706 [Vol. 34, 162. Somatic Syn.desis in Daphne odora.11*' The Chromosome Behavior in Meiosis
|
|
|
- Mavis Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 706 [Vol. 34, 162. Somatic Syn.desis in Daphne odora.11*' The Chromosome Behavior in Meiosis By Tosisuke HIRAOKA Botanical Institute, College of Science, Kyoto University (Comm. by Y. KUWADA, M.J.A., Dec. 12, 1958) In the first paper, the behavior in mitosis of the chromosomes in somatic syndesis in Daphne odora was reported (Hiraoka, 1958). In the present paper, the behavior in meiosis will be reported. Material and methods. The observations were made in sporogenous cells, pollen mother cells, and pollen grains by the methods of acetocarmine smear and paraffin section preparation (Hiraoka, 1958). In some cases, fresh pollen mother cells were observed in situ in the anther with liquid paraffin as mounting medium. Observation. 1) Premeiotic mitoses and the last interphase just preceding meiosis. In the premeiotic mitoses including the last one, the chromosome behavior is similar to that observed in the ordinary somatic mitosis. The somatic syndesis takes place in anaphase and the complete or incomplete liberation from the syndesis is observed in prophase (cf. Hiraoka, 1958). When the last interphase approaches, the mitotic process proceeds synchronously in all cells in the loculus. In interphasic nuclei, the chromosomal bodies are found distributed along the nuclear periphery. The chromosomal bodies are somewhat irregular in outline and show a vacuolated structure. The number of these bodies observed in each nucleus varies to some extent, but the number of highest frequency is 14, a number which is the haploid (Table I). One or two nucleoli of different sizes are found in the nucleus. The nucleolus is spherical in shape and frequently shows a vacuolated structure (Fig. 1). Table I. Last premeiotic interphase 2) Meiosis. When the meiosis commences, the chromosomal bodies become more irregular in outline than in the interphase. In some cases they show several fine threads projecting out of their surface. The vacuolated structure of the bodies which is observed in the in- *) Studies on the mechanism of nuclear division, IV. This investigation is supported by a Grant from the " Jimbun Kagaku Kenkyuhi " of the Ministry of Education.
2 No. 10] Somatic Syndesis in Daphne odora. II 707 terphase is now transformed into a thread structure irregularly entangled. As the thread structure is more distinctly observed in the bodies, the bodies become more indistinct in their outline (chromonema stage, Fig. 2). At this stage, some of the chromosomal bodies may join together with their projecting threads, but in the majority of cases they maintain their individuality. In the next stage the irregular outline of the bodies is rendered smooth again, and the chromonema threads which appeared to form the reticular structure are transformed into a form of more or less regular spiral or zig-zag. In some favourable cases, two spirals which lie side by side are discriminable in the body (Fig. 3). As the spirality becomes distinct in the bodies, the bodies are stained more intensely with the nuclear stains. These bodies are gradually condensed, finally to form the densely stainable massive bodies or prochromosomes (prochromosome stage, Hiraoka, 1941, Fig. 4). In the course of the prochromosome formation, a tendency of these bodies of gathering on one side of the nucleus is recognizable. These prochromosomes are in size nearly equal to or somewhat smaller than the chromosomal bodies in the interphase. Their number is estimated at 14 on the fact that this number occurs most frequently (Table II). The prochromosomes are, therefore, in reality, double chromosomes in this case of somatic syndesis taking place in the premeiotic mitosis. In this stage the part of the nuclear membrane on the side opposite to the localized chromosome group is often found separated from the surrounding cytoplasm, indicating that the pollen mother cells are extremely sensitive to the fixative. In the following stage, the prochromosomes become loosened, and very frequently, two loosely coiled spirals, sometimes twisting around and sometimes parallel with each other, are observable coming out of the prochromosome body (Fig. 5). The formation of the prochromosomes and this unravelling process do not always take place synchronously in all the prochromosomes in the nucleus, so that some of the prochromosomes remain massive, while others have been unravelled into two spirals (unravelling stage, Hiraoka, 1941). The two spirals are then drawn out from a loosely coiled state into two uncoiled threads, and the threads of a pair become dificultly distinguishable from the threads of other pairs. To speak in other words, it becomes hardly recognizable which two are the original two in pair. The leptotene nucleus is thus formed (Fig 6). Table II. Prochromosome stage
3 708 T. EIRAOKA [Vol. 34, In this plant, in the stages from late leptotene to early pachytene, it is very difficult to obtain well fixed figures. In the majority of cases, the so-called extrusion of nuclear substances occurs. It takes place in regular order from the top to the base of the anther, while in the region near the basal part of the anther the pollen mother cells usually show no extrusion at all. When living pollen mother Fig. 1. Interphase just preceding meiosis. Fig. 2. Chromonema stage. Fig 3. Early prochromosome stage. Fig. 4. Prochromosome stage. Fig. 5. Unravelling stage. Fig. 6. Leptotene. Fig. 7. Synaptic stage. Fig. 8. Pachytene. Fig. 9. Strepsitene. Fig. 10. Diakinesis. Fig metaphase. Fig. 12. Interkinesis. All from paraffin section preparations x
4 No. 10] Somatic Syndesis in Daphne odora. II 709 cells in these stages are observed in situ in the anther, no such extrusion is recognizable to occur. This result of observation points to the conclusion that the extrusion phenomenon is an artifact caused by fixation. Therefore, the following description is based on the result of observation of the pollen mother cells in the basal part of the anther where no extrusion takes place. In the leptotene the chromosome threads come to gather in some degree to form a mass (the so-called synizesis, Fig. 6). The chromosome threads are distributed evenly in the mass, but later they show some tendency of parallel arrangement (Fig. 7). Some of them are found looped out of the mass, and occasionally some indications of side by side pairing of two threads are recognizable. The threads then become distinctly thicker, and as the contraction en masse is rendered looser, the thick spiremes appearing to be of the structure of a series of disks are found distributed evenly in the nucleus, the pachytene stage (Fig. 8). In the diplotene, the duality of the spiremes is not clearly discernible along the whole length, but recognizable in places. In the strepsitene, the spiremes are much thicker and come together, to some extent, to locate in the central region of the nucleus (Fig. 9). Then the stage diakinesis follows, at which 14 bivalents are found distributed in the peripheral region of the nucleus. One or two of the bivalents are of ring shape and the rests are of dumbbel shape (Fig. 10). After the nuclear membrane and the nucleolus have disappeared, these bivalent chromosomes form a nuclear plate (Fig. 11). In acetocarmine preparations, there are some indications of the spiral structure of the chromosomes. The disjunction behavior of chromosomes at anaphase is not always normal, in some cases there occurring non-disjunction or chromosome lagging. The anaphasic chromosome pairing which is observed in somatic mitosis is not recognizable to occur in this case of meiosis. In the telophase, the polarized orientation of the chromosomes disappears rapidly, and in the early telophase the chromosomes are evenly distributed along the periphery of the nucleus, no trace of the polarization being recognizable at all. One or two nucleoli are formed in symmetrical positions in the sister nuclei. When the telophasic internal change takes place in the chromosomes, the chromosomes become irregular in outline, and the internal structure is rendered more or less looser, but each chromosome remains being individually distinguishable from others even in interkinetic nuclei (Fig. 12). The chromosome counting in the daughter nuclei in this stage shows that the number varies to some extent in accordance with the observed fact that here in the anaphase the non-disjunction and chromosome lagging occasionally occur (Table III). The high sterility of this plant may originate from these abnormalities in
5 710 T. HIRAOKA [Vol. 34, chromosome behavior (Osawa, 1913). A comparison of Table III with Table IV (II-metaphase) shows that the chromosomal elements appear in haploid number more frequently in interkinesis (61.10/c) than in second metaphase (49.0 o ). This fact may be taken as due to the fact that some non-disjunction chromosomes remain still in paired state during interkinesis. Table III. Interkinesis In the second metaphase the chromosomes are spherical or more or less ellipsoidal, and show no marked difference in shape from the chromosomes in the first anaphase. The numbers of chromosomes obtained in the second metaphase are given in Table IV, which also vary to some extent. In the anaphase, the chromosomes, logitudinally divided, are separated to poles. No chromosome pairing was observed in the anaphase. However, in view of the facts that the chromosomes of second metaphase are free from pairing, and that the haploid number is found more frequently in pollen nuclei (61.4%) than in second metaphase plates (49.0%), it seems probable that pairing might occur at the second anaphase between certain chromosomes, as a result of introduction of some extra chromosomes by non-disjunction. When the chromosomes reach the pole, their polarized orientation disappears rapidly. In the tetrad nuclei thus formed, the chromosomes are evenly distributed in peripheral regions. Table IV. Second metaphase 3) Pollen grains. The mature pollen grains vary in size. A small grain may appear to have only 10 chromosomal bodies contained in its nucleus, but in the majority of cases where pollen grains are of large sizes the number of these bodies amounts to 14, the haploid number, a result showing the free state of chromosomes from pairing. The statistical data are given in Table V. Table V. Pollen grains
6 No. 10) Somatic Syndesis in Daphne odora. II. 711 Conclusion.. While in some Diptera (Stevens, 1910; Metz and Nonidez, 1921; Metz, 1927; and others) it has been reported that the somatic syndesis in the last premeiotic ana- and telophase is maintained throughout the growth period, the synaptic stage being in these cases considered ineffective (Culex) or observably completely omitted (Asilus and Drosophila), in Daphne the result of observation appears to show that the pairing at the last premeiotic anaphase is cancelled at leptotene stage, and that in the following stage, the meiotic syndesis takes place afresh between homologous chromosomes. In view of the fact, however, that in leptotene and zygotene stages the nucleus is in a highly hydrated state, in different degrees in different species (Hiraoka,it rather seems more likely that the cancellation of pairing at leptotene stage in Daphne is a mere result from nuclear hydration in this stage or a temporary phenomenon of seeming dispairing due to swelling of chromosome matrix (old matrix) by hydration, not involving in it any fundamental change in synaptic activity. While in mitosis chromosome pairing takes place in anaphase, in meiosis it does not, if we disregard a possibility of occurrence of non-disjunction. However, we observed some cases of non-disjunction, and the results of chromosome counting suggest that while in the first anaphase no active pairing occurs there is a certain possibility of pairing in the second anaphase taking place between the chromosomes originating from non-disjunction. The non-disjunction is an abnormal behavior, however, and we should like to conclude that in Daphne, the behavior in meiosis of chromosomes in somatic syndesis is conforming as in mitosis with Darlington's view on chromosome association (Darlington, 1937). References Darlington, C. D. (1937): Recent Advances in Cytology, London. Hiraoka, T. (1941): Cytologia, 11. (1952) : Cytologia, 17. (1958): Proc. Japan Acad., 34, 700. Metz, C. W. (1927): Ztschr. Zellf. mikr. Anat., 4. Metz, C. W., and Nonidez, J. F. (1921): Jour. Exp. Zool., 32, Osawa, I. (1913): Jour. Agr. Imp. Univ. Tokyo, 4. Stevens, N. M. (1910): Jour. Exp. Zool., 8.
 Meiosis http://biology.tutorvista.com/cell/meiosis.html MEIOSIS It is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number is halved from the diploid number (2n) to a haploid number (n). Like mitosis
Meiosis http://biology.tutorvista.com/cell/meiosis.html MEIOSIS It is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number is halved from the diploid number (2n) to a haploid number (n). Like mitosis
The Gametic Cell Cycle
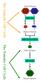 The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS
 CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell. Phases of cell
CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell. Phases of cell
The interphase is further divided into three phases, which are as follows:
 Cell Division Phases of Cell Cycle The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases: a. Interphase: The phase between subsequent cell divisions is called the interphase. The interphase lasts for more than
Cell Division Phases of Cell Cycle The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases: a. Interphase: The phase between subsequent cell divisions is called the interphase. The interphase lasts for more than
Class XI Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Biology
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Class XI Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Biology
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 1 CH 10 CELL CYCLE & CELL DIVISION CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Growth and reproduction are characteristics of living cells and organisms. Cell Cycle The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its
1 CH 10 CELL CYCLE & CELL DIVISION CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Growth and reproduction are characteristics of living cells and organisms. Cell Cycle The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 49 49 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Meiosis results in a. Production of gametes b. Reduction in the number of chromosomes c. Introduction
CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 49 49 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Meiosis results in a. Production of gametes b. Reduction in the number of chromosomes c. Introduction
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-10
 Chapter-10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION POINTS TO REMEMBER Cell cycle : The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesis the other constitutents of the cell and eventually divides
Chapter-10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION POINTS TO REMEMBER Cell cycle : The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesis the other constitutents of the cell and eventually divides
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
NCERT. not to be published CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 CELL CYCLE 162 BIOLOGY
 162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: MEIOSIS
 MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
How did that single cell develop into a body with more than a trillion cells?
 CELL DIVISION Cell division is a process which leads to cell multiplication. It occurs in both plants and animals. Original cells which undergo division are known as parent cells and the new on ones resulting
CELL DIVISION Cell division is a process which leads to cell multiplication. It occurs in both plants and animals. Original cells which undergo division are known as parent cells and the new on ones resulting
Cell Division (Meiosis)
 Cell Division (Meiosis) Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Diploid (2n) haploid (n) Meiosis is sexual reproduction. Two divisions (meiosis
Cell Division (Meiosis) Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Diploid (2n) haploid (n) Meiosis is sexual reproduction. Two divisions (meiosis
General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division [ Contents: Cell Cycle,
 General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division A complete General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division for you competitive examinations such as UPSC, IAS, Banking SBI PO, Railway Group-D, SSC, CGL
General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division A complete General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division for you competitive examinations such as UPSC, IAS, Banking SBI PO, Railway Group-D, SSC, CGL
EXERCISE - 1 NEETIIT.COM. - Phase (3) Anaphase (4) G 2. (1) Plectonemic (2) Paranemic (3) Helical (4) Irregular
 1. Synapsis found in between - (1) Nonhomologous chromosome (2) Homologous chromosome (3) Nonhomologous and homologous chromosome (4) Chromatids 2. During cytokinesis in plants, which of the following
1. Synapsis found in between - (1) Nonhomologous chromosome (2) Homologous chromosome (3) Nonhomologous and homologous chromosome (4) Chromatids 2. During cytokinesis in plants, which of the following
Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes. Packet #29
 Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes Packet #29 Introduction Meiosis, discovered in 1883, was first observed through the fertilized egg and individual gametes, sperm and unfertilized egg,
Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes Packet #29 Introduction Meiosis, discovered in 1883, was first observed through the fertilized egg and individual gametes, sperm and unfertilized egg,
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
CELL REPRODUCTION. Mitotic M phase Mitosis. Chromosomes divide. Cytokinesis. Cytoplasm and cell membrane divide. Chromosomes as Packaged Genes
 CELL REPRODUCTION Kimberly Lozano Biology 490 Spring 2010 CELL CYCLE Interphase G1: Growth (1) New organelles form within the cell. S: Synthesis Cell duplicates its DNA. G2: Growth (2) Cell prepares for
CELL REPRODUCTION Kimberly Lozano Biology 490 Spring 2010 CELL CYCLE Interphase G1: Growth (1) New organelles form within the cell. S: Synthesis Cell duplicates its DNA. G2: Growth (2) Cell prepares for
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES
 CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
11.4 Meiosis. Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad
 11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
Cell Division. Mitosis
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Sexual life cycle. Sexual life cycle. Fertilization. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n)
 Sexual life cycle Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n) Chapter 11 Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of Haploid cells (n) Gametes have only 1 set of
Sexual life cycle Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n) Chapter 11 Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of Haploid cells (n) Gametes have only 1 set of
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
Purposes of Cell Division
 Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Bell Ringer 02/02/15. Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures.
 Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
AP Biology Fall Semester Set 1
 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
E. Incorrect! At telophase II, cells are nearly completed with meiosis, with no cross-over.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
Meiosis: M-Phase part 2. How is meiosis different from mitosis? Some terms: Some terms: Some terms:
 M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
Review of Terms. Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome. Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome
 Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes
 BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes 1) Cell division is an important process in all living things. State any four reasons to support your answer. New cells
BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes 1) Cell division is an important process in all living things. State any four reasons to support your answer. New cells
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division
 AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
gametes Gametes somatic cells diploid (2n) haploid (n)
 Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Overview of Meiosis Meiosis is a form of cell division that leads to the production of gametes. Gametes: egg cells and sperm cells (reproductive) -contain half the number of chromosomes of an adult body
Visualizing Meiosis Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide
 Visualizing Meiosis Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide #35-1140 Paper #35-1141 Laminated Background Meiosis Basics Organisms with cells that contain a nucleus are called eukaryotes. The nucleus contains
Visualizing Meiosis Poster Illustrated Teacher's Guide #35-1140 Paper #35-1141 Laminated Background Meiosis Basics Organisms with cells that contain a nucleus are called eukaryotes. The nucleus contains
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 162 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
162 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: SIMULATION OF MEIOSIS EVOLUTION. Activity #9
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
Name: Date: Period: Cell Cycles and DNA Study Guide
 Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University
 CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
Reproduction & Cell Types
 Reproduction & Cell Types TYPES OF REPRODUCTION Asexual Relies on MITOSIS All of the parent s DNA goes to the offspring Sexual Relies on MEIOSIS Used to create sex cells TYPES OF CELLS Body Cells Includes
Reproduction & Cell Types TYPES OF REPRODUCTION Asexual Relies on MITOSIS All of the parent s DNA goes to the offspring Sexual Relies on MEIOSIS Used to create sex cells TYPES OF CELLS Body Cells Includes
Mitosis and Meiosis: Chromosome Simulation Carolina Distance Learning Investigation Manual
 Mitosis and Meiosis: Chromosome Simulation Carolina Distance Learning Investigation Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 3 OBJECTIVES... 3 TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3
Mitosis and Meiosis: Chromosome Simulation Carolina Distance Learning Investigation Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 3 OBJECTIVES... 3 TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3
CYTOLOGICAL STUDIES IN CULEX 11. DIPLOID AND MEIOTIC DIVISIONS
 CYTOLOGICAL STUDIES IN CULEX 11. DIPLOID AND MEIOTIC DIVISIONS SISTER MARY GRELL, O.S.B. Biological Laboratory, Fordham University, New York Received August 8, 1945 INTRODUCTION ART I of this study (GRELL
CYTOLOGICAL STUDIES IN CULEX 11. DIPLOID AND MEIOTIC DIVISIONS SISTER MARY GRELL, O.S.B. Biological Laboratory, Fordham University, New York Received August 8, 1945 INTRODUCTION ART I of this study (GRELL
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
BW #16. What are the phases of mitosis in order?
 BW #16 What are the phases of mitosis in order? COMPARING MITOSIS & MEIOSIS CELL DIVISION! Cell Cycle.how living things GROW!! Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase --------------- Cytokinesis
BW #16 What are the phases of mitosis in order? COMPARING MITOSIS & MEIOSIS CELL DIVISION! Cell Cycle.how living things GROW!! Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase --------------- Cytokinesis
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
LECTURE 10A: MEIO S S
 LECTURE 10A: MEIOSIS Meiosis Definition INTRODUCTION 1. Meiosis is the production of gametes, which is a reduction division which means a diploid gamete produces haploid gametes - from a full complement
LECTURE 10A: MEIOSIS Meiosis Definition INTRODUCTION 1. Meiosis is the production of gametes, which is a reduction division which means a diploid gamete produces haploid gametes - from a full complement
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction
 10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction Growth is a characteristic of all living things. You started out as a single cell. That cell quickly divided into two cells. Two cells became four and four became eight.
10.1 Growth and Cell Reproduction Growth is a characteristic of all living things. You started out as a single cell. That cell quickly divided into two cells. Two cells became four and four became eight.
Cell Division. Mitosis 11/8/2016
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
cycle & cell the division
 the cycle & celldivision the cell cycle Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division called the cell cycle. The cell cycle makes it possible for organisms to grow and
the cycle & celldivision the cell cycle Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division called the cell cycle. The cell cycle makes it possible for organisms to grow and
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
MEIOSIS. Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities.
 MEIOSIS Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities. Stages and Steps of Meiosis Interphase Same as in Mitosis 3 stages G1, S, G2 DNA replication and cell growth Meiosis I Prophase
MEIOSIS Stages of Meiosis, Gametogenesis, Sex Determination, & Abnormalities. Stages and Steps of Meiosis Interphase Same as in Mitosis 3 stages G1, S, G2 DNA replication and cell growth Meiosis I Prophase
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
5. As compared to the human sperm cell, the human egg cell contains more... a) cytoplasm c) centrosomes b) mitochondria d) chromosomes
 BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
11-4 Meiosis. Chromosome Number
 11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Sexual reproduction shuffles and recombines genes from two parents. During gametogenesis, genes are segregated and assorted (shuffled) into gemetes, and at fertilization,
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Sexual reproduction shuffles and recombines genes from two parents. During gametogenesis, genes are segregated and assorted (shuffled) into gemetes, and at fertilization,
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction
 Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders
 Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Biology Notes 2. Mitosis vs Meiosis
 Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Typical Life Cycle of Algae and Fungi. 5 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
2. is the period of growth and development for a cell. 3. During interphase, most cells go through three stages rapid growth and
 Chapter 5 Lesson 1- General Lesson Outline Directions: Use the words below to fill in the outline of the text from lesson one. If the word is used more than once, it is followed by the number of times
Chapter 5 Lesson 1- General Lesson Outline Directions: Use the words below to fill in the outline of the text from lesson one. If the word is used more than once, it is followed by the number of times
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
WarmUp 1. C. a phosphate group is removed
 WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Cell Division. Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 2/9/2016. Dr. Saud Alamri
 Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
SCIENCE M E I O S I S
 SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
Lab #12 Biology 10 BCC Topic: Mitosis and Meiosis Simulation Lab
 Lab #12 Biology 10 BCC Topic: Mitosis and Meiosis Simulation Lab Background: Mitosis With the exception of the original cells on Earth, all new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are
Lab #12 Biology 10 BCC Topic: Mitosis and Meiosis Simulation Lab Background: Mitosis With the exception of the original cells on Earth, all new cells come from previously existing cells. New cells are
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
MEIOSIS. KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 MEIOSIS MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. MEIOSIS : CELL TYPES You have Body cells and Gametes Body cells are also called somatic cells. Germ cells develop
MEIOSIS MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. MEIOSIS : CELL TYPES You have Body cells and Gametes Body cells are also called somatic cells. Germ cells develop
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4
 SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
Meiosis. Section 8-3
 Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
Meiosis Section 8-3 Meiosis process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number in the original cell For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive
Cellular Reproduction
 Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic):
 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
4/6/2014. Chromosome Number
 Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Meiosis 1of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division. A. Definitions:
 Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
