Dave Mackas 1 and Jackie King 2
|
|
|
- Baldric McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classification of Zooplankton Life History Strategies Ctenophores Medusae Pteropod s 0.2 Free-spawning Copepods Reproduction PC Euphausiid Chaetognaths Salp/Doliolid -0.6 Sacspawning Copepods Cladoceran Amphipods Mysid Reproduction P C1 Dave Mackas 1 and Jackie King 2 Fisheries & Oceans Canada 1 Institute of Ocean Sciences & 2 Pacific Biological Station
2 Outline of Talk: Motivation for the analysis LHS theory - historical summary Ordination of zooplankton LHS traits Analysis methods Choice of traits Results & Interpretations Comparison to anomaly time series
3 Motivation: Understanding who wins Zooplankton communities include many species & strategies. A few are usually dominant, others always rare, others show intense, unpredictable outbreaks Ave. climatology vs. Ugly(?) Reality
4 Historical Background (1) r vs. K theory (e.g. Pianka 1970, Levins 1968) Investment in reproduction, rapid growth & dispersal vs. Investment in survival and ability to compete (Doesn t t consider age structure within the population, nor constraints imposed by morphology)
5 Historical Background (2) Demographic Theory (e.g. Winemiller & Rose, 1992) Three end-members: Opportunist - quick turnover ( r strategy) Equilibrium high survival rate, especially of juveniles ( K strategy) Periodic fecundity very high, but reached at older age (betting on eventual big win ) (Subsequent analyses identify additional LHS classes: Salmonid, Intermediate )
6 Historical Background: What about zooplankton?? Intensive research on individual traits within a few major taxonomic groups Egg number and survival for freevs. sac-spawning copepods Egg production vs. food availability Brooding Seasonal dormancy & resting eggs So far, little inter-group comparison
7 Our approach: Multivariate ordination of LHS (Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) of species-species distance matrix derived from species-traits matrix, King & McFarlane 2003) to identify: Life-history traits that covary across taxa Taxa that share similar strategies
8 Issues and obstacles encountered: Qualitative diversity of zooplankton LHS is much greater than for fish Within-species plasticity of some traits Information gaps for some life stages (especially survival rate) < often cannot do LxMx integration (Nevertheless, can rank/classify taxa on each trait. This is sufficient for PCoA ordination)
9 Choice of taxa: 36 temperate-subarctic marine spp. (many are present & occasionally dominant in northern California Current System) Free-spawning copepods: Calanus marshallae,, C. pacificus,, C. finmarchicus, Neocalanus plumchrus, Metridia, Temora, Paracalanus, Eucalanus, Rhincalanus Sac-spawning copepods: Pseudocalanus, Pareuchaeta, Eurytemora, Oithona similis Copepods with resting eggs: Acartia longiremis,, A. tonsa,, A. hudsonica, Centropages, Temora, Eurytemora Euphausiids: Euphausia pacifica, Thysanoessa spinifera Hyperiid amphipod: Parathemisto pacifica Gammariid amphipod: Calliopius laevisculus Cladoceran: Evadne Chaetognaths: Sagitta elegans, Eukrohnia Shelled Pteropods: Limacina,, Clio Planktonic tunicates: Salpa fusiformis (salp) Dolioletta (doliolid) Oikopleura (appendicularian) Ctenophores: Pleurobrachia, Mnemipopsis, Beroe Scyphozoan medusa: Aurelia aurita Hydrozoan medusae: Aglantha digitale, Aequorea
10 Reproductive : Log Fecundity r (per day) Lifespan (years) Iteroparous vs. Semelparous Mode of reproduction: Separate sexes? Hermaphroditic? Parthenogenetic? Alternating sexual/vegetative? Parental brooding: Free spawning Retain eggs Retain larvae Three categories of LHS traits: Growth : Log Adult size Somatic growth rate Fraction of lifespan in adult body form Refuges (Depth & Dormancy): Extent of diel migration Ontogenic migration? Dormancy As egg As adult/late juvenile Lipid storage? Benthic stage?
11 Ordination Results
12 PCoA on reproductive traits First 2 coordinates are significant PCo1 PCo2 Percent Variation Eigenvector log Fecundity r (per day) Lifespan (years) Iteroparous/Semelparous Mode of reproduction Parental brooding
13 Ordination of reproductive traits
14 Ordination of reproductive traits High r & fecundity Reproduction mostly sexual Some hermaphrodites Relatively low r Long life span Iteroparous High r, Short-lifespan, Semelparous, Repid vegetative reproduction Low fecundity Iteroparous Parental brooding
15 PCoA on growth traits First 2 coordinates are significant PCo1 PCo2 Percent Variation Eigenvector log Adult size (dry weight) Somatic growth (per day) Proportion juvenile/adult
16 Ordination of growth traits
17 Ordination of growth traits Large adult size, Rapid somatic growth, Diverse morphology or indirect development Intermediate adult size Low daily growth Direct development most of life in adult body form Small adult size, Rapid somatic growth
18 PCoA on refuge traits First 2 coordinates are significant PCo1 PCo2 Percent Variation Eigenvector Extent of diel migration Ontogenic migration Dormancy Storage of lipids Benthic stage Daytime depth
19 Ordination of refuge traits
20 Ordination of refuge traits Benthic stage or resting egg Remain active & near surface Large diel migration Deep daytime depth Ontogenetic migration, Lipid storage Dormancy as adult or late juvenile
21 Scores on lead axes from each PCoA are intercorrelated, mostly due to size dependence of rates
22 Additional 3D views Clusters sharing taxonomic & morphologic similarity: (I) Large vs. small copepods
23 Additional 3D views Clusters sharing taxonomic & morphologic similarity: (II) Large crustaceans vs. Salps/Doliolids
24 Additional 3D views Clusters sharing taxonomic & morphologic similarity: (III) Chaetognaths vs. Pteropods
25 Comparison with Time Series - Initial expectations: Sign of response correlated with LHS? Some LHS favored during some ocean regimes (response to environmental change similar within a LHS cluster) Time scale of response correlated with LHS Rapid decay of temporal autocorrelation by opportunists (=spikey time series) Slow decorrelation by equilibrium and periodic groups (time series contain gradual trends and multi- year fluctuations)
26 Comparison with Time Series- Results Interesting, but more complicated than expectation.. Anomaly time series provide examples of: Anticorrelation within LHS clusters Differences in amplitude & time scale between LHS clusters Differences in time scale within LHS clusters
27 Anticorrelation within LHS clusters Species replacement, driven by shifting faunal boundaries, not by LHS difference
28 Contrasts of sign & time scale within LHS clusters (2) Salp time series definitely spikey Doliolid time series more like the copepods
29 Gradients of amplitude & time scale between LHS clusters Trend and Regime responses within cool water zoogeographic cluster are modulated by reproductive and dormancy strategies
30 Summary PCoA ordination summarized variability among zooplankton life history strategies ALL observed strategies persist locally and are represented ~globally LHS clusters map strongly onto taxonomy, but with some surprises Interannual change (in our region) is dominated by shifting zoogeographic affinity, but modulated by LHS (True elsewhere?)
31 Future Directions Include within-species plasticity of LHS ( point < range description of traits) Improve classification & quantification of multi-phase LHS (sexual-asexual, asexual, active- dormant, planktonic-benthic, direct development vs. metamorphosis) Include more taxa Compare with other regions
32 BIG thanks to the following for advice & data: Mary Arai & Jenny Purcell (medusae( medusae) Carol Lalli (pteropods) Jaime Gomez-Gutierrez, Gutierrez, Tracy Shaw, Leah Feinberg & Bill Peterson (euphausiids( euphausiids) Andrew Hirst (growth rate theory) Xenia Kosobokova (chaetognaths) Moira Galbraith (size & abundance trends)
33
34 Spares & extras
35 LHS of Marine Invertebrates (summary from Ramirez-Llorda 2002) Most comparisons have been among benthic taxa Tradeoffs of fecundity vs. other modes of parental investment (egg size, brooding,.) Effects of food availability Gradients with increasing latitude and depth (fewer and larger eggs)
36 Historical Background (3) Fish LHS refinements (e.g. King & McFarlane 2003) Two additional clusters: Salmonid resemble opportunistic but large adults & eggs; split life cycle between ocean & FW Intermediate resemble periodic but shorter life span and lower fecundity
Interannual changes in the zooplankton community structure on the southeastern Bering Sea shelf and Chukchi Sea during summers of
 Interannual changes in the zooplankton community structure on the southeastern Bering Sea shelf and Chukchi Sea during summers of 1991 29 22 27 Shiberia Chukchi Sea Alaska Pacific Summer Water Bering Sea
Interannual changes in the zooplankton community structure on the southeastern Bering Sea shelf and Chukchi Sea during summers of 1991 29 22 27 Shiberia Chukchi Sea Alaska Pacific Summer Water Bering Sea
Copepods as indicator species for comparing pelagic ecosystem models
 Copepods as indicator species for comparing pelagic ecosystem models Outline Harold P. Batchelder Oregon State University Corvallis, OR hbatchelder@coas.oregonstate.edu Ecosystem Model Types Decisions
Copepods as indicator species for comparing pelagic ecosystem models Outline Harold P. Batchelder Oregon State University Corvallis, OR hbatchelder@coas.oregonstate.edu Ecosystem Model Types Decisions
Cross-shore exchange processes, and their effect on zooplankton biomass and community composition patterns in the Northeast Pacific
 Cross-shore exchange processes, and their effect on zooplankton biomass and community composition patterns in the Northeast Pacific D.L. Mackas Fisheries & Oceans Canada Institute of Ocean Sciences K.O.
Cross-shore exchange processes, and their effect on zooplankton biomass and community composition patterns in the Northeast Pacific D.L. Mackas Fisheries & Oceans Canada Institute of Ocean Sciences K.O.
Diel Vertical Migration OCN 621
 Diel Vertical Migration OCN 621 Outline Definition Who does it? How fast? Migration cues Why? Variations: seasonal, ontogenic, reverse Biogeochemical implications Diel Vertical Migration: Definitions Usually
Diel Vertical Migration OCN 621 Outline Definition Who does it? How fast? Migration cues Why? Variations: seasonal, ontogenic, reverse Biogeochemical implications Diel Vertical Migration: Definitions Usually
A Comparison of the Anomalous Ocean Conditions observed off the West Coast of Canada in 2014 and 2015.
 A Comparison of the Anomalous Ocean Conditions observed off the West Coast of Canada in 2014 and 2015. Peter Chandler, Marie Robert, Moira Galbraith Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries and Oceans Canada,
A Comparison of the Anomalous Ocean Conditions observed off the West Coast of Canada in 2014 and 2015. Peter Chandler, Marie Robert, Moira Galbraith Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries and Oceans Canada,
Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 19
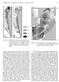 Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 19 Figure 18. Distribution of zooplankton biomass (mg m 3 ) near the western coast of Kamchatka in the 0-50 m layer: 1 = 100-500, 2 = 500-1,000,
Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 19 Figure 18. Distribution of zooplankton biomass (mg m 3 ) near the western coast of Kamchatka in the 0-50 m layer: 1 = 100-500, 2 = 500-1,000,
Interannual variations in vital rates of copepods and euphausiids during the RISE study
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc004826, 2009 Interannual variations in vital rates of copepods and euphausiids during the RISE study 2004 2006 C. Tracy Shaw, 1 Leah R. Feinberg,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc004826, 2009 Interannual variations in vital rates of copepods and euphausiids during the RISE study 2004 2006 C. Tracy Shaw, 1 Leah R. Feinberg,
2001 State of the Ocean: Chemical and Biological Oceanographic Conditions in the Newfoundland Region
 Stock Status Report G2-2 (2) 1 State of the Ocean: Chemical and Biological Oceanographic Conditions in the Background The Altantic Zone Monitoring Program (AZMP) was implemented in 1998 with the aim of
Stock Status Report G2-2 (2) 1 State of the Ocean: Chemical and Biological Oceanographic Conditions in the Background The Altantic Zone Monitoring Program (AZMP) was implemented in 1998 with the aim of
Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 1 ABSTRACT
 Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 1 ABSTRACT The major Russian reports addressing Okhotsk Sea zooplankton published from 194 to 1999 are reviewed. Topics include a summary of
Zooplankton of the Okhotsk Sea: A Review of Russian Studies 1 ABSTRACT The major Russian reports addressing Okhotsk Sea zooplankton published from 194 to 1999 are reviewed. Topics include a summary of
The Grand Unified Theory Of Copepods
 The Grand Unified Theory Of Copepods 1 ϘϘϘ1Ϙ1Ϙ111Ϙ ϘϘ111Ϙ Nick Record, Andrew Pershing, Frederic Maps ϘϘ1Ϙ11 University of Maine / Gulf of Maine Research Institute 1ϘϘ11 1ϘϘϘ1ϘϘϘϘ1Ϙ1Ϙ ESSAS 2011 111ϘϘ1Ϙ11Ϙ1ϘϘ1
The Grand Unified Theory Of Copepods 1 ϘϘϘ1Ϙ1Ϙ111Ϙ ϘϘ111Ϙ Nick Record, Andrew Pershing, Frederic Maps ϘϘ1Ϙ11 University of Maine / Gulf of Maine Research Institute 1ϘϘ11 1ϘϘϘ1ϘϘϘϘ1Ϙ1Ϙ ESSAS 2011 111ϘϘ1Ϙ11Ϙ1ϘϘ1
Dominant Types of Plankton. Phytoplankton Size. Diatoms. Diatoms. Each size has advantages & disadvantages Small cells
 Dominant Types of Plankton Phytoplankton Diatoms dominant in neritic & upwelling zones Microflagellates dominant in oceanic zone Dinoflagellates dominant in transitional situations Zooplankton Protozoa
Dominant Types of Plankton Phytoplankton Diatoms dominant in neritic & upwelling zones Microflagellates dominant in oceanic zone Dinoflagellates dominant in transitional situations Zooplankton Protozoa
Fish Conservation and Management
 Fish Conservation and Management CONS 486 Life history: Reproduction Ross Chapter 3 Reproduction topics Reproduction Fecundity Life history strategies Reproductive Schedules Semelparity vs iteroparity
Fish Conservation and Management CONS 486 Life history: Reproduction Ross Chapter 3 Reproduction topics Reproduction Fecundity Life history strategies Reproductive Schedules Semelparity vs iteroparity
5. Reproduction and Recruitment
 5. Reproduction and Recruitment Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Reproductive effort Developmental types Developmental trends What is recruitment Factors affecting recruitment Process of larval habitat selection
5. Reproduction and Recruitment Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Reproductive effort Developmental types Developmental trends What is recruitment Factors affecting recruitment Process of larval habitat selection
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Life history evolution
 Life history evolution Key concepts ˆ Cole s paradox ˆ Tradeoffs ad the evolution of iteroparity ˆ Bet hedging in random environments Life history theory The life history of a species consists of its life
Life history evolution Key concepts ˆ Cole s paradox ˆ Tradeoffs ad the evolution of iteroparity ˆ Bet hedging in random environments Life history theory The life history of a species consists of its life
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems. Niche Diversification Hypothesis Assumptions:
 Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
Current controversies in Marine Ecology with an emphasis on Coral reef systems Open vs closed populations (already Discussed) The extent and importance of larval dispersal Maintenance of Diversity Equilibrial
5. Reproduction and Recruitment
 5. Reproduction and Recruitment Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Reproductive effort Developmental types Trends in reproductive ecology What is recruitment? Factors affecting recruitment Process of larval
5. Reproduction and Recruitment Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Reproductive effort Developmental types Trends in reproductive ecology What is recruitment? Factors affecting recruitment Process of larval
Chapter 6 Lecture. Life History Strategies. Spring 2013
 Chapter 6 Lecture Life History Strategies Spring 2013 6.1 Introduction: Diversity of Life History Strategies Variation in breeding strategies, fecundity, and probability of survival at different stages
Chapter 6 Lecture Life History Strategies Spring 2013 6.1 Introduction: Diversity of Life History Strategies Variation in breeding strategies, fecundity, and probability of survival at different stages
Zooplankton anomalies in the California Current system before and during the warm ocean conditions of 2005
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L22S07, doi:10.1029/2006gl027930, 2006 Zooplankton anomalies in the California Current system before and during the warm ocean conditions of 2005 D. L. Mackas, 1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L22S07, doi:10.1029/2006gl027930, 2006 Zooplankton anomalies in the California Current system before and during the warm ocean conditions of 2005 D. L. Mackas, 1
Figure 12. Modeled pycnocline depth changes for the period relative to the period , based on the depth of the sigma=26.
 Figure 12. Modeled pycnocline depth changes for the period 1977-97 relative to the period 1964-75, based on the depth of the sigma=26.4 isopycnal of the model hindcast. From Capotondi et al. (2004). Figure
Figure 12. Modeled pycnocline depth changes for the period 1977-97 relative to the period 1964-75, based on the depth of the sigma=26.4 isopycnal of the model hindcast. From Capotondi et al. (2004). Figure
A Review of Russian Studies
 A Review of Russian Studies Alexei I. Pinchuk Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks Fairbanks, Alaska A.J. Paul Seward Marine Center Laboratory Institute of Marine Science University
A Review of Russian Studies Alexei I. Pinchuk Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks Fairbanks, Alaska A.J. Paul Seward Marine Center Laboratory Institute of Marine Science University
Ecology 302: Lecture VI. Evolution of Life Histories
 Ecology 302: Lecture VI. Evolution of Life Histories (Ricklefs, Chapter 7; Life Histories, pp.46-48; Knowledge Project.) Spawning sockeye salmon (Oncorhyncus nerka). The adaptive significance (if any)
Ecology 302: Lecture VI. Evolution of Life Histories (Ricklefs, Chapter 7; Life Histories, pp.46-48; Knowledge Project.) Spawning sockeye salmon (Oncorhyncus nerka). The adaptive significance (if any)
Figure 11. Modeled pycnocline depth changes (CI = 5 m) for the period relative to the period , based on the depth of the sigma=26.
 Figure 11. Modeled pycnocline depth changes (CI = 5 m) for the period 1977-97 relative to the period 1964-75, based on the depth of the sigma=26.4 isopycnal of the model hindcast. Blue indicates shoaling.
Figure 11. Modeled pycnocline depth changes (CI = 5 m) for the period 1977-97 relative to the period 1964-75, based on the depth of the sigma=26.4 isopycnal of the model hindcast. Blue indicates shoaling.
Tidal and subtidal currents influence deep copepod aggregations along a shelf-basin margin
 The following supplement accompanies the article Tidal and subtidal currents influence deep copepod aggregations along a shelf-basin margin Kimberley T. A. Davies*, Tetjana Ross, Christopher T. Taggart
The following supplement accompanies the article Tidal and subtidal currents influence deep copepod aggregations along a shelf-basin margin Kimberley T. A. Davies*, Tetjana Ross, Christopher T. Taggart
VI) Population and Community Stability. VI) Population and Community Stability. I. Background / questions - refer back to succession
 VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state? C) At climax, are populations
VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state? C) At climax, are populations
VI) Population and Community Stability. VI) Population and Community Stability
 VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state? C) At climax, are populations
VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state? C) At climax, are populations
Individual-Based modeling of Copepods MAR524 Unit 11
 Individual-Based modeling of Copepods MAR524 Unit 11 Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth Outline Copepod
Individual-Based modeling of Copepods MAR524 Unit 11 Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth Outline Copepod
The Impact of Changing Sea Ice and Hydrographic Conditions on Biological Communities in the Northern Bering and Chukchi Seas
 The Impact of Changing Sea Ice and Hydrographic Conditions on Biological Communities in the Northern Bering and Chukchi Seas Jacqueline M. Grebmeier 1, Lee W. Cooper 1, and Karen E. Frey 2 1 University
The Impact of Changing Sea Ice and Hydrographic Conditions on Biological Communities in the Northern Bering and Chukchi Seas Jacqueline M. Grebmeier 1, Lee W. Cooper 1, and Karen E. Frey 2 1 University
Oceanographic assessment of the planktonic communities in the northeastern Chukchi Sea. Report for Survey year 2011
 Oceanographic assessment of the planktonic communities in the northeastern Chukchi Sea Report for Survey year 211 Russell R Hopcroft, Jennifer Questel, Pallavi Hariharan, Chris Stark, Cheryl Clarke-Hopcroft
Oceanographic assessment of the planktonic communities in the northeastern Chukchi Sea Report for Survey year 211 Russell R Hopcroft, Jennifer Questel, Pallavi Hariharan, Chris Stark, Cheryl Clarke-Hopcroft
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live
 History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live B. Etymology study of the origin and development of a word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869)
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live B. Etymology study of the origin and development of a word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869)
Plankton response to El Niño and La Niña 1999 in the southern region of the California Current
 Progress in Oceanography 54 (2002) 33 58 www.elsevier.com/locate/pocean Plankton response to El Niño 1997 1998 and La Niña 1999 in the southern region of the California Current B.E. Lavaniegos ab,, L.C.
Progress in Oceanography 54 (2002) 33 58 www.elsevier.com/locate/pocean Plankton response to El Niño 1997 1998 and La Niña 1999 in the southern region of the California Current B.E. Lavaniegos ab,, L.C.
VI) Population and Community Stability
 Proportional abundance VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state?
Proportional abundance VI) Population and Community Stability I. Background / questions - refer back to succession A) Do marine communities trend toward climax states? B) Is there a single climax state?
 Title NOTES ON SOME ANMAL PLANKTONS COLL FROM THE SEA OF JAPAN OFF SAN'N-D Author(s) Furuhashi, Kenzo Citation PUBLCATONS OF THE SETO MARNE BO LABORATORY (1952), 2(2): 257-260 ssue Date 1952-10-05 URL
Title NOTES ON SOME ANMAL PLANKTONS COLL FROM THE SEA OF JAPAN OFF SAN'N-D Author(s) Furuhashi, Kenzo Citation PUBLCATONS OF THE SETO MARNE BO LABORATORY (1952), 2(2): 257-260 ssue Date 1952-10-05 URL
Metridia pacifica, Calanus finmarchicus, Calanus pacificus,
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF in OCEANOGRAPHY JAMES FRANK HEBARD for the Ph. D. (Name) (Degree) (Major) Date thesis is presented May 13, 1966 Title DISTRIBUTION OF EUPHAUSIACEA AND COPEPODA OFF OREGON IN
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF in OCEANOGRAPHY JAMES FRANK HEBARD for the Ph. D. (Name) (Degree) (Major) Date thesis is presented May 13, 1966 Title DISTRIBUTION OF EUPHAUSIACEA AND COPEPODA OFF OREGON IN
Individual-Based modeling of Copepods
 Individual-Based modeling of Copepods Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth May 4, 2008 Outline Copepod Life
Individual-Based modeling of Copepods Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth May 4, 2008 Outline Copepod Life
Metacommunities Spatial Ecology of Communities
 Spatial Ecology of Communities Four perspectives for multiple species Patch dynamics principles of metapopulation models (patchy pops, Levins) Mass effects principles of source-sink and rescue effects
Spatial Ecology of Communities Four perspectives for multiple species Patch dynamics principles of metapopulation models (patchy pops, Levins) Mass effects principles of source-sink and rescue effects
Announcements. Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations
 Announcements Geology Primary Fields of Oceanography Chemistry Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations Next Thursday quiz on Kirchman reading (microbes) Moving from physical to biological
Announcements Geology Primary Fields of Oceanography Chemistry Third problem site due November 30 Review calculations Next Thursday quiz on Kirchman reading (microbes) Moving from physical to biological
Transport and coastal zooplankton communities in the northern California Current system
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047927, 2011 Transport and coastal zooplankton communities in the northern California Current system Hongsheng Bi, 1 William T. Peterson, 2 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047927, 2011 Transport and coastal zooplankton communities in the northern California Current system Hongsheng Bi, 1 William T. Peterson, 2 and
History and meaning of the word Ecology A. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live
 History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
History and meaning of the word Ecology. Definition 1. Oikos, ology - the study of the house - the place we live. Etymology - origin and development of the the word 1. Earliest - Haeckel (1869) - comprehensive
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY
 BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY AN INTRODUCTION 0 ^ J ty - y\ 2 S CAROL M. LALLI and TIMOTHY R. PARSONS University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada PERGAMON PRESS OXFORD NEW YORK SEOUL TOKYO ABOUT THIS VOLUME
Competition-induced starvation drives large-scale population cycles in Antarctic krill
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0177 Competition-induced starvation drives large-scale population cycles in Antarctic krill Alexey
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0177 Competition-induced starvation drives large-scale population cycles in Antarctic krill Alexey
Feeding: Metazoan Predators
 Feeding: Metazoan Predators What do Metazoans Eat? Other metazoans (carnivores) e.g., chaetognaths eat copepods & copepods eat smaller crustaceans phytoplankton (herbivores) esp. larger ones like diatoms
Feeding: Metazoan Predators What do Metazoans Eat? Other metazoans (carnivores) e.g., chaetognaths eat copepods & copepods eat smaller crustaceans phytoplankton (herbivores) esp. larger ones like diatoms
Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam
 Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam Topics: Genetic concepts from the lecture notes including; o Mitosis and Meiosis, Homologous Chromosomes, Haploid vs Diploid cells Reproductive Strategies Heaviest
Reproduction and Evolution Practice Exam Topics: Genetic concepts from the lecture notes including; o Mitosis and Meiosis, Homologous Chromosomes, Haploid vs Diploid cells Reproductive Strategies Heaviest
The biological importance of the major ocean currents
 The biological importance of the major ocean currents Squid and the western boundary currents Illex illecebrosus, the short-finned squid Squid use the Gulf Stream to facilitate their migration. The center
The biological importance of the major ocean currents Squid and the western boundary currents Illex illecebrosus, the short-finned squid Squid use the Gulf Stream to facilitate their migration. The center
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 14: Life Histories: 2. Components of life histories: Growth, fecundity and survivorship. 3. Components of life histories:
 BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 14: Life Histories: Lecture summary: Components of life histories: Growth. Fecundity. Survivorship. Reproductive value. Trade-offs. r- and K-selection. Habitat templates. Clutch
BIOS 3010: Ecology Lecture 14: Life Histories: Lecture summary: Components of life histories: Growth. Fecundity. Survivorship. Reproductive value. Trade-offs. r- and K-selection. Habitat templates. Clutch
Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units :
 Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 274: , 2004 Published June 24 Mar Ecol Prog Ser
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 274: 235 25, 24 Published June 24 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Ocean climate, euphausiids and auklet nesting: inter-annual trends and variation in phenology, diet and growth of
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 274: 235 25, 24 Published June 24 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Ocean climate, euphausiids and auklet nesting: inter-annual trends and variation in phenology, diet and growth of
IB 153 Fall 2006 Life histories and population regulation 9/21/2006. Life history classification schemes. r/k selection (MacArthur and Wilson 1967)
 IB 153 Fall 26 Life histories and 9/21/26 Today's lecture: 1. Finish discussion on life histories 2. Review exponential and logistic growth equations 3. Effects of density on vital rates and consequences
IB 153 Fall 26 Life histories and 9/21/26 Today's lecture: 1. Finish discussion on life histories 2. Review exponential and logistic growth equations 3. Effects of density on vital rates and consequences
Chapter 8. Sponges Phylum Porifera Basic characteristics: simple asymmetric sessile
 Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
Chapter 8 Key Concepts Sponges are asymmetric, sessile animals that filter food from the water circulating through their bodies. Sponges provide habitats for other animals. Cnidarians and ctenophores exhibit
Aquaculture Biology Laboratory
 Aquaculture Biology Laboratory Faculty of Fisheries Nagasaki University Professor: Dr. Atsushi Hagiwara (hagiwara@net.nagasaki-u.ac.jp) Associate Professor: Dr. Yoshitaka Sakakura (sakakura@net.nagasaki-u.ac.jp)
Aquaculture Biology Laboratory Faculty of Fisheries Nagasaki University Professor: Dr. Atsushi Hagiwara (hagiwara@net.nagasaki-u.ac.jp) Associate Professor: Dr. Yoshitaka Sakakura (sakakura@net.nagasaki-u.ac.jp)
Chapter 8. Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms
 Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Cnidarians: Animals with Stinging Cells Phylum Cnidaria Includes hydroids, corals, and sea anemones Coelenterate: synonym Named for their cnidocytes
Chapter 8 Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms Cnidarians: Animals with Stinging Cells Phylum Cnidaria Includes hydroids, corals, and sea anemones Coelenterate: synonym Named for their cnidocytes
Canada 1+1. Ocean Station "Papa" Detailed Zooplankton Data: Brenda J. Waddell and Skip McKinnell
 Scientific Excellence Resource Protection & Conservation Benefits for Canadians Excellence scientifique Protection et conservation des ressources Benefices aux Canadiens Ocean Station "Papa" Detailed Zooplankton
Scientific Excellence Resource Protection & Conservation Benefits for Canadians Excellence scientifique Protection et conservation des ressources Benefices aux Canadiens Ocean Station "Papa" Detailed Zooplankton
Crucial factors affecting reproductive investment of marine fishes in a changing climate
 Crucial factors affecting reproductive investment of marine fishes in a changing climate Olav Sigurd Kjesbu Institute of Marine Research and Hjort Centre for Marine Ecosystem Dynamics 2016 PICES Annual
Crucial factors affecting reproductive investment of marine fishes in a changing climate Olav Sigurd Kjesbu Institute of Marine Research and Hjort Centre for Marine Ecosystem Dynamics 2016 PICES Annual
SHIFT IN SIZE-AT-AGE OF THE STRAIT OF GEORGIA POPULATION OF PACIFIC HAKE (MERLUCCIUS PRODUCTUS)
 SHIFT IN SIZE-AT-AGE OF THE STRAIT OF GEORGIA POPULATION OF PACIFIC HAKE (MERLUCCIUS PRODUCTUS) JACQUELYNNE R. KING Pacific Biological Station Fisheries and Oceans Canada Nanaimo, British Columbia V9S
SHIFT IN SIZE-AT-AGE OF THE STRAIT OF GEORGIA POPULATION OF PACIFIC HAKE (MERLUCCIUS PRODUCTUS) JACQUELYNNE R. KING Pacific Biological Station Fisheries and Oceans Canada Nanaimo, British Columbia V9S
Porifera. Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin '"'. , ' I.
 , ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
, ' Porifera Thomas M. Frost Trout Lake Station Center for Limnology University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 4 '"'. Chapter Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. External Morphology
Zooplankton Investigations in the Setonaikai (Inland Sea of Japan),IV.*
 Journal of the Oceanographical Society of Japan Vol.25, No.3, pp.145 to 150, June 1969 Zooplankton Investigations in the Setonaikai (Inland Sea of Japan),IV.* Occurrence of Zooplankton in the Sea Regions
Journal of the Oceanographical Society of Japan Vol.25, No.3, pp.145 to 150, June 1969 Zooplankton Investigations in the Setonaikai (Inland Sea of Japan),IV.* Occurrence of Zooplankton in the Sea Regions
Life History Evolution
 Life history evolution References Stearns (1992) The Evolution of Life Histories Roff (2002) Review Partridge & Harvey (1988) Science 241: 1449-1455 1 Overview Life history traits Life history : how individuals
Life history evolution References Stearns (1992) The Evolution of Life Histories Roff (2002) Review Partridge & Harvey (1988) Science 241: 1449-1455 1 Overview Life history traits Life history : how individuals
Growth and development of Pseudocalanus spp. in the northern Gulf of Alaska
 Growth and development of Pseudocalanus spp. in the northern Gulf of Alaska HUI LIU AND RUSSELL R. HOPCROFT* INSTITUTE OF MARINE SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS, AK 99775-7220, USA PRESENT ADDRESS:
Growth and development of Pseudocalanus spp. in the northern Gulf of Alaska HUI LIU AND RUSSELL R. HOPCROFT* INSTITUTE OF MARINE SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS, AK 99775-7220, USA PRESENT ADDRESS:
Integrated North Sea zooplankton identification: A combination of morphology, DNA and proteome analyses towards a cost and time-effictive application
 Integrated North Sea zooplankton identification: A combination of morphology, DNA and proteome analyses towards a cost and time-effictive application Silke Laakmann, Thomas Knebelsberger, Sabine Holst
Integrated North Sea zooplankton identification: A combination of morphology, DNA and proteome analyses towards a cost and time-effictive application Silke Laakmann, Thomas Knebelsberger, Sabine Holst
What is Growth? Increment in biomass Increase in volume Increase in length or area Cell division, expansion and differentiation. Fig. 35.
 What is Growth? Increment in biomass Increase in volume Increase in length or area Cell division, expansion and differentiation Fig. 35.18 Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin
What is Growth? Increment in biomass Increase in volume Increase in length or area Cell division, expansion and differentiation Fig. 35.18 Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin
Spatial-Temporal Patchiness. Patchiness Defined
 Spatial-Temporal Patchiness Steady State vs. Non-Steady State Box Models Chaos, Non-linearity Spectral Analysis Small-Scale Variability Medium-Scale Variability Large-Scale Variability The Paradox of the
Spatial-Temporal Patchiness Steady State vs. Non-Steady State Box Models Chaos, Non-linearity Spectral Analysis Small-Scale Variability Medium-Scale Variability Large-Scale Variability The Paradox of the
Population dynamics model of Copepoda (Neocalanus cristatus) in the northwestern subarctic Pacific
 Population dynamics model of Copepoda (Neocalanus cristatus) in the northwestern subarctic Pacific Zooplankton production symposium S1-3319 3, May, 27, Hiroshima Michio J. Kishi 1)2) and Takeshi Terui
Population dynamics model of Copepoda (Neocalanus cristatus) in the northwestern subarctic Pacific Zooplankton production symposium S1-3319 3, May, 27, Hiroshima Michio J. Kishi 1)2) and Takeshi Terui
Understanding the role of the YS Bottom Cold Water ( 10 C) on the survival strategy of Euphausia pacifica throughout the hot summer
 Understanding the role of the YS Bottom Cold Water ( 10 C) on the survival strategy of Euphausia pacifica throughout the hot summer Euphausia pacifica Se-J. Ju, H.S. Kim, W.S. Kim, D.H. Kang and A.R. Ko
Understanding the role of the YS Bottom Cold Water ( 10 C) on the survival strategy of Euphausia pacifica throughout the hot summer Euphausia pacifica Se-J. Ju, H.S. Kim, W.S. Kim, D.H. Kang and A.R. Ko
over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT
 Interannual Variability of Synoptic Scale Winds over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT Steve Morey Mark Bourassa Austin Todd COAPS/FSU This work is sponsored by the NASA Ocean Vector
Interannual Variability of Synoptic Scale Winds over the Northern West Florida Shelf from SeaWinds and ASCAT Steve Morey Mark Bourassa Austin Todd COAPS/FSU This work is sponsored by the NASA Ocean Vector
Environmental changes
 Environmental changes What are the fishery, environmental, and trophic effects in historical data? Can we use short-term predictions from multiple regression models? Two kind of predictions: What happens
Environmental changes What are the fishery, environmental, and trophic effects in historical data? Can we use short-term predictions from multiple regression models? Two kind of predictions: What happens
Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling
 Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling Part I Steve Railsback Humboldt State University Department of Mathematics & Lang, Railsback & Associates Arcata, California USA www.langrailsback.com 1 Outline 1.
Lecture 2: Individual-based Modelling Part I Steve Railsback Humboldt State University Department of Mathematics & Lang, Railsback & Associates Arcata, California USA www.langrailsback.com 1 Outline 1.
SPECIATION. REPRODUCTIVE BARRIERS PREZYGOTIC: Barriers that prevent fertilization. Habitat isolation Populations can t get together
 SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
Available from Deakin Research Online:
 This is the published version: Hays, G.C. 1995, Diel vertical migration behaviour of Calanus hyperboreus at temperate latitudes, Marine ecology progress series, vol. 127, pp. 301 304. Available from Deakin
This is the published version: Hays, G.C. 1995, Diel vertical migration behaviour of Calanus hyperboreus at temperate latitudes, Marine ecology progress series, vol. 127, pp. 301 304. Available from Deakin
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
1 Published June 30 I
 Vol. 9: 1-11. 1982 1 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published June 30 I Zooplankton Communities in the Bristol Channel and Severn Estuary N. R. Collins and R. Williams Natural
Vol. 9: 1-11. 1982 1 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published June 30 I Zooplankton Communities in the Bristol Channel and Severn Estuary N. R. Collins and R. Williams Natural
Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis. Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis. Alpha- Diversity. Alpha diversity definition(s)
 Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis Diversity - alpha, beta (, gamma) Beta- Diversity in practice: Ecological Distances Unsupervised Learning: Clustering, etc
Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis Lecture 2: Diversity, Distances, adonis Diversity - alpha, beta (, gamma) Beta- Diversity in practice: Ecological Distances Unsupervised Learning: Clustering, etc
Biological Signature of Scotian Shelf Water Crossovers on Georges Bank During Spring 1997
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Graduate School of Oceanography Faculty Publications Graduate School of Oceanography 2003 Biological Signature of Scotian Shelf Water Crossovers on Georges
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Graduate School of Oceanography Faculty Publications Graduate School of Oceanography 2003 Biological Signature of Scotian Shelf Water Crossovers on Georges
Reproductive success of Pacific copepods in the Arctic Ocean and the possibility of changes in the Arctic ecosystem
 Polar Biol (2015) 38:1075 1079 DOI 10.1007/s00300-015-1658-3 SHORT NOTE Reproductive success of Pacific copepods in the Arctic Ocean and the possibility of changes in the Arctic ecosystem Kohei Matsuno
Polar Biol (2015) 38:1075 1079 DOI 10.1007/s00300-015-1658-3 SHORT NOTE Reproductive success of Pacific copepods in the Arctic Ocean and the possibility of changes in the Arctic ecosystem Kohei Matsuno
아산만해역중형동물플랑크톤의시공간적변동
 The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 1 10, February 2006 아산만해역중형동물플랑크톤의시공간적변동 Á Á 1 Á 2 û w y w 1Ÿ w y œw 2 sw w w lœw Spatio-temporal Variation of Mesozooplankton
The Sea Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 1 10, February 2006 아산만해역중형동물플랑크톤의시공간적변동 Á Á 1 Á 2 û w y w 1Ÿ w y œw 2 sw w w lœw Spatio-temporal Variation of Mesozooplankton
262 Stockhausen and Hermann Modeling Larval Dispersion of Rockfish
 Stockhausen and Hermann Modeling Larval Dispersion of Rockfish 6 6 6 6 0 6 6 6 0 0 0 00 0 6 6 0 0 Figure. Sample IBM tracks for larvae released on April,. Numbered circles denote release locations; numbered
Stockhausen and Hermann Modeling Larval Dispersion of Rockfish 6 6 6 6 0 6 6 6 0 0 0 00 0 6 6 0 0 Figure. Sample IBM tracks for larvae released on April,. Numbered circles denote release locations; numbered
Changes in Coastal Ecosystems in the NE Pacific Ocean
 Changes in Coastal Ecosystems in the NE Pacific Ocean Paul J. Harrison 1, Frank Whitney 2, David Mackas 2, Richard Beamish 3, Marc Trudel 3, and R. Ian Perry 3 1 AMCE Program, Hong Kong University of Science
Changes in Coastal Ecosystems in the NE Pacific Ocean Paul J. Harrison 1, Frank Whitney 2, David Mackas 2, Richard Beamish 3, Marc Trudel 3, and R. Ian Perry 3 1 AMCE Program, Hong Kong University of Science
Ctenophores peeking into the group of unidentified species
 Ctenophores peeking into the group of unidentified species Morphological and molecular evidence reveal underestimated ctenophore species richness Majaneva Sanna, Hosia A, Halsband C, Lehtiniemi M, Majaneva
Ctenophores peeking into the group of unidentified species Morphological and molecular evidence reveal underestimated ctenophore species richness Majaneva Sanna, Hosia A, Halsband C, Lehtiniemi M, Majaneva
Body length, weight and chemical composition of the ontogenetically migrating copepods in the Western Subarctic Gyre of North Pacific Ocean
 Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan 55(2): 0000, 2008 The Plankton Society of Japan 2008 1) 1) Deborah K. Steinberg 2) 1) 8900056 45020 2) Verginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, P.O.
Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan 55(2): 0000, 2008 The Plankton Society of Japan 2008 1) 1) Deborah K. Steinberg 2) 1) 8900056 45020 2) Verginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, P.O.
IMO HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER. Description of the proposed model groups defined under Tier 1. Submitted by Norway
 INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE 47th session Agenda item 2 MEPC 47/INF.11 28 December 2001 ENGLISH ONLY HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER Description
INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION E IMO MARINE ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION COMMITTEE 47th session Agenda item 2 MEPC 47/INF.11 28 December 2001 ENGLISH ONLY HARMFUL AQUATIC ORGANISMS IN BALLAST WATER Description
Temperature. (1) directly controls metabolic rates of ectotherms (invertebrates, fish) Individual species
 Temperature (1) directly controls metabolic rates of ectotherms (invertebrates, fish) Individual species (2) controls concentrations (3) is relatively predictable over and can provide a basis for species.
Temperature (1) directly controls metabolic rates of ectotherms (invertebrates, fish) Individual species (2) controls concentrations (3) is relatively predictable over and can provide a basis for species.
Changes in dominance of copepods off Baja California during the El Niño and La Niña
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 277: 147 165, 2004 Published August 16 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Changes in dominance of copepods off Baja California during the 1997 1999 El Niño and La Niña Luis C. Jiménez-Pérez
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 277: 147 165, 2004 Published August 16 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Changes in dominance of copepods off Baja California during the 1997 1999 El Niño and La Niña Luis C. Jiménez-Pérez
Chapter 6 Reading Questions
 Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
Chapter 6 Reading Questions 1. Fill in 5 key events in the re-establishment of the New England forest in the Opening Story: 1. Farmers begin leaving 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Broadleaf forest reestablished 2.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
Maintenance of species diversity
 1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
1. Ecological succession A) Definition: the sequential, predictable change in species composition over time foling a disturbance - Primary succession succession starts from a completely empty community
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Deep-Sea Research II
 Deep-Sea Research II 55 (2008) 2086 2105 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Deep-Sea Research II journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dsr2 Palmer LTER: Patterns of distribution of five dominant
Deep-Sea Research II 55 (2008) 2086 2105 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Deep-Sea Research II journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dsr2 Palmer LTER: Patterns of distribution of five dominant
A RECORD OF PLANKTON ON THE ECHO-SOUNDER. By D. H. Cushing and I. D. Richardson
 J. Mar. bioi.ass. U.K. (1956) 35, 231-24 Printed in Great Britain 231 A RECORD OF PLANKTON ON THE ECHO-SOUNDER By D. H. Cushing and I. D. Richardson Fisheries Laboratory, Lowestoft (Text-figs. 1-3) A number
J. Mar. bioi.ass. U.K. (1956) 35, 231-24 Printed in Great Britain 231 A RECORD OF PLANKTON ON THE ECHO-SOUNDER By D. H. Cushing and I. D. Richardson Fisheries Laboratory, Lowestoft (Text-figs. 1-3) A number
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Restoration Project Annual Report
 Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Restoration Project Annual Report Ecology and Demographics of Pacific Sand Lance, Ammodytes hexapterus Pallas, in Lower Cook Inlet, Alaska Restoration Project 99306 Final Report
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Restoration Project Annual Report Ecology and Demographics of Pacific Sand Lance, Ammodytes hexapterus Pallas, in Lower Cook Inlet, Alaska Restoration Project 99306 Final Report
What larval culture of Diadema antillarum
 What larval culture of Diadema antillarum, the long-spined sea urchin, the keystone herbivore of western tropical Atlantic coral reefs, tells us about Keys water quality Martin A. Moe A disease in 1983
What larval culture of Diadema antillarum, the long-spined sea urchin, the keystone herbivore of western tropical Atlantic coral reefs, tells us about Keys water quality Martin A. Moe A disease in 1983
Larvae. Juvenile. Adult. Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae. Pelagic Environment. settlement.
 13 - Marine Ecology Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae Larvae survive, grow, develop, disperse reproduce Pelagic Environment Benthic Environment settlement Adult Juvenile
13 - Marine Ecology Bipartite life cycle of benthic marine fishes with pelagic larvae Larvae survive, grow, develop, disperse reproduce Pelagic Environment Benthic Environment settlement Adult Juvenile
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I. Kingdom Animalia
 Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
Module 4: Marine Invertebrates I Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Animalia Contains the largest number of species We will split them into 2 large groups Invertebrates- Animals w/o a backbone Vertebrates- Animals
Oceanographic conditions in the JARPNII survey area from 2000 to 2013 using FRA-ROMS data
 Oceanographic conditions in the JARPNII survey area from 2000 to 2013 using FRA-ROMS data MAKOTO OKAZAKI 1, MASACHIKA MASUJIMA 1, HIROTO MURASE 2 AND KENJI MORINAGA 2 1 National Research Institute of Fisheries
Oceanographic conditions in the JARPNII survey area from 2000 to 2013 using FRA-ROMS data MAKOTO OKAZAKI 1, MASACHIKA MASUJIMA 1, HIROTO MURASE 2 AND KENJI MORINAGA 2 1 National Research Institute of Fisheries
Existing modelling studies on shellfish
 Existing modelling studies on shellfish Laboratoire Ressources Halieutiques IFREMER Port-en-Bessin, France Worldwide production of cultured shellfish GENIMPACT February 2007 Main species and producers
Existing modelling studies on shellfish Laboratoire Ressources Halieutiques IFREMER Port-en-Bessin, France Worldwide production of cultured shellfish GENIMPACT February 2007 Main species and producers
Data Processing and Analysis: Literature Update. FISH 538 Emma DeWitt Cotter
 Data Processing and Analysis: Literature Update FISH 538 Emma DeWitt Cotter Calibration Results Acoustic Data Hydrographic data Abundance Estimations Known Target Strength Curves Survey Track Geography
Data Processing and Analysis: Literature Update FISH 538 Emma DeWitt Cotter Calibration Results Acoustic Data Hydrographic data Abundance Estimations Known Target Strength Curves Survey Track Geography
5/31/17. Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS. Page 88
 Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information 1. Deriving values of scaling exponents of surface area versus body mass (b A ) by applying Euclidean geometry to additional dimensional measurements in the study species Given
1 Supplementary Information 1. Deriving values of scaling exponents of surface area versus body mass (b A ) by applying Euclidean geometry to additional dimensional measurements in the study species Given
Appendix 12J Winter-Run Chinook Salmon Life Cycle Modeling
 Appendix 12J Winter-Run Chinook Salmon Life Cycle Modeling Line items and numbers identified or noted as No Action Alternative represent the Existing Conditions/No Project/No Action Condition (described
Appendix 12J Winter-Run Chinook Salmon Life Cycle Modeling Line items and numbers identified or noted as No Action Alternative represent the Existing Conditions/No Project/No Action Condition (described
Phytoplankton. Zooplankton. Nutrients
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
HOW TRAITS ARE INTERRELATED THROUGH. Survival. Fecundity. Survival and fecundity both depend on Feeding. To eat. To survive.
 --5 What is a key trait? A property that is a main determinant of an individual s fitness HOW TRAITS ARE INTERRELATED THROUGH TRADE-OFFS IN ZOOPLANKTON* m m. mm.5 mm. mm Commonly used fitness measures:
--5 What is a key trait? A property that is a main determinant of an individual s fitness HOW TRAITS ARE INTERRELATED THROUGH TRADE-OFFS IN ZOOPLANKTON* m m. mm.5 mm. mm Commonly used fitness measures:
Outline u Krill u Pteropods u Copepods u Forams
 Ocean Acidification Impacts on Marine Plankton in Alaskan Waters Richard A. Feely 1, Nina Bednarsek 1,2 and Shallin Busch 3 1 Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory/NOAA, 2 JISAO/UW, 3 NWFSC/NOAA Outline
Ocean Acidification Impacts on Marine Plankton in Alaskan Waters Richard A. Feely 1, Nina Bednarsek 1,2 and Shallin Busch 3 1 Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory/NOAA, 2 JISAO/UW, 3 NWFSC/NOAA Outline
53 contributors for 35 individual reports in 2009 show 5% of figures today
 A Group Approach to Understanding Ecosystem Dynamics in the Northeast Pacific Ocean William Crawford and James Irvine, Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) * * * 53 contributors for 35 individual reports
A Group Approach to Understanding Ecosystem Dynamics in the Northeast Pacific Ocean William Crawford and James Irvine, Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) * * * 53 contributors for 35 individual reports
