Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation
|
|
|
- Sophie Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bchem 675 Lecture 9 Electrostatics-Lecture 2 Debye-Hückel: Continued Counter ion condensation
2 Ion:ion interactions What is the free energy of ion:ion interactions ΔG i-i? Consider an ion in a solution with many other ions: ΔG i i = n i µ i i n i is the number of ions that the reference ion interacts with and µ i-i is the chemical potential for each ion that interacts with the reference. The chemical potential of a single ionic species will be related to the work of charging up a mole of ions of interest while in the proximity of other ions. w ch arg ing = (z i e o )2 8πε o εr i In terms of chemical potential: Δµ i i = N A w ch arg ing Δµ i i = N A z i e o 2 ψ ψ is the electrostatic potential of the ion
3 In order to determine the chemical potential change for the interaction between the total ionic assembly and the ion of interest we must know the electrostatic field at each individual ion that is a result of the other ions in solution. This requires information about the spatial distribution of the ions in the solution relative to the reference ion.
4
5 Erich Armand Arthur Joseph Hückel (in Engl. often spelled Huckel or Hueckel) b. August 9, 1896, Berlin, Germany d. 1980, Marburg, Germany A German physicist and physical chemist. He is known for two major contributions: (a) The Debye-Hückel theory of electrolytic solutions, (b) The Hückel method of approximate molecular orbital (MO) calculations on p-electron systems.
6 Petrus (Peter) Josephus Wilhelmus Debye was born March 24, 1884, at Maastricht, the Netherlands. Debye won Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1936, "for his contributions to our knowledge of molecular structure through his investigations on dipole moments and on the diffraction of X-rays and electrons in gases". Debye died on November 2, 1966, and was buried on Pleasant Grove Cemetery, Cayuga Heights, Tompkins County, New York, U.S.A.
7 Debye-Hückel Model 1923 Treatment: A reference ion residing in a dielectric continuum. Dielectric constant is 80 Reference ion is charged-therefore, in its immediate vicinity there will be neutralization by the continuum of charge that surrounds it. At equilibrium the charge on the central ion will be exactly counterbalanced by the counter charge atmosphere: Principle of Electroneutrality: z i e o X i = 0
8
9 Assumptions of Debye Huckel 1. A central reference ion of a specific charge can be represented as a point charge. 2. This central charge is surrounded by a cloud of smeared-out charge contributed by the participation of all other ions in solution. 3. The electrostatic potential field in the solution can be described by an equation that combines and linearizes the Poisson and Boltzmann equations. 4. No ion-ion interactions except the electrostatic interaction given by the 1/r 2 dependence are to be considered. 5. The solvent simply provides the dielectric medium, and the ion-solvent interactions can be ignored, so the bulk permitivity of the solvent can be used.
10 Figure The excess charge in a given volume, dv, of the cloud can be related to the electrostatic potential existing between the central ion and the small volume element under consideration.
11 Poisson Equation 1 d r dr r2 ( dψ dr ) = ρ r ε o ε Relates the charge distribution, ρ, to the electrostatic potential, Ψ, in a spherically symmetrical system. The total charge in a given volume element is found by adding together all of the charges that reside in the volume: ρ r = n i z i e o The total charge available in the system will be described by the sum of all charged elements in solution.
12 Ionic Strength provides a means of quantifying the charge in an electrolyte solution I = 1 2 n i z i 2 Return to charge excess, ρ, in the volume element Each of the particles n i can be characterized using the n Boltzmann distribution: i = n o U / kt i e U>0:distribution of the ions is less than the bulk U<0: distribution of ions is increased relative to the bulk. Since all interactions are electrostatic: U=z i e o ψ r, the Boltzmann n relationship becomes i = n o i e z i e oψ r / kt and ρ r = ρ r = n i o z i e o e z i e oψ r / kt n i z i e o
13 ρ r = n i o z i e o e z i e oψ r / kt Assume that z i e o Ψ r /kt<<1 can be written as a Taylor series in which only the first 2 terms are considered. e z i e o ψ r /kt ρ r = ρ r = n o i z i e o (1 z i e oψ r ) kt n o i z i e o n i o z i 2 e o 2 ψ r kt The first term is zero-electroneutrality-and ρ r = n o i z 2 i e 2 o ψ r kt This is the linearized Boltzmann equation
14 Combine the linearized Boltzmann equation with the Poisson equation-each relating charge density in the volume element, dv, to the distance from the reference ion,r. In this equation all of the terms on the right hand of the previous equation are collected into the single variable, κ 2. Solve the equation by integrating from r=0 to r=. Next page 1 r 2 r r2 ( ψ dr ) = 1 ε o εkt 1 r 2 r r2 ( ψ dr ) = κ 2 ψ r n i o z i 2 e o 2 ψ r kt
15 ψ r = z i e o 4πε o εr The Debye Length or κ -1 : The effective radius of the charge atmosphere surrounding the central ion. What parameters contribute to this effective radius: κ 2 = κ 2 = 1 ε o εkt e o 2 i o n i z 2 2 i e o i o n i z i 2 ε o εkt κ 2 = e o 2 N A o 2 n i z i ε o εkt i IonicStrength I = 1 2 n i z i 2 κ 2 = 2e o 2 N A I ε o εkt
16 ω-ionic strength Charge distribution as a function of distance from the central ion.
17 Implications for biomolecular interactions
18 Double stranded nucleic acids and counterion Condensation (vh, J&H-Ch. 3, Section 3.8) Nucleic acids are polyanions-therefore salts will interact with them in a more specialized manner than with garden variety proteins. These interactions are important both for the stability of the nucleic acid and its interactions with other biomolecules.
19 Treat double stranded DNA as a cylinder with regularly Spaced charges. What is the spacing of the charges? Helical rise (B-DNA)=0.34 nm 2 phosphate groups/base pair Average charge spacing=0.34nm/2=0.17nm Cations will, of course, associate with the phosphates of the Backbone. To what extent do cations associate with the Backbone? What is the effective charge on Double Stranded DNA?
20 Start with Coulomb s Law Consider all of the charges on the backbone: There are N charges and each charge j interacts with all other charges k along the backbone. N N e 2 r jk is the distance between the j=1 k j εr jk charges. Debye Hückel can be used to introduce the effect of cation Screening-use κ 8πe 2 κ = ( 100εk B T )1/2 I 1/2 This describes a diffuse conterion atmosphere around the helix.
21 Counterion Condensation Direct condensation of small ions on a polyelectrolyte: Gerald Manning Depends on the valence of the ion-z and b-the average spacing of the charges along the helical axis. ξ = e 2 (εbk B T) Where ξ is a dimensionless parameter. If ξ>1 condensation occurs.
22 Polyelectrolyte in water at 25 o C, ξ=0.71/b B-DNA b=0.17nm ξ=4.2 Cations condense onto DNA What is the extent of condensation? Or What fraction of the charge on DNA remains uncompensated? 1/Zξ=0.24 for DNA in aqueous Na + environment. 76% of the phosphate charges are compensated. Theory vs. experiment: Good agreement (NMR measurements of counterions)
23 Repercussions for nucleic acid stability and its interactions with other molecules.
Biochemistry 675, Lecture 8 Electrostatic Interactions
 Biochemistry 675, Lecture 8 Electrostatic Interactions Previous Classes Hydrophobic Effect Hydrogen Bonds Today: Electrostatic Interactions Reading: Handout:P.R. Bergethon & E.R. Simons, Biophysical Chemistry,
Biochemistry 675, Lecture 8 Electrostatic Interactions Previous Classes Hydrophobic Effect Hydrogen Bonds Today: Electrostatic Interactions Reading: Handout:P.R. Bergethon & E.R. Simons, Biophysical Chemistry,
8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology
 Assignment # 4 8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology Coulomb Interactions 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions scales as Q 2 E c.
Assignment # 4 8.592J HST.452J: Statistical Physics in Biology Coulomb Interactions 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions scales as Q 2 E c.
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Peter Debye and Electrochemistry
 Peter Debye and Electrochemistry A K Shukla and T Prem Kumar A K Shukla is Professor and Chairman, Solid State and Structural Chemistry Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests
Peter Debye and Electrochemistry A K Shukla and T Prem Kumar A K Shukla is Professor and Chairman, Solid State and Structural Chemistry Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
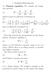 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
2 Structure. 2.1 Coulomb interactions
 2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
Module 8: "Stability of Colloids" Lecture 38: "" The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c )
 The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The Lecture Contains: Calculation for CCC (n c ) Relation between surface charge and electrostatic potential Extensions to DLVO theory file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture38/38_1.htm[6/16/2012
The change in free energy on transferring an ion from a medium of low dielectric constantε1 to one of high dielectric constant ε2:
 The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
The Born Energy of an Ion The free energy density of an electric field E arising from a charge is ½(ε 0 ε E 2 ) per unit volume Integrating the energy density of an ion over all of space = Born energy:
V = 2ze 2 n. . a. i=1
 IITS: Statistical Physics in Biology Assignment # 3 KU Leuven 5/29/2013 Coulomb Interactions & Polymers 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions
IITS: Statistical Physics in Biology Assignment # 3 KU Leuven 5/29/2013 Coulomb Interactions & Polymers 1. Flory Theory: The Coulomb energy of a ball of charge Q and dimension R in d spacial dimensions
Multimedia : Boundary Lubrication Podcast, Briscoe, et al. Nature , ( )
 3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
3.05 Nanomechanics of Materials and Biomaterials Thursday 04/05/07 Prof. C. Ortiz, MITDMSE I LECTURE 14: TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE LAYER (EDL) Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #11 : INTRODUCTION TO TE ELECTRICAL DOUBLE
Solvation and Macromolecular Structure. The structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules are strongly influenced by water:
 Overview Solvation and Macromolecular Structure The structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules are strongly influenced by water: Electrostatic effects: charges are screened by water molecules
Overview Solvation and Macromolecular Structure The structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules are strongly influenced by water: Electrostatic effects: charges are screened by water molecules
Chapter 11 section 6 and Chapter 8 Sections 1-4 from Atkins
 Lecture Announce: Chapter 11 section 6 and Chapter 8 Sections 1-4 from Atkins Outline: osmotic pressure electrolyte solutions phase diagrams of mixtures Gibbs phase rule liquid-vapor distillation azeotropes
Lecture Announce: Chapter 11 section 6 and Chapter 8 Sections 1-4 from Atkins Outline: osmotic pressure electrolyte solutions phase diagrams of mixtures Gibbs phase rule liquid-vapor distillation azeotropes
Continuum Electrostatics for Ionic Solutions with Nonuniform Ionic Sizes
 Continuum Electrostatics for Ionic Solutions with Nonuniform Ionic Sizes Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) University of California, San Diego, USA Supported
Continuum Electrostatics for Ionic Solutions with Nonuniform Ionic Sizes Bo Li Department of Mathematics and Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) University of California, San Diego, USA Supported
Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 044903 2005 Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte Zhi-Jie Tan and Shi-Jie Chen a) Department of Physics and
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 044903 2005 Electrostatic correlations and fluctuations for ion binding to a finite length polyelectrolyte Zhi-Jie Tan and Shi-Jie Chen a) Department of Physics and
1044 Lecture #14 of 18
 Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Lecture #14 of 18 1044 1045 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 13 main concepts: Section 1.2.3: Diffuse double layer structure Sections 13.1 & 13.2: Gibbs adsorption isotherm; Electrocapillary
Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia
 University of Groningen Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Peptide folding in non-aqueous environments investigated with molecular dynamics simulations Soto Becerra, Patricia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
Electrostatic Interactions in Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Biomolecules: Bulk Structures and Induced Surface Pattern Formation
 Electrostatic Interactions in Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Biomolecules: Bulk Structures and Induced Surface Pattern Formation Monica Olvera de la Cruz F. J. Solis, P. Gonzalez- Mozuleos (theory) E.
Electrostatic Interactions in Mixtures of Cationic and Anionic Biomolecules: Bulk Structures and Induced Surface Pattern Formation Monica Olvera de la Cruz F. J. Solis, P. Gonzalez- Mozuleos (theory) E.
Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1
 Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 06/04/2018 All living cells exhibit an electrical potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. This
Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 06/04/2018 All living cells exhibit an electrical potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. This
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics
 Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics Molecular surfaces The Hydrophobic Effect Electrostatics Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Electrostatic maps Electrostatic surfaces in MOE 15.1 The
Molecular Modeling -- Lecture 15 Surfaces and electrostatics Molecular surfaces The Hydrophobic Effect Electrostatics Poisson-Boltzmann Equation Electrostatic maps Electrostatic surfaces in MOE 15.1 The
Electrolyte Solutions
 Chapter 8 Electrolyte Solutions In the last few chapters of this book, we will deal with several specific types of chemical systems. The first one is solutions and equilibria involving electrolytes, which
Chapter 8 Electrolyte Solutions In the last few chapters of this book, we will deal with several specific types of chemical systems. The first one is solutions and equilibria involving electrolytes, which
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Electrical double layer
 Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Electrical double layer Márta Berka és István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://dragon.unideb.hu/~kolloid/ 7. lecture Adsorption of strong electrolytes from
Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions
 Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/ 1 Water as
Lectures 11-13: Electrostatics of Salty Solutions Lecturer: Brigita Urbanc Office: 1-909 (E-mail: brigita@drexel.edu) Course website: www.physics.drexel.edu/~brigita/courses/biophys_011-01/ 1 Water as
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
All-atom Molecular Mechanics. Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE /27/2010
 All-atom Molecular Mechanics Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE 535 09/27/2010 Outline Molecular models Molecular mechanics Force Fields Potential energy function functional form parameters and parameterization
All-atom Molecular Mechanics Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE 535 09/27/2010 Outline Molecular models Molecular mechanics Force Fields Potential energy function functional form parameters and parameterization
Molecule Matters van der Waals Molecules
 Molecule Matters van der Waals Molecules 3. Rg HF Complexes are Debye Molecules! E Arunan In this article, Debye s contributions to understanding van der Waals attractive forces, specifically, dipole induced
Molecule Matters van der Waals Molecules 3. Rg HF Complexes are Debye Molecules! E Arunan In this article, Debye s contributions to understanding van der Waals attractive forces, specifically, dipole induced
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications History of Nanotechnology: Time Line Democritus in ancient Greece: concept of atom 1900 : Rutherford : discovery of atomic nucleus The first TEM was
Chapter 3. Crystal Binding
 Chapter 3. Crystal Binding Energy of a crystal and crystal binding Cohesive energy of Molecular crystals Ionic crystals Metallic crystals Elasticity What causes matter to exist in three different forms?
Chapter 3. Crystal Binding Energy of a crystal and crystal binding Cohesive energy of Molecular crystals Ionic crystals Metallic crystals Elasticity What causes matter to exist in three different forms?
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry
 Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lecture No. 4 Date :25/10 /2012 Dr. Mohammed Hamed --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lecture No. 4 Date :25/10 /2012 Dr. Mohammed Hamed --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany
 Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Research Statement. Shenggao Zhou. November 3, 2014
 Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
Shenggao Zhou November 3, My research focuses on: () Scientific computing and numerical analysis (numerical PDEs, numerical optimization, computational fluid dynamics, and level-set method for interface
MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES
 - 1 - MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES Summary of Fundamental Molecular Interactions Q1Q Ion-Ion U ( r) = 4 r πεε o µ Q cosθ U ( r) = 4πεε o r µ 1µ U ( r) 3 r µ 1 µ U ( r) 6 r µ 1 α U ( r) 6 r Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole
- 1 - MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS NOTES Summary of Fundamental Molecular Interactions Q1Q Ion-Ion U ( r) = 4 r πεε o µ Q cosθ U ( r) = 4πεε o r µ 1µ U ( r) 3 r µ 1 µ U ( r) 6 r µ 1 α U ( r) 6 r Ion-Dipole Dipole-Dipole
Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[
![Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[ Electrolytes. Chapter Basics = = 131 2[ ]. (c) From both of the above = = 120 8[](/thumbs/83/88791608.jpg) Chapter 1 Electrolytes 1.1 Basics Here we consider species that dissociate into positively and negatively charged species in solution. 1. Consider: 1 H (g) + 1 Cl (g) + ()+ () = { } = (+ )+ ( ) = 167[
Chapter 1 Electrolytes 1.1 Basics Here we consider species that dissociate into positively and negatively charged species in solution. 1. Consider: 1 H (g) + 1 Cl (g) + ()+ () = { } = (+ )+ ( ) = 167[
The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 263 (2003) 156 161 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcis The effect of surface dipoles and of the field generated by a polarization gradient on the repulsive force Haohao
INTRODUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHODS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN
 INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:18 No:03 1 Analytical Derivation of Diffusio-osmosis Electric Potential and Velocity Distribution of an Electrolyte in a Fine Capillary
Aqueous solutions. Solubility of different compounds in water
 Aqueous solutions Solubility of different compounds in water The dissolution of molecules into water (in any solvent actually) causes a volume change of the solution; the size of this volume change is
Aqueous solutions Solubility of different compounds in water The dissolution of molecules into water (in any solvent actually) causes a volume change of the solution; the size of this volume change is
Activities and Activity Coefficients
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 017 Activities and Activity Coefficients We now finish answering the question we asked during our last lecture, what is the form of the chemical potential i (T,P,x i )
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry Fall 017 Activities and Activity Coefficients We now finish answering the question we asked during our last lecture, what is the form of the chemical potential i (T,P,x i )
Chem 321 Lecture 11 - Chemical Activities 10/3/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 11 - Chemical Activities 10/3/13 One of the assumptions that has been made in equilibrium calculations thus far has been to equate K to a ratio of concentrations.
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 11 - Chemical Activities 10/3/13 One of the assumptions that has been made in equilibrium calculations thus far has been to equate K to a ratio of concentrations.
Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte. M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Classical Models of the Interface between an Electrode and Electrolyte M.Sc. Ekaterina Gongadze Faculty of Informatics and Electrical Engineering Comsol Conference
Molecular Forces in Biological Systems - Electrostatic Interactions; - Shielding of charged objects in solution
 Molecular Forces in Biological Systems - Electrostatic Interactions; - Shielding of charged objects in solution Electrostatic self-energy, effects of size and dielectric constant q q r r ε ε 1 ε 2? δq
Molecular Forces in Biological Systems - Electrostatic Interactions; - Shielding of charged objects in solution Electrostatic self-energy, effects of size and dielectric constant q q r r ε ε 1 ε 2? δq
Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Boston Dependence of Potential and Ion Distribution on Electrokinetic Radius in Infinite and Finite-length Nano-channels Jarrod Schiffbauer *,1, Josh Fernandez 2,
Charged Polymers. Introduction and Terminology:
 Introduction and Terminology: Charged Polymers Charged polymers are common in both nature and technology, often in solutions, gels, or swellable solids. Such polymers contain ionizable units that, according
Introduction and Terminology: Charged Polymers Charged polymers are common in both nature and technology, often in solutions, gels, or swellable solids. Such polymers contain ionizable units that, according
Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules
 Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules E.Allahyarov 1,2, H.Löwen 1 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik II, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, D-4225 Düsseldorf, Germany 2 Institute for
Effective interaction between helical bio-molecules E.Allahyarov 1,2, H.Löwen 1 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik II, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, D-4225 Düsseldorf, Germany 2 Institute for
Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards
 Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards One Hundred Years of Electrified Interfaces: The Poisson-Boltzmann theory and some recent developments
Soft Matter - Theoretical and Industrial Challenges Celebrating the Pioneering Work of Sir Sam Edwards One Hundred Years of Electrified Interfaces: The Poisson-Boltzmann theory and some recent developments
Lecture: P1_Wk1_L1 IntraMolecular Interactions. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012
 Lecture: IntraMolecular Interactions Distinguish between IntraMolecular (within a molecule) and InterMolecular (between molecules) Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012 1
Lecture: IntraMolecular Interactions Distinguish between IntraMolecular (within a molecule) and InterMolecular (between molecules) Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University 2012 1
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms. How to make a mineral from the start of atoms?
 Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties
 Biophysical Journal Volume 78 February 2000 699 706 699 Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties Chandra N. Patra and Arun Yethiraj Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 78 February 2000 699 706 699 Density Functional Theory for the Nonspecific Binding of Salt to Polyelectrolytes: Thermodynamic Properties Chandra N. Patra and Arun Yethiraj Department
Fundamental Principles to Tutorials. Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution. Giuseppe Milano
 III Advanced School on Biomolecular Simulation: Fundamental Principles to Tutorials Multiscale Methods from Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution Giuseppe Milano Reference Rob Phillips,
III Advanced School on Biomolecular Simulation: Fundamental Principles to Tutorials Multiscale Methods from Lecture 3: Introduction to Electrostatics in Salty Solution Giuseppe Milano Reference Rob Phillips,
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS
 Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Stability of colloidal systems
 Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Stability of colloidal systems Colloidal stability DLVO theory Electric double layer in colloidal systems Processes to induce charges at surfaces Key parameters for electric forces (ζ-potential, Debye
Rama Abbady. Zina Smadi. Diala Abu-Hassan
 1 Rama Abbady Zina Smadi Diala Abu-Hassan (00:00) (10:00) Types of Molecules in the Cell 1. Water Molecules: a large portion of the cell mass is water (70% of total cell mass). 2. Organic molecules (carbon
1 Rama Abbady Zina Smadi Diala Abu-Hassan (00:00) (10:00) Types of Molecules in the Cell 1. Water Molecules: a large portion of the cell mass is water (70% of total cell mass). 2. Organic molecules (carbon
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles. Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles
 Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
C deposits (63.5/2) g of copper; the quantity passed is therefore
 7. SOLUTIONS OF ELECTROLYTES n Faraday s Laws, Molar Conductivity, and Weak Electrolytes 7.1. 96 500 C deposits (63.5/2) g of copper; the quantity passed is therefore 96 500 0.04 2 63.5 C The current was
7. SOLUTIONS OF ELECTROLYTES n Faraday s Laws, Molar Conductivity, and Weak Electrolytes 7.1. 96 500 C deposits (63.5/2) g of copper; the quantity passed is therefore 96 500 0.04 2 63.5 C The current was
Complicated, short range. þq 1 Q 2 /4p3 0 r (Coulomb energy) Q 2 u 2 /6(4p3 0 ) 2 ktr 4. u 2 1 u2 2 =3ð4p3 0Þ 2 ktr 6 ðkeesom energyþ
 Bonding ¼ Type of interaction Interaction energy w(r) Covalent, metallic Complicated, short range Charge charge þq 1 Q 2 /4p3 0 r (Coulomb energy) Charge dipole Qu cos q/4p3 0 r 2 Q 2 u 2 /6(4p3 0 ) 2
Bonding ¼ Type of interaction Interaction energy w(r) Covalent, metallic Complicated, short range Charge charge þq 1 Q 2 /4p3 0 r (Coulomb energy) Charge dipole Qu cos q/4p3 0 r 2 Q 2 u 2 /6(4p3 0 ) 2
(Electrostatics in Biology)
 Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 (Electrostatics
Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 (Electrostatics
(name) Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant. Final Exam
 10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications
 Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
Electrochemical Properties of Materials for Electrical Energy Storage Applications Lecture Note 3 October 11, 2013 Kwang Kim Yonsei Univ., KOREA kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 Y 88.91 8 O 16.00 7 N 14.01 34 Se
Biochemistry 530: Introduction to Structural Biology. Autumn Quarter 2014 BIOC 530
 Biochemistry 530: Introduction to Structural Biology Autumn Quarter 2014 Course Information Course Description Graduate-level discussion of the structure, function, and chemistry of proteins and nucleic
Biochemistry 530: Introduction to Structural Biology Autumn Quarter 2014 Course Information Course Description Graduate-level discussion of the structure, function, and chemistry of proteins and nucleic
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores. Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory
 Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores Ulrich F. Keyser Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory Acknowledgements Delft Cees Dekker, Nynke H. Dekker, Serge G. Lemay R. Smeets,
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores Ulrich F. Keyser Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory Acknowledgements Delft Cees Dekker, Nynke H. Dekker, Serge G. Lemay R. Smeets,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016](/thumbs/76/73264929.jpg) Polyelectrolyte Polypeptide Scaling Laws Via Mechanical and Dielectric Relaxation Measurements Jorge Monreal University of South Florida arxiv:1609.05358v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 Dated: March 1, 2018
Polyelectrolyte Polypeptide Scaling Laws Via Mechanical and Dielectric Relaxation Measurements Jorge Monreal University of South Florida arxiv:1609.05358v1 [cond-mat.soft] 17 Sep 2016 Dated: March 1, 2018
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
BIOC 530 Fall, 2011 BIOC 530
 Fall, 2011 Course Information Course Description Graduate-level discussion of the structure, function, and chemistry of proteins and nucleic acids, control of enzymatic reactions. Please see the course
Fall, 2011 Course Information Course Description Graduate-level discussion of the structure, function, and chemistry of proteins and nucleic acids, control of enzymatic reactions. Please see the course
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics
 II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
Contents. 2. Fluids. 1. Introduction
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces)
 Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces) 1: Debye layer, Zeta potential, Electrokinetics 2: Electrophoresis, Electroosmosis 3: Dielectrophoresis 4: InterDebye layer force, VanDer Waals
Key Concepts for section IV (Electrokinetics and Forces) 1: Debye layer, Zeta potential, Electrokinetics 2: Electrophoresis, Electroosmosis 3: Dielectrophoresis 4: InterDebye layer force, VanDer Waals
A More Detailed Look at Chemical Equilibria
 A More Detailed Look at Chemical Equilibria effect of ionic strength on solubility calculation of ionic strength activity coefficients effect of ionic strength and size/charge of ions on activity coefficients
A More Detailed Look at Chemical Equilibria effect of ionic strength on solubility calculation of ionic strength activity coefficients effect of ionic strength and size/charge of ions on activity coefficients
957 Lecture #13 of 18
 Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Lecture #13 of 18 957 958 Q: What was in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction
Soft Matter and Biological Physics
 Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
3. Solutions W = N!/(N A!N B!) (3.1) Using Stirling s approximation ln(n!) = NlnN N: ΔS mix = k (N A lnn + N B lnn N A lnn A N B lnn B ) (3.
 3. Solutions Many biological processes occur between molecules in aqueous solution. In addition, many protein and nucleic acid molecules adopt three-dimensional structure ( fold ) in aqueous solution.
3. Solutions Many biological processes occur between molecules in aqueous solution. In addition, many protein and nucleic acid molecules adopt three-dimensional structure ( fold ) in aqueous solution.
PH 202-1E Fall Electric Forces and Electric Fields. Lectures 1-4. Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition)
 PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
Material Properties & Characterization - Surfaces
 1) XPS Spectrum analysis: The figure below shows an XPS spectrum measured on the surface of a clean insoluble homo-polyether. Using the formulas and tables in this document, answer the following questions:
1) XPS Spectrum analysis: The figure below shows an XPS spectrum measured on the surface of a clean insoluble homo-polyether. Using the formulas and tables in this document, answer the following questions:
 Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 14: Redox reactions
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 14: Redox reactions Marc R. Roussel February 8, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 14: Redox reactions February 8, 2018 1 / 12 Review: Oxidation states The oxidation state
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 14: Redox reactions Marc R. Roussel February 8, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 14: Redox reactions February 8, 2018 1 / 12 Review: Oxidation states The oxidation state
Colloid Chemistry. La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross.
 Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Colloid Chemistry La chimica moderna e la sua comunicazione Silvia Gross Istituto Dipartimento di Scienze di e Scienze Tecnologie Chimiche Molecolari ISTM-CNR, Università Università degli Studi degli Studi
Supporting Information. The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction. between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation.
 Supporting Information The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation study Lili Sun 1, Marcin Tabaka 1, Sen Hou 1, Lin Li 2, Krzysztof Burdzy
Supporting Information The hinge region strengthens the nonspecific interaction between lac-repressor and DNA: a computer simulation study Lili Sun 1, Marcin Tabaka 1, Sen Hou 1, Lin Li 2, Krzysztof Burdzy
*blood and bones contain colloids. *milk is a good example of a colloidal dispersion.
 Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Mean-Field Description of Ionic Size Effects
 Mean-Field Description of Ionic Size Effects Bo Li Department of Mathematics and NSF Center for Theoretical Biological Physics University of California, San Diego Work Supported by NSF, NIH, CSC, CTBP
Mean-Field Description of Ionic Size Effects Bo Li Department of Mathematics and NSF Center for Theoretical Biological Physics University of California, San Diego Work Supported by NSF, NIH, CSC, CTBP
Electrostatic Interactions of Peptides with Lipid Membranes: Competitive Binding between Cationic Peptides and Divalent Counterions
 Electrostatic Interactions of Peptides with Lipid Membranes: Competitive Binding between Cationic Peptides and Divalent Counterions by Roham Rahnamaye Farzami A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo
Electrostatic Interactions of Peptides with Lipid Membranes: Competitive Binding between Cationic Peptides and Divalent Counterions by Roham Rahnamaye Farzami A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo
Chapter 10 Effect of Electrolytes on Chemical Equilibria
 Chapter 10 Effect of Electrolytes on Chemical Equilibria The equilibrium constants for chemical reactions should be written in terms of the activities of the participating species. The activity of a species
Chapter 10 Effect of Electrolytes on Chemical Equilibria The equilibrium constants for chemical reactions should be written in terms of the activities of the participating species. The activity of a species
Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III
 NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
NPTEL Chemical Engineering Interfacial Engineering Module 3: Lecture 4 Electrostatic Double Layer Force: Part III Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati
EXAM I COURSE TFY4310 MOLECULAR BIOPHYSICS December Suggested resolution
 page 1 of 7 EXAM I COURSE TFY4310 MOLECULAR BIOPHYSICS December 2013 Suggested resolution Exercise 1. [total: 25 p] a) [t: 5 p] Describe the bonding [1.5 p] and the molecular orbitals [1.5 p] of the ethylene
page 1 of 7 EXAM I COURSE TFY4310 MOLECULAR BIOPHYSICS December 2013 Suggested resolution Exercise 1. [total: 25 p] a) [t: 5 p] Describe the bonding [1.5 p] and the molecular orbitals [1.5 p] of the ethylene
690 Lecture #10 of 18
 Lecture #10 of 18 690 691 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapters 4 & 5 main concepts: Section 4.4.2: Section 5.1: Section 5.2: Section 5.3 & 5.9: Fick s Second Law of Diffusion Overview of
Lecture #10 of 18 690 691 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapters 4 & 5 main concepts: Section 4.4.2: Section 5.1: Section 5.2: Section 5.3 & 5.9: Fick s Second Law of Diffusion Overview of
Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents
 Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents Laurent Helden Jules Mikhael. Physikalisches Institut Universität Stuttgart Model system for hard core interactions accessible fortirm-measurements.
Depletion forces induced by spherical depletion agents Laurent Helden Jules Mikhael. Physikalisches Institut Universität Stuttgart Model system for hard core interactions accessible fortirm-measurements.
Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces
 5042 J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5042-5057 Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces Itamar Borukhov, David Andelman,*, and Henri Orland School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and
5042 J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 5042-5057 Effect of Polyelectrolyte Adsorption on Intercolloidal Forces Itamar Borukhov, David Andelman,*, and Henri Orland School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and
Biophysics II. Hydrophobic Bio-molecules. Key points to be covered. Molecular Interactions in Bio-molecular Structures - van der Waals Interaction
 Biophysics II Key points to be covered By A/Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Biophysics & Micro/nanostructures Lab Department of Physics, NUS 1. van der Waals Interaction 2. Hydrogen bond 3. Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic
Biophysics II Key points to be covered By A/Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Biophysics & Micro/nanostructures Lab Department of Physics, NUS 1. van der Waals Interaction 2. Hydrogen bond 3. Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic
Molecular Simulation III
 Molecular Simulation III Quantum Chemistry Classical Mechanics E = Ψ H Ψ ΨΨ U = E bond +E angle +E torsion +E non-bond Molecular Dynamics Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center
Molecular Simulation III Quantum Chemistry Classical Mechanics E = Ψ H Ψ ΨΨ U = E bond +E angle +E torsion +E non-bond Molecular Dynamics Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.bm] 6 Apr 2016](/thumbs/88/115645706.jpg) Multi-shell model of ion-induced nucleic acid condensation Igor S. Tolokh Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA Aleksander Drozdetski Department of Physics, Virginia
Multi-shell model of ion-induced nucleic acid condensation Igor S. Tolokh Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA Aleksander Drozdetski Department of Physics, Virginia
Atoms & Their Interactions
 Lecture 2 Atoms & Their Interactions Si: the heart of electronic materials Intel, 300mm Si wafer, 200 μm thick and 48-core CPU ( cloud computing on a chip ) Twin Creeks Technologies, San Jose, Si wafer,
Lecture 2 Atoms & Their Interactions Si: the heart of electronic materials Intel, 300mm Si wafer, 200 μm thick and 48-core CPU ( cloud computing on a chip ) Twin Creeks Technologies, San Jose, Si wafer,
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7 Forms of Carbon Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter The kinetic-molecular theory
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7 Forms of Carbon Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter The kinetic-molecular theory
Dynamical simulations of DNA supercoiling and compression
 554 Biochemical Society Transactions (2013) Volume 41, part 2 Dynamical simulations of DNA supercoiling and compression David Swigon* 1, Sookkyung Lim and Yongsam Kim *Department of Mathematics, University
554 Biochemical Society Transactions (2013) Volume 41, part 2 Dynamical simulations of DNA supercoiling and compression David Swigon* 1, Sookkyung Lim and Yongsam Kim *Department of Mathematics, University
We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
Atoms, electrons and Solids
 Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Atoms, electrons and Solids Shell model of an atom negative electron orbiting a positive nucleus QM tells that to minimize total energy the electrons fill up shells. Each orbit in a shell has a specific
Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together.
 Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Basics of Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Properties of substances are largely dependent on the bonds holding the material together. Basics of Bonding A chemical bond occurs when atoms or
Roles of Boundary Conditions in DNA Simulations: Analysis of Ion Distributions with the Finite-Difference Poisson-Boltzmann Method
 554 Biophysical Journal Volume 97 July 2009 554 562 Roles of Boundary Conditions in DNA Simulations: Analysis of Ion Distributions with the Finite-Difference Poisson-Boltzmann Method Xiang Ye, Qin Cai,
554 Biophysical Journal Volume 97 July 2009 554 562 Roles of Boundary Conditions in DNA Simulations: Analysis of Ion Distributions with the Finite-Difference Poisson-Boltzmann Method Xiang Ye, Qin Cai,
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
