Chem 345 Reaction List: Chem 343 Reactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes).
|
|
|
- Leon Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). uc - optically active LG 2 optically active uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to leaving group) must be unhindered. Alpha carbon inverted in the reaction. Leaving group must be good (conjugate pka less than or equal to 0) Good LG's: I -, Br -, Ts -, etc... More hindered the alpha carbon or the more basic the nucleophile, the more likely that E2 outcompetes 2. uc - optically active LG 1 racemic uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to leaving group) must be tertiary or secondary. Primary alpha carbons can undergo 1 if a resonance stabilized carbocation is involved. Alpha carbon scrambled in the reaction. Leaving group must be good (conjugate pka less than or equal to 0) Good LG's: I -, Br -, Ts -, etc... Can undergo rearrangements to give a more stable carbocation.
2 Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 2 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). 2 4 optically active LG E1 Alpha carbon (carbon attached to leaving group) must be tertiary or secondary. Primary alpha carbons can undergo 1 if a resonance stabilized carbocation is involved. The most substituted alkene is the major product (aitzev's rule) on-nucleophilic acids like sulfuric acid work best Alcohols are commonly used as leaving groups as sulfuric acid can protonate them to turn them into good leaving groups. Base LG optically active E2 T The strength of the base necessary is dependent on the hindrance of the alpha carbon due to competition from the 2 reaction. Tertiary alpha carbons (no competition with 2): a moderate base (conj. pka 10) can be used econdary alpha carbons: a strong base (conj. pka 15 or higher necessary) Primary alpha carbons: a strong, bulky base such as KtBu necessary. Major product dependent on base used. mall base->more substituted alkene. Bulky base (KtBu)->less substituted alkene. Leaving group and beta hydrogen must be anticoplanar. Leaving group must be good (conjugate pka less than or equal to 0) Good LG's: I -, Br -, Ts -, etc... 's cannot be eliminated by an E2 mechanism.
3 Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 3 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). PCC C 2 2 secondary alcohol becomes ketone. 343 reaction) (Primary alcohol becomes aldehyde PBr 3 Br (Works for methyl, primary, and secondary alcohols via 2 reaction. Does not react with tertiary alcohols. 343 reaction) or 2 Cr 4 2 (econdary alcohols are converted into ketones) 343 eaction
4 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam I eactions: Page 4 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). cat. 2 4 Acid catalyst should be a strong one like Ts, 2 4, or. cat Acid catalyst should be a strong one like Ts, 2 4, or. cat Acid catalyst can be a weak acid like Ac. group ends up cis to the smaller substituent on the aldehyde or ketone. 2 cat. a C cat Acid technically not needed for imine cleavage C KC C Ac acid or base acid or base emiacetals are mechanistic intermediates only. Very few are stable enough to be synthetic products.
5 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam I eactions: Page 5 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). MgBr 3 + Li 3 + rganolithiums behave just like Grignards ab 4 Et ab 4 Et 2 cat. Ac ab 3 C eductive amination C cat. a About any base capable of pulling a proton off an can be used. (conj. pka 10 or more) KC 4 C 2
6 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam I eactions: Page 6 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). PPh 3 (Just an 2 eaction) Br PPh 3 Base PPh 3 PPh 3 Wittig eagent (Base needs to be strong like KtBu, a, a 2, or BuLi) PPh 3 onstabilized Wittig onstabilized Wittigs typically give Z tabilized Wittigs typically give E PPh 3 tabilized Wittig onstabilized Wittigs typically give Z tabilized Wittigs typically give E X Mg MgX (X can be I, Br, or ) X 2.0 eq. Li Li (X can be I, Br, or ) (LiX is byproduct) It is okay if you do not mention 2.0 eq. X BuLi Li Lithium alogen Exchange (Don't make BuLi this way)
7 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 7 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). Br (This works when is methyl or primary sp 3 carbon). 2 reaction cat. 2 4 (Fisher esterification: This works for methyl, primary, or secondary alcohols but not tertiary alcohols) a cat. 2 4 or cat. a cat. 2 4 Works for tertiary esters (carbonyl oxygen bond remains intact) 2 2 Et 3 Et 3
8 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 8 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). DCC Et /Pd /Pd
9 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 9 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). Boc 2 Et 3 Boc Fmoc 2 Et 3 Fmoc Z 2 Et 3 Z cat a
10 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 10 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). MgBr 3 + Me Li 3 + Me excess MgBr + excess Li 3 + LiAl C 2 excess MgBr 3 + C 2 excess Li 3 +
11 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 11 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). LiAl LiAl LiAl LiAl Li 3 + MgBr
12 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam II eactions: Page 12 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). The mechanisms of these reactions are fair game for exam III. eactions on this page only work on ketones and aldehydes ' Baeyer-Villiger mcpba ' Migration rder: >3 C>2 >1 C>Me mcpba mcpba ' Beckmann 2 oxime Migration rder: Whichever group is opposite the migrates so 3 C>2 >1 C>Me> ' Ts, Et 3 Ts ' Δ 2 ' 1.) 2, 2.) Ts, Et 3 3.) Δ, 2 1.) 2, 2.) Ts, Et 3 3.) Δ, 2 Δ 2, 2 4, 2 eaction can also be done in a single step.
13 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 13 D excess D D D excess D D D D Al 3 (eaction does not work when the ring is strongly deactivated) It can work with halobenzenes, but not anything more deactivated) 2 Br 2 Br Al 3 FeBr Δ useful way to make ortho substituted benzene rings
14 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 14 Al 3 excess ave to use large excess, otherwise multiple alkylations occur. is an alkyl group (sp 3 C). ot a particularly clean reaction as rearrangements occur quite frequently as well. emmenson eduction Zng Ph Wolff-Kishner eduction K 2 2 Δ Ph educes ketones and aldehydes Vilsmeier-aack eaction P 3 2 DMF DMF= (eaction does not work when the ring is strongly deactivated) It can work with halobenzenes, but not anything more deactivated)
15 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 15 andmeyer equence: 2 /Pd/C 2 2 a 2, Br CuBr Br Br When using CuBr or Cu, the acid used in the first step should match. a 2, Cu CuC 2 3 P C 2 Cu 2 2 KI I
16 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 16 Electrophilic Aromatic ubstitution: Approximate eactivity X C > > > > > ~ > > > > =alkyl, aryl If isn't a carbonyl group, the can be protonated in strongly acidic media (changing the nature of the group) Activating X=F,, Br, I Deactivating X C > > > > > ~ > > > > =alkyl, aryl ortho para directors para typically favored X=F,, Br, I meta directors
17 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 17 ucleophilic aromatic substitution 2 2 aet Et If the ring is benzene, then a nitro group has to be present in the ortho or para position to the leaving group. The ring can be a heterocycle as well. Especially if there is a present in the ring and there is a pi bond to it. For example: If the ring is a pyridine ring, the leaving group is in the 2,4,or 6 position. ucleophiles can be primary or secondary amines, hydroxide, etc... If ydroxide is the nucleophile, and acid workup step is needed o detectable reaction
18 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 18 2 a 2 3 via benzyne 2 a
19 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam III eactions: Page 19 You do not have to memorize the uzuki/eck mechanisms. You do need to understand what is happening in the main steps and identify them. uzuki eaction Pd Base X B X can be Br or I Base can be a, a 2 C 3, ame, Et 3, etc... Li B(Me) 3 TF or Et B Boronic acids can react with a lot of reagents, so it is best to use it right away in a uzuki reaction and not carry it through a bunch of steps. eck eaction Pd Base X can be Br or I X Works best with monosubstituted alkenes Base can be a, a 2 C 3, ame, Et 3, etc... Product is often the E (trans) alkene Grubbs ing osing Metathesis PCy u PCy 3 C In the mechanism, the Grubbs Catalyst can be abbreviated as: u C 2 The mechanism is akin to the Wittig mechanism, but all of the steps are reversible.
20 Chem 345 Exam IV eaction List Page 20 2 Br 2, a Br 2, a' ' ' ofmann earrangement via isocyanate Br 2 ame Me C 2 Me a 3 Δ Curtius earrangement C isocyanate C 2 2 via Carbamic Acid (Very unstable) C Carbamate ester Also known as urethane C 2 Urea
21 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 21 Aldol reactions are tricky due to multiple products depending on time, temperature, and exact reagent/solvent. They can also depend on how much of each starting material. Aldol reactions can be acid or base catalyzed. In a synthetic laboratory setting, base catalyzed reactions are far more prevalent than acid catalyzed aldol reactions. The acid catalyzed reactions typically use complex Lewis Acids that I have not talked about. The following reactions are reliable enough to be used in synthesis type questions and predict the products. a (r other strong alkoxide base) If you want to stop at the 3-hydroxycarbonyl, you should use the LDA method. LDA Li LDA Li LDA steals the proton to give the less substituted enolate. Li 1.) 2.) 3 + You stop at the 3-hydroxycarbonyl Method works best if the electrophile is an aldehyde. K (r other strong alkoxide base) (You do not stop at the 1,3-hydroxycarbonyl) You can use this reaction, as long as an aldehyde and a ketone are used and the aldehyde does not have an enolizable proton K (r other strong 5 3 alkoxide base) 4 3 Intramolecular aldols are clean if a five or six-member ring can be formed. Aldehydes make better electophiles than ketones. It is helpful to start the numbering at the electrophile. 2
22 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 22 aisen reactions are base mediated only. There is not an acid version. Also, you need a full equivalent of base to get these to work. If you write cat. base, that will be counted wrong. In the case of the first reaction, a catalytic amount of alkoxide in alcohol will give the transesterification product. The following reactions are okay for you to use during synthesis and predict the products. The aisen product needs a proton on the carbon between the two carbonyls, otherwise the reaction will not work. If the final product contains an ester, than the base/solvent must match the end ester. Exceptions include the use of KtBu and tbu which are too hindered for transesterification. ydroxide or water cannot be used. aet 3 + Et Et cat. ame Et Et Et Me Me Crossed aisen or Mixed aisen condensations can be done using LDA or you can use an electrophile that does not have an enolizable proton. Li Et 3 + Et Et aet Et 3 + Et ere the base/solvent does not match, but it does not matter. aet 3 + Me Et ere the base/solvent does not match, but it does not matter aet Et Et
23 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 23 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. ame MeI Me Me Me Base must match ester or use KtBu, tbu or LDA and ether Instead of MeI, you can use any primary or methyl halide or tosylate. The conjugate acid of the anion has a pka of approximately 10, so secondary alkyl halides can be used, but the yield will be lower due to competition with elimination. Tertiary halides are too hindered and end up giving E2 products. KtBu EtI Me Me tbu Me Me For the second deprotonation, a nonnucleophilic base like KtBu in tbu or LDA in ether. If a nucleophilic base like a primary or secondary alkoxide could result in the reverse aisen reaction, and a lower yield. The alkyl halide could be a methyl, primary, or secondary halide/tosylate. a 3 + Δ Δ cat You can combine the three steps above in one step. Me Me dimethyl malonate 1.) ame, Me 2.) MeI 3.) KtBu, tbu 4.) EtI 5.) Δ cat. 2 4, 2 If you start with a malonic ester, then the product is a substituted carboxylic acid.
24 Chem 345 Exam IV eaction List Page 24 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. You do not need to know the mechanisms for the reactions in the rectangles. Mannich: cat. Ac 2 eed an aldehyde, primary or secondary amine, and a ketone. Cat. Ac is used to catalyze the imine formation. Knoevenagel Condensation: The nucleophile comes from a C 2 sandwiched between two electron withdrawing groups. Possible EWG's include C, 2, and Carbonyls.
25 Chem 345 Exam IV eaction List Page 25 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. You do not need to know the mechanisms for the reactions in the rectangles. LDA C 3 I Deprotonation occurs at the least hindered acidic proton. A primary halide can also be used. econdary and tertiary halides will give too much E2 products to be useful. 2.0 eq. LDA or 2.0 eq. a C 3 I You need two equivalents of a strong base, otherwise deprotonation stops at the middle proton. A primary halide can also be used. econdary and tertiary halides will give too much E2 products to be useful. 3 + LDA LDA LDA is strong enough to doubly deprotonate 1,3 dicarbonyls which can do 2 reactions The more reactive enolate reacts first. 1.0 eq. Br Me or primary halide Br Me, primary, or secondary halide
26 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 26 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. Michael eaction: 1,5 dicarbonyls are the product when a Michael acceptor is used as the electrophile. Though the carbonyl can compete as an electrophile, the major product is typically the addition to the alkene. Lecture Videos: Michael Breakdown, Michael eaction, obinson Annulation a (r other strong base) LDA 3 + LDA can be used to pull off the least hindered acidic proton. Common Michael Acceptors Me C Me Methyl vinyl ketone will often result in the obinson Annulation when an alkoxide is used as the base. Me K Et racemic
27 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 27 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. Umpolung reaction where an aldehyde carbon acts like a nucleophile. Unlike the dithiane reactions earlier, the steps in these mechanisms are all reversible. We should cover these on Wed. ov. 23. Lecture Videos: Umpolung Breakdown, Benzoin Condensation, tetter eaction Benzoin condensation KC Et You cannot have acid present, otherwise a cyanohydrin may form. For this reaction to work with cyanide, the aldehyde may not have an enolizable proton. Et 3 2-hydroxycarbonyl In the thiazolium catalyzed version, the aldehyde can have an enolizable proton. tetter eaction: If a Michael acceptor is present, then a 1,4-dicarbonyl is formed instead of the 2-hydroxycarbonyl. Et 3
28 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 28 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. You do not need to know the mechanisms for the reactions in the rectangles. We should cover these on Wed. ov. 23. Lecture Videos: Corey-eebach Dithiane Chemistry pka ~30 BuLi Acid base reaction Can undergo reactions like any organolithium Li Li 3 + racemic Li optically active 3 + optically active Li EtBr Unlike normal organolithiums, deprotonated dithianes can be nucleophiles in 2 reactions with methyl and primary halides. econdary halides give elimination products in large quantities. Tertiary halides only give E2 products. g 2 2 The dithiane can be thought as a protecting group that can be removed with g 2 and water. 2 aney i The dithiane can be replaced with two hydrogens by using 2 and aney ickel
29 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 29 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. We will hopefully cover these reactions on Wednesday. Their mechanisms are doable and not difficult, but I will not put them on this exam due to time. These reactions will not be on the exam. Lecture Videos: Enamine synthesis Enamine formation: eaction works best with secondary amines, but can work with primary amines and ammonia. Typically, secondary amines are used for the alkylation reactions below. Br should be sp 2 C
30 Chem 345 eaction List: Exam IV eactions: Page 30 You can use these reactions in predict the product type and synthesis questions. We covered cuprates on Monday, ov. 28. If they appear on Exam IV, it will be minor (four points at most). 2.0 eq. Li CuI 2 CuLi 2 CuLi 3 + Li Et EtBr racemic enolate intermediate can be alkylated by a primary or Me halide in an 2 reaction 2 CuLi Cuprates react with acid chlorides to give ketones or attack Michael acceptors to give enolates, which can be protonated.
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
ANSWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 249H
 AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
Loudon Chapter 19 Review: Aldehydes and Ketones CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Chem 263 March 7, 2006
 Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Amines. Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality. primary secondary tertiary quaternary
 Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
R N R N R N. primary secondary tertiary
 Chapter 19 Amines omenclature o assification of amines Amines are classified as 1, 2, or 3 based on how many R groups are attached to the nitrogen R R R R R R primary secondary tertiary When there are
Chapter 19 Amines omenclature o assification of amines Amines are classified as 1, 2, or 3 based on how many R groups are attached to the nitrogen R R R R R R primary secondary tertiary When there are
Structure and Reactivity: Prerequired Knowledge
 Structure and eactivity: Prerequired Knowledge!!! The concepts presented in this summary are required for lecture and examination!!! 1. Important Principles in rganic Chemistry In general, structures which
Structure and eactivity: Prerequired Knowledge!!! The concepts presented in this summary are required for lecture and examination!!! 1. Important Principles in rganic Chemistry In general, structures which
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis]
![Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Lecture 13A 05/11/12. Amines. [Sn2; Hofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis]](/thumbs/86/93838793.jpg) Lecture 13A 05/11/12 Amines [Sn2; ofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Curtius and ofmann rearrangements Both of these, in principle,
Lecture 13A 05/11/12 Amines [Sn2; ofmann elimination; reduction of alkyl azides, amides, nitriles, imines; reductive amination; Gabriel synthesis] Curtius and ofmann rearrangements Both of these, in principle,
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Amines Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Amines: structure and nomenclature
 Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Topic 4 Aldehydes and Ketones
 4-1 Topic 4 Aldehydes and Ketones 16.1 4-2 Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehyde ketone The polarized oxygen-carbon -bond renders aldehydes and ketones electrophilic: ' The electrophilicity of the oxygen-carbon
4-1 Topic 4 Aldehydes and Ketones 16.1 4-2 Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehyde ketone The polarized oxygen-carbon -bond renders aldehydes and ketones electrophilic: ' The electrophilicity of the oxygen-carbon
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Chem 263 Nov 3, 2016
 hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 36 Synthesis of Amines
 Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
Organocopper Reagents
 rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Alcohols: Contain a hydroxy group( OH) bonded to an sp 2 or sp 3 hybridized
 Lecture Notes hem 51B S. King hapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides I. Introduction Alcohols, ether, and epoxides are 3 functional groups that contain σ-bonds. Alcohols: ontain a hydroxy group( ) bonded
Lecture Notes hem 51B S. King hapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides I. Introduction Alcohols, ether, and epoxides are 3 functional groups that contain σ-bonds. Alcohols: ontain a hydroxy group( ) bonded
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. 1. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
 hapter 15 eactions of Aromatic ompounds 1. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution eactions v verall reaction reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis hang opyright S 3 2 S 4 S 3 2. A General Mechanism
hapter 15 eactions of Aromatic ompounds 1. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution eactions v verall reaction reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis hang opyright S 3 2 S 4 S 3 2. A General Mechanism
Chapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution
 hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
Chemistry Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers
 Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 12. Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation-Reduction & Organometallic Compounds. Structure
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
Carbonyl Chemistry. aldehydes ketones. carboxylic acid and derivatives. Wednesday, April 29, 2009
 Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Key ideas: In EAS, pi bond is Nu and undergoes addition.
 Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 13 Reactions of Arenes Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 . 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
. 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH. 22- REACTIONS OF BENZENE AND ITS DERIVATIVES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION GENERAL MECHANISM Benzene reacts with very few reagents. It DOES NOT undergo typical addition reactions. Why? If we can get benzene to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION GENERAL MECHANISM Benzene reacts with very few reagents. It DOES NOT undergo typical addition reactions. Why? If we can get benzene to
EWG EWG EWG EDG EDG EDG
 Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Chem 263 Nov 24, Properties of Carboxylic Acids
 Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi 1 Recall the electophilic addition of HBr (or Br2) to alkenes H + nu cleophile H Br H
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Dr. Mishu Singh Department of chemistry Maharana Pratap Govt.P.G.College Hardoi 1 Recall the electophilic addition of HBr (or Br2) to alkenes H + nu cleophile H Br H
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/22/2018
 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
Chem 263 Nov 7, elimination reaction. There are many reagents that can be used for this reaction. Only three are given in this course:
 hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
Carbon-heteroatom single bonds basic C N C X. X= F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide C O. epoxide Chapter 14 H. alcohols acidic H C S C. thiols.
 hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products
 hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
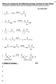 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chem 263 Nov 19, Cl 2
 Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice
 Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
CH 3 CHCH 3 CH 3 CHCH 3 Isopropyl cation. Oxomium ion intermediate. intermediate (an electrophile)
 Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Chem 342 Organic Chemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009
 hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes. With an appropriate catalyst, however, benzene will react
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 November 02, The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck!
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
Section Practice Exam II Solutions
 Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton)
 314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones
 Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Basic Organic Chemistry
 Basic rganic hemistry ourse code: EM 12162 (Pre-requisites : EM 11122) hapter 06 hemistry of Aldehydes & Ketones Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana ffice: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720 (Mobile) Email: dinesh@kln.ac.lk
Basic rganic hemistry ourse code: EM 12162 (Pre-requisites : EM 11122) hapter 06 hemistry of Aldehydes & Ketones Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana ffice: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720 (Mobile) Email: dinesh@kln.ac.lk
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
