CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key
|
|
|
- Howard Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it. or a. b. c. pka Table R=H or sp 3 C HCl H R H R H R R H R H R R H R H H R R H R R H H R SH HC
2 2.) This is a critical thinking problem. Using the base strengths of the anions, predict which reaction arrow you should use. The pka table on the previous page is one you should know. will have it on the first exam. After that Assume all of these products have approximately the same basicity (conj. pka ~15). ( ) Point the large arrow to the weakest base. f the numbers are close (say within six or so, it is reversible. f it is ten, then it can be reversible but does slow slowly. f it is greater than ten, not gonna happen) a. conj. pka ~ 15 H Me conj. pka ~ 15 b. Cl H conj. pka ~ -5 Me Cl conj. pka ~ 15 c. H conj. pka ~ 20 Me conj. pka ~ 15 d. H conj. pka ~ 45 Me conj. pka ~ 15 e. conj. pka ~ 10 C H Me C conj. pka ~ 15
3 3.) Draw mechanisms for the following reactions. Label the products as acetals, hemiacetals, imines, or cyanohydrins. A. cat. ah H H 2 H Hemiacetal B. H cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 H Hemiacetal
4 C. H cat. H 2 S 4 EtH Acetal
5 D. cat. AcH H 2 imine
6 E. cat. ah HC H Cyanohydrin C F. KC AcH H Cyanohydrin C
7 4.) Predict the products: A. cat. H 2 S 4 H B. KC H H C C. H 2 cat. AcH D. cat. H 2 S 4 H optically active H optically active E. cat. AcH H 2 F. cat. ah C HC H
8 5.) The following compounds come from a carbonyl (ketone or aldehyde). Fill in the boxes A. H cat. H 2 S 4 H ketone or aldehyde conditions B. cat. H 2 S 4 Ph H 2 Ph ketone or aldehyde conditions C. cat. H 2 S 4 H ketone or aldehyde conditions D. H cat. ah, HC or KC, AcH optically active C optically active ketone or aldehyde conditions E. ketone or aldehyde H cat. H 2 S 4 conditions H
9 6.) Draw the mechanisms for the following reactions. Show all curved arrows and intermediates: a. H 2 trace AcH s the product? Why or why not? Two Possibilities: The product is achiral, so it is neither optically active nor. r
10 6.) continued: b. Me Me H 2 trace AcH
11 7.) Predict the products: a.) H 2 Ph Ph trace AcH Major b.) H 2 trace AcH H 2 3 signals in 1 H MR
12 8.) Critical thinking: The following acetals when exposed to acid and water, aldehydes are formed. Which acetal is cleaved faster and why? Draw the mechanism of the formation of benzaldehyde from each of these acetals. Acetal A Acetal B
13 8.) Continued Acetal B is cleaved slower than A. When the first is protonated and leaves to form the carbocation, the is still tethered and will back before water can add. n the case of acetal A, the becomes completely detached and becomes less likely to come back as it diffuses away.
14 9.) Write the mechanisms for the following problems: a. abd 4 EtH H D b. H 1.) excess MeMgBr/Et 2 2.) H 3 + H H
15 a.) 10.) Using CD 3 D and abd 4 as your sole sources of deuterium, synthesize the following compounds. D abd 4 EtH H b.) D D 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + MgBr H D D PCC CH 2 Cl 2 c.) D D H 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + D D MgBr CD 3 D H H D D HBr Mg Et 2 D D H Br 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + MgBr PCC CH 2 Cl 2 CD 3 D d.) D D CD 3 Br acd 3 ah CD 3 D
16 e.) H 1.) Et 2 Mg 2.) H 3 + Et 2 MgBr Br CD 3 H H CD 3 CD 3 PBr 3 D 3 C Br Mg Et 2 D 3 C MgBr 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + H PBr 3 CD 3 f.) CD 3 D CD 3 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + Mg Et 2 H BrMg CD 3 Br CD 3 g.) CD 3 D PBr 3 D 3 C Br Mg Et 2 CD 3 D D 3 C MgBr 1.) Et 2 2.) H 3 + PBr 3 H CD 3 h.) D CD 3 D a D h. is just an acid base reaction. That is all. MgBr
17 11.) MR Problem: Predict the MRs of the following compounds:
18
19
20 12.) C 9 H 8. The MR is from the Sigma Aldrich Company.
21 13.) Chem 343 review: S 1 vs. S 2 vs. E2 The nucleophiles below (except for one) are all good enough nucleophiles to work in a S 2 reaction (except one). They have various base strengths which is inversely proportional to the strength of the conjugate acid. The basicity of a nucleophile as well as the hindrance of the electrophile provides a good measure whether a reaction will undergo S 1 or S 2 or E2. f the alpha carbon (the carbon connected to the good leaving group) is tertiary, then only nucleophiles whose conjugate acids have a pka less than 5 will give S 1 products in an appreciative amount. f the pka is above 5, then E2 becomes the major pathway. (At pka of five expect a complex mixture of E2 and S 1 products). f the alpha carbon is secondary, when the conjugate acid is 10 or below, then S 2 is the major product. When it is 15 or above, then E2 is the major product. f the alpha carbon is primary, the major pathway is S 2 except when a bulky base like tbu - is used, then E2 happens. f the alpha carbon is a methyl group, then E2 is impossible and S 2 is the only option besides no reaction. Even tbu - will react with Me in a S 2 reaction. Write next to each nucleophile what the approximate pka of its conjugate acid is. Then, react it with each of the four electrophiles. Write the major pathway and major product. (32 reactions total). ucleophiles Electrophiles conj. pka ~ 25 Br conj. pka ~ -5 C conj. pka ~ 15 conj. pka ~ 15 optically active S conj. pka ~ 10 conj. pka ~ 10 C conj. pka ~ 5 conj. pka ~ 10 Me
22 a. Br S 1 Br b. Br S 2 Br optically active optically active c. Br S 2 Br d. e. Br Me S 2 E2 MeBr f. E2 optically active g. E2 h. Me S 2
23 i. E2 j. S 2 Ph optically active optically active k. S 2 l. Me S 2 Me m. C E2 n. C E2 optically active o. C S 2 p. C S 2 Me
24 r. E2 s. E2 optically active t. S 2 u. S 2 v. S Me E2 w. S 2 S S optically active optically active x. S S 2 S y. S Me S 2 S
25 z. C E2 aa. C S 2 C optically active optically active ab. C S 2 C ac. ad. C Me S 2 E2 and S 1 Me C ae. S 2 optically active af. S 2 optically active ag. S 2 Me
26 14.) From the MR provided, determine the structure of the following compound. Assign the peaks Ha, Hb, Hc etc. accordingly. The MR spectra are from the Sigma-Aldrich Corporation. ntegrations are in bold above each signal. C 8 H DBE
27 15.) From the MR provided, determine the structure of the following compound. Assign the peaks Ha, Hb, Hc etc. accordingly. The MR spectra are from the Sigma-Aldrich Corporation. ntegrations are in bold above each signal. C 4 H 9 1 DBE
28 16.) From the MR provided, determine the structure of the following compound. Assign the peaks Ha, Hb, Hc etc. accordingly. The MR spectra are from the Sigma-Aldrich Corporation. ntegrations are in bold above each signal. All signals are shown. C 3 H DBE
29 17.) From the MR provided, determine the structure of the following compound. Assign the peaks Ha, Hb, Hc etc. accordingly. The MR spectra are from the Sigma-Aldrich Corporation. ntegrations are in bold above each signal. C 9 H DBE
30 18.) From the MR provided, determine the structure of the following compound. The MR spectra are from the Sigma-Aldrich Corporation. ntegrations are in bold above each signal. C 9 H 10 5 DBE
31 19.) Sometimes it is possible to combine two reactions in the same pot to get a new reaction. Draw the mechanism for the following reactions a.) AcH H H 3 b.) AcH KC H C
32 c.) H 4 Cl H 2 KC C
33 20.) ne way to make amines is to treat an imine with sodium borohydride in EtH. Draw the mechanism of the following two step sequence. AcH MeH 2 abh 4 EtH H
34 21.) Sodium cyanoborohydride is a weaker hydride source than sodium borohydride. Why is sodium cyanoborohydride weaker than sodium borohydride? The nitrile group is a strongly electronegative and electron withdrawing group. t pulls electron density from the boron which then pulls electron density from the hydrogens. The hydrogens then have less electron density and are thus less likely to attack a carbonyl. H H B a C Sodium Cyanoborohydride H t is a very handy reagent, because you do not need to preform the imine. The imine can be made in situ, so a two step procedure becomes a one step procedure. Draw the mechanism for the reaction. Hint: This goes through an imine reaction. n this mechanism try to avoid making a negative nitrogen. egative nitrogens are very basic and you should try to avoid them if possible. AcH MeH 2 abh 3 C H What goes wrong if abh4 is used instead? What major side reaction takes place? The aldehyde can be reduced by sodium borohydride to give an alcohol.
35 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Acetal formation cat. H 2 S 4 H Mechanism: cat. H 2 S 4 H Summary (Key words): Acetals are made under acidic conditions, so no basic compounds can be used in the mechanism. The mechanism consists of hemiacetal formation followed by an S1 reaction. The carbonyl oxygen is lost as water. Acetals are useful to protect ketones and aldehydes from nucleophiles such as Grignards. Acetal formation is reversible.
36 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Acetal Cleavage cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 H H Mechanism: cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 Summary (Key words): Acetals are cleaved by acid and water. The carbonyl oxygen comes from water. Acetals are useful to protect ketones and aldehydes from nucleophiles such as Grignards. All steps in the mechanism are reversible.
37 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: mine Formation cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 Mechanism: cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 Summary (Key words): f a strong acid is used, then it must be catalytic. t is not necessary for the carbonyl before the amine attacks. Reaction generates water. All steps are reversible.
38 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: mine Hydrolysis cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 H 2 Mechanism: cat. H 2 S 4 H 2 Summary (Key words): mines are slightly basic. t is not necessary for there to be an acid catalyst. mines are water sensitive and are readily converted to carbonyls. All steps are reversible.
39 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Cyanohydrin Formation AcH, KC or cat. ah, HC C H Mechanisms: AcH, KC cat. ah, HC Summary (Key words): Reaction is reversible. Cyanohydrins are base sensitive. Cyanide is a good nucleophile. t attacks the carbonyl directly.
40 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Cyanohydrin cleavage H cat. ah C Mechanism: H cat. ah C Summary (Key words): All steps reversible. Cyanohydrins are base sensitive.
41 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride abh 4 EtH H Mechanism: abh 4 EtH Summary (Key words): Addition of the hydride to carbonyl is irreversible. The hydrogen that attacks the carbonyl carbon comes from sodium borohydride. The proton that adds to the oxygen comes from the alcohol solvent. Sodium borohydride is basic. t can also deprotonate H s (cyanohydrins, hemiacetals)
42 Chem 345 Reaction Sheets: Reaction of a ketone with a Grignard Reagent 1.) MeMgBr, Et 2 2.) H 3 + H Mechanism: 1.) MeMgBr, Et 2 2.) H 3 + Preparation of a Grignard Reagent: Mg MeBr MeMgBr Summary (Key words): Addition of the carbon group to the carbonyl is irreversible. Always a two step procedure. Grignards are really strong bases. t will react with acidic hydrogens very quickly. This includes H s on cyanohydrins or hemiacetals.
Chem 263 March 7, 2006
 Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
REALLY, REALLY STRONG BASES. DO NOT FORGET THIS!!!!!
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 4 Key Grignard (RMgX) Problem Set You will be using Grignard reagents throughout this course to make carbon-carbon bonds. To use them effectively, it will require some knowledge from
CHEM 345 Problem Set 4 Key Grignard (RMgX) Problem Set You will be using Grignard reagents throughout this course to make carbon-carbon bonds. To use them effectively, it will require some knowledge from
p Bonds as Electrophiles
 Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections:
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Loudon Chapter 19 Review: Aldehydes and Ketones CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP
 TE CEMISTY F TE CABYL GUP Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2007 andout A C C You will be able to download copies of the handouts from this course at http://users.ox.ac.uk/~magd1571/teaching/teaching.htm
TE CEMISTY F TE CABYL GUP Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2007 andout A C C You will be able to download copies of the handouts from this course at http://users.ox.ac.uk/~magd1571/teaching/teaching.htm
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Lecture 15. More Carbonyl Chemistry. Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first O R'OH, H + OR" 2R"OH R + H 2 O OR" 3/8/16
 Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Section Practice Exam II Solutions
 Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Chem 263 Nov 3, 2016
 hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
Suggested solutions for Chapter 6
 s for Chapter 6 6 PRBLEM 1 Draw mechanisms for these reactions: NaB 4 Et, 2 1. LiAl 4 C 2. 2 Rehearsal of a simple but important mechanism that works for all aldehydes and ketones. Draw out the B 4 and
s for Chapter 6 6 PRBLEM 1 Draw mechanisms for these reactions: NaB 4 Et, 2 1. LiAl 4 C 2. 2 Rehearsal of a simple but important mechanism that works for all aldehydes and ketones. Draw out the B 4 and
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones
 Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
1- Reaction at the carbonyl carbon (Nucleophilic addition reactions).
 Reactions of aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and Ketones undergo many reactions to give a wide variety of useful derivatives. There are two general kinds of reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo:
Reactions of aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and Ketones undergo many reactions to give a wide variety of useful derivatives. There are two general kinds of reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo:
The Claisen Condensation
 Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Chemistry 14D Winter 2017 Final Exam Part A Page 1
 Chemistry 14D Winter 2017 Final Exam Part A Page 1 Please use the backs of the exam pages for scratch space. Please do not use the exam margins for this purpose. All reactants and solvents written above
Chemistry 14D Winter 2017 Final Exam Part A Page 1 Please use the backs of the exam pages for scratch space. Please do not use the exam margins for this purpose. All reactants and solvents written above
18.8 Oxidation. Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium
 18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
Chapter 22 Amines. Nomenclature Amines are classified according to the degree of substitution at nitrogen.
 CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
FIRST EXAMINATION. Name: CHM 332
 ame: CM 332 FIRST EXAMIATI All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is,
ame: CM 332 FIRST EXAMIATI All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is,
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
Chem 263 March 28, 2006
 Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Chem 112A: Final Exam
 Chem 112A: Final Exam December 14th, 2011 Please provide all answers in the spaces provided. You are not allowed to use a calculator for this exam, but you may use molecular model kits. nly cyclohexane
Chem 112A: Final Exam December 14th, 2011 Please provide all answers in the spaces provided. You are not allowed to use a calculator for this exam, but you may use molecular model kits. nly cyclohexane
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
c. Oxidizing agent shown here oxidizes 2º alcohols to ketones and 1º alcohols to carboxylic acids. 3º alcohols DO NOT REACT.
 Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Aldehydes and Ketones
 9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids. Acids Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids.
 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION
 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
8-3 This exercise is worked out on page 293 as "Working with Concepts".
 Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) are compounds with an OH attached to a carbonyl. Nitriles (RC N) are compounds a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Naming Carboxylic Acids 1. Replace
Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) are compounds with an OH attached to a carbonyl. Nitriles (RC N) are compounds a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Naming Carboxylic Acids 1. Replace
18.10 Conjugate Additions O O. O X BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CCH 3 ± ± BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. TsOH 1 O C O O W 3 CH 3 CCH 3 CH 3 CCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3
 80 NJUGATE ADDITINS 779 An attempt to form a Grignard reagent from 5-bromo- 2-pentanone is doomed to failure because the Grignard will react with the carbonyl group Therefore, the carbonyl group is first
80 NJUGATE ADDITINS 779 An attempt to form a Grignard reagent from 5-bromo- 2-pentanone is doomed to failure because the Grignard will react with the carbonyl group Therefore, the carbonyl group is first
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
Chem 263 Nov 24, Properties of Carboxylic Acids
 Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 ov 24, 2009 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Effect of nucleophile on reaction
 1 Effect of nucleophile on reaction X DS c X c c X DS c + X cleophile not involved in DS of S N 1 so does not effect the reaction (well obviously it controls the formula of the product!) cleophile has
1 Effect of nucleophile on reaction X DS c X c c X DS c + X cleophile not involved in DS of S N 1 so does not effect the reaction (well obviously it controls the formula of the product!) cleophile has
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
Chemistry Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers
 Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Homework for Chapter 7 Chem 2310
 omework for Chapter 7 Chem 2310 Name I. Introduction to Reactions 1. Explain why the following fits the definition of a chemical reaction. C 3 Na C 3 Na 2. Using the chemical reaction above, give all compounds
omework for Chapter 7 Chem 2310 Name I. Introduction to Reactions 1. Explain why the following fits the definition of a chemical reaction. C 3 Na C 3 Na 2. Using the chemical reaction above, give all compounds
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams.
 2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
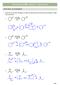 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
hem A225 Notes Page 67 I. Introduction hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group (=) with no other heteroatoms attached. An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen attached;
The problem is that your product still has a-protons, and can keep on forming enolates to get more methyl groups added:
 Lecture 13 Notes November 7, 2012 We are going to start with some examples of proline-catalyzed reactions. In each case, you can draw a mechanism that would involve proline as a chiral catalyst, and one
Lecture 13 Notes November 7, 2012 We are going to start with some examples of proline-catalyzed reactions. In each case, you can draw a mechanism that would involve proline as a chiral catalyst, and one
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chem 263 Nov 7, elimination reaction. There are many reagents that can be used for this reaction. Only three are given in this course:
 hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes. I. Introduction
 1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 4. Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m.
 CHEM 347 Quiz # 4 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 9 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 4 Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m. Student Name (Printed)
CHEM 347 Quiz # 4 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 9 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 4 Due in Monsanto Hall 103 by: Friday, April 4 th, 2014, 7:00 p.m. Student Name (Printed)
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
 Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
Chapter 9:Nucleophiles & Substitution Reactions
 1. a. Place the following nucleophiles in order of strength (1= strongest; 3 = weakest). i. ii. b. Place the following in order of leaving group ability (1= best; 7 = worst). (A pka table may help you!)
1. a. Place the following nucleophiles in order of strength (1= strongest; 3 = weakest). i. ii. b. Place the following in order of leaving group ability (1= best; 7 = worst). (A pka table may help you!)
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 3. Monday, July 21 st, :30 a.m.
 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
Carbonyl Chemistry IV + C O C. Lecture 10. Chemistry /30/02
 arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview
 22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
Aldehydes and Ketones 2. Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde.
 Aldehydes and Ketones 2 Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde. The Wittig Reaction Wittig reaction, named for German chemist Georg Wittig, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979 for
Aldehydes and Ketones 2 Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde. The Wittig Reaction Wittig reaction, named for German chemist Georg Wittig, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979 for
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
 Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Chem 345 Reaction List: Chem 343 Reactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes).
 Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). uc - optically active LG 2 optically active uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to
Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). uc - optically active LG 2 optically active uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to
Lecture 18. Oxidation and Reduction. Oxidation. Reduction O CH 4 CH 3 OH H C H. Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
Important Note: We will NOT accept papers written in pencil back for re-marking after they have been returned to you. Please do not ask!
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text )
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 12.1 12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text 13.1 13.11) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 12.1 12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text 13.1 13.11) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
Loudon Chapter 10 Review: Alcohols & Thiols Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/26/2016
 Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
Reactions SN2 and SN1
 Reactions SN2 and SN1 Reactivity: Functional groups can be interconverted using a great variety of reagents. Millions of organic molecules have been synthesized via a series of functional-group interconversions.
Reactions SN2 and SN1 Reactivity: Functional groups can be interconverted using a great variety of reagents. Millions of organic molecules have been synthesized via a series of functional-group interconversions.
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
