Modularization of Signal Transduction Pathways: detecting the trend of development among various species
|
|
|
- Wendy Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modularization of Signal Transduction Pathways: detecting the trend of development among various species By Losiana Nayak & Rajat K. De Machine Intelligence Unit Indian Statistical Institute 203 B. T. Road, Kolkata West Bengal, India {losiana_t,
2 Overall Goal To create valid partitions in Signal Transduction Pathways (STPs) to study, analyze and model them
3 What is a STP? Signal: any communication that encodes a message Signal Transduction: conversion of a signal from extracellular environment to functional changes within the cell Signal transduction pathway: series of steps that enable signal transmission through physical barriers like biological membranes
4
5 Why Study STP? Abnormal signal transduction is responsible for many diseases. Ex: Cancer (uncontrolled cell growth) Atherosclerosis (thickening of the walls of arteries) Rheumatoid arthritis (structural changes in lining of joints) Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's Disease (structural changes in the bowel wall)
6 Difficulty in study of STP! Signal transduction pathways are complex biochemical networks of biomolecules and chemical compounds. Each member s function is dependent on other intra and inter network member(s). Study of such a network s function and its relation with other signaling networks is quite difficult as a whole. So a sound strategy to study these complex networks is to decompose them into smaller units or modules.
7 Existing Algorithms Graph partitioning Algorithms Require partition number and size Rigid Community Finding Algorithms Consider Modularity Recognize naturally existing partitions Flexible can t create partitions when natural partitions don t exist
8 Modularization Process, which divides a pathway into smaller units, called modules A module can be defined as a subset of the original network, that tends to self-sufficiency have minimal dependency on the rest part of the network
9 Algorithm starts with the node having maximum number of the relations in a given network A module is created initially by including immediate neighbors of the starting node Members are included or deleted from a module based on the complexity value After completion of one module, construction of next module starts Process is repeated till all the nodes of the network get included into one of the modules
10 M O D U L A R I Z A T I O N FOR C=3 Human MAPK Signaling Pathway
11 We are getting more no. of biologically significant modules for c=3 with minimum no. of singleton and small modules. Modules GRB2, Ras and ERK divide effectively the classic MAPK pathway Modules MEKK1, MKK4, MKK7 and JNK are constituting JNK pathway p38 pathway is divided into modules p38, ASK1 and TAK1
12 There is a gradual development in MAPK pathway starting from Dog to Human and Mouse.
13 Modularization for c = 3, 4 Human calcium signaling pathway with 4 biologically significant modules marked with black lines for c = 3 and 4.
14 Modules obtained from human calcium signalling pathway for different c- values are given for comparison. Columns N and R contain no. of nodes and relations present in a module respectively
15 Human Wnt Signaling Pathway modularized for c=3
16 Modules of human Wnt Signaling Pathway The cell membrane portion of the canonical Wnt pathway is included in module WNT16 The steps of the canonical Wnt pathway taking place around the PP2AC protein scaffold is divided into modules (DVL1)1, AXIN1 and CTNNB1 The part of canonical Wnt pathway around and inside nucleus is enclosed in module LEF1 Module (DVL1)2 is made up of the Planar cell polarity pathway Module PLCB1 is comprised of the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway We cannot associate any biological significance to the very small Tp53 module
17
18 Innovative Aspects A complex biological system can be divided into simpler partitions for further analysis Modularization algorithm provides better modules than the existing graph partitioning and community finding algorithms Species-wise module comparisons establish trend of development and pathway sophistication among different species The algorithm is a way to delve deeper into complex systems.
19 THANK YOU
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
Automated Assignment of Backbone NMR Data using Artificial Intelligence
 Automated Assignment of Backbone NMR Data using Artificial Intelligence John Emmons στ, Steven Johnson τ, Timothy Urness*, and Adina Kilpatrick* Department of Computer Science and Mathematics Department
Automated Assignment of Backbone NMR Data using Artificial Intelligence John Emmons στ, Steven Johnson τ, Timothy Urness*, and Adina Kilpatrick* Department of Computer Science and Mathematics Department
A Multiobjective GO based Approach to Protein Complex Detection
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Technology 4 (2012 ) 555 560 C3IT-2012 A Multiobjective GO based Approach to Protein Complex Detection Sumanta Ray a, Moumita De b, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Technology 4 (2012 ) 555 560 C3IT-2012 A Multiobjective GO based Approach to Protein Complex Detection Sumanta Ray a, Moumita De b, Anirban Mukhopadhyay
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles
 BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
1 Undirected Graphical Models. 2 Markov Random Fields (MRFs)
 Machine Learning (ML, F16) Lecture#07 (Thursday Nov. 3rd) Lecturer: Byron Boots Undirected Graphical Models 1 Undirected Graphical Models In the previous lecture, we discussed directed graphical models.
Machine Learning (ML, F16) Lecture#07 (Thursday Nov. 3rd) Lecturer: Byron Boots Undirected Graphical Models 1 Undirected Graphical Models In the previous lecture, we discussed directed graphical models.
3 : Representation of Undirected GM
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 3 : Representation of Undirected GM Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Longqi Cai, Man-Chia Chang 1 MRF vs BN There are two types of graphical models:
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 3 : Representation of Undirected GM Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Longqi Cai, Man-Chia Chang 1 MRF vs BN There are two types of graphical models:
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective
 Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
The EGF Signaling Pathway! Introduction! Introduction! Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3. EGF promotes cell growth
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
More on NP and Reductions
 Indian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, Kancheepuram Chennai 600 127, India An Autonomous Institute under MHRD, Govt of India http://www.iiitdm.ac.in COM 501 Advanced Data
Indian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, Kancheepuram Chennai 600 127, India An Autonomous Institute under MHRD, Govt of India http://www.iiitdm.ac.in COM 501 Advanced Data
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Host-Pathogen Interaction. PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur
 Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction
 Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
Biochemistry: A Review and Introduction CHAPTER 1 Chem 40/ Chem 35/ Fundamentals of 1 Outline: I. Essence of Biochemistry II. Essential Elements for Living Systems III. Classes of Organic Compounds IV.
Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring
 Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring Student Outcomes Students find solutions to polynomial equations where the polynomial expression is not factored into linear factors. Students construct
Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring Student Outcomes Students find solutions to polynomial equations where the polynomial expression is not factored into linear factors. Students construct
Biological Networks: Comparison, Conservation, and Evolution via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor
 Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis
 From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis David Gilbert drg@brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Bioinformatics Research Centre, University of Glasgow and Monika Heiner
From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis David Gilbert drg@brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Bioinformatics Research Centre, University of Glasgow and Monika Heiner
Computational Genomics. Systems biology. Putting it together: Data integration using graphical models
 02-710 Computational Genomics Systems biology Putting it together: Data integration using graphical models High throughput data So far in this class we discussed several different types of high throughput
02-710 Computational Genomics Systems biology Putting it together: Data integration using graphical models High throughput data So far in this class we discussed several different types of high throughput
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization
 Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Fixed Perimeter Rectangles
 Rectangles You have a flexible fence of length L = 13 meters. You want to use all of this fence to enclose a rectangular plot of land of at least 8 square meters in area. 1. Determine a function for the
Rectangles You have a flexible fence of length L = 13 meters. You want to use all of this fence to enclose a rectangular plot of land of at least 8 square meters in area. 1. Determine a function for the
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Cellular Systems Biology or Biological Network Analysis
 Cellular Systems Biology or Biological Network Analysis Joel S. Bader Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University (c) 2012 December 4, 2012 1 Preface Cells are systems. Standard engineering
Cellular Systems Biology or Biological Network Analysis Joel S. Bader Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University (c) 2012 December 4, 2012 1 Preface Cells are systems. Standard engineering
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways
 MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Gibbs Fields & Markov Random Fields
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F10) Lecture#7 (Tuesday September 21) Gibbs Fields & Markov Random Fields Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Bradford Neuman 1 1 Gibbs Fields Like a Bayes Net, a
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F10) Lecture#7 (Tuesday September 21) Gibbs Fields & Markov Random Fields Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Bradford Neuman 1 1 Gibbs Fields Like a Bayes Net, a
How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts:
 Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION
 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields
 Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields 40-956 Advanced Topics in AI: Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Soleymani Spring 2015 Markov Random Field Structure: undirected
Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields 40-956 Advanced Topics in AI: Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Soleymani Spring 2015 Markov Random Field Structure: undirected
Cellular Biology. Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution
 Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Vertex Identifying Code in Infinite Hexagonal Grid
 Gexin Yu gyu@wm.edu College of William and Mary Joint work with Ari Cukierman Definitions and Motivation Goal: put sensors in a network to detect which machine failed Definitions and Motivation Goal: put
Gexin Yu gyu@wm.edu College of William and Mary Joint work with Ari Cukierman Definitions and Motivation Goal: put sensors in a network to detect which machine failed Definitions and Motivation Goal: put
KEGGgraph: Application Examples
 KEGGgraph: Application Examples Jitao David Zhang April 30, 2018 Abstract In this vignette, we demonstrate the application of KEGGgraph as flexible module in analysis pipelines targeting heterogenous biological
KEGGgraph: Application Examples Jitao David Zhang April 30, 2018 Abstract In this vignette, we demonstrate the application of KEGGgraph as flexible module in analysis pipelines targeting heterogenous biological
BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction
 BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction What is Bioinformatics? The term was first coined in 1988 by Dr. Hwa Lim The original definition was : a collective term for data compilation, organisation, analysis and
BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction What is Bioinformatics? The term was first coined in 1988 by Dr. Hwa Lim The original definition was : a collective term for data compilation, organisation, analysis and
Chapter 1. DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d
 Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
86 Part 4 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION
 86 Part 4 Chapter # AN INTEGRATION OF THE DESCRIPTIONS OF GENE NETWORKS AND THEIR MODELS PRESENTED IN SIGMOID (CELLERATOR) AND GENENET Podkolodny N.L. *1, 2, Podkolodnaya N.N. 1, Miginsky D.S. 1, Poplavsky
86 Part 4 Chapter # AN INTEGRATION OF THE DESCRIPTIONS OF GENE NETWORKS AND THEIR MODELS PRESENTED IN SIGMOID (CELLERATOR) AND GENENET Podkolodny N.L. *1, 2, Podkolodnaya N.N. 1, Miginsky D.S. 1, Poplavsky
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways
 State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways Youcef Derbal Ryerson University yderbal@ryerson.ca Abstract Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways are frequently deregulated in human
State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways Youcef Derbal Ryerson University yderbal@ryerson.ca Abstract Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways are frequently deregulated in human
Protein-protein interaction networks Prof. Peter Csermely
 Protein-Protein Interaction Networks 1 Department of Medical Chemistry Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary www.linkgroup.hu csermely@eok.sote.hu Advantages of multi-disciplinarity Networks have general
Protein-Protein Interaction Networks 1 Department of Medical Chemistry Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary www.linkgroup.hu csermely@eok.sote.hu Advantages of multi-disciplinarity Networks have general
V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks
 V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks In the first half of this lecture section, we use the theory of network flows to give constructive proofs of Menger s theorem. These proofs lead directly to algorithms
V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks In the first half of this lecture section, we use the theory of network flows to give constructive proofs of Menger s theorem. These proofs lead directly to algorithms
JEE (Advanced) Total 145 marks questions were from class 11th syllabus and 215 marks questions were from class 12th syllabus.
 2018 JEE (Advanced) A Detailed Analysis by Resonance After introducing major changes in IIT Admission Process in 2013, on 20-May-2018 (Sunday) JEE Advanced 2018, stage-2 for IIT Admission Process was conducted
2018 JEE (Advanced) A Detailed Analysis by Resonance After introducing major changes in IIT Admission Process in 2013, on 20-May-2018 (Sunday) JEE Advanced 2018, stage-2 for IIT Admission Process was conducted
Biology Slide 1 of 31
 Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
MULE: An Efficient Algorithm for Detecting Frequent Subgraphs in Biological Networks
 MULE: An Efficient Algorithm for Detecting Frequent Subgraphs in Biological Networks Mehmet Koyutürk, Ananth Grama, & Wojciech Szpankowski http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/koyuturk/pathway/ Purdue University
MULE: An Efficient Algorithm for Detecting Frequent Subgraphs in Biological Networks Mehmet Koyutürk, Ananth Grama, & Wojciech Szpankowski http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/koyuturk/pathway/ Purdue University
Cell organelles. Cell Wall
 Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations
 Lecture 18, Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations 1 Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations In this lecture we talked about graphical models and
Lecture 18, Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations 1 Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations In this lecture we talked about graphical models and
Form a Hypothesis. Variables in an Experiment Dependent Variable what is being measured (data) Form a Hypothesis 2. Form a Hypothesis 3 15:03 DRY MIX
 Scientific Method 1. Ask a question (Make observation) 2. Do some research 3. Form a Hypothesis MUST BE TESTABLE!! A possible explanation for a phenomenon. 4. Test Hypothesis/collect data (experiment time!)
Scientific Method 1. Ask a question (Make observation) 2. Do some research 3. Form a Hypothesis MUST BE TESTABLE!! A possible explanation for a phenomenon. 4. Test Hypothesis/collect data (experiment time!)
Structure Learning: the good, the bad, the ugly
 Readings: K&F: 15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 15.5 Structure Learning: the good, the bad, the ugly Graphical Models 10708 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 29 th, 2006 1 Understanding the uniform
Readings: K&F: 15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 15.5 Structure Learning: the good, the bad, the ugly Graphical Models 10708 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 29 th, 2006 1 Understanding the uniform
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
Biology: End of Semester Projects The end of the semester is HERE!!!
 Biology: End of Semester Projects The end of the semester is HERE!!! We will be doing a project that will sum up what we have done this semester. It will help you review the material in one of the units
Biology: End of Semester Projects The end of the semester is HERE!!! We will be doing a project that will sum up what we have done this semester. It will help you review the material in one of the units
Supplementary Figures
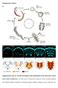 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
What Are The Core Concepts in Biochemistry? Part II. Abstract
 What Are The Core Concepts in Biochemistry? Part II Abstract Biochemistry recently introduced subject in science as our understanding improves with better technology in the field. The aim of this study
What Are The Core Concepts in Biochemistry? Part II Abstract Biochemistry recently introduced subject in science as our understanding improves with better technology in the field. The aim of this study
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
MODEL-FREE LINKAGE AND ASSOCIATION MAPPING OF COMPLEX TRAITS USING QUANTITATIVE ENDOPHENOTYPES
 MODEL-FREE LINKAGE AND ASSOCIATION MAPPING OF COMPLEX TRAITS USING QUANTITATIVE ENDOPHENOTYPES Saurabh Ghosh Human Genetics Unit Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata Most common diseases are caused by
MODEL-FREE LINKAGE AND ASSOCIATION MAPPING OF COMPLEX TRAITS USING QUANTITATIVE ENDOPHENOTYPES Saurabh Ghosh Human Genetics Unit Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata Most common diseases are caused by
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 2, February ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 2, February-2015 273 Analogizing And Investigating Some Applications of Metabolic Pathway Analysis Methods Gourav Mukherjee 1,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 2, February-2015 273 Analogizing And Investigating Some Applications of Metabolic Pathway Analysis Methods Gourav Mukherjee 1,
2012 Univ Aguilera Lecture. Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture Notes Fall 2009
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture Notes Fall 2009 October 28, 2009 Byoung-Tak Zhang School of omputer Science and Engineering & ognitive Science, Brain Science, and Bioinformatics Seoul National University
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture Notes Fall 2009 October 28, 2009 Byoung-Tak Zhang School of omputer Science and Engineering & ognitive Science, Brain Science, and Bioinformatics Seoul National University
Across and Beyond the Cell Are Peptide Strings
 Across and Beyond the Cell Are Peptide Strings Razvan Tudor Radulescu Molecular Concepts Research (MCR), Munich, Germany E-mail: ratura@gmx.net Mottos: "No great discovery was ever made without a bold
Across and Beyond the Cell Are Peptide Strings Razvan Tudor Radulescu Molecular Concepts Research (MCR), Munich, Germany E-mail: ratura@gmx.net Mottos: "No great discovery was ever made without a bold
13.1 Biological Classification - Kingdoms and Domains Modern species are divided into three large groups, or domains. Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Chapter 13 Prospecting for Biological Gold Biodiversity and Classification 13.1 Biological Classification- How Many Species Exist? Biodiversity is the variety within and among living species Number of
Chapter 13 Prospecting for Biological Gold Biodiversity and Classification 13.1 Biological Classification- How Many Species Exist? Biodiversity is the variety within and among living species Number of
Directed and Undirected Graphical Models
 Directed and Undirected Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Machine Learning: Neural Networks and Advanced Models (AA2) Last Lecture Refresher Lecture Plan Directed
Directed and Undirected Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Machine Learning: Neural Networks and Advanced Models (AA2) Last Lecture Refresher Lecture Plan Directed
Undirected Graphical Models
 Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Problem Set 3 September 25, 2009
 September 25, 2009 General Instructions: 1. You are expected to state all your assumptions and provide step-by-step solutions to the numerical problems. Unless indicated otherwise, the computational problems
September 25, 2009 General Instructions: 1. You are expected to state all your assumptions and provide step-by-step solutions to the numerical problems. Unless indicated otherwise, the computational problems
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g6pdcbhodqo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vjuqrcg_suw
 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g6pdcbhodqo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vjuqrcg_suw Life as we don t know it The same, even when we re different All life on Earth shares: The same, even when we re
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g6pdcbhodqo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vjuqrcg_suw Life as we don t know it The same, even when we re different All life on Earth shares: The same, even when we re
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science GRADE 7
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network
 Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network Sari Bombino Helsinki 27.3.2007 UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI Department of Computer Science Seminar on Computational
Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network Sari Bombino Helsinki 27.3.2007 UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI Department of Computer Science Seminar on Computational
Introduction. Spatial Multi-Agent Systems. The Need for a Theory
 Introduction Spatial Multi-Agent Systems A spatial multi-agent system is a decentralized system composed of numerous identically programmed agents that either form or are embedded in a geometric space.
Introduction Spatial Multi-Agent Systems A spatial multi-agent system is a decentralized system composed of numerous identically programmed agents that either form or are embedded in a geometric space.
Semester Test Review. 2 nd Semester
 Semester Test Review 2 nd Semester 1. Element A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. 2. Chemical compound A chemical substance consisting of two
Semester Test Review 2 nd Semester 1. Element A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. 2. Chemical compound A chemical substance consisting of two
Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks. Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks
 DOI: 0.5772/intechopen.69804 Provisional chapter Chapter 8 Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks Stefano Schivo, Jeroen
DOI: 0.5772/intechopen.69804 Provisional chapter Chapter 8 Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks Computational Modeling of Complex Protein Activity Networks Stefano Schivo, Jeroen
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Half-Yearly Exam 2013 Subject: BIOLOGY Level: INT 1 st Yr Time: 2hrs Name: Course: Year: SECTION A: Answer ALL questions in this section
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Half-Yearly Exam 2013 Subject: BIOLOGY Level: INT 1 st Yr Time: 2hrs Name: Course: Year: SECTION A: Answer ALL questions in this section
Interaction Network Analysis
 CSI/BIF 5330 Interaction etwork Analsis Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Balor Universit Biological etworks Definition Maps of biochemical reactions, interactions, regulations
CSI/BIF 5330 Interaction etwork Analsis Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Balor Universit Biological etworks Definition Maps of biochemical reactions, interactions, regulations
8.1 Life is cellular
 8.1 Life is cellular Early Microscopes In 1665, Englishman Robert Hooke used a microscope to look at a slice of cork. Cork was made of tiny, empty chambers that Hooke called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
8.1 Life is cellular Early Microscopes In 1665, Englishman Robert Hooke used a microscope to look at a slice of cork. Cork was made of tiny, empty chambers that Hooke called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Cells: 2 Star. 7. The diagram below represents a cell.
 ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Unit 1: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems Big Ideas The cell is the basic scientific unit of all living things. Cells must interact with the external environment to meet their basic needs. Your health
Network Biology: Understanding the cell s functional organization. Albert-László Barabási Zoltán N. Oltvai
 Network Biology: Understanding the cell s functional organization Albert-László Barabási Zoltán N. Oltvai Outline: Evolutionary origin of scale-free networks Motifs, modules and hierarchical networks Network
Network Biology: Understanding the cell s functional organization Albert-László Barabási Zoltán N. Oltvai Outline: Evolutionary origin of scale-free networks Motifs, modules and hierarchical networks Network
From Distributions to Markov Networks. Sargur Srihari
 From Distributions to Markov Networks Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics The task: How to encode independencies in given distribution P in a graph structure G Theorems concerning What type of Independencies?
From Distributions to Markov Networks Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics The task: How to encode independencies in given distribution P in a graph structure G Theorems concerning What type of Independencies?
38050 Povo Trento (Italy), Via Sommarive 14 CAUSAL P-CALCULUS FOR BIOCHEMICAL MODELLING
 UNIVERSITY OF TRENTO DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 38050 Povo Trento (Italy), Via Sommarive 14 http://www.dit.unitn.it CAUSAL P-CALCULUS FOR BIOCHEMICAL MODELLING M. Curti, P.
UNIVERSITY OF TRENTO DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY 38050 Povo Trento (Italy), Via Sommarive 14 http://www.dit.unitn.it CAUSAL P-CALCULUS FOR BIOCHEMICAL MODELLING M. Curti, P.
Basic Biology. Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology
 Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
15-780: Graduate Artificial Intelligence. Bayesian networks: Construction and inference
 15-780: Graduate Artificial Intelligence ayesian networks: Construction and inference ayesian networks: Notations ayesian networks are directed acyclic graphs. Conditional probability tables (CPTs) P(Lo)
15-780: Graduate Artificial Intelligence ayesian networks: Construction and inference ayesian networks: Notations ayesian networks are directed acyclic graphs. Conditional probability tables (CPTs) P(Lo)
Comparative analysis of various modularization algorithms and species specific study of VEGF signaling pathways
 J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2010, 3, 931-941 doi:10.4236/jbise.2010.310124 Published Online October 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise/). Comparative analysis of various modularization
J. Biomedical Science and Engineering, 2010, 3, 931-941 doi:10.4236/jbise.2010.310124 Published Online October 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbise/). Comparative analysis of various modularization
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
OPERATIONS RESEARCH. Transportation and Assignment Problems
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Chapter 2 Transportation and Assignment Problems Prof. Bibhas C. Giri Department of Mathematics Jadavpur University Kolkata, India Email: bcgiri.jumath@gmail.com 1.0 Introduction In
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Chapter 2 Transportation and Assignment Problems Prof. Bibhas C. Giri Department of Mathematics Jadavpur University Kolkata, India Email: bcgiri.jumath@gmail.com 1.0 Introduction In
CS Lecture 3. More Bayesian Networks
 CS 6347 Lecture 3 More Bayesian Networks Recap Last time: Complexity challenges Representing distributions Computing probabilities/doing inference Introduction to Bayesian networks Today: D-separation,
CS 6347 Lecture 3 More Bayesian Networks Recap Last time: Complexity challenges Representing distributions Computing probabilities/doing inference Introduction to Bayesian networks Today: D-separation,
Plant Stimuli pp Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39. Plant Behavioural Responses. Plant Hormones. Plant Hormones pp
 Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39 Plants exist in environments that are constantly changing. Like animals, plants must be able to detect and react to stimuli in the environment. Unlike animals, plants can
Topic 3: Plant Behaviour Ch. 39 Plants exist in environments that are constantly changing. Like animals, plants must be able to detect and react to stimuli in the environment. Unlike animals, plants can
the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Chemical structure Covalent bond Ionic bond
 Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
In the Stone Age. Stephan Holzer. Yuval Emek - Technion Roger Wattenhofer - ETH Zürich
 The Power of a Leader In the Stone Age - MIT Yuval Emek - Technion Roger Wattenhofer - ETH Zürich 2nd Workshop on Biological Distributed Algorithms, October 11-12, 2014 in Austin, Texas USA The Power of
The Power of a Leader In the Stone Age - MIT Yuval Emek - Technion Roger Wattenhofer - ETH Zürich 2nd Workshop on Biological Distributed Algorithms, October 11-12, 2014 in Austin, Texas USA The Power of
Biological Pathways Representation by Petri Nets and extension
 Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Matter and Substances Section 3-1
 Matter and Substances Section 3-1 Key Idea: All matter is made up of atoms. An atom has a positively charges core surrounded by a negatively charged region. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that
Matter and Substances Section 3-1 Key Idea: All matter is made up of atoms. An atom has a positively charges core surrounded by a negatively charged region. An atom is the smallest unit of matter that
Quantitative analysis of intracellular communication and signaling errors in signaling networks
 Quantitative analysis of intracellular communication and signaling errors in signaling networks Habibi et al. Habibi et al. BMC Systems Biology 014, 8:89 Habibi et al. BMC Systems Biology 014, 8:89 METHODOLOGY
Quantitative analysis of intracellular communication and signaling errors in signaling networks Habibi et al. Habibi et al. BMC Systems Biology 014, 8:89 Habibi et al. BMC Systems Biology 014, 8:89 METHODOLOGY
Weather Outlook. 1 July 2016 METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH GROUP. INDIA HEADQUART ERS G 31 Quest Offices DLF Golf Course Road Gurgaon India
 Weather Outlook 1 July 2016 METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH GROUP INDIA HEADQUART ERS G 31 Quest Offices DLF Golf Course Road Gurgaon 122 002 India NORTH AMERICA 350 Fifth Avenue 59 th Floor, New York City NY
Weather Outlook 1 July 2016 METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH GROUP INDIA HEADQUART ERS G 31 Quest Offices DLF Golf Course Road Gurgaon 122 002 India NORTH AMERICA 350 Fifth Avenue 59 th Floor, New York City NY
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Principles of Pattern Recognition. C. A. Murthy Machine Intelligence Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata
 Principles of Pattern Recognition C. A. Murthy Machine Intelligence Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata e-mail: murthy@isical.ac.in Pattern Recognition Measurement Space > Feature Space >Decision
Principles of Pattern Recognition C. A. Murthy Machine Intelligence Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata e-mail: murthy@isical.ac.in Pattern Recognition Measurement Space > Feature Space >Decision
Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) Inorganic Molecules: (Do NOT contain carbon)
 Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) 1.) Carbohydrates: Quick source of energy 2.) Lipids: Long-term energy storage 3.) Proteins: Raw materials and enzyme action (catalysts) Inorganic Molecules: (Do
Organic Molecules: (All contain carbon) 1.) Carbohydrates: Quick source of energy 2.) Lipids: Long-term energy storage 3.) Proteins: Raw materials and enzyme action (catalysts) Inorganic Molecules: (Do
Life is Cellular. At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work?
 Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model
 Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model D.Y. Geng, G. Hu, L. Wang, N. Jia and F.X. Wang Province-Ministry Joint Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic
Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model D.Y. Geng, G. Hu, L. Wang, N. Jia and F.X. Wang Province-Ministry Joint Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic
