Is Greenland Really That Big?
|
|
|
- Mervyn Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Details Learning Resources Completion Time: About one period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Is Greenland Really That Big? Overview NASA s Operation IceBridge images Earth s polar ice in unprecedented detail to better understand processes that connect the Polar Regions with the global climate system. IceBridge uses a specialized fleet of aircraft and the most sophisticated suite of science instruments ever assembled to gather data on sea ice, glaciers, and ice sheets. The data gathered today will allow future scientists to better understand and model climate change. It is no exaggeration to say that teachers, those who work in support of teachers, and parents are literally raising the next generation of scientists for whom this data will be critical. pages/icebridge/index.html Materials Attached activity worksheet One of the places Operation IceBridge gathers data is Greenland, an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark. This lesson/activity starts with figuring the area of an irregular figure Greenland. From there the lesson can be extended to different map projections, comparisons, cartography, limits, and history. Objectives Estimate the area of an irregular figure Compare geometric areas Understand map projections Understand the importance of a 3D model Lesson Preparation Watch the video Is Greenland Really THAT big? Procedure Complete the attached worksheet activity. Extension Use Polar, Van der Grinten, or the Winkel tripel projections with similar questions. 1
2 Is Greenland Really THAT big? Learning Resources Resources See attached worksheet Assessment n/a Credits Mark Buesing, 2013 PolarTREC teacher. 2
3 Is Greenland Really THAT big? Learning Resources National Science Education Standards (NSES) Content Standards, Grades 9-12 Content Standard A: Science As Inquiry a. Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry Content Standard G: History and Nature of Science a. Science as a human endeavor b. Nature of scientific knowledge c. Historical perspectives Other Standards Common Core State Standards Mathematics CCSS: HSG-GMD.B.4 Identify the shapes of two-dimensional cross-sections of three-dimensional objects, and identify three-dimensional objects generated by rotations of two-dimensional objects. HSG-MG.A.3 Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios). HSN-Q.A.3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. G-MG.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder). 8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as 3x108 and the population of the world as 7x109, and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. 3
4 Is Greenland Really THAT big Plan: As an introduction watch the video Is Greenland Really THAT big? Part 1: Use the figure below to estimate the area of Greenland. Each square represents 8,600 square kilometers. First discuss with a partner how you are going to do this.
5 Questions: 1. What did you figure for the area of Greenland? 2. Is your partner s estimate close to yours? If not, why not? Work together until you agree on an area. 3. Would larger or smaller squares make the estimate more accurate? Explain. 4. How small would you want the squares in order to get the most accurate estimate? 5. Is there a limit as to how small the squares could be? Explain. 6. Give two reasons why it someone would want to know the area of an island. Go over these answers before moving on: 1. 2,166,000 square kilometers. How many estimates were over this value? How many were under this value? Does the shape of an irregular figure make a difference as to how close an estimate is to the actual value? 2. Answers will vary. 3. Smaller squares would make the estimate more accurate because more squares would be completely filled thereby reducing the area where estimates need to be made. 4. As small as possible or as small as can be seen. 5. Answers will vary, but this may be a good time to talk about the Area Postulate, limits, or numerical integration. 6. Answers will vary. To determine infrastructure needs, to sell land, to develop the land for industrial purposes, to calculate quantities of resources, to determine what fraction is not covered by ice (specific to Greenland)
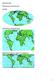
6 MERCATOR PROJECTION (lines of latitude and longitude form right angles): Starting with the Mercator projection trace Greenland onto a piece of paper and cut it out, like in the video. Questions: 1. Compare Greenland to other land areas. List at least two areas that are about the same as Greenland. 2. Google the areas you are comparing and record them. 3. Based on the actual area of Greenland given by your teacher, are you close? By what factor are you in error? (For example, if you thought you had an area of 100 and the actual area was 20, you are in error by a factor of 5.) 4. Does the Mercator projection better represent the true area of polar or equatorial regions? (Hint: look closely at the spacing of the lines of latitude and longitude on the map.) 5. If the Mercator projection is so inaccurate, why is it used?
7 Answers: 1. South America, Africa, most of North America, Russia, and many others 2. South America = 18 million sq km, Africa = 30 million sq km, North America (minus Alaska) = 23 million sq km, Russia = 17 million sq km Equitorial regions - the lines of longitude are parallel on a Mercator projection (they converge at the poles) and lines of latitude get progrssively further apart (they are evenly spaced on the earth ignoring the equitorial bulge) 5. It was very useful in navigation as it preserved angles. Straight lines on a Mercator projection are lines of constant heading or direction. In the days of navigating by stars, sun, and compass, this was useful. Today it is rarely used.
8 ROBINSON PROJECTION (lines of latitude are horizontal and lines of longitude are curved more and more): Using the Robinson projection, trace Greenland onto a piece of paper and cut it out. Questions: 1. Compare Greenland to other land areas. List at least two areas that are about the same as Greenland. 2. Google the areas you are comparing and record them. 3. Based on the actual area of Greenland given by your teacher, are you close? By what factor are you in error? (For example, if you thought you had an area of 100 and the actual area was 20, you are in error by a factor of 5.) 4. Does the Robinson projection better represent the true area of polar or equatorial regions? (Hint: look closely at the grid on the map.) 5. If the Robinson projection is inaccurate, why is it used? 6. What is the only map that shows the true sizes and spatial relationships of Earth?
9 1. Answers will vary: US, China, Australia, Europe 2. US = 10 million sq km, China = 10 million sq km, Australia = 7.7 million sq km, Europe = 10 million sq km Equitorial regions 5. The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that tries to create a visually appealing map without heavy distortion. The National Geographic Society replaced the Robinson projection with the Winkel tripel projection in A globe! Optional: discuss 3D models Extension: Use Polar, Van der Grinten, or the Winkel tripel projections with similar questions. All images are Wikimedia Commons CC-SA-3.0.
Key Concepts: perspective representations/accounts spatial scales
 Unit 1 Lesson 2 6 G1.1.1 Describe how geographers use mapping to represent places and natural and human phenomena in the world. 7 H1.2.3 Identify the point of view (perspective of the author) and context
Unit 1 Lesson 2 6 G1.1.1 Describe how geographers use mapping to represent places and natural and human phenomena in the world. 7 H1.2.3 Identify the point of view (perspective of the author) and context
PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET)
 PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET) Name: Date: Period: Note: Correct answers on some problems are indicated with a yellow highlight. PROJECTIONS 1. Here
PROJECTIONS AND COORDINATES EXPLORED THROUGH GOOGLE EARTH EXERCISE (SOLUTION SHEET) Name: Date: Period: Note: Correct answers on some problems are indicated with a yellow highlight. PROJECTIONS 1. Here
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
 MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
1/28/16. EGM101 Skills Toolbox. Oblate spheroid. The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections. Geoid
 EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
Pool Canvas. Add. Creation Settings. Chapter 1--Objectives and Tools of World Regional Geography. Description Instructions.
 1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
History of Cartography,
 Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
GPS Measurement Protocol
 GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
GPS Measurement Protocol Purpose To determine the latitude, longitude, and elevation of your school and of all your GLOBE sites Overview The GPS receiver will be used to determine the latitude, longitude
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
Global Climate Change Overview: Students will learn about global climate change, what causes global warming, and scientific projections about climate change in the near future. Levels V-VI Grades 9-12
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
Understanding Projections
 GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2
 ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2 Mark Westcott LMU Munich June 15, 2015 1 / 31 Topics for this session: Geographic Coordinate Systems Projections Projected Coordinate Systems Geocoding 2 / 31 Some
ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2 Mark Westcott LMU Munich June 15, 2015 1 / 31 Topics for this session: Geographic Coordinate Systems Projections Projected Coordinate Systems Geocoding 2 / 31 Some
Welcome to PolarConnect. With Kelly McCarthy and NASA s Operation IceBridge
 Welcome to PolarConnect With Kelly McCarthy and NASA s Operation IceBridge 5 May 2016 If you are joining by phone, please mute your phone. Press *6 to mute and *6 to unmute. Participant Introductions In
Welcome to PolarConnect With Kelly McCarthy and NASA s Operation IceBridge 5 May 2016 If you are joining by phone, please mute your phone. Press *6 to mute and *6 to unmute. Participant Introductions In
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Unit 2 Study Guide: The World in Spatial Terms
 Name Date Hour Unit 2 Study Guide: The World in Spatial Terms TEST is WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 19 TH This study guide contains all the concepts that will be on your test. Vocabulary words and concepts will
Name Date Hour Unit 2 Study Guide: The World in Spatial Terms TEST is WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 19 TH This study guide contains all the concepts that will be on your test. Vocabulary words and concepts will
Studying the Ocean Using Live Data
 Studying the Ocean Using Live Data Overview The Argo buoy project is a major oceanographic study that harnesses the power of automated unmanned buoys traveling the world s oceans (http://www.argo.ucsd.edu/).
Studying the Ocean Using Live Data Overview The Argo buoy project is a major oceanographic study that harnesses the power of automated unmanned buoys traveling the world s oceans (http://www.argo.ucsd.edu/).
Approximate Proxies. Details. Materials. Learning Resources
 Details Learning Resources Completion Time: Less than a week Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Approximate Proxies Overview The sediment in Lake El gygytgyn, (pronounced EL-ge- GIT-gin) located in
Details Learning Resources Completion Time: Less than a week Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Approximate Proxies Overview The sediment in Lake El gygytgyn, (pronounced EL-ge- GIT-gin) located in
What is Geography? *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study.
 World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
Map Skills Lesson 1. Materials: maps, pencils, Lesson 1 Worksheet, strips of paper, grid paper
 Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet. Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about!
 Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Arctic Impacts. Details. Materials. Learning Resources
 Details Learning Resources Completion Time: About one period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Arctic Impacts Overview Lake El gygytgyn (67. o N, 17 o E) is one of the best preserved large asteroid
Details Learning Resources Completion Time: About one period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Arctic Impacts Overview Lake El gygytgyn (67. o N, 17 o E) is one of the best preserved large asteroid
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Essential Questions What are the major physical components of the world, and how are they represented on a map? 3.4
 Third Grade Social Studies Unit One Six Weeks GEOGRAPHY Originally compiled by Russellville In order for students to understand that geography influences the development of a region as well as the interactions
Third Grade Social Studies Unit One Six Weeks GEOGRAPHY Originally compiled by Russellville In order for students to understand that geography influences the development of a region as well as the interactions
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Evidence for Continental Drift and The Theory of Plate Tectonics Did you know that the coal that is mined in Pennsylvania was actually formed from tropical plant life near the Equator? How did it travel
Introduction to Cartography Part II
 Introduction to Cartography Part II Introduction to Cartography Map Projections GIS GPS Remote Sensing Misrepresentation with Maps Map Projections Mathematical method for systematically transforming a
Introduction to Cartography Part II Introduction to Cartography Map Projections GIS GPS Remote Sensing Misrepresentation with Maps Map Projections Mathematical method for systematically transforming a
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Wayne E. Sirmon GEO 301 World Regional Geography
 Wayne E. Sirmon GEO 301 Geography 301 Geography 301 MAP: A graphic representation of a portion of the earth s surface dawn to scale, as seen from above. Types of Maps Climate maps give general information
Wayne E. Sirmon GEO 301 Geography 301 Geography 301 MAP: A graphic representation of a portion of the earth s surface dawn to scale, as seen from above. Types of Maps Climate maps give general information
A Correlation of. Eastern Hemisphere. Ohio s Learning Standards Social Studies: K-12 Grade 6
 A Correlation of Eastern Hemisphere To Grade 6 to,, Grade 6 Introduction This document demonstrates how, Eastern Hemisphere, Ohio Edition, meets : K-12 Social Studies for Grade 6. Correlation page references
A Correlation of Eastern Hemisphere To Grade 6 to,, Grade 6 Introduction This document demonstrates how, Eastern Hemisphere, Ohio Edition, meets : K-12 Social Studies for Grade 6. Correlation page references
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
World Geography. Teacher s Guide
 World Geography Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management.................................................
World Geography Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management.................................................
SEA ICE AND GLOBAL WARMING
 jkjk SEA ICE AND GLOBAL WARMING Lesson plan for grades K- 3 By: Laura Sanders, Environmental Science Institute, March 2011 Length of lesson: two 30- minute class periods SOURCES AND RESOURCES: Atmospheric
jkjk SEA ICE AND GLOBAL WARMING Lesson plan for grades K- 3 By: Laura Sanders, Environmental Science Institute, March 2011 Length of lesson: two 30- minute class periods SOURCES AND RESOURCES: Atmospheric
Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets
 Details Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets Overview Working in groups students will use common materials to create layers of snow and
Details Completion Time: About 1 period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Ice Cores: Modeling Ice Sheets Overview Working in groups students will use common materials to create layers of snow and
Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change
 Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 1 >> Page 1 EYEWITNESSES TO CHANGE NATIVE PEOPLES OBSERVE CLIMATE CHANGES IN THE ARCTIC Living With Change Sachs Harbour, Canada
Activity 1 Eyewitnesses to Change Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 1 >> Page 1 EYEWITNESSES TO CHANGE NATIVE PEOPLES OBSERVE CLIMATE CHANGES IN THE ARCTIC Living With Change Sachs Harbour, Canada
LET S GO ON A ROAD TRIP
 Partner School News June 2016 In this issue: Education Children Around the World www.opportunityeducation.org Road Trip Start Writing Right Now Teaching Tip of the Month Focus on Schools LET S GO ON A
Partner School News June 2016 In this issue: Education Children Around the World www.opportunityeducation.org Road Trip Start Writing Right Now Teaching Tip of the Month Focus on Schools LET S GO ON A
Recall: The scale transformation
 Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools)
 A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
Sample file. Teacher Guide ... Before You Teach. Our resource has been created for ease of use by both TEACHERS and STUDENTS alike.
 8 7 9 10 12 13 14 11 Introduction T his resource provides ready-to-use information and activities for remedial students in grades five to eight. Written to grade and using simplified language and vocabulary,
8 7 9 10 12 13 14 11 Introduction T his resource provides ready-to-use information and activities for remedial students in grades five to eight. Written to grade and using simplified language and vocabulary,
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Discovering stars. LAB: Analyzing the geometric pattern of constellations. POST: Exploring
Some of these parallels are very important. In the Northern Hemisphere, there is the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle.
 PDF 2 Geographic coordinates 1 The geographic coordinates system is network of imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that are drawn on globes or maps. These lines are called parallels (lines of latitude)
PDF 2 Geographic coordinates 1 The geographic coordinates system is network of imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that are drawn on globes or maps. These lines are called parallels (lines of latitude)
Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship
 Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship Lesson 2.1 Studying Geography I. Displaying the Earth s Surface A. A globe of the Earth best shows the sizes of continents and the shapes of landmasses
Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship Lesson 2.1 Studying Geography I. Displaying the Earth s Surface A. A globe of the Earth best shows the sizes of continents and the shapes of landmasses
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts.
 MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Telescopes and Observatories. Parent Guide, page 1 of 2. OurStory: Exploring the Sky. Read the Directions sheets for step-by-step instructions.
 Parent Guide, page 1 of 2 Read the Directions sheets for step-by-step instructions. SUMMARY In this activity, children and adults will watch and discuss a short video about how people use telescopes. WHY
Parent Guide, page 1 of 2 Read the Directions sheets for step-by-step instructions. SUMMARY In this activity, children and adults will watch and discuss a short video about how people use telescopes. WHY
Maps and Map Projections
 38 The Global Positioning System The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a modern technology for determining a location on Earth. This high-tech system was originally created for military applications but
38 The Global Positioning System The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a modern technology for determining a location on Earth. This high-tech system was originally created for military applications but
Pangaea Revisited. Original Source: Dr. Leslie Sautter (Dept. of Geology, College of Charleston)
 Original Source: Dr. Leslie Sautter (Dept. of Geology, College of Charleston) Grade Level: SC Standards: National Standards: 5 th & 8 th Grade 5 th IIIA2a,b,c 8 th IIIB4a,d Earth and Space Science Content
Original Source: Dr. Leslie Sautter (Dept. of Geology, College of Charleston) Grade Level: SC Standards: National Standards: 5 th & 8 th Grade 5 th IIIA2a,b,c 8 th IIIB4a,d Earth and Space Science Content
Homework. Oceanography and Climate Review due Friday Feb 12 th (test day!!)
 Homework Oceanography and Climate Review due Friday Feb 12 th (test day!!) Learning Targets I can define the term climate and explain the factors that influence the climate of an area. I can identify the
Homework Oceanography and Climate Review due Friday Feb 12 th (test day!!) Learning Targets I can define the term climate and explain the factors that influence the climate of an area. I can identify the
What Do You See? FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory. Area Determination: Frequency and Cover
 What Do You See? Message of the Day: Many options exist to determine the size, area, or extent of a feature on a landscape FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory Lecture 7: Measures of Land Area Frequency
What Do You See? Message of the Day: Many options exist to determine the size, area, or extent of a feature on a landscape FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory Lecture 7: Measures of Land Area Frequency
D) 15 N, 160 W A) prevailing wind direction
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents latitude and longitude lines on Earth. Points A through E represent locations on Earth. Arrows represent direction of rotation.
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents latitude and longitude lines on Earth. Points A through E represent locations on Earth. Arrows represent direction of rotation.
Google Earth. Overview: Targeted Alaska Grade Level Expectations: Objectives: Materials: Grades 5-8
 Overview: Students become familiar with using the Google Earth interface to navigate around the planet. Using the zoom and tilt features, students practice moving around the planet with the navigation
Overview: Students become familiar with using the Google Earth interface to navigate around the planet. Using the zoom and tilt features, students practice moving around the planet with the navigation
Location. Look over the indicators of location on your handout. What things about Baltimore s location make it unique from other places?
 Objective We will review the 5 Themes of Geography to explain why each place on earth is unique. We will apply the concepts related to the 5 Themes of Geography to Baltimore Tuesday, September 7, 2010
Objective We will review the 5 Themes of Geography to explain why each place on earth is unique. We will apply the concepts related to the 5 Themes of Geography to Baltimore Tuesday, September 7, 2010
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
Create a Topographic Profile of Beacon Valley
 Details Create a Topographic Profile of Beacon Valley Completion Time: About a week Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Overview Beacon Valley is recognized by scientists as one of the most Mars-like
Details Create a Topographic Profile of Beacon Valley Completion Time: About a week Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Overview Beacon Valley is recognized by scientists as one of the most Mars-like
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude
 Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
Science4. Student s book. Natural
 Science4 Student s book Natural Contents LESSON Page VALUES COMMUNICATION AND CRITICAL SPIRIT COMPETENCES AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES 1. The Earth 4 to 17 Taking care of our planet. Explaining the Solar
Science4 Student s book Natural Contents LESSON Page VALUES COMMUNICATION AND CRITICAL SPIRIT COMPETENCES AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES 1. The Earth 4 to 17 Taking care of our planet. Explaining the Solar
Pikes Lane Primary School. Geography Statement of Practice
 Pikes Lane Primary School Geography Statement of Practice Subject Leader: Mrs Cawley Subject Link Governor: Mr Scholar & Mrs Azad Last Updated: September 2016 Review Date: September 2017 Aims and objectives
Pikes Lane Primary School Geography Statement of Practice Subject Leader: Mrs Cawley Subject Link Governor: Mr Scholar & Mrs Azad Last Updated: September 2016 Review Date: September 2017 Aims and objectives
MAPPING MARS TEACHER PAGE
 TEACHER PAGE Background Information This lesson introduces students to some common map projections and representations (e.g., globes or close-ups) and asks them to consider the ways that each representation
TEACHER PAGE Background Information This lesson introduces students to some common map projections and representations (e.g., globes or close-ups) and asks them to consider the ways that each representation
C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data
 C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data Purpose Students will work with short- and longterm air temperature data in order to better understand the differences between weather and climate.
C1: From Weather to Climate Looking at Air Temperature Data Purpose Students will work with short- and longterm air temperature data in order to better understand the differences between weather and climate.
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
ST AMBROSE CATHOLIC PRIMARY SCHOOL Geography Policy
 ST AMBROSE CATHOLIC PRIMARY SCHOOL Geography Policy 2017-2018 Our school policy is developed in accordance with the National Curriculum for Geography and Foundation Stage Curriculum for Understanding of
ST AMBROSE CATHOLIC PRIMARY SCHOOL Geography Policy 2017-2018 Our school policy is developed in accordance with the National Curriculum for Geography and Foundation Stage Curriculum for Understanding of
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
RISING SEA. Reading Practice. Paragraph 1. INCREASED TEMPERATURES
 Reading Practice RISING SEA Paragraph 1. INCREASED TEMPERATURES The average air temperature at the surface of the earth has risen this century, as has the temperature of ocean surface waters. Because water
Reading Practice RISING SEA Paragraph 1. INCREASED TEMPERATURES The average air temperature at the surface of the earth has risen this century, as has the temperature of ocean surface waters. Because water
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
New National Curriculum Geography Skills Planning KS1
 New National Curriculum Geography Skills Planning KS1 Enquiry Question Objective-essential knowledge skills or understanding Locational Knowledge Standards /Success Criteria Lesson progression over half
New National Curriculum Geography Skills Planning KS1 Enquiry Question Objective-essential knowledge skills or understanding Locational Knowledge Standards /Success Criteria Lesson progression over half
World Geography. Test Pack
 World Geography Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher......... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well....... vi Test-Taking Strategies for Power Basics........ vii Pretest.......
World Geography Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher......... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well....... vi Test-Taking Strategies for Power Basics........ vii Pretest.......
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage MAPPING W O RL D HERITAGE Where are sites of significant
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activityengage MAPPING W O RL D HERITAGE Where are sites of significant
Social Studies Tools (Maps & Sources) Test Study Guide
 Social Studies Tools (Maps & Sources) Test Study Guide Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Period: Directions: Complete this study guide as a way to prepare for your test on our Social Studies Tools unit about maps
Social Studies Tools (Maps & Sources) Test Study Guide Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Period: Directions: Complete this study guide as a way to prepare for your test on our Social Studies Tools unit about maps
Sea Ice and Satellites
 Sea Ice and Satellites Overview: Students explore satellites: what they are, how they work, how they are used, and how to interpret satellite images of sea ice using Google Earth. (NOTE: This lesson may
Sea Ice and Satellites Overview: Students explore satellites: what they are, how they work, how they are used, and how to interpret satellite images of sea ice using Google Earth. (NOTE: This lesson may
What is Geography? Lecture 1 The Earth As A Rotating Planet. What is Geography? What is geography? Subfields of Geography?
 Lecture 1 The Earth As A Rotating Planet Geog210 Physical Geography What is Geography? Much more than place names and locations The study of spatial variation How and why things differ from place to place
Lecture 1 The Earth As A Rotating Planet Geog210 Physical Geography What is Geography? Much more than place names and locations The study of spatial variation How and why things differ from place to place
2. What does the map scale tell the map reader? a ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the length given to that distance on a map
 AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
Geography involves the study of places: their locations, their characteristics, and how humans use and move around them.
 Physical Geography Looking at the Earth Geography involves the study of places: their locations, their characteristics, and how humans use and move around them. NEXT Physical Geography Looking at the Earth
Physical Geography Looking at the Earth Geography involves the study of places: their locations, their characteristics, and how humans use and move around them. NEXT Physical Geography Looking at the Earth
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Module 2 Educator s Guide Overview
 Module 2 Educator s Guide Overview Water, water almost everywhere? Module Overview The presence of water in solid, liquid, and gaseous forms is one of the primary factors that distinguishes Earth from
Module 2 Educator s Guide Overview Water, water almost everywhere? Module Overview The presence of water in solid, liquid, and gaseous forms is one of the primary factors that distinguishes Earth from
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
MAPS MAPS MAPS.
 www.atozmapsonline.com MODERN MAPS MAPS MAPS MAPS AtoZ Maps Online TM is the world s most comprehensive collection of royalty-free downloadable maps for schools, academic institutions, and public libraries.
www.atozmapsonline.com MODERN MAPS MAPS MAPS MAPS AtoZ Maps Online TM is the world s most comprehensive collection of royalty-free downloadable maps for schools, academic institutions, and public libraries.
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Lesson Plan: Plate Tectonics
 Lesson Plan: Plate Tectonics Lesson Plan: Plate Tectonics Lesson Plan Content: This lesson plan and slide presentation is to be used in conjunction with: 1 x plate tectonics teacher briefing 1 x plate
Lesson Plan: Plate Tectonics Lesson Plan: Plate Tectonics Lesson Plan Content: This lesson plan and slide presentation is to be used in conjunction with: 1 x plate tectonics teacher briefing 1 x plate
GEOGRAPHY CURRICULUM OVERVIEW
 GEOGRAPHY CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Geographical knowledge Progression Statement Autumn Spring Summer Year 1 UK and Local Area: Physical Themes: Name, locate and identify characteristics of the 4 countries and
GEOGRAPHY CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Geographical knowledge Progression Statement Autumn Spring Summer Year 1 UK and Local Area: Physical Themes: Name, locate and identify characteristics of the 4 countries and
locate the world s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of
 Year 3 and 4 Geography study- Autumn 2 2017 National curriculum: Locational knowledge locate the world s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South
Year 3 and 4 Geography study- Autumn 2 2017 National curriculum: Locational knowledge locate the world s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South
Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth
 Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 2: Representations of Earth 1. A rhumb line on a Mercator projection is a line of. a. true size b. true shape c. true compass bearing d. true location 2. Maximum longitude
01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December 22.
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: Introducing Physical Geography 6e Chapter Number: 01 Question Type: Multiple Choice 01) The Sun s rays strike the surface of the Earth at 90 degrees at the on December
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Tuition, Medical and Behaviour Support Service
 Tuition, Medical and Behaviour Support Service Curriculum Policy - Primary Geography Reviewed: October 2018 Next Review: October 2019 Responsibility: Andrea Snow AIMS AND PRINCIPLES The national curriculum
Tuition, Medical and Behaviour Support Service Curriculum Policy - Primary Geography Reviewed: October 2018 Next Review: October 2019 Responsibility: Andrea Snow AIMS AND PRINCIPLES The national curriculum
Geography. Programmes of study for Key Stages 1-3
 Geography Programmes of study for Key Stages 1-3 February 2013 Contents Purpose of study 3 Aims 3 Attainment targets 3 Subject content 4 Key Stage 1 4 Key Stage 2 5 Key Stage 3 6 2 Purpose of study A high-quality
Geography Programmes of study for Key Stages 1-3 February 2013 Contents Purpose of study 3 Aims 3 Attainment targets 3 Subject content 4 Key Stage 1 4 Key Stage 2 5 Key Stage 3 6 2 Purpose of study A high-quality
IELTS Academic Reading Sample 1 - Rising Sea RISING SEA
 IELTS Academic Reading Sample 1 - Rising Sea You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 15-28 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below. RISING SEA Paragraph 1 - INCREASED TEMPERATURES The average
IELTS Academic Reading Sample 1 - Rising Sea You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 15-28 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below. RISING SEA Paragraph 1 - INCREASED TEMPERATURES The average
Q25: Record the wavelength of each colored line according to the scale given.
 C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
C. Measurement Errors and Uncertainties The term "error" signifies a deviation of the result from some "true" value. Often in science, we cannot know what the true value is, and we can only determine estimates
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles. Name
 GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
Cartography the art of making maps
 Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
Cartography the art of making maps A map is a drawing or a picture of the earths surface, showing how things are related to each other by distance, direction and size. Maps are used for: Navigation Distance
Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave?
 Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave? Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 3 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 3 ARCTIC HEAT WAVE? THE RATE OF CLIMATE CHANGE Are Ice Caps Melting Faster? From 1979 to 2002, seasonal melting
Activity 3 Arctic Heat Wave? Forces of Change >> Arctic >> Activity 3 >> Page 1 ACTIVITY 3 ARCTIC HEAT WAVE? THE RATE OF CLIMATE CHANGE Are Ice Caps Melting Faster? From 1979 to 2002, seasonal melting
Map Projections. is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer
 Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
Map Projections is about presenting the round Earth on a flat surface.map Projections: Vermeer s Cartographer What is a map projection? A projection is a way to make a flat representation of the Earth
EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page
 EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
The Mystery of the Destroyed Weather Station
 Details Learning Resources Completion Time: Less than a week Permission: Download and Share The Mystery of the Destroyed Weather Station Overview: Students use data and pictures of a destroyed wind sensor,
Details Learning Resources Completion Time: Less than a week Permission: Download and Share The Mystery of the Destroyed Weather Station Overview: Students use data and pictures of a destroyed wind sensor,
12e. Cultural Anthropology. The Human Challenge. WILLIAM A. HAVILAND University of Vermont. HARALD E. L. PRINS Kansas State University
 12e Cultural Anthropology The Human Challenge WILLIAM A. HAVILAND University of Vermont HARALD E. L. PRINS Kansas State University DANA WALRATH University of Vermont BUNNY MCBRIDE Kansas State University
12e Cultural Anthropology The Human Challenge WILLIAM A. HAVILAND University of Vermont HARALD E. L. PRINS Kansas State University DANA WALRATH University of Vermont BUNNY MCBRIDE Kansas State University
