Rearrangement: a single reactant rearranges its
|
|
|
- Samuel Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical reactivity. First, reactions can be organized by what kindsof reactions occur. Then, we can study howthose reactions occur. Bothneed to happen in order to fully understand organic chemistry. Four general types of organic reactions: 1. Addition 2. Elimination 3. Substitution 4. Rearrangement Addition: combination of two molecules into one. Elimination: one molecule splits into two. Substitution:two molecules exchange parts to give two new products. 4. Rearrangement: a single reactant rearranges its atoms to give an isomeric product. ch5 Page 1 ch5 Page 2
2 5.2 How organic reactions occur: Mechanisms In a clock, we see the hands move but the mechanism behind the face is what causes the movement. In an organic reaction, we see the transformation that has occurred. The mechanismdescribes the steps that cause the changes we observe. Mechanismsfor organic reactions are the series of steps in a reaction sequence from reactant to product Bond-making or bond-breaking Steps can occur one at a time or at the same time (concerted) Bond formation or breakage can be symmetrical or unsymmetrical. 5.3 Radical reactions Radical: highly reactive molecule or atom with an odd number of electrons (usually 7) in its valence shell (instead of the stable octet). Some example radicals: Fishhook arrowshows the movement of only one electron. Homolytic: symmetrical -electrons move one at a time - radical reactions Heterolytic: unsymmetrical -electrons move as a pair - polar reactions Radical substitution: Rad + A : B Radical addition: Rad + ch5 Page 3 ch5 Page 4
3 Steps in radical substitution There are three types of steps in a radical substitution reaction: 5.4 Polar reactions Differences in electronegativities make electron-rich and electron-poor regions in any polar molecule. 1. Initiation: homolytic formation of two reactive species with unpaired electrons -often initiated by light (hν) 2. Propagation: reaction of radical with molecul3e to make a new radical. Bond polarity can be increased by acid-base reactions: 3. Termination: combination of two radicals to form a stable product. Even though electronegativities are similar between C-S and C-I, these bonds are polar because the electrons in the large S and I atoms are polarizable-they can easily respond to other nearby charges. ch5 Page 5 ch5 Page 6
4 Nucleophiles and electrophiles Nucleophiles and electrophiles Because unlike charges attract, electron-rich sites seek out and react with electron-poor sites. Nucleophile: electron-rich (-or δ-) atom that seeks out an electron-poor atom (nucleus-loving) -Must have lone pair of electrons! Nucleophiles are Lewis bases. Electrophile: electron-poor (+ or δ+) atom that receives electrons from a nucleophile (electron-loving) Electrophiles are Lewis acids. When drawing a mechanism, a curved doubleheaded arrow is used to show the movement of a pair of electrons, from nucleophile to electrophile (Never the other way around!!) When the electrophile is an H, it's an acid-base reaction! CH 3 O - + H 3 O + ch5 Page 7 ch5 Page 8
5 5.5 Addition of HBr to ethylene Finding the nucleophile and electrophile is the key to almost every organic reaction. Let's start with a simple addition reaction. Mechanism of addition of HBr to ethylene The mechanism of this reaction happens in two steps: 1. The πelectrons from the nucleophilic double bond attack the electrophilic hydrogen on HBr, forming a new C-H σbond. Ethylene contains an electron-rich π bond The pair of electrons can act as a nucleophile when there is a strong acid present. HBris a strong acid and contains an electron-poor H. The δ+ H acts as a strong attractor for electrons from another molecule. The H is the electrophile in this reaction. 2. This leaves the other carbon (formerly of the πbond) with only 6 electrons and an empty p orbital -a positively charged carbocation. Simultaneously, two electrons from the H-Br σbond move onto bromine, making a bromide ion. The bromide ion donates an electron pair to the + carbocation, forming a C-Br σbond and yielding the neutral addition product. ch5 Page 9 ch5 Page 10
6 5.6 Using curved arrows in polar reaction mechanisms Using curved arrows in polar reaction mechanisms Practice and the knowledge of a few rules will help you draw correct curved arrows for reaction mechanisms. 1. Electrons always move froma nucleophile (Nu: or Nu: - ) toan electrophile (E or E + ). Always start with an electron pair! Electrons usually flow from one of these nucleophiles: 3. The electrophile can be either positively charged or neutral. i. Positive electrophiles become neutral products. ii. Neutral electrophiles become negative products. Electrons usually flow to one of these electrophiles: 4. Never exceed a first-or second-row atom's octet. Carbon never makes more than four bonds! Hydrogen never makes more than one bond! 2. The nucleophile can be either negatively charged or neutral. i. Negative nucleophiles become neutral products. ii. Neutral nucleophiles become positive products. ch5 Page 11 ch5 Page 12
7 5.7 Equilibria, rates, and energy changes Reactions can move either forward or reverse to reach equilibrium. Recall from general chemistry that the equilibrium constant, K eq, is the ratio of product concentrations over reactant concentrations (each raised to the power of the balancing coefficient) For aa + bb cc + dd, For the reaction we just studied, there is a very large equilibrium constant. K eq > 1000 means the reaction goes to completion -the amount of unreacted starting material will usually be undetectable. (The product concentration is 1000x the reactant concentration at equilibrium) Free energy and equilibrium In order for a reaction to proceed to completion, the products must be lower in potential energy than the reactants. (Reactive high-energy molecules lose energy until they become more stable low-energy molecules.) This change of potential energy during a reaction is called the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG). For K eq > 1, ΔG o must be negative (the system releases energy to become more stable). This is a spontaneous process. For K eq < 1, ΔG o must be positive (the system would have to gain potential energy and become less stable in order to proceed as written) ΔGis influenced by two energetic properties: enthalpy and entropy. ΔG = ΔH -TΔS Enthalpy change (ΔH)is related to the strength of bonds that are broken and formed. A favorable enthalpy change will have stronger (more stable) bonds in the product. Entropy change (ΔS)is related to freedom of motion and dispersion of energy. Elimination: A B + C: favorable entropy change Addition: A + B C: unfavorable entropy change ch5 Page 13 ch5 Page 14
8 5.8 Bond dissociation energies Whenever a bond is formed, energy is released (like the sound made when two magnets hit each other). 5.9 Energy diagrams and transition states In the reaction of HBr and ethylene, the first step is formation of the carbocation. Whenever a bond is broken, energy is absorbed (like the force required for you to pull two magnets apart). Bond dissociation energy (D): amount of energy required to break a bond to produce two radical fragments: This energy is mostly dependent of the type of bond, not the molecule that the bond is in. The highest energy, most unstable point in one step of a reaction is called the transition state. The transition state occurs when the C-H bond is partially formed and the H-Br bond is partially broken. Among the weakest bonds are those that can readily produce radicals: Cl-Cl 242 kj/mol Br-Br 194 HO-OH 211 σbonds become stronger the more scharacter they have CH 3 -H 439 kj/mol H 2 C=CH-H 464 HC C-H 558 ch5 Page 15 ch5 Page 16
9 Activation energy and free energy The energy needed to go from reactant to transition state is the activation energy (ΔG ). Kinetics vs. equilibrium Activation energy determines kinetics. Gibbs free energy change determines equilibrium. The size of the activation energydetermines the rate of the reaction (whether it will occur quickly or slowly). A high ΔG means very few of the molecules in the sample will have enough energy to reach the transition state and the reaction will be slow. A low ΔG means most of the molecules will already have enough energy to reach the transition state and the reaction will be fastat room temperature. The energy difference between the reactant and the product is the standard free energy difference, ΔG o -as we saw before, this determines what the equilibrium constant will be. A reaction with a very high activation energy may never reach its equilibrium mixture of products because it is too slow! (The combustion of gasoline has a large equilibrium constant -the products are favored energetically -but at room temperature, the reaction is too slow to observe.) Solution: heat the reaction so more molecules have enough energy to reach the transition state Solution: use a catalyst so there is a series of different, lower-energy transition states. ch5 Page 17 ch5 Page 18
10 5.10 Intermediates An intermediate is the product of one step of the reaction, and reactant of the next step. In the complete energy diagram, intermediates are minima in the curve, while transition states are maxima in the curve. Catalysts and enzymes make reactions faster by changing the mechanism to have several lower-energy transition states ch5 Page 19
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
10/26/2010. An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene. to Ethylene
 6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes
 Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Nucleophile. Reaction Intermediate. Introduction to Reaction mechanisms. Definitions 2/25/2012
 Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
2/28/2011. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
Classification of Reactions by:
 lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.4 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - Organic Reactions I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. cleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a chemical
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. cleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a chemical
10/6/2010. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: Acids and Bases
 There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2,
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #12 Thurs., Oct.13, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6 How alkenes react: curved arrows to show
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms
 hapter 6 hemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms hemical Reactivity Enthalpy A simple chemical reaction can be broken down into bond creating and bond breaking components: A-B + Y-Z A-Y + B-Z A-B A
hapter 6 hemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms hemical Reactivity Enthalpy A simple chemical reaction can be broken down into bond creating and bond breaking components: A-B + Y-Z A-Y + B-Z A-B A
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases
 BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
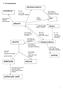 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases"
 Chapter 3 Acids and Bases BrØnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton Acids and Bases Reactions of BrØnsted-Lowry Acids
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases BrØnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton Acids and Bases Reactions of BrØnsted-Lowry Acids
Chemical Kinetics. Goal. Objectives
 4 Chemical Kinetics To understand the physical Goal factors that determine reaction rates. bjectives After this chapter, you should be able to: describe the factors that determine reaction rates. identify
4 Chemical Kinetics To understand the physical Goal factors that determine reaction rates. bjectives After this chapter, you should be able to: describe the factors that determine reaction rates. identify
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 3 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What is the major product of the following reaction?
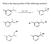 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Chapter 2 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.8 - HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION AND RADICALS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
dihalogenoalkane H 2, KOH alcoholic heat under reflux Elimination PCl 5, PBr 3, PI 3 Heat under reflux substitution KOH aqueous heat under reflux
 7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7/19/2011. Models of Solution. State of Equilibrium. State of Equilibrium Chemical Reaction
 Models of Solution Chemistry- I State of Equilibrium A covered cup of coffee will not be colder than or warmer than the room temperature Heat is defined as a form of energy that flows from a high temperature
Models of Solution Chemistry- I State of Equilibrium A covered cup of coffee will not be colder than or warmer than the room temperature Heat is defined as a form of energy that flows from a high temperature
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation
 Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation Eric J. Kantorows ki California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 3 Overview 3.1 Lewis
Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation Eric J. Kantorows ki California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 3 Overview 3.1 Lewis
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - Organic Reactions I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
The Electrophile. S N 2 and E2 least stable most stable least hindered most hindered. S N 1 and E1. > x > >
 The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Organic Chemistry. Organic Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Basic chemistry for general biology. Electrons and orbitals, and how bonds make happy atoms
 Basic chemistry for general biology Electrons and orbitals, and how bonds make happy atoms A review (I hope) Atoms are composed of three elementary particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons Protons (H+)
Basic chemistry for general biology Electrons and orbitals, and how bonds make happy atoms A review (I hope) Atoms are composed of three elementary particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons Protons (H+)
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
1. In most stable molecules, all the atoms will have filled valence shells. Vigabatrin -
 Your goal should be to understand, not memorize, the material presented in your organic chemistry course. The following principles should be learned as you begin your study of organic chemistry, then used
Your goal should be to understand, not memorize, the material presented in your organic chemistry course. The following principles should be learned as you begin your study of organic chemistry, then used
Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7
 Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds.
 Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
GENERAL BONDING REVIEW
 GENERAL BONDING REVIEW Chapter 8 November 2, 2016 Questions to Consider 1. What is meant by the term chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? 3. How do atoms bond with each
GENERAL BONDING REVIEW Chapter 8 November 2, 2016 Questions to Consider 1. What is meant by the term chemical bond? 2. Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? 3. How do atoms bond with each
Enduring Understandings & Essential Knowledge for AP Chemistry
 Enduring Understandings & Essential Knowledge for AP Chemistry Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements
Enduring Understandings & Essential Knowledge for AP Chemistry Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements
Chapter 9. Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination
 Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds
 Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds Kinds of chemical bonds: 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic Useful guideline: Octet rule Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share e - to achieve
Chpt 8 Chemical Bonding Forces holding atoms together = Chemical Bonds Kinds of chemical bonds: 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic Useful guideline: Octet rule Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share e - to achieve
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
Collision Theory. Unit 12: Chapter 18. Reaction Rates. Activation Energy. Reversible Reactions. Reversible Reactions. Reaction Rates and Equilibrium
 Collision Theory For reactions to occur collisions between particles must have Unit 12: Chapter 18 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium the proper orientation enough kinetic energy See Both In Action 1 2 Activation
Collision Theory For reactions to occur collisions between particles must have Unit 12: Chapter 18 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium the proper orientation enough kinetic energy See Both In Action 1 2 Activation
Two atoms share electrons to make a covalent bond. The differenceof the electronegativites of those two atoms determines how polar that bond is.
 Chapter 2: Polar covalent bonds; Acids and bases The reactivity of organic compounds is often defined by the polarities of the covalent bonds in the molecule. Polar covalent bonds: an intermediate between
Chapter 2: Polar covalent bonds; Acids and bases The reactivity of organic compounds is often defined by the polarities of the covalent bonds in the molecule. Polar covalent bonds: an intermediate between
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Introduction to Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry Unit. Definition. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology 07/04/2016. Chemistry 30
 Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Kinetics. 1. Consider the following reaction: 3 A 2 B How is the average rate of appearance of B related to the average rate of disappearance of A?
 Kinetics 1. Consider the following reaction: 3 A 2 B How is the average rate of appearance of B related to the average rate of disappearance of A? A. [A]/ t = [B]/ t B. [A]/ t = (2/3)( [B]/ t) C. [A]/
Kinetics 1. Consider the following reaction: 3 A 2 B How is the average rate of appearance of B related to the average rate of disappearance of A? A. [A]/ t = [B]/ t B. [A]/ t = (2/3)( [B]/ t) C. [A]/
Organic Chemistry. Radical Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic
 Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3
 Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A
 An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux
 Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux Objectives 1. Identify structural features (pi bonds, bond polarity, lone pairs) of a compound 2. Determine whether a structural
Lab Activity 9: Introduction to Organic Chemical Reactivity, Lab 5 Prelab, Reflux Objectives 1. Identify structural features (pi bonds, bond polarity, lone pairs) of a compound 2. Determine whether a structural
Chapter Seven. Chemical Reactions: Energy, Rates, and Equilibrium
 Chapter Seven Chemical Reactions: Energy, Rates, and Equilibrium Endothermic vs. Exothermic 2 Endothermic: A process or reaction that absorbs heat and has a positive ΔH. Exothermic: A process or reaction
Chapter Seven Chemical Reactions: Energy, Rates, and Equilibrium Endothermic vs. Exothermic 2 Endothermic: A process or reaction that absorbs heat and has a positive ΔH. Exothermic: A process or reaction
Basics of Thermodynamics: Easy learning by Dr. Anjana Sen
 Basics of Thermodynamics: Easy learning by Dr. Anjana Sen Part 1: Theory and concept Part 2: Definitions and equations Part 3: Laws of Thermodynamics Part 1: theory and concept Thermodynamics means conversion
Basics of Thermodynamics: Easy learning by Dr. Anjana Sen Part 1: Theory and concept Part 2: Definitions and equations Part 3: Laws of Thermodynamics Part 1: theory and concept Thermodynamics means conversion
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
Reaction mechanisms offer us insights into how reactions work / how molecules react with one another.
 Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
QUESTIONSHEET 1. ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION I (Nitration)
 TOPI4 ASWERS & MARK SEMES QUESTIOSEET 1 ELETROPILI SUBSTITUTIO I (itration) a) πelectrons in arenes are delocalised electrophiles are less strongly attracted b) (i) O2 O 3 2 O (ii) oncentrated sulfuric
TOPI4 ASWERS & MARK SEMES QUESTIOSEET 1 ELETROPILI SUBSTITUTIO I (itration) a) πelectrons in arenes are delocalised electrophiles are less strongly attracted b) (i) O2 O 3 2 O (ii) oncentrated sulfuric
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008
 CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding. Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds What is a molecule? A molecular compound? A molecule is a neutral group of atoms joined together by covalent bonds A molecular compound is
Chapter 8 : Covalent Bonding Section 8.1: Molecular Compounds What is a molecule? A molecular compound? A molecule is a neutral group of atoms joined together by covalent bonds A molecular compound is
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination
 Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Chapter 8 Covalent Boding Molecules & Molecular Compounds In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases exist as atoms. They are monatomic; monatomic they consist of single atoms. Hydrogen chloride
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16 1980 - #7 (a) State the physical significance of entropy. Entropy (S) is a measure of randomness or disorder in a system. (b) From each of
Name AP CHEM / / Collected AP Exam Essay Answers for Chapter 16 1980 - #7 (a) State the physical significance of entropy. Entropy (S) is a measure of randomness or disorder in a system. (b) From each of
Some Arrow-Pushing Guidelines (Section 1.14) 1. Arrows follow electron movement.
 Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 1 Notes 1 Note: The headers and associated chapters don t actually jive with the textbook we are using this summer. But otherwise this highlights a lot of the chemistry from Organic
Chapter Nine. Chapter Nine. Chemical Bonds: A Preview. Chemical Bonds. Electrostatic Attractions and Repulsions. Energy of Interaction
 1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
Section 6.2 1/13/2014. Most Chemical Compounds. Molecular (or Covalent) Compound. Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
 Section 6.2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Most Chemical Compounds Are molecules, a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. It is a single unit capable of existing on
Section 6.2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Most Chemical Compounds Are molecules, a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. It is a single unit capable of existing on
Outline for Today. Monday, Nov. 12. Wednesday Friday. Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding. Bond Enthalpies. Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding
 Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1. Oxidative Addition
 Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds
 Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
