Relative Age-dating -- Discovery of Important Stratigraphic Principles
|
|
|
- Jemima Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX Abstract: When piecing together the geologic history of the Earth, geologists rely on several key relative age-dating principles that allow us to determine the relative ages of rocks and the timing of significant geologic events In a typical Historical Geology class or textbook, instructors/authors briefly discuss the important early researchers in the geological sciences, and then give the name of the stratigraphic principle, useful for relative age-dating of rocks and events, that these 17th and 18th century scientists are credited with discovering After the instructor/author defines these principles, students are usually shown several examples so they can see how the principle can be applied But why not start with the examples and let students discover these principles for themselves? Students are split into small groups which each work to discover a different relative agedating principle The groups are shown photos and given the following handout with drawings of rock outcrops illustrating the various principles This handout includes worksheets for which they must answer a series of prompts that help lead them to the discovery of their relative age-dating principle Groups must also invent a name for their principle, and select a spokesperson who will present the group s results to the rest of the class Note: The simple classroom demonstration by your instructor of the deposition of sediments referred to in Example 1 and Example 2 utilizes a large graduated cylinder filled with water and sediment ranging in size from gravel to clay I shake it up and then set it down quickly on the front table, so students can see how sediment will actually settle out of water in flat-lying layers--larger, heavier particles first--parallel to the Earth s surface and parallel to each other
2 R Steinberg DMC/4-08 EARTH HISTORY 1404 Example 1: Y S P Q Four different rock units (layers of different rock types), labeled Y, S, P, and Q, are seen in a road cut, as shown schematically above: 1) Are the rocks igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic? (Which?) 2) S and Q are the same kind of rock called (Example: Granite, marble, limestone, etc) 3) Y is the rock type called 4) P is the rock type called (Think carefully about the simple classroom demonstration by your instructor of the deposition of sediments) 5) Which rock layer in Example 1 above is oldest? 6) Which rock layer in Example 1 above is youngest? 7) List all four of the rock units of Example 1 in chronologic sequence, with the oldest on the bottom (Geologists always order rock units and events with the oldest on the bottom and the youngest on the top) Youngest Oldest 8) This example illustrates one of the most fundamental and useful principles for relative age-dating of rocks Describe and invent a name for the general principle useful in relative age-dating that is represented here:
3 Page 2 Example 2: T N L R Four different rock units (different rock types) are seen in a road cut and labeled T, N, L, R: 1) Are the rocks igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic? 2) Give a more specific identification (name) for all of the layers: T (Example: Granite, marble, limestone, etc) N L R (Think carefully about the simple classroom demonstration by your instructor of the deposition of sediments) 3) Do you think that when the layers in this example formed, they were already tilted? If not, when would the tilting (or deformation, a type of geologic event) have occurred, relative to their formation? 4) Which rock layer is oldest? 5) Which rock layer is youngest? 6) List all four of the rock units in chronologic sequence, with the oldest on the bottom (Geologists always order rock units and events with the oldest on the bottom and the youngest on the top) Include "Deformation" in its correct chronologic position, relative to the rock layers T, N, L, and R Youngest Oldest 7) Describe and invent a name for the general principle (or principles) useful in relative age-dating represented by this example:
4 Example 3a: Page 3 The Grand Canyon is a spectacular example of the erosive power of rivers The Canyon stretches for almost 100 miles in northern Arizona, and is one mile deep in some places The walls of the Grand Canyon exhibit an exceptionally wellexposed sequence of sedimentary rocks These are extremely useful when illustrating the remarkable geologic history of the Colorado Plateau, as well as various stratigraphic principles and geologic history in general Note in the cross section of the Grand Canyon, on the next page, that similar rocks (same age, thickness, and rock type) can be seen on both the North Rim and the South Rim, with a very large gap (many miles wide) in between 1) What used to be where the gap is now? 2) What, in general, caused the gap to form? Example 3b: Now, consider another example, closer to home (a thought experiment): You are driving in the Hill Country, heading NW along Interstate 10, just west of San Antonio As you zoom along, you notice a very distinct sequence of sedimentary rocks on your right (East) You glance to the rocky roadcut on the left (West) side of the highway and quickly note the same distinctive sequence of rocks 3) What used to be where the large highway road cut (you are driving through) is now? 4) What, in general, caused the gap (road cut) to form? 5) Describe and invent a name for the general principle useful in relative age-dating represented by these two examples: (Hint: What could you infer about the rocks on the North Rim of the Grand Canyon if you only knew details about the South Rim rocks, such as age, thickness, and rock type of the various layers?)
5 Page 4 Grand Canyon Cross Section page (Couldn t be included in this format-- can be found as pdf in Supporting Materials file)
6 Example 4a: Z R Two different rock units (of different rock types) are seen in a road cut: 1) Describe what you see: 2) What kind of rock is represented by Z? (Example: Granite, marble, limestone, etc) 3) What kind of rock is represented by R? 4) What kind of rock are the small pieces? 5) What do you think is represented by the uneven line of contact between the two different rock types? Page 5 6) Would your thoughts change if you examined this contact and were able to detect a thin layer of shale exactly at the contact, and realized it was probably an ancient soil layer? Example 4b: The two examples below show the same general rule for relative age relationships as illustrated by Example 4a above: 1 2 Example 1 is very similar to the Example 4a above The contact between the two different rock types exhibits an ancient, well-preserved soil layer Example 2 shows an igneous intrusion that has intruded up and into overlying layers of shale 7) Describe and invent a name for the general principle useful in relative age-dating that is represented by these examples: (Hint: Consider, in particular, the relative age of the small pieces of rock that appear to be included within a different rock type in all of the examples)
7 Page 6 Example 5a: A B Two different rock units (of different rock type) are seen in a road cut: 1) The rock unit labeled 'A' is a type of sedimentary rock called 2) The rock unit labeled 'B' is an igneous intrusion called a (it cuts across overlying layers) 3) Describe what you see: 4) Which rock unit, A or B, is older? 5) Why? Example 5b: In this next example, there are three kinds of sedimentary rocks: 6) (rock type) 7) (rock type) 8) (rock type) 9) What kind of geologic feature curves from the top of the diagram to the bottom? 10) What are the relative ages of the rocks compared to this feature? 11) Why? 12) These two examples illustrate one of the most fundamental and useful principles for relative age-dating Describe and invent a name for the general principle that is represented by both Example 5a and 5b:
Relative Age-dating -- Discovery of Important Stratigraphic Principles Y
 R Steinberg DMC/4-08 EARTH HISTORY 1404 Example 1: Y S P Q Four different rock units (layers of different rock types), labeled Y, S, P, and Q, are seen in a road cut, as shown schematically above: 1) Are
R Steinberg DMC/4-08 EARTH HISTORY 1404 Example 1: Y S P Q Four different rock units (layers of different rock types), labeled Y, S, P, and Q, are seen in a road cut, as shown schematically above: 1) Are
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Lab 4: Structures and Geologic Maps
 Key Questions: GEOL 1311 Earth Science Lab 4 Structures and Geologic Maps What shapes do rock bodies take in the Earth? How do two-dimensional visualizations of the Earth, such as maps and cross-sections
Key Questions: GEOL 1311 Earth Science Lab 4 Structures and Geologic Maps What shapes do rock bodies take in the Earth? How do two-dimensional visualizations of the Earth, such as maps and cross-sections
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012
 1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
ENVI.2030L Geologic Time
 Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
Geology Test Review Answers
 Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
3. Bedrock from which entire geologic time period is missing between rock units 5 and 6? The fault most likely occurred after
 Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE
 GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmar.edu For the maps accompanying
GEOLOGIC MAPS AND GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES A TEXAS EXAMPLE Roger Steinberg Assistant Professor of Geology Del Mar College 101 Baldwin Corpus Christi, TX 78404 361-698-1665 rsteinb@delmar.edu For the maps accompanying
Name Geo 4 Practice Match the principle on the left (column A) with the definition (or part of the definition) on the right (column B).
 Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
The Rocky Road Game. Sedimentary Rock. Igneous Rock. Start. Metamorphic Rock. Finish. Zone of Transportation. Weathering Way.
 Sedimentary Rock Deposition Depot Zone of Transportation Transported: Advance 3 Weathering Way The Rocky Road Game Uplift: Advance 5 Lithification Lane Crystallization Crossway Submerge Detour take the
Sedimentary Rock Deposition Depot Zone of Transportation Transported: Advance 3 Weathering Way The Rocky Road Game Uplift: Advance 5 Lithification Lane Crystallization Crossway Submerge Detour take the
Part 1: Observations for the Edwards Formation
 Name: Spring 2018 Professor name: Class Time: The Virtual Field trip is to be completed by your self. You should not work with a partner. This is not group work. Nor should you search for answers on the
Name: Spring 2018 Professor name: Class Time: The Virtual Field trip is to be completed by your self. You should not work with a partner. This is not group work. Nor should you search for answers on the
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore BEDRO CK For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore BEDRO CK For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Science 20. Unit C: The Changing Earth. Assignment Booklet C1
 Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment Booklet C FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter Assignment Total Possible Marks 60 Your Mark Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment
Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment Booklet C FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter Assignment Total Possible Marks 60 Your Mark Science 20 Unit C: The Changing Earth Assignment
Principles of Geology
 Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Deep Time: How Old Is Old?
 Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers. Rocks. Year 8 Science Chapter 8
 Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Questions for the Edwards formation
 Name: Professor name: Class Time: The Virtual Field trip is to be completed by your self. You should not work with a partner. This is not group work. Nor should you search for answers on the internet.
Name: Professor name: Class Time: The Virtual Field trip is to be completed by your self. You should not work with a partner. This is not group work. Nor should you search for answers on the internet.
Big News About Old Rocks
 Non-fiction: Big News About Old Rocks Big News About Old Rocks Grand Old Canyon Rocks reveal new clues to a complicated history. Some small rocks from Arizona s Grand Canyon recently led scientists to
Non-fiction: Big News About Old Rocks Big News About Old Rocks Grand Old Canyon Rocks reveal new clues to a complicated history. Some small rocks from Arizona s Grand Canyon recently led scientists to
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities
 Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
Science 2015 Earth Science. Study Guide
 Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Determining geological ages
 Determining geological ages Relative ages placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. Absolute dates define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event.
Determining geological ages Relative ages placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. Absolute dates define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event.
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
Page 1. Name:
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
8. GEOLOGIC TIME LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
Part I. PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts:
 Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Student Name: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory #13 Structural Geology II Drawing and Analyzing Folds and Faults Grade: Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units
Version Date 6/26/17. Disciplinary Core Ideas (Framework)
 1 Earth Is Rock 1 What's the Story of This Place? Students consider the history of Earth and begin to think about rock and landforms as a source of for Earth s past. An Earth tour provides a sense of the
1 Earth Is Rock 1 What's the Story of This Place? Students consider the history of Earth and begin to think about rock and landforms as a source of for Earth s past. An Earth tour provides a sense of the
Relative Dating. The Rock Cycle. Key Concept Scientists can interpret the sequence of events in Earth s history by studying rock layers.
 2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
Geologic Time. Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann
 Geologic Time Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann Procedure Plate tectonics Classroom activity #1 What is geologic time? Relative age dating Absolute age dating Classroom activity #2 T C What is
Geologic Time Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann Procedure Plate tectonics Classroom activity #1 What is geologic time? Relative age dating Absolute age dating Classroom activity #2 T C What is
Relative Dating Exercises
 Laboratory 1 Relative Dating Exercises Pamela J. W. Gore Department of Geology, Georgia Perimeter College Clarkston, GA 30021 Copyright 1998-2005 Pamela J. W. Gore Examine the geologic cross sections which
Laboratory 1 Relative Dating Exercises Pamela J. W. Gore Department of Geology, Georgia Perimeter College Clarkston, GA 30021 Copyright 1998-2005 Pamela J. W. Gore Examine the geologic cross sections which
The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks & Minerals Activity 1: Geologic Time
 Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Geologic Time
 Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Geologic Time Name: Refer to the Geologic Time Lab for the information you need to complete this worksheet (http://commons.wvc.edu/rdawes/g101ocl/labs/geotimelab.html). All calculations
Geology 101 Lab Worksheet: Geologic Time Name: Refer to the Geologic Time Lab for the information you need to complete this worksheet (http://commons.wvc.edu/rdawes/g101ocl/labs/geotimelab.html). All calculations
Section 5. Rock Units and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES
 DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
FOSS LANDFORMS 8/1/2012. Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams. Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science
 8/1/2012 Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science FOSS LANDFORMS Photo by Joanne Johnson Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams Learning Progression Landforms Prerequisite
8/1/2012 Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science FOSS LANDFORMS Photo by Joanne Johnson Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams Learning Progression Landforms Prerequisite
GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES
 DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson
 Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson Introduction: It isn't possible to bring all of outdoors into the classroom, and stratigraphic
Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson Introduction: It isn't possible to bring all of outdoors into the classroom, and stratigraphic
9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES
 LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES Your work will be graded on the basis of its accuracy, completion, clarity, neatness, legibility, and correct spelling of
LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES Your work will be graded on the basis of its accuracy, completion, clarity, neatness, legibility, and correct spelling of
II. Knowing and Understanding the Six Principles of Stratigraphy:
 Student Name(s): Physical Geology 101 Laboratory Relative Dating of Rocks Using Stratigraphic Principles Grade: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to learn and apply the concepts of
Student Name(s): Physical Geology 101 Laboratory Relative Dating of Rocks Using Stratigraphic Principles Grade: I. Introduction & Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to learn and apply the concepts of
GY 112L Earth History
 GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
Directed Reading page
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1D5NLH 1 Earth's crust is made of plates that move slowly. This movement changes the appearance of the Earth's crust
SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1D5NLH 1 Earth's crust is made of plates that move slowly. This movement changes the appearance of the Earth's crust
9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS
 LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS Refer to Laboratory 8 in your Lab Manual on pages 207-226 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your
LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS Refer to Laboratory 8 in your Lab Manual on pages 207-226 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your
Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock sequence!
 Mr. Sandomenico Welcome!!!! Today we will begin a new unit! The Earth s History!!!!! Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock
Mr. Sandomenico Welcome!!!! Today we will begin a new unit! The Earth s History!!!!! Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock
C E C U R R I C U L U M I E N S C B L E I T A. i N T E G R A T I N G A R T S i n O N A T I D U C B L I P U. Student Learning Objectives:
 We athering E Q U I T A B L E S C I E N C E C U R R I C U L U M Lesson 1 i N T E G R A T I N G A R T S i n P U B L I C E D U C A T I O N NGSS Science Standard: 4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns
We athering E Q U I T A B L E S C I E N C E C U R R I C U L U M Lesson 1 i N T E G R A T I N G A R T S i n P U B L I C E D U C A T I O N NGSS Science Standard: 4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns
Science. Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core. DUE: June 4, 2013
 Science Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core DUE: June 4, 2013 Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned
Science Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core DUE: June 4, 2013 Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
UNCONFORMITY. Commonly four types of unconformities are distinguished by geologists: a) Disconformity (Parallel Unconformity)
 UNCONFORMITY Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea level variations. They are a feature of stratified rocks, and are therefore
UNCONFORMITY Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea level variations. They are a feature of stratified rocks, and are therefore
STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY LABORATORY
 Structural Geology Lab 1 STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY LABORATORY INTRODUCTION Geologists have named the structures found on the earth: flat lying strata, anticlines, synclines, faults. These can be exposed by a
Structural Geology Lab 1 STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY LABORATORY INTRODUCTION Geologists have named the structures found on the earth: flat lying strata, anticlines, synclines, faults. These can be exposed by a
Modeling the Rock Cycle
 P a g e 1 Name Modeling the Rock Cycle Background Information: Like the Earth itself, rocks are in a constant state of change. Rocks are solids made up of different minerals. Scientists usually classify
P a g e 1 Name Modeling the Rock Cycle Background Information: Like the Earth itself, rocks are in a constant state of change. Rocks are solids made up of different minerals. Scientists usually classify
Type of Exercise: In-Class Activity or Laboratory Exercise.
 Using Lava Flows & Volcanic Structures on Mars to Introduce the Concept of Relative Dating in Introductory Courses Audeliz Matias Skidmore College, Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 amatias@skidmore.edu Type
Using Lava Flows & Volcanic Structures on Mars to Introduce the Concept of Relative Dating in Introductory Courses Audeliz Matias Skidmore College, Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 amatias@skidmore.edu Type
Regents Earth Science
 Regents Earth Science Earth s History Name Section Rock Correlation Lab Lab# Introduction: The Cayuga Lake Basin contains one of the scenic Finger Lakes of central New York State. During the Devonian Period,
Regents Earth Science Earth s History Name Section Rock Correlation Lab Lab# Introduction: The Cayuga Lake Basin contains one of the scenic Finger Lakes of central New York State. During the Devonian Period,
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with
 Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks.
 Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
N30 E-45 SE S25 E-10 SW N85 W-80 NE
 Geologic aps and tructures Name Geology 100 Harbor section Read h. 7 before you begin. The objectives of this lab are for you to learn the basic geologic structures in 3- and to develop some facility in
Geologic aps and tructures Name Geology 100 Harbor section Read h. 7 before you begin. The objectives of this lab are for you to learn the basic geologic structures in 3- and to develop some facility in
November 3, SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers.
 Aims: November 3, 2016 SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent
Aims: November 3, 2016 SWABT interpret cross-sections with index fossils and unconformities to determine relative ages of rock layers. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent
PENNSYLVANIA. Ordinary processes at Earth's surface and just below it cause rocks to change and soils to form. Page 1 of 3. S8.A.1.1.
 Know: Understand: Do: S8.D.1.1.1 -- Essential Explain the rock cycle as changes in the solid earth and rock types found in Pennsylvania (igneous - granite, basalt, obsidian, pumice, ; sedimentary - limestone,
Know: Understand: Do: S8.D.1.1.1 -- Essential Explain the rock cycle as changes in the solid earth and rock types found in Pennsylvania (igneous - granite, basalt, obsidian, pumice, ; sedimentary - limestone,
S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition
 S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition c. Classify rocks by their process of formation d. Describe
S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition c. Classify rocks by their process of formation d. Describe
2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 An Introduction to Geology Earth, 10e - Chapter 1 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College 3 The Science of Geology Geology is the science that pursues an understanding of planet Earth. Physical geology
1 An Introduction to Geology Earth, 10e - Chapter 1 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College 3 The Science of Geology Geology is the science that pursues an understanding of planet Earth. Physical geology
General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating
 General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
a) Piedmont: e) Monument: f) Plateau: g) Mesa: h) Butte: i) Playa: j) Perennial Stream:
 Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday CEEES/SC 10110L-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #11: Arid Environments & Landforms Readings: See handout at http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-deserts/index.html.
Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday CEEES/SC 10110L-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #11: Arid Environments & Landforms Readings: See handout at http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-deserts/index.html.
TITLE OF LESSON PLAN: Rocks
 TITLE OF LESSON PLAN: Rocks LENGTH OF LESSON: One class period GRADE LEVEL: 6-8 SUBJECT AREA: Earth Science CREDIT: Betsy Hedberg, former middle school teacher and current freelance curriculum writer and
TITLE OF LESSON PLAN: Rocks LENGTH OF LESSON: One class period GRADE LEVEL: 6-8 SUBJECT AREA: Earth Science CREDIT: Betsy Hedberg, former middle school teacher and current freelance curriculum writer and
Geoscience 001 Fall Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation
 Geoscience 00 Fall 2005 Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation The purpose of this week s lab is to gain some more experience and practice in identifying rocks and then interpreting the geologic
Geoscience 00 Fall 2005 Rock Identification and Contextual Interpretation The purpose of this week s lab is to gain some more experience and practice in identifying rocks and then interpreting the geologic
Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle.
 Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle. Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Explain the difference between rocks
Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle. Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Explain the difference between rocks
Field Trip to Tempe Butte
 Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
Synopsis Field Trip to Tempe Butte So far you have been identifying rocks and mapping their locations without actually going there. Now it is your chance to put it all together and see real rocks out in
GEOLOGIC TIME. Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS
 GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 10e Tarbuck & Lutgens An Introduction to Geology Earth, 10e - Chapter 1 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College 4 The Science of Geology Geology is the
1 Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 10e Tarbuck & Lutgens An Introduction to Geology Earth, 10e - Chapter 1 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College 4 The Science of Geology Geology is the
ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can we use the Mars Map and photographs of Mars to learn about the geologic history of the planet?
 GRADE LEVEL(S) 4 6 LENGTH 60 minutes MATERIALS Giant Destination Mars Map Mars Mapping Student Sheet Colored Markers (red, green, blue) VOCABULARY Crater Erode Ejecta Channel Sun Angle Sequence ESSENTIAL
GRADE LEVEL(S) 4 6 LENGTH 60 minutes MATERIALS Giant Destination Mars Map Mars Mapping Student Sheet Colored Markers (red, green, blue) VOCABULARY Crater Erode Ejecta Channel Sun Angle Sequence ESSENTIAL
Directed Reading A. Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First? Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Determining the age of objects or events in relation to
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First? Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Determining the age of objects or events in relation to
Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit
 Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit Text: Chapters 8 Lab: Exercise 6 Name Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Page 1 Geology 12: Geologic Time 8.1: The Geologic Time Scale Today, we know that Earth is approximately
Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit Text: Chapters 8 Lab: Exercise 6 Name Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Page 1 Geology 12: Geologic Time 8.1: The Geologic Time Scale Today, we know that Earth is approximately
Stratigraphy. Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their
 Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE
 EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE Human beings have used Earth s resources since prehistoric times. We made tools from stones. We mined raw materials to refine and manufacture into
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE Human beings have used Earth s resources since prehistoric times. We made tools from stones. We mined raw materials to refine and manufacture into
Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson
 Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson Introduction: It isn't possible to bring all of outdoors into the classroom, and stratigraphic
Cross-Cutting Relationships Cross-Cutting and Sequencing Lab Earth Science Essentials-Advanced by Russ Colson Introduction: It isn't possible to bring all of outdoors into the classroom, and stratigraphic
Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record.
 UNCONFORMITIES Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record. The contact represents time when no sediment
UNCONFORMITIES Unconformities are depositional contacts that overlie rocks distinctly older than they are. They are often called gaps in the sedimentary record. The contact represents time when no sediment
weathering and cooling and solidification compaction and cementation SEDIMENTARY ROCK
 OVERHEAD MASTER] The Rock Cycle Goal Use this overhead master to show the rock cycie diagram (included in the Teacher's Resource) to your class. cooling and solidification weathering and compaction and
OVERHEAD MASTER] The Rock Cycle Goal Use this overhead master to show the rock cycie diagram (included in the Teacher's Resource) to your class. cooling and solidification weathering and compaction and
GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS
 NAME GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence.
NAME GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence.
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale
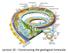 Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Name Class Date. 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. In your own words, write a definition for the term rock cycle. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
Famous Rock Groups Candice McQueen
 Famous Rock Groups Candice McQueen Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with the definitions of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rock. Then, using rock identification books, students will
Famous Rock Groups Candice McQueen Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with the definitions of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rock. Then, using rock identification books, students will
OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE. FULL OPTION SCIENCE SYSTEM Middle School
 FULL OPTION SCIENCE SYSTEM Middle School OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE Human beings have used Earth s resources since prehistoric times. We made tools from stones. We mined raw materials to refine and
FULL OPTION SCIENCE SYSTEM Middle School OVERVIEW EARTH HISTORY COURSE Human beings have used Earth s resources since prehistoric times. We made tools from stones. We mined raw materials to refine and
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
c) metamorphosis d) rock transformation a) melting and cooling b) heat and pressure a) igneous rock b) sedimentary rock
 Quizizz Rocks and Soil Name : Class : Date : 1. The process where rocks is transformed from one type to another is called a) rock cycle b) water cycle c) metamorphosis d) rock transformation 2. How are
Quizizz Rocks and Soil Name : Class : Date : 1. The process where rocks is transformed from one type to another is called a) rock cycle b) water cycle c) metamorphosis d) rock transformation 2. How are
Law of Superposition Law of Superposition
 History of Earth Relative Dating In the same way that a history book shows an order of events, layers of rock (called strata) show the sequence of events that took place in the past. Using a few basic
History of Earth Relative Dating In the same way that a history book shows an order of events, layers of rock (called strata) show the sequence of events that took place in the past. Using a few basic
PHYSIOGRAPHIC REGIONS OF THE LOWER 48 UNITED STATES
 PHYSIOGRAPHIC REGIONS OF THE LOWER 48 UNITED STATES LAURENTIAN UPLAND 1. Superior Upland ATLANTIC PLAIN 2. Continental Shelf (not on map) 3. Coastal Plain a. Embayed section b. Sea Island section c. Floridian
PHYSIOGRAPHIC REGIONS OF THE LOWER 48 UNITED STATES LAURENTIAN UPLAND 1. Superior Upland ATLANTIC PLAIN 2. Continental Shelf (not on map) 3. Coastal Plain a. Embayed section b. Sea Island section c. Floridian
Earth History: Record in the Rocks
 Earth History: Record in the Rocks The geologic history of Earth can be read from rocks if you know what to look for. In this presentation, you will see examples of many types of clues, stored in rocks.
Earth History: Record in the Rocks The geologic history of Earth can be read from rocks if you know what to look for. In this presentation, you will see examples of many types of clues, stored in rocks.
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically
 Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
2nd Grade Changing of Earth
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
FOSS Earth, Cycles, and Change Module The Regents of the University of California Can be duplicated for classroom or workshop use.
 Shadow Challenges 1. Work in pairs. Take turns tracing the outline of your partner s shadow, including his or her feet. 2. Label each shadow with the owner s name and time of day it was drawn. 3. Try to
Shadow Challenges 1. Work in pairs. Take turns tracing the outline of your partner s shadow, including his or her feet. 2. Label each shadow with the owner s name and time of day it was drawn. 3. Try to
Required Materials Plummer, C., Physical geology. Columbus, OH: McGraw Hill Higher Education
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Many students perceive the age
 30 Understanding Fossils and Relative Dating by Inquiry BY JOANNA RICHISON, DEBORAH HERRINGTON, AND STEPHEN MATTOX CONTENT AREA Earth science GRADE LEVEL Many students perceive the age of the Earth in
30 Understanding Fossils and Relative Dating by Inquiry BY JOANNA RICHISON, DEBORAH HERRINGTON, AND STEPHEN MATTOX CONTENT AREA Earth science GRADE LEVEL Many students perceive the age of the Earth in
GEOL Introductory Geology: Exploring Planet Earth Fall 2010 Test #2 October 18, 2010
 GEOL 101 - Introductory Geology: Exploring Planet Earth Fall 2010 Test #2 October 18, 2010 Name KEY ID# KEY Multiple choice questions (2 points each). 1. What type of metamorphic rock is formed over large
GEOL 101 - Introductory Geology: Exploring Planet Earth Fall 2010 Test #2 October 18, 2010 Name KEY ID# KEY Multiple choice questions (2 points each). 1. What type of metamorphic rock is formed over large
Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework
 Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework Completion Complete each statement. 1. A(n) is a solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally. 2. Rocks are generally classified as igneous,, or
Rock Cycle and Rock Types Homework Completion Complete each statement. 1. A(n) is a solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally. 2. Rocks are generally classified as igneous,, or
