Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3
|
|
|
- Sheena Parsons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules would not be a product of one of the propagation steps involved in free-radical halogenation? 3. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 4. On the basis of your knowledge of the reaction of halogens with alkanes, decide which product you would not expect to be formed in even small quantities in the bromination of ethane? A. BrCH 2 CH 2 Br B. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Br C. CH 3 CHBr 2 D. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 E. BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 Br
2 5. Consider the following tertiary carbon radical. What orbital does the radical (single unpaired electron) occupy? A. s orbital B. sp 2 orbital C. sp 3 orbital D. p orbital E. sp orbital 6. What is the major product of the following reaction? 7. Which of the following is not a chain termination step in free-radical halogenation? A. B. E. 8. Which of the following reactions would be classified as a propagation? A. B. E. All of these are involved in the propagation. 9. Predict the major product of the following reaction.
3 The reaction does not take place. 10. Which of the following molecules has six tertiary hydrogen atoms? A. B. C. D. E. 11. What is the major product of the following reaction? 12. Predict the major product of the following reaction.
4 13. Why is it that iodine does not do free-radical halogenations? A. Light cannot homolytically cleave the I I bond as it does for Br 2 and Cl 2. B. The iodine radical is too unreactive to abstract hydrogen atoms from even tertiary carbons. C. Carbon radicals will not abstract an iodine atom from I 2. D. Iodine is far too reactive and typically explodes in the presence of organic compounds. E. Iodine atoms recombine faster than the other halogens and thus terminate the reaction too rapidly. 14. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 15. Consider the result of a free-radical halogenation of an alkane, using the interhalogen compound Br Cl. On the basis of what you know of the mechanism of this type of halogenation, decide which of the following statements would be true of the process? (Assume that Br Cl cannot disproportionate to Br 2 and Cl 2 under the reaction conditions.) A. Halogenation would occur and create a carbon-chlorine bond with the selectivity typically observed for chlorination. B. Halogenation would occur and create a carbon-chlorine bond with the selectivity typically observed for bromination. C. Halogenation would occur to create a carbon-bromine bond with the selectivity typically observed for chlorination. D. Halogenation would occur to create a carbon-bromine bond with the selectivity typically observed for bromination. E. Roughly equal amounts of bromination and chlorination would occur, with a selectivity intermediate between the two. 16. The product of free-radical halo-genation reactions is an alkyl halide. The major amount of this halide forms during the second step of propagation. However, you should be aware that one possible termination step also forms alkyl halides. Why does the majority of the alkyl halide product come from the propagation step and not the termination step?
5 A. At any given time during the reaction, the concentration of both the alkyl radical and the halide radical is high enough that they can readily come together to form alkyl halides during propagation. B. At any given time during the reaction, the concentration of both the alkyl radical and the halide radical is so low that the chance of each of them finding the other to form alkyl halides during a termination step is very small. C. The initiation step converts 100% of the halogen to halide radicals through a light- or heatinduced homolytic bond cleavage. This step ensures that there is always a high concentration of halide radical present for reactivity in a propagation step. D. The second step of propagation (combination of an alkyl radical with a halide radical) is highly endothermic and therefore takes place very rapidly. E. Once the alkyl halide forms during a termination step, the carbon-halogen bond is broken in a homolytic fashion and the newly generated carbon radical goes back into a propagation step for further reactivity. 17. Predict the major product of the following reaction. A. B. C. D. E. 18. When we use the word "mechanism" in describing a chemical reaction, what does this word refer to? A. A mechanism provides insight into electron movement and bonding that takes place during a chemical transformation. B. A mechanism provides a useful means of predicting the product(s) of chemical reactions. C. A mechanism provides unequivocal proof of the given pathway (in terms of electron movement and bonding) that a reaction follows. D. Both A and B are correct. E. Both B and C are correct.
6 19. Predict the major product of the following reaction. The reaction does not take place. 20. The reaction of methane with I 2 in the presence of heat or light does not result in the formation of methyl iodide. The most accurate reason for this is described by which of the following statements? A. The dissociation energy for I 2 is sufficiently high (36 kcal/mol) to ensure that iodine radical (I ) is not able to form by a homolytic cleavage of I 2. B. A very high energy of activation is required for the abstraction of a hydrogen atom by the iodine radical (I ). This energy is sufficiently high to make this step thermodynamically unfavorable. C. The reaction of I with a C!H bond is extremely exothermic and therefore does not take place. D. The reaction of I with a C!H bond generates sufficient energy to cause an explosion, thereby destroying any of the methyl iodide that is formed. E. The second step of propagation (reaction of CH 3 with I 2 ) does not take place. Therefore, methyl iodide is not formed.
CHEM 241 ALCOHOLS AND ALKYL HALIDES CHAP 5 ASSIGN
 CEM 241 ALCOOLS AND ALKYL ALIDES CAP 5 ASSIGN 1. What is the IUPAC name of the compound below? A. 3-isobutyl-2-hexanol B. 2-methyl-5-propyl-6-heptanol C. 2-methyl-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)octane D. 6-methyl-3-propyl-2-heptanol
CEM 241 ALCOOLS AND ALKYL ALIDES CAP 5 ASSIGN 1. What is the IUPAC name of the compound below? A. 3-isobutyl-2-hexanol B. 2-methyl-5-propyl-6-heptanol C. 2-methyl-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)octane D. 6-methyl-3-propyl-2-heptanol
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A
 An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Organic Chemistry. Radical Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.8 - HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION AND RADICALS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
What is the major product of the following reaction?
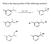 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
CHEM Lecture 6
 EM 494 Special Topics in hemistry Illinois at hicago EM 494 - Lecture 6 Prof. Duncan Wardrop October 15, 2012 Midterm Papers Factors that ontrol ydrocarbon Acidity Factors that ontrol ydrocarbon onformation
EM 494 Special Topics in hemistry Illinois at hicago EM 494 - Lecture 6 Prof. Duncan Wardrop October 15, 2012 Midterm Papers Factors that ontrol ydrocarbon Acidity Factors that ontrol ydrocarbon onformation
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
The Simplest Alkanes. Physical Properties 2/16/2012. Butanes are still gases. bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 n-pentane.
 The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Chapter 20. Mass Spectroscopy
 Chapter 20 Mass Spectroscopy Mass Spectrometry (MS) Mass spectrometry is a technique used for measuring the molecular weight and determining the molecular formula of an organic compound. Mass Spectrometry
Chapter 20 Mass Spectroscopy Mass Spectrometry (MS) Mass spectrometry is a technique used for measuring the molecular weight and determining the molecular formula of an organic compound. Mass Spectrometry
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
Introduction to Alkanes
 Introduction to Alkanes Alkanes do not react with most reagents for two reasons. First, carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds are very strong due to good orbital overlap. Second, the carbon-hydrogen
Introduction to Alkanes Alkanes do not react with most reagents for two reasons. First, carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds are very strong due to good orbital overlap. Second, the carbon-hydrogen
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2
 Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2 Key Terms For Unit 3 Free Radical Chain Reaction Homolytic Cleavage Free Radical Initiation Propagation
Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2 Key Terms For Unit 3 Free Radical Chain Reaction Homolytic Cleavage Free Radical Initiation Propagation
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic
 Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Organic Chemistry. for Students of Medicine and Biology 大学化学 III 和大学化学 III(2)
 Organic Chemistry for Students of Medicine and Biology 大学化学 III 和大学化学 III(2) March 4, 2015 Refining of petroleum, a major natural source of alkanes Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes ( 烷烃和环烷烃 ) March 3,
Organic Chemistry for Students of Medicine and Biology 大学化学 III 和大学化学 III(2) March 4, 2015 Refining of petroleum, a major natural source of alkanes Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes ( 烷烃和环烷烃 ) March 3,
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Alkyl alides: Their Synthesis by alogenation of Alkanes and Their Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions. Friday, ctober
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Alkyl alides: Their Synthesis by alogenation of Alkanes and Their Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions. Friday, ctober
THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
The C-X bond gets longerand weakergoing down the periodic table.
 Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
1. When methane is photochlorinated a small amount of ethane is found in the product. Give a full mechanism to account for presence of the ethane.
 Chemistry 51 DS Quiz 2 1. When methane is photochlorinated a small amount of ethane is found in the product. Give a full mechanism to account for presence of the ethane. 2. When 2,3-dimethylbutane is monochlorinated
Chemistry 51 DS Quiz 2 1. When methane is photochlorinated a small amount of ethane is found in the product. Give a full mechanism to account for presence of the ethane. 2. When 2,3-dimethylbutane is monochlorinated
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions
 Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Identify the condition that causes a bond in CCl 4 to break in the upper atmosphere. Deduce an equation for the formation of the reactive species.
 Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Mass Spectroscopy. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Mass Spectroscopy Dr. Sapna Gupta What is Mass Spectroscopy It is an analytical technique for measuring the mass-tocharge ratio (m/z) of ions in the gas phase. Mass spectrometry is our most valuable analytical
Mass Spectroscopy Dr. Sapna Gupta What is Mass Spectroscopy It is an analytical technique for measuring the mass-tocharge ratio (m/z) of ions in the gas phase. Mass spectrometry is our most valuable analytical
Straight. C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized. Butane, C 4 H 10 H 3 C
 Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Ch.10 Alkyl Halides. Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides.
 Ch.10 Alkyl alides Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides. F F C C F Trichloroethylene (a solvent) alothane (an inhaled anesthetic)
Ch.10 Alkyl alides Organic halides are valuable as industrial solvents, inhaled anesthetics in medicine, refrigerants, and pesticides. F F C C F Trichloroethylene (a solvent) alothane (an inhaled anesthetic)
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2018
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Chapter 04 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides part 01
 hapter 04 Alcohols and Alkyl alides part 01 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook Functional Groups A functional group is a structural feature in a molecule that has characteristic reactivity. A functional
hapter 04 Alcohols and Alkyl alides part 01 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook Functional Groups A functional group is a structural feature in a molecule that has characteristic reactivity. A functional
Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7
 Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Sevada Chamras, Ph.D. Glendale Community College Chemistry 105 Exam. 3 Lecture Notes Chapters 6 & 7 Description: Examples: 3 Major Types of Organic Halides: 1. Alkyl Halides: Chapter 6 (Part 1/2) : Alkyl
Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light. This is the overall reaction, but a more complex mixture of products is actually formed
 8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
10/6/2010. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions Organic chemical reactions
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
Please hand your completed booklet to your Chemistry tutor when you begin A Level Chemistry in September
 #THIS I S TH E P L AC E A-LEVEL CHEMSITRY NAME: You should complete this work ready for starting Year 1 A Level Chemistry. If there are any questions that you cannot do, even after using your GCSE notes
#THIS I S TH E P L AC E A-LEVEL CHEMSITRY NAME: You should complete this work ready for starting Year 1 A Level Chemistry. If there are any questions that you cannot do, even after using your GCSE notes
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Chemistry 125 First Semester Final Examination Name
 Chemistry 125 First Semester Final Examination Name December 15, 1999 The exam budgets 150 minutes, but you may have 180 minutes to finish it. Good answers can fit in the space provided. 1. (36 minutes)
Chemistry 125 First Semester Final Examination Name December 15, 1999 The exam budgets 150 minutes, but you may have 180 minutes to finish it. Good answers can fit in the space provided. 1. (36 minutes)
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry. Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School
 Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds.
 This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
10-bromo-1-methyl-1-cyclodecene *** 7. (E)-1-bromo-2-chloro-3-methyl-2-pentene. will accept trans *** 8. (E)-2,4,8-trimethyl-4-nonene
 10-bromo-1-methyl-1-cyclodecene *** 7. (E)-1-bromo-2-chloro-3-methyl-2-pentene will accept trans *** 8. (E)-2,4,8-trimethyl-4-nonene will accept trans B. Determine whether the following pairs of structures
10-bromo-1-methyl-1-cyclodecene *** 7. (E)-1-bromo-2-chloro-3-methyl-2-pentene will accept trans *** 8. (E)-2,4,8-trimethyl-4-nonene will accept trans B. Determine whether the following pairs of structures
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Classification of Reactions by:
 lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
Nucleophile. Reaction Intermediate. Introduction to Reaction mechanisms. Definitions 2/25/2012
 Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 7-1. Alkyl Halides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide? An
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 7-1. Alkyl Halides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide? An
α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical
 C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
Allyl radicals are especially stable due to resonance ( and double bond switch places):
 Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no C=C double bonds, C and H atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending.
 Alkanes Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no = double bonds, and atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending. The alkanes have similar chemistry to one another because they
Alkanes Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no = double bonds, and atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending. The alkanes have similar chemistry to one another because they
Worksheet Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval.
 CH 334 Form A First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
CH 334 Form A First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
CHEM 163 MIDTERM October 23, 2001 Dr. John C. Vederas
 CHEM 163 MIDTERM October 23, 2001 Dr. John C. Vederas I. Structure and Nomenclature - 56 Points - A. Draw structures for which names are given, or name the given structures by any correct (systematic or
CHEM 163 MIDTERM October 23, 2001 Dr. John C. Vederas I. Structure and Nomenclature - 56 Points - A. Draw structures for which names are given, or name the given structures by any correct (systematic or
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
Monday /3/2017. (Lecture No. 3-4 : Alkanes )
 Babylon University / Pharmacy Collage Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry Monday.. 13-16/3/2017 (Lecture No. 3-4 : Alkanes ) Classification by structure: the family The basis of organic chemistry, we
Babylon University / Pharmacy Collage Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry Monday.. 13-16/3/2017 (Lecture No. 3-4 : Alkanes ) Classification by structure: the family The basis of organic chemistry, we
CHEM Exam 2 October 25, 2007
 CEM 3311-200 Exam 2 October 25, 2007 By printing my name below, I pledge that "On my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on
CEM 3311-200 Exam 2 October 25, 2007 By printing my name below, I pledge that "On my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on
These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds.
 These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds. C n H 2n+2 The part of an Alkane obtained after the removing the one
These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds. C n H 2n+2 The part of an Alkane obtained after the removing the one
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Rearrangement: a single reactant rearranges its
 Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes
 Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes Types of Steps in Reac)on Mechanisms Bond forma)on or breakage can be symmetrical or unsymmetrical Symmetrical- homoly)c Unsymmetrical- heteroly)c Indica)ng Steps in Mechanisms
Radical Reac)ons of Alkanes Types of Steps in Reac)on Mechanisms Bond forma)on or breakage can be symmetrical or unsymmetrical Symmetrical- homoly)c Unsymmetrical- heteroly)c Indica)ng Steps in Mechanisms
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 Practice Questions : Chem 226 / Exam 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about benzene is correct?
Practice Questions : Chem 226 / Exam 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about benzene is correct?
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules
 12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
 Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (1) (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes?
 1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes? (c) Name the alkene below using E-Z nomenclature. H 3 C H C C CH 2
1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes? (c) Name the alkene below using E-Z nomenclature. H 3 C H C C CH 2
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
Electronegativity Scale F > O > Cl, N > Br > C, H
 Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval.
 CH 334 Form B First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
CH 334 Form B First Midterm Exam Monday, October 16, 2017 Name KEY You may use model kits but no other material with chemical information without instructor approval. Please do not use any electronic devices
2/28/2011. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
