Grade 10 Science EXAM REVIEW Multiple Choice
|
|
|
- Pierce Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Grade 10 Science EXAM REVIEW Multiple Choice 1) An example of a chemical reaction is: a) chopping wood b) breaking glass c) dissolving salt d) burning paper 2) An atom of sodium loses electrons to become a charged ion. The number of protons and electons in the ion are: a) 11 protons and 11 electrons b) 11 protons and 12 electrons c) 11 protons and 10 electrons d) 12 protons and 11 electrons 3) Which of the following statements are correct? a) Metals bond when they share electrons. b) Non-metals bond when they gain electrons. c) Non-metals bond when they share electrons d) All of the above e) Only (b) and (c) are correct 4) Which of the following is an ionic compound? a) Ca b) CO 2 c) CO 3-2 d) O 3 e) NaNO 3 5) Covalent bond are due to the: a) transfer of electrons from one atom to another. b) attraction between ions of identical charge. c) gain or loss of protons by atoms. d) sharing of two electrons by two atoms. 6) In any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants is always equal to the total mass of materials produced. This is known as the Law of: a) Conservation of Mass b) Chemical Reactions c) Constant Proportion d) Conservation of Energy 7) What is the total number of atoms in the formula Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3? a) 3 b) 7 c) 15 d) 17 e) 21 8) A single displacement reaction is the: a) release of heat during a reaction b) joining together of two elements to form a compound. c) exchange of metals between two different compounds. d) displacement of one metal in a compound by another metal. 9) Which of the following is an example of a synthesis reaction? a) Heating copper (II) carbonate to produce carbon dioxide and copper (II) oxide. b) Reacting sodium with water to produce hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide. c) Passing electricity through water to produce hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. d) Heating copper in oxygen to produce copper (II) oxide. 10) An example of a double displacemnt reaction would be: a) 2H 2 O 2H 2 + O 2 b) 2KI + Pb(NO 3 ) 2 2KNO 3 + PbI 2 c) 2KClO 3 2KCl + 3O 2 d) 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O 11) A solution has a ph of 8. How is this solution best described? a) strongly basic b) slightly basic c) slightly acidic d) strongly acidic 12) An acid of ph = 4 is: a) twice as acidic as an acid of ph = 6. b) 100 times less acidic than an acid of ph = 6 c) 10 times more acidic than an acid of ph = 5 d) half as acidic as an acid of ph = 2
2 13) Which of the following statements is true? a) Phosphorescent objects continue to glow after light is no longer shining on them. b) The moon is a luminous object. c) Incandescent bulbs are more efficient than fluorescent bulbs. d) Glow worms that produce light are using triboluminescence. e) Opaque objects only transmit some of the light that interacts with the object. 14) Which of the following types of electromagnetic radiation both causes Cancer and is used to treat Cancer? a) microwaves b) UV c) gamma radiation d) IR 15) A light ray strikes a plane mirror at an angle of 70 between the incident ray and the mirror. The angle of reflection is: a) 20 b) 70 c) 30 d) 80 16) Fill in the blanks in the following statements: When human eyes see virtual images in mirrors, they are projecting the rays back behind the mirror to create images. a) incident, inverted b) incident, upright c) reflected, inverted d) reflected, upright 17) Which of the following statements is false? a) A converging mirror bends incoming parallel rays to a focus. b) A diverging mirror spreads incoming parallel rays apart. c) A diverging mirror only produces a virtual image. d) A converging mirror only produces real images. e) None of the above statements are false. 18) Where should you place an object in front of a converging mirror to produce an inverted, real image that is larger than the object? a) At F b) At C c) Beyond C d) Between F and C 19) Which condition must be true for total internal reflection to occur? a) The light ray must bend toward the normal. b) The angle of refraction must be greater than the angle of incidence. c) The angle of incidence must be less than the critical angle. d) Light must be traveling faster in the first medium than in the second. 20) Which of the following applications does NOT utilize the principle of total internal reflection? a) diamonds b) fibre optics c) a rainbow d) telescope 21) The image created by a diverging lens is: a) virtual, upright, smaller and closer to the lens b) virtual, upright, larger and farther from the lens c) virtual, inverted, smaller and closer to the lens d) virtual, inverted, larger and farther from the lens 22) Which of the following is an object that will produce partial reflection and refraction? a) a mirror on the Hubble telescope b) a clean window at dusk c) a piece of aluminum foil d) a fibre optic cable
3 23) Myopia (near-sightedness) is best corrected by: a) shortening the length from the lens to the retina. b) lengthening the length from the lens to the retina. c) increases the amount that light is bent before it approaches the eye d) a combination of the two lenses, because we need to produce a real image. 24) The part of the microscope which is used for focusing on low power is: a) revolving nosepiece b) diaphragm c) coarse adjustment d) fine adjustment 25) If an object is viewed through a 15x ocular lens and a 10x objective lens, the magnification is: a) 25x b) 150x c) 1500x d) 5x 26) The organelle in plant cells that is green and is used primarily in photosynthesis is: a) mitochondria b) vacuole c) chloroplast d) ribosome 27) The mitochondria are the organelles that produce energy. What reaction takes place in these organelles? a) photosynthesis b) specialization c) the reaction between fat molecules and bile. d) the reaction between sugar and oxygen. 28) Which of the following statements about stomata is false? a) They open when they are full of water. b) They open when there is lots of sunlight. c) There are many more of them on the top side of leaves. d) They are part of a leaf structure called guard cells. 29) During late interphase, just before the phases of mitosis begin: a) the chromosomes shorten and thicken b) the chromosomes make copies of themselves c) the chromosomes line up along the middle of the nucleus d) the chromosomes separate to the two sides of the nucleus 30) Cells spend most of their time at: a) interphase b) prophase c) mitosis d) cytokinesis 31) The correct order of mitosis is: a) telophase, prophase, interphase, anaphase, metaphase, cytokinesis b) prophase, telophase, interphase, metaphase, anaphase, cytokinesis c) interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis d) interphase, anaphase, prophase, metaphase, telophase, cytokinesis 32) One type of cell in your body that cannot divide is: a) nerve b) bone c) skin d) blood 33) Which of the following does NOT occur after a flower has helped a plant to reproduce sexually? a) the seed is blown away by the wind b) the seed is encased in fruit, which is eaten by an animal c) birds, bees and bats drink nectar from the flower d) the seed forms a burr, which attaches to an animal s fur 34) The structure in the digestive system that produces amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch molecules, is called the: a) saliva b) stomach c) salivary gland d) teeth 35) The organ that stores bile to break down fatty foods is called the: a) liver b) gall bladder c) pancreas d) duodenum
4 36) The structure that prevents food from entering the trachea is the: a) epiglottis b) esophagus c) pharyx d) bronchi 37) Blood vessels that absorb oxygen and discard carbon dioxide in the lungs are the: a) veins b) aorta c) arteries d) capillaries 38) Which one of these statements is false? a) Arteries are under high pressure. b) Arteries carry blood away from the heart. c) Veins are composed of a system of valves. d) Capillaries are very large blood vessels. Fill in the Blanks 1) A change such as melting ice or bending a piece of metal is classified as a(n) change. 2) A pure substance composed of only one type of atom can be further classified as a(n). 3) The incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide and water, but also and. 4) Litmus paper is an indicator that turns red in a solution. 5) A combustion gives off a large amount of energy because it is a(n) reaction. 6) Our microscopes are light microscopes, because they have two lenses. 7) The circle of light that is seen when one looks through a microscope is called the. 8) The organelles that act as a transport system to and from the nucleus are the. 9) The tubes that run from the roots to the leaves within the stems are called the. 10) The process in which material moves from an area of high concentration to low concentration is called. 11) Plants photosynthesize using light energy, and to form glucose and oxygen. 12) Cytokinesis occurs in plant cells when a forms between the two new daughter cells. In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches off, forming a between the daughter cells. 13) If a group of cells start to divide uncontrollably, they will form a. 14) The cell cycle of an embryo will be than that of an adult muscle cell. 15) A fertilized egg into the various kinds of cells found in an adult organism. 16) A cell that has not differentiated into a specific type is called a. 17) The only artery that is de-oxygenated, and the only vein that is oxygenated are found between the heart and the. True or False 1) CO 2 is an example of a compound, since it contains both carbon and oxygen. 2) Mixtures can be separated easily by physical changes, such as boiling and filtering. 3) O 2 is an atom of an element. 4) When describing matter, you must always describe the clarity (clear, translucent, opaque). 5) A test for oxygen gas is that a glowing splint bursts into flame in its presence. 6) Dissolving is an example of a chemical change, since there is often a change of colour. 7) Ribosomes are responsible for making protein. 8) The endoplasmic reticulum is a channel for moving molecules through cells. 9) Cilia are long, tail-like structure used for movement 10) Use low power to get your slide in focus before medium or high power. 11) Chloroplasts are organelles that can only be found in animal cells. 12) The stage is what the microscope rests on. 13) Mitochondria provide energy to the cell. 14) The nucleus provides energy to the cell. 15) Vacuoles and cell walls keep animal cells stiff. 16) Cell walls are only found in onion cells. 17) You should always focus a specimen first at high power.
5 18) Mitochondria are responsible for making and storing protein. 19) When there is plenty of water, stomata swell, which causes them to close. 20) Mitosis is the division of the nucleus 21) At interphase, chromosomes are called chromatin. 22) All the cells in your body divide at the exact same speed. 23) A cloned animal is always the same sex as the surrogate parent. 24) If the fertilized egg from a mouse has 22 chromosomes, you should expect 22 chromosomes in the muscle cell of the same mouse. 25 ) Frogs are similar to humans since they breathe with their lungs only. 26) The liver is responsible for producing emergency sugar for the body. 27) Exchange of O 2 and CO 2 occurs in the bronchi of the lungs. 28) Blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle on each side of the heart. Matching optical center A) High energy electromagnetic radiation. microwaves B) Reflection of light off an irregular or dull surface. mirage C) Used in neon lights. light emitting diode D) Often used in Christmas lights. myopia E) Reflection of light off a smooth surface. diffuse reflection F) Electromagnetic radiation with a long wavelength. center of curvature G) The center of a sphere whose surface has been used to make a mirror. X- Ray H) The exact center of a lens. specular reflection I) When light rays come together to a single point. diverge J) When light rays spread apart from each other. electric discharge K) Effect caused by increased refraction as air heats up. movie projector L) A technology that makes use of lenses. hyperopia M) Can be corrected with a converging lens. converge N) Can be corrected with a diverging lens. Short Answer 1) Write the symbol for the atom that: a) has 6 valence electrons and in is period 3 b) tends to lose three electrons to become isoelectronic with argon c) is an alkali metal in period 5 2a) Draw a Bohr-Rutherford diagram and a Lewis Structure for a neutral oxygen atom. Then draw a Lewis Structure for the ion that oxygen is likely to become in order to be more stable. b) Aluminum is a metal that is likely to bond ionically with oxygen to help it to gain stability. (i) Draw Lewis Structures showing the transfer of electrons (USE ARROWS!) that occurs to produce ions. (ii) Draw Lewis Structures of the ions that form. (iii) Write the formula for aluminum oxide that shows the ratio of the ions in the crystal lattice. c) Oxygen can also gain stability by covalently bonding to itself. Draw a Lewis diagram of an oxygen molecule, showing your rough work, and a cleaned-up version. 3) Write the formula for the following substances: a) magnesium phosphate b) copper (II) sulphide c) chlorine gas d) dichlorine tetroxide d) sodium e) ozone 4) Write the name for the following substances: a) FeBr 2 b) NH 4 NO 3 c) HCl d) SO 2 e) F 2
6 5) Balance the following equations: a) Sn + N 2 Sn 3 N 4 b) H 3 PO 4 + Ca Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + H 2 c) FeS + O 2 Fe 2 O 3 + SO 2 6) Sodium metal reacts with sulfuric acid solution to produce a solution of sodium sulfate and hydrogen gas. (i) Write a word equation to represent the reaction described above. (ii) Write a skeleton equation (including subscripts) for the reaction and balance it. (iii) Name the type of reaction. b) How could you test for the presence of hydrogen gas as a product for the above reaction? Describe the gas test, and then write a balanced skeleton equation (including subscripts) to represent the hydrogen gas test. Finally, name the type of reaction it represents. 7a) What observation would be made when 25 ml of tin (IV) hydroxide solution is put in a beaker, and a few drops of phenolphthalein are added? b) Now a solution of hydrochloric acid (of comparable concentration) is added to the tin (IV) hydroxide solution, drop by drop, until the solution suddenly loses its colour. Write a skeletal equation for this reaction and write two terms that could be used to describe the type of reaction. Do not worry about subscripts this time. 8) Locate the image in the mirror below and show how the eye can see the entire image in the mirror. 9) Locate and describe the characteristics of the image in the following mirror. S: A: L: T: 10) Draw and label a diagram to show a light ray passing from a medium with a higher index of refraction to a medium with a lower index of refraction. Label all angles and rays appropriately. 11) You want to scoop a fish out of water. Where should you aim relative to the fish image in order to catch it. Explain using a diagram.
7 12) Locate and describe the image that is formed from the lens below: S: A: L: T: O 2F F F 2F 13) What is the speed of light in zircon? Index of Refraction Ice 1.31 Quartz 1.46 Vegetable Oil 1.47 Olive Oil 1.48 Acrylic 1.49 Zircon 1.92 Diamond ) A diverging lens has a focal length of 22 cm. An upright, virtual image is located 10 cm behind the lens. Where is the object located? 15) A 16 cm tall rose is placed in front of a converging lens with a magnification of A real, inverted, image is noticed on the other side of the lens. What is the height of the rose s image? 16) Label any five structures on a microscope, a plant cell or an animal cell (diagrams would be provided). 17) Fill in the following chart: Organelle Function Plant, Animal or Both produces protein plant only chromosomes 18a) Identify the phase of mitosis when each of the following occurs: Chromosomes separate to either side of the cell. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Chromosomes shorten and thicken. The nuclear membrane starts to reappear. b) Label the phases of the cell cycle visible in the picture below: 19) Label any four organs of the digestive system, and explain their function.
8 Long Answer 1) You need to demonstrate that the Law of Conservation of Mass is always true. The only reactants that you have are vinegar and baking soda, which you know create bubbles when they are mixed. Describe how you will prove the Law of Conservation of Mass using these reactants in a typical lab. 2) You have been given two solids that look very alike. The formulas for the solids are written on the containers. You are then told that one of the solids is ionic and the other is molecular. a) Describe how you could identify the solids as ionic or molecular from their formulae. b) Describe two experiments you could do in the lab that could help you to identify the solids as ionic or molecular. Be sure to include the results of the experiments that identify the substance. 3) A car uses three different kinds of mirrors. Name each kind of mirror a car uses, the function of the mirror and why that particular kind of mirror has been chosen for that function. 4) Discuss three similarities and two differences between a camera and a movie projector. 5) Explain how rainbows are created in the sky after it rains. Include a diagram in your answer. 6) What are four important steps when putting away a microscope? 7) What happens to the chromosomes during late interphase? Why is this event so important during asexual cell division? 8) Compare cancer cells to healthy cells. Give three reasons why cancer cells can kill. 9) Describe three ways that leaves prevent water loss. 10a) Why do plants have to photosynthesize? b) Do plants respire? Why? 11) Discuss three differences between inhaled air and exhaled air. What structures in the respiratory system are responsible for these differences? 12) Draw the path of blood through the following heart. Be sure to identify whether the blood is oxygenated or de-oxygenated, where the blood came from, where it is going, and the main sections of the heart (ie. chambers, important arteries and veins) that the blood passes through.
2. Label animal and plant cells. 3. Differentiate between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
 SNC2D/2DN FINAL EXAM REVIEW ANSWERS UNIT 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Describe the structure and function of cell structures and organelles. Nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus
SNC2D/2DN FINAL EXAM REVIEW ANSWERS UNIT 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Describe the structure and function of cell structures and organelles. Nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus
SNC 2P FINAL EXAM REVIEW. Attached to the back of the exam will be a copy of a periodic table and a list of the polyatomic ions.
 Date of exam: Wednesday, January 29th, 2014 Time of exam: 8:15 am Location: Room 212 Length of exam: 1.5 hrs The exam is worth 10% of your final mark. Attached to the back of the exam will be a copy of
Date of exam: Wednesday, January 29th, 2014 Time of exam: 8:15 am Location: Room 212 Length of exam: 1.5 hrs The exam is worth 10% of your final mark. Attached to the back of the exam will be a copy of
SNC2D Exam Review Questions
 CHEMISTRY SNC2D Exam Review Questions 1. Fill in this chart using the periodic table: Element potassium # Valence Electrons (no. of electrons in the outer shell) Valence (number of electrons lost or gained
CHEMISTRY SNC2D Exam Review Questions 1. Fill in this chart using the periodic table: Element potassium # Valence Electrons (no. of electrons in the outer shell) Valence (number of electrons lost or gained
Military High School AL- Ain. Grade 10 &11. Biology Sample Questions. Student Name: Computer #:
 Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
SNC 2D1 EXAM REVIEW Chemistry 1. Which element has 9 protons? 2. Which element has 26 neutrons? 3. What name is given to the elements in group #2?
 Date: Name: SNC 2D1 EXAM REVIEW Chemistry 1. Which element has 9 protons? 2. Which element has 26 neutrons? 3. What name is given to the elements in group #2? 4. What is the charge on the ions of elements
Date: Name: SNC 2D1 EXAM REVIEW Chemistry 1. Which element has 9 protons? 2. Which element has 26 neutrons? 3. What name is given to the elements in group #2? 4. What is the charge on the ions of elements
Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period
 2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
2017-2018 Semester 1 Study Guide Name Period Chapter 1: Scientific Method and Microscopes (p. 2-31 and A-1 through A-17) Vocab: experiment, hypothesis, scientific theory, scientific law, controlled experiment,
SNC2D SNC2D Exam Review Name:
 CHEMISTRY 1. Element with 9 protons: 2. Element with 7 neutrons: 3. Horizontal row in the periodic table: 4. Vertical column in the periodic table: 5. The name of the elements in group #1: 6. The name
CHEMISTRY 1. Element with 9 protons: 2. Element with 7 neutrons: 3. Horizontal row in the periodic table: 4. Vertical column in the periodic table: 5. The name of the elements in group #1: 6. The name
Mitochondria. Nickname: Batteries. bean shaped. Structure: Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell)
 The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
The City School PAF Chapter
 The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet Answer Key May 2015 SCIENCE Class 7 The City School / PAF Chapter/ Comprehensive Worksheet/ May 2015/ Science/ Class 7 / Ans Key Page 1 of 6 SECTION
The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet Answer Key May 2015 SCIENCE Class 7 The City School / PAF Chapter/ Comprehensive Worksheet/ May 2015/ Science/ Class 7 / Ans Key Page 1 of 6 SECTION
The City School PAF Chapter
 The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet May 2015 SCIENCE Class 7 Candidate Name: Index Number: Section: Branch/Campus: Date: Maximum Marks: 100 Time Allowed: 2 hours 0minutes INSTRUCTIONS:
The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet May 2015 SCIENCE Class 7 Candidate Name: Index Number: Section: Branch/Campus: Date: Maximum Marks: 100 Time Allowed: 2 hours 0minutes INSTRUCTIONS:
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome
 BIOLOGY UNIT REVIEW SNC 2D PART A: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING 1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome 2. The replicated
BIOLOGY UNIT REVIEW SNC 2D PART A: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING 1. Which of these organelles are found only in plant cells? a) cell membranes c) mitochondria b) chloroplast d) ribosome 2. The replicated
Table of Contents. Chapter Preview. 4.1 Photosynthesis. 4.2 Respiration. 4.3 Cell Division. 4.4 Cell Differentiation
 Table of Contents Chapter Preview 4.1 Photosynthesis 4.2 Respiration 4.3 Cell Division 4.4 Cell Differentiation Chapter Preview Questions 1. All living things are made of a. tissues. b. muscles. c. cells.
Table of Contents Chapter Preview 4.1 Photosynthesis 4.2 Respiration 4.3 Cell Division 4.4 Cell Differentiation Chapter Preview Questions 1. All living things are made of a. tissues. b. muscles. c. cells.
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
B I O. 1. B I O A N A L Y Z E T H E C E L L A S A L I V I N G S Y S T E M.
 Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
 Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Photosynthesis. Synthesizing food from light
 Photosynthesis Synthesizing food from light 7.5A recognize that radiant energy from the Sun is transformed into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis Consider a Hamburger.. It contains
Photosynthesis Synthesizing food from light 7.5A recognize that radiant energy from the Sun is transformed into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis Consider a Hamburger.. It contains
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Chapter 4 and Chapter 5. Chapter 5
 Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Summary Chapter 4 The nucleus controls the functions of life. Chromosomes found within the nucleus contain the genes that store the information to make proteins. (4.1) Genetic information
Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Summary Chapter 4 The nucleus controls the functions of life. Chromosomes found within the nucleus contain the genes that store the information to make proteins. (4.1) Genetic information
Cell Function Practice From Earth s atmosphere, carbon dioxide is used by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria during the process of
 ell Function Practice Name: Date: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions? 4. Which molecule in plant cells first captures the radiant energy from sunlight?. TP. oxygen. DN D. water.
ell Function Practice Name: Date: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions? 4. Which molecule in plant cells first captures the radiant energy from sunlight?. TP. oxygen. DN D. water.
Exam Prep Questions. (a) i. State the function of each of the following parts of the flower. Petal - Anther - (2 marks) Develops into a seed,
 Exam Prep Questions 1. Fig. 1.1 shows a cross-section through a flower. (IGCSE 2011) (a) i. State the function of each of the following parts of the flower. Petal - Anther - (2 marks) ii. Name the part
Exam Prep Questions 1. Fig. 1.1 shows a cross-section through a flower. (IGCSE 2011) (a) i. State the function of each of the following parts of the flower. Petal - Anther - (2 marks) ii. Name the part
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka
 Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy
 Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Science 1206 Chemistry Unit Sample Final Exam Key
 Science 1206 Chemistry Unit Sample Final Exam Key 1. A gas is proved to be carbon dioxide if: (a) a glowing splint bursts into flames in the gas. (b) a wet piece of red litmus goes blue in the gas. (c)
Science 1206 Chemistry Unit Sample Final Exam Key 1. A gas is proved to be carbon dioxide if: (a) a glowing splint bursts into flames in the gas. (b) a wet piece of red litmus goes blue in the gas. (c)
The student might demonstrate the ability to achieve this standard by: Making a chart comparing the similar functions of plant and animal cells.
 1: Life, Cell Biology: All living organisms are composed of cells, from just one to many trillions, whose details are usually visible only through a microscope. s 1.a) Cells function similarly in all living
1: Life, Cell Biology: All living organisms are composed of cells, from just one to many trillions, whose details are usually visible only through a microscope. s 1.a) Cells function similarly in all living
Basic Chemistry. Chemistry Review. Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology
 Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
CELL STRUCTURE. What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide?
 CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
7.1.2 Cell Functions. 104 minutes. 137 marks. Page 1 of 30
 7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure
 STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE:
 CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE: 2016-2017 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 AND 2 UNIT 1 MASTER COPY 11-15-16 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT
CRAWFORDSVILLE COMMUNITY SCHOOL CORPORATION GRADE LEVEL: SEVENTH SUBJECT: SCIENCE DATE: 2016-2017 GRADING PERIOD: QUARTER 1 AND 2 UNIT 1 MASTER COPY 11-15-16 CONTENT STANDARD INDICATORS SKILLS ASSESSMENT
The Chemistry of Biology
 The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Biology Honors Mid-Term Review
 Biology Honors Mid-Term Review Please be on time to class. Avoid scheduling appointments or leaving class early. Exam Date: December 15 th and 16 th This study guide packet is due the day of the mid-term
Biology Honors Mid-Term Review Please be on time to class. Avoid scheduling appointments or leaving class early. Exam Date: December 15 th and 16 th This study guide packet is due the day of the mid-term
Biology Unit 3 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Chemistry Spring Packet Study Guide for Benchmark Exam
 Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
It helps scientists understand the workings of the human body and of other animals and plants
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory. * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things.
 Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things. Since they are so small, before the invention of the microscope (around 1590), no one
Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things. Since they are so small, before the invention of the microscope (around 1590), no one
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Midterm Review Guide. Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer.
 Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Page 1. Name: UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2016 Science I & II Duration: 3 Hours Index No:- 1) The most essential organelle that should be present in a typical cell
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Ms. Stacey-Ann Joseph HSB TEST 1
 SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
SECTION A: LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Circle the most appropriate answer for each question. 1. Which are not organisms? A. Bacteria B. Cars C. Trees D. Wolves 2. Which is defined by the power
8th GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCE: 2nd SEMESTER EXAM OUTLINE
 1) Light is an wave. Electromagnetic LIGHT 2) Draw, label, and give an example of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio - Radios Micro The appliance in your house Infra- Thermal Visible What
1) Light is an wave. Electromagnetic LIGHT 2) Draw, label, and give an example of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio - Radios Micro The appliance in your house Infra- Thermal Visible What
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle
 Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
7. Chlorine has an atomic number of 17, how many electrons does it have in its outermost (third) shell? a. 7 c. 2 e. 8 b. 4 d. 10
 Multiple Choice: 1-32 (1.5 points each). Circle the best answer here and fill in your bubble sheet. This portion of the exam will be graded using the bubble sheets only. 1. According to modern science,
Multiple Choice: 1-32 (1.5 points each). Circle the best answer here and fill in your bubble sheet. This portion of the exam will be graded using the bubble sheets only. 1. According to modern science,
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Elements and Isotopes
 Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction
 Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
Bio 10: 10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Lesson Objectives Explain the problems that growth causes for cells. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction. Lesson Summary Limits to Cell Size There
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Mr. Hines
 Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Mr. Hines Chapter 2.1 The nature of Matter Learning Target 1 List and describe the four things in the universe and their relationship 2 Explain what matter is. 3
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Mr. Hines Chapter 2.1 The nature of Matter Learning Target 1 List and describe the four things in the universe and their relationship 2 Explain what matter is. 3
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Name: Grade 5 ( ) Date:
 SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
SCIENCE REVISION ANSWER KEY. QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: 1. Mollusks 2. Vertebrates 3. Invertebrates 4. Arthropods 5. Archaebacterial
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
2-1 The Nature of Matter. Atoms
 2-1 The Nature of Matter Atoms What do we call the smallest unit of matter? Who named it? What does it mean in Greek? How many atoms would make a row 1cm long? What does this indicate? Atoms are made up
2-1 The Nature of Matter Atoms What do we call the smallest unit of matter? Who named it? What does it mean in Greek? How many atoms would make a row 1cm long? What does this indicate? Atoms are made up
The Cell in Action. The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle
 The Cell in Action The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle References Information and Most Images Holt Science & Technology, North Carolina, Grade 7. Holt, Rinehart and Winston:
The Cell in Action The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle References Information and Most Images Holt Science & Technology, North Carolina, Grade 7. Holt, Rinehart and Winston:
Table of Contents. Chapter 4 Cell Processes and Energy. Chapter Preview. 4.1 Photosynthesis. 4.2 Respiration. 4.3 Cell Division
 Table of Contents Chapter Preview 4.1 Photosynthesis 4.2 Respiration 4.3 Cell Division 4.4 Cell Differentiation Chapter Preview Questions 1. All living things are made of a. tissues. b. muscles. c. cells.
Table of Contents Chapter Preview 4.1 Photosynthesis 4.2 Respiration 4.3 Cell Division 4.4 Cell Differentiation Chapter Preview Questions 1. All living things are made of a. tissues. b. muscles. c. cells.
Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life.
 Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life. Using a Microscope - Worksheet (diagram and functions of a microscope) - Lab (p. 394-395) What you are viewing under a microscope (P.393) - Magnified image
Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life. Using a Microscope - Worksheet (diagram and functions of a microscope) - Lab (p. 394-395) What you are viewing under a microscope (P.393) - Magnified image
Form 4. The vision of the school: Distinct Environment for Refined Education. Primary four 2017 /
 The vision of the school: Distinct Environment for Refined Education Primary four 2017 / 2018-1- Lesson one :- Complete:- The cell The basic unit of Structure and function 1- The building unit of animals
The vision of the school: Distinct Environment for Refined Education Primary four 2017 / 2018-1- Lesson one :- Complete:- The cell The basic unit of Structure and function 1- The building unit of animals
Cells: 3 Star. Which row in the chart below best explains the movement of some molecules between the model cell and the solution in the beaker?
 ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
Chapter Two Test Chemistry. 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23
 Name Chapter Two Test Chemistry 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23 2. The nucleus is made up of all of the following: A. Electrons C. Protons
Name Chapter Two Test Chemistry 1. If an atom contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, its atomic number is A. 1 C. 12 B. 11 D. 23 2. The nucleus is made up of all of the following: A. Electrons C. Protons
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
WANGANUI HIGH SCHOOL
 Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER
 SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
SCIENCE REVISION BOOKLET MID SEMESTER 1-2018 NAME: GRADE: 5 ( ) DATE: 1 QA: KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING. a. Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box below: Air sacs, arthropods, Cytoplasm,
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Cell Biology. AQA Biology topic 1
 Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Cell Biology AQA Biology topic 1 1.1 Cell Structure Plant and Animal cells (eukaryotic cells) Eukaryotic cells have these features: 1) Cytoplasm 2) Genetic material within a nucleus 3) Cell Membrane Typical
Microscope History Robert Hooke
 1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
Cells Key Words. Task. Key words. Write a definition for each of the key words listed below. Microscope. Plant cell. Animal Cell.
 KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
KS3 Science Cells Cells Key Words Task Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words Microscope Plant cell Animal Cell Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
School. Team Number. Optics
 School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
Unit 2: The Properties of Water, Organic Macromolecules, Enzymes, Digestion (questions)
 Table 1: ph Values of Common Substances 1. Observe Table 1, which substance has the highest concentration of H+ ions? a. Water b. Baking soda solution c. Lemon juice d. Sodium hydroxide solution 2. Which
Table 1: ph Values of Common Substances 1. Observe Table 1, which substance has the highest concentration of H+ ions? a. Water b. Baking soda solution c. Lemon juice d. Sodium hydroxide solution 2. Which
plant cell tissue nerve cell paramecium
 plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
Reason... (2) Reason... (2) Reason... (2)
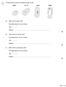 1 The figure below shows four different types of cell. (a) Which cell is a plant cell? Give one reason for your answer. Cell... Reason... (b) Which cell is an animal cell? Give one reason for your answer.
1 The figure below shows four different types of cell. (a) Which cell is a plant cell? Give one reason for your answer. Cell... Reason... (b) Which cell is an animal cell? Give one reason for your answer.
Biology. The study of life
 Biology The study of life Genesis 1:11 Then God said, Let the land produce vegetation: seed-bearing plants and trees on the land that bear fruit with seed in it, according to their various kinds. Genesis
Biology The study of life Genesis 1:11 Then God said, Let the land produce vegetation: seed-bearing plants and trees on the land that bear fruit with seed in it, according to their various kinds. Genesis
1.1 Characteristics common to organisms
 Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
Biology Form 3 Page 5 Ms. R. Buttigieg 1.1 Characteristics common to organisms see GCSE Biology pg. 292 Biology is the study of living things. We call living things organisms. Plants and animals are ALL
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
5. The cells in the liver that detoxify poison substances contain lots of a. smooth ER b. rough ER c. Golgi apparatus d. lysosomes e.
 Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper
2.1 CELL STRUCTURE. The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life.
 2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
Chemistry Released Questions
 Name: Date: 1. What was Niels Bohr s prediction about the location of the electrons in an atom? 3. An atom with which atomic diagram has chemical properties most similar to calcium? A. Electrons pair with
Name: Date: 1. What was Niels Bohr s prediction about the location of the electrons in an atom? 3. An atom with which atomic diagram has chemical properties most similar to calcium? A. Electrons pair with
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards
 Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
