.1/TS9.7, Recent advances in computational geodynamics (co-organized), 13:30 15:00, Room G10 GM8.2/GD2.10/TS4.5, Seafloor- and Subseafloor Expression of Tectonic and Geomorphic Processes (co-organized), 13:30 15:00, Room G2 SM6.4/GD3.7/GMPV15/TS11.7, Structure of the continental upper mantle (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B5 TS2.4/EMRP4.5, Flow in transforming porous media (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B13 TS6.9/GMPV25, Melt Evolution, Sole Development & Tectonic Emplacement of Ophiolites (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1 PSD8.1, GD8.1/TS9.7 - Recent advances in computational geodynamics, 15:30 16:15, Room R5 PSD8.5, GD2.5/GMPV10/TS9.8 - Long-term rheological behavior of the lithosphere inferred from observations and models at laboratory and geological time and spatial scales, 15:30 16:15, Room R7 PSD8.22, GD5.1/GMPV18/SM5.2/TS Subduction dynamics from surface to deep mantle, 16:30 17:15, Room R7 PSD15.2, GM3.1/TS4.4 - Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes, 15:30 16:15, Room B7 SM6.4/GD3.7/GMPV15/TS11.7, Structure of the continental upper mantle (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B5 TS2.4/EMRP4.5, Flow in transforming porous media (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B13 TS6.9/GMPV25, Melt Evolution, Sole Development & Tectonic Emplacement of Ophiolites (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1 Friday, 12 April FR1, 08:30 10:00 GD3.5/CR1.5/EMRP4.4/G6.4/TS10.8, Crustal structure and geodynamic evolution in the Antarctic and Arctic regions (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G11 FR2, 10:30 12:00 GM7.13, Asian rivers: from mountain to ocean (co-listed), 08:30 10:00, Room G3 PSD8.21, GD5.3/TS Orogenesis and Geodynamics related to the collision with microplates, 08:30 09:15, Room R12 TS1.1, Open Session on Tectonics and Structural Geology, 08:30 12:00, Room PICO Spot 1 TS6.6/GD5.6/GMPV20/SM5.3, Nature and physical properties of the plate interface in subduction zones: Cross-disciplinary views from Geodynamics-Geochemistry-Seismology-Modeling (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1 TS10.3, The Tethyan Heart and Sole of Pangea, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 CR5.1, Creep and fracture of Earth and planetary materials: from ice to olivine (co-listed), 10:30 12:00, Room G13 GD3.5/CR1.5/EMRP4.4/G6.4/TS10.8, Crustal structure and geodynamic evolution in the Antarctic and Arctic regions (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room G11 Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 5
6 Powered by TCPDF ( Programme Group Schedule TS Orals and PICOs 6 FR3, 13:30 15:00 FR4, 15:30 17:00 GM3.1/TS4.4, Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room G3 TS1.1, Open Session on Tectonics and Structural Geology, 08:30 12:00, Room PICO Spot 1 TS6.6/GD5.6/GMPV20/SM5.3, Nature and physical properties of the plate interface in subduction zones: Cross-disciplinary views from Geodynamics-Geochemistry-Seismology-Modeling (co-organized), 08:30 12:00, Room B1 TS10.3, The Tethyan Heart and Sole of Pangea, 08:30 12:00, Room B13 GD5.1/GMPV18/SM5.2/TS6.10, Subduction dynamics from surface to deep mantle (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G10 GM3.1/TS4.4, Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room G3 SM1.3/ESSI2.13/GD8.6/GMPV44/TS9.11, Integrated Research Infrastructures and Services to users: supporting excellence in a science for society (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 TS6.4/GD5.7/GM3.6/GMPV42, Integrating Multiple Techniques to Determine the Evolution of the Himalayan-Karakorum-Tibetan Orogenic System: Surface, Sub-surface & Deep Earth Processes (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1 TS10.2, The Gondwana, 13:30 15:00, Room B13 GD5.1/GMPV18/SM5.2/TS6.10, Subduction dynamics from surface to deep mantle (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room G10 GD5.3/TS6.12, Orogenesis and Geodynamics related to the collision with microplates (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room G11 GM3.1/TS4.4, Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes (co-organized), 10:30 17:00, Room G3 SM1.3/ESSI2.13/GD8.6/GMPV44/TS9.11, Integrated Research Infrastructures and Services to users: supporting excellence in a science for society (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B3 SSP3.4/GD8.8/GM7.12/TS4.6, New horizons in provenance research (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room B11 TS3.1/EMRP4.2, Fluid-rock interaction, deformation mechanisms and microstructural development in shear zones (co-organized), 15:30 17:00, Room B13 TS6.4/GD5.7/GM3.6/GMPV42, Integrating Multiple Techniques to Determine the Evolution of the Himalayan-Karakorum-Tibetan Orogenic System: Surface, Sub-surface & Deep Earth Processes (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B1
7 TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Posters Monday, 08 April MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO5, 17:30 19:00 PSD4.12, TS8.3/G6.5/NH4.7/SM5.7 - Seismotectonics and crustal deformation in Africa, 12:15 13:00, Room B4 GD1.0, Open Session in Geodynamics (POSTER only) (co-listed), Blue Posters, B262 B265 GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7, The evolution of plate tectonics recorded in the geological record: a journey to the verticals (including Augustus Love Medal Lecture) (co-organized), Blue Posters, B266 B284 GMPV8/GD3.8/TS11.9, Enigmas of origin and evolution of layered mantle lithosphere in different geodynamic settings (co-organized), Blue Posters, B295 B305 GMPV9/GD2.13/TS11.8, Evolution of the lithospheric mantle: a petrological and geochemical perspective from the non-cratonic mantle xenoliths and orogenic peridotites (co-organized), Blue Posters, B306 B318 SM2.1/GD2.7/NH5.8/TS8.4, Large Earthquake and Tsunami Activity (co-organized), Blue Posters, B133 B143 TS4.8/GM3.8, TOPO-EUROPE: Coupled deep earth - surface processes, and their role in shaping Europe's topography (co-organized), Blue Posters, B144 B159 TS8.1/NH4.6/SM2.2, Active Tectonics and the Earthquake Cycle (co-organized), Blue Posters, B160 B191 TS8.2, Earthquake Geology: methodological aspects and case studies (co-organized), Blue Posters, B192 B204 TS8.3/G6.5/NH4.7/SM5.7, Seismotectonics and crustal deformation in Africa (co-organized), Blue Posters, B205 B220 Related: PSD4.12, see MOL TS9.5, Advances in paleostress/strain reconstructions in tectonic studies : methods, applications, perspectives, Blue Posters, B221 B233 TS10.4, Lessons on tectonic processes from the Caledonides, Blue Posters, B234 B249 TS10.5/GMPV41, Structural, metamorphic and magmatic evolution of the margin of Baltica and Laurentia and other Mesoproterozoic orogens (co-organized), Blue Posters, B250 B261 Tuesday, 09 April TU2, 10:30 12:00 PSD8.12, GD4.1/SM5.4/TS5.5 - Evolution of passive margins and adjacent continents with emphasis on the North and South Atlantic, 10:30 11:15, Room R7 TUL, 12:15 13:15 TU4, 15:30 17:00 PSD14.2, GMPV30/NH2.2/TS3.5 - The mechanics of volcanic and sub-volcanic systems: modelling, experiments and field observations, 11:30 12:15, Room B7 PSD2.3, ERE2.2/TS1.2 - Field methods and analysis of field data for CO2 geological storage, 12:15 13:00, Room R5 PSD4.8, TS6.1 - The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), 12:15 13:00, Room B7 PSD4.13, TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7 - The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes, 16:30 17:15, Room Programme Group Schedule TS Posters 1
8 TU5, 17:30 19:00 WE2, 10:30 12:00 B7 Programme Group Schedule TS Posters 2 ERE2.2/TS1.2, Field methods and analysis of field data for CO2 geological storage (co-organized), Blue Posters, B128 B143 Related: PSD2.3, see TUL G3.1/CR3.9/GD1.4/TS1.5, Glacial Isostatic Adjustment, Mantle Viscosity and Ice Sheet Fluctuations (co-organized), Red Posters, R25 R43 GD4.1/SM5.4/TS5.5, Evolution of passive margins and adjacent continents with emphasis on the North and South Atlantic (co-organized), Blue Posters, B367 B386 Related: PSD8.12, see TU2 GMPV30/NH2.2/TS3.5, The mechanics of volcanic and sub-volcanic systems: modelling, experiments and field observations (co-organized), Blue Posters, B405 B428 Related: PSD14.2, see TU2 GMPV36/TS3.4, Volcanoes: Tectonics, Deformation, Geodesy (co-organized), Blue Posters, B429 B448 TS3.1/EMRP4.2, Fluid-rock interaction, deformation mechanisms and microstructural development in shear zones (co-organized), Blue Posters, B240 B269 TS5.1/GD4.3/SM5.5/SSP3.7, The evolution of passive continental margins: From rifting to post- break-up processes (co-organized), Blue Posters, B270 B312 Related: PSD4.13, see TU4 TS5.2/GD4.4, From the East African Rift through Afar to the Gulf of Aden: insights into rift basins, oceanic propagators, and mature ridges and rifted margins evolution (co-organized), Blue Posters, B313 B325 TS5.3/SM5.6, Tectonics and seismicity of continental extension zones (co-organized), Blue Posters, B326 B341 TS9.1/GD8.2, Recent advances in analogue and numerical modeling of tectonic processes (co-organized), Blue Posters, B342 B366 Wednesday, 10 April PSD4.7, TS4.1/GM3.5/SSP3.8 - Tectonics, sedimentation and surface processes: from the erosional engine to basin deposition (jointly sponsored by the Geological Society of London and the Geological Society of America), 10:30 11:15, Room B7 PSD8.19, GD1.2/EMRP4.1/GMPV12/SM6.5/TS Anisotropy and small-scale heterogeneity in the Solid Earth: Observations, models and implications, 10:30 11:15, Room R12 WEL, 12:15 13:15 PSD2.4, ERE3.1/TS3.6 - Structural interpretation and evolution of mineral systems from geological, geochemical and geophysical data, 12:15 13:00, Room R7 WE5, 17:30 19:00 EMRP1.3, Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling and physical properties: implications for natural hazards (co-listed), Blue Posters, B61 B72 EMRP1.4/SM4.9/TS2.8, Mechanical heterogeneity and their transient evolution along fault zones (co-organized), Blue Posters, B73 B85 ERE3.1/TS3.6, Structural interpretation and evolution of mineral systems from geological, geochemical and geophysical data (co-organized), Blue Posters, B39 B55 Related: PSD2.4, see WEL GD1.2/EMRP4.1/GMPV12/SM6.5/TS11.5, Anisotropy and small-scale heterogeneity in the Solid Earth: Observations, models and implications (co-organized), Blue Posters, B249 B274 Related: PSD8.19, see WE2 GD4.2/GMPV27/SM5.1/TS5.6, Mid-ocean ridge processes and their consequences: a discussion on melting, hydrothermalism and dynamics at ocean spreading centers (co-organized), Blue Posters, B275 B284
9 TH2, 10:30 12:00 TH4, 15:30 17:00 TH5, 17:30 19:00 SM4.4/TS9.9, Active seismic investigations of the Earth's crust (co-organized), Blue Posters, B98 B112 TS4.1/GM3.5/SSP3.8, Tectonics, sedimentation and surface processes: from the erosional engine to basin deposition (jointly sponsored by the Geological Society of London and the Geological Society of America) (co-organized), Blue Posters, B128 B144 Related: PSD4.7, see WE2 TS6.1, The Alpine convergence zone and the Mediterranean Sea (including Stephan Mueller Medal lecture by Leigh H. Royden), Blue Posters, B145 B188 Related: PSD4.8, see TUL TS6.3, Tectonics and lithospheric structure of the Indo-Eurasia collision zone, Blue Posters, B189 B200 TS9.4/G5.4/GMPV47/NH2.6, Crustal faulting and deformation processes observed by InSAR, pixel offsets, GPS, and modelling techniques (co-organized), Blue Posters, B201 B229 TS10.1/GD3.9, Geodynamics of the Western Mediterranean and Northwest Africa (co-organized), Blue Posters, B230 B248 Thursday, 11 April SM1.1, Open Session on Seismology (including Beno Gutenberg Medal Lecture) (co-listed), Blue Posters, B26 B41 PSD8.1, GD8.1/TS9.7 - Recent advances in computational geodynamics, 15:30 16:15, Room R5 PSD8.5, GD2.5/GMPV10/TS9.8 - Long-term rheological behavior of the lithosphere inferred from observations and models at laboratory and geological time and spatial scales, 15:30 16:15, Room R7 PSD8.22, GD5.1/GMPV18/SM5.2/TS Subduction dynamics from surface to deep mantle, 16:30 17:15, Room R7 PSD15.2, GM3.1/TS4.4 - Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes, 15:30 16:15, Room B7 GD2.5/GMPV10/TS9.8, Long-term rheological behavior of the lithosphere inferred from observations and models at laboratory and geological time and spatial scales (co-organized), Blue Posters, B170 B181 Related: PSD8.5, see TH4 GD5.1/GMPV18/SM5.2/TS6.10, Subduction dynamics from surface to deep mantle (co-organized), Blue Posters, B182 B195 Related: PSD8.22, see TH4 GD8.1/TS9.7, Recent advances in computational geodynamics (co-organized), Blue Posters, B208 B229 Related: PSD8.1, see TH4 GM8.2/GD2.10/TS4.5, Seafloor- and Subseafloor Expression of Tectonic and Geomorphic Processes (co-organized), Blue Posters, B371 B385 SSP3.3, Limnogeology - reading the geological record of lakes (sponsored by the IAS) (co-listed), Blue Posters, B778 B796 TS2.5/GD2.8, Fluids-rocks-tectonics interactions in basins and orogens, and feed-back with geodynamics (co-organized), Blue Posters, B62 B82 TS6.4/GD5.7/GM3.6/GMPV42, Integrating Multiple Techniques to Determine the Evolution of the Himalayan-Karakorum-Tibetan Orogenic System: Surface, Sub-surface & Deep Earth Processes (co-organized), Blue Posters, B83 B96 TS6.6/GD5.6/GMPV20/SM5.3, Nature and physical properties of the plate interface in subduction zones: Cross-disciplinary views from Geodynamics-Geochemistry-Seismology-Modeling (co-organized), Blue Posters, B97 B108 TS6.7/GMPV19, Orogeny, continental growth and magmatism across Eurasia (co-organized), Blue Posters, B109 B129 TS6.9/GMPV25, Melt Evolution, Sole Development & Tectonic Emplacement of Ophiolites (co-organized), Blue Posters, B130 B141 Programme Group Schedule TS Posters 3
10 Powered by TCPDF ( Programme Group Schedule TS Posters 4 FR1, 08:30 10:00 FR2, 10:30 12:00 FR3, 13:30 15:00 FR4, 15:30 17:00 FR5, 17:30 19:00 TS10.2, The Gondwana, Blue Posters, B142 B155 TS10.3, The Tethyan Heart and Sole of Pangea, Blue Posters, B156 B169 Friday, 12 April PSD8.21, GD5.3/TS Orogenesis and Geodynamics related to the collision with microplates, 08:30 09:15, Room R12 SM1.3/ESSI2.13/GD8.6/GMPV44/TS9.11, Integrated Research Infrastructures and Services to users: supporting excellence in a science for society (co-organized), Blue Posters, B33 B51 GD5.3/TS6.12, Orogenesis and Geodynamics related to the collision with microplates (co-organized), Blue Posters, B285 B290 Related: PSD8.21, see FR1 SM6.3/GD2.11/GMPV26/TS11.6, Moho (co-organized), Blue Posters, B141 B155 SSP3.4/GD8.8/GM7.12/TS4.6, New horizons in provenance research (co-organized), Blue Posters, B714 B722 TS2.2, Quantifying spatial variations of fracture characteristics of outcrop analogues (Poster Only), Blue Posters, B175 B184 TS2.3/ERE5.5, Faulted and fractured reservoirs: structure and uncertainty, mechanics, reactions and flow (co-organized), Blue Posters, B185 B208 TS2.4/EMRP4.5, Flow in transforming porous media (co-organized), Blue Posters, B209 B221 TS9.6, Geophysical methods in the service of Structural Geology, Blue Posters, B222 B232 CR5.1, Creep and fracture of Earth and planetary materials: from ice to olivine (co-listed), Blue Posters, B634 B641 GD3.5/CR1.5/EMRP4.4/G6.4/TS10.8, Crustal structure and geodynamic evolution in the Antarctic and Arctic regions (co-organized), Blue Posters, B260 B272 SM6.4/GD3.7/GMPV15/TS11.7, Structure of the continental upper mantle (co-organized), Blue Posters, B156 B165 GD3.5/CR1.5/EMRP4.4/G6.4/TS10.8, Crustal structure and geodynamic evolution in the Antarctic and Arctic regions (co-organized), Blue Posters, B273 B284 SM6.4/GD3.7/GMPV15/TS11.7, Structure of the continental upper mantle (co-organized), Blue Posters, B166 B174 GM3.1/TS4.4, Tectonics, Climate and Earth Surface processes (co-organized), Blue Posters, B423 B463 Related: PSD15.2, see TH4 GM7.13, Asian rivers: from mountain to ocean (co-listed), Blue Posters, B464 B474
GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7
 GD Geodynamics Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 TU3, 13:30 15:00 Monday, 08 April Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30
GD Geodynamics Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 TU3, 13:30 15:00 Monday, 08 April Medal Lecture) (co-organized), 08:30
SM2.1/GD2.7/NH5.8/TS8.4, Large Earthquake and Tsunami Activity (co-organized), 13:30 17:00, Room B3
 SM Seismology Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 Monday, 08 April SM1.2/AS4.13, Research and Development in Nuclear Explosion
SM Seismology Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 Monday, 08 April SM1.2/AS4.13, Research and Development in Nuclear Explosion
TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals Monday, 28 April
 TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals Monday, 28 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 GD3.2/TS9.7, Recent advances in computational geodynamics (co-organized),
TS Tectonics & Structural Geology Orals Monday, 28 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 GD3.2/TS9.7, Recent advances in computational geodynamics (co-organized),
GD3.3/GM3.3/GMPV16/TS4.7
 GM Geomorphology Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 MO5, 17:30 19:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 TUL, 12:15 13:15 TU3, 13:30 15:00 Monday, 08 April
GM Geomorphology Orals and PICOs MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 MO5, 17:30 19:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 TUL, 12:15 13:15 TU3, 13:30 15:00 Monday, 08 April
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
B13 SSS2.5/GM6.10/HS8.3.7/SSP3.1.20
 SSP Stratigraphy, Sedimentology & Palaeontology Orals Monday, 28 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 GM1.7, Non-continuous palaeoenvironmental
SSP Stratigraphy, Sedimentology & Palaeontology Orals Monday, 28 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 GM1.7, Non-continuous palaeoenvironmental
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES GENERAL SUBJECTS. GEODESY and GRAVITY
 COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Captain s Tryouts 2017
 Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
OS Ocean Sciences (#EGU17OS) Orals Monday, 24 April. Tuesday, 25 April
 OS Ocean Sciences (#EGU17OS) Orals MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 Monday, 24 April OS1.2/AS1.20/CL1.29, The North
OS Ocean Sciences (#EGU17OS) Orals MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MOL, 12:15 13:15 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 Monday, 24 April OS1.2/AS1.20/CL1.29, The North
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 19, 20, 21, & 2 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on December 14, 2004. Mark answers on a scantron sheet, which will be provided.
Y6 GMPV5.8/AS4.18/CL3.9
 CL Climate: Past, Present, Future (#EGU15CL) Orals Monday, 13 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 CL3.6/AS1.25, Extreme Events and
CL Climate: Past, Present, Future (#EGU15CL) Orals Monday, 13 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 TU2, 10:30 12:00 CL3.6/AS1.25, Extreme Events and
Plate Tectonics. I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move
 Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Plate Tectonics I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics II. A Mosaic of Plates III. Types of Plate Boundaries IV. How Plates Move I. The Discovery of Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift (Alfred Wegener) Proposed
Chapter. Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc.
 Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Announcements. Manganese nodule distribution
 Announcements Lithospheric plates not as brittle as previously thought ESCI 322 Meet in Env. Studies Bldg Rm 60 at 1 PM on Tuesday One week (Thursday): Quiz on Booth 1994 and discussion. (Lots of odd terms
Announcements Lithospheric plates not as brittle as previously thought ESCI 322 Meet in Env. Studies Bldg Rm 60 at 1 PM on Tuesday One week (Thursday): Quiz on Booth 1994 and discussion. (Lots of odd terms
CL Climate: Past, Present, Future Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April. Tuesday, 09 April. EGU General Assembly 2013
 CL Climate: Past, Present, Future Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 MO5, 17:30 19:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 CL0, Open Session on Climate: Past,
CL Climate: Past, Present, Future Orals and PICOs Monday, 08 April MO1, 08:30 10:00 MO2, 10:30 12:00 MO3, 13:30 15:00 MO4, 15:30 17:00 MO5, 17:30 19:00 TU1, 08:30 10:00 CL0, Open Session on Climate: Past,
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built?
 Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
Plate Tectonics GEOL 101 Lecture 22 How Are Mountains Built? The Grand Tetons, Wyoming First a Brief Review of Sea Floor Spreading Prop: Test 3 Invitations Break-Up of a Continent and Origin of an Ocean
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
GENERAL GEOLOGY Fall Chapter 18: The Sea Floor. Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli
 GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
Marine Science and Oceanography
 Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
1. I can describe evidence for continental drift theory (e.g., fossil evidence, mountain belts, paleoglaciation)
 Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm
 Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
CONTENT. A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction. B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence
 Name Earth Science Date Period TOPIC THE DYNAMIC EARTH CONTENT A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence C. Theory of Plate Tectonics
Name Earth Science Date Period TOPIC THE DYNAMIC EARTH CONTENT A. Changes in the Crust Facts Changes Construction and Destruction B. Continental Drift What is it? Evidence C. Theory of Plate Tectonics
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
Geology 101 Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name The readings for plate tectonics will be in four different chapters: 2, 4, 10 and 11. If you have questions, please let me know. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics:
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Evidence from the Surface. Chapter 02. Continental Drift. Fossil Evidence for Pangaea. Seafloor Spreading. Seafloor Spreading 1/31/2012
 Evidence from the Surface Surface landforms Continental shelf and slope Abyssal Plane Mid-oceanic ridge Oceanic Trenches Chapter 02 Continental Drift Continental Drift - a hypothesis that the continents
Evidence from the Surface Surface landforms Continental shelf and slope Abyssal Plane Mid-oceanic ridge Oceanic Trenches Chapter 02 Continental Drift Continental Drift - a hypothesis that the continents
Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches. Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes
 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Global Problems in Geology Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches Orogenic Belts Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes Development of Continental
Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Global Problems in Geology Distribution of Continents Mid-ocean Ridges Trenches Orogenic Belts Deformation Metamorphism Volcanism Earthquakes Development of Continental
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Mountain Building. Mountain Building
 Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Mountain Building Mountain building has occurred during the recent geologic past American Cordillera the western margin of the Americas from Cape Horn to Alaska Includes the Andes and Rocky Mountains Alpine
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
 UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
UNIT 1 THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH 1.1.Earth s interior layers The interior of the Earth can be divided into layers according to: -Composition layers ( organized in order of increasing density
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
Wilson cycle. 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting
 Wilson cycle 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting Stages of the Wilson Cycle Intracontinental Rifts 1. Contemporary examples (EAR, RGR, Baikal, Rhine graben) 2. Mechanical aspects. Characteristics
Wilson cycle 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting Stages of the Wilson Cycle Intracontinental Rifts 1. Contemporary examples (EAR, RGR, Baikal, Rhine graben) 2. Mechanical aspects. Characteristics
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Science 10 PROVINCIAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET. Unit 4. Earth Science
 Science 10 PROVNCAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET Unit 4 Earth Science Student nstructions 1. Ensure that you have blank paper and a Data Booklet. 2. Record all answers on a separate piece of paper. 3. Answer keys
Science 10 PROVNCAL EXAM STUDY BOOKLET Unit 4 Earth Science Student nstructions 1. Ensure that you have blank paper and a Data Booklet. 2. Record all answers on a separate piece of paper. 3. Answer keys
Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Banded Iron Formation
 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Banded Iron Formation Rocks Big rocks into pebbles, Pebbles into sand. I really hold a million, million Rocks here in my hand. Florence Parry Heide How do rocks change? How are
Rocks and the Rock Cycle Banded Iron Formation Rocks Big rocks into pebbles, Pebbles into sand. I really hold a million, million Rocks here in my hand. Florence Parry Heide How do rocks change? How are
5. Convergent boundaries produce a relatively low number of earthquakes compared to other boundaries. a. True
 1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
The Afar Rift Consortium
 The Afar Rift Consortium University of Bristol University of Oxford University of Cambridge British Geological Survey University of Rochester University of Auckland, NZ Opportunistic programme following
The Afar Rift Consortium University of Bristol University of Oxford University of Cambridge British Geological Survey University of Rochester University of Auckland, NZ Opportunistic programme following
Yanbu University College. General Studies Department. PHSC001 Course. Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions
 Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Yanbu University College General Studies Department PHSC001 Course Chapter9 (Basic Geology: Earthquakes and volcanoes ) Worksheet Solutions Phsc001 worksheet9 solutions, yuc Page 1-6 Chapter 9 worksheet
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Lecture 4.1 Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Full file at
 Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Dr. Yildirim Dilek Department of Earth Sciences Miami University, USA
 Dr. Yildirim Dilek Department of Earth Sciences Miami University, USA 40 years of successful, field-based, inter-disciplinary exploration of the Earth processes and training of the future generations of
Dr. Yildirim Dilek Department of Earth Sciences Miami University, USA 40 years of successful, field-based, inter-disciplinary exploration of the Earth processes and training of the future generations of
TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE. Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University
 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University 1 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor
TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor of Geoscience Winona State University 1 TEACHING PLATE TECTONICS FROM THE EVIDENCE Stephen T. Allard Associate Professor
Earthscope in the Northern Rockies Workshop
 Earthscope in the Northern Rockies Workshop Co-conveners: David Foster - University of Florida Paul Mueller - University of Florida David Mogk - Montana State University EarthScope in the Northern Rockies
Earthscope in the Northern Rockies Workshop Co-conveners: David Foster - University of Florida Paul Mueller - University of Florida David Mogk - Montana State University EarthScope in the Northern Rockies
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20
 Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić *** N.B. The material presented in these lectures is from the principal textbooks, other books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from
LECTURE 1 - Introduction Hrvoje Tkalčić *** N.B. The material presented in these lectures is from the principal textbooks, other books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
Refer to the map on page 173 to answer the following questions.
 Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
Chapter 8-1 Plate Tectonics 1. Brainstorm the type of evidence that would indicate a climate change and how this evidence supports the theory of continental drift. Tropical fossils in cold regions Evidence
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
12/3/2014. Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7. Continental drift: an idea before its time
 Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Continental drift: an idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed
Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Earth Science, 13e Chapter 7 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Continental drift: an idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed
PLATE TECTONICS. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift- Wegener s Evidence
 Continental Drift PLATE TECTONICS E.B. Taylor (1910) and Alfred Wegener (1915) published on Continental Drift. Continental Drift Wegener s evidence 1. Fit of the Continents 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Rock Type
Continental Drift PLATE TECTONICS E.B. Taylor (1910) and Alfred Wegener (1915) published on Continental Drift. Continental Drift Wegener s evidence 1. Fit of the Continents 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Rock Type
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms
 Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1 No School 2 E 3 O *Vocabulary *Continental Drift Notes and Sea Floor
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/2 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1 No School 2 E 3 O *Vocabulary *Continental Drift Notes and Sea Floor
FINAL EXAM Crustal Deformation CONVERGE DIVERGENT PLATES MANTLE PLUMES FLUX BASALTIC GRANITIC
 Crustal Deformation Reading: Chapter 10 Pages 283-304 Review Questions 4, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 FINAL EXAM NOON TO 2 PM, TUESDAY DEC. 5 HERE: Natural Science 101 BRING A SCAN TRON TURN IN YOUR REVIEW
Crustal Deformation Reading: Chapter 10 Pages 283-304 Review Questions 4, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 FINAL EXAM NOON TO 2 PM, TUESDAY DEC. 5 HERE: Natural Science 101 BRING A SCAN TRON TURN IN YOUR REVIEW
EXPLORING. liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED
 EXPLORING liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES PAUL M. DAVIS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
EXPLORING liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES PAUL M. DAVIS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
Plate tectonics - 3. Homework 1: Due Monday. Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics. EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System.
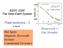 2500 EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System Plate tectonics - 3 17 Sep 08 Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics Depth (m) 6000 0 9 36 100 155 Homework 1: Due Monday Review: Fracture zone
2500 EESC 2200 The Solid Earth System Plate tectonics - 3 17 Sep 08 Hot Spots Magnetic Reversals Isostasy Continental Tectonics Depth (m) 6000 0 9 36 100 155 Homework 1: Due Monday Review: Fracture zone
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
Geology 101. Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics
 Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
Geology 101 Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics (p. 21) Reading Guide for Plate Tectonics Name You should have read this section during the first week of the quarter. You should re-read this section and review
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds
 Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
The continental lithosphere
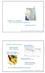 Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Chapter 4: Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 4: Plate Tectonics K2 in the Himalaya, inset round submersible (beneath the submarine) that went to the Marianas Trench in 1960 http://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/james-cameron-presents-record-setting-deep-sea-expedition-article-1.1215139
Chapter 4: Plate Tectonics K2 in the Himalaya, inset round submersible (beneath the submarine) that went to the Marianas Trench in 1960 http://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/james-cameron-presents-record-setting-deep-sea-expedition-article-1.1215139
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
The Earth s Structure from Travel Times
 from Travel Times Spherically symmetric structure: PREM - Crustal Structure - Upper Mantle structure Phase transitions Anisotropy - Lower Mantle Structure D D - Structure of of the Outer and Inner Core
from Travel Times Spherically symmetric structure: PREM - Crustal Structure - Upper Mantle structure Phase transitions Anisotropy - Lower Mantle Structure D D - Structure of of the Outer and Inner Core
Plate Tectonics. Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15
 1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
Theory of Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries. Lecture 23. Geol 101 (Kite) Quiz 9, April Geol 101 (Kite) Quiz 9, April 2006
 Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries Lecture 23 Prop: Test 3 Invitations Geol 101 (Kite) Quiz 9, April 2005 ******************************* * You are cordially invited * Name * to attend
Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries Lecture 23 Prop: Test 3 Invitations Geol 101 (Kite) Quiz 9, April 2005 ******************************* * You are cordially invited * Name * to attend
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
Important information from Chapter 1
 Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries. Lecture Continental Fit 2. Similar Rocks, Ages 3. Similar Fossils 4. Widespread Glaciation
 Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries Lecture 21 Prop: Test 3 Invitations Alfred Wegener s Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Continental Fit 2. Similar Rocks, Ages 3. Similar Fossils 4. Widespread
Sea-Floor Spreading, Subduction,& Plate Boundaries Lecture 21 Prop: Test 3 Invitations Alfred Wegener s Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Continental Fit 2. Similar Rocks, Ages 3. Similar Fossils 4. Widespread
Plate Tectonics. A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism
 Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism B. Seafloor Spreading 1. Earthquakes and volcanoes 2. Seafloor maps and dates 3. Continental drift revisited
Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism B. Seafloor Spreading 1. Earthquakes and volcanoes 2. Seafloor maps and dates 3. Continental drift revisited
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
Civilization exists by geologic consent, subject to change without notice William Durant
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics Civilization exists by geologic consent, subject to change without notice William Durant Properties of the Planets Size Density Distance from sun Chemistry
89.325 Geology for Engineers Plate Tectonics Civilization exists by geologic consent, subject to change without notice William Durant Properties of the Planets Size Density Distance from sun Chemistry
1. What is Wegener s theory of continental drift? 2. What were the 4 evidences supporting his theory? 3. Why wasn t Wegener s theory excepted?
 Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Notebook 7a and 7b Objective (left-side): Students will be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to make predictions about plate interactions. Mapping Reflection 1. What is Wegener
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with
 Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with depth Spheroid: with a longer major
Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with depth Spheroid: with a longer major
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) ONE single landmass
Plate Tectonics. Goal 2.1
 Plate Tectonics Goal 2.1 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics: An Overview Think About It Look at the map below. Which two continents look like they d fit together? Focus Question How do Earth s tectonic plates cause
Plate Tectonics Goal 2.1 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics: An Overview Think About It Look at the map below. Which two continents look like they d fit together? Focus Question How do Earth s tectonic plates cause
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 3, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Continental ice sheets increase the weight of the Earth
