UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
|
|
|
- Sheila Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A.C. 0/2/2 Item No. 4.8 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the S.Y.B.Sc. Program: B.Sc. Course: GEOLOGY (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic year )
2 S.Y.B.Sc. GEOLOGY Syllabus Credit Based and Grading System To be implemented from the Academic year SEMESTER III Course Code UNIT TOPICS Credits L / Week Palaeontology & Stratigraphy USGE30 I Palaeontology I II Palaeontology II 2 III Stratigraphy Crystallography I Characteristic of Crystals USGE302 II The thirty-two crystal classes and possible forms of each class 2 III X-ray Diffraction and Crystal imperfections Applied Geology USGE303 I II Field Geology Geomorphology and Cartography III Hydrogeology 2 USGEP30 USGEP302 USGEP303 Practical based on all the three courses in theory 3 9 2
3 SEMESTER IV Course Code UNIT TOPICS Credits L / Week Economic Mineral Deposits USGE40 I Introduction & Ore Genesis I II Ore Genesis I 2 III Ore Genesis II Optical Mineralogy and Systematic Mineralogy. USGE402 I Optical Properties of Minerals II Systematic Mineralogy: part I 2 III Systematic Mineralogy: part II Applied Geology USGE403 USGEP40 USGEP402 USGEP403 I Field Geology II Geomorphology and Cartography 2 III Hydrogeology Practical based on all the three courses in theory 3 9 3
4 Course Code Title Credits USGE30 PALAEONTOLOGY AND STRATIGRAPHY 2 Credits (45 lectures ) UNIT : PALAEONTOLOGY - I Modern concept of origin of life, principles and theories of evolution, mechanism & pattern of evolution, causes of migration, dispersal and extinction of organisms. Invertebrate Palaeontology: Brief study of evolutionary trends of: Lamellibranches, Gastropods, Cephalopods, and Trilobites, Echinoids, Graptolites. Trace fossils and Index fossils, Value of trace fossils in palaeoenvironmental interpretation, 5 Lectures UNIT II: PALAEONTOLOGY - II Micro-palaentology: Introduction, definition, different types of microfossils, their size range and composition, branches, uses. Introduction to Palynology: spores and pollens. Palaeobotany: Definition, conditions and different modes of preservation of plant fossils, classification and distribution of plants through geological ages. Brief study of following genera with respect to their characteristics and distribution: Ptillophyllum, Glossopteris, Gangamopteris, Vertebraria and Nilsonia. Record of plant fossils in India with reference to Gondwana and Post-Gondwana Flora. 5 Lectures UNIT III : STRATIGRAPHY Development of stratigraphic concepts, importance of stratigraphy. Stratigraphic classification & nomenclature, study of stratigraphic elements, lithostratigraphy and its units. Chronostratigraphy and its units, biostrtigraphy and its units; inter-relationship between lithostratigraphic, chronostratigraphic and biostrtigraphic units. Introduction to chemostratigraphy (oxygen and carbon), magnetostratigraphy and seismic stratigraphy. Stratification: processes controlling stratification- physical, chemical and biological. Vertical succession, lithological uniformity, heterogeneity, patterned succession, alternations, varves, cycles (symmetrical and asymmetrical). Lateral variations and facies concept. Unconformity: importance of unconformities, Classification, Structural classification and environmental classification. and evidence of unconformities. 5 Lectures 4
5 Course Code Title Credits USGE302 CRYSTALLOGRAPHY 2 Credits (45 lectures ) UNIT I: CHARACTERISTIC OF CRYSTALS Atomic arrangement in crystals, Bravais Lattices, Crystal symmetry, Elements of symmetry: Planes, Axes and Centre, Axis of inversion symmetry, Crystallographic axes, Miller Indices, Axial ratios, Classification of crystals, Stereographic projections of symmetry, Graphical symbols used in stereographic illustrations. 5 Lectures UNIT II: THE THIRTY-TWO CRYSTAL CLASSES AND POSSIBLE FORMS OF EACH CLASS Forms and crystal morphology, Name of forms, Illustration and description of forms, open forms and closed forms, point groups and crystal systems, Derivation of 32 classes of symmetry with Hermann-Mauguin symbols, Characteristic symmetry, and relationships between crystal axes and symmetry notation of crystal systems. 5 Lectures UNIT III: X-RAY DIFFRACTION AND CRYSTAL IMPERFECTIONS Twin crystals: Twin axis, Twin plane, Composition plane. Types of Twinning: Simple and Multiple contact twins, Simple and Multiple penetration twins, Cyclic twins, Twinning in Feldspars: Carlsbad, Manebech, Baveno, Albite, Albite-Carlsbad. X-ray Diffraction: Brief introduction of X-rays, Diffraction effects and Bragg equation, Application of X-rays in crystallography and mineralogy. 5 Lectures 5
6 Course Code Title Credits USGE303 APPLIED GEOLOGY 2 Credits (45 lectures ) UNIT : FIELD GEOLOGY Nature of Geologic Surveying: Definition & Aim. Uses of geologic surveying. Diversity of Surveys. Scope of geological field-work. Study of Outcrops: Likely places. Examination. Tracing. Importance of Contacts: Discrimination between different types of contacts. Eruptive contacts. Obscure bedding. Discrimination of Strike and Dip: Degree of accuracy. Cross-bedding. Bevelling of outcrops. Settling of beds. 5 Lectures Field Correlation: Attitude of contorted strata. Attitude of eruptive contacts. Field Observations: Schedule for Field Observations. General Suggestions for Field work: Beginning a field problem. Collecting and trimming samples. Taking photographs. Degree and accuracy of field work. UNIT II: GEOMORPHOLOGY AND CARTOGRAPHY Basic Concepts of Geomorphology: a) Energy for landform change, Isotopic dating, other methods b) Geomorphic Systems: people as Geomorphic Agents, People as creators of Landforms, Problems of using the Environment. c) Landforms controlled by Faults: Rift valley, Fault scarp features, Features associated with strike slip faulting, Block faulted landscape. d) Landforms controlled by Folds: Anticlines and Monoclines. Landforms of eroded folds. e) Drainage patterns on folds: Antecedent, Superimposed, Captured drainage. Volcanogenic landforms and intrusions: a) Energy of volcanic eruptions, b) Products of Volcano: Lava Flow, Pyroclasts. c) Types of Volcano: Scoria or Cinder Cones, Composite or Strato Volcanoes, Shied Volcanoes, Domes. d) Types of Eruptions: Volcanic Explosion, Pyroclastic flow. e) Erosion of Volcanic features: Plutons Intrusions. (5 lectures) 5 Lectures Weathering and Landforms: i) Weathering process: Physical, Chemical ii) Landforms produced by weathering: Corestones, Tors, Pits, Pans, Caverns, Rills, Duricrust. 6
7 Fluvial Processes and Landforms: a) Fluvial Transport and Deposition: Alluvial Fans, Floodplains and Terraces, Alluvial Bars, Braided Channels, Straight and Meandering Channels. b) Discharge of Water: Hydrograph Shapes, Flood Frequency, Patterns of Discharge. Eolian Processes and Landforms:. Eolian erosion. 2. Eolian transport and deposition. 3. Loess. Unit III: HYDROGEOLOGY Ground Water: Definition Hydrogeologic cycle: Precipitation. Evapo-transportation and Phreatophytes. Runoff and Hydrograph Components. Infiltration. Subsurface movement of water. Zones of groundwater. Water table. Discharge of ground water. Springs. 5 Lectures Occurrence of ground water: Origin of ground water. Rock properties affecting ground water. Vertical distribution of ground water. Geological formations as aquifers. Types of aquifers. Ground water movement: Darcy s Law. Coefficient of permeability. Ground water flow-lines and flow-nets 7
8 Semester III USGEP30 PRACTICAL: PALAEONTOLOGY AND STRATIGRAPHY Cr a) Identification (morphology, classification, geological distribution) and study of evolutionary trends of: trilobite, brachiopods, lamellibranchs, gastropods, cephalopods, echinoids, graptolites. b) Identification of micro fossils (morphology and geological distribution) : Two each from foraminifera, ostracods and radiolarians. c) Identification plant fossils: Gangamopteris, Glossopteris, Ptillophyllum, Nilsonia, Cladophlebis, Schizoneura, Vertebraria. Semester III USGEP302 PRACTICAL : CRYSTALLOGRAPHY a) Study of Symmetry: i. Symmetry elements of 32 classes of symmetry ii. Stereographic projections of Symmetry elements of 32 classes of symmetry Cr b) Study of all possible forms of crystals belonging to the following Fourteen classes of symmetry: i. CUBIC SYSTEM: Galena, Tetrahedrite & Pyrite classes ii. TETRAGONAL SYSTEM: Zircon, Chalcopyrite, Nickel sulfate classes iii. HEXAGONAL SYSTEM: Beryl, Apatite & Beta- Quartz classes. iv. TRIGONAL SYSTEM: Calcite, Tourmaline and Alpha- Quartz classes. v. ORTHORHOMBIC SYSTEM: Barite class. vi. MONOCLINIC SYSTEM: Gypsum class. vii. TRICLINIC SYSTEM: Axinite class. c) Study of Twin-axis, Twin plane and composition plane of the following types of Twin crystals: i. Simple contact twinning: Spinel, Rutile, Aragonite, Gypsum, Augite, Orthoclase (Baveno, Manebach, Carlsbad). ii. Simple penetration twinning: Staurolite, Augite, Orthoclase (Carlsbad-partially penetrant). iii. Multiple contact twinning: Albite. iv. Multiple penetration twinning: Fluorite, Diamond (Star), Chrysoberyl (Wheel). v. Multiple cyclic twinning: Aragonite, Chrysoberyl (Wheel). d) Measurement of Axial ratios of Tetragonal and Orthorhombic crystals by Formula calculation and Graphical methods 8
9 Semester III USGEP303 PRACTICAL Paper III APPLIED GEOLOGY Cr Drawing of Block and Profile Diagrams to indicate following features: Dip and strike of beds. Current bedding and cross bedding Graded Bedding Pillow Lavas. Contact zone details of Sills, Dykes and Batholiths. Laccolith, Lopolith and Phacolith. Three-dimensional details of inclined lineation. Flow cleavage and fracture cleavage relationship.. Types of folds and their features. Types of faults and their features. Horse, Drag and Brecciation in Faults. GEOMORPHOLOGY AND CARTOGRAPHY Measurement of areas enclosed within curves. HYDROGEOLOGY Problems on permeability, porosity and rate of flow and aquifer depths from resistivity data. 9
10 SEMESTER IV Course Code Title Credits USGE 40 ECONOMIC MINERAL DEPOSITS 2 Credits (45 lectures ) UNIT ORE GENESIS -I Introduction, definition of metalliferous and non-metalliferous deposits, ore mineral, gangue, tenor of ore, industial minerals, overburden and country rock. Classification of economically important metalliferous and non-metalliferous mineral deposits. Stratabound and stratiform ore deposits. Structural and stratigraphic controls on mineralization, metallogenic epochs and provinces. Processes of formation of mineral deposits. Magmatic concentration (early and late magmatic mineral deposits) Sublimation and pegmatatic deposits 5 Lectures UNIT II ORE GENESIS II Hydrothermal processes, cavity filling and metasomatism: Hydrothermal processes: Principle, character of solution, types of openings in rocks, factors affecting deposition from hydrothermal solutions, wall rock alterations. Cavity filling deposits: processes of formation and characteristic features of: fissure veins and its types (in brief), stock work, saddle veins, ladder veins, pitches and flats, breccia filling deposits, solution cavity fillings. Contact Metasomatic Deposits: definition, criteria of replacement, resulting mineral deposits. Sedimentation deposits, Metamorphic deposits. Evaporation deposits: brief account of non-metallic deposits of ocean water, lake water, ground water and hot springs. Residual deposits: conditions favouring formation of residual deposits. Mechanical concentration: principles and processes of formation of placer deposits (eluvial, alluvial, beach and aeolian). 5 lectures UNIT III ORE GENESIS - III Oxidation and solution in the zone of oxidation, ore deposits in the zone of oxidation. Supergene sulphide enrichment: requirements for supergene sulphide deposition, recognition of sulphide enrichment. Gossans and cappings, role of iron gossans, limonite and false gossans. Distribution of mineral deposits Formation, association and Indian distribution of following ore minerals: Mica, Copper, Manganese, Lead and Zinc, Bauxite, Chromite, Gold 5 Lectures 0
11 Course Code Title Credits USGE 402 UNIT I: OPTICAL MINERALOGY AND SYSTEMATIC MINERALOGY OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS 2 Credits (45 lectures ) Nature and behaviour of light: Non-polarised and Polarised light, Refraction and Refractive index, Double refraction, Nicol prism and Filter poloroid, Isotropic and Anisotropic substances, Polarizing Microscope: Its Construction and Working. Optical characteristics: Relief, Becke s test, Twinkling, Pleochroism, Birefringence, Polarization colours, Newton s scale, Extinction and Extinction angle, Anomalous polarization colours, Uniaxial and Biaxial minerals, Optical indicatrix, Interference figures, Optic sign, Sign of elongation, Use of Quartz wedge, Mica plate and Gypsum plate. 5 Lectures UNIT II: SYSTEMATIC MINERALOGY: PART I Stability relationships, Condition of formation, Crystallography, Physical and optical properties, Composition and structure, Diagnostic Features, Occurrence and Uses of: i. Silica Group ii. Feldspar Group iii. Feldspathoid Group iv. Mica Group 5 lectures UNIT III: SYSTEMATIC MINERALOGY: PART II Stability relationships, Condition of formation, Crystallography, Physical and optical properties, Composition and structure, Diagnostic Features, Occurrence and Uses of: i. Amphibole Group ii. Pyroxene Group iii. Olivine Group iv. Garnet Group v. Zeolite Group 5 Lectures
12 Course Code USGE403 Title APPLIED GEOLOGY Credits 2 Credits (45 lectures ) UNIT I : APPLED GEOLOGY Preparation of Geological Reports: General instructions. Parts of Manuscript report. General outline of Report. Abstract. Introduction. Summary and Conclusions. Recommendations. Geography. Stratigraphy and Petrography. Geologic structure. Geologic History. Economic considerations. Quotations and Footnotes. Table of contents. Index. Instruments and Methods of Geologic Mapping: a) Clinometer and Brunton Compass: their construction and use. Clinometer and compass method of reconnaissance mapping. b) Hand Levels: Their construction and use. Hand Level Method of Determination of Dip and Strike. Hand Level Traverses. c) Altimeter: Its construction and use.altimeter techniques, including horizontal control, system of recording stations, note taking and correction of readings. UNIT II : GEOMORPHOLOGY AND CARTOGRAPHY Coastal Processes and Landforms: Dominant influences on Coastal Landforms, Sea level changes. Erosional land forms of the coast. Depositional landforms of the coast. Karst Processes and Landforms: Limestone Solution and erosion rates. Surface landforms: Minor solution sculpture, Enclosed depressions. caves and springs. Glaciers and Glaciated landforms: Glaciers: Ice movement, flow patterns, forms of glacier surfaces Glaciated erosional landforms and glaciated depositional landforms CARTOGRAPHIC AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS: Topographic Analysis: Topographical profiles Projected profiles and Superimposed profiles Spur Profiles. Slope Analysis: Morphological Mapping by Savigear s Method. Generalized Contour Map. Drainage basin analysis: a) Linear aspects. b) Areal aspects 5 Lectures 5 Lectures 2
13 UNIT III : HYDROGEOLOGY Artificial recharge of ground water: Concept, methods, water spreading. waste water reused. Recharge mounds. Induced recharge. 5 Lectures Surface Investigations of Ground water: Test-drilling. Resistivity logging. Potential logging. Temperature logging. Semester IV USGEP40 PRACTICAL: ECONOMIC MINERAL DEPOSITS Identification (with the help of physical properties), chemical composition, origin and Indian occurrences of Ore minerals and Industrial minerals of following minerals. Barite Barytes Bauxite Biotite Calcite Chalcopyrite Chromite Cuprite Dolomite Fluorite Galena Garnet Graphite Gypsum Hematite Ilmenite Kyanite Limonite Magnesite Magnetite Malachite Marble Muscovite Psilomelane Pyrite Pyrolusite Serpentine Sphalerite Stibnite Talc Tourmaline Semester IV USGEP402 PRACTICAL: MINERALOGY Cr Study of Physical and Optical characters, mode of formation and occurrence in Rock types of the following Igneous and Metamorphic Minerals: Igneous rock forming minerals: Quartz, Orthoclase, Microcline, Albite, Labrador Nepheline, Sodalite, Muscovite, Biotite, Hornblende, Augite, Aegirine, Hypersthen Tourmaline and Apatite. Metamorphic minerals: Garnet, Staurolite, Chlorite, Talc, Serpentine, Actinolite, Tremolite, Anthophyllite, Epidote, Andalusite, Kyanite, Sillimanite, Calcite, Dolomite, Asbestos, Chrysolite, Magnesite. Study of Physical properties, mode of occurrence and conditions of origin of the following Secondary minerals: Quartz (Rock crystal), Amethyst, Calcite (Rhombohedral, Scalenohedral & Nailhead spar), Stilbite, Scolecite, Mesolite, Chabazite, Laumontite,, Apophyllite (Prismatic & Pyramidal), Gyrolite and Okenite. 3
14 Determination of An-content of Plagioclase by symmetrical extinction method on Polarizing Microscope stage. Semester IV USGEP403 PRACTICAL: GEOMORPHOLOGY AND CARTOGRAPHY Cr GEOMORPHOLOGY AND CARTOGRAPHY Topographic Profiles, Projected Profiles, Superimposed Profiles and Spur Profiles. Longitudinal and cross valley profiles. Drainage basin analysis Linear aspects. Hypsometric analysis. HYDROGEOLOGY Skeleton diagrams to plot shape of water table. Seismic Refraction problem, Resistivity problem Construction of Flow nets. 4
15 LIST OF RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS USGE30. Elements of Micropalaeontology: G. Bignot 2. Introduction to Palaeontology: Arnold 3. Invertebrate Palaeontology and Evolution: Clarkson 4. Principles of Invertebrate Palaeontology: R. Shrock & W. Twenhofel 5. Principles of Palaeontology: D. Romp & S. Stanley 6. Principles of Palaeontology: T. Olivier 7. Micropalaeontology: Jones 8. A Practical Approach to Sedimentology: Roy Lindholm 9. Basic Concepts of Historical Geology: E.W.Spencer 0. Historical Geology: Dunbar. Principles of Stratigraphy: Weller 2. Fundamentals of Historical Geology & Stratigraphy of India: Ravindra Kumar 3. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy : G. Nichols RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS LIST OF RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS USGE302. Rutley s Elements of Mineralogy (27 TH Edition) H.H. Read and Revised by C.D. Gribble (CBS Publications) 2. Manuel of Mineralogy (2 st Edition) Cornelius, S. Hurlbut Jr., Cornelius Klein (J. Wiley & Sons) 3. Textbook of Mineralogy Dana and Ford (Asia Publishing House) 4. Elements of Mineralogy : Berry, Mason and Dietrich (W.H Freeman and Company) 5. Rock Forming Minerals: Deer, Howie, Zussman. 6. Mineralogy (2 nd Edition) Dexter Perkins ( PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd) 7. Minerals Hans- R. Wenk and A. Bulakh (Cambridge University Press) LIST OF RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS USGE303 and 403. Manuel of Field Geology: Compton R.J. 2. Field Geology: Lahee. 3. Earth's changing Surface. By M.J. Selby 4. Techniques in geomorphology. By C.A.M. King 5. Groundwater Hydrology: Todd D.K. 6. Groundwater Assessment, Development and Management: Karant K.R. 7. Groundwater: Raghunath H.M. 5
16 LIST OF RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS USGE 40. A Practical Approach to Sedimentology: Roy Lindholm 2. Basic Concepts of Historical Geology: E.W.Spencer 3. Historical Geology: Dunbar 4. Principles of Stratigraphy: Weller 5. Fundamentals of Historical Geology & Stratigraphy of India: Ravindra Kumar 6. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy : G. Nichols 7. Economic mineral deposits: Jensen and Bateman 8. Ore geology and Industrial minerals, An introduction : A.M. Evans LIST OF RECOMMENDED REFERENCE BOOKS USGE402. Rutley s Elements of Mineralogy (27 TH Edition) H.H. Read and Revised by C.D. Gribble (CBS Publications) 2. Manuel of Mineralogy (2 st Edition) Cornelius,S. Hurlbut Jr., Cornelius Klein (J. Wiley & Sons) 3. Textbook of Mineralogy Dana and Ford (Asia Publishing House) 4. Optical Mineralogy (2 nd Edition) A.F Rogers an P.F Kerr (McGraw- Hill) 5. Elements of Mineralogy : Berry, Mason and Dietrich (W.H Freeman and Company) 6. Rock Forming Minerals: Deer, Howie, Zussman. 7. Optical Mineralogy (2 nd Edition) David Shelly (Elsevier) 8. Introduction to Optical Mineralogy (Third Edition) W.D Nesse (Oxford University Press) 9. Mineralogy (2 nd Edition) Dexter Perkins ( PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd) 0. Minerals Hans- R. Wenk and A. Bulakh (Cambridge University Press) 6
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus for B.Sc IV th Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc IV th Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.Geo.4.01 - Economic Geology S.Geo.4.02 - Optical mineralogy
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc IV th Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.Geo.4.01 - Economic Geology S.Geo.4.02 - Optical mineralogy
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus for B.Sc IV Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc IV Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.Geo.4.01 - Economic Geology S.Geo.4.02 - Optical mineralogy
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc IV Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.Geo.4.01 - Economic Geology S.Geo.4.02 - Optical mineralogy
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus forb.sc III rd Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus forb.sc III rd Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.3.01 Stratigraphy, General and Invertebrate Paleontology
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus forb.sc III rd Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.3.01 Stratigraphy, General and Invertebrate Paleontology
St. Xavier s College Mumbai
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
B.SC lst YEAR GEOLOGY
 1 B.SC lst YEAR GEOLOGY - 2010-11 Scheme of examination, Maximum marks assigned to the paper and Internal assessment Ist SEMESTER Max. Marks Theory I.A. Periods/ Week Paper-101 General Geology 50 45 05
1 B.SC lst YEAR GEOLOGY - 2010-11 Scheme of examination, Maximum marks assigned to the paper and Internal assessment Ist SEMESTER Max. Marks Theory I.A. Periods/ Week Paper-101 General Geology 50 45 05
Deccan Education Society s FERGUSSON COLLEGE, PUNE (AUTONOMOUS) PROPOSED SYLLABUS UNDER AUTONOMY. SECOND YEAR B.Sc. SEMESTER III
 Deccan Education Society s FERGUSSON COLLEGE, PUNE (AUTONOMOUS) PROPOSED SYLLABUS UNDER AUTONOMY SECOND YEAR B.Sc. SEMESTER III PROPOSED SYLLABUS FOR S.Y.B.Sc. GEOLOGY Academic Year 017-018 PAPER CODE:
Deccan Education Society s FERGUSSON COLLEGE, PUNE (AUTONOMOUS) PROPOSED SYLLABUS UNDER AUTONOMY SECOND YEAR B.Sc. SEMESTER III PROPOSED SYLLABUS FOR S.Y.B.Sc. GEOLOGY Academic Year 017-018 PAPER CODE:
ACHARYA NAGARJUNA UNIVERSITY :: NAGARJUNANAGAR CBCS -B. Sc. GEOLOGY Syllabus With effective from
 ACHARYA NAGARJUNA UNIVERSITY :: NAGARJUNANAGAR-522 510 CBCS -B. Sc. GEOLOGY Syllabus With effective from 2015-16 S.No Semester Title of the Paper Max.Marks. 1 Semester-I P-I Physical Geology & Crystallography
ACHARYA NAGARJUNA UNIVERSITY :: NAGARJUNANAGAR-522 510 CBCS -B. Sc. GEOLOGY Syllabus With effective from 2015-16 S.No Semester Title of the Paper Max.Marks. 1 Semester-I P-I Physical Geology & Crystallography
And the study of mineral the branch in geology is termed as mineralogy. (Refer Slide Time: 0:29)
 Earth Sciences for Civil Engineering Professor Javed N Malik Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 2 Lecture No 6 Rock-Forming Minerals and their Properties (Part-2)
Earth Sciences for Civil Engineering Professor Javed N Malik Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 2 Lecture No 6 Rock-Forming Minerals and their Properties (Part-2)
Mineralogy ( ) Chapter 5: Crystallography
 Hashemite University Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of earth and environmental sciences Mineralogy (1201220) Chapter 5: Crystallography Dr. Faten Al-Slaty First Semester 2015/2016
Hashemite University Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of earth and environmental sciences Mineralogy (1201220) Chapter 5: Crystallography Dr. Faten Al-Slaty First Semester 2015/2016
Solapur University, Solapur. Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year
 Solapur University, Solapur Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year- 2015-16 Course Structure Total Credit 16 - (Theory (4 x 3) = 12+Practical
Solapur University, Solapur Syllabus for B.Sc. II- Geochemistry - (IDS) Semester System - CGPA To be implemented from Academic Year- 2015-16 Course Structure Total Credit 16 - (Theory (4 x 3) = 12+Practical
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus for BSc II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for BSc II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.2.01-Introduction to Petrology, Geotectonics and Economic
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for BSc II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.2.01-Introduction to Petrology, Geotectonics and Economic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DURGAPUR DEPARTMENT OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DURGAPUR DEPARTMENT OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES Curriculum & Syllabi for B. Tech. Course SECOND/ FOURTH SEMESTER Sub. Code Subject L-T-P Credits ES 01 ENVIRONMENTAL
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DURGAPUR DEPARTMENT OF EARTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES Curriculum & Syllabi for B. Tech. Course SECOND/ FOURTH SEMESTER Sub. Code Subject L-T-P Credits ES 01 ENVIRONMENTAL
R.Suhasini., Assistant Professor Page 1
 UNIT I PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Geology in civil engineering branches of geology structure of earth and its composition weathering of rocks scale of weathering soils - landforms and processes associated with river,
UNIT I PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Geology in civil engineering branches of geology structure of earth and its composition weathering of rocks scale of weathering soils - landforms and processes associated with river,
GEOLOGY CLASS-XI THEORY
 CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS for Classes XI & XII 337 338 CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS for Classes XI & XII CLASS-XI THEORY One Paper 3 Hours 7O Unit Unitwise Weightage Periods I. General Geology and Physical Geology
CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS for Classes XI & XII 337 338 CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS for Classes XI & XII CLASS-XI THEORY One Paper 3 Hours 7O Unit Unitwise Weightage Periods I. General Geology and Physical Geology
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
 A.C. 10/2/2012 Item No..22 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the M.Sc. Semester I and II Program: M.Sc. Course : GEOLOGY (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic year 2012
A.C. 10/2/2012 Item No..22 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the M.Sc. Semester I and II Program: M.Sc. Course : GEOLOGY (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with effect from the academic year 2012
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
About Earth Materials
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Sedimentation & Stratigraphy. Lab 3: Heavy Mineral Analysis Using the Franz Magnetic Separator
 Sedimentation & Stratigraphy Name I. Introduction Lab 3: Heavy Mineral Analysis Using the Franz Magnetic Separator In Lab 2, we used sand size-distributions to determine if the sediments were derived from
Sedimentation & Stratigraphy Name I. Introduction Lab 3: Heavy Mineral Analysis Using the Franz Magnetic Separator In Lab 2, we used sand size-distributions to determine if the sediments were derived from
Last Time. GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy. Polymorphs & Polymorphism. Other Crystal Structures. Other Crystal Structures. This Week s Agenda
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy 1. Polymorphs and Polymorphism 2. Pseudomorphs and other definitions 3. Crystal Habit Lecture 7: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture?)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy 1. Polymorphs and Polymorphism 2. Pseudomorphs and other definitions 3. Crystal Habit Lecture 7: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture?)
NAME OF THE PROGRAMME : M.Sc. GEOLOGY PROGRAMME OUTCOME
 NAME OF THE PROGRAMME : M.Sc. GEOLOGY PROGRAMME OUTCOME 1. Understanding development of landforms through Earth's external processes by various geological agents; marine processes and formation of marine
NAME OF THE PROGRAMME : M.Sc. GEOLOGY PROGRAMME OUTCOME 1. Understanding development of landforms through Earth's external processes by various geological agents; marine processes and formation of marine
Scheme of Examination, Maximum Marks and Internal Assessment
 B.Sc. 1 st Year Geology w.e.f. session 2016-2017 Scheme of Examination, Maximum Marks and Internal Assessment 1 st Semester Paper Code Title of Paper Max. Marks Theory I.A. Periods/Week Paper-101 General
B.Sc. 1 st Year Geology w.e.f. session 2016-2017 Scheme of Examination, Maximum Marks and Internal Assessment 1 st Semester Paper Code Title of Paper Max. Marks Theory I.A. Periods/Week Paper-101 General
Pre-Lab Reading Questions ES202
 ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
GY-343 Petrology Petrographic Microscope Laboratory
 Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
Earth Materials II Review Optical Mineralogy and Igneous Minerals
 Earth Materials II Review Optical Mineralogy and Igneous Minerals Refractive Index and Angle of Refraction Refractive Index(R. I. ) = velocity of light in a vacuum velocity of light in a medium The refractive
Earth Materials II Review Optical Mineralogy and Igneous Minerals Refractive Index and Angle of Refraction Refractive Index(R. I. ) = velocity of light in a vacuum velocity of light in a medium The refractive
Metamorphism (means changed form
 Metamorphism (means changed form) is recrystallization without melting of a previously existing rock at depth in response to a change in the environment of temperature, pressure, and fluids. Common minerals
Metamorphism (means changed form) is recrystallization without melting of a previously existing rock at depth in response to a change in the environment of temperature, pressure, and fluids. Common minerals
St. Xavier s College Mumbai. Syllabus For B.Sc.II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus For B.Sc.II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.2.01-Introduction to Petrology, Geotectonics and Economic
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus For B.Sc.II nd Semester Courses in Geology (November 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.2.01-Introduction to Petrology, Geotectonics and Economic
OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2018 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE
 OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2018 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE SHOW THEM Fossils of New York and more! Please sign in at the Earth Science Table before you start
OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2018 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE SHOW THEM Fossils of New York and more! Please sign in at the Earth Science Table before you start
Analytical Techniques. Semester II: Field work/report + viva Semester III: Semester IV: Beneficiation
 Approved syllabus for M.Sc. Geology by the members of Board of Studies for the Sessions The syllabus with the paper combinations is as under Semester I: Paper I: Geomorphology Paper III: Mineralogy and
Approved syllabus for M.Sc. Geology by the members of Board of Studies for the Sessions The syllabus with the paper combinations is as under Semester I: Paper I: Geomorphology Paper III: Mineralogy and
Example Quiz on Earthquakes
 Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Biaxial Minerals This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014
 1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy
 1 Lab # 3: Biaxial minerals ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy In this laboratory session we will introduce the concepts of the Biaxial Indicatrix, Optic Axes, Vibration Directions and Ray Paths,
1 Lab # 3: Biaxial minerals ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy In this laboratory session we will introduce the concepts of the Biaxial Indicatrix, Optic Axes, Vibration Directions and Ray Paths,
Rocks and Minerals C Key. Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida
 Rocks and Minerals C Key Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Station 1 Answer: Azurite 2. What is the chemical formula Answer: Cu 3 (CO 3 ) 2 (OH) 2 3. What element
Rocks and Minerals C Key Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Station 1 Answer: Azurite 2. What is the chemical formula Answer: Cu 3 (CO 3 ) 2 (OH) 2 3. What element
UNIVERSITY OF LIMPOPO
 UNDERGRADUATE GEOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF LIMPOPO Module / Course Descriptions GEOL 101 Introduction to Geology Credits: 15 4 X 45 minutes 1 x 3 hours 1 x 45 minutes 1 Physical properties of Planet Earth. Earthquakes
UNDERGRADUATE GEOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF LIMPOPO Module / Course Descriptions GEOL 101 Introduction to Geology Credits: 15 4 X 45 minutes 1 x 3 hours 1 x 45 minutes 1 Physical properties of Planet Earth. Earthquakes
Mineral List : Rock List:
 Team Name Mineral List : A. Lepidolite B. Calcite C. Dolomite D. Feldspar E. Halite AB. Quartz AC. Apatite AD.Hematite AE. Magnetite BC. Galena BD. Pyrite BE. Gypsum CD. Chalcopyrite CE. Staurolite DE.
Team Name Mineral List : A. Lepidolite B. Calcite C. Dolomite D. Feldspar E. Halite AB. Quartz AC. Apatite AD.Hematite AE. Magnetite BC. Galena BD. Pyrite BE. Gypsum CD. Chalcopyrite CE. Staurolite DE.
Geol 5310 (Spr 09) Lab 1 Review of Optical Mineralogy (9/9/09) Due Date: Wed., September 16.
 Geol 5310 (Spr 09) Lab 1 Review of Optical Mineralogy (9/9/09) Due Date: Wed., September 16. Name_ Score /36 Objective: Re-familiarize yourself with the optical properties of minerals and concepts like,
Geol 5310 (Spr 09) Lab 1 Review of Optical Mineralogy (9/9/09) Due Date: Wed., September 16. Name_ Score /36 Objective: Re-familiarize yourself with the optical properties of minerals and concepts like,
GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7b: Optical Mineralogy Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick Last Time 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and light transmission Light
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7b: Optical Mineralogy Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick Last Time 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and light transmission Light
Geology : Embedded Inquiry
 Geology : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Geology : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms. From:
 Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms From: http://webmineral.com/data/rhodochrosite.shtml The Physical Properties of Minerals Color Streak Luster Hardness External Crystal Form Cleavage The
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms From: http://webmineral.com/data/rhodochrosite.shtml The Physical Properties of Minerals Color Streak Luster Hardness External Crystal Form Cleavage The
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Matter and Minerals. Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more).
 1 2 Matter and Minerals Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more). continued... 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Also crystalline,
1 2 Matter and Minerals Earth 9 th edition Chapter 3 Minerals: summary in haiku form "Mineral" defined: natural, inorganic, solid (and two more). continued... 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Also crystalline,
Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets
 1 Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets June 1999 Exam June 2000 Exam January 2001 Exam June 2001Exam June 2002 Exam June 2003 Exam June 2004 Exam August 2005 Exam
1 Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets June 1999 Exam June 2000 Exam January 2001 Exam June 2001Exam June 2002 Exam June 2003 Exam June 2004 Exam August 2005 Exam
GEOLOGY CURRICULUM. Unit 1: Introduction to Geology
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Foundation Unit A.M. THURSDAY, 20 May hour
 Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY - GL1 Foundation Unit A.M. THURSDAY, 20 May 2010 1 hour Question 1 Question 2. 1211 01 01 Question 3 Question 4 Total 60 ADDITIONAL
Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1211/01 GEOLOGY - GL1 Foundation Unit A.M. THURSDAY, 20 May 2010 1 hour Question 1 Question 2. 1211 01 01 Question 3 Question 4 Total 60 ADDITIONAL
Required Materials Plummer, C., Physical geology. Columbus, OH: McGraw Hill Higher Education
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates
 Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
Why are some minerals harder than others? Their atomic structure and chemical formula. This is how we classify minerals! Silicates and Non-Silicates Part #1 - Silicates: Silicon and Oxygen make up 70%
SUBJECT GEOLOGY PAGE 1
 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) (THREE YEAR DEGREE COURSE) SUBJECT GEOLOGY PAGE 1 COURSE STRUCTURE FIRST YEAR PAPER 101: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY PAPER 102: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY PAPER 103: CRYSTALLOGRAPHY AND MINERALOGY
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) (THREE YEAR DEGREE COURSE) SUBJECT GEOLOGY PAGE 1 COURSE STRUCTURE FIRST YEAR PAPER 101: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY PAPER 102: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY PAPER 103: CRYSTALLOGRAPHY AND MINERALOGY
OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2017 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE. New York s Gemstone
 OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2017 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE 2017 SHOW THEME Garnet -variety: ALMANDINE New York s Gemstone Please sign in at the Earth Science
OFFICIAL MID-HUDSON VALLEY GEM & MINERAL SOCIETY (MHVG&MS) 2017 EARTH SCIENCE SCAVENGER HUNT QUESTIONNAIRE 2017 SHOW THEME Garnet -variety: ALMANDINE New York s Gemstone Please sign in at the Earth Science
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University
 E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes
 Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 2 MARKS
 YEAR : II SEMESTER : III DEPARTMENT : CIVIL CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 1. What is Physical weathering? 2. Define Stratigraphy and Palaeontology? 3. What is meant by chemical weathering 4. Describe
YEAR : II SEMESTER : III DEPARTMENT : CIVIL CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 1. What is Physical weathering? 2. Define Stratigraphy and Palaeontology? 3. What is meant by chemical weathering 4. Describe
Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM)
 Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 6: Plate Tectonics and Volcanism Calbuco volcano (Chile) (March, 2015) https://www.reddit.com/r/photoshopbattles/comments/
Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 6: Plate Tectonics and Volcanism Calbuco volcano (Chile) (March, 2015) https://www.reddit.com/r/photoshopbattles/comments/
Igneous petrology EOSC 321
 Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 2: Determination of plagioclase composition. Mafic and intermediate plutonic rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Determine plagioclase composition
Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 2: Determination of plagioclase composition. Mafic and intermediate plutonic rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Determine plagioclase composition
Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. Symmetry. EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation.
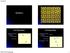 Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Chapter 4. Diamonds are forever EARTH MATERIALS: MINERALS AND ROCKS. covalent bonds. ionic bonds of sodium chloride transfer or. exchange of electrons
 Chapter 4 EARTH MATERIALS: MINERALS AND ROCKS Diamonds are forever Electron structure of the carbon atom (carbon-12). The electrons, each with a charge of 1, are represented as a negatively charged cloud
Chapter 4 EARTH MATERIALS: MINERALS AND ROCKS Diamonds are forever Electron structure of the carbon atom (carbon-12). The electrons, each with a charge of 1, are represented as a negatively charged cloud
University of Pune Three Year B. Sc. Degree Course in GEOLOGY S.Y.B.Sc. Syllabus (To be implemented from Academic Year )
 University of Pune Three Year B. Sc. Degree Course in GEOLOGY S.Y.B.Sc. Syllabus (To be implemented from Academic Year 2014-15) 1 SEMESTER-I Paper-I: GL: 211 Mineralogy UNIT I DESCRIPTIVE MINERALOGY (No.
University of Pune Three Year B. Sc. Degree Course in GEOLOGY S.Y.B.Sc. Syllabus (To be implemented from Academic Year 2014-15) 1 SEMESTER-I Paper-I: GL: 211 Mineralogy UNIT I DESCRIPTIVE MINERALOGY (No.
God Wholeness Rocks Minerals (Chemical bonds, Crystals) Chemical elements Atoms Something Nothing God
 God Wholeness Rocks Minerals (Chemical bonds, Crystals) Chemical elements Atoms Something Nothing God Theme 4. Cristals and Minerals 4.1. Elements 4.2. Identifying minerals 4.3. Common minerals 4.1. Elements
God Wholeness Rocks Minerals (Chemical bonds, Crystals) Chemical elements Atoms Something Nothing God Theme 4. Cristals and Minerals 4.1. Elements 4.2. Identifying minerals 4.3. Common minerals 4.1. Elements
Contents. Acknowledgments INTRODUCTION 3 HOW ARE MINERALS IDENTIFIED? 39 MATERIALS OF THE SOLID EARTH 15 FUNDAMENTALS OF CRYSTAL STRUCTURES 63
 Table of Preface Acknowledgments 1 2 xiii xv INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Formation of Earth s chemical elements in supernovae 4 1.2 Birth of the solar system and Earth 5 1.3 Accretion and early history of the Earth
Table of Preface Acknowledgments 1 2 xiii xv INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Formation of Earth s chemical elements in supernovae 4 1.2 Birth of the solar system and Earth 5 1.3 Accretion and early history of the Earth
Semester Plan (Practical / tutorials / Assignment)
 16/10/17 13/09/17 19/09/17 05/09/17 25/09/17 06/09/17 12/09/17 08/09/17 18/09/17 30/08/17 05/09/17 08/08/17 11/09/17 16/08/17 08/08/17 01/08/17 24/07/17 10/08/17 01/08/17 25/08/17 20/07/17 26/07/17 25/07/17
16/10/17 13/09/17 19/09/17 05/09/17 25/09/17 06/09/17 12/09/17 08/09/17 18/09/17 30/08/17 05/09/17 08/08/17 11/09/17 16/08/17 08/08/17 01/08/17 24/07/17 10/08/17 01/08/17 25/08/17 20/07/17 26/07/17 25/07/17
S.Y.B.Sc Syllabus Revision Workshop (3 rd - 4 th October 2008) Geology Dept, Fergusson College, Pune
 S.Y.B.Sc Syllabus Revision Workshop (3 rd - 4 th October 2008) Geology Dept, Fergusson College, Pune-411004 PROPOSED REVISED SYLLABUS TO BE IMPLEMENTED FROM YEAR 2009-2010 1 UNIVERSITY OF PUNE S.Y.B.Sc
S.Y.B.Sc Syllabus Revision Workshop (3 rd - 4 th October 2008) Geology Dept, Fergusson College, Pune-411004 PROPOSED REVISED SYLLABUS TO BE IMPLEMENTED FROM YEAR 2009-2010 1 UNIVERSITY OF PUNE S.Y.B.Sc
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Office in Natural Resources Building, Room 322 (970) 491-7826 warnercnr.colostate.edu/geosciences-home (http:// warnercnr.colostate.edu/geosciences-home) Richard Aster, Department
DEPARTMENT OF GEOSCIENCES Office in Natural Resources Building, Room 322 (970) 491-7826 warnercnr.colostate.edu/geosciences-home (http:// warnercnr.colostate.edu/geosciences-home) Richard Aster, Department
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
GEOL 251 Minerals and Rocks 2018 Schedule and General Course Information
 GEOL 251 Minerals and Rocks 2018 Schedule and General Course Information Goals In this core paper, you will study practical and theoretical aspects of minerals and their occurrence in the different rock
GEOL 251 Minerals and Rocks 2018 Schedule and General Course Information Goals In this core paper, you will study practical and theoretical aspects of minerals and their occurrence in the different rock
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc
 1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc 2. Which material is made mostly of the mineral quartz? A) sulfuric acid B) pencil lead C) plaster of paris D)
1. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite B) fluorite C) galena D) talc 2. Which material is made mostly of the mineral quartz? A) sulfuric acid B) pencil lead C) plaster of paris D)
SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
 GEOL 100 CIC Approval: 12/12/2002 BOT APPROVAL: STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Spring 2003 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
GEOL 100 CIC Approval: 12/12/2002 BOT APPROVAL: STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Spring 2003 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS
 GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses Are Required
GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses Are Required
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Economic Ores. - Mostly metals
 Economic Ores - Mostly metals Intro points An ore is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. Gangue is the commercially valueless material
Economic Ores - Mostly metals Intro points An ore is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. Gangue is the commercially valueless material
THE UNIVERSITY OF BURDWAN
 THE UNIVERSITY OF BURDWAN Syllabus for B.SC. 3-Yr. Degree Course in Geology (General) w.e.f. 2014-15 1. For Three year B.Sc (General) course in Geology the total marks is 400 in Part-I, Part-II and Part-III.
THE UNIVERSITY OF BURDWAN Syllabus for B.SC. 3-Yr. Degree Course in Geology (General) w.e.f. 2014-15 1. For Three year B.Sc (General) course in Geology the total marks is 400 in Part-I, Part-II and Part-III.
Geology 12 Exam Review Package
 Geology 12 Exam Review Package Exam Date: Supplies: Thursday June 11 th, 1:00pm to 4:00pm Pen, pencil, eraser, calculator (all graphing calculators will have their memories cleared at the start of the
Geology 12 Exam Review Package Exam Date: Supplies: Thursday June 11 th, 1:00pm to 4:00pm Pen, pencil, eraser, calculator (all graphing calculators will have their memories cleared at the start of the
Figure 1.2. Growth of the world s population through history. Notice the sharp drop due to the Black Death that struck Europe in 1348, and the sharp
 Figure 1.2. Growth of the world s population through history. Notice the sharp drop due to the Black Death that struck Europe in 1348, and the sharp rise that occurred in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.
Figure 1.2. Growth of the world s population through history. Notice the sharp drop due to the Black Death that struck Europe in 1348, and the sharp rise that occurred in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.
Indian Statistical Institute Junior Research Fellowship in Geology, Entrance Examination 2015
 Indian Statistical Institute Junior Research Fellowship in Geology, Entrance Examination 2015 BOOKLET No. Afternoon TEST CODE: GEB Time: 2 hours Part I - one question 1 X 25 = 25 Part II five questions
Indian Statistical Institute Junior Research Fellowship in Geology, Entrance Examination 2015 BOOKLET No. Afternoon TEST CODE: GEB Time: 2 hours Part I - one question 1 X 25 = 25 Part II five questions
ESS Minerals. Lee. 1. The table below shows some properties of four different minerals.
 Name: ESS Minerals Pd. 1. The table below shows some properties of four different minerals. The minerals listed in the table are varieties of which mineral? (A) garnet (B) magnetite (C) olivine (D) quartz
Name: ESS Minerals Pd. 1. The table below shows some properties of four different minerals. The minerals listed in the table are varieties of which mineral? (A) garnet (B) magnetite (C) olivine (D) quartz
1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire
 UNIT 3 EXAM ROCKS AND MINERALS NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire FRANCONIA, N.H. Crowds
UNIT 3 EXAM ROCKS AND MINERALS NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on on the photographs and news article below. Old Man s Loss Felt in New Hampshire FRANCONIA, N.H. Crowds
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
Section 11.1 pp Where Mountains Form
 Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
Unit 2 Exam: Rocks & Minerals
 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the 2001 edition of the Earth Science Reference Tables, the map and cross section below, and your knowledge of Earth science. The shaded
MINERALOGY LABORATORY Metamorphic Rocks and Minerals
 Some of the samples used in Mineralogy Lab are museum specimens. Please do not destroy or heist them. You can do just about anything you want to the grungy ones, but be nice to the pretty specimens as
Some of the samples used in Mineralogy Lab are museum specimens. Please do not destroy or heist them. You can do just about anything you want to the grungy ones, but be nice to the pretty specimens as
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
Name: 1) What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water? A) 6.1 g/cm 3 C) 1.8 g/cm 3 B) 5.7 g/cm 3 D) 12.2 g/cm 3 2) In which two Earth
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
Objectives of this Lab. Introduction. The Petrographic Microscope
 Geological Sciences 101 Lab #9 Introduction to Petrology Objectives of this Lab 1. Understand how the minerals and textures of rocks reflect the processes by which they were formed. 2. Understand how rocks
Geological Sciences 101 Lab #9 Introduction to Petrology Objectives of this Lab 1. Understand how the minerals and textures of rocks reflect the processes by which they were formed. 2. Understand how rocks
CHAPTER 1: MINERALS: DEFINITION, PROPERTIES AND OCCURRENCES. Sarah Lambart
 CHAPTER 1: MINERALS: DEFINITION, PROPERTIES AND OCCURRENCES Sarah Lambart CONTENT OF CHAPTER 1 Goal: learn how to describe and classify minerals 3 elements of classification: chemistry, structure and environment
CHAPTER 1: MINERALS: DEFINITION, PROPERTIES AND OCCURRENCES Sarah Lambart CONTENT OF CHAPTER 1 Goal: learn how to describe and classify minerals 3 elements of classification: chemistry, structure and environment
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Rocks and Minerals Exam KEY. Princeton Science Olympiad Invitational
 For Office Use Only: Part 1: / Part 2: / Score: /150 Team Number: 0 Team Name: KEY Participant names: 2016-2017 Rocks and Minerals Exam KEY Princeton Science Olympiad Invitational Instructions (optional):
For Office Use Only: Part 1: / Part 2: / Score: /150 Team Number: 0 Team Name: KEY Participant names: 2016-2017 Rocks and Minerals Exam KEY Princeton Science Olympiad Invitational Instructions (optional):
40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture
 Event: Judge: Rocks & Minerals Pierre couture 40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture 1-4 Minerals (50 points total) 5-7 Igneous Rocks (50 points total)
Event: Judge: Rocks & Minerals Pierre couture 40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture 1-4 Minerals (50 points total) 5-7 Igneous Rocks (50 points total)
CHAPTER 5: CRYSTAL DEFECTS AND TWINNING. Sarah Lambart
 CHAPTER 5: CRYSTAL DEFECTS AND TWINNING Sarah Lambart RECAP CHAP. 4 Hermann-Mauguin symbols 32 crystal classes Miller indices Crystal forms RECAP CHAP. 4 Crystal System Crystal Class Symmetry Name of Class
CHAPTER 5: CRYSTAL DEFECTS AND TWINNING Sarah Lambart RECAP CHAP. 4 Hermann-Mauguin symbols 32 crystal classes Miller indices Crystal forms RECAP CHAP. 4 Crystal System Crystal Class Symmetry Name of Class
Minerals Please do not write on this test packet.
 Please do not write on this test packet. 1. The diagram below shows the index minerals of Mohs hardness scale compared with the hardness of some common objects. 2. Base your answer to the following question
Please do not write on this test packet. 1. The diagram below shows the index minerals of Mohs hardness scale compared with the hardness of some common objects. 2. Base your answer to the following question
COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition
 COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition Overview Of Earth ch 1 Earth's place in solar system, galaxy, universe Atmosphere,
COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition Overview Of Earth ch 1 Earth's place in solar system, galaxy, universe Atmosphere,
Real-Life Applications: Economic Mineral Deposits
 Real-Life Applications: Economic Mineral Deposits Economic Minerals Economic minerals are minerals that can be extracted, processed and marketed for a profit. Various factors determine if a mineral is
Real-Life Applications: Economic Mineral Deposits Economic Minerals Economic minerals are minerals that can be extracted, processed and marketed for a profit. Various factors determine if a mineral is
Name Petrology Spring 2006
 Igneous rocks lab Part I Due Tuesday 3/7 Igneous rock classification and textures For each of the rocks below, describe the texture, determine whether the rock is plutonic or volcanic, and describe its
Igneous rocks lab Part I Due Tuesday 3/7 Igneous rock classification and textures For each of the rocks below, describe the texture, determine whether the rock is plutonic or volcanic, and describe its
Earth Science. Explain how Earth's biogeochemical cycles create a balance of materials. Examine the importance of biogeochemical cycles.
 Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
CE6301-ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Prepared by : A.M.Arun Mohan AP/Civil. Engineering Geology - 16 marks TWO MARK QUSETIONS. Unit-I.
 Prepared by : A.M.Arun Mohan AP/Civil Engineering Geology - 16 marks TWO MARK QUSETIONS Unit-I 1. Describe the internal structure of the earth. 2. Give the earth quake belt of India. 3. Define between
Prepared by : A.M.Arun Mohan AP/Civil Engineering Geology - 16 marks TWO MARK QUSETIONS Unit-I 1. Describe the internal structure of the earth. 2. Give the earth quake belt of India. 3. Define between
abrasion the rubbing, grinding, and bumping of rocks that cause physical weathering (SRB, IG)
 FOSS Soils, Rocks, and Landforms Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 abrasion the rubbing, grinding, and bumping of rocks that cause physical weathering (SRB, IG) acid a substance that geologists use to
FOSS Soils, Rocks, and Landforms Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 abrasion the rubbing, grinding, and bumping of rocks that cause physical weathering (SRB, IG) acid a substance that geologists use to
NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS - May ~012
 04-8S-14 Geology (May 2012) Page 1 of 10 NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS - May ~012 04-85-14 Geology 3 hours duration NOTES: A. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to
04-8S-14 Geology (May 2012) Page 1 of 10 NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS - May ~012 04-85-14 Geology 3 hours duration NOTES: A. If doubt exists as to the interpretation of any question, the candidate is urged to
4. The diagram of Bowen's Reaction Series below indicates the relative temperatures at which specific minerals crystallize as magma cools.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral. 1. The luster of this mineral could
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral. 1. The luster of this mineral could
