Indication of the presence of metazoan fossils from the neo-proterozoics of indravati basin
|
|
|
- Eugene Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
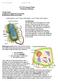
1 Volume: 2, Issue: 4, April e-issn: p-issn: Impact Factor: Amitanshu Shekhar Jha Assistant Professor Geology, Department of Geology, Govt P.G College V.S. Shettippnawar (I.F.S.) Conservator of Forest, Government of Chhattisgarh Apratim Jha (S.R.F.) SRF, Government Agriculture College Correspondence: Amitanshu Shekhar Jha Assistant Professor Geology, Department of Geology, Govt P.G College Indication of the presence of metazoan fossils from the neo-proterozoics of indravati basin Amitanshu Shekhar Jha, V.S. Shettippnawar (I.F.S.), Apratim Jha (S.R.F.) Abstract Abstract: This is the first report on the occurrence of the metazoan fossils from the NEO- PROTEROZOIC INDRAVATI GROUP of rocks in the Bastar District of Chhattisgarh State in central India. These Metazoan Fossils are of tubular morphology and occur as reef builders in the lime stones of Kanger Formation. Prior to this report, cynobacterial life forms represented by stromatolytes were the only known fossil occurrence within the Indravati Basin. The occurrence of Metazoan fossils indicate that the condition existed for the evolution of higher life forms during the later part of the Proterozoic in the region. Keywords: Neoproterozoic, Metazoa, Indravati, Group, Chattisgarh, Palaeontology 1. Introduction This is the first report on the occurrence of the metazoan fossils from the NEO- PROTEROZOIC INDRAVATI GROUP of rocks in the Bastar District of Chhattisgarh State in central India. These Metazoan Fossils are of tubular morphology and occur as reef builders in the lime stones of Kanger Formation. Prior to this report, cynobacterial life forms represented by stromatolytes were the only known fossil occurrence within the Indravati Basin. The occurrence of Metazoan fossils indicates that the condition existed for the evolution of higher life forms during the later part of the Proterozoic in the region. We speculate that the newly discovered fossils are from taxon coelenterate. Further study is in progress. Indravati Group occurs almost at the centre of an ensemble of Meso-to Neoproterozoic (1.8 to 0.5 Ga) platformal basins in the Peninsular India. Most of these intracratonic basins preserve multiple cycles of sedimentation of ortho quartzite, shale and carbonate suite of rocks, which have been slowly deposited in the shallow shelf environments over periods of millions of years. Vertical block movements along faulted margins guided configuration of individual basins of deposition.indravati Basin derives its name from the River Indravati flowing east to west through this group of rocks, most of which occur in the Bastar District in the southern Chhattisgarh and Koraput District in south western Orissa. We are not aware of any radiometric age from the sediments of the Indravati Basin. Ramakrishnan assumes conjecturally that Tirathgarh Formation at the base of Indravati Basin would date about 1400 Ma. Following Ramakrishnans assumption, Mainkar assumes that the Tokapal kimberlite eruption event between the periods of deposition of Kanger and Formation, would age about 1050Ma. Stromatolyte reef complexes have been reported from the Formation. Species of stromatolytes described include Gymnosolen, conophyton, Colonella, Tongussida (Baicalia, Anabaria) and Kussiellida. These stromatolytes probably represent an Upper Riphean assemblage ( Ma). Geological Survey of India (personal discussion with GSI geologists) commonly prefers to correlate the entire package of Indravati Group of rocks with the Upper Chhattisgarh Group of rocks in the adjoining Chhattisgarh Basin (figure 1a). Glauconitic sand stones at the base of Chhattisgarh Basin have returned K-Ar dates of Ma (personal communication, GSI). The Stromatolyte assemblage found in the Raipur Formation of Upper Chattisgarh Group of rocks is however known to represent Upper Riphean assemblage. Outcrops of fossiliferous lime stones were discovered by our team in the kanger valley 30 km south of at latitude N and longitude E in the southern part of Indravati Basin. These outcrops show extensive occurrence of reef forming tubular fossils Patchy outcrops of these fossiliferous lime stone having a bedding thickness of 5 or more, have been observed ~ 305 ~
2 to extend up to a couple of kilometers. Material and method: We have done detailed geological mapping of the kanger valley region and made several visits to collect insitu samples and consulted with several geologists. Result and discussion: These newly discovered fossils occur as clustered assemblages of hollow tubes, with diameters ranging from a few mm to 1.5 cm. Hallow tubes have layers of walls of silicified carbonate each wall is few mm in thickness. Mostly, the tubes occur in either single or in clusters. Another distinct feature of this fossil is the growth of concentric elliptical sheaths compressed at one end whereas marked gap in the other end. The inner most hollow tube generally has a circular cross section, but the sheaths surrounding the inner most tube could be elliptical. In cross sectional view the differential weathering can be seen as concentric ridges of siliceous carbonate tube alternating with depressed calcite filled intra-tubular space indicating that there may be presence of soft and hard parts of the specimen. The tubes and clusters of tubes appear to have grown generally upwards in different directions. Lower portion of the specimen is occupied by numerous small tubular bodies oriented in different directions. Preliminary observations suggest that these fossils are primitive sessile metazoans. Their well preserved simple, hollow tubular morphology suggests that they had firm skeletal support, which was calcified during early diagenesis. It appears that these sessile organisms grew in a tidal flat environment where rapid early carbonate cementation facilitated exceptionally good fossilization. The preliminary observation leads to the following speculations: 1) The circular to elliptical concentric sheaths around the bigger tubes appear to be fossilized exoskeleton of Cnidarians (Coelentrata). 2) The simple tubular body and the multi-tubular organization suggest that these fossils could be primitive coral and sponges of taxon.porifera. Small tube like structure visible (to the naked eye) between inter ridge portions around the hollow tube whether these features are internal transport system within organism is a topic of further study. Whether the concentric ring like layers surrounding the bigger tubes had helped in building up of the skeletal structure of the organism, and in between concentric calcareous sheaths was the tissue of the specimen. Spicules of Porifera have been reported from as old as Mesoproterozoic rocks of eastern Siberia. Neoproterozoic Porifera have been described from different parts of the world, e.g. Grand Canyon in Arizona, central Africa,Britain and Himalaya However, within the Precambrians,Cnidaria fossils apparently lacked mineralized skeleton needed to fossilize, and preservation was only in the form of impressions,unlike the fossils reported in this paper. Cnidarians with hard skeletons as in corals appear to proliferate only from the Cambrian age and younger. The reef built by these metazoan fossils in the Kanger Formation is also unique. the first metazoan reefs have only been described from the terminal Neoproterozoic (550 Ma), e.g. Nama Group of southern Namibia. The youngest speculated date from the Indravati Group is about 700 Ma!! Proterozoic rocks preserve varieties of flora and fauna. Cyanophyta (stromatolytes ) were the main life forms during Proterozoic. Evidences of more evolved organisms are also found in rocks even older than 900 million years. Metazoan fossils (Ediacarian biota ) found as impressions in Ediacaria hills of south Australia are 600 million years old. Similar fossils from the same age have been found in England and Wales (the Charnian Biota ), Africa, Russia and North America. A rich assemblage of the impressions of soft bodied Metazoans (multi cellular) was also discovered from the Late Precambrian rocks of south eastern Newfoundland, Canada. ~ 306 ~
3 Location Map Samples Collected From the Site ~ 307 ~
4 Two tubes of different dimensions are adjacent with each other the first tube has inner diameter 0.5 centimeter. whereas the large tube has diameter of 1.5 centimeter. ~ 308 ~
5 Conclusion: This is the first reported metazoan fossil from the Indravati basin. Trace fossils of dubious origins have been described from Semri Group of Vindhyan Super Group of rocks Recently Stromatolites deposited by cyanobacterian life forms are, however, quite commonly found in the Proterozoic. This significant find of metazoan fossils in the Indravati Basin proves that the conditions suitable for the growth of higher life forms existed during the Neo proterozoic. The state of preservation of these fossils appears to be exceptionally good. Assigning a definite taxonomic group or phyla to these metazoan fossils would require further detailed study. The authors are also trying to understand the growth environment of these metazoans and their conditions of fossilization in the limestone reefs of Kanger Formation. Acknowledgement: The authors express their gratitude to Biplob Chatterjee, Director Geowale services, Neeharika Jha, Director, Geological Survey of India for their kind support and guidance. Dr. Kantimati Kulkarni (Agarkar Institute of Palaeontology) has given valuable suggestions and information. Prachi awasthi deputy director ministry of minning chattisgarh. Basant Rath, Department of Geology, Government P.G.College, is acknowledgwed for his help during field work.the authors also would like to thanks to Prof.R.C.Joshi H.O.D.Geology,Govt.P.G.College, for their support in writing this paper. References 1. Ramakrishnan,M., Stratigraphy, sedimentary environment and evolution of the Late Proterozoic Indravati Basin, Central India, Memoir J Geol Soc Ind,1987, Vol 6,pp Mainkar,D., Lehman,B., Haggerthy, SE., The craterfacies kimberlite system of Tokapal, Bastar District, Chattisgarh, India, Lithos, 2004, Vol 76,Issue 7-8,pp Geological Mao of India- 1:2 million, The Geological Survey of India, Crookshank, H., Geology of southern Bastar and Jeypore from the Bailadila to the Eastern Ghats, Geol. Surv. Ind. Mem., 1963, V Wood, R, The ecological evolution of reefs, Annu. Rev.Ecol.Syst., 1998, v 29,pp Schnitzer W.A. E. Flugel (Ed)- Fossil Algae, Heidelberg, 1977,pp Gathania R.C., Ahlulavalia A.R. and Gupta, V.J., Stromatolytes from Indravati Group, Orissa, Res Bull (Sci), Punjab University, 1983, V 111, p Walter, M.R.,Stromatolytes, Elsevier,Amsterdam,1976,p Pinna,G., The illustrated Encyclopedia of fossils facts on file, 1990,pp ~ 309 ~
Shield was above sea-level during the Cambrian and provided the sediment for the basins.
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #8, Winter 2014 Platforms and Paleozoic life-forms Lab day: Tu W Th 1. Schematic geologic cross-sections A-B and C-D (shown below) cross the edge of the continental platform
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
11/5/2015. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. The Geologic Time Scale
 GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
Welcome to General Geology!!
 Welcome to General Geology!! Professor Weeden: lori_weeden@uml.edu x3344 Olney 402B Class webpage: http://faculty.uml.edu/lweeden/gengeo.htm Text: Murck, BW & Skinner, BJ (2012) Visualizing Geology 3 rd
Welcome to General Geology!! Professor Weeden: lori_weeden@uml.edu x3344 Olney 402B Class webpage: http://faculty.uml.edu/lweeden/gengeo.htm Text: Murck, BW & Skinner, BJ (2012) Visualizing Geology 3 rd
CHAPTER 3 GEOLOGY OF INDRAVATI BASIN
 CHAPTER 3 GEOLOGY OF INDRAVATI BASIN CHAPTER3 GEOLOGY OF INDRAVATI BASIN 3.1 GEOLOGY OF THE INDRAVATI BASIN - HISTORICAL ACCOUNT Neoproterozoic intracratonic lndravati basin covers an area of about 9000
CHAPTER 3 GEOLOGY OF INDRAVATI BASIN CHAPTER3 GEOLOGY OF INDRAVATI BASIN 3.1 GEOLOGY OF THE INDRAVATI BASIN - HISTORICAL ACCOUNT Neoproterozoic intracratonic lndravati basin covers an area of about 9000
Geology Test Review Answers
 Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
6/30/2018. Geologic Time. Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Geologic Time Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time The Importance of a Time Scale Interpreting Earth s history is an important goal of the science of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Geologic Time Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time The Importance of a Time Scale Interpreting Earth s history is an important goal of the science of
geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years
 Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
ENVI.2030L Geologic Time
 Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Laboratory 7 Geologic Time
 (Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
(Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
Objectives. Vocabulary. Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch.
 The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Relative Age-dating -- Discovery of Important Stratigraphic Principles
 Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmaredu Abstract: When piecing together the geologic history of the Earth, geologists
Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmaredu Abstract: When piecing together the geologic history of the Earth, geologists
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1:
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lecture 24: Paleozoic 1: Laurentia Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time (before the exam) The Cambrian Explosion A) Why a Cambrian explosion B)
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon
 Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Ch. 12 Proterozoic Eon Proterozoic Eon is ~ 1.95 billion years in duration, from 2.5 Ga to 0.543 Ga 2.5 Ga 1.6 Ga 1.0 Ga 0.54 Ga Paleoproterozoic Era Mesoproterozoic Era Neoproterozoic Era PROTEROZOIC
Field Trip 1 Tunnel Mill, Vernon, Indiana: Waldron Shale
 Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Field Trip 1 Tunnel Mill, Vernon, Indiana: Waldron Shale On this trip we will visit Tunnel Mill, which is located just south of Vernon, Indiana in the
Geol G308 Paleontology and Geology of Indiana Name: Field Trip 1 Tunnel Mill, Vernon, Indiana: Waldron Shale On this trip we will visit Tunnel Mill, which is located just south of Vernon, Indiana in the
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks
 Earth Sciences 083F Plate Tectonics Exercises Plate tectonics is a model for the dynamic behaviour of Earth s lithosphere. Outlining stable areas of lithosphere are narrow zones (plate boundaries) in which
Earth Sciences 083F Plate Tectonics Exercises Plate tectonics is a model for the dynamic behaviour of Earth s lithosphere. Outlining stable areas of lithosphere are narrow zones (plate boundaries) in which
GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 Lecture Goals: A) Eukaryote Life forms (Acritarchs) B) Metazoans (Ediacaran Fauna) GY 112 Lecture Notes Proterozoic Life forms Textbook reference: Levin 7 th edition
Page 1. Name:
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Geologic Change over Time. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit S15-1211-01 A.M. MONDAY, 11 May 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 15 2. 14 Mark Awarded
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY GL1 Foundation Unit S15-1211-01 A.M. MONDAY, 11 May 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 15 2. 14 Mark Awarded
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
GEOLOGIC TIME. Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS
 GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Name. GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps. I. Properties of Earth Materials
 I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating)
 Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating) Use the following sketch of a geological cross section to answer questions 1 to 3. 1. The most important principle used to determine the
Answers to Section G: Time and the Fossil Record (Relative Dating) Use the following sketch of a geological cross section to answer questions 1 to 3. 1. The most important principle used to determine the
Geological History of the Grand Canyon
 Geological History of the Grand Canyon For a copy of this assignment, print a copy of this web page. The Project Your job is to write a short paper that describes the geological history of the Grand Canyon
Geological History of the Grand Canyon For a copy of this assignment, print a copy of this web page. The Project Your job is to write a short paper that describes the geological history of the Grand Canyon
Ediacaria and Hiemalora - Disc-like Attachments. of Benthic Organisms from the White Sea and. Arctic Siberia (Russia)
 Ediacaria and Hiemalora - Disc-like Attachments of Benthic Organisms from the White Sea and Arctic Siberia (Russia) E. A. Serezhnikova Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, 123 Profsoyuznaya,
Ediacaria and Hiemalora - Disc-like Attachments of Benthic Organisms from the White Sea and Arctic Siberia (Russia) E. A. Serezhnikova Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, 123 Profsoyuznaya,
GY 112L: Earth History Lab
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112L: Earth History Lab Week 11 Paleozoic Part 2 Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Today s Agenda The Paleozoic Part 2 (Lab 8 exercises) 1) Sponges & Stromatoporoids 2)
Stromatoporoids around the Georgetown, Kentucky area
 Stromatoporoids around the Georgetown, Kentucky area If you have ever visited and / or travelled around the area of Georgetown, Scott County, Kentucky you might have noted white watermelon shaped rocks
Stromatoporoids around the Georgetown, Kentucky area If you have ever visited and / or travelled around the area of Georgetown, Scott County, Kentucky you might have noted white watermelon shaped rocks
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois
 Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois Primary objectives for this fieldtrip 1) Collect and identify the fossils of the Racine Reef Complex. 2) Discuss procedures for collecting fossil
Field trip to Racine Reef Complex, Thornton Quarry, Illinois Primary objectives for this fieldtrip 1) Collect and identify the fossils of the Racine Reef Complex. 2) Discuss procedures for collecting fossil
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
FOR Sand Stone Quarry Village : Chhirraleva Tehsil : Basna District : Mahasamund
 Project Report FOR Sand Stone Quarry at Village : Chhirraleva Tehsil : Basna District : Mahasamund Contents 1. About the Firm... 1 2. Location of the Project... 1 3. Environmental Setting of Project...
Project Report FOR Sand Stone Quarry at Village : Chhirraleva Tehsil : Basna District : Mahasamund Contents 1. About the Firm... 1 2. Location of the Project... 1 3. Environmental Setting of Project...
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers. Rocks. Year 8 Science Chapter 8
 Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Relative Age-dating -- Discovery of Important Stratigraphic Principles Y
 R Steinberg DMC/4-08 EARTH HISTORY 1404 Example 1: Y S P Q Four different rock units (layers of different rock types), labeled Y, S, P, and Q, are seen in a road cut, as shown schematically above: 1) Are
R Steinberg DMC/4-08 EARTH HISTORY 1404 Example 1: Y S P Q Four different rock units (layers of different rock types), labeled Y, S, P, and Q, are seen in a road cut, as shown schematically above: 1) Are
TRACE FOSSIL FOSSIL ICE CORE RELATIVE DATING SUPERPOSITION ABSOLUTE DATING GEOLOGIC COLUMN UNIFORMITARIANISM HALF-LIFE RADIOACTIVE DECAY
 THIS IS NOT THE SAME TEST. YOU MUST ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. NAME: Bubble the circle below U3L1 Write the letter next to the vocab term VOCAB MATCH 1 A. O B. O C. O D. O 1 2 A. O B. O C. O D. O 2 3 A. O B.
THIS IS NOT THE SAME TEST. YOU MUST ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. NAME: Bubble the circle below U3L1 Write the letter next to the vocab term VOCAB MATCH 1 A. O B. O C. O D. O 1 2 A. O B. O C. O D. O 2 3 A. O B.
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Geology and Geomorphology. Unit title: Unit code: F3SL 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Geology and Geomorphology Unit code: F3SL 34 Unit purpose: This Unit provides an introduction to geology and geomorphology.
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Geology and Geomorphology Unit code: F3SL 34 Unit purpose: This Unit provides an introduction to geology and geomorphology.
Geologic History. Earth is very, very old
 Geologic History Earth is very, very old Earth s History The history of Earth and the ages of rocks can be investigated and understood by studying rocks and fossils. Evidence of ancient, often extinct
Geologic History Earth is very, very old Earth s History The history of Earth and the ages of rocks can be investigated and understood by studying rocks and fossils. Evidence of ancient, often extinct
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
The Welsh Borderland. Geologically recent surface deposits. The Welsh Borderland
 The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?
![3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? 3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?](/thumbs/89/98260180.jpg) Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Name: Date: Period: Page 1
 Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
Comparative Taphonomy of the Vendian Genera. Beltanelloides and Nemiana as a Key to their True. Nature
 Comparative Taphonomy of the Vendian Genera Beltanelloides and Nemiana as a Key to their True Nature M. V. Leonov Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Science, 123 Profsoyuznaya, Moscow, 117868,
Comparative Taphonomy of the Vendian Genera Beltanelloides and Nemiana as a Key to their True Nature M. V. Leonov Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Science, 123 Profsoyuznaya, Moscow, 117868,
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Geologic Time. Decoding the Age of our Planet & North Carolina
 Geologic Time Decoding the Age of our Planet & North Carolina The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era,
Geologic Time Decoding the Age of our Planet & North Carolina The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, Lobster Lake, Maine. Text by Robert G. Marvinney. Maine Geological Survey
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, 1998 Lobster Lake, Maine 45 o 51 7.91 N, 69 o 30 53.88 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Introduction
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities October, 1998 Lobster Lake, Maine 45 o 51 7.91 N, 69 o 30 53.88 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Introduction
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 4 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
2/13/17. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination
 A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
Principles of Geology
 Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores
 Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
2/5/17. #7 Geologic Time #7 Geologic Time
 #7 #7 = all of time since Earth formed (4.6 billion years ago, b.y.a.). Geologists study rocks, fossils, geologic structures (faults, folds) to characterize Earth's history. Natural disasters involve present-day.
#7 #7 = all of time since Earth formed (4.6 billion years ago, b.y.a.). Geologists study rocks, fossils, geologic structures (faults, folds) to characterize Earth's history. Natural disasters involve present-day.
Earth History Exam. The remains of an early dinosaur could be found at reference point A. A B. B C. C D. D. page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables and your knowledge of Earth science. The accompanying cross section shows undisturbed sedimentary bedrock.
Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the Earth Science Reference Tables and your knowledge of Earth science. The accompanying cross section shows undisturbed sedimentary bedrock.
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14. Essentials of Geology, 8e. Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College
 The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources. Chapters 5 & 6
 Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources Chapters 5 & 6 How Do Fossils Form? Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks like sandstone, limestone, and shale In Virginia, most
Fossils, Geologic Time, Absolute & Relative Dating, and Natural Resources Chapters 5 & 6 How Do Fossils Form? Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks like sandstone, limestone, and shale In Virginia, most
State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks.
 Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks & Minerals Activity 1: Geologic Time
 Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES. Loulousis
 CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES Loulousis Bellringer What are 5 visual clues that help you determine if someone is older or younger than you? Color of hair Wrinkles in
CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES Loulousis Bellringer What are 5 visual clues that help you determine if someone is older or younger than you? Color of hair Wrinkles in
Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other.
 FOSS Earth History Course Glossary (10-4-04) Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other. Absolute age: The exact age of an object (such as a rock or artifact); found
FOSS Earth History Course Glossary (10-4-04) Abrasion: The physical weathering of rocks by particles rubbing against each other. Absolute age: The exact age of an object (such as a rock or artifact); found
Michigan s Geology and Groundwater
 Michigan s Geology and Groundwater Ralph J. Haefner Deputy Director U.S. Geological Survey Michigan-Ohio Water Science Center Lansing, Michigan Outline About the USGS Geology 101 Michigan s geology Bedrock
Michigan s Geology and Groundwater Ralph J. Haefner Deputy Director U.S. Geological Survey Michigan-Ohio Water Science Center Lansing, Michigan Outline About the USGS Geology 101 Michigan s geology Bedrock
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Lecture Outline Friday Feb. 21 Wednesday Feb. 28, 2018 Questions? Key Points for today What are the 5 relative age dating principles and how do you apply the principles to determine a geologic history
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks
 The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
6. Relative and Absolute Dating
 6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Upper Ordovician reefs in the Hudson Bay Basin: Porosity evolution and hydrocarbon charge
 Upper Ordovician reefs in the Hudson Bay Basin: Porosity evolution and hydrocarbon charge Denis Lavoie 1, Ariane Castagner 2, Omid Haeri Ardakani 3, André Desrochers 2 1 Geological Survey of Canada, Québec
Upper Ordovician reefs in the Hudson Bay Basin: Porosity evolution and hydrocarbon charge Denis Lavoie 1, Ariane Castagner 2, Omid Haeri Ardakani 3, André Desrochers 2 1 Geological Survey of Canada, Québec
Chapter 8 TIMING THE GEOLOGIC RECORD
 Chapter 8 Fossils (cont.): Petrified Forest, Arizona. These ancient logs are millions of years old. Their substance was completely replaced by silica, which preserved all the original details of form.
Chapter 8 Fossils (cont.): Petrified Forest, Arizona. These ancient logs are millions of years old. Their substance was completely replaced by silica, which preserved all the original details of form.
November 3, SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers.
 Aims: November 3, 2016 SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent
Aims: November 3, 2016 SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Ordovician. System. Cambrian. System
 443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
443 495 543 Late Middle Early Late Middle Early Ordovician System Cambrian System Earth History, Ch. 13 1 Ch. 13 Review: Early Paleozoic life & Burgess Shale fauna Most animal phyla originated in Cambrian;
GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Geology Assignment. DUE: Mon. Sept. 19
 GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Geology Assignment DUE: Mon. Sept. 19 Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition:
GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Geology Assignment DUE: Mon. Sept. 19 Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition:
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically
 Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
SPECIALIST GEOLOGY SERVICES
 SPECIALIST GEOLOGY SERVICES rpsgroup.com/energy RPS ENERGY an independent global energy consultancy RPS Energy is part of RPS Group which has been listed on the main London Stock Exchange since 1995. It
SPECIALIST GEOLOGY SERVICES rpsgroup.com/energy RPS ENERGY an independent global energy consultancy RPS Energy is part of RPS Group which has been listed on the main London Stock Exchange since 1995. It
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17
 Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Massive cross-bedded sandstone strata in Mt Zion USA (courtesy of Lawrie Davidson)
 Sedimentary rocks are formed from clasts (broken pieces) of earlier rock and organic material. They are the product of weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation. 1. Sedimentary strata
Sedimentary rocks are formed from clasts (broken pieces) of earlier rock and organic material. They are the product of weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation. 1. Sedimentary strata
Anthill Resources Yukon - An Update on the Einarson Project
 Anthill Resources Yukon - An Update on the Einarson Project The Eastern Extension of a Carlin-type Gold Trend in the Selwyn Basin Anthill Resources Ltd Yukon Claim Holdings Over 2400 km 2 Property Location
Anthill Resources Yukon - An Update on the Einarson Project The Eastern Extension of a Carlin-type Gold Trend in the Selwyn Basin Anthill Resources Ltd Yukon Claim Holdings Over 2400 km 2 Property Location
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
Timing of Geologic Events. Geologic Time Terms. Laws / Principles of Stratigraphy
 Geologic Time Terms Hadean Archean Proterozoic Phanerozoic Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic(Tertiary) Cambrian Unconformity Angular unconformity Half-life Alpha particle Beta particle Gamma ray Neutron UT How
Geologic Time Terms Hadean Archean Proterozoic Phanerozoic Paleozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic(Tertiary) Cambrian Unconformity Angular unconformity Half-life Alpha particle Beta particle Gamma ray Neutron UT How
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Key Concepts Determining geological ages
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Superposition and horizontality tell stories in rocks. Key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Superposition and horizontality tell stories in rocks. Key
