Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines
|
|
|
- Bertram Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines FACT SHEET I: GEOMORPHOLOGICAL HAZARDS CONFINED AND UNCONFINED WATERCOURSES Channel migration and erosion can create substantial risk to inappropriately located infrastructure and result in the need to armour or train channels, which impacts channel form and function and can result in degraded aquatic habitat. The Credit Valley Conservation Authority: Regulation of Development, Interference with Wetlands and Alterations to Shorelines and Watercourses and the CVC Watercourse and Valleyland Protection Policies provide guidance with regards to addressing hazards associated with channel migration to alleviate these risks and reduce the need for structural solutions. The main goal is to reduce risk by eliminating development within hazard areas, thereby reducing impact to channel function including sediment transport and channel migration. This also reduces the potential disruption or fragmentation of aquatic and terrestrial habitat. There are two approaches presented by Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (2001) for determining the erosion hazard limit for watercourses. These two approaches are based on the relationship between the watercourse and its valley. These are defined as confined and unconfined systems. Confined systems are those where the watercourse is located in a well defined valley corridor or where valley wall contact is possible, whereas unconfined systems are systems where the watercourse is located within a poorly defined valley with limited or no discernable slopes. Another potential type of unconfined channel is where the channel is misfit to its valley. Misfit valleys occur where the valley was created by other processes, such as glaciation, or where historic flows (such as from glacial outwash) were substantially larger than current dominant flows. Under these conditions the valley width can be significantly larger than expected from the scale of the present watercourse. The two types of systems are treated differently to address the difference in potential hazard. In unconfined systems the hazard is from channel erosion and migration. As such, unconfined systems require a meander belt width and associated erosion allowance. Confined systems, on the other hand, require both channel migration or erosion and slope processes to be considered. As such, they require both a toe erosion allowance (i.e., the setback that ensures the safety if the toe of the slope adjacent to the channel erodes) and a stable slope allowance (i.e., the setback that ensures the safety if slumping or slope failure occurs). Pg 1
2 Unconfined Systems Delineation of erosion hazards in unconfined systems require the determination of a meander belt width, which is usually composed of the largest meander amplitude an allowance for erosion and a factor of safety, if required (Figure 2). The meander belt width defines the area the watercourse currently occupies and that could potentially occupy in the future. Methods for determining meander belt widths are outlined in the Toronto and Region Conservation Authority s Belt Width Delineation Procedure. A list of resources describing other methods of hazard delineation and meander belt width assessment can be found in Appendix C. In all cases the meander belt width should address the equilibrium planform of the watercourse through an assessment of the largest meander amplitude, potential future erosion (usually based on a 100 year timing window), and in some cases a factor of safety associated with anticipated future changes in the hydraulic or sediment regime, or systematic adjustments (e.g., downcutting or channel widening) (Figure 2). An additional easement may be necessary for an access allowance. Depending on setting, antecedent conditions, historic changes or modifications to the watercourse, and potential future impact to watercourse hydrology or sediment regime one method may be more appropriate than another in quantifying the meander belt width. Where possible, meander belt widths should be calculated from channel measurements. Modeling approaches should be reserved for heavily impacted channels or where substantial changes to hydrology are anticipated. As noted, given the stability or potential for long term evolution (systematic adjustment) of a given watercourse additional allowances may be required. Given the complexity and diversity of watercourses within the CVC watershed, the appropriate methodology should be agreed upon in consultation with CVC staff before proceeding with the assessment. Figure 1: a) Anatomy of a meander belt width (unconfined). Pg 2
3 Figure 2: b) Planform view of erosion setback in an unconfined system Confined Systems Delineation of erosion hazards for confined systems requires 1) the quantification of rates of erosion at the toe of slope to determine a toe erosion allowance (both lateral and downstream) and 2) determination of the location of the stable top of bank. 1) Confined systems require a toe erosion allowance to account for the 100-year erosion limit for areas where the watercourse is within 15 m of the valley wall. This is used instead of a meander belt width in confined systems. The erosion setback should address lateral and downstream migration of meanders, long term anticipated systematic adjustments in the watercourse (where applicable), and, in some cases, a factor of safety associated with anticipated future changes in the hydraulic or sediment regime (Figure 3a). The toe erosion allowance should be determined based on a detailed geomorphological study or based on CVC Watercourse and Valleyland Policy or Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Guidelines. Where a detailed study is not completed, the setback should be applied along the entire length of the top of slope. Where a detailed study is completed the setbacks can be applied where erosion issues would be anticipated due to proximity of the watercourse, downstream and lateral migration, and potential future adjustments (Figure 3b). Pg 3
4 2) The geotechnically stable top of slope is determined through a geotechnical analysis that quantifies a factor of safety and may be steeper or gentler than 3:1. Under Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Guidelines the minimum stable slope allowance is 3:1 and is applied in conjunction with any required erosion setbacks that are applied from the toe of slope. The determination of the stable top of slope accounts for conditions where slopes are over steepened or where the Creek is within 15 m of the toe of slope and, as such, where the stability of the existing top of slope may pose a risk to infrastructure (Figure 4). An additional easement may be required for an access setback. a) b) Figure 2: Planform view of erosion setback treatment without (a) and with (b) detailed study (confined). Pg 4
5 Figure 3: Cross-section of a geotechnically stable top of slope (confined). Geomorphological Assessment for Confined and Unconfined Systems Quantifying hazards associated with channel migration is best addressed through a geomorphological assessment that includes an evaluation of channel stability, and quantification of potential channel adjustment, through historical assessment and/or acceptable modeling techniques. To provide the required insight into the hazard delineation, a geomorphological assessment must be completed by a qualified fluvial geomorphologist, with at minimum their masters degree in fluvial geomorphology and their Professional Geoscientist designation or equivalent qualification at the discretion of the Conservation Authority. The following activities, at minimum, should be included in the geomorphological assessment: Reach delineation based on scientifically defensible methodology (e.g. Montgomery and Buffington, 1997, Richards et al. 1997, Toronto and Region Conservation Authority, 2004); Rapid assessment to evaluate stability of reaches based on acceptable rapid assessment protocols (e.g., Index of Stability (Downs, 1995), Rapid Geomorphological Assessment (Ontario Ministry of the Environment, 2003), or other suitable methods in consultation with CVC staff; Mapping of areas of channel erosion, valley wall contact and active slope processes; Quantification of channel adjustment and migration (both lateral and downstream) through an historical assessment by way of aerial photographic interpretation and/or inferred through measures from adjacent infrastructure (at minimum 25 year time span should be assessed); Pg 5
6 Where historical observations cannot be made, or significant change in the flow regime is anticipated, modeling approaches may be required (acceptable modeling approaches should be decided in consultation with CVC staff); and Where an additional factor of safety associated with anticipated future changes in the hydraulic or sediment regime, or systematic adjustments (such as downcutting or channel widening) are not provided, this must be supported by appropriate rationale. It should be noted that the geomorphological assessment only provides erosion hazard delineation. Complete constraint mapping needs to take into account requirements of other disciplines. For example additional setbacks or buffers associated with flooding hazards or natural heritage features may be required. Any hazard delineation should start with pre-project consultation with CVC staff. Additional information is available in the CVC Watercourse and Valleyland Protection Policies. Checklist Geomorphological assessment that provides information on reach delineation and reach-by-reach stability including: Identification of reach breaks Reach-by-reach descriptions including physical conditions and stability Identification, documentation and mapping of areas of channel erosion, valley wall contact and active slope processes: Quantification of channel migration, widening and potential downcutting or scour, based on historical observation or acceptable modeling In unconfined systems: determination of meander belt width which includes an erosion allowance and factor of safety, if required In confined systems: determination of a toe erosion allowance and the location of the stable top of bank (in combination with an appropriate geotechnical report) Appropriate rationale where an additional factor of safety is, or is not applied Pg 6
Sixteen Mile Creek Tributaries Meander Belt Width Assessment November 2009
 SIXTEEN MILE CREEK TRIBUTARIES THE CATHOLIC CEMETERIES OF THE DIOCESE OF HAMILTON -MEANDER BELT WIDTH ASSESSMENT - Report to: Attention: From: Director of Cemeteries Catholic Cemeteries of the Diocese
SIXTEEN MILE CREEK TRIBUTARIES THE CATHOLIC CEMETERIES OF THE DIOCESE OF HAMILTON -MEANDER BELT WIDTH ASSESSMENT - Report to: Attention: From: Director of Cemeteries Catholic Cemeteries of the Diocese
Defining the Limit of Regulated Areas. C.1 Defining the River or Stream Flood Hazard 138. C.2 Defining the River or Stream Erosion Hazard 139
 C.1 Defining the River or Stream Flood Hazard 138 C.2 Defining the River or Stream Erosion Hazard 139 C.3 Defining Watercourses 141 C.4 Defining the Lake Ontario Shoreline Flood, Erosion and Dynamic Beach
C.1 Defining the River or Stream Flood Hazard 138 C.2 Defining the River or Stream Erosion Hazard 139 C.3 Defining Watercourses 141 C.4 Defining the Lake Ontario Shoreline Flood, Erosion and Dynamic Beach
Belt Width Delineation Procedures
 Belt Width Delineation Procedures Report to: Attention: Report No: 5 Shoreham Drive, Downsview, Ontario M3N 1S4 Mr. Ryan Ness 98-023 Date: Sept 27, 2001 (Revised January 30, 2004) Submitted by: Table of
Belt Width Delineation Procedures Report to: Attention: Report No: 5 Shoreham Drive, Downsview, Ontario M3N 1S4 Mr. Ryan Ness 98-023 Date: Sept 27, 2001 (Revised January 30, 2004) Submitted by: Table of
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment. Appendix E. River Corridor Delineation Process. VT Agency of Natural Resources. April, E0 - April, 2004
 Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill
 1 When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill Robin McKillop 1, Dan McParland 1 & Cassie Scobie 2 TRIECA conference March 22-23, 2017 1 Palmer Environmental
1 When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill Robin McKillop 1, Dan McParland 1 & Cassie Scobie 2 TRIECA conference March 22-23, 2017 1 Palmer Environmental
LONG POINT REGION CONSERVATION AUTHORITY
 LONG POINT REGION CONSERVATION AUTHORITY Reference Manual DETERMINATION OF REGULATION LIMITS L o n g P o i n t R e g i o n C o n s e r v a t i o n A u t h o r i t y D e t e r m i n a t i o n o f R e g
LONG POINT REGION CONSERVATION AUTHORITY Reference Manual DETERMINATION OF REGULATION LIMITS L o n g P o i n t R e g i o n C o n s e r v a t i o n A u t h o r i t y D e t e r m i n a t i o n o f R e g
Wetland & Floodplain Functional Assessments and Mapping To Protect and Restore Riverine Systems in Vermont. Mike Kline and Laura Lapierre Vermont DEC
 Wetland & Floodplain Functional Assessments and Mapping To Protect and Restore Riverine Systems in Vermont Mike Kline and Laura Lapierre Vermont DEC NWI+ Hydro-Geomorphic Characterization of Wetlands and
Wetland & Floodplain Functional Assessments and Mapping To Protect and Restore Riverine Systems in Vermont Mike Kline and Laura Lapierre Vermont DEC NWI+ Hydro-Geomorphic Characterization of Wetlands and
Urfe Creek Geomorphic Assessment William Jackson Drive and Earl Grey Avenue City of Pickering Regional Municipality of Durham
 GUIDING SOLUTIONS IN THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT Urfe Creek Geomorphic Assessment William Jackson Drive and Earl Grey Avenue City of Pickering Regional Municipality of Durham Prepared For: Trillium Housing
GUIDING SOLUTIONS IN THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT Urfe Creek Geomorphic Assessment William Jackson Drive and Earl Grey Avenue City of Pickering Regional Municipality of Durham Prepared For: Trillium Housing
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel. February 24 th, UMSRS
 Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta
 Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
Date: July Ref:
 Final Report Bovaird Drive Class EA Stream Crossing Geomorphological Assessment Date: July 2012 Ref: 01-10-34 2500, Meadowpine Blvd. Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 6C4 Canada (905) 877-9531
Final Report Bovaird Drive Class EA Stream Crossing Geomorphological Assessment Date: July 2012 Ref: 01-10-34 2500, Meadowpine Blvd. Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 6C4 Canada (905) 877-9531
10/8/ W01. Daniel Catiglione First Gulf Corporation 3751 Victoria Park Avenue Toronto, ON M1W 3Z4
 10/8/2014 Daniel Catiglione First Gulf Corporation 3751 Victoria Park Avenue Toronto, ON M1W 3Z4 Dear Sir, Subject: Lower Morrison Creek Meander Belt Width Assessment MMM was retained by First Gulf Corporation
10/8/2014 Daniel Catiglione First Gulf Corporation 3751 Victoria Park Avenue Toronto, ON M1W 3Z4 Dear Sir, Subject: Lower Morrison Creek Meander Belt Width Assessment MMM was retained by First Gulf Corporation
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes
 Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN
 ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
APPLIED FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY
 APPLIED FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY Where have we come from, where do we go? Roger TJ Phillips Mariëtte Pushkar and Peter Ashmore Value of Geomorphologists in River Management Start with Historical Geology and
APPLIED FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY Where have we come from, where do we go? Roger TJ Phillips Mariëtte Pushkar and Peter Ashmore Value of Geomorphologists in River Management Start with Historical Geology and
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods
 Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Edward R. Sajecki Commissioner of Planning and Building. Conservation Authority Regulations and Mapping
 Corporate Report Clerk s Files Originator s Files EC.19.CON DATE: TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Chair and Members of Planning and Development Committee Meeting Date: April 3, 2006 Edward R. Sajecki Commissioner of
Corporate Report Clerk s Files Originator s Files EC.19.CON DATE: TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Chair and Members of Planning and Development Committee Meeting Date: April 3, 2006 Edward R. Sajecki Commissioner of
Protecting the Storm Damage Prevention and Flood Control Interests of Coastal Resource Areas
 Protecting the Storm Damage Prevention and Flood Control Interests of Coastal Resource Areas Presented by: Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection & Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management
Protecting the Storm Damage Prevention and Flood Control Interests of Coastal Resource Areas Presented by: Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection & Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management
The Use of Higher-Resolution Satellite Imagery, LiDAR and Drones in River Applications:
 The Use of Higher-Resolution Satellite Imagery, LiDAR and Drones in River Applications: Meander Belt Width Assessments to Effluent Plume Delineation Joanna Eyquem, P.Geo., Principal Fluvial Geomorphology,
The Use of Higher-Resolution Satellite Imagery, LiDAR and Drones in River Applications: Meander Belt Width Assessments to Effluent Plume Delineation Joanna Eyquem, P.Geo., Principal Fluvial Geomorphology,
Fluvial Geomorphology Report. Appendix. Teston Road Class Environmental Assessment Pine Valley Drive to Weston Road Environmental Study Report
 Teston Road Class Environmental Assessment Pine Valley Drive to Weston Road Environmental Study Report Appendix J Fluvial Geomorphology Report Accessible formats are available upon request. TESTON ROAD
Teston Road Class Environmental Assessment Pine Valley Drive to Weston Road Environmental Study Report Appendix J Fluvial Geomorphology Report Accessible formats are available upon request. TESTON ROAD
Ways To Identify Background Verses Accelerated Erosion
 Ways To Identify Background Verses Accelerated Erosion Establish Background Condition From Old Ground Photos, Aerial Photos, and Maps Compare Rate Over Time At the Same Location, or for Reaches Channel
Ways To Identify Background Verses Accelerated Erosion Establish Background Condition From Old Ground Photos, Aerial Photos, and Maps Compare Rate Over Time At the Same Location, or for Reaches Channel
Appendix S Geomorphic Assessment
 Appendix S Geomorphic Assessment FINAL REPORT Caledon Road Improvements EA Geomorphic Assessment Date: May 2014 Ref: 01-12-34/02 2500 Meadowpine Blvd. Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 6C4 Canada
Appendix S Geomorphic Assessment FINAL REPORT Caledon Road Improvements EA Geomorphic Assessment Date: May 2014 Ref: 01-12-34/02 2500 Meadowpine Blvd. Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 6C4 Canada
Merton Tertiary Planning Study: Geomorphic Assessment Fourteen Mile Creek and Associated Tributaries - Final Report V-1
 Merton Tertiary Planning Study: Geomorphic Assessment Fourteen Mile Creek and Associated Tributaries - Final Report V-1 December 2013 Ref: 01-12-61 2500, MeadowpineBlvd.Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario,
Merton Tertiary Planning Study: Geomorphic Assessment Fourteen Mile Creek and Associated Tributaries - Final Report V-1 December 2013 Ref: 01-12-61 2500, MeadowpineBlvd.Suite 200 Address Mississauga, Ontario,
Appendix C. Greater Cardinal Creek Subwatershed Management Plan. Conceptual Channel Naturalization Design at Old Montreal Road (under separate cover)
 Appendix C Greater Cardinal Creek Subwatershed Management Plan Conceptual Channel Naturalization Design at Old Montreal Road (under separate cover) CARDINAL CREEK CONCEPTUAL CHANNEL NATURALIZATION DESIGN
Appendix C Greater Cardinal Creek Subwatershed Management Plan Conceptual Channel Naturalization Design at Old Montreal Road (under separate cover) CARDINAL CREEK CONCEPTUAL CHANNEL NATURALIZATION DESIGN
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
WITNESS STATEMENT. John Parish, P.Geo. ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD. Case No. PL File No. PL Prepared for:
 WITNESS STATEMENT OF John Parish, P.Geo. ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD Case No. PL141318 File No. PL141320 Prepared for: Bronte Green Corporation ( Bronte Green ) Prepared by: John Parish, P.Geo. Matrix Solutions
WITNESS STATEMENT OF John Parish, P.Geo. ONTARIO MUNICIPAL BOARD Case No. PL141318 File No. PL141320 Prepared for: Bronte Green Corporation ( Bronte Green ) Prepared by: John Parish, P.Geo. Matrix Solutions
New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal
 NHACC Annual Meeting 2012 New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal Peter J. Walker CROOKED STREAMS are a menace to life and crops in the areas bordering on their banks.
NHACC Annual Meeting 2012 New Approaches to Restoring NH s Rivers Natural Channel Design and Dam Removal Peter J. Walker CROOKED STREAMS are a menace to life and crops in the areas bordering on their banks.
PHASE 1 STREAM GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT. Castleton River, Rutland County Vermont. Final Report
 PHASE 1 STREAM GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT Castleton River, Rutland County Vermont Final Report September 15, 2005 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION.. 3 STUDY AREA BACKGROUND... 5 METHODOLOGY 5 DATA INPUTS/STUDY
PHASE 1 STREAM GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT Castleton River, Rutland County Vermont Final Report September 15, 2005 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION.. 3 STUDY AREA BACKGROUND... 5 METHODOLOGY 5 DATA INPUTS/STUDY
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO
 GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO Prepared For Trout Unlimited 300 North Main Street, Hailey, Idaho, 83333 Prepared By P. O. Box 8578, 140 E. Broadway, Suite 23,
GENERAL SUMMARY BIG WOOD RIVER GEOMORPHIC ASSESSMENT BLAINE COUNTY, IDAHO Prepared For Trout Unlimited 300 North Main Street, Hailey, Idaho, 83333 Prepared By P. O. Box 8578, 140 E. Broadway, Suite 23,
Delimiting Freedom Space for Rivers Using GIS and Remote Sensing:
 Delimiting Freedom Space for Rivers Using GIS and Remote Sensing: Updating existing tools to manage functional and resilient river systems Joanna Eyquem and Fabien Hugue (AECOM) Pascale Biron (University
Delimiting Freedom Space for Rivers Using GIS and Remote Sensing: Updating existing tools to manage functional and resilient river systems Joanna Eyquem and Fabien Hugue (AECOM) Pascale Biron (University
Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire. 1 May 2013
 Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire 1 May 2013 1 Hydrology 2 Basic Hydrology Low flows most common Flows that fill the stream to the banks and higher are much less common Filling the stream to the
Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire 1 May 2013 1 Hydrology 2 Basic Hydrology Low flows most common Flows that fill the stream to the banks and higher are much less common Filling the stream to the
Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards
 Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards Julie Moore, P.E. July 9, 2012 Agenda Traditional approach to river management Understanding flood-related hazards Common flood and flood
Identifying, Understanding and Addressing Flood-Related Hazards Julie Moore, P.E. July 9, 2012 Agenda Traditional approach to river management Understanding flood-related hazards Common flood and flood
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018
 Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
Thank you to all of our 2015 sponsors: Media Partner
 Thank you to all of our 2015 sponsors: Media Partner Fluvial System Concepts and Their Application in Greenfield Stream Corridor Realignment Dr. Paul Villard, P.Geo. GEO Morphix Ltd. Overview Major realignment
Thank you to all of our 2015 sponsors: Media Partner Fluvial System Concepts and Their Application in Greenfield Stream Corridor Realignment Dr. Paul Villard, P.Geo. GEO Morphix Ltd. Overview Major realignment
What are the issues?
 Water Quality along Lake Huron What are the issues? Lake Huron Water Quality Algal fouling Irregular, less frequent, less widespread, but some significant local events Influences Tributaries contribute;
Water Quality along Lake Huron What are the issues? Lake Huron Water Quality Algal fouling Irregular, less frequent, less widespread, but some significant local events Influences Tributaries contribute;
ONTARIO REGULATION 156/06. made under the CONSERVATION AUTHORITIES ACT
 ONTARIO REGULATION 156/06 made under the CONSERVATION AUTHORITIES ACT Made: April 28, 2006 Approved: May 4, 2006 Filed: May 4, 2006 Published on e-laws: May 8, 2006 Printed in The Ontario Gazette: May
ONTARIO REGULATION 156/06 made under the CONSERVATION AUTHORITIES ACT Made: April 28, 2006 Approved: May 4, 2006 Filed: May 4, 2006 Published on e-laws: May 8, 2006 Printed in The Ontario Gazette: May
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment
 Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
patersongroup Consulting Engineers April 20, 2010 File: PG1887-LET.01R Novatech Engineering Consultants Suite 200, 240 Michael Cowpland Drive
 patersongroup April 20, 2010 File: PG1887-LET.01R Novatech Engineering Consultants Suite 200, 240 Michael Cowpland Drive Ottawa, Ontario K2M 1P6 Attention: Mr. Adam Thompson Consulting Engineers 28 Concourse
patersongroup April 20, 2010 File: PG1887-LET.01R Novatech Engineering Consultants Suite 200, 240 Michael Cowpland Drive Ottawa, Ontario K2M 1P6 Attention: Mr. Adam Thompson Consulting Engineers 28 Concourse
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough
 Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
Connecticut Coastal Management Program
 Connecticut Coastal Management Program Fact Sheet for SHORELINE FLOOD AND EROSION CONTROL STRUCTURES What are Shoreline Flood and Erosion Control Structures? The Connecticut General Statutes (CGS) define
Connecticut Coastal Management Program Fact Sheet for SHORELINE FLOOD AND EROSION CONTROL STRUCTURES What are Shoreline Flood and Erosion Control Structures? The Connecticut General Statutes (CGS) define
Rapid Geomorphic Assessments: RGA s
 Establishing Current Reference Conditions Rates and concentrations of suspended-sediment transport vary over time and space due to factors such as precipitation characteristics and discharge, geology,
Establishing Current Reference Conditions Rates and concentrations of suspended-sediment transport vary over time and space due to factors such as precipitation characteristics and discharge, geology,
PolyMet NorthMet Project
 RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin
 Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
Opportunities to Improve Ecological Functions of Floodplains and Reduce Flood Risk along Major Rivers in the Puget Sound Basin Christopher Konrad, US Geological Survey Tim Beechie, NOAA Fisheries Managing
DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS
 DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS Presented by: James G. Mac Broom, P.E. Milone & Mac Broom, Inc. October 2011 CLEAR GOALS and OBJECTIVES Fish Passage Habitat Defragmentation Water Quality Dam Failure
DAM REMOVAL ENGINEERING ISSUES & OPTIONS Presented by: James G. Mac Broom, P.E. Milone & Mac Broom, Inc. October 2011 CLEAR GOALS and OBJECTIVES Fish Passage Habitat Defragmentation Water Quality Dam Failure
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
via via CCTA File /6 Train Avenue West and 70 Yonge Street South, Springwater Natural Hazard Study
 January 16, 217 via via email (vsimpson@ipsconsulting.com) CCTA File 416428 Vanessa Simpson, B.ID, M.PL. Junior Planner/ Planning Technician Innovative Planning Solutions 1 Dunlop Street East, Suite 21
January 16, 217 via via email (vsimpson@ipsconsulting.com) CCTA File 416428 Vanessa Simpson, B.ID, M.PL. Junior Planner/ Planning Technician Innovative Planning Solutions 1 Dunlop Street East, Suite 21
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Meander belt delineation: Developing a predictive model for meander belt width
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository October 2017 Meander belt delineation: Developing a predictive model for meander belt width Julia Howett The University
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository October 2017 Meander belt delineation: Developing a predictive model for meander belt width Julia Howett The University
Sprague River Basin Restoration Post Project Evaluations: Lessons Learned and Future Applications
 River Restoration Northwest, 2015 Sprague River Basin Restoration Post Project Evaluations: Lessons Learned and Future Applications Mark R. Tompkins, P.E., Ph.D. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Klamath Tribes Larry
River Restoration Northwest, 2015 Sprague River Basin Restoration Post Project Evaluations: Lessons Learned and Future Applications Mark R. Tompkins, P.E., Ph.D. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Klamath Tribes Larry
Dolores River Watershed Study
 CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS... 1
 Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Riparian Assessment. Steps in the right direction... Drainage Basin/Watershed: Start by Thinking Big. Riparian Assessment vs.
 Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS
 LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
The last three sections of the main body of this report consist of:
 Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
OBJECTIVES. Fluvial Geomorphology? STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT
 STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT Greg Babbit Graduate Research Assistant Dept. Forestry, Wildlife & Fisheries Seneca Creek, Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia OBJECTIVES Introduce basic
STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT Greg Babbit Graduate Research Assistant Dept. Forestry, Wildlife & Fisheries Seneca Creek, Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia OBJECTIVES Introduce basic
AASHTO Extreme Weather Events Symposium Vermont s Road and Rivers - Managing for the Future
 AASHTO Extreme Weather Events Symposium Vermont s Road and Rivers - Managing for the Future May 22, 2013 PLANET EARTH 2 2 MANY MANYYEARS AGO 23,000 years ago there was more than 8,000 feet of glacier over
AASHTO Extreme Weather Events Symposium Vermont s Road and Rivers - Managing for the Future May 22, 2013 PLANET EARTH 2 2 MANY MANYYEARS AGO 23,000 years ago there was more than 8,000 feet of glacier over
Limitation to qualitative stability indicators. the real world is a continuum, not a dichotomy ~ 100 % 30 % ~ 100 % ~ 40 %
 Stream Stability Assessment & BEHI Surveys Joe Rathbun MDEQ Water Resources Division rathbunj@michigan.gov 517--373 517 373--8868 Stability Stream can transport its water and sediment inputs without changing
Stream Stability Assessment & BEHI Surveys Joe Rathbun MDEQ Water Resources Division rathbunj@michigan.gov 517--373 517 373--8868 Stability Stream can transport its water and sediment inputs without changing
CASE STUDIES. Introduction
 Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Appendix F. Fluvial Geomorphology Report. Krosno Creek Flood Reduction Project PROJECT FILE REPORT CITY OF PICKERING
 Krosno Creek Flood Reduction Project PROJECT FILE REPORT CITY OF PICKERING Appendix F Fluvial Geomorphology Report TMIG THE MUNICIPAL INFRASTRUCTURE GROUP LTD December 10, 2013 Steve Hollingworth The
Krosno Creek Flood Reduction Project PROJECT FILE REPORT CITY OF PICKERING Appendix F Fluvial Geomorphology Report TMIG THE MUNICIPAL INFRASTRUCTURE GROUP LTD December 10, 2013 Steve Hollingworth The
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET
 SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology
 Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training
 Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training Using Fluvial Geomorphology (FGM) to Reduce Conflicts Between Transportation Assets and Rivers Roy Schiff, Jessica Louisos, and Jim MacBroom, Milone & MacBroom Tim
Massachusetts Rivers & Roads Training Using Fluvial Geomorphology (FGM) to Reduce Conflicts Between Transportation Assets and Rivers Roy Schiff, Jessica Louisos, and Jim MacBroom, Milone & MacBroom Tim
Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms
 Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
Distinct landscape features with important biologic, hydrologic, geomorphic, and biogeochemical functions.
 1 Distinct landscape features with important biologic, hydrologic, geomorphic, and biogeochemical functions. Have distinguishing characteristics that include low slopes, well drained soils, intermittent
1 Distinct landscape features with important biologic, hydrologic, geomorphic, and biogeochemical functions. Have distinguishing characteristics that include low slopes, well drained soils, intermittent
Geomorphology Studies
 Geomorphology Studies Technical Workgroup Meeting February 14, 2012 Prepared by: Tetra Tech Prepared for: Alaska Energy Authority Overall Goal Geomorphology Studies Two studies Geomorphology Study (RSP
Geomorphology Studies Technical Workgroup Meeting February 14, 2012 Prepared by: Tetra Tech Prepared for: Alaska Energy Authority Overall Goal Geomorphology Studies Two studies Geomorphology Study (RSP
Assessment. Assessment
 2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
NATURAL RIVER. Karima Attia Nile Research Institute
 NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
RAILWAYS AND FISH: HOW TO PROTECT AND ENHANCE FISH HABITAT VALUES AT STREAM CROSSINGS THROUGH PROJECT DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
 RAILWAYS AND FISH: HOW TO PROTECT AND ENHANCE FISH HABITAT VALUES AT STREAM CROSSINGS THROUGH PROJECT DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION Rail Environment Conference November 2016 AGENDA Objective Background Benefits
RAILWAYS AND FISH: HOW TO PROTECT AND ENHANCE FISH HABITAT VALUES AT STREAM CROSSINGS THROUGH PROJECT DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION Rail Environment Conference November 2016 AGENDA Objective Background Benefits
FLOOD HAZARD AREA AND RIVER CORRIDOR PROTECTION PROCEDURE
 DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION FLOOD HAZARD AREA AND RIVER CORRIDOR PROTECTION PROCEDURE DECEMBER 5, 2014 1 DEC Flood Hazard Area and River Corridor Protection Procedure Table of Contents 1.0
DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION FLOOD HAZARD AREA AND RIVER CORRIDOR PROTECTION PROCEDURE DECEMBER 5, 2014 1 DEC Flood Hazard Area and River Corridor Protection Procedure Table of Contents 1.0
Aquifer an underground zone or layer of sand, gravel, or porous rock that is saturated with water.
 Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
4.17 Spain. Catalonia
 4.17 Spain Catalonia In Spain, inundation studies are the responsibility of the respective Hydrographic Confederations of each river basin (River Basin Authorities). The actual status of inundation studies
4.17 Spain Catalonia In Spain, inundation studies are the responsibility of the respective Hydrographic Confederations of each river basin (River Basin Authorities). The actual status of inundation studies
Frequently Asked Questions about River Corridors
 Frequently Asked Questions about River Corridors 1. What are river corridors and why are they important? ANR River Corridors encompass the area of land surrounding a river that provides for the meandering,
Frequently Asked Questions about River Corridors 1. What are river corridors and why are they important? ANR River Corridors encompass the area of land surrounding a river that provides for the meandering,
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points
 Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan
 Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
EXISTING CONDITIONS : EAST SEGMENT
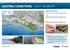 EXISTING CONDITIONS : Area of Natural and Interest (ANSI) Environmentally Waterfront Trail Wetlands Hazard Setback Dunes Private Shoreline road ends Unsafe shoreline access Waterfront Trail on route FISH
EXISTING CONDITIONS : Area of Natural and Interest (ANSI) Environmentally Waterfront Trail Wetlands Hazard Setback Dunes Private Shoreline road ends Unsafe shoreline access Waterfront Trail on route FISH
Rock Sizing for Bank Stabilisation
 Rock Sizing for Bank Stabilisation WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Lower bank rock stabilisation with voids filled with small rocks Photo 2 Rock stabilisation with plants introduced at time of rock
Rock Sizing for Bank Stabilisation WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Lower bank rock stabilisation with voids filled with small rocks Photo 2 Rock stabilisation with plants introduced at time of rock
Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration
 Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration MACC Annual Environmental Conference 2017 March 3, 2017 Tim Dexter, MassDOT Highway Division 1 Leading the Nation in Transportation
Best Management Practices for Coldwater Fisheries Enhancement and Restoration MACC Annual Environmental Conference 2017 March 3, 2017 Tim Dexter, MassDOT Highway Division 1 Leading the Nation in Transportation
River Morphology. EAD 511 River management
 River Morphology EAD 511 River management Introduction FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY Webster's New World Dictionary defines fluvial as: of, found in, or produced by a river or rivers. The same reference defines
River Morphology EAD 511 River management Introduction FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY Webster's New World Dictionary defines fluvial as: of, found in, or produced by a river or rivers. The same reference defines
A GEOMORPHOLOGICAL APPROACH TO RESTORATION OF INCISED RIVERS. David L. Rosgen 1
 Proceedings of the Conference on Management of Landscapes Disturbed by Channel Incision, 1997 S.S.Y. Wang, E.J. Langendoen and F.D. Shields, Jr. (eds.) ISBN 0-937099-05-8 A GEOMORPHOLOGICAL APPROACH TO
Proceedings of the Conference on Management of Landscapes Disturbed by Channel Incision, 1997 S.S.Y. Wang, E.J. Langendoen and F.D. Shields, Jr. (eds.) ISBN 0-937099-05-8 A GEOMORPHOLOGICAL APPROACH TO
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION
 FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION Godaire, Jeanne E., Bureau of Reclamation, P.O. Box 25007, Denver, CO 80225, 303-445- 3164, jgodaire@usbr.gov; Russell,
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE ENTIAT RIVER, WA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR STREAM RESTORATION Godaire, Jeanne E., Bureau of Reclamation, P.O. Box 25007, Denver, CO 80225, 303-445- 3164, jgodaire@usbr.gov; Russell,
Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades?
 Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades? Faith Fitzpatrick USGS WI Water Science Center, Middleton, WI fafitzpa@usgs.gov
Diagnostic Geomorphic Methods for Understanding Future Behavior of Lake Superior Streams What Have We Learned in Two Decades? Faith Fitzpatrick USGS WI Water Science Center, Middleton, WI fafitzpa@usgs.gov
Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces
 Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces 23 rd International Petroleum Environmental Conference New Orleans, Louisiana November 8-10, 2016 Introduction
Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces 23 rd International Petroleum Environmental Conference New Orleans, Louisiana November 8-10, 2016 Introduction
May 7, Roger Leventhal, P.E. Marin County Public Works Laurel Collins Watershed Sciences
 May 7, 2013 Roger Leventhal, P.E. Marin County Public Works Laurel Collins Watershed Sciences Background Funded in 2009 under EPA 2100 Grant for $30k and managed by SFEP Project Goals: Update original
May 7, 2013 Roger Leventhal, P.E. Marin County Public Works Laurel Collins Watershed Sciences Background Funded in 2009 under EPA 2100 Grant for $30k and managed by SFEP Project Goals: Update original
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS 7. FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY... 7-7. Watershed Objectives Indicators and Targets... 7-7.2 Objectives of Technical Update... 7-2 7.3 Data Sources and Monitoring... 7-3
FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS 7. FLUVIAL GEOMORPHOLOGY... 7-7. Watershed Objectives Indicators and Targets... 7-7.2 Objectives of Technical Update... 7-2 7.3 Data Sources and Monitoring... 7-3
Fluvial Geomorphic Assessment and River Corridor Planning in the Wood-Pawcatuck Watershed, RI and CT
 Fluvial Geomorphic Assessment and River Corridor Planning in the Wood-Pawcatuck Watershed, RI and CT Prepared for Wood-Pawcatuck Watershed Association Hope Valley, RI Prepared by John Field Field Geology
Fluvial Geomorphic Assessment and River Corridor Planning in the Wood-Pawcatuck Watershed, RI and CT Prepared for Wood-Pawcatuck Watershed Association Hope Valley, RI Prepared by John Field Field Geology
HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE
 PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
Fluvial Processes in River Engineering
 Fluvial Processes in River Engineering Howard H. Chang San Diego State University... A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLTCATION John Wiley & Sons New York Chicbester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS PARTI FLUVIAL
Fluvial Processes in River Engineering Howard H. Chang San Diego State University... A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLTCATION John Wiley & Sons New York Chicbester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS PARTI FLUVIAL
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007
 Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
Session 1 Healthy Streams Stream Hydraulics Natural Channel Design
 Session 1 Healthy Streams Stream Hydraulics Natural Channel Design Bill Brant Heart of America Flyfishers Black & Veatch Kansas City, MO February 21, 2014 http://www.bobswebspace.com Audience? What do
Session 1 Healthy Streams Stream Hydraulics Natural Channel Design Bill Brant Heart of America Flyfishers Black & Veatch Kansas City, MO February 21, 2014 http://www.bobswebspace.com Audience? What do
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6
 Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Appendix E Rosgen Classification
 Appendix E Stream Type s Using the morphometric parameters described above, stream reaches are classified into 7 major stream types (Aa+ through G) based on s (1996) criteria. The relevant stream classifications
Appendix E Stream Type s Using the morphometric parameters described above, stream reaches are classified into 7 major stream types (Aa+ through G) based on s (1996) criteria. The relevant stream classifications
Channel Migration Assessment Clallam County: Pacific WRIA 20
 April 2013 Final Version April 2018 April 2013 Final Version April 2018 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Channel Migration Zones... 1 1.2 CMZs Developed by Department of Ecology for the
April 2013 Final Version April 2018 April 2013 Final Version April 2018 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Channel Migration Zones... 1 1.2 CMZs Developed by Department of Ecology for the
Association of State Floodplain Managers, Inc.
 Association of State Floodplain Managers, Inc. 2809 Fish Hatchery Road, Suite 204, Madison, WI 53713 Phone: 608-274-0123 Fax: 608-274-0696 Email: asfpm@floods.org Website: www.floods.org Need for Updating
Association of State Floodplain Managers, Inc. 2809 Fish Hatchery Road, Suite 204, Madison, WI 53713 Phone: 608-274-0123 Fax: 608-274-0696 Email: asfpm@floods.org Website: www.floods.org Need for Updating
Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping
 Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping E.1 Introduction Different types of shallow flooding commonly occur throughout the United States. Types of flows that result in shallow flooding
Appendix E Guidance for Shallow Flooding Analyses and Mapping E.1 Introduction Different types of shallow flooding commonly occur throughout the United States. Types of flows that result in shallow flooding
2. Background/Overview of Conditions
 2. Background/Overview of Conditions This section provides background information on the relevant conditions within the Town of Oakville that impact the formation and evolution of watercourses, including
2. Background/Overview of Conditions This section provides background information on the relevant conditions within the Town of Oakville that impact the formation and evolution of watercourses, including
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability
 Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability Stream Restoration Forum: Science and Regulatory Connections Andrew C. Wilcox Department of Geosciences University
Perspectives on river restoration science, geomorphic processes, and channel stability Stream Restoration Forum: Science and Regulatory Connections Andrew C. Wilcox Department of Geosciences University
EFFECTS OF RIPARIAN RETENTION (IN WATERSHEDS) ON ALLUVIAL FANS
 EFFECTS OF RIPARIAN RETENTION (IN WATERSHEDS) ON ALLUVIAL FANS TIM GILES GEOMORPHOLOGIST FLNRO EFFECTS OF RIPARIAN RETENTION (IN WATERSHEDS) ON ALLUVIAL FANS Description of alluvial fans Three case studies
EFFECTS OF RIPARIAN RETENTION (IN WATERSHEDS) ON ALLUVIAL FANS TIM GILES GEOMORPHOLOGIST FLNRO EFFECTS OF RIPARIAN RETENTION (IN WATERSHEDS) ON ALLUVIAL FANS Description of alluvial fans Three case studies
