A DFT study on the NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,βunsaturated acyl-azoliums. A base catalysed C-C bond-formation step.
|
|
|
- Myles Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A DFT study on the NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,βunsaturated acyl-azoliums. A base catalysed C-C bond-formation step. Supporting Information Luis R. Domingo, a * José A. Sáez b and Manuel Arnó a a Departamento de Química Orgánica, Universidad de Valencia, Dr. Moliner 50, E Burjassot, Valencia, Spain. b Instituto de Tecnología Química UPV-CSIC, Camino de Vera s/n, Valencia, Spain. domingo@utopia.uv.es web: Index SI2 SI4 SI7 SI8 SI8 SI9 Study of the acid and base catalysed conjugated additions of the enol of acetyl acetone 2 to acyl-azolium intermediate 20. Full ELF bonding analysis along the conjugated nucleophilic approach of enol 21 to acyl-azolium 20. Total energies, in gas phase (MPWB1K/6-31G**) and in toluene (MPWB1K/6-311G**), of the stationary points involved in the NHC catalysed reaction of but- 2-ynal 14 with methyl 2-oxopropanoate 15. MPWB1K/6-31+G** total and relative energies, in gas phase and in toluene, of the stationary points involved in the acid and base catalysed conjugated nucleophilic addition of enol 21 to acyl-azolium intermediate 20. MPWB1K/6-31G** total and relative enthalpies, entropies and free energies of the stationary points involved in the C-C bond-formation step. MPWB1K/6-31G** computed total energies, unique imaginary frequency, and cartesian coordinates of the stationary points involved in the NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,β-unsaturated acyl-azoliums.
2 SI2 1. Study of the acid and base catalysed conjugated additions of the enol of acetyl acetone 2 to acyl-azolium intermediate 20. In order to assert the base catalyst role of chloride anion in these NHC catalysed annulation reactions of α,β-unsaturated acyl-azolium intermediates, the C-C bondformation step in the reactions involving acetyl acetone 2 was analysed (see Scheme 2 in the manuscript). Two paths were studied for this step (see Scheme S1): i) path a corresponds to the acid catalysed conjugated addition of enol 28; and ii) path b corresponds to the base catalysed conjugated addition of enol 28 to acyl-azolium intermediate 20. Relative energies, in gas phase and in toluene (single point energies from gas phase geometries), are given in Table S1. O 28 OH O 1 N N N Cl TS acid catalysis TS base catalysis O H O O N N O O N N N O N Cl + HCl Scheme S1. Relative energies in toluene, in kcal/mol, are given in italic. Table S1. Total (E, in au) and relative a ( E, in kcal/mol) energies, in gas phase and in toluene, of the stationary points involved in the conjugated nucleophilic attack of enol 28 on acyl-azolium intermediate 20. Gas phase Toluene MPWB1K/6-31G** MPWB1K/6-311G** E E E E TS TS (a) Relative to 20 plus 28. Along path a, the enol hydrogen of 28 forms a hydrogen bond (HB) with the carbonyl oxygen of acyl-azolium 20, thus activating electrophilically this α,β-
3 SI3 unsaturated acyl-azolium intermediate. The activation energy associated with the conjugated addition of enol 28 to 20, via TS7, is 17.7 kcal/mol; the C-C bondformation step being exothermic by kcal/mol. This activation energy is similar to that found in the conjugated addition of enol 21 to acyl-azolium 20. Along path b, the enol hydrogen of 28 forms a HB with the chloride anion, thus activating nucleophilically enol 28. The activation energy associated with the conjugated addition of enol 28 to 20, via TS8, is 12.3 kcal/mol; the C-C bondformation step being endothermic by 3.7 kcal/mol. Although this activation energy is 6.1 kcal/mol higher than that associated with the conjugated addition of enol 21 to 20, via TS2, TS8 remains 5.4 kcal/mol below TS7, showing that the base catalysed reaction is yet again favoured over the acid catalysed one. The geometries of the transition states (TSs) involved in the acid and base catalysed conjugated additions of enol 28 to acyl-azolium 20 are given in Figure S1. At TS7, associated with the acid catalysed nucleophilic attack of enol 28 on the conjugated C3 carbon of acyl-azolium intermediate 20, the length of the C3-C6 forming bond is Å. At this TS, the length of the O8-H9 bond is Å, while the distance between the acidic H9 hydrogen and the carbonyl O4 oxygen is Å; this short H9- O4 distance points to a strong HB. At TS8, associated with the base catalysed nucleophilic attack of enol 28 on the conjugated C3 carbon of acyl-azolium 20, the length of the C3-C6 forming bond is Å. At this TS, the length of the O8-H9 bond is Å, while the distance between the acidic H9 hydrogen and chloride anion is Å; this short H9-Cl - distance points to a strong HB. These geometrical parameters are similar to those found at TS2. Figure S1. Gas phase geometries of the TSs involved in the acid and base catalysed conjugated additions of enol 28 to acyl-azolium 20.
4 SI4 2. ELF bonding analysis along the conjugated nucleophilic approach of enol 21 to acylazolium 20. In order to understand the C-C bond formation process along the conjugated nucleophilic approach of enol 21 to acyl-azolium 20, a topological ELF analysis along the IRC of the corresponding reaction path was carried out, finding ten phases associated to relevant electron density changes. Each of these phases represent a bonding change along the reaction path. The most relevant ELF valence basins and their corresponding N populations of selected points along the reaction path are given in Table S2. For the sake of simplicity, only the monosynaptic V(A) and the disynaptic V(A,B) basins involved in the forming and breaking bond processes will be discussed. In Phase I, d(c3-c6) Å, the presence of two disynaptic basins at acylazolium 20, namely V(C2,C3) and V'(C2,C3), with a population of 1.71 and 1.63e, together with the presence of two disynaptic basins at enol 21, V(C6,C7) and V'(C6,C7), with a population of 1.79 and 1.71e, which account for the C2=C3 and C6=C7 double bonds, are the most remarkable feature of the reagents. In enol 21, the disynaptic basin V(O8,H9), which integrates 1.98e, suggest the presence of a O-H σ bond. In Phase II, > d(c3-c6) Å, the disynaptic basins V(C2,C3) and V'(C2,C3) of acyl-azolium 20 merge into a new disynaptic basin, namely V(C2,C3), with a population of 3.25e. In Phase III, > d(c3-c6) Å, the disynaptic basins V(C6,C7) and V'(C6,C7) of enol 21 merge into the disynaptic basin V(C6,C7), which integrates 3.30e. It is in Phase IV, > d(c3-c6) Å, where the electron density experiences the first significant change towards the C-C bond formation. Thus, a monosynaptic basin located at C6, V(C6), integrating 0.40e, appears at enol 21. Additionally, a monosynaptic basin, V(C2), integrating 0.30e, appears at the C2 carbon of acyl-azolium 20. Note that the appearance of this V(C2) monosynaptic basin, which has been observed in other ELF analyses of polar reactions, 2 remains until Phase VII. The second most relevant change along the IRC appears in Phase V, > d(c3-c6) Å, with the creation of a new monosynaptic basin at C3, V(C3), integrating 0.17e, while the monosynaptic basin V(C6) increases its electronic integration to 0.45e. Note that monosynaptic basins V(C3) and V(C6) are responsible for the formation of the new C3-C6 single bond in the next phase. Note that TS2 is located in Phase V.
5 SI5 Table S2. Valence basin populations N calculated from the ELF along the ten phases associated with the nucleophilic approach of enol 21 to acyl-azolium 20. d(a-b) stands for the distance between A and B atoms (in angstroms). I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X Phase TS2 d(c3-c6) d(o9-h9) d(cl-h9) V(C1,C2) V(C2,C3) V'(C2,C3) 1.63 V(C1,O4) V(C6,C7) V'(C6,C7) V(C7,O8) V(C2) V(C3) 0.17 V(C6) V(C3,C6) V(O8,H9) V(H9) V(H9,Cl10) Indeed, it is in Phase VI, > d(c3-c6) Å, where the formation of the C3-C6 single bond is initiated with the creation of the new disynaptic basin V(C3,C6), which integrates 0.91e. This disynaptic basin comes from the merging of monosynaptic basins V(C3) and V(C6), which have disappeared at the beginning of this phase. Immediately after the formation of the C3-C6 single bond, in Phase VII, > d(c3- C6) Å, the H9 hydrogen transfer process from the O8 oxygen to the chloride anion starts, d(o8-h9) = Å. From Phase I to Phase VI, the population of the V(O8,H9) disynaptic basin varied from 1.98 to 2.04e. It is in Phase VII where this disynaptic basin disappears and a monosynaptic basin, namely V(H9), with a population of 0.47e, appears at H9. In Phase VIII, > d(c3-c6) Å, the monosynaptic basin V(C2) disappears. In Phase IX, > d(c3-c6) Å, the monosynaptic basin V(H9) disappears to be replaced by the new V(H9,Cl10) disynaptic basin with 1.38e, indicating that the H9-Cl10 single bond-formation takes place. Finally, in Phase X, > d(c3-c6) Å, only the increase of the population of the disynaptic basins V(C3,C6) and V(H9,Cl10) is observed. At the end of this phase, both C3-C6 and H9-Cl10 single bonds have been completely formed.
6 SI6 References 1 (a) L. R. Domingo, P. Pérez, M. J. Aurell, J. A. Sáez, Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, (b) L. R. Domingo, P. Pérez, J. A. Sáez, J. A. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 107.
7 SI7 Table S3. Total energies, in au, in gas phase and in toluene, of the stationary points involved in the NHC catalysed reaction of but-2-ynal 14 with methyl 2-oxopropanoate 15. gas phase Toluene MPWB1K/6-31G** MPWB1K/6-311G** TS Cl TS HCl TS TS TS TS
8 SI8 Table S4. MPWB1K/6-31+G** total (E, in au) and relative a ( E, in kcal/mol) energies, in gas phase and in toluene, of the stationary points involved in the acid and base catalysed conjugated nucleophilic addition of enol 21 to acyl-azolium intermediate 20. Gas phase Toluene E E E E TS TS (a) Relative to 20 plus 21. Table S5. MPWB1K/6-31G** total and relative a enthalpies (H and H), entropies (S and S) free Energies (G and G), computed at 40 C and 1 atm in toluene, of the stationary points involved in the C-C bond-formation step. H H S S G G au kcal/mol cal/mol K cal/mol K au kcal/mol TS TS TS (a) Relative to 20 plus 21.
9 SI9 MPWB1K/6-31G** computed total energies, unique imaginary frequency, and cartesian coordinates of the stationary points involved NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,β-unsaturated acyl-azoliums. 14 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C O C C H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C N N N C C C H H H H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C C C N N N C C C
10 SI10 C C O C H O H H H H H H H H H H H O O H H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C O C C C N N N C C C H H H H H H H H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u.
11 SI11 C C C C C N N N C C C H H H H H H H H H H O H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C O C N C N N C C H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u.
12 SI12 C C C O O C H H H O H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C N N N C C C C C C O C O C H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H O H H H
13 SI HCl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C N N N C C C C C C O C O C H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H O H H H Cl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C C C N N N C C C
14 SI14 C C O C H O H H H H H H H H H H H O O H H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C C C N N N C C C C C O C H O H H H H H H H H H H H
15 SI15 O O H H H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C O O C C N N C C O C C C N C C H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C
16 SI16 C O O C C N N C C O C C C N C C H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C N N N C C C C C C O C O C
17 SI17 H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H O H H H Cl E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C O H H C H H H C O C H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C N N N C C C C
18 SI18 C C O H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl C H H H C O C H H H E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. C C C C N N N C C C C C C O H H O H H H H H H H
19 SI19 H H H H H Cl C H H H C O C H H H TS1 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C O C C C N N N C C C H H H H H H H H H H H TS2 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C N N
20 SI20 N C C C C C C O C O C H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H O H H H Cl TS3 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C C C N N N C C C C C O C H O H H
21 SI21 H H H H H H H H H O O H H H H H TS4 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C C C N N N C C C C C O C H O H H H H H H H H H H H O O H H H H H
22 SI22 TS5 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C O O C C N N C C O C C C N C C H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl TS6 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C N N N
23 SI23 C C C C C C O C O C H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H O H H H Cl TS7 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C N N N C C C C C C O H H O H H H H
24 SI24 H H H H H H H H Cl C H H H C O C H H H TS8 E(RmPW+HF-B95) = a.u. 1 imaginary frequency: cm -1 C C C C N N N C C C C C C O H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H Cl C H H
25 SI25 H C O C H H H
Article A Molecular Electron Density Theory Study of the Reactivity of Azomethine Imine in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions
![Article A Molecular Electron Density Theory Study of the Reactivity of Azomethine Imine in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions Article A Molecular Electron Density Theory Study of the Reactivity of Azomethine Imine in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions](/thumbs/96/128939755.jpg) Article A Molecular Electron Density Theory Study of the Reactivity of Azomethine Imine in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions Luis R. Domingo* and Mar Ríos-Gutiérrez Department of Organic Chemistry, University
Article A Molecular Electron Density Theory Study of the Reactivity of Azomethine Imine in [3+2] Cycloaddition Reactions Luis R. Domingo* and Mar Ríos-Gutiérrez Department of Organic Chemistry, University
Theoretical study of the BF 3-promoted rearrangement of oxiranyl N-methyliminodiacetic acid boronates
 Theoretical study of the BF 3-promoted rearrangement of oxiranyl N-methyliminodiacetic acid boronates Margarita M. Vallejos a* and Silvina C. Pellegrinet b* a Laboratorio de Química Orgánica, IQUIBA-NEA,
Theoretical study of the BF 3-promoted rearrangement of oxiranyl N-methyliminodiacetic acid boronates Margarita M. Vallejos a* and Silvina C. Pellegrinet b* a Laboratorio de Química Orgánica, IQUIBA-NEA,
Conjugate Addition Reactions 2:02 PM
 1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Supporting Information. P,N Ligands. General Information:
 Supporting Information A Dynamic Kinetic C Cross Coupling for the Asymmetric Synthesis of Axially Chiral,N Ligands edro Ramírez-López, Abel Ros, *, Beatriz Estepa, Rosario Fernández, *, Béla Fiser, Enrique
Supporting Information A Dynamic Kinetic C Cross Coupling for the Asymmetric Synthesis of Axially Chiral,N Ligands edro Ramírez-López, Abel Ros, *, Beatriz Estepa, Rosario Fernández, *, Béla Fiser, Enrique
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
O Enolate. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid O B. Enolate. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid. Enolate. O O Enolate
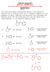 CM 234, Spring 2017 QUIZ #12 ANSWER KEY (hit the RETURN Button to return to the Main Quiz Page) QUESTIN 1 MC34r The following Aldol condensation product was formed by reaction of an enolate anion and a
CM 234, Spring 2017 QUIZ #12 ANSWER KEY (hit the RETURN Button to return to the Main Quiz Page) QUESTIN 1 MC34r The following Aldol condensation product was formed by reaction of an enolate anion and a
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
Catalysts in Petroleum Refining & Petrochemicals
 Iridium homogeneous catalysts following outer-sphere mechanisms Luis A. Oro Departamento de Química Inorgánica, Instituto de Síntesis Química y Catálisis Homogénea, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, 50010-Zaragoza,
Iridium homogeneous catalysts following outer-sphere mechanisms Luis A. Oro Departamento de Química Inorgánica, Instituto de Síntesis Química y Catálisis Homogénea, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, 50010-Zaragoza,
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study.
 Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
Thiourea Derivatives as Brønsted Acid Organocatalysts
 Supporting Information Thiourea Derivatives as Brønsted Acid Organocatalysts Ádám Madarász, Zsolt Dósa, Szilárd Varga, * Tibor Soós, Antal Csámpai, Imre Pápai * Institute of Organic Chemistry, Research
Supporting Information Thiourea Derivatives as Brønsted Acid Organocatalysts Ádám Madarász, Zsolt Dósa, Szilárd Varga, * Tibor Soós, Antal Csámpai, Imre Pápai * Institute of Organic Chemistry, Research
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Supporting Information. The preference for dual-gold(i) catalysis in the hydro(alkoxylation vs phenoxylation) of alkynes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for The preference for dual-gold(i) catalysis in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for The preference for dual-gold(i) catalysis in
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position
 Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
Understanding the Mechanism of the Intramolecular Stetter Reaction. A DFT Study
 Molecules 2012, 17, 1335-1353; doi:10.3390/molecules17021335 Article PE ACCESS molecules ISS 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Understanding the Mechanism of the Intramolecular Stetter eaction.
Molecules 2012, 17, 1335-1353; doi:10.3390/molecules17021335 Article PE ACCESS molecules ISS 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Understanding the Mechanism of the Intramolecular Stetter eaction.
Summary of π Bond Chemistry
 Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
Supplementary Figure S1 Stable structures of I, I', II, and II' optimized at the
 H C Si 2.492 (2.348) 1.867 (2.005) Fe O 2.106 (2.077) 2.360 (2.497) N 1.126 (1.115) 2.105 (2.175) I quintet (triplet) 0.0 (+4.1) kcal/mol II triplet (quintet) 0.0 (+4.3) kcal/mol 1.857 (2.076) 2.536 (2.351)
H C Si 2.492 (2.348) 1.867 (2.005) Fe O 2.106 (2.077) 2.360 (2.497) N 1.126 (1.115) 2.105 (2.175) I quintet (triplet) 0.0 (+4.1) kcal/mol II triplet (quintet) 0.0 (+4.3) kcal/mol 1.857 (2.076) 2.536 (2.351)
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
The Innocent role of Sc 3+ on Non-Heme Fe catalyst in O 2 environment
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information For The Innocent role of Sc 3+ on Non-Heme Fe catalyst in O 2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information For The Innocent role of Sc 3+ on Non-Heme Fe catalyst in O 2
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Suggested solutions for Chapter 27
 uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
MINDO Forces Study of the Uncatalysed and Acid-Catalysed
 MINDO Forces Study of the Uncatalysed and Acid-Catalysed Friedel-Crafts Reactions Between CH 3 F and CH 4 Amel G. Abed and Salim M. Khalil Chemistry Department, College of Science, University of Mu'tah,
MINDO Forces Study of the Uncatalysed and Acid-Catalysed Friedel-Crafts Reactions Between CH 3 F and CH 4 Amel G. Abed and Salim M. Khalil Chemistry Department, College of Science, University of Mu'tah,
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
A theoretical analysis of the reactivity of acyl derivatives of azaheterocycles as dienophiles in cycloaddition reactions
 doi:10.3390/ecsoc-21-04732 Type of the Paper (Abstract, Meeting Report, Preface, Proceedings, etc.) A theoretical analysis of the reactivity of acyl derivatives of azaheterocycles as dienophiles in cycloaddition
doi:10.3390/ecsoc-21-04732 Type of the Paper (Abstract, Meeting Report, Preface, Proceedings, etc.) A theoretical analysis of the reactivity of acyl derivatives of azaheterocycles as dienophiles in cycloaddition
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Reaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. Reactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b.
 eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
Supplementary Material
 . ISOMERIC ADDUCT STABILITY IN THE ADDITION OF ATOMIC RADICALS TO TOLUENE: H, O( 3 P), F and Cl. Victor Hugo Uc a,c, Alfonso Hernández-Laguna b, André Grand c and Annik Vivier-Bunge a a Departamento de
. ISOMERIC ADDUCT STABILITY IN THE ADDITION OF ATOMIC RADICALS TO TOLUENE: H, O( 3 P), F and Cl. Victor Hugo Uc a,c, Alfonso Hernández-Laguna b, André Grand c and Annik Vivier-Bunge a a Departamento de
Electronic Supplementary Information. for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information for Two Chiral Catalysts in Action: Insights on Cooperativity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information for Two Chiral Catalysts in Action: Insights on Cooperativity
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
Cyclams with ambidentate methylthiazolyl pendants for a stable, inert and selective Cu(II) coordination
 Supporting Information for: Cyclams with ambidentate methylthiazolyl pendants for a stable, inert and selective Cu(II) coordination Aurora Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Zakaria Halime, Luís M. P. Lima, Maryline
Supporting Information for: Cyclams with ambidentate methylthiazolyl pendants for a stable, inert and selective Cu(II) coordination Aurora Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Zakaria Halime, Luís M. P. Lima, Maryline
10/26/2010. An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene. to Ethylene
 6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Homework Problem Set 5 Solutions. E e + H corr (a.u.) a.) Determine the bond dissociation enthalpy of ethane in kcal/mol (1 a.u. = kcal/mol).
 Chemistry 380.37 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework Problem Set 5 Solutions 1. Given below are the sum of electronic and thermal enthalpies, E e + H corr, from Hartree-Fock calculations using a 6-31G(d) basis
Chemistry 380.37 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework Problem Set 5 Solutions 1. Given below are the sum of electronic and thermal enthalpies, E e + H corr, from Hartree-Fock calculations using a 6-31G(d) basis
The mechanism of the nitration of methylbenzene is an electrophilic substitution.
 Q1.Many aromatic nitro compounds are used as explosives. One of the most famous is 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, originally called trinitrotoluene or TNT. This compound, shown below, can be prepared
Q1.Many aromatic nitro compounds are used as explosives. One of the most famous is 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, originally called trinitrotoluene or TNT. This compound, shown below, can be prepared
The Reaction Electronic Flux Perspective on the Mechanism of the Zimmerman Di- -Methane Rearrangement
 Supporting Information The Reaction Electronic Flux Perspective on the Mechanism of the Zimmerman Di- -Methane Rearrangement Ricardo A. Matute*, 1,2,3 Patricia Pérez, 4 Eduardo Chamorro, 4 Nery Villegas-Escobar,
Supporting Information The Reaction Electronic Flux Perspective on the Mechanism of the Zimmerman Di- -Methane Rearrangement Ricardo A. Matute*, 1,2,3 Patricia Pérez, 4 Eduardo Chamorro, 4 Nery Villegas-Escobar,
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Chem 263 Nov 19, Cl 2
 Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Michael and Aldol CH391 December 4, 2002
 Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
(5) a. b. (6) N H CH 3 N H O H O (7) CH 3 O (8) OCH 3 2. explanation:
 ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry. CHE 322, Organic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1
 State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry CHE 22, rganic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1 Please answer all questions specifically, concisely, and readably in the spaces
State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry CHE 22, rganic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1 Please answer all questions specifically, concisely, and readably in the spaces
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Conjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions
 onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and
 Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and α,β Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo,
Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and α,β Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo,
Reactivity of the carbon carbon double bond towards nucleophilic additions. A DFT analysis
 Reactivity of the carbon carbon double bond towards nucleophilic additions. A DFT analysis Luis R. Domingo, a, * Patricia Pérez b and Renato Contreras c a Departamento de Química Orgánica, Instituto de
Reactivity of the carbon carbon double bond towards nucleophilic additions. A DFT analysis Luis R. Domingo, a, * Patricia Pérez b and Renato Contreras c a Departamento de Química Orgánica, Instituto de
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
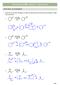 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Supporting Information Chromogenic detection of aqueous formaldehyde using functionalized silica nanoparticles
 Supporting Information Chromogenic detection of aqueous formaldehyde using functionalized silica nanoparticles Sameh El Sayed,,,, II, Lluis Pascual,,,, Maurizio Licchelli, II * Ramón Martínez- Máñez,,,
Supporting Information Chromogenic detection of aqueous formaldehyde using functionalized silica nanoparticles Sameh El Sayed,,,, II, Lluis Pascual,,,, Maurizio Licchelli, II * Ramón Martínez- Máñez,,,
*VI-1 C NC II-2 C NC V-2 C NC **VI-2 C NC II-3 C NC V-3 C NC IX-1 C NC IV-1 C NC VII-1 C NC IX-2 C NC IV-2 C NC VII-2 C NC V-1 C NC VIII-1 C NC
 *VI-1 C NC II-2 C NC V-2 C NC **VI-2 C NC II-3 C NC V-3 C NC IX-1 C NC IV-1 C NC VII-1 C NC IX-2 C NC IV-2 C NC VII-2 C NC V-1 C NC VIII-1 C NC Chemistry 131 Quiz 7 Summer 2011 Form A NAME: Key Chapter
*VI-1 C NC II-2 C NC V-2 C NC **VI-2 C NC II-3 C NC V-3 C NC IX-1 C NC IV-1 C NC VII-1 C NC IX-2 C NC IV-2 C NC VII-2 C NC V-1 C NC VIII-1 C NC Chemistry 131 Quiz 7 Summer 2011 Form A NAME: Key Chapter
11/26/ Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
 9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP
 Lecture 15 Thermodynamics I Heat vs. Temperature Enthalpy and Work Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Average Bond Enthalpy Thermodynamics The relationship between chemical reactions and heat. What causes
Lecture 15 Thermodynamics I Heat vs. Temperature Enthalpy and Work Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Average Bond Enthalpy Thermodynamics The relationship between chemical reactions and heat. What causes
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry
 Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry PAPER Cite this: Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 1618 Received 19th December 2016, Accepted 16th January 2017 DOI: 10.1039/c6ob02768g rsc.li/obc 1. Introduction Since the
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry PAPER Cite this: Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 1618 Received 19th December 2016, Accepted 16th January 2017 DOI: 10.1039/c6ob02768g rsc.li/obc 1. Introduction Since the
CHEMISTRY. Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition. Reactions of Alkenes
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition Module Tag CHE_P9_M7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition Module Tag CHE_P9_M7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes Structure:
 Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
p Bonds as Electrophiles
 Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation
 L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation Fragmentation reactions Spectrum interpretation Confirmation of ion structural assignment Biomolecule dissociation Fragmentation reactions 1. Fragmentation reactions of
L.7. Mass Spectrum Interpretation Fragmentation reactions Spectrum interpretation Confirmation of ion structural assignment Biomolecule dissociation Fragmentation reactions 1. Fragmentation reactions of
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry
 A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry Counting valence electrons (v.e.) with the ionic model 1. Look at the total charge of the complex Ph 3 P Cl Rh Ph 3 P PPh 3 OC CO 2 Fe OC CO Co + charge:0 charge:
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry Counting valence electrons (v.e.) with the ionic model 1. Look at the total charge of the complex Ph 3 P Cl Rh Ph 3 P PPh 3 OC CO 2 Fe OC CO Co + charge:0 charge:
If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it
 Text Related to Segment.04 00 laude E. Wintner If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it should be true that the corresponding acid will be stronger than would be so
Text Related to Segment.04 00 laude E. Wintner If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it should be true that the corresponding acid will be stronger than would be so
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
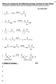 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Answers to HT2, Chemistry A
 Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
1- Reaction at the carbonyl carbon (Nucleophilic addition reactions).
 Reactions of aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and Ketones undergo many reactions to give a wide variety of useful derivatives. There are two general kinds of reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo:
Reactions of aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and Ketones undergo many reactions to give a wide variety of useful derivatives. There are two general kinds of reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo:
Supporting Information Mechanism of Ullmann Coupling Reaction of Chloroarene on Au/Pd Alloy Nanocluster: A DFT Study
 Supporting Information Mechanism of Ullmann Coupling Reaction of Chloroarene on Au/Pd Alloy Nanocluster: A DFT Study Jittima Meeprasert 1, Supawadee Namuangruk 1,*, Bundet Boekfa 2,3, Raghu N. Dhital 4,
Supporting Information Mechanism of Ullmann Coupling Reaction of Chloroarene on Au/Pd Alloy Nanocluster: A DFT Study Jittima Meeprasert 1, Supawadee Namuangruk 1,*, Bundet Boekfa 2,3, Raghu N. Dhital 4,
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium
 Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
ANSWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 249H
 AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Size Selective Adsorption in Nanoporous Polymers from Coumarin Photo-Cross-Linked Columnar Liquid Crystals Alberto Concellón, Albertus P. H. J. Schenning,, Pilar Romero, Mercedes
Supporting Information Size Selective Adsorption in Nanoporous Polymers from Coumarin Photo-Cross-Linked Columnar Liquid Crystals Alberto Concellón, Albertus P. H. J. Schenning,, Pilar Romero, Mercedes
Modular P,S-Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Asymmetric
 Phosphinite-Thioethers derived from Chiral Epoxides. Modular P,S-Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Substitutions Xisco Caldentey, and Miquel A. Pericàs,, * Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia
Phosphinite-Thioethers derived from Chiral Epoxides. Modular P,S-Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Substitutions Xisco Caldentey, and Miquel A. Pericàs,, * Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia
Received: 16 March 2010, Revised: 19 July 2010, Accepted: 2 August 2010, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 12 November 2010
 Research Article Received: 16 March 2010, Revised: 19 July 2010, Accepted: 2 August 2010, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 12 November 2010 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI 10.1002/poc.1790 Concerted
Research Article Received: 16 March 2010, Revised: 19 July 2010, Accepted: 2 August 2010, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 12 November 2010 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI 10.1002/poc.1790 Concerted
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
CHEMICAL KINETICS Order and molecularity of reactions with examples, zero and first order reaction with examples
 CHEMICAL KINETICS Topic-2 Order and molecularity of reactions with examples, zero and first der reaction with examples VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. What is der of as reaction? Ans: The sum of the powers
CHEMICAL KINETICS Topic-2 Order and molecularity of reactions with examples, zero and first der reaction with examples VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. What is der of as reaction? Ans: The sum of the powers
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217
 Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
