Iterative 3D gravity inversion with integration of seismologic data
|
|
|
- Homer Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp ; SEP.-DEC Iterative 3D gravity inversion with integration of seismologic data C. BRAITENBERG and M. ZADRO Department of Earth Sciences, University of Trieste, Italy (Received October 4, 1998; accepted August 5, 1999) Abstract. Depending on the a priori knowledge, different methods can be chosen for gravity inversion. The method we propose is suitable for cases in which little is known about the crustal structure, except the presence of a sharp density contrast, as occurs at the Moho or at the base of a sedimentary basin. The method combines the downward continuation with the direct evaluation of the gravity field of the undulations of the boundary surface in an iterative process. The a priori assumption of the reference depth of the boundary and density across the surface is necessary. If the depth of the boundary is known along a profile or in single points from seismologic (or other) investigations, this piece of information is used to anchor the boundary. In lack of such knowledge general geophysical considerations must be used to obtain an estimate of the boundary in the undisturbed state. The method is tested in a 3D synthetic model situation, evaluating the effect of erroneous a priori assumptions and noise. 1. The inversion method We consider the problem of determining the oscillations of an horizontal boundary, which is part of a layered structure model of the lithosphere. This boundary could be for example the crust/mantle interface or the base of a sedimentary basin. This problem has been approached before by Parker (1972) and Granser (1987). The methodology we propose is an iterative solution that alternates the downward continuation with the direct calculation of the gravity field of the model. The method has been tested in 2.5D synthetic model situations (Braitenberg et al., 1997), and is extended to 3D synthetic models here. Let g 0 (x, y) be the Bouguer gravity anomaly field, and d be the reference depth of the boundary. Let r (x, y) be the oscillation of the boundary, defined as the deviation from the depth Corresponding author: C. Braitenberg, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Trieste, Via Weiss 1, Trieste, Italy; phone: ; fax: ; berg@univ.trieste.it 1999 Osservatorio Geofisico Sperimentale 469
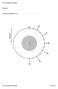
2 BRAITENBERG and ZADRO Fig. 1 - Synthetic gravity field with gaussian noise (0.5 mgal standard deviation). Model: two superposed prisms. Extension of the prisms is 40-60km, 35-65km, 8-9km upper, 45-55km, 45-55km, 9-10km lower, respectively. Density 0.4 g/cm 3. The dots refer to the position of constraining depths. Profile AA' is discussed in the following. d. With g d (x, y) the downward continued field to the depth d, and on taking the Fourier Transforms (FT) of the field, we obtain: where k x,k y are the wavenumbers along the coordinate axes. Assuming that the field is generated by a sheet mass located at depth d, the surface density of the sheet mass σ (x, y) is given by: 470 g ( k, k ) = e g ( k, k ) d x y dγ 2 2 x y γ = k + k o x y (1)
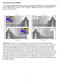
3 3D gravity inversion Fig. 2 - Model gravity and model root along profile AA' and respective inverted curves for iteration steps 1 through 6. σ (, ) 1 xy πg g ( x, y) 1 πg FT 1 d g d ( k x, k y 2 2 ), = = [ ] (2) with FT -1 the inverse Fourier Transform and G the gravitational constant. We may interpret the sheet mass with horizontally varying surface density as the oscillating boundary which separates two layers, and across which we have a density contrast Δρ. The oscillation amplitude of the boundary is then given by 1 r( x, y) = σ( x, y). Δρ 1 (3) Only in first approximation though does the gravity field generated by the vertically expanded boundary coincide with the field g 0 (x, y), as shown by Parker (1977). We approximate the vertically expanded boundary with a series of rectangular prisms and calculate the gravity field by applying the algorithm developed by Nagy (1966). The residual gravity field δg 1 (x, y) is defined as the difference between the observed field (g 0 (x,y)) and the field (g 1 (x,y)) generated by the series of prisms, δg ( x, y) = g ( x, y) g ( x, y) (4) 471
4 BRAITENBERG and ZADRO Fig. 3 - Maximum extension of root normalized to correct value. a) for varying reference depth at fixed density contrasts b) for varying density contrast at fixed reference depths. The residual field is downward continued and a correction to the surface density of the sheet mass is obtained as in Eq. (2). The correction affects the oscillation amplitude of the density boundary according to Eq. (3). This procedure is repeated iteratively, obtaining at each iteration step k the residual gravity field δg k (x, y) and the oscillation amplitude of the boundary r k (x, y). The iterations are repeated until the root mean square (rms) gravity residual has reached an acceptable value or until the successive iteration does not give a considerable improvement to the results. If seismic data regarding the depth of the studied boundary are available, they can be integrated into the inversion procedure. If the seismological depth estimation is available in definite points or along a profile, a set of inversions will be carried out for the different values of the reference depth (d) and the density contrast (Δρ). The value (d) is accepted, for which the mean square difference between the depth of the boundary obtained from gravity inversion and from seismological investigations is minimal. An important step in the inversion is the choice of the frequency limitation of the downward continuation, which is obtained with a frequency filter (h (γ)). The need for limitation is connected to the exponential multiplication factor that defines the continuation, and which makes the downward continuation unstable towards high frequencies. Besides the arguments of numerical kind, a problem inherent to the geophysical situation makes a limitation in frequency necessary. As the gravity field (g 0 (x, y)) is explained by the oscillation of the boundary, the field (g 0 (x, y)) should not contain energies due to masses posed above the oscillating boundary. Generally, the frequency range of the field generated by more superficial masses shifts to higher frequencies; therefore, the method of low-pass filtering the gravity data in the process of inversion manages, to a large extent, to separate the fields of masses posed above the boundary, 472
5 3D gravity inversion Fig. 4 - Map of the 3D inverted root after 6 iterations with position of constraining data (dots) and profile AA'. if the filter is chosen appropriately. 2. Synthetic example We test the inversion method on a synthetic Moho root. The root has the shape of two rectangular prisms set one on top of each other. Let the width, length and height of the upper prism be equal to 20 km, 30 km and 1km, that of the lower prism equal to 10 km, 10 km and 1 km, respectively. The top of the prisms is located at 8 km and 9 km, respectively. The lowest extension of the root is then at a 10 km depth and the density contrast is 0.4 g/cm 3. The prisms are centered on a point grid of 1 km sampling. We add gaussian noise (standard deviation 0.5 mgal) to the synthetic gravity field. The gravity field is graphed in Fig. 1, the maximum anomaly having a value of 10 mgal. The black dots mark the positions where the 473
6 BRAITENBERG and ZADRO Table 1 - Root mean square deviation of the depths of the boundary obtained by the gravity inversion from the constraining depths. The root mean square deviation in km, for different density contrasts (g/cm 3 ) and reference depths of the boundary (km). Reference depth of boundary (km) Density contrast (g/cm 3 ) depth of the root will be acquired from secondary information sources, such as seismic sounding. First, a range of geophysically plausible values for the reference depth and density contrast of the boundary must be defined. In this case we allow the reference depth to vary between 4 km and 16 km and the density contrast between -0.2 g/cm 3 and -0.6 g/cm 3. With P m the cutoff wavelength, we define the filter function h (γ) as: [ P m ] h( γ) =. 51+ cos( πγ ). (5) We choose the cutoff wavelength P m = 11 km; the base of the prisms used for the direct calculation of the gravity field is square, with sides equal to 5 km. The constraining values for the root are used to find the adequate density contrast and boundary reference depth. A certain amount of iterations is fixed (in this case 6) and for every couple a test inversion is made. In Table 1 the root mean square (rms) deviation of the inverted root from the constraining points is given for different couples of density and reference depths. The particular number of iterations chosen does not influence the resulting depth/density couple. It is seen that the couple with reference depth 8 km and density contrast -0.4 g/cm 3 is the one for which the rms deviation is minimal. The improvement of the model root and the modeled gravity field at every iteration step along profile AA' is shown in Fig. 2. After 6 iterative steps the iteration does not contribute to an appreciable enhancement of the gravity residual, and the iteration is ceased. How the solution depends on the value of the boundary depth is shown in Fig. 3a, where for different density contrast (-0.2 g/cm 3 through -0.6 g/cm 3 ) the boundary depth varies in the range from 4 km to 16 km. The maximum penetration of the modeled boundary normalized by the synthetic model value (2 km), is graphed. For greater boundary depths the root is overestimated. A similar experiment is shown in Fig. 3b for different boundary, depths (4 km through 16 km) and varying density contrast. The effect of the density contrasts is less, a small density contrast again leading to an overestimated root. The solution for the root is graphed in Fig. 4. The 474
7 3D gravity inversion maximum depth of the modeled root is 10 km, which is the correct value. 3. Conclusion and discussion We have discussed a 3D gravity inversion method which aims at modeling gravity data with the oscillations of an interface which marks a strong density contrast. The solution depends on the values of the density contrast and the reference depth of the boundary. These two parameters can be constrained if additional information from seismology defining the boundary depth (e.g. along a profile), is available. The method was applied and tested successfully for 2.5D models in the SE-Alps (Braitenberg et al., 1997) and in the Karakoram-Kohistan area (Braitenberg and Drigo, 1998). Subsequently, a 3D Moho inversion was applied to the SE-Alps on a geographic window of Longitude E and Latitude N (Zadro and Braitenberg, 1997). For details and results we refer to the cited papers. Acknowledgements. This research was financed partially by CNR grants and and for 60% by MURST. The paper was presented at the 2 nd Joint Meeting IAG and IgeC, 7-12 September, 1998, Trieste, Italy. References Braitenberg C. and Drigo R. ; 1998: A crustal model from gravity inversion in Karakorum. In: Proceedings of the Int. Symp. on Current crustal movement and hazard reduction in East Asia and Soth-East Asia, Wuhan, November 4-7, 1997, Braitenberg C., Pettenati F. and Zadro M.; 1997: Spectral and classical methods in the evaluation of Moho undulations from gravity data: the NE Italian Alps and isostasy. J. Geodynamics, 23, Granser H.; 1987: Nonlinear inversion of gravity data using the Schmidt-Lichtenstein approach. Geophysics, 52, Nagy D.; 1966: The gravitational attraction of a right rectangular prism. Geophysics, 30, Parker R. L.; 1972: The rapid calculation of potential anomalies, Geophys. J.R. Astr. Soc., 31, Zadro M. and Braitenberg C.; 1997: Spectral methods in gravity inversion: the geopotential field and its derivatives. Annali di Geofisica. Vol. 40,
A global high resolution mean sea surface from multi mission satellite altimetry
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 439-443; SEP.-DEC. 1999 A global high resolution mean sea surface from multi mission satellite altimetry P. KNUDSEN and O. ANDERSEN Kort
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 439-443; SEP.-DEC. 1999 A global high resolution mean sea surface from multi mission satellite altimetry P. KNUDSEN and O. ANDERSEN Kort
Comparison between EGM96 and FCUL96B tailored geopotential model for the north-east Atlantic
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 255-259; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Comparison between EGM96 and FCUL96B tailored geopotential model for the north-east Atlantic J. C. CATALAO (1)
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 255-259; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Comparison between EGM96 and FCUL96B tailored geopotential model for the north-east Atlantic J. C. CATALAO (1)
New gravimetric quasigeoid of Slovakia
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 211-217; SEP.-DEC. 1999 New gravimetric quasigeoid of Slovakia M. MOJZEŠ and J. JANÁK Departament of Theoretical Geodesy, Slovak University
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 211-217; SEP.-DEC. 1999 New gravimetric quasigeoid of Slovakia M. MOJZEŠ and J. JANÁK Departament of Theoretical Geodesy, Slovak University
Difference between geoid undulation and quasigeoid height in Hungary
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 571-575; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Difference between geoid undulation and quasigeoid height in Hungary J. ÁDÁM Department of Geodesy, Technical University
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 571-575; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Difference between geoid undulation and quasigeoid height in Hungary J. ÁDÁM Department of Geodesy, Technical University
RTC and density variations in the estimation of local geoids
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 589-595; SEP.-DEC. 1999 RTC and density variations in the estimation of local geoids L. BIAGI (1),R.DE STEFANO (2), F. SANSÒ (3) AND C.
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 589-595; SEP.-DEC. 1999 RTC and density variations in the estimation of local geoids L. BIAGI (1),R.DE STEFANO (2), F. SANSÒ (3) AND C.
Two-step data analysis for future satellite gravity field solutions: a simulation study
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp.6-66; SEP.-DEC. 999 Two-step data analysis for future satellite gravity field solutions: a simulation study J. KUSCHE, K. H. ILK and S.
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp.6-66; SEP.-DEC. 999 Two-step data analysis for future satellite gravity field solutions: a simulation study J. KUSCHE, K. H. ILK and S.
Gravimetry data validation in Algeria
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 205-210; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Gravimetry data validation in Algeria S.A. BENAHMED DAHO and S. KAHLOUCHE National Centre of Spatial Techniques,
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 205-210; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Gravimetry data validation in Algeria S.A. BENAHMED DAHO and S. KAHLOUCHE National Centre of Spatial Techniques,
LithoFLEX Tutorial INTRODUCTION 2 FREE MAPPING SOFTWARE GEOSOFT 3 DATA FORMAT 3 DATA DESCRIPTION / DUMMY VALUES 4 STUDY AREA 5
 LithoFLEX Tutorial INTRODUCTION 2 FREE MAPPING SOFTWARE GEOSOFT 3 DATA FORMAT 3 DATA DESCRIPTION / DUMMY VALUES 4 STUDY AREA 5 A. GRAVITY FORWARD CALCULATION 8 a) GRAVITY EFFECT OF AN UNDULATING LAYER
LithoFLEX Tutorial INTRODUCTION 2 FREE MAPPING SOFTWARE GEOSOFT 3 DATA FORMAT 3 DATA DESCRIPTION / DUMMY VALUES 4 STUDY AREA 5 A. GRAVITY FORWARD CALCULATION 8 a) GRAVITY EFFECT OF AN UNDULATING LAYER
Polarization analysis on three-component seismic data
 Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol., n. -, pp. 9-; Sep.-Dec. Polarization analysis on three-component seismic data P. Capizzi, L. De Luca and M. Vitale Department of Chemistry and Physics
Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol., n. -, pp. 9-; Sep.-Dec. Polarization analysis on three-component seismic data P. Capizzi, L. De Luca and M. Vitale Department of Chemistry and Physics
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A
 Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
Potential Field investigation of Williston Basin Basement
 Potential Field investigation of Williston Basin Basement Jiakang Li* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Canada Summary Major faults and domains are identified in the Precambrian basement of
Potential Field investigation of Williston Basin Basement Jiakang Li* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Canada Summary Major faults and domains are identified in the Precambrian basement of
Full Tensor Gradient of Simulated Gravity Data for Prospect Scale Delineation
 J. Math. Fund. Sci., Vol. 46, No., 014, 107-14 107 Full Tensor Gradient of Simulated Gravity Data for Prospect Scale Delineation Hendra Grandis* & Darharta Dahrin Applied Geophysics Research Group, Faculty
J. Math. Fund. Sci., Vol. 46, No., 014, 107-14 107 Full Tensor Gradient of Simulated Gravity Data for Prospect Scale Delineation Hendra Grandis* & Darharta Dahrin Applied Geophysics Research Group, Faculty
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements
 Introduction to the use of gravity measurements Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds, Chpt 2, for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds, Chpt 2, for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
Lab 8: Gravity and Isostasy (35 points)
 it's not the most important thing in your life right now. But what is important is gravity. Arnold Schwarzenegger as Colonel John Matrix, Commando (Check out this classic of American cinema!) Lab 8: Gravity
it's not the most important thing in your life right now. But what is important is gravity. Arnold Schwarzenegger as Colonel John Matrix, Commando (Check out this classic of American cinema!) Lab 8: Gravity
Determination of the relative soil compactness in the foundation condition by microgravity data
 Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol. 54, n. 2, pp. 129-143; June 2013 DOI 10.4430/bgta0088 Determination of the relative soil compactness in the foundation condition by microgravity data V.E.
Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata Vol. 54, n. 2, pp. 129-143; June 2013 DOI 10.4430/bgta0088 Determination of the relative soil compactness in the foundation condition by microgravity data V.E.
Gravity inversion of basement relief constrained by the knowledge of depth at isolated points
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 61, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1996); E 1702-1714,13 FIGS., 5 TABLES. Gravity inversion of basement relief constrained by the knowledge of depth at isolated points Jorge W. D. Leao*, Paulo
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 61, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 1996); E 1702-1714,13 FIGS., 5 TABLES. Gravity inversion of basement relief constrained by the knowledge of depth at isolated points Jorge W. D. Leao*, Paulo
Magnetic Case Study: Raglan Mine Laura Davis May 24, 2006
 Magnetic Case Study: Raglan Mine Laura Davis May 24, 2006 Research Objectives The objective of this study was to test the tools available in EMIGMA (PetRos Eikon) for their utility in analyzing magnetic
Magnetic Case Study: Raglan Mine Laura Davis May 24, 2006 Research Objectives The objective of this study was to test the tools available in EMIGMA (PetRos Eikon) for their utility in analyzing magnetic
Latest Geoid Determinations for the Republic of Croatia
 Latest Geoid Determinations for the Republic of Croatia T. Bašić *, Ž. Hećimović ** * Faculty of Geodesy, University of Zagreb, HR-10000 Zagreb, Kačićeva 26, Croatia ** Av. M. Držića 76, 10000 Zagreb,
Latest Geoid Determinations for the Republic of Croatia T. Bašić *, Ž. Hećimović ** * Faculty of Geodesy, University of Zagreb, HR-10000 Zagreb, Kačićeva 26, Croatia ** Av. M. Držića 76, 10000 Zagreb,
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data
 Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
9. Density Structure. The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Density Structure
 84 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Density Structure 9. Density Structure Although the primary focus for the development of the AuSREM model was the creation of 3-D seismic wavespeed
84 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Density Structure 9. Density Structure Although the primary focus for the development of the AuSREM model was the creation of 3-D seismic wavespeed
Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge
 GSA Data Repository 176 1 5 6 7 9 1 11 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge Hanchao Jian 1,, Satish C. Singh *, Yongshun
GSA Data Repository 176 1 5 6 7 9 1 11 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge Hanchao Jian 1,, Satish C. Singh *, Yongshun
Computers & Geosciences
 Computers & Geosciences 51 (2013) 247 254 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Computers & Geosciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo Preferential filtering for gravity anomaly
Computers & Geosciences 51 (2013) 247 254 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Computers & Geosciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo Preferential filtering for gravity anomaly
scale Three-dimensional Modelling
 Lithospheric-scale scale Three-dimensional Modelling (Application to the EARS and Plateau) Girma Woldetinsae (Geological Survey of Ethiopia) and H.-J. Götze R. Hackney S. Schmidt (Institut für Geowissenschaften
Lithospheric-scale scale Three-dimensional Modelling (Application to the EARS and Plateau) Girma Woldetinsae (Geological Survey of Ethiopia) and H.-J. Götze R. Hackney S. Schmidt (Institut für Geowissenschaften
r 1 r 2 r 3 Dr is what matters!
 Today s Agenda Gravity - Background & basic intuition - Data reduction - Use of the instrument - See textbook for detailed quantitative discussion - Measure height of Millikan or S. Mudd What and Why Gravity
Today s Agenda Gravity - Background & basic intuition - Data reduction - Use of the instrument - See textbook for detailed quantitative discussion - Measure height of Millikan or S. Mudd What and Why Gravity
Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF GRAVITY DATA IN THE VIENNA BASIN REGION BY MEANS OF THE QUASI SINGULAR POINTS METHOD
 QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF GRAVITY DATA IN THE VIENNA BASIN REGION BY MEANS OF THE QUASI SINGULAR POINTS METHOD I. S. ELISEEVA 1, W. SEIBERL 2, P. SLAPANSKY 2, R. PAŠTEKA 3, R. ARNDT 2 1 VNIIGeofizika
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF GRAVITY DATA IN THE VIENNA BASIN REGION BY MEANS OF THE QUASI SINGULAR POINTS METHOD I. S. ELISEEVA 1, W. SEIBERL 2, P. SLAPANSKY 2, R. PAŠTEKA 3, R. ARNDT 2 1 VNIIGeofizika
The first high-precision gravimetric geoid of Hungary: HGG2013
 Server on Geodesy, Seismology and Environmental Sciences Published Online 2013 (http://airy.ual.es/) The first high-precision gravimetric geoid of Hungary: HGG2013 Abstract V. Corchete Higher Polytechnic
Server on Geodesy, Seismology and Environmental Sciences Published Online 2013 (http://airy.ual.es/) The first high-precision gravimetric geoid of Hungary: HGG2013 Abstract V. Corchete Higher Polytechnic
APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY
 APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY Timur TEZEL Supervisor: Takuo SHIBUTANI MEE07169 ABSTRACT In this study I tried to determine the shear wave velocity structure in the crust
APPLICATION OF RECEIVER FUNCTION TECHNIQUE TO WESTERN TURKEY Timur TEZEL Supervisor: Takuo SHIBUTANI MEE07169 ABSTRACT In this study I tried to determine the shear wave velocity structure in the crust
OPTIMAL FORWARD CALCULATION METHOD OF THE MARUSSI TENSOR DUE TO A GEOLOGIC STRUCTURE AT GOCE HEIGHT
 OPTIMAL FORWARD CALCULATION METHOD OF THE MARUSSI TENSOR DUE TO A GEOLOGIC STRUCTURE AT GOCE HEIGHT Leonardo Uieda (1), Everton P. Bomfim (,3), Carla Braitenberg (3), and Eder Molina () (1) Observatório
OPTIMAL FORWARD CALCULATION METHOD OF THE MARUSSI TENSOR DUE TO A GEOLOGIC STRUCTURE AT GOCE HEIGHT Leonardo Uieda (1), Everton P. Bomfim (,3), Carla Braitenberg (3), and Eder Molina () (1) Observatório
Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich
 Seminar des FA Ultraschallprüfung Vortrag 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=20944 Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich Thomas
Seminar des FA Ultraschallprüfung Vortrag 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=20944 Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich Thomas
Global geophysics and wave propagation
 Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
Global geophysics and wave propagation Reading: Fowler p76 83 Remote sensing Geophysical methods Seismology Gravity and bathymetry Magnetics Heat flow Seismology: Directly samples the physical properties
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B. Figure 6. Student Registration No. ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Version 2
 ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
Wavelet Modeling of the Gravity Field over Japan
 29 the colored noise by the applied wavelet method with weights homogeneous in space and dependent on scale at one hand, and to keep in mind the difficulty in determining proper relative weights to respective
29 the colored noise by the applied wavelet method with weights homogeneous in space and dependent on scale at one hand, and to keep in mind the difficulty in determining proper relative weights to respective
Palaeozoic oceanic crust preserved beneath the eastern Mediterranean
 Palaeozoic oceanic crust preserved beneath the eastern Mediterranean Roi Granot Magnetic Anomaly Data Total field Three components 75 m 75 m Total field 250 m Overhauser Three-axial fluxgate Overhauser
Palaeozoic oceanic crust preserved beneath the eastern Mediterranean Roi Granot Magnetic Anomaly Data Total field Three components 75 m 75 m Total field 250 m Overhauser Three-axial fluxgate Overhauser
A two-step point mass method for regional gravity field modeling: a case study over the Auvergne test area
 A two-step point mass method for regional gravity field modeling: a case study over the Auvergne test area - Geodätische Woche 2014 - Session 2 - Schwerefeld und Geoid Miao Lin, Heiner Denker, Jürgen Müller
A two-step point mass method for regional gravity field modeling: a case study over the Auvergne test area - Geodätische Woche 2014 - Session 2 - Schwerefeld und Geoid Miao Lin, Heiner Denker, Jürgen Müller
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES
 FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES Vilma Castillejos Hernandez Supervisor: Tatsuhiko Hara MEE10508 ABSTRACT We performed time domain moment tensor
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION USING WAVEFORM DATA FROM A BROADBAND STATION IN THE PHILIPPINES Vilma Castillejos Hernandez Supervisor: Tatsuhiko Hara MEE10508 ABSTRACT We performed time domain moment tensor
Isostacy: Compensation of Topography and Isostatic Geoid Anomalies
 Isostacy: Compensation of Topography and Isostatic Geoid Anomalies November 3, 2016 1 Isostacy One of the major goals of interpreting planetary gravity fields is to understand how topography positive (
Isostacy: Compensation of Topography and Isostatic Geoid Anomalies November 3, 2016 1 Isostacy One of the major goals of interpreting planetary gravity fields is to understand how topography positive (
C5 Magnetic exploration methods data analysis techniques
 C5 Magnetic exploration methods data analysis techniques C5.1 Data processing and corrections After magnetic field data have been collected a number of corrections are applied to simplify the interpretation.
C5 Magnetic exploration methods data analysis techniques C5.1 Data processing and corrections After magnetic field data have been collected a number of corrections are applied to simplify the interpretation.
DR
 DR2003071 0 0 270 0 30 0 90 0 60 0 120 0 150 0 90 0 180 0 180 0 A) RadialReceiverFunctions B ackazimuth (in degrees relative to north) -135-90 -45 0 45 90 135 180-5.0-2.5 Tangential R eceiver Functions
DR2003071 0 0 270 0 30 0 90 0 60 0 120 0 150 0 90 0 180 0 180 0 A) RadialReceiverFunctions B ackazimuth (in degrees relative to north) -135-90 -45 0 45 90 135 180-5.0-2.5 Tangential R eceiver Functions
Magnetic and Gravity Methods for Geothermal Exploration
 Magnetic and Gravity Methods for Geothermal Exploration Dr. Hendra Grandis Geophysics - ITB method and survey procedure Aero- or ground magnetic (covers a large area) Schlumberger resistivity mapping and
Magnetic and Gravity Methods for Geothermal Exploration Dr. Hendra Grandis Geophysics - ITB method and survey procedure Aero- or ground magnetic (covers a large area) Schlumberger resistivity mapping and
44031 Crustal Compensation Rate In Central Anatolian Region And Comparison Of Seismic Activity
 44031 Crustal Compensation Rate In Central Anatolian Region And Comparison Of Seismic Activity B. Oruç* (Kocaeli University), T. Sönmez (Kocaeli University), E. Ulutaş (Kocaeli University), H.H. Selim
44031 Crustal Compensation Rate In Central Anatolian Region And Comparison Of Seismic Activity B. Oruç* (Kocaeli University), T. Sönmez (Kocaeli University), E. Ulutaş (Kocaeli University), H.H. Selim
GRAVITY EXPLORATION. subsurface density. (material property) Gravity anomalies of some simple shapes
 GRAVITY EXPLORATION g at surface (observation) subsurface density (material property) subsurface geology Gravity anomalies of some simple shapes Reminder: we are working with values about... 0.01-0.001
GRAVITY EXPLORATION g at surface (observation) subsurface density (material property) subsurface geology Gravity anomalies of some simple shapes Reminder: we are working with values about... 0.01-0.001
Analysis of Different Methodologies to Calculate Bouguer Gravity Anomalies in the Argentine Continental Margin
 Geosciences 2014, 4(2): 33-41 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20140402.02 Analysis of Different Methodologies to Calculate Bouguer Gravity Anomalies in the Argentine Continental Margin Ana C. Pedraza De Marchi 1,2,*,
Geosciences 2014, 4(2): 33-41 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20140402.02 Analysis of Different Methodologies to Calculate Bouguer Gravity Anomalies in the Argentine Continental Margin Ana C. Pedraza De Marchi 1,2,*,
ESA training. Gravity, magnetics and gradients for mapping and modelling. Jörg Ebbing. Department of Geosciences Kiel University
 ESA training Gravity, magnetics and gradients for mapping and modelling Jörg Ebbing Department of Geosciences Kiel University Contributions from: Eldar Baykiev (Trondheim), Des Fitzgerald (Melbourne),
ESA training Gravity, magnetics and gradients for mapping and modelling Jörg Ebbing Department of Geosciences Kiel University Contributions from: Eldar Baykiev (Trondheim), Des Fitzgerald (Melbourne),
Last Time. Today s s Agenda. Geophysics. Geophysics. Geophysics. MAS 603: Geological Oceanography. Lecture 21: Geophysics 1: Gravity
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time MAS 603: Geological Oceanography Extinctions Lecture 21: 1: http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/for/lowres/forn441l.jpg Today s s Agenda Introduction
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time MAS 603: Geological Oceanography Extinctions Lecture 21: 1: http://www.cartoonstock.com/newscartoons/cartoonists/for/lowres/forn441l.jpg Today s s Agenda Introduction
Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
 GSA Data Repository Item: 2007183 Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Brian J. demartin 1*, Robert
GSA Data Repository Item: 2007183 Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Brian J. demartin 1*, Robert
The thermal and density structure of passive margins
 The thermal and density structure of passive margins Magdalena Scheck-Wenderoth, Yuriy Maystrenko, Julia Autin, Hans Jürgen Götze, Sabine Schmidt, Christian Reichert basins in their plate-tectonic setting
The thermal and density structure of passive margins Magdalena Scheck-Wenderoth, Yuriy Maystrenko, Julia Autin, Hans Jürgen Götze, Sabine Schmidt, Christian Reichert basins in their plate-tectonic setting
Arctic Ocean Mean Sea Surface, Geoid and Gravity from Surface Data, Icesat and GRACE a reference for Cryosat sea-ice mapping
 Arctic Ocean Mean Sea Surface, Geoid and Gravity from Surface Data, Icesat and GRACE a reference for Cryosat sea-ice mapping R. Forsberg and H. Skourup, Geodynamics Dept., DNSC rf@spacecenter.dk Arctic
Arctic Ocean Mean Sea Surface, Geoid and Gravity from Surface Data, Icesat and GRACE a reference for Cryosat sea-ice mapping R. Forsberg and H. Skourup, Geodynamics Dept., DNSC rf@spacecenter.dk Arctic
(b) What is the amplitude at the altitude of a satellite of 400 km?
 Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
Practice final quiz 2015 Geodynamics 2015 1 a) Complete the following table. parameter symbol units temperature T C or K thermal conductivity heat capacity density coefficient of thermal expansion volumetric)
ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity
 I. Geomagnetism Name ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of the earth and inclined
I. Geomagnetism Name ENVI.2030L - Plate Tectonics - Geomagnetism, Earthquakes, and Gravity The earth's magnetic field can be viewed as a simple bar magnet located near the center of the earth and inclined
3D Geometry of the Xade Complex inferred from Gravity and Magnetic Data
 Geophysical Case Histories 3D Geometry of the Xade Complex inferred from Gravity and Magnetic Data 1. British Geological Survey, Edinburgh, United Kingdom Paper 92 Pouliquen, G. [1], Key, R. [1] ABSTRACT
Geophysical Case Histories 3D Geometry of the Xade Complex inferred from Gravity and Magnetic Data 1. British Geological Survey, Edinburgh, United Kingdom Paper 92 Pouliquen, G. [1], Key, R. [1] ABSTRACT
Development and evaluation of a new Canadian geoid model
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 227-238; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Development and evaluation of a new Canadian geoid model G. FOTOPOULOS, C. KOTSAKIS and M.G. SIDERIS Department
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 3-4, pp. 227-238; SEP.-DEC. 1999 Development and evaluation of a new Canadian geoid model G. FOTOPOULOS, C. KOTSAKIS and M.G. SIDERIS Department
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements
 Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
OZ SEEBASE TM. Datasets. Digital Elevation Model
 Digital Elevation Model 10 Digital Elevation Models (DEM s) often show the youngest structures, and any active geological structures. They are widely used for neotectonic analysis. The composition of eroding
Digital Elevation Model 10 Digital Elevation Models (DEM s) often show the youngest structures, and any active geological structures. They are widely used for neotectonic analysis. The composition of eroding
Use of Geostatistically-constrained Potential Field Inversion and Downhole Drilling to Predict Distribution of Sulphide and Uranium Mineralisation
 Use of Geostatistically-constrained Potential Field Inversion and Downhole Drilling to Predict Distribution of Sulphide and Uranium Mineralisation Matthew Zengerer Talk Outline Introduction Purpose and
Use of Geostatistically-constrained Potential Field Inversion and Downhole Drilling to Predict Distribution of Sulphide and Uranium Mineralisation Matthew Zengerer Talk Outline Introduction Purpose and
Blind fault Configuration in Osaka, Japan based on 2D gravity inversion
 Blind fault Configuration in Osaka, Japan based on 2D gravity inversion N. Inoue & N. Kitada Geo-research Institute, Osaka, Japan K. Takemura Institute for Geothermal Sciences, Kyoto University, Beppu,
Blind fault Configuration in Osaka, Japan based on 2D gravity inversion N. Inoue & N. Kitada Geo-research Institute, Osaka, Japan K. Takemura Institute for Geothermal Sciences, Kyoto University, Beppu,
P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin
 P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin M. Malinowski* (Institute of Geophysics PAS), A. Ribodetti (Geosciences Azur CNRS UMR)
P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin M. Malinowski* (Institute of Geophysics PAS), A. Ribodetti (Geosciences Azur CNRS UMR)
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet.
 17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
Calibration/validation of GOCE data by terrestrial torsion balance observations
 Calibration/validation of GOCE data by terrestrial torsion balance observations Gy. Tóth 1, J. Ádám 1, L. Földváry 1,4, I.N. Tziavos 2, H. Denker 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Surveying, Budapest University
Calibration/validation of GOCE data by terrestrial torsion balance observations Gy. Tóth 1, J. Ádám 1, L. Földváry 1,4, I.N. Tziavos 2, H. Denker 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Surveying, Budapest University
Note that gravity exploration is different to seismic exploration in the following way:
 224B3 Other factors that cause changes in g and need to be corrected Note that gravity exploration is different to seismic exploration in the following way: In a seismic survey, the travel time depends
224B3 Other factors that cause changes in g and need to be corrected Note that gravity exploration is different to seismic exploration in the following way: In a seismic survey, the travel time depends
SHORT PERIOD SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION FROM AMBIENT NOISE TOMOGRAPHY IN WESTERN CHINA. Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration 1,2
 SHORT PERIOD SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION FROM AMBIENT NOISE TOMOGRAPHY IN WESTERN CHINA Michael H. Ritzwoller 1, Yingjie Yang 1, Michael Pasyanos 2, Sihua Zheng 3, University of Colorado at Boulder 1, Lawrence
SHORT PERIOD SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION FROM AMBIENT NOISE TOMOGRAPHY IN WESTERN CHINA Michael H. Ritzwoller 1, Yingjie Yang 1, Michael Pasyanos 2, Sihua Zheng 3, University of Colorado at Boulder 1, Lawrence
Gravity Support for Hydrocarbon Exploration at the Prospect Level
 Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (1): 1-6 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2011 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.org Journal of Emerging Trends
Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 2 (1): 1-6 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2011 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.org Journal of Emerging Trends
Determination of density contrasts for a three-dimensional sub-surface intermediate layer
 Earth Planets Space, 55, 463 471, 2003 Determination of density contrasts for a three-dimensional sub-surface intermediate layer I. L. Ateya 1 and S. Takemoto 2 1 Department of Geomatics Engineering and
Earth Planets Space, 55, 463 471, 2003 Determination of density contrasts for a three-dimensional sub-surface intermediate layer I. L. Ateya 1 and S. Takemoto 2 1 Department of Geomatics Engineering and
Constraints on Shallow Low-Viscosity Earth Layers from Future GOCE Data
 Constraints on Shallow Low-Viscosity Earth Layers from Future GOCE Data Hugo Schotman 1,2, Bert Vermeersen 2, Pieter Visser 2 1 2 3 rd International GOCE User Workshop, ESA Esrin, 7 November 2006 glacial-isostatic
Constraints on Shallow Low-Viscosity Earth Layers from Future GOCE Data Hugo Schotman 1,2, Bert Vermeersen 2, Pieter Visser 2 1 2 3 rd International GOCE User Workshop, ESA Esrin, 7 November 2006 glacial-isostatic
CHAPTER 4 POTENTIAL FIELD MODELLING
 CHAPTER 4 POTENTIAL FIELD MODELLING POTENTIAL FIELD MODELLING The reference dataset used for the potential field modelling is the Gravity anomaly map and Magnetic anomaly map of the Atlantic region of
CHAPTER 4 POTENTIAL FIELD MODELLING POTENTIAL FIELD MODELLING The reference dataset used for the potential field modelling is the Gravity anomaly map and Magnetic anomaly map of the Atlantic region of
Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory
 Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory Jeffrey D. Duda, Suzanne Morris, Michelle Werness, and Benjamin H. McNeill Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa
Analysis of the 500 mb height fields and waves: testing Rossby wave theory Jeffrey D. Duda, Suzanne Morris, Michelle Werness, and Benjamin H. McNeill Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences, Iowa
Error Propagation with Geographic Specificity for Very High Degree Geopotential Models
 Error Propagation with Geographic Specificity for Very igh Degree Geopotential Models.K. Pavlis and J. Saleh Raytheon ITSS Corporation, 1616 McCormick Drive, Upper Marlboro, Maryland 20774, USA ikolaos_pavlis@raytheon.com
Error Propagation with Geographic Specificity for Very igh Degree Geopotential Models.K. Pavlis and J. Saleh Raytheon ITSS Corporation, 1616 McCormick Drive, Upper Marlboro, Maryland 20774, USA ikolaos_pavlis@raytheon.com
GRAVIMETRIC MAP OF CHILE. Services Mining and Engineering Geophysics Instituto Geográfico Militar
 GRAVIMETRIC MAP OF CHILE Araneda M., Rivas L., Avendaño M, Sottolichio G., Rubio W. Services Mining and Engineering Geophysics segmi@netexpress.cl) Instituto Geográfico Militar (lrivas@igm.cl) Abstract
GRAVIMETRIC MAP OF CHILE Araneda M., Rivas L., Avendaño M, Sottolichio G., Rubio W. Services Mining and Engineering Geophysics segmi@netexpress.cl) Instituto Geográfico Militar (lrivas@igm.cl) Abstract
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY
 Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
INTRODUCTION TO APPLIED GEOPHYSICS
 INTRODUCTION TO APPLIED GEOPHYSICS EXPLORING THE SHALL0W SUBSURFACE H. Robert Burger Anne F. Sheehan Craig H.Jones VERSITY OF COLORADO VERSITY OF COLORADO W. W. NORTON & COMPANY NEW YORK LONDON Contents
INTRODUCTION TO APPLIED GEOPHYSICS EXPLORING THE SHALL0W SUBSURFACE H. Robert Burger Anne F. Sheehan Craig H.Jones VERSITY OF COLORADO VERSITY OF COLORADO W. W. NORTON & COMPANY NEW YORK LONDON Contents
Summary. 2D potential field migration of gravity fields and their gradients. For a 2D gravity field, we can define the complex intensity:
 Michael S. Zhdanov*, The University of Utah and TechnoImaging, Xiaojun Liu, The University of Utah, and Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging Summary We introduce 2D potential field migration for the interpretation
Michael S. Zhdanov*, The University of Utah and TechnoImaging, Xiaojun Liu, The University of Utah, and Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging Summary We introduce 2D potential field migration for the interpretation
Gravitational attraction of a vertical pyramid model of flat top-and-bottom with depth-wise parabolic density variation
 Gravitational attraction of a vertical pyramid model of flat top-and-bottom with depth-wise parabolic density variation Anand P Gokula and Rambhatla G Sastry Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute
Gravitational attraction of a vertical pyramid model of flat top-and-bottom with depth-wise parabolic density variation Anand P Gokula and Rambhatla G Sastry Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES GENERAL SUBJECTS. GEODESY and GRAVITY
 COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
COMPOSITION and PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Composition and structure of the continental crust Composition and structure of the core Composition and structure of the mantle Composition and structure of the oceanic
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east structural knot
 49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
Status of the European Gravimetric Quasigeoid
 Status of the European Gravimetric Quasigeoid C. Voigt, H. Denker {voigt,denker}@ife.uni-hannover.de 1 Introduction 2 The European Gravity and Geoid Project (EGGP) 3 Data Sets 4 Quasigeoid Computation
Status of the European Gravimetric Quasigeoid C. Voigt, H. Denker {voigt,denker}@ife.uni-hannover.de 1 Introduction 2 The European Gravity and Geoid Project (EGGP) 3 Data Sets 4 Quasigeoid Computation
Northern Sicily, September 6, 2002 earthquake: investigation on peculiar macroseismic effects
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 6, December 2003 Northern Sicily, September 6, 2002 earthquake: investigation on peculiar macroseismic effects Calvino Gasparini, Patrizia Tosi and Valerio De Rubeis Istituto
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 46, N. 6, December 2003 Northern Sicily, September 6, 2002 earthquake: investigation on peculiar macroseismic effects Calvino Gasparini, Patrizia Tosi and Valerio De Rubeis Istituto
Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Configuration in Sadiya Block, Upper Assam, India
 P-225 Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Summary G.K.Ghosh *, S.K.Basha, V.K. Kulshreshth Gravity and magnetic data were collected jointly by National
P-225 Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Summary G.K.Ghosh *, S.K.Basha, V.K. Kulshreshth Gravity and magnetic data were collected jointly by National
Inversion of Phase Data for a Phase Velocity Map 101. Summary for CIDER12 Non-Seismologists
 Inversion of Phase Data for a Phase Velocity Map 101 Summary for CIDER12 Non-Seismologists 1. Setting up a Linear System of Equations This is a quick-and-dirty, not-peer reviewed summary of how a dataset
Inversion of Phase Data for a Phase Velocity Map 101 Summary for CIDER12 Non-Seismologists 1. Setting up a Linear System of Equations This is a quick-and-dirty, not-peer reviewed summary of how a dataset
Co-seismic Gravity Changes Computed for a Spherical Earth Model Applicable to GRACE Data
 Chapter 2 Co-seismic Gravity Changes Computed for a Spherical Earth Model Applicable to GRACE Data W.Sun,G.Fu,andSh.Okubo Abstract Dislocation theories were developed conventionally for a deformed earth
Chapter 2 Co-seismic Gravity Changes Computed for a Spherical Earth Model Applicable to GRACE Data W.Sun,G.Fu,andSh.Okubo Abstract Dislocation theories were developed conventionally for a deformed earth
Detailed Geoid Model for Africa Final Report
 Detailed Geoid Model for Africa Final Report Hussein A. Abd-Elmotaal Minia University, Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Egypt abdelmotaal@lycos.com 1. Over View This report summaries
Detailed Geoid Model for Africa Final Report Hussein A. Abd-Elmotaal Minia University, Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Egypt abdelmotaal@lycos.com 1. Over View This report summaries
Principles of Applied Geophysics
 Principles of Applied Geophysics Fifth edition D.S. Parasnis Professor emeritus of Applied Geophysics Department of Applied Geophysics, University ofluled, Lulea, Sweden Fellow of the Royal Swedish Academy
Principles of Applied Geophysics Fifth edition D.S. Parasnis Professor emeritus of Applied Geophysics Department of Applied Geophysics, University ofluled, Lulea, Sweden Fellow of the Royal Swedish Academy
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Data Repository Item
 Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE. V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva
 HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
CHALLENGES TO THE SWARM MISSION: ON DIFFERENT INTERNAL SHA MAGNETIC FIELD MODELS OF THE EARTH IN DEPENDENCE ON SATELLITE ALTITUDES
 CHALLENGES TO THE SWARM MISSION: ON DIFFERENT INTERNAL SHA MAGNETIC FIELD MODELS OF THE EARTH IN DEPENDENCE ON SATELLITE ALTITUDES Wigor A. Webers Helmholtz- Zentrum Potsdam, Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum,
CHALLENGES TO THE SWARM MISSION: ON DIFFERENT INTERNAL SHA MAGNETIC FIELD MODELS OF THE EARTH IN DEPENDENCE ON SATELLITE ALTITUDES Wigor A. Webers Helmholtz- Zentrum Potsdam, Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum,
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b
 Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION OF LOCAL EARTHQUAKES IN MALAY PENINSULA
 FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION OF LOCAL EARTHQUAKES IN MALAY PENINSULA Siti Norbaizura MAT SAID Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE10505 ABSTRACT Since November 30, 2007, small local earthquakes have been observed
FOCAL MECHANISM DETERMINATION OF LOCAL EARTHQUAKES IN MALAY PENINSULA Siti Norbaizura MAT SAID Supervisor: Tatsuhiko HARA MEE10505 ABSTRACT Since November 30, 2007, small local earthquakes have been observed
HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL
 Mt. Everest HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL -Niraj Manandhar Head, Geodetic Survey Branch Survey Department, Geodetic Survey Branch Project Background Air Borne Gravity Survey Project was
Mt. Everest HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL -Niraj Manandhar Head, Geodetic Survey Branch Survey Department, Geodetic Survey Branch Project Background Air Borne Gravity Survey Project was
Euler Deconvolution Technique for Gravity Survey
 Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6(11): 1891-1897, 2010 2010, INSInet Publication Euler Deconvolution Technique for Gravity Survey 12,3 Piyaphong Chenrai, 2 Jayson Meyers, 1,4 Punya Charusiri 1 Earthquake
Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6(11): 1891-1897, 2010 2010, INSInet Publication Euler Deconvolution Technique for Gravity Survey 12,3 Piyaphong Chenrai, 2 Jayson Meyers, 1,4 Punya Charusiri 1 Earthquake
COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY AND TIME-DOMAIN OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS FOR BOREHOLE STATION'S INVERSE PROBLEMS
 Paper No. COFDE COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY AND TIME-DOMAIN OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS FOR BOREHOLE STATION'S INVERSE PROBLEMS Florent DE MARTIN 1 ABSTRACT This paper compares the use of frequency and time-domain
Paper No. COFDE COMPARISON OF FREQUENCY AND TIME-DOMAIN OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS FOR BOREHOLE STATION'S INVERSE PROBLEMS Florent DE MARTIN 1 ABSTRACT This paper compares the use of frequency and time-domain
Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks. B. Feignier. CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement
 Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks B. Feignier CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement Introduction Over the last 40 years, the increase in computational
Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks B. Feignier CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement Introduction Over the last 40 years, the increase in computational
Depth and shape solutions from residual gravity anomalies due to simple geometric structures using a statistical approach
 Contributions to Geophysics and Geodesy Vol. 47/2, 2017 (113 132) Depth and shape solutions from residual gravity anomalies due to simple geometric structures using a statistical approach El-Sayed ABDELRAHMAN,
Contributions to Geophysics and Geodesy Vol. 47/2, 2017 (113 132) Depth and shape solutions from residual gravity anomalies due to simple geometric structures using a statistical approach El-Sayed ABDELRAHMAN,
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) for processing seismic datasets: a case study at Campi Flegrei
 Independent Component Analysis (ICA) for processing seismic datasets: a case study at Campi Flegrei De Lauro E. 1 ; De Martino S. 1 ; Falanga M. 1 ; Petrosino S. 2 1 Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell'informazione
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) for processing seismic datasets: a case study at Campi Flegrei De Lauro E. 1 ; De Martino S. 1 ; Falanga M. 1 ; Petrosino S. 2 1 Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell'informazione
Long-period Ground Motion Characteristics of the Osaka Sedimentary Basin during the 2011 Great Tohoku Earthquake
 Long-period Ground Motion Characteristics of the Osaka Sedimentary Basin during the 2011 Great Tohoku Earthquake K. Sato, K. Asano & T. Iwata Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Japan
Long-period Ground Motion Characteristics of the Osaka Sedimentary Basin during the 2011 Great Tohoku Earthquake K. Sato, K. Asano & T. Iwata Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Japan
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Composite memory variables for viscoelastic synthetic seismograms
 Geophys. J. Int. (1995) 121,634-639 RESEARCH NOTE Composite memory variables for viscoelastic synthetic seismograms Tong Xu George A. McMechan Center for Lithospheric Studies, The University of Texas at
Geophys. J. Int. (1995) 121,634-639 RESEARCH NOTE Composite memory variables for viscoelastic synthetic seismograms Tong Xu George A. McMechan Center for Lithospheric Studies, The University of Texas at
