Marine Sediments EPSS15 Spring 2017 Lab 4
|
|
|
- Junior Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marine Sediments EPSS15 Spring 2017 Lab 4 Why Sediments? Record of Earth s history - Tectonic plate movement - Past changes in climate - Ancient ocean circulation currents - Cataclysmic events 1
2 Classification Genetic - Sediments distinguished according to processes by which they originate: Physical Chemical Biological Terrigenous Cosmogenous Hydrogenous Biogenous Descriptive Sediments distinguished according to differences in physical properties and chemical make-up Texture, size Composition Terrigenous Sediments derived from erosion of continental or island rocks Transport mechanisms include rivers, wind, turbidity currents, glaciers Terrigenous sediments: Continental margin sediments Transported mainly by rivers, wave erosion, turbidity currents Abyssal clays Windblown dust prevalent in abyssal plains due to lack of other sediments 2
3 Terrigenous (cont d) Sediments derived from erosion of continental or island rocks Transport mechanisms include rivers, wind, turbidity currents, glaciers Terrigenous sediments: Volcanogenic sediments Windblown ash from volcanoes, wave-eroded volcanic rocks Glacial marine sediments Ice rafted debris Cosmogenous Inorganic sediments that originate from accumulation of materials from outer space (very rare) Cosmic spherules Small, globular masses Interplanetary dust Removed from deep sea sediment by strong magnets Impact deposits Form when large asteroids or comets collide with Earth These impacts blast meteorite material great distances 3
4 4/28/17 Hydrogenous Minerals that precipitate from seawater by chemical reactions Only a small portion of marine sediments Hydrothermal sediments are produced by leaching at MOR Manganese nodules are found in abyssal seafloor composed of mainly MnO2 and Fe2O3 Continental analog; evaporites in dried lakes Biogenous Mostly skeletal material produced by marine organisms such as plankton When organisms die, their remains sink to the ocean floor and eventually lithify (become rock) Oozes are sediments made up of >30% biogenous material. Calcareous oozes: contain skeletal materials of CaCO3 Siliceous oozes: contain skeletal materials of SiO2*nH2O Phosphates: skeletal material of bones and teeth of vertebrates 4
5 Biogenous (cont d) Phytoplankton (algae) Zooplankton (animal) Calcareous ooze CaCO 3 Calcite- most common biogenic form of CaCO 3 Aragonite- least common biogenic form of CaCO 3 Coccolithophores Chalk- fine-grained white sed rock Foraminifera Chambered tests Siliceous ooze SiO 2* nh 2 0 Diatoms Diatomite fine-grained white sed rock Radiolarians Spherical tests Opal- the biogenic form of silica Carbonate Compensation Depth (CCD) Solubility of CaCO 3 varies in seawater The CCD is the depth at which rate of dissolution of CaCO 3 is equal to its rate of accumulation Depth of CCD is controlled by temperature, pressure, local chemistry, and biological productivity. CO 2 + H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 + CaCO 3 Ca HCO 3 - * Concentration of CO 2 is higher in colder, deeper waters * More CO 2, more carbonic acid, more CaCO 3 dissolution 5
6 Carbonate Compensation Depth (CCD) Descriptive Classification Diameter (mm) Name Grain size Transport Energy >256 Boulder Coarse grained High Energy Cobble 64-4 Pebble 4-2 Granule Sand Silt < Clay Fine Grained Low Energy Gravel Sand Mud 6
7 Descriptive Classification cont d Well Rounded Rounded Subrounded Subangular Angular Very Angular Distribution of Marine Sediments Terrigenous Dominant along continental margins and deep oceans Turbidites dominate on continental rises and abyssal plains Glacial sediments dominate at high latitudes Range from coarse to fine Hydrogenous exist in diverse environments such as MOR and ocean basins Biogenous Calcareous ooze- warm shallow regions above CCD Siliceous ooze- colder regions of high surface activity; below CCD 7
8 Distribution of marine sediments 8
EPSS 15 Fall 2017 Introduction to Oceanography. Marine Sediments
 EPSS 15 Fall 2017 Introduction to Oceanography Marine Sediments INTRODUCTION There are two basic methods used for classification of marine sediments: genetic and descriptive. Genetic classifications distinguish
EPSS 15 Fall 2017 Introduction to Oceanography Marine Sediments INTRODUCTION There are two basic methods used for classification of marine sediments: genetic and descriptive. Genetic classifications distinguish
Question. What caused the recent explosive eruptions of hot ash and gas at Kilauea s Halema uma u crater:
 OCN 201 Deep Sea Sediments Question What caused the recent explosive eruptions of hot ash and gas at Kilauea s Halema uma u crater: A. The interaction of lava with seawater B. Drainage of the lava lake
OCN 201 Deep Sea Sediments Question What caused the recent explosive eruptions of hot ash and gas at Kilauea s Halema uma u crater: A. The interaction of lava with seawater B. Drainage of the lava lake
OCN 201: Deep-Sea Sediments
 OCN 201: Deep-Sea Sediments Eric Heinen De Carlo, F2011 Where is the Sediment? Continental Margins: 87% (covers ~21% of ocean area) Deep-ocean floor: 13% ~21% ~87% Sediment Deposition Rates (time to deposit
OCN 201: Deep-Sea Sediments Eric Heinen De Carlo, F2011 Where is the Sediment? Continental Margins: 87% (covers ~21% of ocean area) Deep-ocean floor: 13% ~21% ~87% Sediment Deposition Rates (time to deposit
Chapter 4 Marine Sediments
 Chapter 4 Marine Sediments Chapter Overview Marine sediments are important because contain a record of Earth history & provide clues to understand it Marine organism distribution Ocean floor movements
Chapter 4 Marine Sediments Chapter Overview Marine sediments are important because contain a record of Earth history & provide clues to understand it Marine organism distribution Ocean floor movements
Marine Sediments. Introductory Oceanography. Ray Rector: Instructor
 Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
Processes affecting continental shelves
 Marine Sediments Continental Shelves Processes affecting continental shelves 1. Glaciation 2. Sea-level change (±130 m during continental glaciation) 3. Waves and currents 4. Sedimentation 5. Carbonate
Marine Sediments Continental Shelves Processes affecting continental shelves 1. Glaciation 2. Sea-level change (±130 m during continental glaciation) 3. Waves and currents 4. Sedimentation 5. Carbonate
Marine Sediments Chapter Four Chapter Overview Marine Sediments Approaching the bottom (Alvin) Marine Sediments Classification of Marine Sediments
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Marine Sediments Chapter Four Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history. Marine sediments provide many important resources. Marine sediments have origins
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Marine Sediments Chapter Four Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history. Marine sediments provide many important resources. Marine sediments have origins
Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions
 Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 15 and 16 Outline I. Deep sea sedimentation Detrital sediments
Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 15 and 16 Outline I. Deep sea sedimentation Detrital sediments
Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography. -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography
 Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography Sediments Sources of sediment: 1. living organisms (biogenic:
Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography Sediments Sources of sediment: 1. living organisms (biogenic:
2/16/2014. Chapter Overview. Marine Sediments. Approaching the bottom (Alvin) Classification of Marine Sediments. Marine Sediments
 Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history. Marine sediments provide many important resources. Marine sediments have origins from a variety of sources. Marine Sediments Chapter
Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history. Marine sediments provide many important resources. Marine sediments have origins from a variety of sources. Marine Sediments Chapter
Reading Material. See class website. Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall
 Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
Announcements. First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today.
 Announcements First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today. Intertidal, Lowes Cove, ME Marine Sediments: Clues to the ocean s past There
Announcements First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today. Intertidal, Lowes Cove, ME Marine Sediments: Clues to the ocean s past There
Essentials of Oceanography
 Chapter Chapter 1 4 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Marine Sediments Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history.
Chapter Chapter 1 4 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Marine Sediments Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Marine sediments contain a record of Earth history.
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Laboratory#6 Sediment Particle Size Distribution and Turbidity Flows
 Laboratory#6 Sediment Particle Size Distribution and Turbidity Flows Although this laboratory will pertain to oceanic sediments similar processes can also be observed on land and other aquatic systems
Laboratory#6 Sediment Particle Size Distribution and Turbidity Flows Although this laboratory will pertain to oceanic sediments similar processes can also be observed on land and other aquatic systems
Earth s Seafloors. Ocean Basins and Continental Margins. Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Seafloors Ocean Basins and Continental Margins Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types
Earth s Seafloors Ocean Basins and Continental Margins Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor
 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor The ocean floor regions are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor, and the mid-ocean ridge. 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Continental Margins A continental
14.2 Ocean Floor Features Mapping the Ocean Floor The ocean floor regions are the continental margins, the ocean basin floor, and the mid-ocean ridge. 14.2 Ocean Floor Features Continental Margins A continental
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Introduction to Oceanography
 Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 10: Marine sediment 2 Midterm review session (Q&A): Thursday, Oct. 26, 5:00p-6:00p, Dodd 147 Extra credit video screening: Friday, Oct. 27, 3:00-4:00p, Location TBD
Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 10: Marine sediment 2 Midterm review session (Q&A): Thursday, Oct. 26, 5:00p-6:00p, Dodd 147 Extra credit video screening: Friday, Oct. 27, 3:00-4:00p, Location TBD
Oceanography Lecture 6
 Oceanography Lecture 6 Defining Boundaries: 3) 1. Review 2. : a. Introduction b. Classification: Size vs.. Origin c. Factors that control sedimentation d. Sedimentation in the Oceans i. Shelf Sedimentation
Oceanography Lecture 6 Defining Boundaries: 3) 1. Review 2. : a. Introduction b. Classification: Size vs.. Origin c. Factors that control sedimentation d. Sedimentation in the Oceans i. Shelf Sedimentation
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14. Essentials of Geology, 8e. Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College
 The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
Ocean Sediments. Key Concepts
 Ocean Sediments Key Concepts 1. What are the processes that control what types of sediments are deposited in which places? 2. Conversely, how can we use the sedimentary record to figure out tectonic and
Ocean Sediments Key Concepts 1. What are the processes that control what types of sediments are deposited in which places? 2. Conversely, how can we use the sedimentary record to figure out tectonic and
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks
 The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
are unconsolidated particulate materials that either precipitate from or are deposited by a fluid (e.g., water, wind);
 Sediments... are unconsolidated particulate materials that either precipitate from or are deposited by a fluid (e.g., water, wind); provide information about the past depositional environments and climatic
Sediments... are unconsolidated particulate materials that either precipitate from or are deposited by a fluid (e.g., water, wind); provide information about the past depositional environments and climatic
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
CARBONATES. part 3 MICRITES, CHALK and CHERTS: a very simple introduction to carbonates and silica in deep ocean waters
 CARBONATES part 3 MICRITES, CHALK and CHERTS: a very simple introduction to carbonates and silica in deep ocean waters notes from lecture: a quick summary Chalk (in white) and Chert Nodules (in black)
CARBONATES part 3 MICRITES, CHALK and CHERTS: a very simple introduction to carbonates and silica in deep ocean waters notes from lecture: a quick summary Chalk (in white) and Chert Nodules (in black)
CHAPTER 3 Ocean Basins
 Review: What Drives Plate Motions: (1) Density vs. Gravity: causes oceanic crust to sink in subduction zones, causes crust to extend at spreading ridges (called ridge push, but the ridge is not pushing,
Review: What Drives Plate Motions: (1) Density vs. Gravity: causes oceanic crust to sink in subduction zones, causes crust to extend at spreading ridges (called ridge push, but the ridge is not pushing,
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Chapter 9 Lecture Outline. Oceans: The Last Frontier
 Chapter 9 Lecture Outline Oceans: The Last Frontier The Vast World Ocean Earth is referred to as the blue planet 71% of Earth s surface is oceans and marginal seas Continents and islands comprise the remaining
Chapter 9 Lecture Outline Oceans: The Last Frontier The Vast World Ocean Earth is referred to as the blue planet 71% of Earth s surface is oceans and marginal seas Continents and islands comprise the remaining
Directed Reading. Section: The Water Planet. surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water ocean. d. global ocean.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Ocean Sediments OCN Nov 2016
 Ocean Sediments OCN 401 10 Nov 2016 Outline Significance & terms Origin & distribution of major types of marine sediments Delivery - dissolution destruction mid-ocean ridges Significance of ocean sediments
Ocean Sediments OCN 401 10 Nov 2016 Outline Significance & terms Origin & distribution of major types of marine sediments Delivery - dissolution destruction mid-ocean ridges Significance of ocean sediments
Sand. Sand is any eroded material (igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary) that has a grain size from 1/16 th to 2 millimeters in size.
 Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3 What we ll learn today:! 1. Describe the world s five oceans! 2. Understand patterns of ocean circulation! 3.
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3 What we ll learn today:! 1. Describe the world s five oceans! 2. Understand patterns of ocean circulation! 3.
The Sea Floor and Its Sediments OCEA 101
 The Sea Floor and Its Sediments OCEA 101 Measuring the depth of the ocean 85BC Posidonius measured depth of Med using rope and rock as ~2000m. Same idea used for next 2000 yrs using graduated ropes and
The Sea Floor and Its Sediments OCEA 101 Measuring the depth of the ocean 85BC Posidonius measured depth of Med using rope and rock as ~2000m. Same idea used for next 2000 yrs using graduated ropes and
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
 http://www.neic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/pands/global.html Global Seismicity and World Cities This map displays the worldwide hazard to cities by large earthquakes. When earthquakes occur near cities, the potential
http://www.neic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/pands/global.html Global Seismicity and World Cities This map displays the worldwide hazard to cities by large earthquakes. When earthquakes occur near cities, the potential
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Chapter 5. The Sedimentary Archives
 Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Introduction to Oceanography. Introduction to Oceanography. Easternmost Pacific Plate Evolution. Southern CA Evolution. Coast Ranges & Central Valley
 Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 9: California Tectonics, Marine 120 110 100 90 80 70 sediment Introduction to Oceanography 45 40 35 30 EXPLANATION Peak acceleration, expressed as a fraction of standard
Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 9: California Tectonics, Marine 120 110 100 90 80 70 sediment Introduction to Oceanography 45 40 35 30 EXPLANATION Peak acceleration, expressed as a fraction of standard
Introduction to Oceanography. Introduction to Oceanography
 Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 9: California Tectonics, Marine 120 110 100 90 80 70 sediment 45 40 35 30 EXPLANATION Peak acceleration, expressed as a fraction of standard gravity (g) 25 0.4 0.2
Introduction to Oceanography Lecture 9: California Tectonics, Marine 120 110 100 90 80 70 sediment 45 40 35 30 EXPLANATION Peak acceleration, expressed as a fraction of standard gravity (g) 25 0.4 0.2
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface
 Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
SCOPE 35 Scales and Global Change (1988)
 1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Learning Outcomes: Logistics: Classification System: bold Metamorphic Igneous Sedimentary Sedimentary rock classification schemes.
 Oceanography Marine rocks Learning Outcomes: Classify rocks into one of the three main categories: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Classify marine sedimentary rocks into a more detailed classification
Oceanography Marine rocks Learning Outcomes: Classify rocks into one of the three main categories: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Classify marine sedimentary rocks into a more detailed classification
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
The boundary between two formations (or any distinct layers) is called a contact. Sedimentary rocks cover 75% of continents.
 Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels
 Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels Chapter 4 Please read chapter 5: sediments for next class and start chapter 6 on seawater for Thursday Basic concepts in Chapter 4 Bathymetry the measurement of
Ocean Basins, Bathymetry and Sea Levels Chapter 4 Please read chapter 5: sediments for next class and start chapter 6 on seawater for Thursday Basic concepts in Chapter 4 Bathymetry the measurement of
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Sedimentation. Ocean Sediments Chapter 5. Paleoceanography. Lecture #6 Week #4. A.K. Morris, Ph.D.
 Sedimentation Ocean Sediments Chapter 5 A time capsule to the past Principle of superposition going deeper in the sediment means looking further into the past Oceanography Lecture #6 1 2 Fig. 5.1 Paleoceanography
Sedimentation Ocean Sediments Chapter 5 A time capsule to the past Principle of superposition going deeper in the sediment means looking further into the past Oceanography Lecture #6 1 2 Fig. 5.1 Paleoceanography
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Your teacher will show you a sample or diagram of each, and show you a settling column. Draw these, and label your diagrams (8 pts) Ungraded:
 From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
Section 14.1 The Vast World Ocean This section discusses how much of Earth is covered by water and how that water is studied.
 Section 14.1 The Vast World Ocean This section discusses how much of Earth is covered by water and how that water is studied. Reading Strategy Building Vocabulary As you read the section, define each term
Section 14.1 The Vast World Ocean This section discusses how much of Earth is covered by water and how that water is studied. Reading Strategy Building Vocabulary As you read the section, define each term
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth
 From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth 1 Questions your students might ask? What are rocks made of? What are minerals? What are minerals? What is the difference between Fool
From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth 1 Questions your students might ask? What are rocks made of? What are minerals? What are minerals? What is the difference between Fool
Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky
 Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky Objectives of Today s Lecture Refresher on Sedimentary Depositional Systems and Rock Classifications Transgressive and Regressive Marine Environments Carbonate Depositional
Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky Objectives of Today s Lecture Refresher on Sedimentary Depositional Systems and Rock Classifications Transgressive and Regressive Marine Environments Carbonate Depositional
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments
 Chapter 3 Notes 1 Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments A. The Tectonic Setting 1.Factors that determine the kind of sedimentary rock that will be formed in a particular area: a. the climate under which processes
Chapter 3 Notes 1 Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments A. The Tectonic Setting 1.Factors that determine the kind of sedimentary rock that will be formed in a particular area: a. the climate under which processes
1/31/2013. Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes. Weathering Mechanisms. Wind abrasion forming Ventifacts
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Sediments and. Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Bottom Line Sedimentary rocks form from particles accumulated in sedimentary layers Sedimentary layers can be formed by clastic or detrital particles (e.g., sand grains,
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Bottom Line Sedimentary rocks form from particles accumulated in sedimentary layers Sedimentary layers can be formed by clastic or detrital particles (e.g., sand grains,
Chapter 14: The Ocean Floor
 Chapter 14: The Ocean Floor Section 1: The Vast World Ocean I. The Blue Planet Group # II. Geography of the Oceans Group # III. Mapping the Ocean Floor Group # A. Sonar Group # B. Satellites Group # C.
Chapter 14: The Ocean Floor Section 1: The Vast World Ocean I. The Blue Planet Group # II. Geography of the Oceans Group # III. Mapping the Ocean Floor Group # A. Sonar Group # B. Satellites Group # C.
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks. Sedimentary Processes and Rocks
 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks Sedimentary Processes and Rocks Origins of Sedimentary Rocks Sediment transport and texture Sedimentary structures Lithification Classifying
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks Sedimentary Processes and Rocks Origins of Sedimentary Rocks Sediment transport and texture Sedimentary structures Lithification Classifying
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Rockall Plateau. OCN 201: Shelf Sediments
 Rockall Plateau OCN 201: Shelf Sediments Classification by Size Classification by Mode of Formation Detrital sediments Transported and deposited as particles Derived from weathering of pre-existing rocks
Rockall Plateau OCN 201: Shelf Sediments Classification by Size Classification by Mode of Formation Detrital sediments Transported and deposited as particles Derived from weathering of pre-existing rocks
Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream as it enters a lake. At which points along the stream are erosion and deposition dominant?
 1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 4 Physical Oceanography - IV (Refer Slide Time:
Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 4 Physical Oceanography - IV (Refer Slide Time:
Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 11B-1. Deep-Sea Sediments. Bottom Pictures: Anne Jennings, NOAA/NGDC, Department of Commerce.
 Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 11B-1 Deep-Sea Sediments Sediments are particles (broken pieces, bits of stuff) that cover the ocean floor. Ocean sediments are typically broken 1 into
Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 11B-1 Deep-Sea Sediments Sediments are particles (broken pieces, bits of stuff) that cover the ocean floor. Ocean sediments are typically broken 1 into
Sedimentary Features in Expedition 341 Cores: A Guide to Visual Core Description
 Sedimentary Features in Expedition 341 Cores: A Guide to Visual Core Description 1. Typical Deep water Sediments in the Gulf of Alaska 1A & B: Mud and 1C: Laminated mud Description: Mud is representative
Sedimentary Features in Expedition 341 Cores: A Guide to Visual Core Description 1. Typical Deep water Sediments in the Gulf of Alaska 1A & B: Mud and 1C: Laminated mud Description: Mud is representative
Depositional Environment
 Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
GEOL Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section)
 GEOL 333 - Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Sedimentary Rock Classification - As we learned last week, sedimentary rock, which forms by accumulation and lithification
GEOL 333 - Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Sedimentary Rock Classification - As we learned last week, sedimentary rock, which forms by accumulation and lithification
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Ocean Floor. Continental Margins. Divided into 3 major regions. Continental Margins. Ocean Basins. Mid-Ocean Ridges. Include:
 Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
Directed Reading. Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle. made of a. inorganic matter. b. solid organic matter. c. liquid organic matter. d. chemicals.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Question: What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast?
 Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 6. Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Figure 65: Reservoir in a steady state condition where the input flux is equal to the output flux and the reservoir size remains constant.
 7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Exercise 3 Texture of siliciclastic sediments
 Exercise 3 Texture of siliciclastic sediments Siliciclastic sediments are derived from the weathering and erosion of preexisting rocks. Once a sedimentary particle is loosened from its parent rock, it
Exercise 3 Texture of siliciclastic sediments Siliciclastic sediments are derived from the weathering and erosion of preexisting rocks. Once a sedimentary particle is loosened from its parent rock, it
Weathering Cycle Teacher Notes
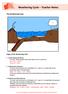 The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13
 The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Earth Science, 13e Chapter 13 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the blue planet Seventy-one percent of Earth s surface
Oceanography 201 Spring 2015 Exam #1
 Name: Student ID No.: Remember to also enter your Student ID number on the computer scan sheet. Signing below will allow us to post your scores (via U.H. ID number) on the class website. Signature Oceanography
Name: Student ID No.: Remember to also enter your Student ID number on the computer scan sheet. Signing below will allow us to post your scores (via U.H. ID number) on the class website. Signature Oceanography
Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p.
 Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p. 2 Mid-Ocean Ridge Province p. 3 Benthic and Pelagic Provinces
Physiography Ocean Provinces p. 1 Dimensions p. 1 Physiographic Provinces p. 2 Continental Margin Province p. 2 Deep-Ocean Basin Province p. 2 Mid-Ocean Ridge Province p. 3 Benthic and Pelagic Provinces
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6
 Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types
 Today s Objective: What Makes Sedimentary Rocks Special? Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types A sedimentary rock can form one of three ways: 1. by the deposition of the weathered remains
Today s Objective: What Makes Sedimentary Rocks Special? Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types A sedimentary rock can form one of three ways: 1. by the deposition of the weathered remains
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
