Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge
|
|
|
- Melvin Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSA Data Repository SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge Hanchao Jian 1,, Satish C. Singh *, Yongshun John Chen 1,* and Jiabiao Li 1 Institute of Theoretical and Applied Geophysics, School of Earth and Space Science, Peking University, Beijing 171, China Laboratoire de Géosciences Marines, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, 1 rue Jussieu, 75 Paris Cedex 5, France School of Oceanography, South University of Science and Technology of China, Shenzhen 5155, China. Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Hangzhou 11, China * s: johnyc@pku.edu.cn (Y.J.C); singh@ipgp.fr (S.S.) SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Seismic experiment and data The -D seismic dataset covers an about 7 km by 7 km box, and consists of 1 OBS covering the central volcano and a total of 5765 air-gun shots (Li et al., 15) (Fig. 1b). Each air gun within the -airgun array had a volume of 15 in. Since the volume was constant for each air gun and thus the bubble sequence was not suppressed, the array provides significant low-frequency energies (- Hz), which are very important to acquire very long-distance records. Shots were fired every minutes (~ m) along a grid of lines spaced at ~ km in the -D box. The raw data has a sampling interval of ms and was converted to SEG-Y format with a length of s for later analysis. Full waveform inversion Unlike travel time tomography that tries to match the travel time information using synthetics from high-frequency approximated ray tracing, full waveform inversion (FWI) matches the waveform using synthetics derived by solving the dynamic wave equations. Since the amplitude information is added, less approximation is involved and no explicit picking is needed (Shipp and Singh, ), FWI provides a higher resolution than tomography, especially for imaging low-velocity anomalies that strongly attenuate the traversing seismic energies and thus prevent effective travel time picking (Wang et al., 1). The largest shortcoming of FWI is the non-linearity problem that can trap the solution into local minima, but it is natural to refine the model by starting from a long-wavelength model constrained by travel time data. We adopted a -D time-domain elastic FWI approach firstly created by Shipp and Singh (), which uses a finite difference method (Levander, 19) for waveform modeling and the adjoint method (Tarantola, 196) for gradient calculations. The misfit function is defined as: 1
2 T S = ( d syn d obs ) T W 1 d ( d syn d obs ), s r where d syn and d obs represent the synthetic and observed seismic waveforms, respectively. The sample-by-sample differences are summed over the recording time (T ), and all shots (s) and receivers (r). The W 1 d is the data covariance matrix, which we made a diagonal matrix to weight different parts of the data. The across-axis profile running around the central volcano (Fig. 1b) was chosen to improve the resolution of the LVA image. Before the FWI, the observed data was preprocessed aiming to reduce the inconsistency between the -D waveform modelling and the - D nature and to enhance SNR over a broad frequency band. We first corrected the crooked geometry by shifting the time axis based on the results from ray tracing in the -D tomography model. This correction is accurate enough for the long-offset crustal phases (Pg and PmP). Then we designed a debubbling filter using the approach of Wood et al. (197) to suppress the bubble energies and thus flatten the amplitude spectra between and Hz. We have not involved the anelasticity in the FWI. Instead we estimated the long-wavelength attenuation structure from the data and a priori information, and then compensated for its effect in the data domain. In the inversion, we have only used the long-offset primary phases in the hydrophone channel (Fig., Fig. DR5), since this part of data has the most linear behavior in FWI and the largest sensitivities to the lower-crustal structures. Within this subset of data, there are basically no S-wave energies and thus it is much less sensitive to the S-wave velocities compared to P-wave velocities. Hence, only the P-wave velocities that were initially extracted from the -D tomography model have been iteratively updated to minimize the data misfit, whereas the S-wave velocities were always related to the P-wave velocities according to the Brocher s regression fit (Brocher, 5). The finite difference modeling used a grid spaced at m, which can assure the accuracy for propagating P waves with a frequency below 1 Hz. During the inversion, a Gaussian smoothing filter (75 m horizontally and 1 m vertically) was applied to suppress high-wavenumber artifacts. Besides, we forced the model update within the lower crust (between km and 1.5 km depth below the sea level) to be symmetrical with respect to the ridge axis, which is a generally valid assumption considering the symmetrical spreading. In order to examine the resolvability of the sparse dataset, we performed extensive synthetic tests using the real-data geometry and source signature, and a synthetic AMC model. We created the synthetic AMC model by adding an AMC-like anomaly (Fig. DRa) and a constant velocity contrast of.75 km/s across the Moho to the tomography model (Fig. a). The input data was generated from the synthetic AMC model with the same finite difference modeling as in the FWI. The inversion was carried out using the same time and offset windowing and inversion strategies as in the real-data inversion, with no Moho velocity contrast in the starting model (Fig. DRa). The result (Fig. DRb and c) indicates that the AMC-like anomaly can be reconstructed with a good vertical resolution, but smeared out laterally due to the limited OBS density. Consequently, the dimension of the anomaly is over-
3 estimated, whereas its amplitude is under-estimated. Besides, due to the limited frequency band and aperture of the input data, an artifact of positive velocity update exists above the AMC. However, the amplitude of this positive update is less than 1/ of that of the negative update atop the AMC. Besides, in the synthetic FWI test, the sharp velocity variation across the Moho interface is partly reconstructed within -1 and 1 km distance, due to the presence of strong PmP reflections. However, PmP reflections are simultaneously affected by the lower-crustal velocities and Moho reflector structures (depth and contrast). The trade-off between these structures is difficult to be eliminated because of the sparse data coverage within the lower crust. In addition, since the data does not contain significant Pn energies that travelling below the Moho interface, the long-wavelength structure across the Moho is not constrained. Consequently, the mantle velocity would be under-estimated, and a negative update immediately above the Moho always accompanies the positive update of mantle velocities. In the real-data FWI, the Moho structure is inaccurate in the starting model, as the -D tomography provided no information in the Moho contrast at all and the accuracy of Moho depth could also be low because of the large picking uncertainties of PmP arrival times. These inaccuracies might be mapped to the lower crust through PmP wave paths, which can be observed in the synthetic FWI test (Fig. DRb). To identify this effect in the real-data FWI, we ran inversions from various starting models where the Moho depth and contrast had been perturbed. By comparing their model updates, we found that the AMC anomaly is constant. Some artifacts may distribute along the PmP wave paths, especially within km above the Moho interface. In this paper, we show the result of the real-data FWI using the starting model without Moho velocity contrast. Despite a good data fit for both Pg and PmP arrivals from the final model, we only focus the interpretation on the AMC structure. REFERENCES CITED Brocher, T. M., 5, Empirical Relations between Elastic Wavespeeds and Density in the Earth's Crust: Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, v. 95, no. 6, p Levander, A. R., 19, Fourth-order finite-difference P-SV seismograms: Geophysics, v. 5, no. 11, p Li, J., Jian, H., Chen, Y. J., Singh, S. C., Ruan, A., Qiu, X., Zhao, M., Wang, X., Niu, X., and Ni, J., 15, Seismic observation of an extremely magmatic accretion at the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge: Geophysical Research Letters. Shipp, R. M., and Singh, S. C.,, Two-dimensional full wavefield inversion of wideaperture marine seismic streamer data: Geophysical Journal International, v. 151, no., p. 5-. Tarantola, A., 196, A strategy for nonlinear elastic inversion of seismic reflection data: Geophysics, v. 51, no. 1, p Wang, H., Singh, Satish C., and Calandra, H., 1, Integrated inversion using combined wave-equation tomography and full waveform inversion: Geophysical Journal International, v. 19, no. 1, p. -6. Wood, L. C., Heiser, R. C., Treitel, S., and Riley, P. L., 197, The debubbling of marine source signatures: Geophysics, v., no., p
4 7 ' 7 ' 1 5 ' 5 ' 5 ' 1 km Figure DR1. Bathymetric map showing locations of data and model profiles. OBSs are shown as circles, and those shown in Fig. DR are labelled with numbers over filled colours. The across-axis shooting profiles running over the five numbered OBS are shown with the corresponding colours. The thick dashed black square marks the location of the horizontal slice of -D tomography model shown in Fig. DRe and f. The rest is the same as in Fig. 1. Figure DR (On next page). OBS data and travel time picking. Receiver gather for OBS a,, b, 5, c, and d, 1 from the corresponding across-axis shooting profile, as shown in Fig. DR1. The red and black curves indicate the manually picked Pg and PmP arrivals used in the -D tomography, respectively. A water-path correction, a water-wave muting, a band-pass filter between - Hz and a time reduction with a velocity of 6.5 km/s were applied to all data sections. Note the time axis is different with that in Fig. and Fig. DR due to the additional water-path correction. One can easily see the reduced amplitude of Pg resembling shadow zones (blue ellipses), which are followed by strong PmP reflections within the gathers (a and c) from the profile running over the central volcano (the green profile in Fig. DR1). However, there is no such feature for the record (b and d) from the other profile, suggesting the localized anomaly in the lower crust beneath the central volcano.
5
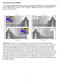
6 a.6 c Depth (km) b Depth (km) Across axis distance (km) Anomaly (km/s) -.6 Anomaly (km/s) Depth (km) Update (km/s) Figure DR. Synthetic FWI test. The geometry and staring model are the same as used in the real-data inversion (Fig. a). The input data was generated from a model that was created by adding an AMC-like anomaly (a, true anomaly) and a constant velocity contrast of.75 km/s across the Moho to the starting model. The FWI was terminated when no significant data misfit reduction could be achieved. The final recovered anomaly relative to the starting model is shown in b (recovered anomaly). The green triangles mark the OBS locations. Note that the colour scales are different in a and b. Depth profiles of the anomalies beneath the ridge axis are compared in c. Note that the anomaly shown here was calculated with respect to the starting model, rather than the reference model shown in Fig. c. The recovered AMC anomaly is smeared out laterally, and thus has a larger dimension but smaller amplitude compared to the true anomaly, whereas the vertical resolution is good. Due to the limited frequency band and aperture of the input data, an artifact of positive velocity update exists above the AMC. However, the amplitude of the positive update is less than 1/ of that of the negative update atop the AMC.
7 Time (s) a Source receiver offset (km) 6 5 b Pg Time (s) Time (s) PmP 1 16 Source receiver offset (km) 6 Pg Across axis distance (km) PmP Across axis distance (km) Figure DR. Data fit. Long-offset waveforms of wide-angle refractions (Pg) and reflections (PmP) for the OBS used in the FWI: a, OBS and b, OBS, whose locations are shown in Fig. DR1, whereas that for OBS is shown in Fig.. In each three-row panel, top: pre-processed real data; middle: synthetic data for the starting model and bottom: synthetic data for the full waveform inverted model. The red curves mark the first-arrivals predicted with a ray tracing in the -D tomography model. The time is reduced with a velocity of 6.5 km/s. Both Pg and PmP are better fitted after the inversion as the AMC s top and Moho contrast have been built up.
8 1 EPR north of Orozco transform EPR south of Garrett transform Depth to top of magma lens (km) RR LS This study Full spreading rate (mm/yr) Figure DR5. Global seismic observations and numerical predictions of the depth to the top of AMC as a function of spreading rate (after Chen and Lin, ). The solid and dashed curves are model predictions with relatively low and high conductive cooling effect that is analogous to hydrothermal cooling in upper crust. Additional data is from the Lucky Strike segment (LS) (Singh et al., 6).
Data Repository Item
 Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, Tim Sears (British Gas, UK), Mark Roberts (IPG Paris, Summary. Introduction P - 92
 P - 92 Fine-Scale P- and S-Wave Velocities From Elastic Full Waveform Inversion of Multi-Component and Time-Lapse Data: Future of Quantitative Seismic Imaging Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, singh@ipgp.jussieu.fr),
P - 92 Fine-Scale P- and S-Wave Velocities From Elastic Full Waveform Inversion of Multi-Component and Time-Lapse Data: Future of Quantitative Seismic Imaging Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, singh@ipgp.jussieu.fr),
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco
 Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
 GSA Data Repository Item: 2007183 Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Brian J. demartin 1*, Robert
GSA Data Repository Item: 2007183 Data Repository Item For: Kinematics and geometry of active detachment faulting beneath the TAG hydrothermal field on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Brian J. demartin 1*, Robert
Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich
 Seminar des FA Ultraschallprüfung Vortrag 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=20944 Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich Thomas
Seminar des FA Ultraschallprüfung Vortrag 1 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=20944 Vollständige Inversion seismischer Wellenfelder - Erderkundung im oberflächennahen Bereich Thomas
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough
 We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
Research Project Report
 Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
Seismic Imaging. William W. Symes. C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September
 Seismic Imaging William W. Symes C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September 2002 www.trip.caam.rice.edu 1 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 How do you turn lots of this... (field seismogram from the
Seismic Imaging William W. Symes C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September 2002 www.trip.caam.rice.edu 1 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 How do you turn lots of this... (field seismogram from the
Structural Cause of Missed Eruption in the Lunayyir Basaltic
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2015140 Supplementary information for the paper Structural Cause of Missed Eruption in the Lunayyir Basaltic Field (Saudi Arabia) in 2009 Koulakov, I., El Khrepy, S., Al-Arifi, N.,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2015140 Supplementary information for the paper Structural Cause of Missed Eruption in the Lunayyir Basaltic Field (Saudi Arabia) in 2009 Koulakov, I., El Khrepy, S., Al-Arifi, N.,
Changbaishan volcanism in northeast China linked to subduction-induced mantle upwelling
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2166 Changbaishan volcanism in northeast China linked to subduction-induced mantle upwelling Youcai Tang, Masayuki Obayashi, Fenglin Niu, Stephen P. Grand, Yongshun
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2166 Changbaishan volcanism in northeast China linked to subduction-induced mantle upwelling Youcai Tang, Masayuki Obayashi, Fenglin Niu, Stephen P. Grand, Yongshun
Tomography of the 2011 Iwaki earthquake (M 7.0) and Fukushima
 1 2 3 Auxiliary materials for Tomography of the 2011 Iwaki earthquake (M 7.0) and Fukushima nuclear power plant area 4 5 6 7 8 9 Ping Tong 1,2, Dapeng Zhao 1 and Dinghui Yang 2 [1] {Department of Geophysics,
1 2 3 Auxiliary materials for Tomography of the 2011 Iwaki earthquake (M 7.0) and Fukushima nuclear power plant area 4 5 6 7 8 9 Ping Tong 1,2, Dapeng Zhao 1 and Dinghui Yang 2 [1] {Department of Geophysics,
3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES
 3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES Barbara Romanowicz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, U. C. Berkeley Dr. Barbara Romanowicz, UC Berkeley (KITP Colloquium 9/11/02) 1 Cartoon
3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES Barbara Romanowicz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, U. C. Berkeley Dr. Barbara Romanowicz, UC Berkeley (KITP Colloquium 9/11/02) 1 Cartoon
Youzuo Lin and Lianjie Huang
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 Building Subsurface Velocity Models with Sharp Interfaces
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 Building Subsurface Velocity Models with Sharp Interfaces
Tu N Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography
 Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion
 Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion Lei Yang, Daniel O. Trad and Wenyong Pan Summary The inverse problem in exploration geophysics usually consists of two
Comparison between least-squares reverse time migration and full-waveform inversion Lei Yang, Daniel O. Trad and Wenyong Pan Summary The inverse problem in exploration geophysics usually consists of two
Full waveform inversion in the Laplace and Laplace-Fourier domains
 Full waveform inversion in the Laplace and Laplace-Fourier domains Changsoo Shin, Wansoo Ha, Wookeen Chung, and Ho Seuk Bae Summary We present a review of Laplace and Laplace-Fourier domain waveform inversion.
Full waveform inversion in the Laplace and Laplace-Fourier domains Changsoo Shin, Wansoo Ha, Wookeen Chung, and Ho Seuk Bae Summary We present a review of Laplace and Laplace-Fourier domain waveform inversion.
Tan K. Wang National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 SEISMIC IMAGING IN THE OCEANS Tan K. Wang National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung, Taiwan, R.O.C. Keywords: Converted wave, multi-channel seismic, ocean-bottom seismometer, travel-time inversion, virtual
SEISMIC IMAGING IN THE OCEANS Tan K. Wang National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung, Taiwan, R.O.C. Keywords: Converted wave, multi-channel seismic, ocean-bottom seismometer, travel-time inversion, virtual
Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones
 DR2009082 Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones Fault Zone Trapped Wave Data and Methods Fault zone trapped waves observed for 2 shots and 5 local
DR2009082 Data Repository: Seismic and Geodetic Evidence For Extensive, Long-Lived Fault Damage Zones Fault Zone Trapped Wave Data and Methods Fault zone trapped waves observed for 2 shots and 5 local
2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing
 403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing
 From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer
 Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
Monitoring the stability of airgun source array signature
 Yuan Ni*, Cheikh Niang, Risto Siliqi, CGGVeritas, France Summary In this paper we study several key factors causing the instability of marine airgun source signatures, and present a method to monitor their
Yuan Ni*, Cheikh Niang, Risto Siliqi, CGGVeritas, France Summary In this paper we study several key factors causing the instability of marine airgun source signatures, and present a method to monitor their
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys
 FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Wei Huang *, Kun Jiao, Denes Vigh, Jerry Kapoor, David Watts, Hongyan Li, David Derharoutian, Xin Cheng WesternGeco Summary Since the 1990s, subsalt imaging in the Gulf of Mexico (GOM) has been a major
Wei Huang *, Kun Jiao, Denes Vigh, Jerry Kapoor, David Watts, Hongyan Li, David Derharoutian, Xin Cheng WesternGeco Summary Since the 1990s, subsalt imaging in the Gulf of Mexico (GOM) has been a major
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data
 Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
Seismic tomography with co-located soft data Mohammad Maysami and Robert G. Clapp ABSTRACT There is a wide range of uncertainties present in seismic data. Limited subsurface illumination is also common,
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical
 Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
Summary. Introduction
 Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Downloaded 05/01/17 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Mapping Imbricate Structures in the Thrust Belt of Southeast Turkey by Large-Offset Seismic Survey Oz Yilmaz*, Anatolian Geophysical, Istanbul, Turkey; and Serdar Uygun, Ali Ölmez, and Emel Çalı, Turkish
Mapping Imbricate Structures in the Thrust Belt of Southeast Turkey by Large-Offset Seismic Survey Oz Yilmaz*, Anatolian Geophysical, Istanbul, Turkey; and Serdar Uygun, Ali Ölmez, and Emel Çalı, Turkish
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements
 Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Towards full waveform inversion: A torturous path
 FWI Towards full waveform inversion: A torturous path J. Helen Isaac and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Full waveform inversion (FWI) can be viewed as an iterative cycle involving forward modelling, pre-stack
FWI Towards full waveform inversion: A torturous path J. Helen Isaac and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Full waveform inversion (FWI) can be viewed as an iterative cycle involving forward modelling, pre-stack
Wenyong Pan and Lianjie Huang. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Geophysics Group, MS D452, Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA
 PROCEEDINGS, 44th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 019 SGP-TR-14 Adaptive Viscoelastic-Waveform Inversion Using the Local Wavelet
PROCEEDINGS, 44th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 019 SGP-TR-14 Adaptive Viscoelastic-Waveform Inversion Using the Local Wavelet
TOM 2.6. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2581
 Oz Yilmaz* and Jie Zhang, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, Texas; and Yan Shixin, PetroChina, Beijing, China Summary PetroChina conducted a multichannel large-offset 2-D seismic survey in the Yumen Oil Field, Northwest
Oz Yilmaz* and Jie Zhang, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, Texas; and Yan Shixin, PetroChina, Beijing, China Summary PetroChina conducted a multichannel large-offset 2-D seismic survey in the Yumen Oil Field, Northwest
Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy Eric Debayle 1, Fabien Dubuffet 1 and Stéphanie
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy Eric Debayle 1, Fabien Dubuffet 1 and Stéphanie
Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) with wave-equation migration. Gary Margrave Rob Ferguson Chad Hogan Banff, 3 Dec. 2010
 Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) with wave-equation migration (WEM) and well control Gary Margrave Rob Ferguson Chad Hogan Banff, 3 Dec. 2010 Outline The FWI cycle The fundamental theorem of FWI Understanding
Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) with wave-equation migration (WEM) and well control Gary Margrave Rob Ferguson Chad Hogan Banff, 3 Dec. 2010 Outline The FWI cycle The fundamental theorem of FWI Understanding
B048 Seabed Properties Derived from Ambient Noise
 B048 Seabed Properties Derived from Ambient Noise E. Muyzert* (Schlumberger Cambridge Research) SUMMARY An extensive study of low-frequency ambient noise wavefields in the seabed has resulted in a new
B048 Seabed Properties Derived from Ambient Noise E. Muyzert* (Schlumberger Cambridge Research) SUMMARY An extensive study of low-frequency ambient noise wavefields in the seabed has resulted in a new
Reflection Seismic Method
 Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
Th Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation
 Th-01-08 Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation D. Boiero* (WesternGeco), C. Strobbia (WesternGeco), L. Velasco (WesternGeco) & P. Vermeer (WesternGeco) SUMMARY Guided waves contain significant information
Th-01-08 Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation D. Boiero* (WesternGeco), C. Strobbia (WesternGeco), L. Velasco (WesternGeco) & P. Vermeer (WesternGeco) SUMMARY Guided waves contain significant information
Final Report for DOEI Project: Bottom Interaction in Long Range Acoustic Propagation
 Final Report for DOEI Project: Bottom Interaction in Long Range Acoustic Propagation Ralph A. Stephen Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution 360 Woods Hole Road (MS#24) Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508)
Final Report for DOEI Project: Bottom Interaction in Long Range Acoustic Propagation Ralph A. Stephen Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution 360 Woods Hole Road (MS#24) Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508)
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS
 Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
The Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy:
 The Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy: 3-D structural model from seismic reflection data, and lithology characterization N. Maercklin 1, M. Vassallo 1, G. Festa2, A. Zollo2, D. Dello Iacono 2 & J. Virieux3
The Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy: 3-D structural model from seismic reflection data, and lithology characterization N. Maercklin 1, M. Vassallo 1, G. Festa2, A. Zollo2, D. Dello Iacono 2 & J. Virieux3
Shallow oceanic crust: Full waveform tomographic images of the seismic layer 2A/2B boundary
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008972, 2012 Shallow oceanic crust: Full waveform tomographic images of the seismic layer 2A/2B boundary Gail L. Christeson, 1 Joanna V. Morgan,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008972, 2012 Shallow oceanic crust: Full waveform tomographic images of the seismic layer 2A/2B boundary Gail L. Christeson, 1 Joanna V. Morgan,
Repeatability in geophysical data processing: A case study of seismic refraction tomography.
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2012, 4 (5):1915-1922 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Repeatability
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2012, 4 (5):1915-1922 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Repeatability
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 1665 1681 Advance Access publication 2013 June 14 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt178 Multiparameter full waveform inversion of multicomponent ocean-bottom-cable
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 1665 1681 Advance Access publication 2013 June 14 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt178 Multiparameter full waveform inversion of multicomponent ocean-bottom-cable
Full waveform inversion of shot gathers in terms of poro-elastic parameters
 Full waveform inversion of shot gathers in terms of poro-elastic parameters Louis De Barros, M. Dietrich To cite this version: Louis De Barros, M. Dietrich. Full waveform inversion of shot gathers in terms
Full waveform inversion of shot gathers in terms of poro-elastic parameters Louis De Barros, M. Dietrich To cite this version: Louis De Barros, M. Dietrich. Full waveform inversion of shot gathers in terms
Registration-guided least-squares waveform inversion
 Registration-guided least-squares waveform inversion Hyoungsu Baek 1, Henri Calandra, Laurent Demanet 1 1 MIT Mathematics department, TOTAL S.A. January 15 013 Abstract Full waveform inversion with frequency
Registration-guided least-squares waveform inversion Hyoungsu Baek 1, Henri Calandra, Laurent Demanet 1 1 MIT Mathematics department, TOTAL S.A. January 15 013 Abstract Full waveform inversion with frequency
Source estimation for frequency-domain FWI with robust penalties
 Source estimation for frequency-domain FWI with robust penalties Aleksandr Y. Aravkin, Tristan van Leeuwen, Henri Calandra, and Felix J. Herrmann Dept. of Earth and Ocean sciences University of British
Source estimation for frequency-domain FWI with robust penalties Aleksandr Y. Aravkin, Tristan van Leeuwen, Henri Calandra, and Felix J. Herrmann Dept. of Earth and Ocean sciences University of British
29th Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies MODELING P WAVE MULTIPATHING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA
 MODELING P WAVE MULTIPATHING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Ali Fatehi and Keith D. Koper Saint Louis University Sponsored by the Air Force Research Laboratory ABSTRACT Contract No. FA8718-06-C-0003 We have used data
MODELING P WAVE MULTIPATHING IN SOUTHEAST ASIA Ali Fatehi and Keith D. Koper Saint Louis University Sponsored by the Air Force Research Laboratory ABSTRACT Contract No. FA8718-06-C-0003 We have used data
Adaptive linear prediction filtering for random noise attenuation Mauricio D. Sacchi* and Mostafa Naghizadeh, University of Alberta
 Adaptive linear prediction filtering for random noise attenuation Mauricio D. Sacchi* and Mostafa Naghizadeh, University of Alberta SUMMARY We propose an algorithm to compute time and space variant prediction
Adaptive linear prediction filtering for random noise attenuation Mauricio D. Sacchi* and Mostafa Naghizadeh, University of Alberta SUMMARY We propose an algorithm to compute time and space variant prediction
W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building
 W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building S. Kapoor* (WesternGeco, LLC), D. Vigh (WesternGeco), H. Li (WesternGeco) & D. Derharoutian (WesternGeco) SUMMARY An accurate earth model
W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building S. Kapoor* (WesternGeco, LLC), D. Vigh (WesternGeco), H. Li (WesternGeco) & D. Derharoutian (WesternGeco) SUMMARY An accurate earth model
Velocity-Interface Structure of the Southwestern Ryukyu Subduction Zone from EW OBS/MCS Data
 Marine Geophysical Researches 22: 265-287, 2001. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Velocity-Interface Structure of the Southwestern Ryukyu Subduction Zone from EW9509-1 OBS/MCS
Marine Geophysical Researches 22: 265-287, 2001. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Velocity-Interface Structure of the Southwestern Ryukyu Subduction Zone from EW9509-1 OBS/MCS
( ) ( ), 1, 1. Downloaded 10/14/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Chao Zhang*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC); Zhikun Sun, GeoTomo LLC Summary Refraction traveltimes have long been applied for deriving long-wavelength statics solutions.
Chao Zhang*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC); Zhikun Sun, GeoTomo LLC Summary Refraction traveltimes have long been applied for deriving long-wavelength statics solutions.
Residual Statics using CSP gathers
 Residual Statics using CSP gathers Xinxiang Li and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT All the conventional methods for residual statics analysis require normal moveout (NMO) correction applied on the seismic data.
Residual Statics using CSP gathers Xinxiang Li and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT All the conventional methods for residual statics analysis require normal moveout (NMO) correction applied on the seismic data.
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS. The data provided by the contractor needed total re-picking and reinterpretation.
 RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS As part of a geotechnical assessment and feasibility planning of channel improvement a shallow marine seismic refraction survey was undertaken. The data was initially processed
RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS As part of a geotechnical assessment and feasibility planning of channel improvement a shallow marine seismic refraction survey was undertaken. The data was initially processed
11th Biennial International Conference & Exposition. Keywords Sub-basalt imaging, Staggered grid; Elastic finite-difference, Full-waveform modeling.
 Sub-basalt imaging using full-wave elastic finite-difference modeling: A synthetic study in the Deccan basalt covered region of India. Karabi Talukdar* and Laxmidhar Behera, CSIR-National Geophysical Research
Sub-basalt imaging using full-wave elastic finite-difference modeling: A synthetic study in the Deccan basalt covered region of India. Karabi Talukdar* and Laxmidhar Behera, CSIR-National Geophysical Research
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310
 Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION. f ad j (t) = 2 Es,r. The kernel
 The failure mode of correlation focusing for model velocity estimation Hyoungsu Baek 1(*), Henri Calandra 2, and Laurent Demanet 1 1 Dept. of Mathematics and Earth Resources Lab, Massachusetts Institute
The failure mode of correlation focusing for model velocity estimation Hyoungsu Baek 1(*), Henri Calandra 2, and Laurent Demanet 1 1 Dept. of Mathematics and Earth Resources Lab, Massachusetts Institute
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site
 Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Oceanic Detachment Faults Generate Compression in Extension
 GSA Data Repository 2017309 Oceanic Detachment Faults Generate Compression in Extension R. Parnell-Turner 1, R. A. Sohn 1, C. Peirce 2, T. J. Reston 3, C. J. MacLeod 4, R. C. Searle 2 and N. M. Simão 2.
GSA Data Repository 2017309 Oceanic Detachment Faults Generate Compression in Extension R. Parnell-Turner 1, R. A. Sohn 1, C. Peirce 2, T. J. Reston 3, C. J. MacLeod 4, R. C. Searle 2 and N. M. Simão 2.
Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image
 GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 76, NO. 5 (SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2011); P. WB169 WB174, 8 FIGS. 10.1190/GEO2010-0392.1 Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image Shuo Ji 1, Tony Huang 1, Kang Fu 2,
GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 76, NO. 5 (SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2011); P. WB169 WB174, 8 FIGS. 10.1190/GEO2010-0392.1 Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image Shuo Ji 1, Tony Huang 1, Kang Fu 2,
Th N Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data
 Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
PHASE TIME INVERSION: A SIMPLE METHOD FOR REGIONAL WAVEFORM INVERSION. Charles A. Langston. University of Memphis
 PHASE TIME INVERSION: A SIMPLE METHOD FOR REGIONAL WAVEFORM INVERSION Charles A. Langston University of Memphis Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office of Nonproliferation Research
PHASE TIME INVERSION: A SIMPLE METHOD FOR REGIONAL WAVEFORM INVERSION Charles A. Langston University of Memphis Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office of Nonproliferation Research
P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin
 P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin M. Malinowski* (Institute of Geophysics PAS), A. Ribodetti (Geosciences Azur CNRS UMR)
P276 Multiparameter Full-Waveform Inversion for Velocity and Attenuation Refining the Imaging of a Sedimentary Basin M. Malinowski* (Institute of Geophysics PAS), A. Ribodetti (Geosciences Azur CNRS UMR)
On the Limitation of Receiver Functions Method: Beyond Conventional Assumptions & Advanced Inversion Techniques
 On the Limitation of Receiver Functions Method: Beyond Conventional Assumptions & Advanced Inversion Techniques Hrvoje Tkalčić RSES, ANU Acknowledgment: RSES Seismology & Mathematical Geophysics Group
On the Limitation of Receiver Functions Method: Beyond Conventional Assumptions & Advanced Inversion Techniques Hrvoje Tkalčić RSES, ANU Acknowledgment: RSES Seismology & Mathematical Geophysics Group
Selected Seismic Observations of Upper-Mantle Discontinuities
 Selected Seismic Observations of Upper-Mantle Discontinuities Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego August 31, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Interface Depth vs. Publication Date Most depths are sampled
Selected Seismic Observations of Upper-Mantle Discontinuities Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego August 31, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Interface Depth vs. Publication Date Most depths are sampled
Global surface-wave tomography
 Global surface-wave tomography Lapo Boschi (lapo@erdw.ethz.ch) October 7, 2009 Love and Rayleigh waves, radial anisotropy Whenever an elastic medium is bounded by a free surface, coherent waves arise that
Global surface-wave tomography Lapo Boschi (lapo@erdw.ethz.ch) October 7, 2009 Love and Rayleigh waves, radial anisotropy Whenever an elastic medium is bounded by a free surface, coherent waves arise that
Attenuation compensation in viscoacoustic reserve-time migration Jianyong Bai*, Guoquan Chen, David Yingst, and Jacques Leveille, ION Geophysical
 Attenuation compensation in viscoacoustic reserve-time migration Jianyong Bai*, Guoquan Chen, David Yingst, and Jacques Leveille, ION Geophysical Summary Seismic waves are attenuated during propagation.
Attenuation compensation in viscoacoustic reserve-time migration Jianyong Bai*, Guoquan Chen, David Yingst, and Jacques Leveille, ION Geophysical Summary Seismic waves are attenuated during propagation.
29th Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 TRANSITION ZONE WAVE PROPAGATION: CHARACTERIZING TRAVEL-TIME AND AMPLITUDE INFORMATION Peter M. Shearer and Jesse F. Lawrence University of California San Diego, Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics
TRANSITION ZONE WAVE PROPAGATION: CHARACTERIZING TRAVEL-TIME AND AMPLITUDE INFORMATION Peter M. Shearer and Jesse F. Lawrence University of California San Diego, Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics
Attenuation compensation in least-squares reverse time migration using the visco-acoustic wave equation
 Attenuation compensation in least-squares reverse time migration using the visco-acoustic wave equation Gaurav Dutta, Kai Lu, Xin Wang and Gerard T. Schuster, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Attenuation compensation in least-squares reverse time migration using the visco-acoustic wave equation Gaurav Dutta, Kai Lu, Xin Wang and Gerard T. Schuster, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1158 Characteristic Slip for 5 great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China. Klinger 1 Y., Etchebes 1 M., Tapponnier 2 P., and Narteau 1 C. 1 Institut de
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1158 Characteristic Slip for 5 great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China. Klinger 1 Y., Etchebes 1 M., Tapponnier 2 P., and Narteau 1 C. 1 Institut de
25th Seismic Research Review - Nuclear Explosion Monitoring: Building the Knowledge Base
 Pn Q UNDER TIBET AND TIENSHAN WITH PRACTICAL AND SCIENTIFIC IMPLICATIONS Jiakang Xie Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University Sponsored by Defense Threat Reduction Agency Contract No. DTRA01-00-C-0048
Pn Q UNDER TIBET AND TIENSHAN WITH PRACTICAL AND SCIENTIFIC IMPLICATIONS Jiakang Xie Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University Sponsored by Defense Threat Reduction Agency Contract No. DTRA01-00-C-0048
A seismic refraction study of the Cocos plate offshore Nicaragua and Costa Rica Harm Van Avendonk (UTIG, UT Austin)
 A seismic refraction study of the Cocos plate offshore Nicaragua and Costa Rica Harm Van Avendonk (UTIG, UT Austin)! October 18, 2012 "#$%&'($)*!+,!-&./(!01!2/(+! Plate tectonics:!!large fluxes of solids
A seismic refraction study of the Cocos plate offshore Nicaragua and Costa Rica Harm Van Avendonk (UTIG, UT Austin)! October 18, 2012 "#$%&'($)*!+,!-&./(!01!2/(+! Plate tectonics:!!large fluxes of solids
F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures
 F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures Yang Zhang 1, Xander Campman 1, Samantha Grandi 1, Shihong Chi 1, M. Nafi Toksöz 1, Mark E. Willis 1, Daniel R. Burns
F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures Yang Zhang 1, Xander Campman 1, Samantha Grandi 1, Shihong Chi 1, M. Nafi Toksöz 1, Mark E. Willis 1, Daniel R. Burns
Full waveform inversion with wave equation migration and well control
 FWI by WEM Full waveform inversion with wave equation migration and well control Gary F. Margrave, Robert J. Ferguson and Chad M. Hogan ABSTRACT We examine the key concepts in full waveform inversion (FWI)
FWI by WEM Full waveform inversion with wave equation migration and well control Gary F. Margrave, Robert J. Ferguson and Chad M. Hogan ABSTRACT We examine the key concepts in full waveform inversion (FWI)
Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
GSA DATA REPOSITORY Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012311 Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart Figure DR1: Flow chart of the algorithm to further clarify the calculation scheme. 2. Reconstruction of the Pre-Glacial Alpine Topography
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012311 Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart Figure DR1: Flow chart of the algorithm to further clarify the calculation scheme. 2. Reconstruction of the Pre-Glacial Alpine Topography
Correction of Ocean-Bottom Seismometer Instrumental Clock Errors Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 1276 1288, June 214, doi: 1.1785/1213157 Correction of Ocean-Bottom Seismometer Instrumental Clock Errors Using Ambient Seismic Noise
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 1276 1288, June 214, doi: 1.1785/1213157 Correction of Ocean-Bottom Seismometer Instrumental Clock Errors Using Ambient Seismic Noise
INVSP gathers of local earthquake seismograms: an approach for modelling the upper crustal P and S velocity structure
 Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 166, 148 154 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03008.x FAST TRACK PAPER INVSP gathers of local earthquake seismograms: an approach for modelling the upper crustal P and S velocity structure
Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 166, 148 154 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03008.x FAST TRACK PAPER INVSP gathers of local earthquake seismograms: an approach for modelling the upper crustal P and S velocity structure
Mathematics of Seismic Imaging Part 1: Modeling and Inverse Problems
 Mathematics of Seismic Imaging Part 1: Modeling and Inverse Problems William W. Symes Rice University 0. Introduction How do you turn lots of this... 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 (field seismogram
Mathematics of Seismic Imaging Part 1: Modeling and Inverse Problems William W. Symes Rice University 0. Introduction How do you turn lots of this... 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 (field seismogram
Probing Mid-Mantle Heterogeneity Using PKP Coda Waves
 Probing Mid-Mantle Heterogeneity Using PKP Coda Waves Michael A.H. Hedlin and Peter M. Shearer Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
Probing Mid-Mantle Heterogeneity Using PKP Coda Waves Michael A.H. Hedlin and Peter M. Shearer Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
Th P7 02 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling
 Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
TOM 1.7. Sparse Norm Reflection Tomography for Handling Velocity Ambiguities
 SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
Anisotropic anelastic seismic full waveform modeling and inversion: Application to North Sea offset VSP data
 CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS DOI: https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2018.3.149-153 Anisotropic anelastic seismic full waveform modeling and inversion: Application to North Sea offset VSP data C. Barnes 1, M. Charara
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS DOI: https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2018.3.149-153 Anisotropic anelastic seismic full waveform modeling and inversion: Application to North Sea offset VSP data C. Barnes 1, M. Charara
MODELING OF WIDE-ANGLE SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES USING THE GAUSSIAN BEAM METHOD
 MODELING OF WIDE-ANGLE SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES USING THE GAUSSIAN BEAM METHOD STEPHEN M. STACY 1 AND ROBERT L. NOWACK 2 ABSTRACT In this study, observed seismic attributes from shot gather 11 of the SAREX experiment
MODELING OF WIDE-ANGLE SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES USING THE GAUSSIAN BEAM METHOD STEPHEN M. STACY 1 AND ROBERT L. NOWACK 2 ABSTRACT In this study, observed seismic attributes from shot gather 11 of the SAREX experiment
Imaging Moho topography beneath the Alps by multdisciplinary seismic tomography
 Imaging Moho topography beneath the Alps by multdisciplinary seismic tomography Edi Kissling ETH Zürich SPP short course February 1+2, 218, Berlin, Germany Alpine Moho map from CSS Moho uncertainty derived
Imaging Moho topography beneath the Alps by multdisciplinary seismic tomography Edi Kissling ETH Zürich SPP short course February 1+2, 218, Berlin, Germany Alpine Moho map from CSS Moho uncertainty derived
Combined tomographic forward and inverse modeling of active seismic refraction profiling data
 Combined tomographic forward and inverse modeling of active seismic refraction profiling data 5 Ivan Koulakov (1) and Heidrun Kopp (2) 10 (1) Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics, SB RAS, Prospekt
Combined tomographic forward and inverse modeling of active seismic refraction profiling data 5 Ivan Koulakov (1) and Heidrun Kopp (2) 10 (1) Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics, SB RAS, Prospekt
Elastic impedance inversion from robust regression method
 Elastic impedance inversion from robust regression method Charles Prisca Samba 1, Liu Jiangping 1 1 Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics,China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074 Hubei, PR China
Elastic impedance inversion from robust regression method Charles Prisca Samba 1, Liu Jiangping 1 1 Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics,China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074 Hubei, PR China
2008 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
STRUCTURE OF THE KOREAN PENINSULA FROM WAVEFORM TRAVEL-TIME ANALYSIS Roland Gritto 1, Jacob E. Siegel 1, and Winston W. Chan 2 Array Information Technology 1 and Harris Corporation 2 Sponsored by Air Force
Multiple Scenario Inversion of Reflection Seismic Prestack Data
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 28, 2018 Multiple Scenario Inversion of Reflection Seismic Prestack Data Hansen, Thomas Mejer; Cordua, Knud Skou; Mosegaard, Klaus Publication date: 2013 Document Version
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 28, 2018 Multiple Scenario Inversion of Reflection Seismic Prestack Data Hansen, Thomas Mejer; Cordua, Knud Skou; Mosegaard, Klaus Publication date: 2013 Document Version
Summary. We present the results of the near-surface characterization for a 3D survey in thrust belt area in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates.
 Near-surface characterization, challenges, and solutions for high-density, high-productivity, Alexander Zarkhidze*, Claudio Strobbia, Abdallah Ibrahim, WesternGeco; Luis Viertel Herrera, Abdulla Al Qadi,
Near-surface characterization, challenges, and solutions for high-density, high-productivity, Alexander Zarkhidze*, Claudio Strobbia, Abdallah Ibrahim, WesternGeco; Luis Viertel Herrera, Abdulla Al Qadi,
3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie Zhang, Wei Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
Absolute strain determination from a calibrated seismic field experiment
 Absolute strain determination Absolute strain determination from a calibrated seismic field experiment David W. Eaton, Adam Pidlisecky, Robert J. Ferguson and Kevin W. Hall ABSTRACT The concepts of displacement
Absolute strain determination Absolute strain determination from a calibrated seismic field experiment David W. Eaton, Adam Pidlisecky, Robert J. Ferguson and Kevin W. Hall ABSTRACT The concepts of displacement
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS. Abstract
 ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
Seismogram Interpretation. Seismogram Interpretation
 Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters
 Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters Yunyue (Elita) Li and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Anisotropic models are recognized as more realistic representations of the subsurface where complex geological
Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters Yunyue (Elita) Li and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Anisotropic models are recognized as more realistic representations of the subsurface where complex geological
There is no pure P- or S-wave land seismic source André J.-M. Pugin*, Geological Survey of Canada, and Oz Yilmaz, Anatolian Geophysical
 There is no pure P- or S-wave land seismic source André J.-M. Pugin*, Geological Survey of Canada, and Oz Yilmaz, Anatolian Geophysical Summary: We conducted a field experiment at a soil site near Ottawa
There is no pure P- or S-wave land seismic source André J.-M. Pugin*, Geological Survey of Canada, and Oz Yilmaz, Anatolian Geophysical Summary: We conducted a field experiment at a soil site near Ottawa
The Improvement of 3D Traveltime Tomographic Inversion Method
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 5, No., 013, pp. 36-40 DOI:10.3968/j.aped.1955438013050.1368 ISSN 195-54X [Print] ISSN 195-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Improvement
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 5, No., 013, pp. 36-40 DOI:10.3968/j.aped.1955438013050.1368 ISSN 195-54X [Print] ISSN 195-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Improvement
Basic Ray Tracing. Rick Aster and Sue Bilek. October 3, 2003
 Basic Ray Tracing Rick Aster and Sue Bilek October 3, 3 A key observation that we can make about a seismic signal is its arrival time. From systematic observations of arrival times, we can deduce useful
Basic Ray Tracing Rick Aster and Sue Bilek October 3, 3 A key observation that we can make about a seismic signal is its arrival time. From systematic observations of arrival times, we can deduce useful
