Classroom Activities
|
|
|
- Jonas Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classroom Activities Thanks to: North Carolina Ag in the Classroom Florida Ag in the Classroom
2 Photosynthesis Promenade Greetings from North Carolina Ag in the Classroom! Ag in the Classroom is happy to share Photosynthesis Promenade with you and your students. It is hoped that using the activities in this manual and the Promenade kit will help your young scientists understand and appreciate one of the most miraculous processes in all of nature. Ag in the Classroom is an educational program provided by the North Carolina Farm Bureau Federation to help teachers enrich instruction as outlined by the Standard Course of Study while helping students to develop an appreciation for agricultures as the source of all our food and fiber. A document outlining the components of NC Ag in the Classroom is contained in this manual. We invite all North Carolina educators to become familiar with all that Ag in the Classroom has to offer and to take advantage of the opportunities available through the program. Photosynthesis Promenade is actually the culminating activity of a set of lesson designs focusing on plant science. There are lessons related to seed parts, germination, plant parts, and pollination. The final lesson focuses on Photosynthesis and its importance to the function of all living things. All of these lessons are included in this teacher's manual. As an anchor component of the plant science study, a book entitled Oh Say Can You Seed, by Bonnie Worth has been selected. The text is written in the fashion of Dr. Seuss and features The Cat in the Hat, Thing One, and Thing Two. The lessons included in this manual go along with Oh Say Can You Seed. The lessons can be taught effectively without the use of the text. A copy of the book is included in the kit. In keeping with the goals and ideals of Ag in the Classroom, Photosynthesis Promenade gives due reference to the farmer and the role that photosynthesis plays in the agricultural industry. It helps students to see that people are all dependent on a number of factors they tend to take for granted. Ag in the Classroom hopes that you and your students find these lessons appealing and helpful in your efforts and that you have great fun as you Dance with the Plants!
3 Bean Dissection Traditional Lesson Design Preparation: Purchase a bag of large lima beans at the supermarket. Count out approximately Dissection activity. 2 beans for each student who will participate in the Bean Place counted beans in a bowl and cover with water. Soak beans overnight. Teacher Information: Introduce the book Oh Say Can You Seed, by Bonnie Worth to the class. Read orally pages 6-15 and discuss. Distribute 2 beans to each student. Place beans on dry paper towels. Discuss seed parts with students as they investigate the beans, Ask students to take beans apart and identify the seed coat, cotyledon(s), and embryo. You may ask students to observe and record findings as they locate seed parts. You may ask students to sketch the seed parts as they locate and identify them. Provide "Ag in the Classroom Bean Book" kits for students to construct as a reference tool for future use. To obtain Bean Book plans, visit
4 BEAN SEED DISSECTION 5E Lesson Design Engagement Activity Bring a bowl of large lima beans, which have been soaked in water overnight to class. Invite students to work individually or in pairs and to take two beans from the bowl and place them on paper towels in their work space. Instruct students to take one of the objects and observe. Ask attention focusing questions such as: Describe what you see. What clues does this lima bean give you about its growth? Exploration Activity Instruct students to investigate one of the beans they have placed on the paper towel. They may use their hands or other simple instruments you may provide. (tweezers, toothpicks, files, etc.) Encourage the use of process skills by asking students to observe size, shape, number of parts, textures, etc. Ask students to record observations in appropriate ways. Ask students to draw a diagram of the parts of a seed and label it. (See picture of the seed.) Explanation Activity Tell students that the bean they have investigated plant has six parts and their bean is one of them. is a part of a plant. Every flowering Ask students to hypothesize which plant part they think the bean might be and explain why. (It is the seed) Instruct students to discuss the three different parts they found when dissecting the bean and hypothesize their purpose. (The seed coat protects the seed, cotyledons provide food prior to germination and photosynthesis, and the embryo is a tiny plant) Ask students how they might test hypotheses. Instruct students to hypothesize as to the needs of the seed in order to germinate/sprout. (water, soil or other medium to hold moisture, warm temperature) Ask students how they might test their hypotheses. Would the same be true for all seeds?
5 Elaboration Activity Allow students to set up and conduct experiments to test hypotheses formed during the Explanation Activity. Have them gather needed resources (books to verify guesses, materials to test needs of seeds) and follow through with experimental activities. Require students to journal findings of all experiments proven or disproved. stating whether hypotheses were Evaluation/Extension Activity Draw, label, and write explanations of the purposes of each part of the seed. Provide "Ag in the Classroom Bean Book" kits for students to construct as a reference tool for future use. To obtain Bean Book plans, visit pdf.
6 BUILD A GREENHOUSE Traditional Lesson Design Materials Needed: potting soil, two clear plastic cups, 1 bean seed, 1 corn sees, 1 pea seed, water, transparent tape, permanent pen With these supplies you can build the greenhouse below. Directions: Place some soil in one of the cups, filling it about halfway up. Plant each of the three seeds equidistant next to the "wall" of the ~.- ~-- plastic cup so you can observe the germination and growth of your plants. Add a 10 ml of water and then place the other cup on top. Tape the cups together. Label seed type above each planting (on top cup). Bean, corn, pea. Once you've completed your mini-greenhouse, observe it over time. Experiment by placing your greenhouse in different locations. If it doesn't grow in one spot, try another. Place your greenhouse in indirect sunlight. Most likely, your plant will quickly outgrow its container. When the plants touch the top of the upper cup, remove the tape and begin watering. Your plants will need to be transplanted to a larger container or into outside soil shortly thereafter. Pointers for making a successful greenhouse using this Ag in the Classroom plan: Seeds should be planted next to the "wall" of the cup so children can see them as they begin to germinate. To get the seeds where they can be seen, put the potting soil into the bottom cup, then use a plastic knife or popsicle stick to push the seeds down into the soil right up next to the "wall" of the cup. Make sure that each seed is visible through the wall of the cup. It is suggested that by planting 3 different seeds children can observe differences in germination and growth. Plant them equidistant around the cup. Have children write name and date on top (or bottom) cup with a permanent marker. Do not put too much water - basically, get the soil moist throughout. Place greenhouses in indirect sunlight. Placing them in direct sunlight will cause them to become too hot and prevent germination and/or proper growth.
7 BUILD A GREENHOUSE 5E Lesson Design Engagement Activity Prepare several greenhouses using printed directions (see traditional lesson). Display one greenhouse for students to investigate. Ask attention focusing questions such as: What is this? What is it called? Have you seen anything like it before? What do you think will happen inside and why? Where should it be kept? Exploration Activity Provide additional greenhouses for students to observe in small groups. Instruct students to deconstruct the greenhouses to investigate the contents. Allow students to observe contents of the greenhouse and record their findings in their science notebook. Ask explorative questions such as: What are the contents of the greenhouse? Why do you think each item was placed in the greenhouse? What is its purpose? What changes do you think have taken place since the time that the greenhouse was assembled? If the greenhouse is reassembled, what do you think will happen? Explanation Activity Provide materials and directions for students to make their own greenhouses. Allow them to do.so. Instruct students to journal their activities and continue to note changes in the greenhouse over a period of several weeks. Ask explorative, measuring, and how/why questions such as: What seeds did you plant? What happens if you plant the seeds deeper or shallower? What happens if you add more or less water. What will this environment cause the seeds to do? What factors are present in the greenhouse which will enable the seeds to germinate and grow? Why will you not need to water the seeds and young plants? Which seed do you predict will germinate first, second, last?
8 Elaboration Activity Provide reference materials for students to view. Challenge them to find text that describes the processes taking place inside their greenhouses. Have them record their findings and cite sources. Ask clarifying questions such as: What term did you find that describes the sprouting of a seed? (germinate/germination) What are the names of the three parts of a seed? (seed coat, cotyledon, embryo) What is the function of each seed part? (the seed coat protects the seed, the cotyledon provides food for the baby plant, the embryo is the baby plant that will grow) What does a seed need in order to germinate? (water, soil or other growing medium, warm temperature) Once a seed has germinated, what does the young plant need in order to grow? (water, soil or other growing medium, appropriate temperature, sunlight) Why did you not need to water the seeds and seedlings inside the greenhouse? (the greenhouse was able to sustain its own water cycle) What are the stages of the water cycle (evaporation, condensation, precipitation) Evaluation/Extension Activity Allow students to continue to care for, observe, and journal the activities associated with their greenhouses. They should remove the tops when the first leaf touches the top of the upper cup. Students may condition the plants to be transplanted outdoors by placing the greenhouses outdoors briefly, adding a few minutes each day. Read orally and discuss pages from the text, Oh Say Can You Seed, by Bonnie Worth.
9 Plant Parts Traditional Lesson Design Read orally pages of Oh Say Can You Seed and discuss. Distribute copies of "Roots, Stems, Leaves." Divide students into six groups. Assign each group a verse of the song to pantomime. Allow time for groups to develop their activities and rehearse them. Play the song using CD, tape, or live accompaniment. Students should sing along and present their "skit" during each verse as appropriate. Tapes and CDs are available for purchase at Note: This activity could be used as an educational presentation at a parent night or school assembly program.
10 Plant Parts 5E Lesson Design Engagement Activity Bring a number of whole plants representing agricultural commodities from your area and place them on tables for students to see. One plant should be placed on each table. Allow students to form small groups and to gather at tables by groups. Ask students to take a look at the plants and share observations. Possible plants for use include: soybeans, greenhouse/nursery plants, cotton, peanuts, sweetpotatoes, corn, cucumber, or any other vegetable plant. Ask attention focusing questions such as: What type of plant do you think your group has? How many plant parts does your plant have? Can you identify the parts of your plant? What time of year do you think your plant was planted? How do you suppose your plant is harvested? Exploration Activity Each group should dissect their plant into specific parts. Challenge students to label the parts and the function of each. Instruct students to journal their activities making sketches and providing written descriptions of each plant part they identify. Ask explorative questions such as: Where on the plant are the parts located? (top, middle, or bottom) Do you see any ways in which the plant is designed to protect itself from predators? What are the colors of the different plant parts? How many different plant parts can you identify? Do you think that the plant you are investigating had more parts than you are able to identify? (ex. A fruit that has been harvested... A flower that has fallen off?) Explanation Activity Provide resource materials for students to research the plants they are investigating. Challenge them to locate information that confirms or disproves their hypotheses about the plants and their parts. Ask students to prepare a presentation about their plant to share with classmates. Presentations should contain information about the parts of the plant and the function of each part.
11 Challenge students to base presentations on information they gathered from their hands-on investigation as well as from resource materials. Ask explanatory questions such as: How do you know the function of each part you have identified? What do you know about the growing conditions needed for the plant you have investigated? What do you know about how to care for your plant? Elaboration Activity Allow student groups to present information about the plants to others in the class. Challenge audience members to question presenters about their plant and its parts. Allow students to list all possible commonalities among plants being investigated. Lead them to the realization that all these plants represent important agricultural commodities produced in North Carolina. Ask elaborative questions such as: What do you know about the uses of your plant? How/where is your plant transported, processed, marketed, and sold? How is your plant beneficial to people and/or animals? Evaluation/Extension Activity Read orally and discuss pages of Oh Say Can You Seed by Bonnie Worth. Sing and pantomime the song, "Roots, Stems, Leaves" by The Banana Slug String Band. Available for purchase in audio or video format at
12 Nbme _ "Oh Say Can You Seed?" By Bonnie Worth Pre/Post Test Directions: See how many of these questions you can answer before hearing the story and then see how muchyou have learned after hearing the story! Circle the "1" if you think the answer is true and circle the "F" if you think the answer is false. Don't change your "Before Hearing Story" answers, but be sure and answer the After Hearing Story" answers correctly!. Before Hearing Story After Hearing Story 1. Every flowering plant starts out as a seed. T F T F 2. Bean seeds have 2 parts. T F T F 3. The baby plant inside of a seed is called the embryo. T F T.. F 4. The cotyledon is where food is stored in the bean seed. T F T F 5. The part of the plant growing above the ground is called the root system. T F T F 6. Food making is done in the roots of the plants. T F T F 7. Photosynthesis is the food-making process done by plants. T F T F 8. Plants give off carbon dioxide. T F T F 9. Bees help carry pollen from T F T F plant to plant. 10. Nuts are fruits. T F T F 11. Bur seeds are "hitchhikers". T F T F 12. Plants are the only living things on Earth that make their own food. T F T F Florida Agriculture in the Classroom, Inc. For more 'Oh Say Can You Seed?" activities go to
13 Glossary for Oh Say Can You Seed'" (pp of text) 1. Carbon dioxide: The gas humans and animals breathe out, and green plants use,to make food. 2. Cotyledon: The first leaf or pair of leaves within the embryo. A part of the seed that stores food. 3. Edible: Fit to eat 4. Embryo: The part of a seed that develops into a new plant, including the stem, leaves and roots. 5. Fertilization: Male (or sperm) cells contained in pollen reach the female (or egg) cells in the ovules and.the combination grows into seeds. 6. Minerals: Materials that is neither animal nor vegetable. Found in rocks and soil, they help animals and plants to grow. 7.. Nectar: The sweet liquidsecreted by a flower to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies and hummingbirds. 8. Numero: The Spanish word for "number". 9. Ovule: The part of the plant in the ovary that contains egg cells and becomes a seed after fertilization. 10. Oxygen: The gas humans and animals breathe in order to stay alive, and green plants produce when making food. 11. Photosynthesis: The process in which green plants, powered by the energy of the sun, combine carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar inside their leaves and release oxygen into the air. 12. Pistil: The ovule-bearing, female reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the stigma, style and ovary. 13. Plantain: A kind of banana that is best eaten when cooked. 14. Pollen: The minute grains that are produced in the anthers of a flower and contain male Sex cells. 15. Stamen: The male reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the anthers and the filaments that support the anthers. LanguageIdeas: Use these vocabulary words to have students illustrate the meanings, make a plant dictionary, put in alphabetical order, use in sentences, make a plant booklet, etc. Lesson Extension: On a separate page, draw a diagram of a plant. Be sure to include the roots, stem, leaves and flowers. Label eclch part. Florida Agriculture in the Classroom, Inc. For more "Oh Say CanYou Seed?" activities go to
14 Glossary for" Oh Say Can You Seed?" (pp of text) 1. Carbon dioxide: The gas humans and animals breathe out, and green plants use,to make food. 2. Cotyledon: The first leaf or pair of leaves within the embryo. A part of the seed that stores food. 3. Edible: fit to eat 4. Embryo: The part of a seed that develops into a new plant. including the stem, leaves and roots. 5. fertilization: Male (or sperm) cells contained in pollen reach the female (or egg) cells in the ovules and the combination grows into seeds. 6. Minerals: Materials that is neither animal nor vegetable. found in rocks and soil, they help animals and plants to grow. 7. Nectar: The sweet liquid secreted by a flower to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies (indhummingblrds. 8. Numero: The Spanish word for "number", 9. Ovule: The part of the plant in the ovary that contains egg cells and becomes a seed after fertilization. 10. Oxygen: The gas humans and animals breathe in order to stay alive, and green plants produce when making food. 11. Photosynthesis: The process in which green plants, powered by the energy of the sun, combine carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar inside their leaves and release oxygen into the"air. " 12. Pistil: The ovule-bearing, female reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the stigma, style and ovary. 13. Plantain: A kind of banana that is best eaten when cooked. 14. Pollen: The minute grains that are produced in the anthers of a flower and contain male Sex cells. 15. Stamen: The male reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the anthers and the filaments that support the anthers. LanguageIdeas: Use these vocabulary words to have students illustrate the meanings, make a plant dictionary, put in alphabetical order, use in sentences, make Q plant booklet, etc. Lesson Extension: On a separate page, draw a diagram of a plant. Be sure to include the roots, stem, leaves and flowers. Label each ~. florida Agriculture in the Classroom, Inc. for more "Oh Say CanYou Seed?" activities go to
15 Nmne ~ _ *Use the phrases about plant parts on the next page to fill in the following table. Write the sentences under the correct headings. One has been done for you. "Oh Say Can You Seed?" Roots Stem Leaves Flowers Grow underground Use the phrases below to fill in the table about plant parts. grows underground acts like a pipe to carry water up the plant photosynthesis occurs pollen is found anchors the plant gives the plant support petals oxygen is released food-making for the plant is done here have different" edges" absorbs minerals from the ground look twisty and hairy is where the leaves are attached stamen stoma is found nectar is found Florida Agriculture in the Classroom, Inc. For more "Oh Say Can You Seed?" activities go to
16 "Oh Say Can You Seed?" (Answer Sheet) "Oh Say CanYou Seed?" Teacher's Answers to Pre/Post Test (page numbers where found in text provided!) 1. T p.7 2. F p. 13 (seeds have 3 parts) 3. T p T p F p. 19 (shoot system) 6. F p. 28 (leaves) 7. T p F p. 29 (oxygen) 9. T p.31 to. T p T p T p.26 '" Completed Chart: Roots Stem Leaves Flowers Grows underground Acts like a pipe to carry Photosynthesis occurs Pollen is found water up the plant - Anchors the plant Is where leaves are attached Food-making i.sdone here Nectar is found Look twisty and hairy Gives the plant support Stoma is found Petals Oxygen is released Absorbs minerals from the ground - Stamen Have different "edges" Florida Agriculture in the Classroom, Inc. For more "Oh Say CanYou Seed?" activities go to
17 Oh Say Can You Seed? Puzzle #2 Crossword Puzzle Clues for Oh Say Can You Seed? 3 2 Across 4. The minute grains that are produced in the anthers of a flower and contain male sex cells. 7. Spanish word for "number". 9. The sweet liquid secreted by a flower to attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. 12. A kind of banana that is best eaten when cooked Down 1. When the male cells contained in pollen reach the female cells in the ovules and cause them to grow into seeds. 2. The process by which green plants, powered by the energy of sunlight, combine carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar inside their leaves and release oxygen into the air. 3. The ovule-bearing, female reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the stigma, style, and ovary. 5. The gas humans and animals must breathe in order to stay alive and which green plants produce when making food. 6. Materials that are neither animal nor vegetable, found in rocks and soil and help animals and plants to grow. 8. The male reproductive part of a flowering plant that includes the anthers and the filaments that support the anthers. 10. The part of the plant in the ovary that contains egg cells and becomes a seed after fertilization. 11. The first leaf or pair of leaves within the embryo that stores food.
18 Student's Name Oh Say Can You Seed? Puzzle #1 E T M 0 P T S C V W 0 E G N Q I V I S 0 R P U E L Z V L U H C Q N M L Y P R N V K H U H A P C E W L L Z J A L Q L A L G X S R F E V Y R U T I D L T E I Z A U N Q u Q T P C G 0 N N Q E L D X L V H P E V E H 0 K L Z S N E G y X 0 T P F N T F N 0 F E R T I L I Z A T I 0 N T C 0 T Y L E D 0 N F M F M U G C 0 V B P I S T I L X T S S P H 0 T 0 S y N T H E S I S W L V W E W U Z N R D L W A Z R C S A V S T A M E N Q c z c Q p J I I B F E M B R Y 0 P P A Cotyledon Embryo Fertilization Food Leaf Minerals Nectar Ovule Oxygen Photosynthesis Pistil Pollen Stamen Sunlight
POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO
 POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO Overview: Students play a game to reinforce vocabulary and concepts learned in the Plant Parts, Seed to Harvest, and Pollination modules during the field trip. Sauvie
POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO Overview: Students play a game to reinforce vocabulary and concepts learned in the Plant Parts, Seed to Harvest, and Pollination modules during the field trip. Sauvie
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Plant Lifecycle 3 rd 5 th Grade
 Key Understandings Students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual process A lifecycle is a continuous cycle that contains: birth, growth, reproduction,
Key Understandings Students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual process A lifecycle is a continuous cycle that contains: birth, growth, reproduction,
GREEN LIFE. Plants and Photosynthesis W 398
 W 398 GREEN LIFE Plants and Photosynthesis Savannah Webb, Former 4-H Extension Agent, Maury County Jennifer Richards, Assistant Professor, 4-H Youth Development MANAGEMENT OF APHIDS AND BYD IN TENNESSEE
W 398 GREEN LIFE Plants and Photosynthesis Savannah Webb, Former 4-H Extension Agent, Maury County Jennifer Richards, Assistant Professor, 4-H Youth Development MANAGEMENT OF APHIDS AND BYD IN TENNESSEE
PLANT LIFECYCLES. Name: Class:
 PLANT LIFECYCLES Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases from the article
PLANT LIFECYCLES Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases from the article
Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit
 Collin Zier Assessment November 2 nd, 2012 Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit Stage One Desired Results Established Goals: Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards for Science 4 th Grade Standard F Life
Collin Zier Assessment November 2 nd, 2012 Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit Stage One Desired Results Established Goals: Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards for Science 4 th Grade Standard F Life
Sample file ISBN: rainbowhorizons.com RHPA70
 PLANTS UNIT OVERVIEW Students get a chance to try out their "green thumbs" as they explore plants. Student notes suitable for an overhead projector explain much of the knowledge-based information contained
PLANTS UNIT OVERVIEW Students get a chance to try out their "green thumbs" as they explore plants. Student notes suitable for an overhead projector explain much of the knowledge-based information contained
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Big Green Lessons. Key Understandings. Standards Alignment. Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade
 Big Green Lessons Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade Key Understandings Standards Alignment In this lesson, students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual
Big Green Lessons Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade Key Understandings Standards Alignment In this lesson, students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual
Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version
 Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
A leaf is. Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
 The leaf system A leaf is Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy a plant organ, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy that s photosynthetic, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy contains chloroplasts, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
The leaf system A leaf is Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy a plant organ, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy that s photosynthetic, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy contains chloroplasts, Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
Plants Week 6 Booklet
 Plants Week 6 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #5 The Vascular System Part 1: What Happened to the Water? Part 2: Looking at Plant Structures Not in Foss- Nonvascular Systems Types of Roots
Plants Week 6 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #5 The Vascular System Part 1: What Happened to the Water? Part 2: Looking at Plant Structures Not in Foss- Nonvascular Systems Types of Roots
Click Teacher Guide: May/June 2018
 Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
8 Reproduction in flowering plants
 Self-assessment questions 8.01 8 Reproduction in flowering plants 1 Which is the most accurate statement? The principal role of a flower in the life cycle of a plant is: (a) attracting insects (b) producing
Self-assessment questions 8.01 8 Reproduction in flowering plants 1 Which is the most accurate statement? The principal role of a flower in the life cycle of a plant is: (a) attracting insects (b) producing
Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab
 Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab Basic Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been on
Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab Basic Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been on
Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide
 Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide Science SOL 4.4 Please use this study guide to study daily for your test! Please keep this study guide in your HOMEWORK FOLDER so that you can use it to study
Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide Science SOL 4.4 Please use this study guide to study daily for your test! Please keep this study guide in your HOMEWORK FOLDER so that you can use it to study
UNIT AT A GLANCE. Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2
 UNIT AT A GLANCE Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2 Introducing the Topic: Activity: Lunch Menu Detectives (Students trace ingredients to plants) Importance of Plants: Read Bits That Grow Big,
UNIT AT A GLANCE Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2 Introducing the Topic: Activity: Lunch Menu Detectives (Students trace ingredients to plants) Importance of Plants: Read Bits That Grow Big,
The grade 5 English science unit, Plants, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab
 Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Life Science. Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like. animals and humans. Like all living. things they need key things to live;
 6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
UNIT 3. PLANTS. PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
1 Evolution of Plants
 1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
1 Evolution of Plants Plant Evolutionary Tree 1 How Did Plant Life Begin? BIBLICAL WORLDVIEW EVOLUTIONARY WORLDVIEW The Biblical worldview is that plants began on the third day of creation, created by
Lotus Flower. Lotus Flower Seeds OBJECTIVES SOMETHING TO SPROUT ABOUT. Something to Sprout About Grades 3 rd 5 th
 CHECK WITH TEACHER TO MAKE SURE THERE ARE TRAYS TO GO UNDER PLANTING CUPS. OBJECTIVES SOMETHING TO SPROUT ABOUT Ppt 2 * Poster in the bag State the objectives. And tell students you will be asking them
CHECK WITH TEACHER TO MAKE SURE THERE ARE TRAYS TO GO UNDER PLANTING CUPS. OBJECTIVES SOMETHING TO SPROUT ABOUT Ppt 2 * Poster in the bag State the objectives. And tell students you will be asking them
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts)
 PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
Parts of a Flower. A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program
 Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Ch. 4- Plants. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy
 Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Define what a plant is. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level List what plants need to live and grow. Explore plant life cycles. Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Objectives Define what a plant is. Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level List what plants need to live and grow. Explore plant life cycles. Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They
 SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce SPECIFIC TOPIC: Living Things and How They Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students
Photosynthesis Promenade
 Photosynthesis Promenade Summary: Students simulate the process of photosynthesis through a wholebody demonstration. Objective Students will be able to illustrate how plants use the sun s energy to make
Photosynthesis Promenade Summary: Students simulate the process of photosynthesis through a wholebody demonstration. Objective Students will be able to illustrate how plants use the sun s energy to make
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Propagating Plants Sexually
 Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant
 The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Focus: Students draw upon their own observations of their plants as well as research and class discussion to explore the life cycle of flowering plants. Specific Curriculum
The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Focus: Students draw upon their own observations of their plants as well as research and class discussion to explore the life cycle of flowering plants. Specific Curriculum
The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants.
 INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Grade Level Suggestion: Grades 4 th to 8 th. Time Frame: minutes.
 I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
b. Leaf: 7. Where are most of the plants carbohydrates made? 8. Where are carbohydrates stored for future use?
 Plant Structures 1. Circle the three main parts of the plant to the left. 2. What does each part below do for the plant? a. Stem: b. Leaf: c. Root: 3. Where does most photosynthesis occur? 4. Where are
Plant Structures 1. Circle the three main parts of the plant to the left. 2. What does each part below do for the plant? a. Stem: b. Leaf: c. Root: 3. Where does most photosynthesis occur? 4. Where are
*Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats.
 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. Reproduction In Plants Plant reproduction is the production of new
2a. General: Describe 3 specialised uses for plants. Plants can be used as: i. raw materials ii. foods iii. medicines
 1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
1a. General: Give examples of advantages of there being a wide variety of plants. Greater number of characteristics for breeding. Bigger choice for use as raw materials, foods and medicines. Provide different
WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration
 WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration Objective Students will be able to describe the role of water in seed germination. : two cups of lima beans milk carton (one pint) water. Questions for the Students
WATER REQUIREMENTS: Teacher Demonstration Objective Students will be able to describe the role of water in seed germination. : two cups of lima beans milk carton (one pint) water. Questions for the Students
Page 1 of 5. New: evidence, measure, nutrients, light, soil, transport, volume, water, warmth, insect, pollen, pollinate, nectar.
 National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Vocabulary. photosynthesis p.48. chlorophyll p.49. sepal p.55. pistil p.55. stamen p.55. ovary p.56. fertilization p.56. dormant p.
 Name: Section: 2 3 4 Vocabulary Word Definition photosynthesis p.48 chlorophyll p.49 sepal p.55 pistil p.55 stamen p.55 ovary p.56 fertilization p.56 dormant p.62 5 6 7 Chapter 2 Lesson 1 What are plants
Name: Section: 2 3 4 Vocabulary Word Definition photosynthesis p.48 chlorophyll p.49 sepal p.55 pistil p.55 stamen p.55 ovary p.56 fertilization p.56 dormant p.62 5 6 7 Chapter 2 Lesson 1 What are plants
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions.
 Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants ROOTS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What supplies a seed plant with the things it needs to survive? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What supplies a seed plant with the things it needs to survive? a.
Directed Reading A. Section: Structures of Seed Plants. is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. is called ROOTS. size.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through a plant is called a. shoots. c. phloem. b. xylem. d. leaves. 2. Vascular
Plant Vocabulary. Define
 Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce
 SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students will be able to:- 1) Identify root,
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: Living Things Reproduce Living Things and How They Reproduce Students will be able to:- 1) Identify root,
Chapter 8 Objectives
 CHAPTER 8 PLANTS 1 Chapter 8 Objectives Section 1: The Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the characteristics all plants share 2. Name the things that a plant needs to live successfully on land 3. Compare vascular
CHAPTER 8 PLANTS 1 Chapter 8 Objectives Section 1: The Plant Kingdom 1. Identify the characteristics all plants share 2. Name the things that a plant needs to live successfully on land 3. Compare vascular
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
2 nd. Science Notebook Insects & Plants. Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds. Name:
 2 nd Science Notebook Insects & Plants Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds Name: 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance Indicators Standard 1: Mathematical Analysis M1.1 Use mathematical
2 nd Science Notebook Insects & Plants Investigation 2: Brassica Seeds Name: 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance Indicators Standard 1: Mathematical Analysis M1.1 Use mathematical
BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN. SC.F The student knows that living things are different but share similar structures.
 activities 38&39 Stomata and Transpiration (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 5 Quarter 4 Activities 38 & 39 SC.F.1.2.3 The student knows that living things are
activities 38&39 Stomata and Transpiration (Sessions I and II) BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 5 Quarter 4 Activities 38 & 39 SC.F.1.2.3 The student knows that living things are
Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Seed Reproduc4on
 Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Seed Reproduc4on Demonstrate an understanding of sexual reproduc4on in flowering plants Describe various methods of plant pollina4on What You ll Learn Examine the life cycles of typical
Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Seed Reproduc4on Demonstrate an understanding of sexual reproduc4on in flowering plants Describe various methods of plant pollina4on What You ll Learn Examine the life cycles of typical
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge
 Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Plant parts and their functions
 UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
UNIT 8 Plant parts and their functions In unit 2, we learnt about the classification and basic parts of plants. Here, we will learn in greater details about the different functions carried out by the plant
The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle
 The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle Week 1 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the specific structures and functions of a wheat plant as well as to the wheat life
The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle Week 1 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the specific structures and functions of a wheat plant as well as to the wheat life
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
OVERVIEW PLANTS AND ANIMALS GRADES 1 2 CONTENT GOALS OVERVIEW CONTENTS
 GRADES 1 2 OVERVIEW CONTENT GOALS The Plants and Animals Module provides experiences that heighten young students awareness of the different ways that plants and animals meet their needs. Students care
GRADES 1 2 OVERVIEW CONTENT GOALS The Plants and Animals Module provides experiences that heighten young students awareness of the different ways that plants and animals meet their needs. Students care
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those
 1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1. Plants. Overview
 Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Plants Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe that plants need water, air, food, and light to grow. Identify
Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Plants Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (1 day = 20 30 minutes) Content to be learned Observe that plants need water, air, food, and light to grow. Identify
Structures of Life Unit Design - Grade 3
 Structures of Life Unit Design - Grade 3 The Structures of Life Module consists of four sequential investigations dealing with observable characteristics of organisms. Students observe, compare, categorize,
Structures of Life Unit Design - Grade 3 The Structures of Life Module consists of four sequential investigations dealing with observable characteristics of organisms. Students observe, compare, categorize,
Shoot System. Root System. below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue. Ground Tissue. Vascular Tissue. above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers)
 Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit
 BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5
![V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5 V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5](/thumbs/77/75709676.jpg) 126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools
 Life Sciences: 4.E.6 Seeds Part 3 of 3 Grade Level 4 Sessions Seasonality Instructional Mode(s) Team Size WPS Benchmarks MA Frameworks Key Words 45-60 min. N/A Whole class N/A 04.SC.LS.06 04.SC.LS.07 04.SC.LS.08
Life Sciences: 4.E.6 Seeds Part 3 of 3 Grade Level 4 Sessions Seasonality Instructional Mode(s) Team Size WPS Benchmarks MA Frameworks Key Words 45-60 min. N/A Whole class N/A 04.SC.LS.06 04.SC.LS.07 04.SC.LS.08
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Core Curriculum/Florida AIMS Education Foundation
 Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scienti c Inquiry...11 Earth Science Constellation Creations... 15 Spatter Paint Stars... 19 Stars in the Sky... 21 The Sun...23 What Goes Up Must Come Down...27
Standards Alignment... 5 Safe Science... 9 Scienti c Inquiry...11 Earth Science Constellation Creations... 15 Spatter Paint Stars... 19 Stars in the Sky... 21 The Sun...23 What Goes Up Must Come Down...27
SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1LEHLS 1 Which seed is carried by the wind? A B C D 2 Which section of the plant is the roots? A Section 3 B Section 1 C
SCI-4 BNES 4.4 Summative Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1LEHLS 1 Which seed is carried by the wind? A B C D 2 Which section of the plant is the roots? A Section 3 B Section 1 C
vascular phloem These 68 vocabulary cards are part of a SCIENCE unit. Please keep this set in: Plants - Standard 6-8
 Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1
 Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
Sex, Bugs, and Pollen s Role
 Sex, Bugs, and Pollen s Role Principle of Plant Biology #4 Reproduction in flowering plants takes place sexually, resulting in the production of a seed. Reproduction can also occur via asexual reproduction.
Sex, Bugs, and Pollen s Role Principle of Plant Biology #4 Reproduction in flowering plants takes place sexually, resulting in the production of a seed. Reproduction can also occur via asexual reproduction.
Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination
 * Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
* Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
Pea Patch Pollination Game
 Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION
 ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences PLANTS AND ANIMALS Plants And Animals Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book
ELEMENTARY SCIENCE PROGRAM MATH, SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION A Collection of Learning Experiences PLANTS AND ANIMALS Plants And Animals Student Activity Book Name This learning experience activity book
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
2. Which of the following is an organism that is made of only one cell? A. a larva B. an oyster C. an amoeba D. a mold
 1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination
 Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
Understanding Sexual Reproduction
 Lesson A3-1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction Horticulture Cluster Illinois Agricultural Education Core Curriculum Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 3. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Understanding
Lesson A3-1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction Horticulture Cluster Illinois Agricultural Education Core Curriculum Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 3. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Understanding
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
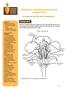 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Directed Reading B. Section: Structures of Seed Plants. 1. What moves water and minerals through a plant? a. xylem c. seeds b. phloem d.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. What moves water and minerals through a plant? a. xylem c. seeds b. phloem d. rhizomes 2. What moves food to all plant parts? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Structures of Seed Plants 1. What moves water and minerals through a plant? a. xylem c. seeds b. phloem d. rhizomes 2. What moves food to all plant parts? a.
All About Plants. What are plants?
 All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS
 TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee?
 o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
Printables for Living Sunlight for Grades 3-5
 Printables for Living Sunlight for Grades 3-5 Printable 1-6 are a series of six diagrams that are designed for teachers to use to review the content of Living Sunlight. Printables 1a-6a are worksheets
Printables for Living Sunlight for Grades 3-5 Printable 1-6 are a series of six diagrams that are designed for teachers to use to review the content of Living Sunlight. Printables 1a-6a are worksheets
MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2016/2017
 S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L M R I E H E L ST THOMAS MORE COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL ZEJTUN MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2016/2017 FORM: 3 Biology Time: 2hrs NOTE: / indicates alternative answers.
S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L M R I E H E L ST THOMAS MORE COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL ZEJTUN MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2016/2017 FORM: 3 Biology Time: 2hrs NOTE: / indicates alternative answers.
Quick Lab. The Structure of Seeds
 3 Seed Plants Key Concept Seed plants produce seeds and are categorized as gymnosperms or angiosperms. What You Will Learn Seed plants differ from seedless plants in three main ways. A seed is composed
3 Seed Plants Key Concept Seed plants produce seeds and are categorized as gymnosperms or angiosperms. What You Will Learn Seed plants differ from seedless plants in three main ways. A seed is composed
Kingdom Plantae. Plants or metaphytes are, autotrophic multicellular eukaryotes, with tissues.
 Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Kingdom Plantae Key words feature bryophytes herbaceous node to release pteridophytes sporangium, leaf (leaves) damp gymnosperms vascular apix cluster angiosperms rhizome sepal shrub tropism fronds calyx
Self-Guided Tour. Plants and the Plant Life Cycle. K to 2nd Grade
 Time Required: 60 min April to October Topic: Observing plant life cycles in the Garden Materials: For each student: Pencil or crayons Clipboards (recommended) Comparison Worksheet Colored dots (recommended)
Time Required: 60 min April to October Topic: Observing plant life cycles in the Garden Materials: For each student: Pencil or crayons Clipboards (recommended) Comparison Worksheet Colored dots (recommended)
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Tree Growth and Development Lesson 2: Understanding the Growth and Decline of Forest Trees Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
Unit B: Tree Growth and Development Lesson 2: Understanding the Growth and Decline of Forest Trees Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following
THINK! Why is it important for a cotyledon to take up so much room inside a seed? (Respond in your science notebook.)
 Germination Plant Unit Reading and Activity Guide When are dispersed from the plant, they can either lay or they can begin to grow immediately given the right conditions. This early stage of seed growth
Germination Plant Unit Reading and Activity Guide When are dispersed from the plant, they can either lay or they can begin to grow immediately given the right conditions. This early stage of seed growth
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction
 Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Objectives. To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants.
 1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
1 Objectives To identify plant structures and functions. To describe the structure of plant cells. To explain the process of reproduction in plants. 2 Main Menu Plant Cell Biology Plant Structures Roots
The Approach Billy utilizes comprehensive sensory integration through song, dance, audience participation and a multidimensional
 The Singing Tree Plant roots have hair! Root hairs increase the surface area of roots to improve absorption of water and minerals. The Approach Billy utilizes comprehensive sensory integration through
The Singing Tree Plant roots have hair! Root hairs increase the surface area of roots to improve absorption of water and minerals. The Approach Billy utilizes comprehensive sensory integration through
Plants. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 Plants Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The leaf s cuticle a. stores water. b. reduces evaporation. c. transports water in the leaf. d.
Plants Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The leaf s cuticle a. stores water. b. reduces evaporation. c. transports water in the leaf. d.
2.2 Botany Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Living things are an important part of our environment.
 2.2 Botany Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Living things are an important part of our environment. Essential Question: How is everything interconnected? How does one living thing rely on another?
2.2 Botany Unit Overview Enduring Understanding: Living things are an important part of our environment. Essential Question: How is everything interconnected? How does one living thing rely on another?
plant cell tissue nerve cell paramecium
 plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
plant or animal cell? these cells carry what cell? what cell? animal cell red blood oxygen sperm root hair cell (of plant) plant or animal cell? cell, tissue or organ? what cell? paramecium, amoeba or
3.02 Morphology (external) and Anatomy (internal) Packet: P5 Plant Leaves you will explore both compound and simple leaves. Enjoy the journey.
 02 Morphology (external) and Anatomy (internal) Packet: P5 Plant Leaves you will explore both compound and simple leaves. Enjoy the journey. Simple Leaf Morphology List five edible plant leaves: 5. Compound
02 Morphology (external) and Anatomy (internal) Packet: P5 Plant Leaves you will explore both compound and simple leaves. Enjoy the journey. Simple Leaf Morphology List five edible plant leaves: 5. Compound
Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 5. Plants. Overview
 Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 5 Plants Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 20 minutes) Content to be learned Distinguish between living and nonliving things. Identify and sort based
Kindergarten Science, Quarter 4, Unit 5 Plants Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 20 minutes) Content to be learned Distinguish between living and nonliving things. Identify and sort based
