EXERCISE - 1 NEETIIT.COM. - Phase (3) Anaphase (4) G 2. (1) Plectonemic (2) Paranemic (3) Helical (4) Irregular
|
|
|
- Denis Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Synapsis found in between - (1) Nonhomologous chromosome (2) Homologous chromosome (3) Nonhomologous and homologous chromosome (4) Chromatids 2. During cytokinesis in plants, which of the following secretes the middle lamella - (1) Golgibody (2) SER (3) RER (4) Lysosomes 3. Pairing of homologous chromosomes is called- (1) Disjunction (2) Synapsis (3) Segregation (4) Polyteny 4. What type of division lead to coenocytic condition- (1) Cryptomitosis (2) Endomitosis (3) Free nuclear div. (4) Dino-mitosis 5. In which stage the centromere lie at equator and arms are directed towards poles - (1) Metaphase of mitosis (2) Metaphase - I (3) Metaphase - II (4) (1) and (3) both 6. Chromosomal morphology (Structure) is best observed at- (1) Prophase (2) Metaphase (3) Interphase (4) Anaphase 7. Cell plate which appears during cytokinesis, ultimately transforms in - (1) Middle lamella (2) Primary wall (3) Sec. wall (4) Plasma membrane 8. Each daughter chromosome in anaphase moves towards opposite poles at the speed of 1 m per minute with the expenditure of energy- (1) 5 ATP (2) 30 ATP (3) 38 ATP (4) 200 ATP 9. Synthesis and storage of ATP molecules required for cell div. takes place in- (1) Prophase (2) G 1 - Phase (3) Anaphase (4) G 2 - Phase 10. In mitosis, the spindle is- (1) Bipolar (2) Multipolar (3) Apolar (4) Random 11. Chiasmata appears during- (1) Diakinesis (2) Synaptotene (3) Diplotene (4) Leptotene 12. Coiling of chromonema in prophase of mitosis is- EXERCISE - 1 (1) Plectonemic (2) Paranemic (3) Helical (4) Irregular 13. How many microspore mother cells are required to produce 80 male gametes in angiosperms- (1) 10 (2) 20 (3) 40 (4) Chromosome number in gynoecium is 12, then in endosperm it will be- (1) 18 (2) 36 (3) 12 (4) The main difference between a dividing animals and plant cell lies in- (1) Cell plate formation (2) Coiling of chromosome (3) Chromosome movement (4) Types of spindle fibres 16. Cytoplasmic structures involved in cell division are - (1) Mitochondria (2) Ribosomes (3) Lysosomes (4) Centrioles 17. Cell division is not present in the cells of- - Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 1
2 (1) Skin (2) Gonads (3) Brain (4) Bone marrow 18. Before cell division, the entire DNA content of the cell gets doubled during interphase. This doubling takes place - (1) At the beginning of the interphase (2) At the end of the interphase (3) Throughout the interphase (4) Somewhere during the middle of the interphase 19. Where can we study mitosis- (1) Brain (2) Nail base (3) Legs (4) Kidneys 20. Tetrad is made of - (1) Four non homologous chromatids (2) Four homologous chromosomes with four chromatids (3) Four non homologous chromosomes (4) Two homologous chromosomes each with two chromatids 21. During meiotic cells division, genetic recombinations between two homologous chromosomes are facilitate by- (1) Movement of centromeres (2) Extrusion of polar bodies (3) Movement of centrioles (4) Formation of synaptonemal complex 22. Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to - (1) Pairing of homologous chromosomes (2) Separation of chromatids (3) Disjunction of homologous chromosomes (4) Crossing over 23. In the somatic cell cycle - (1) In G 1 phase DNA content is double the amount of DNA present in the original cell (2) DNA replication takes place in S-phase (3) A short interphase is followed by a long mitotic phase (4) G 2 phase is followed by mitotic phase 24. What is true about cell cycle - (a) During G 1 phase there is active synthesis of RNA and proteins but no change in its DNA content (b) In synthesis or S phase each chromosome carries a duplicate set of genes (c) During G 2 phase a cell contains double the amount of DNA present in the original diploid cell (2n) (d) In S-phase a cell doubles the original diploid (2n) chromosome number (1) c and (2) a, b and c (3) all (4) b, c and d 25. Mitosis is not found in- (1) Cartilage cells (2) Bone cells (3) Nerve cells (4) All of the above 26. If the cells in the root of an angiosperm have 12 chromosomes, 6 chromosomes will be present in- (1) Synergid (2) Endosperm cell (3) Leaf cell (4) Cotyledonary cell 27. The number of chromosomes present in the leaf tip cells of a plant species, having six chromosomes in each of the four cells of its pollen tetrad, would be- (1) Three (2) Six (3) Twelve (4) Twenty four 28. At which stage during meiotic prophase I the synaptic forces, between homologous chromosomes, are the maximum- (1) Leptotene (2) Zygotene (3) Pachytene (4) Diplotene 29. The number of chromatids in a chromosome at metaphase is - (1) Two each in meiosis and mitosis (2) Two in mitosis and one in meiosis (3) Two in mitosis and four in meiosis (4) One in mitosis and two in meiosis - Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 2
3 30. Find out the incorrect statement - (1) Balbiani rings (puffs) are the sites of RNA synthesis (2) Cytokinesis refers to the division of cytoplasm (3) Tetrad is made of two homologous chromosomes each with two chromatids (4) The chromosome end is called nucleolus 31. Decondensation of chromosome occurs in - (1) Prophase (2) Metaphase (3) Anaphase (4) Telophase 32. The quantity of DNA in a chromosome at metaphase is - (1) Two each in meiosis and mitosis (2) Two in mitosis and one in meiosis (3) Two in mitosis and four in meiosis (4) One in mitosis and two in meiosis 33. A red blood cell was kept in a solution for a few minutes, where it got burst. The solution taken was - (1) Hypotonic (2) Concentrated sugar solution (3) Isotonic (4) Hypertonic 34. Function of telomeres in nucleus is - (1) Poleward movement (2) To initiate the RNA synthesis (3) To seal the ends of chromosome (4) To recognise the homologous chromosome 35. The salivary gland chromosomes in the dipteran larvae, are useful in gene mapping because - (1) These are fused (2) These are much longer in size (3) These are easy to stain (4) They have endoreduplicated chromosomes 36. DNA synthesis takes place in - (1) S phase (2) G 1 phase (3) G 2 phase (4) None 37. When pairing occurs in chromosomes (meiosis) - (1) Leptotene (2) Zygotene (3) Pachytene (4) Diakinesis 38. Most active stage of cell cycle is - (1) Prophase (2) Metaphase (3) Telophase (4) Interphase 39. Which of the following is the method of cytokinesis in plant cell - (1) By cell plate formation(2) By constriction (3) By phragmoplast (4) (1) and (3) both 40. In which stage of cell cycle nucleus becomes bigger - (1) G 1 (2) G 2 (3) S (4) M 41. What happens in interkinesis - (1) DNA - replication (2) Chromosome duplication (3) Preparation of second meiotic div. (4) Resting stage 42. Which can be observed in an interphase nucleus under the light microscope - (1) Chromosomes (2) Nucleosomes (3) Centromere (4) Heterochromatin 43. Angular divergence of spindle decreases at - (1) Metaphase (2) Early anaphase (3) Late anaphase (4) Telophase 44. Minimum number of meiotic div. required to produce 62 pollengrains - (1) 15 (2) 31 (3) 62 (4) 16 - Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 3
4 45. In cell cycle, changes of which stage are not visible under microscope - (1) Interphase (2) Prophase (3) Metaphase (4) Anaphase 46. Which type of division leads to polyploidy- (1) Cryptomitosis (2) Meiosis (3) Endomitosis (4) Amitosis 47. Which of the following not occurs in Anaphase - I but occurs in Anaphase - II - (1) Condensation of chromosomes (2) Poleward movement of chromosome (3) Contraction of spindle fibres (4) Splitting of centromere 48. In which stage of cell division, division of matrix of chromosome occurs - (1) Late prophase (2) Early metaphase (3) Late metaphase (4) Anaphase 49. During G 2 - phase a diploid cell contains the amount of DNA equal to a - (1) Diploid cell (2) Tetraploid cell (3) Haploid cell (4) Nothing can be said 50. Crossing over takes place in- (1) Zygotene (2) Pachytene (3) Diplotene (4) Diakinesis 51. A contractile mid body forms during cytokinesis in - (1) Animals (2) Higher plants (3) Fungi (4) Algae 52. In which order, cytokinesis occurs in plants - (1) Centripetal (2) Centrifugal (3) Oblique (4) Equatorial 53. Meiosis not occurs in- (1) Ovule (2) Anther (3) Microsporangia (4) Shoot tip 54. Which of the two events restore the normal number of chromosomes in life cycle - (1) Mitosis and Meiosis (2) Meiosis and fertilisation (3) Fertilisation and mitosis (4) Only meiosis 55. Number of meiosis required to produce 100 ovules in angiosperms - (1) 125 (2) 100 (3) 25 (4) Constancy of the chromosome number in sexually producing generation is brought by the process of- (1) Meiosis (2) Mitosis (3) Amitosis (4) None 57. Amitosis is characteristic of - (1) Higher plants (2) Higher animals (3) Bryophyta (4) Lower organisms 58. Slipping of chiasmata towards the ends of bivalent is called - (1) Terminalisation (2) Diakinesis (3) Interkinesis (4) Heteropycnosis 59. Which does not occurs in prophase - (1) Hydration of chromatin (2) Dehydration of chromatin (3) Appearance of chromosome (4) Disappearance of nuclear membrane and nucleolus 60. During cell cycle, RNA and protein synthesis takes place during- (1) G 1 and G 2 - phase (2) S - phase (3) M - phase (4) Cytokinesis 61. In which stage of cell division, number of chromosomes best counted - (1) Prophase (2) Metaphase (3) Telophase (4) Interphase 62. Cell division in blue green algae similar to that in- - Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 4
5 (1) Bacteria (2) Brown algae (3) Green algae (4) Higher plants 63. The synaptonemal complex was first observed by- (1) Moore (1905) (2) Farmer and Moore (1905) (3) Mosses (1956) (4) Flemming (1882) 64. A cell is bound to divide, it it has entered - (1) G 2 : phase (2) G 1 - phase (3) Prophase (4) S - phase 65. How many Chromosome shall be present in a diploid cell at mitotic anaphase it its egg cell has ten chromosome- (1) 10 (2) 20 (3) 30 (4) If crossing - over occur at two strand stage then percentage of crossing over is - (1) 50% (2) 60% (3) 70% (4) 100% 67. Meiosis which occur at the time of spore formation is called - (1) Zygotic meiosis (2) Haplontic meiosis (3) Terminal meiosis (4) Intermediate meiosis 68. Chromosome exhibit high level of coiling at which phase of karyokinesis - (1) Prophase (2) Metaphase (3) Telophase (4) Interphase 69. The synaptonemal complex appears - (1) Between homologous chromosomes (2) In zygotene stage (3) Composed of DNA + protein (4) All the above 70. At anaphase - II of meiosis each chromosome contains - (1) 4 DNA (2) 3 DNA (3) 2 DNA (4) 1 DNA 71. During cell division chromosome move towards different poles due to - (1) Centriole (2) Vacuole formation (3) Microtubules (4) Cytokinesis 72. For studying meiosis the relevant plant material usually fixed around - (1) 9-10 AM (2) 4.5 AM (3) 3.5 PM (4) 12 PM 73. Tetrad formation in meiosis occur is - (1) Leptotene (2) Zygotene (3) Pachytene (4) Diplotene 74. In Anaphase - I each chromosome composed of- (1) One chromatid (2) Two chromatid (3) Four chromatid (4) Many chromatid 75. In meiosis, division of centromere occurs during - (1) Interphase (2) Anaphase - I (3) Anaphase - II (4) Metaphase - I 76. In meiosis, nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear during - (1) Zygotene (2) Pachytene (3) Diakinesis (4) Metaphase - I 77. Cell cycle can remain arrested at - (1) G 1 (2) S (3) G 2 (4) M 78. Which of the following are mitotic poisons - (1) Colchicine (2) Mustard gas and Azides(3) Cyanides (4) All the above 79. In cell cycle, which stage is misnomerly called resting phase - (1) S - phase (2) Telophase (3) Cytokinesis (4) Interphase 80. Separation of homologous chromosomes during Anaphase - I is called - - Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 5
6 (1) Synapsis (2) Disjunction (3) Nondisjunction (4) Crossing over 81. In tetrad, the number of non cross chromatids is normally - (1) Four (2) Two (3) One (4) None 82. Sporic meiosis occurs in - (1) Animals (2) Thallophyta (3) Bryophyta (4) All plants except thallophyta 83. If a meristematic cell is placed in a medium containing radio active thymidine, radioactivity will be first observed in- (1) Euchromatin (2) Hetero chromatin (3) Both simultaneously (4) None of the above 84. The metabolism of a cell which decreases during prophase again starts increasing during- (1) Telophase (2) Anaphase (3) Metaphase (4) G 1 - Phase 85. Synthesis of cycline protein occurs in- (1) Permanent tissue (2) Meristem (3) Lignified cells (4) All the types of cell 86. During which stage a diploid cell becomes tetraploid in mitosis - (1) G 2 (2) Prophase (3) Metaphase (4) Anaphase 87. If the number of bivalents are 8 in metaphase-i, what shall be the number of chromosomes in daughter cells after meiosis-i and meiosis-ii respectively- (1) 8 and 4 (2) 4 and 4 (3) 8 and 8 (4) 16 and Homologous chromosomes shows maximum attraction during- (1) Leptotene (2) Zygotene (3) Pachytene (4) Diplotene 89. Ribonuclease, a mitotic poison, inhibits cell cycle in- (1) Interphase (2) Prophase (3) Metaphase (4) Anaphase 90. Dinomitosis occurs in- (1) Procaryotes (2) Mesokaryotes (3) Eucaryotes (4) Akaryotes 91. Stain for cell division- (1) Saffranin (2) Aniline blue (3) PAS (4) Acetocarmine 92. Terminal meiosis occurs in- (1) Sporocyte (2) Gametocyte (3) Zygote (4) Gamete ANSWER-SHEET Qus Ans Qus Ans Qus Ans Qus Ans Qus Ans Free NEET & IIT Study Meterial & Papers Page - 6
CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 1 CH 10 CELL CYCLE & CELL DIVISION CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Growth and reproduction are characteristics of living cells and organisms. Cell Cycle The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its
1 CH 10 CELL CYCLE & CELL DIVISION CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Growth and reproduction are characteristics of living cells and organisms. Cell Cycle The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its
The interphase is further divided into three phases, which are as follows:
 Cell Division Phases of Cell Cycle The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases: a. Interphase: The phase between subsequent cell divisions is called the interphase. The interphase lasts for more than
Cell Division Phases of Cell Cycle The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases: a. Interphase: The phase between subsequent cell divisions is called the interphase. The interphase lasts for more than
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS
 CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-10
 Chapter-10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION POINTS TO REMEMBER Cell cycle : The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesis the other constitutents of the cell and eventually divides
Chapter-10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION POINTS TO REMEMBER Cell cycle : The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesis the other constitutents of the cell and eventually divides
Class XI Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Biology
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Class XI Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Biology
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
 Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Question 1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell? The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. Question 2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell. Phases of cell
CLASS XI CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell. Phases of cell
NCERT. not to be published CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 CELL CYCLE 162 BIOLOGY
 162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
 Meiosis http://biology.tutorvista.com/cell/meiosis.html MEIOSIS It is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number is halved from the diploid number (2n) to a haploid number (n). Like mitosis
Meiosis http://biology.tutorvista.com/cell/meiosis.html MEIOSIS It is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number is halved from the diploid number (2n) to a haploid number (n). Like mitosis
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 49 49 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Meiosis results in a. Production of gametes b. Reduction in the number of chromosomes c. Introduction
CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 49 49 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Meiosis results in a. Production of gametes b. Reduction in the number of chromosomes c. Introduction
BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes
 BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes 1) Cell division is an important process in all living things. State any four reasons to support your answer. New cells
BIOLOGY CLASS 10 Chapter 2 Cell cycle, cell division and structure of chromosomes 1) Cell division is an important process in all living things. State any four reasons to support your answer. New cells
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
The Gametic Cell Cycle
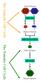 The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 162 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
162 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: MEIOSIS
 MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
Cell Division. Mitosis
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes. Packet #29
 Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes Packet #29 Introduction Meiosis, discovered in 1883, was first observed through the fertilized egg and individual gametes, sperm and unfertilized egg,
Meiosis Production of Chromosome Hybrids & Gametes Packet #29 Introduction Meiosis, discovered in 1883, was first observed through the fertilized egg and individual gametes, sperm and unfertilized egg,
Genetics word list. the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral)
 Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Typical Life Cycle of Algae and Fungi. 5 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
11-4 Meiosis. Chromosome Number
 11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Sexual reproduction shuffles and recombines genes from two parents. During gametogenesis, genes are segregated and assorted (shuffled) into gemetes, and at fertilization,
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Sexual reproduction shuffles and recombines genes from two parents. During gametogenesis, genes are segregated and assorted (shuffled) into gemetes, and at fertilization,
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES
 CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS NOTES DNA - Genetic information is stored in the DNA strand in the form of genes. DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid Genes located on the DNA strand 2 Types of DNA
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Purposes of Cell Division
 Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Cell Division (Meiosis)
 Cell Division (Meiosis) Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Diploid (2n) haploid (n) Meiosis is sexual reproduction. Two divisions (meiosis
Cell Division (Meiosis) Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Diploid (2n) haploid (n) Meiosis is sexual reproduction. Two divisions (meiosis
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
How did that single cell develop into a body with more than a trillion cells?
 CELL DIVISION Cell division is a process which leads to cell multiplication. It occurs in both plants and animals. Original cells which undergo division are known as parent cells and the new on ones resulting
CELL DIVISION Cell division is a process which leads to cell multiplication. It occurs in both plants and animals. Original cells which undergo division are known as parent cells and the new on ones resulting
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
Meiosis. The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced.
 MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
MEIOSIS Meiosis The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the regular number of chromosomes, are produced. diploid (2n) haploid (n) (complete set of chromosomes) (half the regular number of
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Cell Cycle & Division
 Introduction Cell Cycle & Division Rudolf Virchow proposed the Cell lineage theory which states omnis cellula e cellula i.e new cells arise from preexisting cells. However he failed to prove the theory.
Introduction Cell Cycle & Division Rudolf Virchow proposed the Cell lineage theory which states omnis cellula e cellula i.e new cells arise from preexisting cells. However he failed to prove the theory.
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: SIMULATION OF MEIOSIS EVOLUTION. Activity #9
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Roles of Cell Division. Reproduction - Like begets like, more or less. Examples of Cell Numbers. Outline Cell Reproduction
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division [ Contents: Cell Cycle,
 General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division A complete General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division for you competitive examinations such as UPSC, IAS, Banking SBI PO, Railway Group-D, SSC, CGL
General Knowledge on Cell Cycle & Cell Division A complete General knowledge on Cell Cycle and Cell Division for you competitive examinations such as UPSC, IAS, Banking SBI PO, Railway Group-D, SSC, CGL
AP Biology Fall Semester Set 1
 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
STUDY UNIT 1 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS. Klug, Cummings & Spencer Chapter 2. Morphology of eukaryotic metaphase chromosomes. Chromatids
 STUDY UNIT 1 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Klug, Cummings & Spencer Chapter 2 Life depends on cell division and reproduction of organisms. Process involves transfer of genetic material. New somatic (body) cells
STUDY UNIT 1 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Klug, Cummings & Spencer Chapter 2 Life depends on cell division and reproduction of organisms. Process involves transfer of genetic material. New somatic (body) cells
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
Meiosis * OpenStax. This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0.
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the
 MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
MEIOSIS You have body cells and gametes Body cells are known as somatic cells. Germ cells develop into gametes or sex cells. Germ cells are located in the ovaries and testes. Gametes are sex cells: egg
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division
 AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Cell Division. Mitosis 11/8/2016
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
E. Incorrect! At telophase II, cells are nearly completed with meiosis, with no cross-over.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
LECTURE 10A: MEIO S S
 LECTURE 10A: MEIOSIS Meiosis Definition INTRODUCTION 1. Meiosis is the production of gametes, which is a reduction division which means a diploid gamete produces haploid gametes - from a full complement
LECTURE 10A: MEIOSIS Meiosis Definition INTRODUCTION 1. Meiosis is the production of gametes, which is a reduction division which means a diploid gamete produces haploid gametes - from a full complement
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Sexual life cycle. Sexual life cycle. Fertilization. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n)
 Sexual life cycle Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n) Chapter 11 Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of Haploid cells (n) Gametes have only 1 set of
Sexual life cycle Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells (2n) Chapter 11 Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of Haploid cells (n) Gametes have only 1 set of
CELL REPRODUCTION. Mitotic M phase Mitosis. Chromosomes divide. Cytokinesis. Cytoplasm and cell membrane divide. Chromosomes as Packaged Genes
 CELL REPRODUCTION Kimberly Lozano Biology 490 Spring 2010 CELL CYCLE Interphase G1: Growth (1) New organelles form within the cell. S: Synthesis Cell duplicates its DNA. G2: Growth (2) Cell prepares for
CELL REPRODUCTION Kimberly Lozano Biology 490 Spring 2010 CELL CYCLE Interphase G1: Growth (1) New organelles form within the cell. S: Synthesis Cell duplicates its DNA. G2: Growth (2) Cell prepares for
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.9 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University
 CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders
 Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Answers to Review for Unit Test #3: Cellular Reproduction: Mitosis, Meiosis, Karyotypes and Non-disjunction Disorders 1. Clearly explain the difference between the following: a) chromosomes and chromatin
Name: Date: Period: Cell Cycles and DNA Study Guide
 Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Name: Date: Period: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the chemical inside the nucleus of cells that contains hereditary information. DNA is shaped like a double helix/twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Chapter 8 Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida
 Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Meiosis: M-Phase part 2. How is meiosis different from mitosis? Some terms: Some terms: Some terms:
 M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
M-Phase part 2 Meiosis and Cytokinesis Meiosis: A special type of cell division that produces gametes. Cell division that occurs in sex organs. 2 successive nuclear divisions Genetic mistakes (gene and
11.4 Meiosis. Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad
 11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
11.4 Meiosis Vocabulary: Homologous Diploid Haploid Meiosis Crossing-over Tetrad Key Concept: What happens during the process of meiosis? How is MEIOSIS different than mitosis? Blast from the past What
5. As compared to the human sperm cell, the human egg cell contains more... a) cytoplasm c) centrosomes b) mitochondria d) chromosomes
 BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
BIOLOGY - 3201. Quiz: Cell Reproduction. NAME : Multiple Choice. (1% each) 1. Which of the following is NOT true of mitotic cell division? a) It involves nuclear division. b) It involves division of the
Bell Ringer 02/02/15. Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures.
 Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
Match the stages of mitosis to their descriptions and pictures. 1. Nuclear membrane disappears and chromosomes condense 2. Nuclear membrane reappears and cells begin to fully separate Bell Ringer 02/02/15
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division. A. Definitions:
 Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
Biology 067 Section 14 Cell Division A. Definitions: In a human cell, a nucleus holds all the chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes when cells divide every cell in the body has the same set of chromosomes
Review of Terms. Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome. Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome
 Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis?
 Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Sexual Reproduction What is Mitosis? What is the purpose of Mitosis? Growth Repair Asexual reproduction What is the ultimate result of Mitosis? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fyfdfdrymq Somatic cells
Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17
 Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17 1 The Importance of Meiosis Meiosis is a two stage cell division in which the chromosome number of the parental cell is reduced by half. Meiosis is the process by which
Sexual Cell Reproduction Chapter 17 1 The Importance of Meiosis Meiosis is a two stage cell division in which the chromosome number of the parental cell is reduced by half. Meiosis is the process by which
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz Why sexual reproduction? Imagine a world where everyone was IDENTICAL. If we reproduced asexually, that would be our world Boring! Asexual Reproduction vs. Sexual
Sexual Reproduction Science 9- Mr. Klasz Why sexual reproduction? Imagine a world where everyone was IDENTICAL. If we reproduced asexually, that would be our world Boring! Asexual Reproduction vs. Sexual
Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale
 CHAPTER ONE Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale The genetic material is a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each chromosome contains a single long strand of DNA that encodes the information
CHAPTER ONE Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale The genetic material is a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each chromosome contains a single long strand of DNA that encodes the information
Agenda. 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo
 Meiosis SBI 3U Agenda 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo Learning Goals By the end of today s lesson, you will be able: To use proper vocabulary related to this unit, including meiosis,
Meiosis SBI 3U Agenda 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo Learning Goals By the end of today s lesson, you will be able: To use proper vocabulary related to this unit, including meiosis,
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR
 Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION. Preview (Honors)
 CELL GROWTH & DIVISION Mitosis & Meiosis Preview (Honors) Read: Chapter 10-1 Page 256: Define ALL vocabulary Page 257: #1-10 & 14 Page 282: Define Section 11-4 vocabulary 1 Preview (Academic) Read: Chapter
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION Mitosis & Meiosis Preview (Honors) Read: Chapter 10-1 Page 256: Define ALL vocabulary Page 257: #1-10 & 14 Page 282: Define Section 11-4 vocabulary 1 Preview (Academic) Read: Chapter
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58013 1 Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation Willy Cushwa Based on Meiosis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58013 1 Human Biology Chapter 13.4: Meiosis and Genetic Variation Willy Cushwa Based on Meiosis by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4
 SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
