Sediments and. Sedimentary Rocks
|
|
|
- Chad Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
2 Bottom Line Sedimentary rocks form from particles accumulated in sedimentary layers Sedimentary layers can be formed by clastic or detrital particles (e.g., sand grains, shells, bones, clay mud, and so on) minerals that have precipitated out of a water-based solution materials erupted from a volcano Sedimentary layers contain geohistorical information
3
4
5
6
7 Importance of sed rox Forms interface between solid Earth and the biosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere Contains much of the evidence of Earth s biological and climatological history Economic interest Building materials (sand, gravel, etc.) Energy resources (oil, gas, coal) Economic minerals: uranium, iron, placer gold, bauxite, et cetera
8 History of a sedimentary grain Physical or Chemical Weathering Dissolution or Erosion: separating the compound or particle from its original source material Transportation by wind, water, ice, etc. Precipitation or Deposition Burial and possible lithification
9 Weathering Processes Mechanical weathering Chemical weathering
10 Factors Affecting Chemical Weathering Temperature Precipitation Vegetation Industrial pollution upwind
11 Siliciclastic sediments: broken fragments of silicate rocks and mineral grains
12 Sediment derived from the weathering of granitic bedrock.
13 Common minerals in siliciclastic sediments quartz clay mica minor feldspar (weathers easily) rock fragments dark ferromagnesian minerals like amphibole and pyroxene
14 The composition of clastic sediment is primarily a function of... the composition of the source material the distance the sediment has been transported greater distance = higher % of quartz or other chemically stable minerals
15 Carbonate sediments: composed primarily of the minerals calcite (calcium carbonate) or dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate)
16 Common minerals in carbonate sediments calcite dolomite clay iron and magnesium oxides
17 Grain Size Scale Particle Name Grain Diameter Forms Sed Rock... clay < 1/256 mm claystone, shale, mudstone silt 1/16 to 1/256 mm siltstone, shale, mudstone sand 1/16 to 2 mm sandstone gravel > 2 mm conglomerate, breccia
18 Laminated mudstone, Skardu, Himalaya
19
20 Gravel Size Scale Particle Name granule Grain Diameter 2 to 4 mm Forms Sed Rock... conglomerate, breccia pebble 4 to 64 mm ditto cobble 64 to 256 mm ditto boulder >256 mm ditto
21 Grain Shape Angular grains (sand size and larger) indicate that the grains have not been transported a significant distance compared with rounded grains. Grain sphericity is commonly related to composition (spherical, flat, oblate, prolate, et cetera)
22 Clastic grains from source to sink
23 Angular clasts in talus slope
24 Angular gravel sediment
25 Sedimentary breccia, illustrating angular clasts
26 Ripple marks, dunes, cross beds
27 Rippled sand in a stream channel
28 Wind-generated ripples, Death Valley.
29 1.8 billion year old current ripples, Baraboo quartzite, Wisconsin
30 1.8 billion year old current ripples, Baraboo quartzite, Wisconsin. My wife, on the other hand, is ageless.
31 Gypsum sand dunes at White Sands National Monument.
32 Sand blowing over cornice of a sand dune, White Sands National Monument, NM
33 Large sand dunes, Death Valley, California
34 View of the south side of the Skardu Valley, Baltistan, northern Pakistan
35 Large sand dunes, Skardu Basin, Kashmir Himalaya
36 Indus River through Skardu, summer 1981
37 Indus River through Skardu, Spring 1982
38 Large sand dunes, Skardu Basin, Kashmir Himalaya
39 Sand dune impinging on an orchard, Skardu Basin
40 Cross beds in sandstone
41 Submarine sand dunes, Bahamas, as observed from a shuttle orbiter
42 Large cross beds, Zion National Park
43 Lithification: transformation into sedimentary rock Compaction under the weight of overlying sediments Cementation by precipitation of minerals from ground water
44 Environmental information gleaned from analysis of sedimentary rock; the present is the key to interpreting the past
45 Mud cracks on dry lakebed.
46 Mud desiccation (drying) cracks
47 Salt rising through mud cracks on a dry playa lakebed in Death Valley, California. Salts carried by ground water are precipitated as the ground water evaporates at the surface.
48 Tracks on sand surface
49 Alluvial fan, Hunza Valley, Hindu Kush Mtns.
50 Alluvial fan, Death Valley
51 Evaporite deposits (and my wife) on the floor of a playa lake, Death Valley
52
53 Galveston Bay and barrier islands
54
55 Carbonate beach near Cancun, Mexico
56 Carbonate-secreting algae and resulting carbonate sediment
57 Coral reef ( El Garafon ), Isla de las Mujeres, Mexico
58 Great Barrier Reef as observed from a shuttle orbiter
59 Turbidite layers exposed in road cut in Illinois.
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6
 Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
GLG Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks
 GLG 101 - Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks Name Note, Oct 11: I ll be writing this study sheet over the next few days. Each day I will add questions until the entire chapter is done, hopefully
GLG 101 - Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks Name Note, Oct 11: I ll be writing this study sheet over the next few days. Each day I will add questions until the entire chapter is done, hopefully
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks. All sedimentary rocks begin to form when existing rocks are broken down into sediments Sediments are mainly weathered debris
 Rocks! Objectives Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are
Rocks! Objectives Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8
 Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
A Sedimentary Rock is..
 Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks A Sedimentary Rock is.. rock formed from the lithification or crystallization of: 1. Minerals in solution 2. Organic remains 3. Materials produced by living things (biochemical) 4. Clastic
To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks
 To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks Bryce Canyon, Utah Badlands, South Dakota Weathering Whenever rock is exposed
To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks Bryce Canyon, Utah Badlands, South Dakota Weathering Whenever rock is exposed
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types
 Today s Objective: What Makes Sedimentary Rocks Special? Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types A sedimentary rock can form one of three ways: 1. by the deposition of the weathered remains
Today s Objective: What Makes Sedimentary Rocks Special? Sedimentary Rocks - are one of the three main rock types A sedimentary rock can form one of three ways: 1. by the deposition of the weathered remains
ESC102. Sedimentary Rocks. Our keys to the past. Monday, February 11, 13
 ESC102 Sedimentary Rocks Our keys to the past Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form through the accumulation of sediment and the process of lithification. Lithification occurs after deposition
ESC102 Sedimentary Rocks Our keys to the past Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form through the accumulation of sediment and the process of lithification. Lithification occurs after deposition
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks
 The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
1/31/2013. Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes. Weathering Mechanisms. Wind abrasion forming Ventifacts
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Path of desire or path of least resistance?
 Path of desire or path of least resistance? Desire Path: A term in landscape architecture used to describe a path that isn t designed but rather is worn casually away by people finding the shortest distance
Path of desire or path of least resistance? Desire Path: A term in landscape architecture used to describe a path that isn t designed but rather is worn casually away by people finding the shortest distance
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
What is a sedimentary rock?
 Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock
 Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Weathering and Erosion Wherever rock is exposed at Earth s surface, it is continuously being broken down by weathering a set of physical and chemical processes
Chapter 6 Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Weathering and Erosion Wherever rock is exposed at Earth s surface, it is continuously being broken down by weathering a set of physical and chemical processes
As compaction and cementation of these sediments eventually occur, which area will become siltstone? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks. Sedimentary Processes and Rocks
 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks Sedimentary Processes and Rocks Origins of Sedimentary Rocks Sediment transport and texture Sedimentary structures Lithification Classifying
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Processes, Environments, Structures and Rocks Sedimentary Processes and Rocks Origins of Sedimentary Rocks Sediment transport and texture Sedimentary structures Lithification Classifying
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69
 EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Clastic Sedimentary Rocks
 Clastic Sedimentary Rocks Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Alternating sandstones and mudstones in Miocene turbidites Camaggiore di Firenzuola, Firenze, Italy Alessandro Grippo review Mechanical weathering creates
Clastic Sedimentary Rocks Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Alternating sandstones and mudstones in Miocene turbidites Camaggiore di Firenzuola, Firenze, Italy Alessandro Grippo review Mechanical weathering creates
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks. Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring.
 Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION
 Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Guided Notes Rocks & Minerals
 Guided Notes Rocks & Minerals is Mineral 1.What is a Mineral Tests 2.Mineral Properties Cycle 3.Rock Rocks 4.Igneous Rocks 5.Sedimentary Rocks 6. Metamorphic Rocks Reference Tables K. Coder 2015 12. What
Guided Notes Rocks & Minerals is Mineral 1.What is a Mineral Tests 2.Mineral Properties Cycle 3.Rock Rocks 4.Igneous Rocks 5.Sedimentary Rocks 6. Metamorphic Rocks Reference Tables K. Coder 2015 12. What
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20
 Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
4/4. K What I know about Sedimentary Rocks. W What I want to find out about Sedimentary Rocks Sunday, April 7, 13
 Do Now (2 minutes) 4/4 K What I know about Sedimentary Rocks W What I want to find out about Sedimentary Rocks 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. The Rock Cycle What is the rock cycle and how do rocks interrelate? Rock
Do Now (2 minutes) 4/4 K What I know about Sedimentary Rocks W What I want to find out about Sedimentary Rocks 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. The Rock Cycle What is the rock cycle and how do rocks interrelate? Rock
Geology 252, Historical Geology, California State University, Los Angeles - professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo
 LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
Emily and Megan. Earth System Science. Elements of Earth by weight. Crust Elements, by weight. Minerals. Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight
 Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Quiz 1. 3) Which of the following planetary bodies has the least number of impact craters on its surface? A) Mercury B) Mars C) the Moon D) Earth
 Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
CEE 437 Lecture 11 Rock Classification. Thomas Doe
 CEE 437 Lecture 11 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Translation of Mineral Properties to Rock Properties Comparison of mineral properties to rock properties Rocks have lower strength, especially tensile
CEE 437 Lecture 11 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Translation of Mineral Properties to Rock Properties Comparison of mineral properties to rock properties Rocks have lower strength, especially tensile
Clastic Textures. I. What is the sorting of sample numbers 60, 61, and 62? Answers on last page.
 Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary Rocks are produced from weathered debris of older rocks. Sedimentary rocks are produced by the following steps:
 Sedimentary rocks Most figures contained here are fro m Understand ing Earth Fourth Edition by F rank P ress, Raymond Sieve r, John Grotzinge r, and Thomas H. Jor dan Sedimentary Rocks are produced from
Sedimentary rocks Most figures contained here are fro m Understand ing Earth Fourth Edition by F rank P ress, Raymond Sieve r, John Grotzinge r, and Thomas H. Jor dan Sedimentary Rocks are produced from
Sand. Sand is any eroded material (igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary) that has a grain size from 1/16 th to 2 millimeters in size.
 Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification. Thomas Doe
 CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments
 Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Lecture 7: Sedimentary Rocks
 Lecture 7: Sedimentary Rocks 1. Read: Chapter 8 2. Homework #7 due Thursday 12pm 3. Midterm #1 Thursday, September 24 iclicker assignments pick yours up 001 Abreu 003 Agena 004 Albert 006 Araki 091 Atiburcio
Lecture 7: Sedimentary Rocks 1. Read: Chapter 8 2. Homework #7 due Thursday 12pm 3. Midterm #1 Thursday, September 24 iclicker assignments pick yours up 001 Abreu 003 Agena 004 Albert 006 Araki 091 Atiburcio
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Classification of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks are products of weathered, fragmented or dissolved,
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Classification of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks are products of weathered, fragmented or dissolved,
The boundary between two formations (or any distinct layers) is called a contact. Sedimentary rocks cover 75% of continents.
 Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification Video (Mr. White s website) Questions (Pg.
 Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Weathering Cycle Teacher Notes
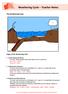 The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 1: Introduction to Rocks and Sedimentary Processes
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 1: Introduction to Rocks and Sedimentary Processes We would not be able to address the interesting questions of dinosaurs and their place in the history of life without the
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 1: Introduction to Rocks and Sedimentary Processes We would not be able to address the interesting questions of dinosaurs and their place in the history of life without the
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Earth Materials Unit: Sedimen ntary Rocks and Processes Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Five and Six Lab: Laboratorry Six Name
 Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Name: Which rock layers appear to be most resistant to weathering? A) A, C, and E B) B and D
 Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Earth s crust is made mostly of Igneous rocks. There are 3 main types of Sedimentary Rocks: 1. Clastic 2. Chemical 3. Organic
 Sedimentary Rocks Earth s crust is made mostly of Igneous rocks. But, most rocks on Earth s s surface are Sedimentary Rocks.. (75%) Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that are made of broken-down
Sedimentary Rocks Earth s crust is made mostly of Igneous rocks. But, most rocks on Earth s s surface are Sedimentary Rocks.. (75%) Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that are made of broken-down
Rocks are made from Minerals
 Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
CHAPTER 3.2: SEDIMENTARY ROCK
 CHAPTER 3.2: SEDIMENTARY ROCK Introduction Second major rock group. Formed from fine constituents of rock usually from mountainous areas which are transported to lower elevation due to certain processes.
CHAPTER 3.2: SEDIMENTARY ROCK Introduction Second major rock group. Formed from fine constituents of rock usually from mountainous areas which are transported to lower elevation due to certain processes.
Crust Elements. Elements of Earth. Minerals. Crystals. Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air
 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
A. IGNEOUS Rocks formed by cooling and hardening of hot molten rock called magma (within crust or at its surface).
 EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS
 LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth
 From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth 1 Questions your students might ask? What are rocks made of? What are minerals? What are minerals? What is the difference between Fool
From Atoms to Minerals to Rocks: The building blocks of the Earth 1 Questions your students might ask? What are rocks made of? What are minerals? What are minerals? What is the difference between Fool
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface.
 The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
Bowen s Chemical Stability Series
 Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
Which sample best shows the physical properties normally associated with regional metamorphism? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D
 1 Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of (1) white quartz (3) pink feldspar (2) aluminum (4) iron 2 The diagram below shows how a sample of the mineral mica breaks
1 Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of (1) white quartz (3) pink feldspar (2) aluminum (4) iron 2 The diagram below shows how a sample of the mineral mica breaks
Sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks form from pre existing rock. igneous, metamorphic or. sedimentary.
 Sedimentary Rocks 1 Sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks form from pre existing rock particles: igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary. 2 3 The parent rock undergoes: Sedimentary rocks WEATHERING TRANSPORTATION
Sedimentary Rocks 1 Sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks form from pre existing rock particles: igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary. 2 3 The parent rock undergoes: Sedimentary rocks WEATHERING TRANSPORTATION
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Metamorphic Rocks. Describe possible changes that result from metamorphism. Include: (i) texture (ii) volume change (iii) chemical change
 Metamorphic Rocks Describe the process of metamorphism Describe possible changes that result from metamorphism. Include: (i) texture (ii) volume change (iii) chemical change Describe the result of selected
Metamorphic Rocks Describe the process of metamorphism Describe possible changes that result from metamorphism. Include: (i) texture (ii) volume change (iii) chemical change Describe the result of selected
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks
 GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
Chapter 5. The Sedimentary Archives
 Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream as it enters a lake. At which points along the stream are erosion and deposition dominant?
 1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
Your teacher will show you a sample or diagram of each, and show you a settling column. Draw these, and label your diagrams (8 pts) Ungraded:
 From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions
 Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Gneiss (a metamorphic rock) from Catalina Island, California Alessandro Grippo review Rocks
Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Gneiss (a metamorphic rock) from Catalina Island, California Alessandro Grippo review Rocks
GEOL 101 Lecture 7. Weathering, Sediments. Rock Cycle. Least Stable. Most Stable. Weathering Ch. 5. Physical. Chemical
 GEOL 101 Lecture 7 Weathering, Sediments S. Kite Photo Bear Butte S.P., SD Rock Cycle Weathering Ch. 5 Physical (later) Chemical (now) Bowen s Reaction Series vs. Goldich s Weathering Series for sand-size
GEOL 101 Lecture 7 Weathering, Sediments S. Kite Photo Bear Butte S.P., SD Rock Cycle Weathering Ch. 5 Physical (later) Chemical (now) Bowen s Reaction Series vs. Goldich s Weathering Series for sand-size
Rocks. Rocks are composed of 1 or more minerals. Rocks are classified based on how they formed (origin). 3 classes of rocks:
 ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers
 1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Types of mechanical aka physical weathering. Mechanical Weathering. Chemical Weathering.
 Lithification Sediments Deposition Sedimentary Rocks Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Transport Erosion Weathering http://www.teachnet-lab.org/ps101/bglasgold/rocks/efcyclep2.gif
Lithification Sediments Deposition Sedimentary Rocks Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Transport Erosion Weathering http://www.teachnet-lab.org/ps101/bglasgold/rocks/efcyclep2.gif
WEATHERING. Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions 10/22/2012
 WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
