Romanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 23, No. 2, Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat
|
|
|
- Camron Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Romanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 3, No., 018 Copyright 018 University of Bucharest Printed in Romania. All rights reserved ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat Received for publication, July, 13, 015 Accepted, February, 0, 017 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ 1*, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ 1, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ 1, BRANISLAVA MITROVIĆ, DRAGAN ŽIVANOV, SAVA BUNČIĆ 3, NIKOLA PAVLOVIĆ 1 1 Institute of Veterinary Medicine of Serbia, Belgrade, Serbia Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Belgrade, Serbia 3 Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Novi Sad, Serbia * Corresponding author: vicamihajlo@yahoo.com Abstract The presence of natural radionuclides in the chain of pig meat production, especially in food and feed additives (premixes), as the most important mutagenic factor, could significantly affect the variability of Salmonella isolates in the pork chain. In the first stage of the study, outlined in this paper, the goal was to determine if radioactivity has any effect on survival/growth of Salmonella in pigs meat.we studied six strains of Salmonella that were exposed to four levels of radioactivity. The differences in Salmonella counts between pork meat homogenates with or without added radioactive uranium were following: the Salmonella counts (log 10 CFU/ml) in control meat homogenate (without added radioactivity) increased from the level of around 7.4 logs (at 30 min storage) to around 9.0 logs, due to growth of the pathogen. No significant differences in this general pattern were observed between the 6 Salmonella serovars tested in the control meat homogenates (without added radioactivity). On the other hand, Salmonella counts in meat homogenate with added radioactivity 38 U (1,, 5, 10 kbq) decreased (by around logs) practically immediately after addition of the uranium, compared with control meat homogenates. Subsequently, Salmonella also grew during storage of meat homogenate with added radioactivity, but to a lesser extent than in control meat homogenates. Salmonella enteritidis () had the highest factor reduction in meat homogenates with radioactivity added 38 U (1, kbq). It had the highest reduction factor around 1.57 to 1.67 logs. In contrast, Salmonella tiphimurium (3) had the highest factor reduction in meat homogenates with radioactivity added 38 U (5, 10 kbq), which ranged from 1.83 to 1.96 logs. Key words: Salmonella spp., meat, natural radionuclide - uranium, radiation, radio sensitivity 1. Introduction Bacteria from Enterobacteriaceae family, Salmonella spp., are the most common contaminants in animal products. Only very few Salmonella serovars of over 000, actually cause the vast majority of human foodborne salmonellosis cases. At the global level, S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium, together, have been the most common ( %) cause of outbreaks of foodborne salmonellosis in the period , and the ratio between the two serovars was 3:1 in favour of S. Enteritidis [1]. It is important to note that the source of infection in most outbreaks caused by S. Enteritidis were eggs and egg products. On the contrary, the source of infection in most outbreaks caused by S. Typhimurium was mostly pork, and to a lesser extent beef. They were followed by serovars S. Agona, S. Virchow, S. Newport, S. Brandenburg, S. Derby and S. Braendrup. In 003, S. Virchow was the third most common serovar isolated in human cases. Main natural reservoirs of Salmonella are swine [,3] and poultry [4], than rodents, ruminants and carnivores. Many other species are infected, thus they are widely spread. Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No.,
2 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ, BRANISLAVA MITROVIĆ, DRAGAN ŽIVANOV, SAVA BUNČIĆ, NIKOLA PAVLOVIĆ The sources of human infection are farm domestic animals, and other animals that live in domesticated areas as pests (mice and rats). Humans are rarely infection source, but still have an important part in Salmonella spreading, since they can contaminate the food through their feces. Salmonella could be transmitted by contact from human to human, especially in case of persons who have deficient immunity (liver cirrhosis, leukemia, lymphoma, HIV). In the last years there have been reports of Salmonella epidemics in children and neonatal wards, in regard to means of spreading and durance epidemic was transmitted by objects and contact. In most European countries, gastroenteritis is caused by S. enteritidis and S. typhimurium [5]. Salmonella spp. is considered firstly pathogenic for animals, and to lesser extent for humans, for human salmonella born diseases there should be a higher infectious dose of agents, measuring for some types of salmonella more than million, even billion germs. Such high amount of Salmonella could only be found in food originating from infected animals (in which salmonella was spread during life or post mortem) or food subject to secondary contamination by humans. This is the reason why salmonellas are the most common cause of food poisoning [6]. Today, mainly for pragmatic reasons and based on cautionary principle, all Salmonella strains are treated as having a potential to cause human foodborne salmonellosis. However, it is known that the strains commonly present in animal feed often serotypically and/or phenotypically differ from the strains commonly present in pigs and/or pig meat. Some advantageous phenotypic variations (e.g. better survival and/or growth ability) can contribute to the natural selection of certain Salmonella strains along the food chain and, ultimately, their ability to reach the consumer. One of the factors that could potentially affect the strain diversity, and thus the selection process, is the mutagenic potential of natural radioactivity present at key points of the meat chain (e.g. farm, animals, meat). In Serbia, data on the diversity of Salmonella isolates in the pork meat, and their potential relationship to natural radioactivity, are very scarce or lacking. Pork is a major source of human salmonellosis [7, 8, 9] and source of approximately 0% / 5-30% / total cases in humans [10]. However, reducing the risk of Salmonella, through pork meat, can significantly contribute to the protection of human health. Uranium and its descendants are significant alpha emitters, but due to the short range of alpha particles, harmful radiation effect is manifested only when entering into a living organism and causing specific intoxication effect that depends on the way of introduction (ingestion, inhalation). Alpha particles penetrate through the tissues of the body, causing ionization effect, and then leading to the formation of free radicals resulting in the changes in molecules, that are very essential for the functioning of cells. Since natural radionuclides are mainly alpha emitters in which the specific power of ionization and hence the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for living organisms is very high (RBE is higher by a factor of 0 compared to gamma and X rays), the effects on living organisms even at low concentrations of natural radionuclides in the environment can be significant. In the use of fertilizers and supplements for animal feed commonly used in Serbia (mono and dicalcium phosphate), the content of uranium 38 in the soil increased, as well as in animal feed and all this resulted in the increase of uranium in plants and other links in the food chain, such as pork meat. The pork chain, considering the share of pig meat in the total meat chain, is one of the important routes of contamination of people by natural radionuclides. In addition, the presence of natural radionuclides in the chain of pig meat production, especially in food and feed additives (premixes), as the most important mutagenic factor could significantly affect the variability of isolates of Salmonella in the pork chain. This problem has become particularly acute in recent years when, in the industrial production of pig and poultry feed, natural phosphates started to be used as a component, where the Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No., 018
3 Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat content of natural radionuclides can reach very high values [11, 1]. Information about potential effects of natural ionizing radiation on health of the general population, health effects of high and lower doses and radio-ecological areals, have been presented for Serbia [13]. The distribution of uranium in the organism of animals is also important [14]. To avoid the toxicity of radionuclides there are ionizing irradiation methods for elimination of bacteria in plant and animal products. In order to eliminate the Salmonella spp. irradiation is used, that unlike our case is not natural but of artificial origin, which represents one option in successful fight against the pathogenic Salmonella, saving the sensor characteristics of meat products. To reduce or eliminate viable Salmonella spp. cells in meat, various doses of ionizing radiation have been suggested in the published literature [15-]. The differences are due to different initial contamination and sensitivity variability of Salmonella spp. used in different studies. Eliminating Salmonella spp. from meat using ionizing radiation, according to international organizations (WHO, FAO, IAEA), is one of the most efficient Salmollella spp. control methods, which also enables the maintenance of desirable sensory properties in the treated foods. Based on extensive experimental data, a recommendation has been given by the Commission of Experts WHO, FAO and IAEA to use ionizing radiation in doses up to 10 kgy for the purpose of decontamination of poultry meat, pork and beef [3]. For the reasons indicated above, the main aim of our long-term investigations is to determine whether and in which way natural radionuclide - uranium in food and feed additives (premixes), in the meat chain, affects microbial meat safety. In the first stage of the study, outlined in this paper, the goal was to determine if radioactivity has any effect on survival/growth of Salmonella in pork meat. So, knowing that radioactivity affects the reduction in growth of salmonella, then objective of the present study was to determine their relationship in case of different uranium levels.. Material and Methods Six Salmonella strains were used in the study: Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (ATCC 1408) (1), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (isolates from feed for pigs) (), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium (isolate from pig organs) (3), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis (ATCC 13076) (1), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis (isolates from feed for pigs) (), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis (isolate from pig organs) (3). Each strain was grown in Brain Heart Infusion broth (Becton, Dichinson and Co.) for 48 hours at 37 o C, and then sub-cultured in fresh broth (4 hours at 37 o C). The cell count in the final broth culture was determined by using a densitometer (DEN-1, Grant-bio, UK), and then diluted in appropriate volume of sterile saline so to achieve 10 6 CFU per ml in this, the primary Salmonella suspension (PSS). Then, 10 ml of the PSS was mixed with 10 g of sterile pig meat (Slaughterhouse "ZZ Trlić") and 80 ml of sterile saline, so to obtain the inoculated pig meat homogenate (IAFH). The IAFH was then divided into two portions: one portion had an equal volume of a solution of uranium of (1 kbq, kbq, 5 kbq and 10 kbq) radioactivity added (IAFH+U; treatment ), while the other portion had an equal volume of sterile saline added (IAFH; control without uranium). Both IAFH+U and IAFH were stored at 8-10 o C, and each was sampled periodically to determine Salmonella counts, after 30 min, 4 hours and after days, by standard spread-plating methodology using Plate Count Agar (HIMEDIA). Natural radioactivity is expressed in the form of uranyl nitrate hexahidrata. We took the next dilution of crystals: U-400 mg/l-(0.4 mg/ml)-(0,1688g of uranyl nitrate to 00 ml/uo (NO3) x 6H0 U-800 mg/l-(0.8 mg/ml)-(0,0844g of uranyl nitrate to 50ml/UO (NO3) x 6H0 Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No.,
4 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ, BRANISLAVA MITROVIĆ, DRAGAN ŽIVANOV, SAVA BUNČIĆ, NIKOLA PAVLOVIĆ U-000 mg/l-( mg/ml)-(0,109g of uranyl nitrate to 50ml/UO (NO3) x 6H0 U-4000mg/l-(4 mg / ml)-(0,419g of uranyl nitrate to 50ml / UO (NO3) x 6H0 This dilution of appropriate concentrations of 1000Bq / 000Bq / 5000Bq / and 10000Bq. They are made at the Institute for Technology of Nuclear and Other Mineral Raw. Why was this dose of uranium chosen? Practice has shown, especially for this case, that imported premixes had a dose of 1 kbq to 5 kbq. Therefore, it was decided to use the dose of 10 kbq in the case as an example of emergency situation. So we get all the possible optional doses that would affect the behavior of Salmonella strains. 3. Results and discussion The differences in Salmonella counts between pig meat homogenates with or without added radioactive uranium (1 kbq) are shown in Figure 1. The Salmonella counts (log10 CFU/ml) in control pig meat homogenate (without added radioactivity) increased from the level of around 7.4 logs (at 30 min storage) to around 9.0 logs, due to growth of the pathogen. No significant differences in this general pattern were observed between the six Salmonella serovars tested in the control feed homogenates (without added radioactivity). 10 S. typhimurium 1 S. typhimurium S. typhimurium 3 S. enteritidis 1 S. enteritidis S. enteritidis 3 8 log10(cfu/ml) , , , , , , Hours Radiation Control Figure 1. Salmonella counts in inoculated meat homogenate without uranium (control IAFH) and with uranium of 1 kbq radioactivity (IAFH+U) during storage On the other hand, Salmonella counts in meat homogenate with added radioactivity (uranium 1 kbq) decreased (by around logs) practically immediately after addition of the uranium, compared with control feed homogenates. Subsequently, Salmonella also grew during storage of the feed homogenate with added radioactivity (especially on the second day), but to a lesser extent than in control feed homogenates. The ultimate Salmonella counts reached in the presence of added radioactivity were significantly reduced compared with those in the control homogenate: by around logs S. Typhimurium strains, or around logs S. Enteritidis strains. During the period from 30 minutes to 4 hours, the reduction factor remained at the same level. Only in S. Typhimurium () reduction factor increased from 0.87 logs to 1.0 logs. Furthermore, as indicated above, the observed added radioactivity-induced reduction rates were more prominent in S. Enteritidis then in S. Typhimurium, especially on the first day. What is important for us this particularly applies to S. Enteritidis-isolates from animal feed () reduction factor was the highest in all three phases of measurement. After the first measurement it was 1.54 logs, after 4 hours 1.57 logs and after 48 hours it amounted to 0.63 logs. In 1340 Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No., 018
5 Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat comparison to other Salmonella strains, the highest factor in reducing the radioactivity and the smallest growth were observed when radioactivity was added. 10 S. typhimurium 1 S. typhimurium S. typhimurium 3 S. enteritidis 1 S. enteritidis S. enteritidis 3 8 log10(cfu/ml) , , , , , , Hours Radiation Control Figure. Salmonella counts in inoculated meat homogenate without uranium (control IAFH) and with uranium of kbq radioactivity (IAFH+U) during storage The Salmonella counts (log10 CFU/ml) in pig meat homogenate with added radioactivity (uranium kbq) were similar to that of the group with the added activity of 1 kbq. The differences in Salmonella counts are shown in Figure. The greatest reduction was after first day: by around logs and the lowest on the second day: by around logs. Reduction factor increased from the starting control at 30 minutes to 4 hours in all strains, and is higher than the groups where 1 kbq of radioactivity was added. It ranged from 0.09 logs in S. Typhimurium (3) to 0.76 logs in S. Typhimurium (). The same as in the previous group, the highest factor of reduction and the lowest point, were found in Salmonella enteritidis () in comparison to the control group, without added radioactivity, by around 1.7 logs after 4 hours, slightly lower reduction was after 30 minutes logs and the lowest at the end of the second day 0.74 logs. Lowest reduction was established in case of S. Enteritidis (1): by around 0.4 logs after 48 hours. It was observed that the levels of growth in all strains were slightly lower compared to strains that have been exposed to radioactivity from 1 kbq. 10 S. typhimurium 1 S. typhimurium S. typhimurium 3 S. enteritidis 1 S. enteritidis S. enteritidis 3 8 log10(cfu/ml) , , , , , , Hours Radiation Control Figure 3. Salmonella counts in inoculated meat homogenate without uranium (control IAFH) and with uranium of 5 kbq radioactivity (IAFH+U) during storage Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No.,
6 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ, BRANISLAVA MITROVIĆ, DRAGAN ŽIVANOV, SAVA BUNČIĆ, NIKOLA PAVLOVIĆ In Figure 3. the differences in Salmonella counts between pig meat homogenates with or without added radioactive uranium (5 kbq) are shown. Here, we see a slight increase differences salmonella counts immediately after 30 min. in comparison to the results in Table, especially for all three S. Typhimurium by around logs. Difference between the Salmonella counts was the largest after first day (by around logs). Salmonella Typhimurium (3) had the biggest differences by around log. The results obtained after the second day show increase in differences between Salmonella counts of the control group with and without added radioactivity by around log. A constant increase of the reduction factor is observed. Salmonella tiphimurium 3 and Salmonella enteritidis () showed biggest differences between salmonella points without and with added uranium after 4 hours: for Salmonella tiphimurium (3) of 1.6 to 1.9 and for S. enteritidis () 1.6 to 1.8 logs. The values of the salmonella points after added uranium were lower in all three phases of measurement compared to Figure. The average ranged from 0. to 0.4 logs. Also, the reduction factors in both groups of salmonella after 48 hours were higher in reference to Figure. These are the values of the reduction factor ranging from 0.6 to 0.9 logs and were higher than the value of reduction factor after 48 hours in Figure, which ranged from 0.4 to 0.7 logs. 10 S. typhimurium 1 S. typhimurium S. typhimurium 3 S. enteritidis 1 S. enteritidis S. enteritidis 3 8 log10(cfu/ml) , , , , , , Hours Radiation Control Figure 4. Salmonella counts in inoculated meat homogenate without uranium (control IAFH) and with uranium of 10 kbq radioactivity (IAFH+U) during storage The highest dose of radioactivity was added to the fourth group of pig meat homogenate with uranium (10 kbq), as shown in Figure 4. At this stage of the experiment the biggest difference in salmonella counts between groups was reached. After 30 min the reduction was by around logs. The greatest reduction of S. Tiphimurium (3) was 1.65 logs in relation to all six strains. The level of reduction after first day was by around 1.6- logs Salmonella tiphimurium (3) had the highest reduction factor after 4 and 48 hours, which amounted to 1.96 logs that is 0.96 logs. Also, after two days, the reduction was by around logs. Greater reduction was observed in S. Typhimurium (3) with value of 0.96 logs. Tendency of decrease in the value of salmonella counts in this phase of the experiment was the highest as compared to the previous three groups. Here, the S. Typhimurium (3) had the lowest point of growth compared to other strains in all three measurements. 134 Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No., 018
7 Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat It is likely that this reduction was due to the effect of added radioactivity, although the exact mechanism of the effect was neither investigated nor explained in the present stage of the study. Furthermore, as indicated above, the observed added radioactivity-induced reduction rates were more prominent in S. Enteritidis then in S. Typhimurium. However, the limited scope of this preliminary study was insufficient to identify either if this difference is serovar- or strain-related, or whether other genotypic or phenotypic characteristics of the pathogen were affected. 4. Conclusion This preliminary study showed that all four levels of radioactivity can significantly reduce 6 Salmonella serovars in pork meat. The greatest reduction is obtained when the added radioactivity was 10 kbq. Only two Salmonella serovars in all four levels of radioactivity show any deviations and significantly reduce the Salmonella counts in pork meat homogenates. This applies to S. Typhimurium (3) and S. enteritidis (). All three S. enteritidis shown in relation to a S. Typhimurium decrease the Salmonella counts when the radioactivity of 1 kbq and kbq was added. This applies particularly to S. Enteritidis () where it was 1.6 logs to 1.7 logs. When the radioactivity of 5 kbq and 10 kbq was added all three S. Typhimurium had greater reduction than S. enteritidis. This applies particularly to S. Typhimurium (3) where it was 1.8 logs to 1.9 logs. In further studies, which are ongoing, these observations must be confirmed and the mechanisms causing these effects explained. Number of data on the content of radionuclides of the uranium and thorium series in feed, food and nutrition is small and the current results can hardly be used to determine their relations in all geographic areas. Therefore, in following period more attention should be turned to the content and transfer of natural radionuclides of uranium and thorium series in animal feeds, especially because the content of natural radionuclides in natural phosphates, which are used in feed for pigs, can reach very high values. 5. Acknowledgement This work has been supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, under project No TR References 1. R.S. HENDRIKSEN. Global monitoring of Salmonella serovar distribution from the World Health Organization Global Foodborne Infections Network Country Data Bank: results of quality assured laboratories from 001 to 007. Foodborne Path. Dis, (011).. J.P. VICO. Salmonellosis in finishing pigs in Spain: prevalence, antimicrobial agent susceptibilities, and risk factor analysis. Food Prot., 74(7), (011). 3 J. GOMEZ-LAGUNA. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella infections in free-range pigs. Vet. J., 190(1), (011). 4. E. FEARNLEY. Salmonella in chicken meat, eggs and humans; Adelaide, South Australia, 008., Int. J.. Food Microbiol, 146(3), 19-7 (011). 5. ANON, International outbreak of Salmonella Typhimurium DT update from Enter-net., WHO (World Health Organisation), Surveillance Programme for Control of Foodborne Infections and Intoxications in Europe, Newsletter, No.69, pp. 4-5 (001). 6. B. BERENDS. Impact on human health of Salmonella spp. on pork in the Netherlands and the anticipated effects of some currently proposed control strategies. Intern. J. Food Microbiol, 44, 19-9 (1998). Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No.,
8 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ, BRANISLAVA MITROVIĆ, DRAGAN ŽIVANOV, SAVA BUNČIĆ, NIKOLA PAVLOVIĆ 7. H.C. WEGENER, D.L. BAGGESEN. Investigation of on outbreak of human salmonellosis caused by Salmonella enterica ssp. enterica serovar infantis by use of pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Int J. Food Microbiol., Sep., 3(1-), (1996). 8. B.R. BERENDS. Impact on human health of Salmonella spp. on pork in the Netherlands and the anticipated effects of some currently proposed control strategies, Int. J. Food Microbiol., Nov 10, 44(3), 19-9 (1998). 9. C.A. HALEY. Salmonella prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility from the National Animal Health Monitoring System Svine 000 and 006 studies, J. Food Prot., 75(3), (01).doi: /036-08X.JFP Erratum in: J Food Prot. OCT, 76(10):1666 (013). 10. G. STEINBACH, M. HARTUNG. Attempt to estimate the share of human Salmonella infections, which are attributable to Salmonella originating from swine. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr, 11(8), (1999). 11. J.D.T. ARUDA-NETO, M.V. MANSO GUEVARA, G.P. NOGUEIRA, M. SAIKI, K. CESTARI, A.C. SHTEJER, A. DEPPMAN, J.W. PEREIRA FILHO, F. GARCIA, L.P. GERALDO, A.N. GOUVEIA, F. GUZMÁN, J. MESA, O. RODRIGUEZ, R. SEMMLER, V.R. VANIN. Long term accumulation of uranium in bones of Wistar rats as a function of in-take dosages. Radioactive Protection Dosimetry; 11(3): (004). 1. T. IZAK-BIRAN, T. SCHLESINGER, R. WEINGARTEN, O. EVEN, Z. SHAMAI, M. ISRAELI. Concentrations of U and Po in animal feed supplements, in poultry meat and eggs. Health Physics 56; (1988). 13. R.D. OBRADOVIĆ-ARSIĆ. Natural Ionizing Radiation and Human Health in Serbia, Nuclear Tehnology&Radiation Protection, 5, 3, pp (010). 14. B. MITROVIĆ. Uranium distribution in broiler organs and possibilities for protection. Radiat. Environ.Biophys., 53, (014). 15. L.L. KUDLA. Control of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium in chicken breast meat by irradiation combined with modified atmosphere packaging. J. Food Prot. 74 (11), (011). 16. R. MITROVIĆ. Improving the Quality of Poultry Products with the Health Aspect of Irradiated. (in Serbian), Second Yugoslav symposium "Science In Poultry", No 3-4, (1988) 17. P.O. LAMUKA. Bacteriological Quality of Freshly Processed Broiler Chickensas Affectedby Carcass Pretreatment and Gamma Iradiation, Journal Of Food Science, 57., (199). 18. K.T. RAJKOVSKI. Effect of gamma or beta radiation on Salmonella DT 104 in ground pork. J. Food Prot, 69(6), (006). 19. I. ROUSSEL. Bulletin International du Centre Europeen Information pour 1 irradiation des aliments a 'Saclay, Revue, Generale De Froid, 1, 74 (1984). 0. V.J. SINANOGLOU. Effects Of gamma radiation on microbiological status, fatty acid composition, and color of vacuum-packaged cold-stored fresh pork meat, J, Food Prot., 7(3), (009). 1. C.H. SOMMERS, K.T. RAJKOWSKI. Radiation inactivation of foodborne pathogens on frozen seafood products, J.Food Prot., 74(4), doi: /036-08X.JFP (011).. M. TURGIS, J. HAN, M. MILLETTE, S. SALMIERI, J. BORSA, M. LACROIX. Effect Of Selected Antimicrobial Compounds On The Radiosensitization Of Salmonella Typhi In Ground Beef, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 48(6), (009), (009). 3. WHO. Food Irradiation. In Point of Fact. No. 40. Geneva, Switzerland (1987) Romanian Biotechnological Letters, Vol. 3, No., 018
Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat
 Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat Received for publication, July, 17, 2015 Accepted,November, 3, 2016 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ 1*, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ 1, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ
Effect of uranium on the radiosensitivity of Salmonella spp. in pork meat Received for publication, July, 17, 2015 Accepted,November, 3, 2016 MIHAJLO VIĆENTIJEVIĆ 1*, DUBRAVKA VUKOVIĆ 1, VUJADIN VUKOVIĆ
STUDY OF FREQUENCY OF SALMONELLA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM MEAT, MEAT PRODUCTS AND ORGANS
 STUDY OF FREQUENCY OF SALMONELLA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM MEAT, MEAT PRODUCTS AND ORGANS CARMEN DAVID 2, R. TRIF 1, E. TÎRZIU 1, ROXANA IRIMESCU 1, R. V. GROS 1 1 - Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Timisoara,
STUDY OF FREQUENCY OF SALMONELLA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM MEAT, MEAT PRODUCTS AND ORGANS CARMEN DAVID 2, R. TRIF 1, E. TÎRZIU 1, ROXANA IRIMESCU 1, R. V. GROS 1 1 - Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Timisoara,
Dynamics of Salmonella Typhimurium shedding from early to peak lay in laying hens
 Dynamics of Salmonella Typhimurium shedding from early to peak lay in laying hens P. SHARMA*, V. PANDE, R. DEVON, A. MCWHORTER and K. K. CHOUSALKAR School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, University
Dynamics of Salmonella Typhimurium shedding from early to peak lay in laying hens P. SHARMA*, V. PANDE, R. DEVON, A. MCWHORTER and K. K. CHOUSALKAR School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, University
Collaborators. Page 1 of 7
 Anti-Salmonella and Anti-Campylobacter Properties of Sodium Metasilicate on Commercially Available Ready-to-Cook Broiler Breast Meat Stored at 4 ± 1 C for 7 Days Collaborators Sally K. Williams, Ph.D.
Anti-Salmonella and Anti-Campylobacter Properties of Sodium Metasilicate on Commercially Available Ready-to-Cook Broiler Breast Meat Stored at 4 ± 1 C for 7 Days Collaborators Sally K. Williams, Ph.D.
Salmonella monitoring data and foodborne outbreaks for 2015 in the European Union
 Salmonella monitoring data and foodborne outbreaks for 2015 in the European Union Valentina Rizzi BIOCONTAM Unit 22 nd EURL- Salmonella Workshop 2017 Zaandam, 29-30 May 2017 OUTLINE EUSR zoonoses-fbo 2015
Salmonella monitoring data and foodborne outbreaks for 2015 in the European Union Valentina Rizzi BIOCONTAM Unit 22 nd EURL- Salmonella Workshop 2017 Zaandam, 29-30 May 2017 OUTLINE EUSR zoonoses-fbo 2015
C.M. Harris*, S.K. Williams* 1. PhD Candidate Department of Animal Sciences Meat and Poultry Processing and Food Safety
 The Antimicrobial Properties of a Vinegar-based Ingredient on Salmonella Typhimurium and Psychrotrophs inoculated in Ground Chicken Breast Meat and stored at 3±1 C for 7 days C.M. Harris*, S.K. Williams*
The Antimicrobial Properties of a Vinegar-based Ingredient on Salmonella Typhimurium and Psychrotrophs inoculated in Ground Chicken Breast Meat and stored at 3±1 C for 7 days C.M. Harris*, S.K. Williams*
Tineke Jones Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Lacombe Research Centre Lacombe, Alberta
 Growth of Escherichia Coli at Chiller Temperatures Tineke Jones Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Lacombe Research Centre Lacombe, Alberta \ Introduction The responses of mesophilic microorganisms to chiller
Growth of Escherichia Coli at Chiller Temperatures Tineke Jones Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Lacombe Research Centre Lacombe, Alberta \ Introduction The responses of mesophilic microorganisms to chiller
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System
 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System 2 3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System is a qualitative test used for the rapid detection and biochemical
3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System 2 3M Food Safety 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System 3M Petrifilm Salmonella Express System is a qualitative test used for the rapid detection and biochemical
Fernando Leite, Connie Gebhart, Randall Singer, Richard Isaacson. University of Minnesota, St. Paul, MN
 VACCINATION AGAINST LAWSONIA INTRACELLULARIS DECREASES SHEDDING OF SALMONELLA ENTERICA SEROVAR TYPHIMURIUM IN CO-INFECTED PIGS AND CHANGES THE HOST GUT MICROBIOME Fernando Leite, Connie Gebhart, Randall
VACCINATION AGAINST LAWSONIA INTRACELLULARIS DECREASES SHEDDING OF SALMONELLA ENTERICA SEROVAR TYPHIMURIUM IN CO-INFECTED PIGS AND CHANGES THE HOST GUT MICROBIOME Fernando Leite, Connie Gebhart, Randall
RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
 RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS Milica M. Rajačić, Nataša B. Sarap, Marija M. Janković, Jelena D. Nikolić, Dragana J. Todorović and Gordana. Pantelić Institute for Nuclear Sciences "Vinča", University
RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS Milica M. Rajačić, Nataša B. Sarap, Marija M. Janković, Jelena D. Nikolić, Dragana J. Todorović and Gordana. Pantelić Institute for Nuclear Sciences "Vinča", University
The effect of short-time microwave exposures on Salmonella typhimurium inoculated onto chicken drumettes
 Short Paper The effect of short-time microwave exposures on Salmonella typhimurium inoculated onto chicken drumettes Jamshidi, A. 1* ; Ghasemi, A. 2 and Mohammadi, A. 3 1 Department of Food Hygiene and
Short Paper The effect of short-time microwave exposures on Salmonella typhimurium inoculated onto chicken drumettes Jamshidi, A. 1* ; Ghasemi, A. 2 and Mohammadi, A. 3 1 Department of Food Hygiene and
Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. Figure 1. Figure 2
 Q1.Electricity is generated in a nuclear power station. Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. (a) Figure 1 shows the first part of the nuclear fission reaction. Complete
Q1.Electricity is generated in a nuclear power station. Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. (a) Figure 1 shows the first part of the nuclear fission reaction. Complete
NRL-Salmonella, Hungary. National Food Chain Safety Office Food and Feed Safety Directorate Erzsébet Adrián 29 May 2018
 NRL-Salmonella, Hungary National Food Chain Safety Office Food and Feed Safety Directorate Erzsébet Adrián 29 May 2018 Structure National Food Chain Safety Office Food and Feed Safety Directorate Official
NRL-Salmonella, Hungary National Food Chain Safety Office Food and Feed Safety Directorate Erzsébet Adrián 29 May 2018 Structure National Food Chain Safety Office Food and Feed Safety Directorate Official
COMMISSION REGULATION (EU)
 26.5.2011 Official Journal of the European Union L 138/45 COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 517/2011 of 25 May 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as
26.5.2011 Official Journal of the European Union L 138/45 COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 517/2011 of 25 May 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as
A. Identify the highly penetrating radioactive emission that exposed the photographic plates.
 Name Unit 3: Nuclear Chemistry Date Part 2 Questions 1. In 1896, Antoine H. Becquerel discovered that a uranium compound could expose a photographic plate wrapped in heavy paper in the absence of light.
Name Unit 3: Nuclear Chemistry Date Part 2 Questions 1. In 1896, Antoine H. Becquerel discovered that a uranium compound could expose a photographic plate wrapped in heavy paper in the absence of light.
Evaluation of non-pathogenic surrogate bacteria as process validation indicators
 Evaluation of non-pathogenic surrogate bacteria as process validation indicators for Salmonella enteric for selected antimicrobial treatments, cold storage and fermentation in meat S. E. Niebuhr 1, A.
Evaluation of non-pathogenic surrogate bacteria as process validation indicators for Salmonella enteric for selected antimicrobial treatments, cold storage and fermentation in meat S. E. Niebuhr 1, A.
Irradiation and contamination
 Irradiation and contamination Irradiation Irradiation means exposure to radiation. Science uses the word radiation to refer to anything that travels in straight lines (rays) from a source. Therefore, irradiation
Irradiation and contamination Irradiation Irradiation means exposure to radiation. Science uses the word radiation to refer to anything that travels in straight lines (rays) from a source. Therefore, irradiation
Estimating the Public Health Impact of Setting Targets at the European Level for the Reduction of Zoonotic Salmonella in Certain Poultry Populations
 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4836-4850; doi:10.3390/ijerph10104836 OPEN ACCESS Review International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4836-4850; doi:10.3390/ijerph10104836 OPEN ACCESS Review International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Industry Learning in Salmonella Control
 Industry Learning in Salmonella Control Dr. Angie Siemens Cargill www.cargill.com CONTROL: to exercise restraint or direction over; dominate; command. CONTROL: to eliminate or prevent the flourishing or
Industry Learning in Salmonella Control Dr. Angie Siemens Cargill www.cargill.com CONTROL: to exercise restraint or direction over; dominate; command. CONTROL: to eliminate or prevent the flourishing or
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
3 S. Heidelberg ESBL Extended spectrum lactamase
 Vol. 25 No. 123 almonella Heidelberg 1 almonella enterica serovar Heidelberg 1 3. Heidelberg EBL Extended spectrum lactamase CTX M 2 EBL. Heidelberg almonella enterica serovar Heidelberg 1 3. Heidelberg
Vol. 25 No. 123 almonella Heidelberg 1 almonella enterica serovar Heidelberg 1 3. Heidelberg EBL Extended spectrum lactamase CTX M 2 EBL. Heidelberg almonella enterica serovar Heidelberg 1 3. Heidelberg
Section 3: Nuclear Radiation Today
 : Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
: Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens
 The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens C. H. JOHANSEN, L. BJERRUM, M. LUND and K. PEDERSEN* Danish Institute for
The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens C. H. JOHANSEN, L. BJERRUM, M. LUND and K. PEDERSEN* Danish Institute for
HALF LIFE. NJSP HMRU June 10, Student Handout CBRNE AWARENESS Module 4 1. Objectives. Student will
 June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp.
 Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp. March 11, 213 Prof Steve Forsythe Pathogen Research Centre, School of Science and Technology Nottingham Trent University Clifton
Use of the 3M Molecular Detection System for Salmonella and Listeria spp. March 11, 213 Prof Steve Forsythe Pathogen Research Centre, School of Science and Technology Nottingham Trent University Clifton
Progress on the biocontrol of foodborne pathogens on leafy greens with non-pathogenic microbes
 Progress on the biocontrol of foodborne pathogens on leafy greens with non-pathogenic microbes M.O. Olanya and D.O. Ukuku USDA Agricultural Research Service, Eastern Regional Research Center, Wyndmoor,
Progress on the biocontrol of foodborne pathogens on leafy greens with non-pathogenic microbes M.O. Olanya and D.O. Ukuku USDA Agricultural Research Service, Eastern Regional Research Center, Wyndmoor,
PCR- TTGE PCR (PCR-TTGE) PCR.
 - m.besharaty89@yahoo.com 2500 (-) (tryptic soy broth) TSB - Typhi (-) m.besharaty89@yahoo.com 2500 enterica enterica Typhimurium (tryptic soy broth) TSB enterica 2500 bongori enterica Typhimurium Typhi
- m.besharaty89@yahoo.com 2500 (-) (tryptic soy broth) TSB - Typhi (-) m.besharaty89@yahoo.com 2500 enterica enterica Typhimurium (tryptic soy broth) TSB enterica 2500 bongori enterica Typhimurium Typhi
Antimicrobial Activity of Cinnamic Acid, Citric Acid, Cinnamaldehyde, and Levulinic Acid Against Foodborne Pathogens
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2014 Antimicrobial Activity of
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2014 Antimicrobial Activity of
Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products
 Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products Introduction Egg products refer to products made by adding other types of food or food additives to eggs
Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products Introduction Egg products refer to products made by adding other types of food or food additives to eggs
Overview. Michelle D. Danyluk University of Florida. 4/14/14
 Michelle D. Danyluk University of Florida mddanyluk@ufl.edu Overview Biological Hazards What is the pathogen of concern? Are all strains created equal? What pathogen is the most resistant to the lethal
Michelle D. Danyluk University of Florida mddanyluk@ufl.edu Overview Biological Hazards What is the pathogen of concern? Are all strains created equal? What pathogen is the most resistant to the lethal
ITALY TRENDS AND SOURCES OF ZOONOSES AND ZOONOTIC AGENTS IN HUMANS, FOODSTUFFS, ANIMALS AND FEEDINGSTUFFS
 ITALY The Report referred to in Article 9 of Directive 2003/99/EC TRENDS AND SOURCES OF ZOONOSES AND ZOONOTIC AGENTS IN HUMANS, FOODSTUFFS, ANIMALS AND FEEDINGSTUFFS including information on foodborne
ITALY The Report referred to in Article 9 of Directive 2003/99/EC TRENDS AND SOURCES OF ZOONOSES AND ZOONOTIC AGENTS IN HUMANS, FOODSTUFFS, ANIMALS AND FEEDINGSTUFFS including information on foodborne
Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates. (Question N EFSA-Q ) Adopted by The Task Force on 28 March 2007
 The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes
 Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment
 Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13168 First edition 2015-07-01 Water quality Simultaneous determination of tritium and carbon 14 activities Test method using liquid scintillation counting Qualité de l eau Détermination
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13168 First edition 2015-07-01 Water quality Simultaneous determination of tritium and carbon 14 activities Test method using liquid scintillation counting Qualité de l eau Détermination
Salmonella in Food 2014
 Salmonella in Food 04 Table : Salmonella spp. in meat Food Type Sampling Site RTE Fresh Meat Broiler Processing NS 0 0 Catering NS 0 0 Unspecified Poultry (Including Turkey, Duck and Unspecified NS 0 0
Salmonella in Food 04 Table : Salmonella spp. in meat Food Type Sampling Site RTE Fresh Meat Broiler Processing NS 0 0 Catering NS 0 0 Unspecified Poultry (Including Turkey, Duck and Unspecified NS 0 0
Survival and Heat Resistance of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Peanut Butter
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 8434 8438 Vol. 77, No. 23 0099-2240/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.06270-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Survival
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 8434 8438 Vol. 77, No. 23 0099-2240/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.06270-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Survival
 IONIZING RADIATION RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS The science of ionizing radiation and its interaction with matter Special interest in the energy absorbed Radiation dosimetry quantitative determination of that
IONIZING RADIATION RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS The science of ionizing radiation and its interaction with matter Special interest in the energy absorbed Radiation dosimetry quantitative determination of that
Gram negative bacilli
 Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Serotype and Phage Type Distribution of Salmonella Strains Isolated from Humans, Cattle, Pigs, and Chickens in The Netherlands from 1984 to 2001
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 3980 3985 Vol. 40, No. 11 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.3980 3985.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 3980 3985 Vol. 40, No. 11 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.3980 3985.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Outbreak of a new serotype Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica, with antigenic formula 11:z 41 : e,n,z 15 in Greece :
 Outbreak of a new serotype Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica, with antigenic formula 11:z 41 : e,n,z 15 in Greece : 2016-2017 An investigation of the Hellenic Centre of Disease Control and Prevention
Outbreak of a new serotype Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica, with antigenic formula 11:z 41 : e,n,z 15 in Greece : 2016-2017 An investigation of the Hellenic Centre of Disease Control and Prevention
Bactericidal Effect of Several Chemicals on Hatching Eggs Inoculated with Salmonella serovar Typhimurium
 2007 Poultry Science Association, Inc. Bactericidal Effect of Several Chemicals on Hatching Eggs Inoculated with Salmonella serovar Typhimurium N. A. Cox,* 1 L. J. Richardson,* R. J. Buhr,* M. T. Musgrove,
2007 Poultry Science Association, Inc. Bactericidal Effect of Several Chemicals on Hatching Eggs Inoculated with Salmonella serovar Typhimurium N. A. Cox,* 1 L. J. Richardson,* R. J. Buhr,* M. T. Musgrove,
Q1. The diagram represents an atom of lithium.
 Q1. The diagram represents an atom of lithium. Complete the diagram by writing in the spaces the name of each type of particle. Use only words given in the box. Each word may be used once or not at all.
Q1. The diagram represents an atom of lithium. Complete the diagram by writing in the spaces the name of each type of particle. Use only words given in the box. Each word may be used once or not at all.
NF VALIDATION Validation of alternative analytical methods Application in food microbiology. Summary report
 ACCREDITATION N 1-0144 PORTEE DISPONIBLE SUR WWW.COFRAC.FR THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC 2130 Woodward Austin, TX 78744 USA NF VALIDATION Validation of alternative analytical methods Application in food microbiology
ACCREDITATION N 1-0144 PORTEE DISPONIBLE SUR WWW.COFRAC.FR THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC 2130 Woodward Austin, TX 78744 USA NF VALIDATION Validation of alternative analytical methods Application in food microbiology
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview
 e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
Pr oject Summar y. Funded by The Beef Checkoff
 Pr oject Summar y Seasonal effects on E. coli O157:H7, multi drug-resistant Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes prevalence and E. coli O157:H7 and Salmonella load on hides and carcasses at cow/bull
Pr oject Summar y Seasonal effects on E. coli O157:H7, multi drug-resistant Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes prevalence and E. coli O157:H7 and Salmonella load on hides and carcasses at cow/bull
(Question N EFSA-Q ) Adopted by The Task Force on 20 February 2007
 Report on the Analysis of the baseline study on the prevalence of Salmonella in holdings of Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline study on the prevalence
Report on the Analysis of the baseline study on the prevalence of Salmonella in holdings of Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline study on the prevalence
Prof. Dr. Biljana Škrbić, Jelena Živančev
 5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
5 th CEFSER Training Course Analysis of chemical contaminants in food and the environment Faculty of Technology, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia 7-11 May 2012 Analysis of heavy elements
Quantitative Risk Assessment of Salmonella spp. in Fermented Pork Sausage (Nham)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 38 : 52-65 (24) Quantitative Risk Assessment of Salmonella spp. in Fermented Pork Sausage (Nham) Sukhuntha Osiriphun, Adisak Pongpoolponsak 2 and Kooranee Tuitemwong 3 ABSTRACT
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 38 : 52-65 (24) Quantitative Risk Assessment of Salmonella spp. in Fermented Pork Sausage (Nham) Sukhuntha Osiriphun, Adisak Pongpoolponsak 2 and Kooranee Tuitemwong 3 ABSTRACT
What type of radiation is emitted when a uranium-238 atom decays? From which part of a uranium-238 atom is the radiation emitted?
 Q1. (a) Some rocks inside the Earth contain uranium-238, a radioactive isotope of uranium. When an atom of uranium-238 decays, it gives out radiation and changes into a thorium-234 atom. What type of radiation
Q1. (a) Some rocks inside the Earth contain uranium-238, a radioactive isotope of uranium. When an atom of uranium-238 decays, it gives out radiation and changes into a thorium-234 atom. What type of radiation
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal
 NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION
 WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N a n d t h e N R C
 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
Salmonella typhimurium in Glucose-Mineral Salts Medium
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1987, p. 1311-1315 0099-2240/87/061311-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 53, No. 6 Effect of NaCl, ph, Temperature, and Atmosphere
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1987, p. 1311-1315 0099-2240/87/061311-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 53, No. 6 Effect of NaCl, ph, Temperature, and Atmosphere
Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella and Campylobacter contamination of poultry during transport and slaughter
 Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella and Campylobacter contamination of poultry during transport and slaughter Geertrui Rasschaert Vakgroep Veterinaire Volksgezondheid & Voedselveiligheid Promotor: Prof.
Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella and Campylobacter contamination of poultry during transport and slaughter Geertrui Rasschaert Vakgroep Veterinaire Volksgezondheid & Voedselveiligheid Promotor: Prof.
Applications for Industry and Environment. Radioisotope and Radiation Technology. International Atomic Energy Agency
 Radioisotope and Radiation Technology Applications for Industry and Environment M. Haji-Saeid Industrial Applications and Chemistry Section IACS Division of Physical and Chemical Sciences (NAPC) Dept.
Radioisotope and Radiation Technology Applications for Industry and Environment M. Haji-Saeid Industrial Applications and Chemistry Section IACS Division of Physical and Chemical Sciences (NAPC) Dept.
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity
 Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system
 I. Abstract. Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system Project Investigator(s): Jorge M. Fonseca 1, Sadhana Ravishankar
I. Abstract. Project Title: Estimation of the area affected by animal feces in vegetable field under overhead sprinkle irrigation system Project Investigator(s): Jorge M. Fonseca 1, Sadhana Ravishankar
The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year.
 ## The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year. Source of background radiation Average amount each year in dose units
## The table shows the average background radiation dose from various sources that a person living in Britain receives in one year. Source of background radiation Average amount each year in dose units
Estimation of Microbial Concentration in Food Products from Qualitative Microbiological Test Data with the MPN Technique
 173 Original Paper Estimation of Microbial Concentration in Food Products from Qualitative Microbiological Test Data with the MPN Technique Hiroshi Fujikawa* Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of
173 Original Paper Estimation of Microbial Concentration in Food Products from Qualitative Microbiological Test Data with the MPN Technique Hiroshi Fujikawa* Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of
It s better to have a half-life than no life! Radioactive Decay Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay
 It s better to have a half-life than no life! Radioactive Decay Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay What does it mean to be radioactive? Some atoms have nuclei that are unstable. These atoms spontaneously decompose
It s better to have a half-life than no life! Radioactive Decay Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay What does it mean to be radioactive? Some atoms have nuclei that are unstable. These atoms spontaneously decompose
Networks. The Salmonella Network, a tool for monitoring Salmonella from farm to fork
 The Salmonella Network, a tool for monitoring Salmonella from farm to fork R. Lailler [renaud.lailler@anses.fr] (1), F. Moury [frederique.moury@anses.fr] (1), S. A. Granier [sophie.granier@anses.fr] (1),
The Salmonella Network, a tool for monitoring Salmonella from farm to fork R. Lailler [renaud.lailler@anses.fr] (1), F. Moury [frederique.moury@anses.fr] (1), S. A. Granier [sophie.granier@anses.fr] (1),
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates. (Question N EFSA-Q A) Adopted by The Task Force on 28 April 2008
 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in turkey flocks, in the EU, 2006-2007 1 Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates
Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in turkey flocks, in the EU, 2006-2007 1 Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates
How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks)
 Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Iodine-131, Iodine-125 and heavy charged particles
 lucas heights 1971 Strict limits for exposure to all kinds of radiation are set and applied worldwide in an attempt to ensure the safe use of nuclear energy and nuclear techniques. These limits are kept
lucas heights 1971 Strict limits for exposure to all kinds of radiation are set and applied worldwide in an attempt to ensure the safe use of nuclear energy and nuclear techniques. These limits are kept
Stories from the Frontline: Investigating causes of salmonellosis in Australia. Name of program
 Stories from the Frontline: Investigating causes of salmonellosis in Australia Salmonellosis in Australia Disease rates among highest in developed world Responsible for majority of foodborne outbreaks
Stories from the Frontline: Investigating causes of salmonellosis in Australia Salmonellosis in Australia Disease rates among highest in developed world Responsible for majority of foodborne outbreaks
Features of Salmonella serovars among food handlers in Kyushu, Japan
 NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 30, 155-159, 2007 Features of Salmonella serovars among food handlers in Kyushu, Japan Koichi Murakami 1, Tatsuo Ishihara 2, Kazumi Horikawa 1, Takahiro Oda 3 1 Division of Pathology
NEW MICROBIOLOGICA, 30, 155-159, 2007 Features of Salmonella serovars among food handlers in Kyushu, Japan Koichi Murakami 1, Tatsuo Ishihara 2, Kazumi Horikawa 1, Takahiro Oda 3 1 Division of Pathology
AEPHY: Nuclear Physics Practise Test
 AEPHY: Nuclear Physics Practise Test Name: OVERALL: Additional 1 mark for units and significant figures. 1. Complete the table below: (2 marks) (63 marks + overall = 64 marks) Element Nuclide Atomic Number
AEPHY: Nuclear Physics Practise Test Name: OVERALL: Additional 1 mark for units and significant figures. 1. Complete the table below: (2 marks) (63 marks + overall = 64 marks) Element Nuclide Atomic Number
Chapter. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
Radiation Awareness Training. Stephen Price Office of Research Safety
 Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Salmonella enteritidis Identification and Isolation
 Department of Microbiology, Qom Branch, Islamic Azad University. Qom, Iran Start Here Advisor Dr.Mohsen Zargar Consulting Advisor Dr.Taghi Salehi Zahraei Presented by Zeinab Yazdanpanah 1 Outcome Enterobacteriaceae
Department of Microbiology, Qom Branch, Islamic Azad University. Qom, Iran Start Here Advisor Dr.Mohsen Zargar Consulting Advisor Dr.Taghi Salehi Zahraei Presented by Zeinab Yazdanpanah 1 Outcome Enterobacteriaceae
COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES
 COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES UNIT: 5 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION TOPIC : CAUSES, EFFECTS AND CONTROL MEASURES
COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES UNIT: 5 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION TOPIC : CAUSES, EFFECTS AND CONTROL MEASURES
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
Bactericidal Activity of Organic Acids against Salmonella typhimurium Attached to Broiler Chicken Skin t
 629 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 60, No.6, 1997, Pages 629-633 Copyright, Intemational Association of Milk, Food and Environmental Sanitarians Bactericidal Activity of Organic s against Salmonella
629 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 60, No.6, 1997, Pages 629-633 Copyright, Intemational Association of Milk, Food and Environmental Sanitarians Bactericidal Activity of Organic s against Salmonella
Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response. Session II. Objectives. Basic Radiation Physics
 Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response Session II Basic Radiation Physics Objectives Discuss the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Describe radioactive decay. Discuss the
Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response Session II Basic Radiation Physics Objectives Discuss the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Describe radioactive decay. Discuss the
Salmonella Prevalence in Turkey Flocks before and after Implementation of the Control Program in Germany
 Agriculture 2013, 3, 342-361; doi:10.3390/agriculture3030342 Article OPEN ACCESS agriculture ISSN 2077-0472 www.mdpi.com/journal/agriculture Salmonella Prevalence in Turkey Flocks before and after Implementation
Agriculture 2013, 3, 342-361; doi:10.3390/agriculture3030342 Article OPEN ACCESS agriculture ISSN 2077-0472 www.mdpi.com/journal/agriculture Salmonella Prevalence in Turkey Flocks before and after Implementation
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY
 INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY Introduction to Internal Dosimetry Importance of External and Internal Exposures by Radiation Type Charged particle radiation (α, p, β) Generally important only for internal
INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY Introduction to Internal Dosimetry Importance of External and Internal Exposures by Radiation Type Charged particle radiation (α, p, β) Generally important only for internal
ISO Water quality Measurement of polonium 210 activity concentration in water by alpha spectrometry
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13161 First edition 2011-10-01 Water quality Measurement of polonium 210 activity concentration in water by alpha spectrometry Qualité de l eau Mesurage de l activité du polonium
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13161 First edition 2011-10-01 Water quality Measurement of polonium 210 activity concentration in water by alpha spectrometry Qualité de l eau Mesurage de l activité du polonium
What happens during nuclear decay? During nuclear decay, atoms of one element can change into atoms of a different element altogether.
 When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
SAMPLING LEVELS AND FREQUENCY
 SAMPLING LEVELS AND FREQUENCY 1 The purpose of this document is to define the minimum number samples which must be taken in accordance with Council Directive 96/23/EC and Commission Decision 97/747/EC.
SAMPLING LEVELS AND FREQUENCY 1 The purpose of this document is to define the minimum number samples which must be taken in accordance with Council Directive 96/23/EC and Commission Decision 97/747/EC.
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF SWEET BASIL AND THYME AGAINST SALMONELLA ENTERICA SEROTYPE ENTERITIDIS IN EGG-BASED PASTA
 Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 67 (1), 213-221, 2015 DOI:10.2298/ABS141118027S ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF SWEET BASIL AND THYME AGAINST SALMONELLA ENTERICA SEROTYPE ENTERITIDIS IN EGG-BASED PASTA Jasmina Stojiljković
Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 67 (1), 213-221, 2015 DOI:10.2298/ABS141118027S ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF SWEET BASIL AND THYME AGAINST SALMONELLA ENTERICA SEROTYPE ENTERITIDIS IN EGG-BASED PASTA Jasmina Stojiljković
Active concentration for material not requiring radiological regulation
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB27742-2011 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net Wayne Zheng et al. ICS 17. 240 F 70 GB National Standard of the People s Republic of China Active
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB27742-2011 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net Wayne Zheng et al. ICS 17. 240 F 70 GB National Standard of the People s Republic of China Active
Scientific Opinion on a quantitative estimation of the public health impact of setting a new target for the reduction of Salmonella in laying hens 1
 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on a quantitative estimation of the public health impact of setting a new target for the 1 EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) 2, 3 European Food Safety Authority
SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on a quantitative estimation of the public health impact of setting a new target for the 1 EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) 2, 3 European Food Safety Authority
ICRP & Alliance, Integrated Protection of People and the Environment
 ICRP & Alliance, Integrated Protection of People and the Environment 4 th International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection October 10-12, 2017, Paris, France Kathryn A. Higley ICRP Committee
ICRP & Alliance, Integrated Protection of People and the Environment 4 th International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection October 10-12, 2017, Paris, France Kathryn A. Higley ICRP Committee
Salmonella in Food Table 1: Salmonella spp. in meat
 Salmonella in Food 2013 Table 1: Salmonella spp. in meat Food Type Sampling Site RTE Status Samples Tested Samples Positive % Positive FRESH MEAT BROILER Processing NS 43 0 0 Slaughterhouse NS 7 0 0 BEEF
Salmonella in Food 2013 Table 1: Salmonella spp. in meat Food Type Sampling Site RTE Status Samples Tested Samples Positive % Positive FRESH MEAT BROILER Processing NS 43 0 0 Slaughterhouse NS 7 0 0 BEEF
Fundamentals of radiation protection
 Fundamentals of radiation protection Kamel ABBAS European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Transuranium Elements, Nuclear Security Unit Via E. Fermi, 2749, I-21027 Ispra, Italy tel. +39-0332-785673,
Fundamentals of radiation protection Kamel ABBAS European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Transuranium Elements, Nuclear Security Unit Via E. Fermi, 2749, I-21027 Ispra, Italy tel. +39-0332-785673,
LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY
 LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 30.4 Radiation and radioactivity Decay series Nuclear radiation is a form of ionizing radiation 30.5 Nuclear decay and half-lives Activity Radioactive dating Radiocarbon
LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 30.4 Radiation and radioactivity Decay series Nuclear radiation is a form of ionizing radiation 30.5 Nuclear decay and half-lives Activity Radioactive dating Radiocarbon
P7 Radioactivity. Student Book answers. P7.1 Atoms and radiation. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 24 Medical Imaging Effects of Radiation We now know what radiation is But what does it mean for our bodies? Radioactivity is quantified in
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 24 Medical Imaging Effects of Radiation We now know what radiation is But what does it mean for our bodies? Radioactivity is quantified in
The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only.
 ATOMS AND NUCLEAR RADIATION PART II Q1. The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only. Two different types of absorber are
ATOMS AND NUCLEAR RADIATION PART II Q1. The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only. Two different types of absorber are
Typhoid Fever Dr. KHALID ALJARALLAH
 Dr. KHALID ALJARALLAH kaljarallah@kfmc.med.sa Main objectives General characteristics (G-, Rod, Facultative anaerobe..etc,) Natural Habitat and transmission root Symptoms Pathogenicity Diagnosis and treatment
Dr. KHALID ALJARALLAH kaljarallah@kfmc.med.sa Main objectives General characteristics (G-, Rod, Facultative anaerobe..etc,) Natural Habitat and transmission root Symptoms Pathogenicity Diagnosis and treatment
SEC. Interpretation Guide. Select E. coli Count Plate
 Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Select E. coli Count Plate is a sample-ready-culture medium system which contains selective agents, nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent, and an indicator
Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Select E. coli Count Plate is a sample-ready-culture medium system which contains selective agents, nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent, and an indicator
The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand
 Introduction The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand M Dufour AIMS NZIMLS South Pacific Congress Gold Coast, August 2011 New Zealand is a geographically
Introduction The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand M Dufour AIMS NZIMLS South Pacific Congress Gold Coast, August 2011 New Zealand is a geographically
Number of protons. 2. What is the nuclear symbol for a radioactive isotope of copper with a mass number of 60? A) Cu
 Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY
 10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
Asymptotic Confidence Ellipses of Parameters for the Beta-Poisson Dose-Response Model
 Thailand Statistician January 2012; 10(1) : 15-39 http://statassoc.or.th Contributed paper Asymptotic Confidence Ellipses of Parameters for the Noppadol Angkanavisal [a,b], Kamon Budsaba* [a,b] and Andrei
Thailand Statistician January 2012; 10(1) : 15-39 http://statassoc.or.th Contributed paper Asymptotic Confidence Ellipses of Parameters for the Noppadol Angkanavisal [a,b], Kamon Budsaba* [a,b] and Andrei
A Nuclear Power Plant
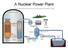 A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
