Light, Spectra, and Ma1er
|
|
|
- Quentin Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Light, Spectra, and Ma1er 1
2 Ideal Black Bodies Amount of light thermally radiated: j = σt 4 Where j = total intensity, T is temperature, and σ = 5.67 x 10-8 W m - 2 K - 4 (constant) Wavelength (nm) 2
3 SoluOon If star A is 9000 K and star B is 3000 K, what is the raoo of the power output of the stars (Power A /Power B ) assuming the stars are the same size? Intensity Intensity A B = P P A B / / A A = P P A B Intensity A = σt 4 A 3
4 SoluOon ( ) K 9000 K P P Intensity Intensity B A B A = = = = = = B A B A T T T T σ σ If star A is 9000 K and star B is 3000 K, what is the raoo of the intensity output of the stars (Power A /Power B)? 4
5 The Solar Spectrum: When we look at the Spectrum of the Sun, we see a distinct distribution of colors. Other stars have similar patterns as do most hot objects. The main difference is where the peak color is. Gustav Kirchhoff (1862) called this kind of emitter a Blackbody. 5
6 CalculaOng The Sun s Temperature So how well does this work? Pre1y well!!!! T Sun 6000 K 6
7 Fraunhofer s Surprise: Joseph von Fraunhofer made an interesong discovery when looking at the Sun. Using a precision dispersing prism, he discovered that the `solar black body` was cut by thousands of dark bands. 7
8 Fraunhofer s Surprise: Fraunhofer tried to test whether this effect was real. 1) He tested with different opocs. 2) He tested by looking at different objects (moon and planets). 8
9 Bunsen`s Solution: Robert Bunsen turned pyromania into one of the great discoveries of modern physics. Bunsen set fire to things in order to figure out what they were made of Gustav Kirchhoff suggested using a prism to break the light apart They quickly discovered that burning substances produced light in narrow bands with unique pa1erns Iron 9
10 Blueprint to Composition: Bunsen and Kirchoff`s trick was the key to finding out the composioon of anything from the light it produced. Many of the lines they found had the same wavelength as those of Fraunhofer`s dark bands. They were seeing the composioon of the Sun! 10
11 Kinds of Spectra: Bunsen found that he could idenofy the signature of different elements in the Fraunhofer spectrum of the Sun. Why were Bunsen`s spectra composed of bright lines while Fraunhofer`s were dark bands? Bunsen`s fires were somulaong emissions from thermal energy in the hot gas. So what are Fraunhofer`s bands? AbsorpOon in (and re- emission from) a cooler gas! 11
12 Types of Spectra Con)nuous: black body radiaoon con)nuous Absorp)on: requires a cool object in front of a hot background (ex: Fraunhofer) discrete Emission: requires a hot object with a cool background (ex: Bunsen) discrete 12
13 Types of Spectra Con)nuous: black body radiaoon con)nuous Absorp)on: requires a cool object in front of a hot background (ex: Fraunhofer) discrete Emission: requires a hot object with a cool background (ex: Bunsen) discrete 13
14 Atoms and Light: Why do elements have the `discrete` interacoons that Bunsen saw? Why do different elements (and molecules) have different interacoons? This has to do with the nature of atoms and how they are put together. 14
15 Dividing the Indivisible : The Plum Pudding Model 1897 J. J. Thomson discovers the electron (he called them corpuscles) Later, electrons are said to have charge = Thomson proposes model of the atom: Atom is divisible NegaOvely charged corpuscles/electrons (plums) PosiOve soup to balance negaove charge (pudding) 15
16 Basic DefiniOons: Element: a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means (defined by number of protons) Atom: the smallest piece of ma1er that is soll an element Molecule: two or more atoms that are bound together by chemical bonds Nucleus: the protons and neutrons bound together at the center of an atom 16
17 Discovering Nothing Two new types of radiaoon discovered: 1. Alpha parocles (α): Helium nucleus 2. Beta parocles (β): electron Rutherford fires alpha parocles at gold foil. Expected only small angle sca1ering due to plum pudding. PosiOve Nucleus Saw mostly no sca1ering with occasional back sca1ering Ma/er is mostly empty space!!!! NegaOve electron 17
18 Rutherford s Atom 1. Mass (posiove nucleus) is highly concentrated at the center 2. Electrons (negaovely charged) circle the nucleus 3. Lots of empty space in between 4. Similar to today s atom Number of protons determine the element type Number of electrons determine the chemical properoes of the atom PosiOve Nucleus NegaOve electron 18
19 Inside the Nucleus Rutherford (1918): Discovers the proton. The proton is about 2000x as massive as the electron and has a charge = +1 James Chadwick (1932): Discovers the neutron. Neither posiove nor negaove, it has about the same mass as a proton Nuclei are made up of protons and neutrons. 19
20 Atoms, Elements, and Isotopes Atoms: Nucleus Protons number determines the element Neutrons number determines the isotope Electrons number determines the chemical properoes 20
21 Atoms, elements, and Isotopes Isotopes: Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same chemical properoes, but different masses, different emission spectra, and parocipate in different nuclear reacoons. Hydrogen Deuterium TriOum Helium e - p + p + p + n p + e - First isotope of hydrogen n e - n n e - Second isotope of hydrogen p + n e - New element: not an isotope of H 21
22 Bohr Atomic Model Energy States: Wave properoes of electrons are important An integer number of wavelengths fit in one orbit p + Electron distances and energies are discrete values E1 E2 e - E ph = hf = hc λ E3 22
23 Bohr Atomic Model Wave properoes of electrons are important An integer number of wavelengths fit in one orbit Electron distances and energies are discrete values 23
24 Atoms and Light: Energy States: Electrons exist in `orbits` (much like planets in the solar system) that are stable at specific separaoons from the nucleus. (due to the wave- like nature of electrons) p + The distance from the nucleus determines the energy of the electron (lower E is closer). E1 E2 e - The spacing of these energy levels is not even. E3 E1è E2 > E2è E3 > E3è E4 etc 24
25 Atoms and Light: So what does all of this have to do with Bunsen and Franhofer lines? 25
26 Atoms and Light: Energy States: If you heat the atom up to high enough temperatures, the electron will jump to higher orbits (higher energy state). p + E1 e - How does `heaong` do this? Collisions E2 E3 26
27 Atoms and Light: Energy States: If you heat the atom up to high enough temperatures, the electron will jump to higher orbits (higher energy state). p + E1 How does `heaong` do this? Collisions E2 e - E3 27
28 Atoms and Light: Emission Energy States: Aqer a Ome, the electron falls back to the lowest energy state. A photon is given off. p + E1 E2 e - The energy of the photon is exactly equal to the energy difference between the two energy states. E3 28
29 Atoms and Light: Absorption Energy States: Process of emission is fully reversible. Electron can absorb a photon and jump to a higher energy level. p + E1 E2 e - The energy of the photon must be exactly equal to the energy difference between the two energy states. E3 29
30 Atoms and Light: Absorption Energy States: Process of emission is fully reversible. Electron can absorb a photon and jump to a higher energy level. p + E1 E2 e - The energy of the photon must be exactly equal to the energy difference between the two energy states. E3 30
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Nuclear Chemistry. Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture
 Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
Atomic Theory. Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom. Saturday, January 20, 18
 Atomic Theory Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom Democritus Theory: Atom, the indivisible particle c. 300 BC Democritus Problem: No scientific evidence c. 300 BC Dalton Theory: The solid sphere model
Atomic Theory Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom Democritus Theory: Atom, the indivisible particle c. 300 BC Democritus Problem: No scientific evidence c. 300 BC Dalton Theory: The solid sphere model
An Introduction to Atomic Theory. VCE Chemistry Unit 1: The Big Ideas of Chemistry Area of Study 1 The Periodic Table
 An Introduction to Atomic Theory VCE Chemistry Unit 1: The Big Ideas of Chemistry Area of Study 1 The Periodic Table From Democritus to Dalton Two thousand years ago, Democritus proposed that matter consisted
An Introduction to Atomic Theory VCE Chemistry Unit 1: The Big Ideas of Chemistry Area of Study 1 The Periodic Table From Democritus to Dalton Two thousand years ago, Democritus proposed that matter consisted
Time to develop a model
 ATOMIC THEORY ONCE UPON A TIME People have been fascinated with matter for a long time. What is matter? What is all this stuff around us made of? Can it be broken down? Are there different types of matter?
ATOMIC THEORY ONCE UPON A TIME People have been fascinated with matter for a long time. What is matter? What is all this stuff around us made of? Can it be broken down? Are there different types of matter?
What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena
 Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
The structure of Atom III
 The structure of Atom III Atomic Structure If, in some cataclysm, all of scientific knowledge were to be destroyed, and only one sentence passed on to the next generations of creatures, what statement
The structure of Atom III Atomic Structure If, in some cataclysm, all of scientific knowledge were to be destroyed, and only one sentence passed on to the next generations of creatures, what statement
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far
 Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011
 Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 8; January 24 2011 Previously on Astro 1 Light as a wave The Kelvin Temperature scale What is a blackbody? Wien s law: λ max (in meters) = (0.0029 K m)/t. The Stefan-Boltzmann
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 8; January 24 2011 Previously on Astro 1 Light as a wave The Kelvin Temperature scale What is a blackbody? Wien s law: λ max (in meters) = (0.0029 K m)/t. The Stefan-Boltzmann
HISTORY OF THE ATOM ATOMA
 S.MORRIS 2006 HISTORY OF THE ATOM 460 BC Democritus develops the idea of atoms he pounded up materials in his pestle and mortar until he had reduced them to smaller and smaller particles which he called
S.MORRIS 2006 HISTORY OF THE ATOM 460 BC Democritus develops the idea of atoms he pounded up materials in his pestle and mortar until he had reduced them to smaller and smaller particles which he called
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
Atomic Theory Development
 Atomic Theory Development Born as early as 400 BC, it took more than 2000 years before Science was ready to accept the idea of atomic structure of matter and another 150 years to develop a good model!
Atomic Theory Development Born as early as 400 BC, it took more than 2000 years before Science was ready to accept the idea of atomic structure of matter and another 150 years to develop a good model!
Ch4 and Ch5. Atomic History and the Atom
 Ch4 and Ch5 Atomic History and the Atom Ch4.2 What are atoms? Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has the element s properties. Ch. 4.3 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher
Ch4 and Ch5 Atomic History and the Atom Ch4.2 What are atoms? Atoms are the smallest part of an element that still has the element s properties. Ch. 4.3 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher
Name Period Date Engage-Atoms 1. What does Bill cut in half?
 Name Period Date Engage-Atoms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmuskig2exi 1. What does Bill cut in half? 2. By cutting this item in half he tries to prove that there are pieces that are uncut- table called
Name Period Date Engage-Atoms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmuskig2exi 1. What does Bill cut in half? 2. By cutting this item in half he tries to prove that there are pieces that are uncut- table called
Notes:&&Unit&4:&Atomics& & & & & & & & & & & & & & & & &
 Name: RegentsChemistry:Mr.Palermo Notes:Unit4:Atomics! www.mrpalermo.com Name: $ Key$Ideas$ Themodernmodeloftheatomhasevolvedoveralongperiodoftimethroughtheworkofmany scientists.(3.1a) Eachatomhasanucleus,withanoverallpositivecharge,surroundedbyoneormorenegatively
Name: RegentsChemistry:Mr.Palermo Notes:Unit4:Atomics! www.mrpalermo.com Name: $ Key$Ideas$ Themodernmodeloftheatomhasevolvedoveralongperiodoftimethroughtheworkofmany scientists.(3.1a) Eachatomhasanucleus,withanoverallpositivecharge,surroundedbyoneormorenegatively
Models of the Atom. Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason
 Models of the Atom Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason First Things First Electrons were accepted to be part of the atom structure by scientists in the1900 s. The first model of the atom was visualized as
Models of the Atom Spencer Clelland & Katelyn Mason First Things First Electrons were accepted to be part of the atom structure by scientists in the1900 s. The first model of the atom was visualized as
Atomic Structure ATOMIC STRUCTURE. All matter is composed of atoms.
 All matter is composed of atoms. ATOMIC STRUCTURE Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the properties of matter HISTORY OF THE ATOM DALTONS ATOMIC THEORY 1808 John Dalton suggested
All matter is composed of atoms. ATOMIC STRUCTURE Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the properties of matter HISTORY OF THE ATOM DALTONS ATOMIC THEORY 1808 John Dalton suggested
LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 29.1 Spectroscopy 29.2 Atoms The first nuclear physics experiment Using the nuclear model 29.3 Bohr s model of atomic quantization
LECTURE 23 SPECTROSCOPY AND ATOMIC MODELS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 29.1 Spectroscopy 29.2 Atoms The first nuclear physics experiment Using the nuclear model 29.3 Bohr s model of atomic quantization
The term valent means outermost, therefore only the electrons on the outermost shell are called valent.
 The atom is the smallest basic unit of an element which possesses the properties of the element. Structure of the Atom The term valent means outermost, therefore only the electrons on the outermost shell
The atom is the smallest basic unit of an element which possesses the properties of the element. Structure of the Atom The term valent means outermost, therefore only the electrons on the outermost shell
Dalton Thompson Rutherford Bohr Modern Model ("Wave. Models of the Atom
 Dalton Thompson Rutherford Bohr Modern Model ("Wave Models of the Atom Mechanical" Model) Aim: To discuss the scientists and their contributions to the current atomic model. Focus: Rutherford's Gold Foil
Dalton Thompson Rutherford Bohr Modern Model ("Wave Models of the Atom Mechanical" Model) Aim: To discuss the scientists and their contributions to the current atomic model. Focus: Rutherford's Gold Foil
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
H CHEM - WED, 9/7/16. Do Now Be ready for notes. Sigfig review problem. Agenda Atomic Theory. Homework. Error Analysis
 H CHEM - WED, 9/7/16 Do Now Be ready for notes. Sigfig review problem Agenda Atomic Theory Error Analysis Homework Possibly atomic theory paragraph THE ATOM DEFINITION TO START Atom smallest particle
H CHEM - WED, 9/7/16 Do Now Be ready for notes. Sigfig review problem Agenda Atomic Theory Error Analysis Homework Possibly atomic theory paragraph THE ATOM DEFINITION TO START Atom smallest particle
Atomic Structure Discovered. Dalton s Atomic Theory. Discovery of the Electron 10/30/2012
 Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
The Atom. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons.
 The Atom Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons. A guy by the name of Bohr created a model for the atom that consisted of an small nucleus surrounded by orbiting
The Atom Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus surrounded by electrons. A guy by the name of Bohr created a model for the atom that consisted of an small nucleus surrounded by orbiting
Atomic Theory. Democritus to the Planetary Model
 Atomic Theory Democritus to the Planetary Model Democritus Greek philosopher (460-370 BCE) Believed in the philosophy of materialism With Leucippus, they though that matter can not be divided infinitely.
Atomic Theory Democritus to the Planetary Model Democritus Greek philosopher (460-370 BCE) Believed in the philosophy of materialism With Leucippus, they though that matter can not be divided infinitely.
Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video
 Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video 2 CH 4- Atoms 1 Discovering the Atom In this lesson we will take a look at the scientists who explored the
Development of Atomic Theory Elements of chemistry- Atoms, the building blocks of matter Video 2 CH 4- Atoms 1 Discovering the Atom In this lesson we will take a look at the scientists who explored the
Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
 Chemistry 1 West Linn High School Unit 2 Packet and Goals Name: Period: Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Unit Goals: As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. describe Dalton
Chemistry 1 West Linn High School Unit 2 Packet and Goals Name: Period: Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Unit Goals: As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. describe Dalton
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics
 Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Atomic Models. A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature. A model can be changed as new information is collected.
 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
What is the current atomic model?
 4.1 Atoms Basic Units of Matter What is the current atomic model? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, such as gases, solids, and liquids. Matter is not sound, heat, or light these are
4.1 Atoms Basic Units of Matter What is the current atomic model? Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, such as gases, solids, and liquids. Matter is not sound, heat, or light these are
ATOM. Rich -Paradis. Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory. Matter can be divided indefinitely. Greeks
 ATOM Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory Greeks Matter can be divided indefinitely matter is made up of particles--4 elements 4 elements --air--fire--water- -- earth Democritus --Discontinuous
ATOM Early Thoughts Aristotle-- Continuous theory Greeks Matter can be divided indefinitely matter is made up of particles--4 elements 4 elements --air--fire--water- -- earth Democritus --Discontinuous
LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39
 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39 April 14, 2011 1 HOW TO MEASURE SPECTRA Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms
PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 19 Dennis Papadopoulos End of Classical Physics Quantization Bohr Atom Chapters 38 39 April 14, 2011 1 HOW TO MEASURE SPECTRA Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms
EARLY VIEWS: The Ancient Greeks
 Feb 7 11:59 AM EARLY VIEWS: The Ancient Greeks Empedocles (c. 450 B.C.) proposed Four Element theory he thought that matter was composed of four elements: AIR, EARTH, FIRE and WATER elements mixed together
Feb 7 11:59 AM EARLY VIEWS: The Ancient Greeks Empedocles (c. 450 B.C.) proposed Four Element theory he thought that matter was composed of four elements: AIR, EARTH, FIRE and WATER elements mixed together
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Table Of Contents. Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter. Unstable Nuclei and Radioactive Decay
 CHEMISTRY 4 Table Of Contents Matter and Change Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Section 4.2 Section 4.3 Section 4.4 Defining the Atom How Atoms Differ Unstable
CHEMISTRY 4 Table Of Contents Matter and Change Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Section 4.2 Section 4.3 Section 4.4 Defining the Atom How Atoms Differ Unstable
History of Atomic Theory
 Unit 2 The Atom History of Atomic Theory A. Democritus and Aristotle Democritus named the "atom" - means indivisible Dalton (with work of Lavoisier, Proust, and Gay-Lussac) 1. atomic theory - first based
Unit 2 The Atom History of Atomic Theory A. Democritus and Aristotle Democritus named the "atom" - means indivisible Dalton (with work of Lavoisier, Proust, and Gay-Lussac) 1. atomic theory - first based
Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee
 Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee Atom The smallest particle of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of the element. The Theory & Evidence for John Dalton s Atomic Theory: Around
Rhonda Alexander IC Science Robert E. Lee Atom The smallest particle of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of the element. The Theory & Evidence for John Dalton s Atomic Theory: Around
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline Slide 2 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that is made up of The particles are or can be broken down into by chemical processes. cannot
Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline Slide 2 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that is made up of The particles are or can be broken down into by chemical processes. cannot
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Atomic Structure. Chemistry Mr. McKenzie
 Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Atomic Structure. All matter is composed of atoms. Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the properties of matter.
 Atomic Structure Atomic Structure All matter is composed of atoms. Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the properties of matter. HISTORY OF THE ATOM suggested that all matter
Atomic Structure Atomic Structure All matter is composed of atoms. Understanding the structure of atoms is critical to understanding the properties of matter. HISTORY OF THE ATOM suggested that all matter
Democritus & Leucippus (~400 BC) Greek philosophers: first to propose that matter is made up of particles called atomos, the Greek word for atoms
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
Atomic Structure Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom Dalton: atoms cannot Thomson: Cathode Ray Tubes Rutherford:
 Atomic Structure n a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; n an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set
Atomic Structure n a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; n an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin
 Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Models of the Atom by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton
Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Models of the Atom by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton
Atomic Theory. Early models
 Atomic Theory Early models Ancient Greece Late 18 th century 4 elements Earth, Water, Wind, Fire: Matter is made up in different combinations of these 4 elements. First atom proposed by Democritus (Greek)
Atomic Theory Early models Ancient Greece Late 18 th century 4 elements Earth, Water, Wind, Fire: Matter is made up in different combinations of these 4 elements. First atom proposed by Democritus (Greek)
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts & Connections
 INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts & Connections Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 5 Models of the Atom by Christopher Hamaker Chapter 5 1 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts & Connections Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 5 Models of the Atom by Christopher Hamaker Chapter 5 1 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter
hf = E 1 - E 2 hc = E 1 - E 2 λ FXA 2008 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA
 1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
Chapter 11 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 11 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The discovery of which particle proved that the atom
Chapter 11 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The discovery of which particle proved that the atom
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
I. History and Development of the Atom
 Unit 3: The Atom I. History and Development of the Atom A. Democritus (around 400 B.C.) Based on his observations of the natural world around him, Democritus was the first to suggest that all matter was
Unit 3: The Atom I. History and Development of the Atom A. Democritus (around 400 B.C.) Based on his observations of the natural world around him, Democritus was the first to suggest that all matter was
Astonomy 62 Lecture #10. Last Time. Applications of Stefan-Boltzmann Law Color Magnitudes Color Index
 Last Time Applications of Stefan-Boltzmann Law Color Magnitudes Color Index Standard Visual Band Filters U B V R I Flux through filter X: F x = 0 F S x d F x F x W x Apparent Color Magnitude: m x,1 m x,2
Last Time Applications of Stefan-Boltzmann Law Color Magnitudes Color Index Standard Visual Band Filters U B V R I Flux through filter X: F x = 0 F S x d F x F x W x Apparent Color Magnitude: m x,1 m x,2
Atomic Structure. A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature.
 Atomic Structure 1 2 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. A model uses familiar
Atomic Structure 1 2 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. A model uses familiar
SNC1D CHEMISTRY 2/8/2013. ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L Atomic Theory (P ) Atomic Theory. Atomic Theory
 SNC1D CHEMISTRY ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L Atomic Theory (P.168-175) Atomic Theory Thousands of years ago Greek philosophers were asking themselves questions like, If you take a gold bar and cut it
SNC1D CHEMISTRY ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L Atomic Theory (P.168-175) Atomic Theory Thousands of years ago Greek philosophers were asking themselves questions like, If you take a gold bar and cut it
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Introduction to Atomic Structure Multiple Choice HW
 Introduction to Atomic Structure Multiple Choice HW PSI Chemistry Name------------------------------------------- Energy and Light 1. What principle is responsible for the pattern below: 2. This principal
Introduction to Atomic Structure Multiple Choice HW PSI Chemistry Name------------------------------------------- Energy and Light 1. What principle is responsible for the pattern below: 2. This principal
Glencoe: Chapter 4. The Structure of the Atom
 Glencoe: Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Section One: Early Ideas about Matter Atomists and Democritus : 400 B.C. From Thrace in Greece. Atoms- Uncut-Table Indivisible parts which cannot be broken
Glencoe: Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Section One: Early Ideas about Matter Atomists and Democritus : 400 B.C. From Thrace in Greece. Atoms- Uncut-Table Indivisible parts which cannot be broken
Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR)
 HSC Physics Year 2016 Mark 95.00 Pages 22 Published Jan 15, 2017 Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR) By Edward (99.95 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Edward. Edward
HSC Physics Year 2016 Mark 95.00 Pages 22 Published Jan 15, 2017 Physics: Quanta to Quarks Option (99.95 ATAR) By Edward (99.95 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Edward. Edward
NOTES ON CHAPTER 4: ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE. 4.1 Introduction to Atoms
 NOTES ON CHAPTER 4: ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE 4.1 Introduction to Atoms The first people to think about the nature of matter were the ancient Greeks. Around 430 B.C, Democritus, a Greek philosopher,
NOTES ON CHAPTER 4: ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE 4.1 Introduction to Atoms The first people to think about the nature of matter were the ancient Greeks. Around 430 B.C, Democritus, a Greek philosopher,
The History of the Atom. How did we learn about the atom?
 The History of the Atom How did we learn about the atom? The Atomic Theory of Matter All matter is made up of fundamental particles. What does fundamental mean? The Greek Philosophers, 400 B.C. Democritus
The History of the Atom How did we learn about the atom? The Atomic Theory of Matter All matter is made up of fundamental particles. What does fundamental mean? The Greek Philosophers, 400 B.C. Democritus
Particle Theory of Matter. By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that:
 Particle Theory of Matter By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that: all matter is made up of very tiny particles each pure substance has its own
Particle Theory of Matter By the late 1700s, scientists had adopted the Particle Theory of Matter. This theory states that: all matter is made up of very tiny particles each pure substance has its own
! Finish Ch. 4.! Start Chapter 10: The Sun.! Homework Due: Oct. 10
 ! Finish Ch. 4! Start Chapter 10: The Sun! Homework Due: Oct. 10 A Spectral Mystery Mystery: Why do so many stars have an absorption spectrum (with certain colors missing)? The atoms that make up these
! Finish Ch. 4! Start Chapter 10: The Sun! Homework Due: Oct. 10 A Spectral Mystery Mystery: Why do so many stars have an absorption spectrum (with certain colors missing)? The atoms that make up these
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013
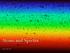 Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
CHAPTER 4: Matter is Made up of Atoms
 CHAPTER 4: Matter is Made up of Atoms ATOMS & THEIR STRUCTURE Aristotle thought matter was made of air, earth, fire and water. Democritus (250 B.C.)- Said the world is made of empty space & tiny particles
CHAPTER 4: Matter is Made up of Atoms ATOMS & THEIR STRUCTURE Aristotle thought matter was made of air, earth, fire and water. Democritus (250 B.C.)- Said the world is made of empty space & tiny particles
Atomic Theory. Contribution to Modern Atomic Theory
 Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Light III The Atom & Spectra. February 12, 2012
 Light III The Atom & Spectra February 12, 2012 Average: 65 20 Test 1 15 10 5 0 0-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 80-90 90-100 Takeaway Message: YOU NEED TO STUDY MORE you need to come to class EVERY DAY (TPS questions
Light III The Atom & Spectra February 12, 2012 Average: 65 20 Test 1 15 10 5 0 0-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 80-90 90-100 Takeaway Message: YOU NEED TO STUDY MORE you need to come to class EVERY DAY (TPS questions
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
Atomic Models. 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models.
 Atomic Models 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models. 2) Students will be able to describe the role of experimental evidence in changing models of the atom. 3) Students will
Atomic Models 1) Students will be able to describe the evolution of atomic models. 2) Students will be able to describe the role of experimental evidence in changing models of the atom. 3) Students will
The Atom. Result for Hydrogen. For example: the emission spectrum of Hydrogen: Screen. light. Hydrogen gas. Diffraction grating (or prism)
 The Atom What was know about the atom in 1900? First, the existence of atoms was not universally accepted at this time, but for those who did think atoms existed, they knew: 1. Atoms are small, but they
The Atom What was know about the atom in 1900? First, the existence of atoms was not universally accepted at this time, but for those who did think atoms existed, they knew: 1. Atoms are small, but they
GraspIT AQA Atomic Structure Questions
 A. Atomic structure Atoms and isotopes 1. a) The diagram shows an atom of Beryllium. Name the parts labelled a, b and c. (3) electron (1) neutron (1) proton (1) b) What is the atomic mass of this atom?
A. Atomic structure Atoms and isotopes 1. a) The diagram shows an atom of Beryllium. Name the parts labelled a, b and c. (3) electron (1) neutron (1) proton (1) b) What is the atomic mass of this atom?
Unit 3. The Atom & Modern Atomic Theory
 Unit 3 The Atom & Modern Atomic Theory Theories of the Atom Early Models & Thoughts: Democritus Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Smallest unit that retains the identity of the element
Unit 3 The Atom & Modern Atomic Theory Theories of the Atom Early Models & Thoughts: Democritus Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Smallest unit that retains the identity of the element
Name: Date: Blk: Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr THOMSON
 Name: Date: Blk: NOTES: ATOMIC STRUCTURE I. History of the Atom Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr 1803 1897 1909 1913 1. DALTON - everything is made of atoms - different elements combine to form compounds
Name: Date: Blk: NOTES: ATOMIC STRUCTURE I. History of the Atom Dalton Thomson Rutherford Bohr 1803 1897 1909 1913 1. DALTON - everything is made of atoms - different elements combine to form compounds
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
 LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR First stage = Protostar PROTOSTAR Cloud of gas and dust many light-years across Gravity tries to pull the materials together Eventually, at the center of the ball of dust and gas,
Do Now: Recall 1. What is an atom? What have you learned about the word atom so far this semester?
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: Recall 1. What is an atom? What have you learned about the word atom so far this semester? Atoms Video: 1. Proper Portioned Giant Atom Model of Science: Structure
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: Recall 1. What is an atom? What have you learned about the word atom so far this semester? Atoms Video: 1. Proper Portioned Giant Atom Model of Science: Structure
Chapter 4. Models of the Atom
 Chapter 4 Models of the Atom Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These particles are molecules or atoms. Molecules can be broken down into atoms
Chapter 4 Models of the Atom Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These particles are molecules or atoms. Molecules can be broken down into atoms
Early Ideas about Matter
 Early Ideas about Matter atom The smallest piece of the element with all the chemical properties of the element an old and new idea Greeks Discontinuists Democritus Continuists Aristotle Discontinuists
Early Ideas about Matter atom The smallest piece of the element with all the chemical properties of the element an old and new idea Greeks Discontinuists Democritus Continuists Aristotle Discontinuists
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4)
 Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
In many ways, Dalton's ideas are still useful today. For example, they help us to understand elements, compounds, and molecules.
 History of the Atom Name: Reading excerpt from Absorb Chemistry for GCSE by Lawrie Ryan http://www.absorblearning.com/chemistry/demo/units/lr301.html Introduction Our understanding of the physical world
History of the Atom Name: Reading excerpt from Absorb Chemistry for GCSE by Lawrie Ryan http://www.absorblearning.com/chemistry/demo/units/lr301.html Introduction Our understanding of the physical world
From Last Time Pearson Education, Inc.
 From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation
 The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff. The Bohr Atom. The Bohr Atom Model of Hydrogen atom. Bohr Atom. Bohr Atom
 Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Scientist wanted to understand how the atom looked. It was known that matter was neutral. It was known that matter had mass
 Atom Models Scientist wanted to understand how the atom looked It was known that matter was neutral It was known that matter had mass They used these ideas to come up with their models, however science
Atom Models Scientist wanted to understand how the atom looked It was known that matter was neutral It was known that matter had mass They used these ideas to come up with their models, however science
BEGINNING OF ATOMIC THEORY
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Development of the Atomic Theory THE BEGINNING OF ATOMIC THEORY 1. What does the word atom mean? a. dividable b. invisible c. hard particles d. not able to
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Development of the Atomic Theory THE BEGINNING OF ATOMIC THEORY 1. What does the word atom mean? a. dividable b. invisible c. hard particles d. not able to
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
4/14/2013 ATOMIC STRUCTURE THE ATOMIC MODEL
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE R E G E N T S C H E M I S T R Y M R S. T I L A R O HISTORY OF THE ATOM O L D A N D M O D E R N A T O M THE ATOMIC MODEL Model of the atom is based on indirect experimental data. Model
ATOMIC STRUCTURE R E G E N T S C H E M I S T R Y M R S. T I L A R O HISTORY OF THE ATOM O L D A N D M O D E R N A T O M THE ATOMIC MODEL Model of the atom is based on indirect experimental data. Model
Atomic Structure. ppst.com
 Atomic Structure ppst.com Defining the Atom The Greek philosopher (460 B.C. 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word ) He believed that atoms were and His ideas
Atomic Structure ppst.com Defining the Atom The Greek philosopher (460 B.C. 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word ) He believed that atoms were and His ideas
AnswerIT! Atoms and isotopes. Structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes Development of the model of the atom.
 AnswerIT! Atoms and isotopes Structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes Development of the model of the atom. Atoms and isotopes - AnswerIT 1. The diameter of an atom is about 0.000 000
AnswerIT! Atoms and isotopes Structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes Development of the model of the atom. Atoms and isotopes - AnswerIT 1. The diameter of an atom is about 0.000 000
The idea of an atom began about 400 B.C. with many Greek philosophers, like Democritus, working to figure out what everything was made of.
 The idea of an atom began about 400 B.C. with many Greek philosophers, like Democritus, working to figure out what everything was made of. Always move & join together Atomas means indivisible I m Aristotle
The idea of an atom began about 400 B.C. with many Greek philosophers, like Democritus, working to figure out what everything was made of. Always move & join together Atomas means indivisible I m Aristotle
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-1 THE ATOM AND ITS NUCLEUS IB Assessment Statements Topic 7.1, The Atom 7.1.1. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-1 THE ATOM AND ITS NUCLEUS IB Assessment Statements Topic 7.1, The Atom 7.1.1. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 *KEY* *KEY* UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY *KEY* *KEY* VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited
*KEY* *KEY* UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY *KEY* *KEY* VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited
Where it came from and what we know now
 Where it came from and what we know now History of the Atom The first mention of the atom came from Democritus in ancient Greece He suggested that the universe was made up of small, indivisible units called
Where it came from and what we know now History of the Atom The first mention of the atom came from Democritus in ancient Greece He suggested that the universe was made up of small, indivisible units called
The Story of the Atom. A history of atomic theory over many years
 The Story of the Atom A history of atomic theory over many years Democritus Many years ago, between 460BC and 370BC the Greek philosophers wondered what we were made of. Leucippus and Democritus came up
The Story of the Atom A history of atomic theory over many years Democritus Many years ago, between 460BC and 370BC the Greek philosophers wondered what we were made of. Leucippus and Democritus came up
Mass number i. Example U (uranium 235) and U (uranium 238) atomic number e. Average atomic mass weighted of the isotopes of that element i.
 CP NT Ch. 4&25 I. Atomic Theory and Structure of the Atom a. Democritus all matter consists of very small, indivisible particles, which he named i. Atom smallest particle of an element that retains all
CP NT Ch. 4&25 I. Atomic Theory and Structure of the Atom a. Democritus all matter consists of very small, indivisible particles, which he named i. Atom smallest particle of an element that retains all
Honors Ch3 and Ch4. Atomic History and the Atom
 Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
Chapter 6. Atoms and Starlight
 Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Name Chemistry-PAP Per. Notes: Atomic Structure
 Name Chemistry-PAP Per. I. Historical Development of the Atomic Model Ancient Greek Model Notes: Atomic Structure Democritus (460-370 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher credited with the first particle
Name Chemistry-PAP Per. I. Historical Development of the Atomic Model Ancient Greek Model Notes: Atomic Structure Democritus (460-370 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher credited with the first particle
3. Particle nature of matter
 3. Particle nature of matter 3.1 atomic nature of matter Democrit(us) 470-380 B.C.: there is only atoms and empty space, everything else is mere opinion (atoms are indivisible) Dalton (chemist) 180: chemical
3. Particle nature of matter 3.1 atomic nature of matter Democrit(us) 470-380 B.C.: there is only atoms and empty space, everything else is mere opinion (atoms are indivisible) Dalton (chemist) 180: chemical
The Nature of Light. Chapter Five
 The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
