Electrostatic Interactions in Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Biomolecules: Bulk Structures and Induced Surface Pattern Formation
|
|
|
- Brice Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrostatic Interactions in Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Biomolecules: Bulk Structures and Induced Surface Pattern Formation Monica Olvera de la Cruz F. J. Solis, P. Gonzalez- Mozuleos (theory) E. Raspaud, J.L. Sikorav, M.J. Bedzyk, Y. H. Cheng, J. Libera (Experiments) Y. Velichko (Simulations)
2 Double Stranded DNA 2 chains each with -1 charge every base pair 3.4 Å Diameter 20 Å Persistence length (rigidity) of 500 Å (150 basepairs) Hydrophilic (hides hydrophobic units) Projection of the two phosphates on the double-helix axis gives linear charge density : Double Stranded DNA: (short=rod; long=semi-flexible) Single Stranded DNA: (flexible) 1 e / 1.7 Å ~ 6 e / nm 1 e / 3.4 Å DNA is one of the most highly charged systems. Strong polyelectrolyte Synthetic example: Poly-Styrene-Sulphonate (100% S): 1 e / 2.5 Å ~ 4 e / nm. Persisitence length 10 Å
3 Strong Polyelectrolyte Solutions Physical Properties Water soluble in monovalent salts at low ionic strength solutions. Simple model: charged chain (flexible, semiflexible or rod-like) Solvated charge groups and ions Water is structureless Chains are stretched to decrease electrostatic repulsions. + - Flexible charged chains and counterions
4 DNA Condensation: precipitation occurs upon the addition of multivalent salt Metallic or organic 3+, 4+, higher multivalent salts (Cobalt hexamine, Spermine, Spermidine) precipitate DNA into toroidal bundles. Single stranded DNA and other flexible polyelectrolytes form compact structures. J. Widom and R.L. Baldwin, J. Mol. Biol., 144 (1980).
5 Phase diagram: nearly universal DNA redissolution In excess of spermine 1 For -Nucleosome core particles Spermine Concentration (M) H1-depleted chromatine fragments - short single-stranded DNA DNA precipitation DNA concentration (M) (Raspaud et al., )
6 Precipitation/condensation of polyelectrolytes Why do equal charges attract? The origin of the counterion driven attraction. Necessary elements to construct a theory.
7 Electrostatically driven selfassembly Cationic-Anionic Biological Complexes Viral assembly Chromosomes structure DNA packing for gene therapy Biotechnology (DNA condensation is used to increase DNA denaturation and cyclization rates by orders of magnitude as in vivo)
8 Virial Assembly: Helical and Sphere-like RNA Virus (Tsuruta et al.) Tobacco Mosaic Virus. One RNA (-) molecule of 6,300 base + 2,000 identical capsid (+) proteins Capsid Hole 2 RNA molecules (3kB) Density RNA crystal Self-assembles from capsid protein + viral RNA solution
9 Chromosome Condensation Transition DNA/Histone electrostatic attraction versus Bending Stiffness. Known structures Nucleus: 23 chromosomes
10 Characteristic length for ionic dissociation/association in water: The Bjerrum length l B kt = 2 e 4πεε 0 l B if d < l B then ion pairing occurs In water, l B = 7.14 Å For a multivalent salt z i : z j Association energy increases by z i z j and l B
11 Simple salts r j Potential at the arbitrary point r : r ij ψ ( r ) = ρ( r') dr' 4πεε 0r r' r i with ρ (r) the total charge density at r How does the charges distribution ρ(r) change with respect to the distance r from a central ion?
12 ρ(r) is related to ψ(r) by the Poisson s eq., ψ(r) = -ρ(r )/εε 0 r If short range correlations are ignored (as in point ions), One can use the Boltzmann s distribution, ρ (r ) = z + e C + 0 e -z +eψ(r)/kt + z - e C - 0 e -z -eψ(r)/kt, The Poisson-Boltzmann (PB) equation. Expanding exponential gives lineaqrized PB or Debye- Hückel (DH) theory: 0 ψ = κ 2 ψ if if r< a r> a * 2 4π lbρ 4 = 3 κ = a * π ρ 2 * a T T*=a/l B
13 Salt-free polyelectrolyte solutions, monovalent counterions In polyelectrolytes the linearized theories are not valid. The chains are strongly perturbed by electrostatics 2 ξ ~1/ κ * ( ρ ) 1 They are stretched due to the repulsions ξ BUT ion association along the chains: Shape depends on how many ions are around the chains
14 Non-linear effects in polyelectrolytes Simple salt Polyelectrolyte in ionic solution r Apply similar calculation? r -Start from the Poisson-Boltzmann equation - BUT linearization is not possible because the approximation z i eψ(r) << kt is not valid ion pairing or ion condensation even at high T*
15 In colloids the"condensed ions renormalized the charge like a double layer in charged surfaces. Away from the macroion the interaction with other charges reflects only the effective charge of the macroion, and follows mean field values (Debye-Huckel, DVLO). Warning. Poisson Boltzmann ignores short range correlations, which can be important in the dense ionic region or double layer.
16 Infinite rods the charge density in Bjerrum length l B units is Monomers z m = -1 ξ M = l B / b the Manning parameter For B DNA, b = 1.7 Å : ξ M = 4.2 if > 1/z c ion condensation b Counterions z c = + 1 «free» ions treated in the Debye-Hückel approximation. «condensed» ions reducing the monomer charge to an effective charge q eff. 2r 0
17 Finite rods: the length effect P. Gonzalez Mozuleos and M. Olvera de la Cruz, 1995 Counterion charge renormalization in 3D, only at finite concentration Size and concentration effects (Alexander et al.,1984) For charged spheres of size R, ion chemical potential far from the spheres, mainly entropic kt ln C, on its surface, mainly enthalpic (electrostatic) -q eff e 2 /4πεε 0 R L 1/κ q eff ~ - R ln C The effective charge increases or the fraction of condensed ion decreases with dilution For rods R~N and the chemical potential ln N term
18 PB similar to equate chemical potential of free and condensed ions to determine the effective charge of the colloid. This can be done for any input charge distributions. For a fractal chains we input the distribution from the center of mass and allow the ions to penetrate the fractal. + - R~N ν ν =1 rod ν=1/2 random walk ν=1/3 dense ionic structure
19 Conformation effects: fraction of condensed counterions (DH for ions only, no chain RPA contribution) q eff ~ - R ln C 1/κ 1/κ (Gonzalez-Mozuelos & Olvera de la Cruz, 1995) dilution
20 Poison-Boltzmann gives rod lowest energy though more ions are condensed in collapsed than in rod. IF SHORT RANGE CORRELATIONS as charge density increases or valence of counterions increases then collapse chains Collapse to denser system of charges due to counterion induced attractions Z=4. Z=1.
21 Two-dimensional lattice of the multivalent counterions around the surface (Rouzina and Bloomfield 1996) and around rods (Arenson et al 1999, Solis and Olvera de la Cruz, 1999) Correlation energy ε c per ion < 0 (attractive) If n : local concentration of the correlated liquid ε c W c ε c (2n) < ε c (n ) Attraction between chains
22 Phase separation of polyelectrolytes with the addition of multivalent ions In dense systems Highly correlated ions leads to attractions (Modified D-H gives no transition in salt solutions) e -κr Repulsions only in dilute with point ions (Brenner & Parsegian, 1972) Ionic glass (Solis + M.O. de la Cruz, 2000, 2001)
23 Phase diagram: nearly universal DNA redissolution in excess of spermine Spermine Concentration (M) In the precipitated region the chains form an ionic crystal DNA precipitation DNA concentration (M) (Raspaud et al., )
24 Polyelectrolyte (PE) Chains in multivalent ions (Gonzalez-Mozuelos et al 95;Solis et al 00, 01; Lee + Thirumalia 00; Liu + Muthukumar 02)) E. Luijten 04 σ m 2.5Å; water at 298K: l B 7.1Å l B / σ m 3; C m = 0.008σ m 3 ~ 1M PE(N=32) + 8(4:1)salt Scaling description: R g ~N ν mer (+1) (+4) coion Charged rods (DD DNA) the precipitation is into bundles ν = 1/3 sphere ν = 0.5 ideal chain ν = coil ν = 1 rigid rod
25 Effective charge d=positive; e=neutral, f=negative Solis + MO de la Cruz 00, 01; Mesina, Holm and Kremer 00; Solis 02, Grosberg et al 02, Grosberg + Tanaka 01 Stability of complexes to segregation or to dissolution Polyelectrolytes collapse; beyond neutralization, re-expansion occurs because the multivalent ions can interact more with co-ions Counterion size has crucial role.
26 Experiments on charge inversion, T4 DNA + - Short DNA fragments Spermine concentration (z c = + 4) Linear DNA Nucleosome Core Particles Spermidine concentration (z c = + 3) No charge inversion - z c = + 2 (Raspaud et al., 1999; De Frutos et al., 2001)
27 Adsorption of Strongly Charged Polyelectrolytes onto Oppositely Charged Surface Driving force: counterion release a b R Correlations along surface if distance between rods larger than adsorbed layer thickness (break down of PB) leads to charge inversion (Netz+ Joanny 99; Dobrynin+ Rubinstein 00).
28 Strongly charged rods in divalent solution b/(1-f ) Polyelectrolytes adsorption onto same charged surfaces studied experimentally via X-Ray Standing waves (Libera, Cheng, Bedzyk). b Adsorbed rods via short range attractions
29 Hg Hg Hg Hg Zn 2- Zn 2- Zn 2- O - O - O - O - Zn 2- Hg Hg Hg Hg Zn 2- Zn 2- O - O - O - O - Hg Hg Hg Hg Zn 2- Zn 2- Zn 2- O - O - O - O - Θ S,Hg Θ S,Zn Time dependence of the Zn and Hg surface condensed layer coverages.the line is drawn to guide the eye.
30 Conclusions on precipitation We have proposed a mechanism for attractions of purely electrostatic nature that describes the phase diagram. Smaller multivalent ions are more efficient condensing polyelectrolytes. In order to observe re-dissolution by adding more multivalent ions one needs small association constants. Mixture of mono and z c -valent cations condensed onto the DNA induce nonuniversal phase diagrams The non-ideal behavior of the free multivalent salt (determine by effective ionic sizes) reduced and may suppressed the DNA overcharging Surface adsorption of polyions described by correlations. Equal charge surface adsorption is possible via oppositely charged ions of valence 2+ (like cell membranes to DNA)
31 Peptide Amphiphiles (PA) nanofibers formed from acidic PAs by dropping the ph below 4.5 (low). Basic PAs self-assembled above ph 9 (middle). Combining acidic and basic PAs at neutral ph selfassembly (top). Only form cylinders. (S. Stupp lab for use as cell support such as laminin)
32 Multi-component micelles? (Solis, de la Cruz, Stupp 04) Use oppositely charge units to built stable nanoaggregates with surface structure if units are otherwise immiscible. Flat surface pattern due to the competition of surface tension and charge density : domain of size L~ A 1/2 is L~( / 2 ) 1/2 The fraction of area f of one unit in the cell of are A determines the pattern structure.
33 F A γ s 1 = 1 + σ 2 Ls 2 2 σ L 2 The phase diagram in 2D looks like this: A o = γ Homogeneous γ Hexagonal Lamella Hexagonal T f f c =0.35, 0.65
34 Pure Coulomb F ~ L Screened F ~ L, L<1/ or F ~ 1/, L>1/ Macrophase segregation Homogeneous γ Hexagonal Hexagonal T f Full segregation
35 Electrostatics generate multicomponent micelles and vesicles with surface patterns With screening the domain size jumps from finite to macroscopic segregation
36 MONTE CARLO EQUAL SIZE AND OPPOSITE CHARGE +1 and -1 Sort range = 3KT, Electrostatic 1/ε ~.1 Conclusion: in two dimensions one can create periodic patterns using the competition among electrostatic and van der Waals interactions
Biological Polyelectrolytes and Biological Complexes
 Biological Polyelectrolytes and Biological Complexes Monica Olvera de la Cruz Francisco Solis Pedro Gonzalez-Mozuelos Eric Raspaud Jean Louis Sikorav Michel Delsanti Luc Belloni Alexander Ermoshkin Alexander
Biological Polyelectrolytes and Biological Complexes Monica Olvera de la Cruz Francisco Solis Pedro Gonzalez-Mozuelos Eric Raspaud Jean Louis Sikorav Michel Delsanti Luc Belloni Alexander Ermoshkin Alexander
8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology
 Assignment # 4 8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology Coulomb Interactions 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions scales as Q 2 E c.
Assignment # 4 8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology Coulomb Interactions 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions scales as Q 2 E c.
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
Coil to Globule Transition: This follows Giant Molecules by Alexander Yu. Grosberg and Alexei R. Khokhlov (1997).
 Coil to Globule Transition: This follows Giant Molecules by Alexander Yu. Grosberg and Alexei R. Khokhlov (1997). The Flory Krigbaum expression for the free energy of a self-avoiding chain is given by,
Coil to Globule Transition: This follows Giant Molecules by Alexander Yu. Grosberg and Alexei R. Khokhlov (1997). The Flory Krigbaum expression for the free energy of a self-avoiding chain is given by,
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation
 Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution
V = 2ze 2 n. . a. i=1
 IITS: Statistical Physics in Biology Assignment # 3 KU Leuven 5/29/2013 Coulomb Interactions & Polymers 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions
IITS: Statistical Physics in Biology Assignment # 3 KU Leuven 5/29/2013 Coulomb Interactions & Polymers 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions
Physics of DNA. R. Podgornik. Laboratory of Physical and Structural Biology. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
 Physics of DNA R. Podgornik Laboratory of Physical and Structural Biology National Institute of Child Health and Human Development National Institutes of Health Bethesda, MD - DNA as a polyelectrolyte
Physics of DNA R. Podgornik Laboratory of Physical and Structural Biology National Institute of Child Health and Human Development National Institutes of Health Bethesda, MD - DNA as a polyelectrolyte
Molecular attractions:
 Molecular attractions: a.) van der Waals interactions b.) electrostatic correlation interactions c.) polyelectrolyte bridging interactions Rudi Podgornik Laboratory of Physical and Structural Biology National
Molecular attractions: a.) van der Waals interactions b.) electrostatic correlation interactions c.) polyelectrolyte bridging interactions Rudi Podgornik Laboratory of Physical and Structural Biology National
2 Structure. 2.1 Coulomb interactions
 2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
DNA Condensation. Matej Marin Advisor: prof. Rudi Podgornik. 4th April 2002
 DNA Condensation Matej Marin Advisor: prof. Rudi Podgornik 4th April 2002 Abstract Recent studies of DNA condensation are reviewed. First, dierent intrachain interactions (based on DNA - DNA interactions
DNA Condensation Matej Marin Advisor: prof. Rudi Podgornik 4th April 2002 Abstract Recent studies of DNA condensation are reviewed. First, dierent intrachain interactions (based on DNA - DNA interactions
Roland R. Netz Max-Planck Institute for Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam, Germany
 282 2 Electrochemical Double Layers 2.7 Polyelectrolytes in Solution and at Surfaces Roland R. Netz Max-Planck Institute for Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam, Germany David Andelman School of Physics and
282 2 Electrochemical Double Layers 2.7 Polyelectrolytes in Solution and at Surfaces Roland R. Netz Max-Planck Institute for Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam, Germany David Andelman School of Physics and
Polyelectrolyte and polyampholyte. effects in synthetic and biological
 arxiv:1103.1908v1 [cond-mat.soft] 9 Mar 2011 Chapter 4 Polyelectrolyte and polyampholyte effects in synthetic and biological macromolecules Ngo Minh Toan, Bae-Yeun Ha and D. Thirumalai 1 2 CHAPTER 4. PE
arxiv:1103.1908v1 [cond-mat.soft] 9 Mar 2011 Chapter 4 Polyelectrolyte and polyampholyte effects in synthetic and biological macromolecules Ngo Minh Toan, Bae-Yeun Ha and D. Thirumalai 1 2 CHAPTER 4. PE
Simple Simulations of DNA Condensation
 130 Biophysical Journal Volume 80 January 2001 130 139 Simple Simulations of DNA Condensation Mark J. Stevens Sandia National Laboratory, P.O. Box 5800, MS 1111, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185 USA ABSTRACT
130 Biophysical Journal Volume 80 January 2001 130 139 Simple Simulations of DNA Condensation Mark J. Stevens Sandia National Laboratory, P.O. Box 5800, MS 1111, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87185 USA ABSTRACT
Generalizations for the Potential of Mean Force between Two Isolated Colloidal Particles from Monte Carlo Simulations
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 252, 326 330 (2002) doi:10.1006/jcis.2002.8497 Generalizations for the Potential of Mean Force between Two Isolated Colloidal Particles from Monte Carlo Simulations
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 252, 326 330 (2002) doi:10.1006/jcis.2002.8497 Generalizations for the Potential of Mean Force between Two Isolated Colloidal Particles from Monte Carlo Simulations
Exchange of Counterions in DNA Condensation. Abstract
 Exchange of Counterions in DNA Condensation Yoshihiro Murayama and Masaki Sano Department of Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan Abstract We measured the fluorescence intensity of DNA-bound
Exchange of Counterions in DNA Condensation Yoshihiro Murayama and Masaki Sano Department of Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan Abstract We measured the fluorescence intensity of DNA-bound
Effect of Counterion Condensation on Rigidity of Semiflexible Polyelectrolytes
 Macromolecules 006, 39, 9519-957 9519 Effect of Counterion Condensation on Rigidity of Semiflexible Polyelectrolytes Andrey V. Dobrynin Polymer Program, Institute of Materials Science and Department of
Macromolecules 006, 39, 9519-957 9519 Effect of Counterion Condensation on Rigidity of Semiflexible Polyelectrolytes Andrey V. Dobrynin Polymer Program, Institute of Materials Science and Department of
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016](/thumbs/76/73264929.jpg) Polyelectrolyte Polypeptide Scaling Laws Via Mechanical and Dielectric Relaxation Measurements Jorge Monreal University of South Florida arxiv:1609.05358v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 Dated: March 1, 2018
Polyelectrolyte Polypeptide Scaling Laws Via Mechanical and Dielectric Relaxation Measurements Jorge Monreal University of South Florida arxiv:1609.05358v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 Dated: March 1, 2018
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit. Lecture 2 (9/11/17)
 16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
16 years ago TODAY (9/11) at 8:46, the first tower was hit at 9:03, the second tower was hit By Anthony Quintano - https://www.flickr.com/photos/quintanomedia/15071865580, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=38538291
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
Density Functional Theory for Planar Electric Double Layers: Closing the Gap between Simple and Polyelectrolytes
 J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7473-7484 7473 Density Functional Theory for Planar Electric Double Layers: Closing the Gap between Simple and Polyelectrolytes Zhidong Li and Jianzhong Wu* Department of Chemical
J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7473-7484 7473 Density Functional Theory for Planar Electric Double Layers: Closing the Gap between Simple and Polyelectrolytes Zhidong Li and Jianzhong Wu* Department of Chemical
Proteins polymer molecules, folded in complex structures. Konstantin Popov Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics
 Proteins polymer molecules, folded in complex structures Konstantin Popov Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics Outline General aspects of polymer theory Size and persistent length of ideal linear
Proteins polymer molecules, folded in complex structures Konstantin Popov Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics Outline General aspects of polymer theory Size and persistent length of ideal linear
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Mar 2003
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Mar 2003 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Mar 2003](/thumbs/81/84522834.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0303455v1 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Mar 2003 The physics of chromatin Contents Helmut Schiessel Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung, Theory Group, P.O.Box 3148, D-55021 Mainz, Germany Abstract.
arxiv:cond-mat/0303455v1 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Mar 2003 The physics of chromatin Contents Helmut Schiessel Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung, Theory Group, P.O.Box 3148, D-55021 Mainz, Germany Abstract.
Swelling and Collapse of Single Polymer Molecules and Gels.
 Swelling and Collapse of Single Polymer Molecules and Gels. Coil-Globule Transition in Single Polymer Molecules. the coil-globule transition If polymer chains are not ideal, interactions of non-neighboring
Swelling and Collapse of Single Polymer Molecules and Gels. Coil-Globule Transition in Single Polymer Molecules. the coil-globule transition If polymer chains are not ideal, interactions of non-neighboring
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016](/thumbs/88/115645706.jpg) Multi-shell model of ion-induced nucleic acid condensation Igor S. Tolokh Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA Aleksander Drozdetski Department of Physics, Virginia
Multi-shell model of ion-induced nucleic acid condensation Igor S. Tolokh Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA Aleksander Drozdetski Department of Physics, Virginia
DNA-Surfactant Interactions. Compaction, Condensation, Decompaction and Phase Separation
 Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2004, 51, 447-469 447 Invited Paper DNA-Surfactant Interactions. Compaction, Condensation, Decompaction and Phase Separation Rita Dias a,b, Mónica Rosa a,b, Alberto
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2004, 51, 447-469 447 Invited Paper DNA-Surfactant Interactions. Compaction, Condensation, Decompaction and Phase Separation Rita Dias a,b, Mónica Rosa a,b, Alberto
Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science
 Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 13 (2008) 376 388 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cocis
Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 13 (2008) 376 388 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cocis
Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 044903 2005 Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte Zhi-Jie Tan and Shi-Jie Chen a) Department of Physics and
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 044903 2005 Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte Zhi-Jie Tan and Shi-Jie Chen a) Department of Physics and
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Supporting Information for: Complexation of β-lactoglobulin Fibrils and Sulfated Polysaccharides
 Supporting Information for: Complexation of β-lactoglobulin Fibrils and Sulfated Polysaccharides Owen G Jones 1, Stephaandschin 1, Jozef Adamcik 1, Ludger Harnau 2, Sreenath Bolisetty 1, and Raffaele Mezzenga
Supporting Information for: Complexation of β-lactoglobulin Fibrils and Sulfated Polysaccharides Owen G Jones 1, Stephaandschin 1, Jozef Adamcik 1, Ludger Harnau 2, Sreenath Bolisetty 1, and Raffaele Mezzenga
Colloids as nucleons
 Colloids as nucleons Willem Kegel & Jan Groenewold Van t Hoff Laboratory Utrecht University The Netherlands Finite-size equilibrium structures macroscopic phase separation Equilibrium clusters & periodic
Colloids as nucleons Willem Kegel & Jan Groenewold Van t Hoff Laboratory Utrecht University The Netherlands Finite-size equilibrium structures macroscopic phase separation Equilibrium clusters & periodic
Lecture 5: Macromolecules, polymers and DNA
 1, polymers and DNA Introduction In this lecture, we focus on a subfield of soft matter: macromolecules and more particularly on polymers. As for the previous chapter about surfactants and electro kinetics,
1, polymers and DNA Introduction In this lecture, we focus on a subfield of soft matter: macromolecules and more particularly on polymers. As for the previous chapter about surfactants and electro kinetics,
Gas-liquid phase separation in oppositely charged colloids: stability and interfacial tension
 7 Gas-liquid phase separation in oppositely charged colloids: stability and interfacial tension We study the phase behaviour and the interfacial tension of the screened Coulomb (Yukawa) restricted primitive
7 Gas-liquid phase separation in oppositely charged colloids: stability and interfacial tension We study the phase behaviour and the interfacial tension of the screened Coulomb (Yukawa) restricted primitive
Computer Simulations of Soft Nanoparticles and Their Interactions with DNA-Like Polyelectrolytes. STOLL, Serge. Abstract
 Book Chapter Computer Simulations of Soft Nanoparticles and Their Interactions with DNA-Like Polyelectrolytes STOLL, Serge Abstract The design of functional molecular architectures and formation of electrostatic
Book Chapter Computer Simulations of Soft Nanoparticles and Their Interactions with DNA-Like Polyelectrolytes STOLL, Serge Abstract The design of functional molecular architectures and formation of electrostatic
(Electrostatics in Biology)
 Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 (Electrostatics
Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 (Electrostatics
Polymer solutions and melts
 Course M6 Lecture 9//004 (JAE) Course M6 Lecture 9//004 Polymer solutions and melts Scattering methods Effects of excluded volume and solvents Dr James Elliott Online teaching material reminder Overheads
Course M6 Lecture 9//004 (JAE) Course M6 Lecture 9//004 Polymer solutions and melts Scattering methods Effects of excluded volume and solvents Dr James Elliott Online teaching material reminder Overheads
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions
 Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/ 1 Water as
Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/ 1 Water as
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
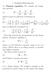 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
Effects of Solvent Mediated Interactions on Electrolytes and Related Electrostatic Systems
 Effects of Solvent Mediated Interactions on Electrolytes and Related Electrostatic Systems Thesis submitted towards the degree Doctor of Philosophy by Yoram Burak Submitted to the Senate of Tel Aviv University
Effects of Solvent Mediated Interactions on Electrolytes and Related Electrostatic Systems Thesis submitted towards the degree Doctor of Philosophy by Yoram Burak Submitted to the Senate of Tel Aviv University
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyampholyte-Polyelectrolyte Complexes in Solutions
 5300 Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5300-5312 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyampholyte-Polyelectrolyte Complexes in Solutions Junhwan Jeon and Andrey V. Dobrynin* Polymer Program, Institute of Materials
5300 Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5300-5312 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyampholyte-Polyelectrolyte Complexes in Solutions Junhwan Jeon and Andrey V. Dobrynin* Polymer Program, Institute of Materials
Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces
 5042 J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5042-5057 Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces Itamar Borukhov, David Andelman,*, and Henri Orland School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and
5042 J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5042-5057 Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces Itamar Borukhov, David Andelman,*, and Henri Orland School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and
Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards
 Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards One Hundred Years of Electrified Interfaces: The Poisson-Boltzmann theory and some recent developments
Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards One Hundred Years of Electrified Interfaces: The Poisson-Boltzmann theory and some recent developments
Research Statement. Shenggao Zhou. November 3, 2014
 Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
Monolayers. Factors affecting the adsorption from solution. Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support
 Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
Monolayers Adsorption as process Adsorption of gases on solids Adsorption of solutions on solids Factors affecting the adsorption from solution Adsorption of amphiphilic molecules on solid support Adsorption
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Brownian Dynamics Simulation of DNA Condensation
 1858 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 October 1999 1858 1870 Brownian Dynamics Simulation of DNA Condensation Pierre-Edouard Sottas, Eric Larquet, Andrzej Stasiak, and Jacques Dubochet Laboratoire d Analyse
1858 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 October 1999 1858 1870 Brownian Dynamics Simulation of DNA Condensation Pierre-Edouard Sottas, Eric Larquet, Andrzej Stasiak, and Jacques Dubochet Laboratoire d Analyse
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Polyampholyte solutions between charged surfaces: Debye Huckel theory
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 20 22 NOVEMBER 1998 Polyampholyte solutions between charged surfaces: Debye Huckel theory Andrey V. Dobrynin a) and Michael Rubinstein Department of Chemistry,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 20 22 NOVEMBER 1998 Polyampholyte solutions between charged surfaces: Debye Huckel theory Andrey V. Dobrynin a) and Michael Rubinstein Department of Chemistry,
Electrostatics and the assembly of an RNA virus
 Electrostatics and the assembly of an RNA virus Citation for published version (APA): Schoot, van der, P. P. A. M., & Bruinsma, R. (2005). Electrostatics and the assembly of an RNA virus. Physical Review
Electrostatics and the assembly of an RNA virus Citation for published version (APA): Schoot, van der, P. P. A. M., & Bruinsma, R. (2005). Electrostatics and the assembly of an RNA virus. Physical Review
Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules
 Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules E.Allahyarov 1,2, H.Löwen 1 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik II, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, D-4225 Düsseldorf, Germany 2 Institute for
Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules E.Allahyarov 1,2, H.Löwen 1 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik II, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, D-4225 Düsseldorf, Germany 2 Institute for
Aqueous solutions. Solubility of different compounds in water
 Aqueous solutions Solubility of different compounds in water The dissolution of molecules into water (in any solvent actually) causes a volume change of the solution; the size of this volume change is
Aqueous solutions Solubility of different compounds in water The dissolution of molecules into water (in any solvent actually) causes a volume change of the solution; the size of this volume change is
Interaction between macroions mediated by divalent rod-like ions
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 November 004 Europhys Lett, 68 (4), pp 494 500 (004) DOI: 10109/epl/i004-1050- Interaction between macroions mediated by divalent rod-like ions K Bohinc 1,,Iglič 1 and S May 3 1
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 November 004 Europhys Lett, 68 (4), pp 494 500 (004) DOI: 10109/epl/i004-1050- Interaction between macroions mediated by divalent rod-like ions K Bohinc 1,,Iglič 1 and S May 3 1
*blood and bones contain colloids. *milk is a good example of a colloidal dispersion.
 Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chapter 2 - Water 9/8/2014. Water exists as a H-bonded network with an average of 4 H-bonds per molecule in ice and 3.4 in liquid. 104.
 Chapter 2 - Water Water exists as a -bonded network with an average of 4 -bonds per molecule in ice and 3.4 in liquid. 104.5 o -bond: An electrostatic attraction between polarized molecules containing
Chapter 2 - Water Water exists as a -bonded network with an average of 4 -bonds per molecule in ice and 3.4 in liquid. 104.5 o -bond: An electrostatic attraction between polarized molecules containing
Charge inversion accompanies DNA condensation. by multivalent ions. Construction, mechanics, and electronics. 11 May 2008.
 Charge inversion accompanies DNA condensation by multivalent ions DNA-based nanotechnology: Construction, mechanics, and electronics 11 May 2008 Serge Lemay Kavli Institute of Nanoscience Delft University
Charge inversion accompanies DNA condensation by multivalent ions DNA-based nanotechnology: Construction, mechanics, and electronics 11 May 2008 Serge Lemay Kavli Institute of Nanoscience Delft University
DNA Condensation Using Self-Assembled Peptides
 DNA Condensation Using Self-Assembled Peptides Angela m. Jimenez, Class of 2008, Major: Chemical Engineering Mentor: Raymond S. Tu, Department of Chemical Engineering ABSTRACT Counterion-mediated DNA-condensation
DNA Condensation Using Self-Assembled Peptides Angela m. Jimenez, Class of 2008, Major: Chemical Engineering Mentor: Raymond S. Tu, Department of Chemical Engineering ABSTRACT Counterion-mediated DNA-condensation
Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties
 Biophysical Journal Volume 78 February 2000 699 706 699 Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties Chandra N. Patra and Arun Yethiraj Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 78 February 2000 699 706 699 Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties Chandra N. Patra and Arun Yethiraj Department
Molecular Driving Forces
 Molecular Driving Forces Statistical Thermodynamics in Chemistry and Biology SUBGfittingen 7 At 216 513 073 / / Ken A. Dill Sarina Bromberg With the assistance of Dirk Stigter on the Electrostatics chapters
Molecular Driving Forces Statistical Thermodynamics in Chemistry and Biology SUBGfittingen 7 At 216 513 073 / / Ken A. Dill Sarina Bromberg With the assistance of Dirk Stigter on the Electrostatics chapters
CHARGED POLYMERS THE STORY SO FAR
 CHARGED POLYMERS THE STORY SO FAR Andrey V Dobrynin Institute of Materials Science &Department of Physics University of Connecticut What are polyelectrolytes? Poly(styrene sulfonate) CH-CH 2 SO Na Poly(methacrylic
CHARGED POLYMERS THE STORY SO FAR Andrey V Dobrynin Institute of Materials Science &Department of Physics University of Connecticut What are polyelectrolytes? Poly(styrene sulfonate) CH-CH 2 SO Na Poly(methacrylic
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces
 Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 83 (2011) 61 68 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfb DNA condensations
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 83 (2011) 61 68 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfb DNA condensations
An Introduction to namic Light Scattering by Macromole cules
 An Introduction to namic Light Scattering by Macromole cules Kenneth S. Schmitz Department of Chemistry University of Missouri-Kansas Kansas City, Missouri City ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich,
An Introduction to namic Light Scattering by Macromole cules Kenneth S. Schmitz Department of Chemistry University of Missouri-Kansas Kansas City, Missouri City ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich,
It is the size of the
 Chapter 2: Literature Review (Note: A modified form of this chapter will be published as Rheology and Colloidal Stability in Paints and Coatings, Proceedings of the Association of Formulation Chemists,
Chapter 2: Literature Review (Note: A modified form of this chapter will be published as Rheology and Colloidal Stability in Paints and Coatings, Proceedings of the Association of Formulation Chemists,
Electrostatic contribution to DNA condensation application of energy minimization in a simple model in strong Coulomb coupling regime.
 lectrostatic contribution to DNA condensation application of energy minimization in a simple model in strong Coulomb coupling regime. Arup K. Mukherjee Department of Physics, Chancellor College, Box 80,
lectrostatic contribution to DNA condensation application of energy minimization in a simple model in strong Coulomb coupling regime. Arup K. Mukherjee Department of Physics, Chancellor College, Box 80,
Equilibrium self-assembly of small RNA viruses
 Equilibrium self-assembly of small RNA viruses R. F. Bruinsma 1,2, M. Comas-Garcia 3, R. F. Garmann 4, A. Y. Grosberg 5 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Equilibrium self-assembly of small RNA viruses R. F. Bruinsma 1,2, M. Comas-Garcia 3, R. F. Garmann 4, A. Y. Grosberg 5 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Flexible Polymer-Induced Condensation and Bundle Formation of DNA and F-Actin Filaments
 1186 Biophysical Journal Volume 80 March 2001 1186 1194 Flexible Polymer-Induced Condensation and Bundle Formation of DNA and F-Actin Filaments Renko de Vries Laboratory of Physical Chemistry and Colloid
1186 Biophysical Journal Volume 80 March 2001 1186 1194 Flexible Polymer-Induced Condensation and Bundle Formation of DNA and F-Actin Filaments Renko de Vries Laboratory of Physical Chemistry and Colloid
Tunable Nanoparticle Arrays at Charged Interfaces
 Tunable Nanoparticle Arrays at Charged Interfaces Supporting Material Sunita Srivastava 1, Dmytro Nykypanchuk 1, Masafumi Fukuto 2 and Oleg Gang 1* 1 Center for Functional Nanomaterials, Brookhaven National
Tunable Nanoparticle Arrays at Charged Interfaces Supporting Material Sunita Srivastava 1, Dmytro Nykypanchuk 1, Masafumi Fukuto 2 and Oleg Gang 1* 1 Center for Functional Nanomaterials, Brookhaven National
Grand-canonical simulation of DNA condensation with two salts, effect of divalent counterion size
 Grand-canonical simulation of DNA condensation with two salts, effect of divalent counterion size Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 1 Faculty of Physics, Hanoi University of Science, Vietnam National University, 334
Grand-canonical simulation of DNA condensation with two salts, effect of divalent counterion size Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 1 Faculty of Physics, Hanoi University of Science, Vietnam National University, 334
Final Morphology of Complex Materials
 120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics
 Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics Molecular surfaces The Hydrophobic Effect Electrostatics Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Electrostatic maps Electrostatic surfaces in MOE 15.1 The
Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics Molecular surfaces The Hydrophobic Effect Electrostatics Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Electrostatic maps Electrostatic surfaces in MOE 15.1 The
Adsorption and depletion of polyelectrolytes from charged surfaces
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, NUMBER 4 22 JULY 2003 Adsorption and depletion of polyelectrolytes from charged surfaces Adi Shafir a) and David Andelman b) School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 119, NUMBER 4 22 JULY 2003 Adsorption and depletion of polyelectrolytes from charged surfaces Adi Shafir a) and David Andelman b) School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond
Confinement of polymer chains and gels
 Confinement of polymer chains and gels Nefeli Georgoulia - Student number: 70732831 1 Introduction Confinement of polymer chains is significant in industrial as well as biological applications. For this
Confinement of polymer chains and gels Nefeli Georgoulia - Student number: 70732831 1 Introduction Confinement of polymer chains is significant in industrial as well as biological applications. For this
Liquid Chromatography
 Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES
 - 1 - MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES Summary of Fundamental Molecular Interactions Q1Q Ion-Ion U ( r) = 4 r πεε o µ Q cosθ U ( r) = 4πεε o r µ 1µ U ( r) 3 r µ 1 µ U ( r) 6 r µ 1 α U ( r) 6 r Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole
- 1 - MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES Summary of Fundamental Molecular Interactions Q1Q Ion-Ion U ( r) = 4 r πεε o µ Q cosθ U ( r) = 4πεε o r µ 1µ U ( r) 3 r µ 1 µ U ( r) 6 r µ 1 α U ( r) 6 r Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole
The existence of distinct states of DNA compaction is vital to
 DNA condensation in two dimensions Ilya Koltover, Kathrin Wagner, and Cyrus R. Safinya Materials Department, Physics Department, and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Program, University of California,
DNA condensation in two dimensions Ilya Koltover, Kathrin Wagner, and Cyrus R. Safinya Materials Department, Physics Department, and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Program, University of California,
Intermolecular and Surface Forces
 Intermolecular and Surface Forces ThirH FHitinn '' I I 111 \J& LM* КтЛ I Km I W I 1 Jacob N. Israelachvili UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SANTA BARBARA, CALIFORNIA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
Intermolecular and Surface Forces ThirH FHitinn '' I I 111 \J& LM* КтЛ I Km I W I 1 Jacob N. Israelachvili UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA SANTA BARBARA, CALIFORNIA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyelectrolyte-Polyampholyte Complexes. Effect of Solvent Quality and Salt Concentration
 24652 J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24652-24665 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyelectrolyte-Polyampholyte Complexes. Effect of Solvent Quality and Salt Concentration Junhwan Jeon and Andrey V. Dobrynin*,,
24652 J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24652-24665 Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyelectrolyte-Polyampholyte Complexes. Effect of Solvent Quality and Salt Concentration Junhwan Jeon and Andrey V. Dobrynin*,,
Ionic polysaccharides, solubility, interactions with surfactants, particle formation, and deposition
 Ionic polysaccharides, solubility, interactions with surfactants, particle formation, and deposition Björn Lindman, Tommy Nylander, Maria Miguel and Lennart Piculell Physical Chemistry 1, Lund University,
Ionic polysaccharides, solubility, interactions with surfactants, particle formation, and deposition Björn Lindman, Tommy Nylander, Maria Miguel and Lennart Piculell Physical Chemistry 1, Lund University,
Nanomechanical Forces Generated by Surface Grafted DNA
 J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 10163-10173 10163 Nanomechanical Forces Generated by Surface Grafted DNA Michael F. Hagan,, Arun Majumdar,, and Arup K. Chakraborty*,,,, Department of Chemical Engineering,
J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 10163-10173 10163 Nanomechanical Forces Generated by Surface Grafted DNA Michael F. Hagan,, Arun Majumdar,, and Arup K. Chakraborty*,,,, Department of Chemical Engineering,
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry
 Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
IV. Ionomer Phenomena
 IV. Ionomer Phenomena (Eisenberg and Kim, Introduction to Ionomers, Wiley, 1998) The modulus, glass transition temperature, viscosity, melt strength, fatigue, and barrier properties are all strongly affected
IV. Ionomer Phenomena (Eisenberg and Kim, Introduction to Ionomers, Wiley, 1998) The modulus, glass transition temperature, viscosity, melt strength, fatigue, and barrier properties are all strongly affected
Torsional Deformation of Double Helix in Interaction and Aggregation of DNA
 6508 J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6508-6518 Torsional Deformation of Double Helix in Interaction and Aggregation of DNA A. G. Cherstvy,, A. A. Kornyshev, and S. eikin*, Institut für Festkörperforschung
6508 J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6508-6518 Torsional Deformation of Double Helix in Interaction and Aggregation of DNA A. G. Cherstvy,, A. A. Kornyshev, and S. eikin*, Institut für Festkörperforschung
Chapter 2 Polymer Physics Concentrated Solutions and Melts
 Chapter 2 Polymer Physics Concentrated Solutions and Melts Chapter 1 discussed the statistical thermodynamics of an isolated polymer chain in a solvent. The conformation of an isolated polymer coil in
Chapter 2 Polymer Physics Concentrated Solutions and Melts Chapter 1 discussed the statistical thermodynamics of an isolated polymer chain in a solvent. The conformation of an isolated polymer coil in
Electrostatics of rigid polyelectrolytes
 Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 11 (2006) 310 315 www.elsevier.com/locate/cocis Electrostatics of rigid polyelectrolytes Gerard C.L. Wong Materials Science and Engineering Dept., Physics
Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 11 (2006) 310 315 www.elsevier.com/locate/cocis Electrostatics of rigid polyelectrolytes Gerard C.L. Wong Materials Science and Engineering Dept., Physics
Fundamental Principles to Tutorials. Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution. Giuseppe Milano
 III Advanced School on Biomolecular Simulation: Fundamental Principles to Tutorials Multiscale Methods from Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution Giuseppe Milano Reference Rob Phillips,
III Advanced School on Biomolecular Simulation: Fundamental Principles to Tutorials Multiscale Methods from Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution Giuseppe Milano Reference Rob Phillips,
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Specific ion effects on the interaction of. hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled
 Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
Supporting Information Specific ion effects on the interaction of hydrophobic and hydrophilic self assembled monolayers T. Rios-Carvajal*, N. R. Pedersen, N. Bovet, S.L.S. Stipp, T. Hassenkam. Nano-Science
The change in free energy on transferring an ion from a medium of low dielectric constantε1 to one of high dielectric constant ε2:
 The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry
 Colloid stability István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry www.kolloid.unideb.hu (Stability of lyophilic colloids see: macromolecular solutions) Stabilities 1.
Colloid stability István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry www.kolloid.unideb.hu (Stability of lyophilic colloids see: macromolecular solutions) Stabilities 1.
Thermodynamics of DNA Binding and Condensation: Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Electrostatic Mechanism
 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3470 available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on J. Mol. Biol. (2000) 296, 1053±1063 Thermodynamics of DNA Binding and Condensation: Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Electrostatic
doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3470 available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on J. Mol. Biol. (2000) 296, 1053±1063 Thermodynamics of DNA Binding and Condensation: Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Electrostatic
Simulation of Nanostructure Formation in Rigid-Chain Polyelectrolyte Solutions
 Simulation of Nanostructure Formation in Rigid-Chain Polyelectrolyte Solutions Dissertation Zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades Dr. Rer. Nat. der Fakultät für Naturwissenschaften der Universität Ulm vorgelegt
Simulation of Nanostructure Formation in Rigid-Chain Polyelectrolyte Solutions Dissertation Zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades Dr. Rer. Nat. der Fakultät für Naturwissenschaften der Universität Ulm vorgelegt
Chapter 12. Insert picture from First page of chapter. Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids
 Chapter 12 Insert picture from First page of chapter Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 12.1 Intermolecular Forces Intermolecular forces
Chapter 12 Insert picture from First page of chapter Intermolecular Forces and the Physical Properties of Liquids and Solids Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 12.1 Intermolecular Forces Intermolecular forces
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS
 Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Electrolyte Solutions
 Chapter 8 Electrolyte Solutions In the last few chapters of this book, we will deal with several specific types of chemical systems. The first one is solutions and equilibria involving electrolytes, which
Chapter 8 Electrolyte Solutions In the last few chapters of this book, we will deal with several specific types of chemical systems. The first one is solutions and equilibria involving electrolytes, which
We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents
 Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents Laurent Helden Jules Mikhael. Physikalisches Institut Universität Stuttgart Model system for hard core interactions accessible fortirm-measurements.
Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents Laurent Helden Jules Mikhael. Physikalisches Institut Universität Stuttgart Model system for hard core interactions accessible fortirm-measurements.
Supporting Information. The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction. between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation.
 Supporting Information The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation study Lili Sun 1, Marcin Tabaka 1, Sen Hou 1, Lin Li 2, Krzysztof Burdzy
Supporting Information The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation study Lili Sun 1, Marcin Tabaka 1, Sen Hou 1, Lin Li 2, Krzysztof Burdzy
Perspective: Coulomb fluids-weak coupling, strong coupling, in between and beyond
 Perspective: Coulomb fluids-weak coupling, strong coupling, in between and beyond Naji, Ali; Kanduc, Matej; Forsman, Jan; Podgornik, Rudolf Published in: Journal of Chemical Physics DOI: 10.1063/1.4824681
Perspective: Coulomb fluids-weak coupling, strong coupling, in between and beyond Naji, Ali; Kanduc, Matej; Forsman, Jan; Podgornik, Rudolf Published in: Journal of Chemical Physics DOI: 10.1063/1.4824681
Interactions of Flexible Macromolecules with Surfaces and Their Role in Viral Assembly
 Interactions of Flexible Macromolecules with Surfaces and Their Role in Viral Assembly Thesis Submitted for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy by Shelly Tzlil Submitted to the Hebrew University Senate December
Interactions of Flexible Macromolecules with Surfaces and Their Role in Viral Assembly Thesis Submitted for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy by Shelly Tzlil Submitted to the Hebrew University Senate December
