COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION
|
|
|
- Lesley Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK 2 Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey 3 Department of Physics, Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract - Everyday cells encounter various stimuli ranging from growth signals to bacterial infections to UV insult to death signals. They must somehow receive these signals, interpret them, integrate different stimuli, and generate the required output. They can do so by an intricate mechanism named intracellular signal transduction. There are various signal transduction pathways within a cell, each of which are designed for a particular stimulus, and all of which can crosstalk among themselves for the careful integration of all stimuli. In this report, only one of these pathways, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway has been simulated. This pathway is activated upon binding of growth factors to their respective cell surface-bound receptors. Activated receptors relay the incoming signal to the cell interior via a cascade of proteins, which are thought to be involved in both the amplification of the signal, and the specificity of the pathway. A generic MAPK pathway activated by the EGF (epidermal growth factor) and the effect of receptor overexpression has been studied, and consistent with experimental evidence, it is shown that the number of EGF receptors on the cell surface is a key factor in the response generated by the pathway. Keywords - MAPK signaling, EGF, computer simulation I. INTRODUCTION Cells can respond to various stimuli, ranging from growth and differentiation factors to stress signals such as ultraviolet (UV) or osmotic shock, through activation of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) (Fig. 1a). Dimerization and autophosphorylation of the receptor is relayed to adaptor proteins that bind to the active receptor, whereby the signal is relayed to the MAPK cascade [1,2]. Activation of the MAPK cascade is achieved through localization of the cytoplasmic SOS protein to the plasma membrane by the RTK-associated adaptor proteins such as Grb2 (Fig. 1b) [3]. SOS can recruit Ras to the receptor and convert it into its active form (called Ras-GTP). The MAPK cascade is a series of enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of each other in turn: active Ras fires the pathway by activating the first kinase of the pathway, Raf. Raf then activates MEK, which in turn phosphorylates MAPK [4]. There exist many different MAPKs and various corresponding upstream Fig. 1. Schematic representation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-activated MAPK signaling cascade. (a) Upon ligand binding RTKs dimerize and recruit adaptor protein Grb2, SOS, and Ras. (b) Activated Ras initiates the firing of three-component MAPK signaling cascade (Raf, MEK and ERK). kinases in a cell. The generic ERK (extracellular signalregulated kinase) MAPK has been studied in this simulation. The activation of the ERK MAPK pathway is alone not sufficient for the cellular response. The duration of the MAPK pathway also contributes to the biological output
2 Report Documentation Page Report Date 25OCT2001 Report Type N/A Dates Covered (from... to) - Title and Subtitle Computer Simulation of Differential Kinetics of MAPK Activation Upon EGF Receptor Overexpression Contract Number Grant Number Program Element Number Author(s) Project Number Task Number Work Unit Number Performing Organization Name(s) and Address(es) School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK Sponsoring/Monitoring Agency Name(s) and Address(es) US Army Research, Development & Standardization Group (UK) PSC 802 Box 15 FPO AE Performing Organization Report Number Sponsor/Monitor s Acronym(s) Sponsor/Monitor s Report Number(s) Distribution/Availability Statement Approved for public release, distribution unlimited Supplementary Notes Papers from the 23rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, October 25-28, 2001, held in Istanbul, Turkey. See also ADM for entire conference on cd-rom., The original document contains color images. Abstract Subject Terms Report Classification Classification of Abstract Classification of this page Limitation of Abstract UU Number of Pages 4
3 generated. A classic example is the cellular response of a special cell type, called PC12 (for pheochromocytoma cells), which show different response to two different growth factors NGF (nerve growth factor) and EGF (epidermal growth factor), although both growth factors activate the same ERK MAPK pathway. In the case of NGF the cells stop dividing and become neuronal, in the case of EGF the cells divide continuously and stay nonneuronal. It has been experimentally shown that while NGF can maintain sustained activation of the ERK pathway (lasting several hours), EGF can only transiently activate ERK (activation declines to basal levels in about 10 minutes) [5]. It has been previously suggested [6] that the key step in generating the differential kinetics is the regulation of the feedback inhibition of SOS by ERK. Although this feedback inhibition does indeed have an unquestionable effect on the MAPK signaling in computer simulations, there is no direct biological evidence to indicate that NGF and EGF receptors can indeed regulate this step directly, hence cannot explain how the intrinsic difference of the two pathways arises. We have therefore set out to investigate a more biologically relevant stage at the receptor level. III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The intracellular events that take place after receptor stimulation (Fig. 1) have been broken down to discrete steps (Fig. 2). Under conditions where ligand (EGF) concentration has been kept constant (100 nm) the response of the pathway has been studied for different levels of EGF Receptor expression (i.e. different number of receptors per cell) over a period of 60 minutes. We have initially used the parameters for EGF and EGFR to simulate the transient ERK MAPK activation. As expected, the components of the MAPK cascade, namely Raf, MEK and ERK, show transient activation in the first 2-10 minutes, after which they return to basal level of activation (Fig. 3). Unlike previous reports that receptor number does not affect the duration of the signal [6], we have successfully demonstrated that increase in the number of EGF receptors is sufficient to maintain sustained activation. Fig. 4 (a-c) shows the activation of Raf, MEK and ERK at 60 minutes in response to increasing receptor concentrations, and the The receptors may influence downstream effects in a number of ways: one major difference between the two receptors is their level of expression in the cell, i.e. the number of receptor molecules displayed on the cell surface. The number of EGF receptors has been estimated to be around 20,000 receptors per cell, while there are at least 130,000 TrkA molecules (NGF receptors) per cell. It has therefore attracted our attention that the amount of receptor present for each signal can be reflected at the downstream components by recruiting and activating more Ras proteins, thereby more ERK. Our hypothesis has been supported by experimental evidence that when EGF receptors are overexpressed in PC12 cells (i.e. increased in number) they can become neuronal even in response to EGF. We have therefore constructed a signaling pathway using the Grb2 adaptor protein for the EGFR receptor in order to reconstitute the response of these cells when EGFR is overexpressed. II. MATERIALS AND METHODS The standard biochemical kinetics simulation software package GEPASI 3.0 [7] has been used in this study to develop a computer simulation of the EGF signal transduction pathway. On the EGF signal transduction pathway the enzyme-catalyzed reactions follow Michaelis- Menten kinetics, while to simulate all other reactions massaction kinetics are used. The kinetic parameters used are listed in our web page and are based on experimentally determined parameters ( /biochem/index.html). Fig. 2. Stepwise representation of the individual reactions used in the simulation. Numbering is arbitrary, and is included for the sake of simplicity.
4 profile of this activation over 60 minutes can be found in Fig. 4d. This 10-fold increase is consistent with the number of naturally occurring EGF versus NGF receptors (20,000 versus 130,000) displayed on the cell surface, hence demonstrates the biological significance of our simulation. Whereas Brightman and Fell have regarded the receptor as an enzyme (or modifier) that can be used over and over in the pathway, in biological systems the receptor in fact forms stoichiometric complexes with the adaptor proteins (e.g. Grb2), catalyzes its phosphorylation, and remains associated with that adaptor protein. Our simulation, on the other hand, accounts for the stoichiometry of receptor-mediated Grb2 activation, and considers only the receptor-associated adaptor protein the active form. IV. CONCLUSION Fig. 3. % Activation of Raf, MEK, and ERK in EGF stimulation, with 11,000 receptors. The duration of the MAPK signal is of fundamental importance to the final biological response, as is clearly demonstrated experimentally in PC12 cells. Many laboratories have devoted their efforts in trying to establish the mechanism by which NGF and EGF can generate this differential response. Our simulation, consistent with experimental data, suggest that receptor number plays a role in this process, although not likely to be the only factor. Fig. 4. The effect of receptor overexpression on the steady-state activation of a) Raf, b) MEK, and c) ERK. The activation levels of Raf, MEK and ERK over time is given in (d).
5 NGF and EGF receptors possess many other properties that are intrinsically different from each other, which will undoubtedly contribute to the kinetics of MAPK activation. Ongoing work is addressed to this issue. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work has been supported by the Research Fund of Bogazici University under the Grant No. 01B301. REFERENCES [1] F. Canals, Signal transmission by epidermal growth factor receptor: coincidence of activation and dimerization, Biochemistry, vol. 31, pp , [2] J. M. Sherrill and J.Kyte, Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor by epidermal growth factor, Biochemistry, vol. 35, pp , [3] A. Sorkin, M. McClure, F. Huang, and R. Carter, Interaction of EGF receptor and grb2 in living cells visualized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy, Curr. Biol., vol. 10, pp , [4] L. Chang and M. Karin, Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades, Nature, vol. 410, pp , [5] C. J. Marshall, Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signalregulated kinase activation, Cell, vol. 80, pp , [6] F. A. Brightman and D. A. Fell, Differential feedback regulation of the MAPK cascade underlies the quantitative differences in EGF and NGF signaling in PC12 cells, FEBS Lett., vol. 482, pp , [7] P. Mendes, Biochemistry by numbers: Simulation of biochemical pathways with GEPASI 3, Trends Biochem. Sci., vol. 22, pp , 1997.
Dual Nature Hidden Layers Neural Networks A Novel Paradigm of Neural Network Architecture
 Dual Nature Hidden Layers Neural Networks A Novel Paradigm of Neural Network Architecture S.Karthikeyan 1, Ravi Prakash 2, B.B.Paul 3 1 Lecturer, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Banaras
Dual Nature Hidden Layers Neural Networks A Novel Paradigm of Neural Network Architecture S.Karthikeyan 1, Ravi Prakash 2, B.B.Paul 3 1 Lecturer, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Banaras
Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction 111202 Here we look at the movement of a signal from the outside of a cell to its inside, where it elicits changes within the cell. These changes are usually mediated
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
The EGF Signaling Pathway! Introduction! Introduction! Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3. EGF promotes cell growth
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 3 Question of the Day: Who is the son of Sevenless? Introduction! Signal transduction involves the changing of a cell s metabolism or gene
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways
 State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways Youcef Derbal Ryerson University yderbal@ryerson.ca Abstract Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways are frequently deregulated in human
State Machine Modeling of MAPK Signaling Pathways Youcef Derbal Ryerson University yderbal@ryerson.ca Abstract Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways are frequently deregulated in human
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
S.S. Şeker, F. Can Boğaziçi University, Dept. of Electrical- Electronics Engg Bebek, İstanbul, Turkey
 THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EM FIELDS AND SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS DUE TO HIGH VOLTAGE TRANSMISSION LINES S.S. Şeker, F. Can Boğaziçi University, Dept. of Electrical- Electronics Engg. 80815 Bebek,
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF EM FIELDS AND SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS DUE TO HIGH VOLTAGE TRANSMISSION LINES S.S. Şeker, F. Can Boğaziçi University, Dept. of Electrical- Electronics Engg. 80815 Bebek,
TUMOUR REMISSION IN RATS BY IRRADIATION WITH NON-THERMAL POWER LEVELS MICROWAVES
 TUMOUR REMISSION IN RATS BY IRRADIATION WITH NON-THERMAL POWER LEVELS MICROWAVES George. Sajin (*), Teodor Sandulescu, Victoria Moraru, Maria Sajin (*) National Research Institute for Microtechnologies,
TUMOUR REMISSION IN RATS BY IRRADIATION WITH NON-THERMAL POWER LEVELS MICROWAVES George. Sajin (*), Teodor Sandulescu, Victoria Moraru, Maria Sajin (*) National Research Institute for Microtechnologies,
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks. Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai
 Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai Intra-cellular biochemical networks Metabolic networks Nodes:
Systems Biology Across Scales: A Personal View XIV. Intra-cellular systems IV: Signal-transduction and networks Sitabhra Sinha IMSc Chennai Intra-cellular biochemical networks Metabolic networks Nodes:
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Crosstalk between MAPK Pathway and Smad-Dependent TGF-β Signal Transduction
 Processes 2014, 2, 570-595; doi:10.3390/pr2030570 Article OPEN ACCESS processes ISSN 2227-9717 www.mdpi.com/journal/processes Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Crosstalk between MAPK Pathway and Smad-Dependent
Processes 2014, 2, 570-595; doi:10.3390/pr2030570 Article OPEN ACCESS processes ISSN 2227-9717 www.mdpi.com/journal/processes Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Crosstalk between MAPK Pathway and Smad-Dependent
Bioinformatics Modelling dynamic behaviour: Modularisation
 Bioinformatics Modelling dynamic behaviour: David Gilbert Bioinformatics Research Centre www.brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow Lecture outline Modelling Enzymatic
Bioinformatics Modelling dynamic behaviour: David Gilbert Bioinformatics Research Centre www.brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Department of Computing Science, University of Glasgow Lecture outline Modelling Enzymatic
Mathematical model of IL6 signal transduction pathway
 Mathematical model of IL6 signal transduction pathway Fnu Steven, Zuyi Huang, Juergen Hahn This document updates the mathematical model of the IL6 signal transduction pathway presented by Singh et al.,
Mathematical model of IL6 signal transduction pathway Fnu Steven, Zuyi Huang, Juergen Hahn This document updates the mathematical model of the IL6 signal transduction pathway presented by Singh et al.,
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology
 Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
Intercellular communication
 Intercellular communication Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Outline General principle of intercellular communicabon Signal molecules
Intercellular communication Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Outline General principle of intercellular communicabon Signal molecules
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%%
 with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
with%dr.%van%buskirk%%% How$to$do$well?$ Before$class:$read$the$corresponding$chapter$ Come$to$class$ready$to$par9cipate$in$Top$Hat$ Don t$miss$an$exam!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!$ But$I m$not$good$with$science
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 11
 56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 11 Network Motifs in Signal Transduction Networks Signal transduction networks Signal transduction networks are composed of interactions between signaling proteins.
56:198:582 Biological Networks Lecture 11 Network Motifs in Signal Transduction Networks Signal transduction networks Signal transduction networks are composed of interactions between signaling proteins.
Problem Set # 3
 20.320 Problem Set # 3 October 1 st, 2010 Due on October 8 th, 2010 at 11:59am. No extensions, no electronic submissions. General Instructions: 1. You are expected to state all your assumptions and provide
20.320 Problem Set # 3 October 1 st, 2010 Due on October 8 th, 2010 at 11:59am. No extensions, no electronic submissions. General Instructions: 1. You are expected to state all your assumptions and provide
Cell Adhesion and Signaling
 Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Cell Adhesion and Signaling mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology 1 Transactivation NATURE REVIEWS CANCER VOLUME 7 FEBRUARY 2007 85 2 Functions of Cell Adhesion cell cycle proliferation
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
BLOCK LMS ADAPTIVE FILTER WITH DETERMINISTIC REFERENCE INPUTS FOR EVENT-RELATED SIGNALS
 BLOCK LMS ADAPTIVE FILTER WIT DETERMINISTIC REFERENCE INPUTS FOR EVENT-RELATED SIGNALS S. Olmos, L. Sörnmo, P. Laguna Dept. of Electroscience, Lund University, Sweden Dept. of Electronics Eng. and Communications,
BLOCK LMS ADAPTIVE FILTER WIT DETERMINISTIC REFERENCE INPUTS FOR EVENT-RELATED SIGNALS S. Olmos, L. Sörnmo, P. Laguna Dept. of Electroscience, Lund University, Sweden Dept. of Electronics Eng. and Communications,
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
A mechanistic study of evolvability using the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade
 EVOLUTION & DEVELOPMENT 5:3, 81 94 (003) A mechanistic study of evolvability using the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade H. F. Nijhout,* A. M. Berg, and W. T. Gibson Department of Biology, Duke
EVOLUTION & DEVELOPMENT 5:3, 81 94 (003) A mechanistic study of evolvability using the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade H. F. Nijhout,* A. M. Berg, and W. T. Gibson Department of Biology, Duke
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Bioinformatics 3. V18 Kinetic Motifs. Fri, Jan 8, 2016
 Bioinformatics 3 V18 Kinetic Motifs Fri, Jan 8, 2016 Modelling of Signalling Pathways Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the kinetic
Bioinformatics 3 V18 Kinetic Motifs Fri, Jan 8, 2016 Modelling of Signalling Pathways Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the kinetic
Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014"
 Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014" Modelling of Signalling Pathways" Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221" 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the
Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014" Modelling of Signalling Pathways" Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221" 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the
Ligand-dependent responses of the ErbB signaling network: experimental and modeling analyses
 Molecular Systems Biology 3; Article number 144; doi:10.1038/msb4100188 Citation: Molecular Systems Biology 3:144 & 2007 EMBO and Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1744-4292/07 www.molecularsystemsbiology.com
Molecular Systems Biology 3; Article number 144; doi:10.1038/msb4100188 Citation: Molecular Systems Biology 3:144 & 2007 EMBO and Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1744-4292/07 www.molecularsystemsbiology.com
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization
 Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
Study of Tricyclic Cascade Networks using Dynamic Optimization Systems Biology interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems Signal transduction
Computational Modeling of the EGFR Network Elucidates Control Mechanisms Regulating Signal Dynamics
 Computational Modeling of the EGFR Network Elucidates Control Mechanisms Regulating Signal Dynamics Dennis Y.Q. Wang 1, Luca Cardelli 2, Andrew Phillips 2, Nir Piterman 3, Jasmin Fisher 2* 1 MRC Biostatistics
Computational Modeling of the EGFR Network Elucidates Control Mechanisms Regulating Signal Dynamics Dennis Y.Q. Wang 1, Luca Cardelli 2, Andrew Phillips 2, Nir Piterman 3, Jasmin Fisher 2* 1 MRC Biostatistics
From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis
 From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis David Gilbert drg@brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Bioinformatics Research Centre, University of Glasgow and Monika Heiner
From Petri Nets to Differential Equations An Integrative Approach for Biochemical Network Analysis David Gilbert drg@brc.dcs.gla.ac.uk Bioinformatics Research Centre, University of Glasgow and Monika Heiner
Cytokines regulate interactions between cells of the hemapoietic system
 Cytokines regulate interactions between cells of the hemapoietic system Some well-known cytokines: Erythropoietin (Epo) G-CSF Thrombopoietin IL-2 INF thrombopoietin Abbas et al. Cellular & Molecular Immunology
Cytokines regulate interactions between cells of the hemapoietic system Some well-known cytokines: Erythropoietin (Epo) G-CSF Thrombopoietin IL-2 INF thrombopoietin Abbas et al. Cellular & Molecular Immunology
Dynamic Stability of Signal Transduction Networks Depending on Downstream and Upstream Specificity of Protein Kinases
 Dynamic Stability of Signal Transduction Networks Depending on Downstream and Upstream Specificity of Protein Kinases Bernd Binder and Reinhart Heinrich Theoretical Biophysics, Institute of Biology, Math.-Nat.
Dynamic Stability of Signal Transduction Networks Depending on Downstream and Upstream Specificity of Protein Kinases Bernd Binder and Reinhart Heinrich Theoretical Biophysics, Institute of Biology, Math.-Nat.
Cell Signaling Reactions
 Cell Signaling Reactions Yasushi Sako l Editors Masahiro Ueda Cell Signaling Reactions Single-Molecular Kinetic Analysis Editor Yasushi Sako Cellular Informatics Laboratory RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
Cell Signaling Reactions Yasushi Sako l Editors Masahiro Ueda Cell Signaling Reactions Single-Molecular Kinetic Analysis Editor Yasushi Sako Cellular Informatics Laboratory RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
Mechanisms of Human Health and Disease. Developmental Biology
 Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
Mechanisms of Human Health and Developmental Biology Joe Schultz joe.schultz@nationwidechildrens.org D6 1 Dev Bio: Mysteries How do fertilized eggs become adults? How do adults make more adults? Why and
PROPERTIES OF PERIFERAL NERVE EXCITATION IN RESPECT OF LOCATION OF COIL FOR MAGNETIC NERVE STIMULATION
 PROPERTIES OF PERIFERAL NERVE EXCITATION IN RESPECT OF LOCATION OF COIL FOR MAGNETIC NERVE STIMULATION O. Hiwaki, H. Kuwano Facult of Information Sciences, Hiroshima Cit Universit, Hiroshima, Japan Abstract-
PROPERTIES OF PERIFERAL NERVE EXCITATION IN RESPECT OF LOCATION OF COIL FOR MAGNETIC NERVE STIMULATION O. Hiwaki, H. Kuwano Facult of Information Sciences, Hiroshima Cit Universit, Hiroshima, Japan Abstract-
Reprogramming what is it? ips. neurones cardiomyocytes. Takahashi K & Yamanaka S. Cell 126, 2006,
 General Mechanisms of Cell Signaling Signaling to Cell Nucleus MUDr. Jan láteník, hd. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotent stem cells! fibroblast Reprogramming what is it? is neurones cardiomyocytes
General Mechanisms of Cell Signaling Signaling to Cell Nucleus MUDr. Jan láteník, hd. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotent stem cells! fibroblast Reprogramming what is it? is neurones cardiomyocytes
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
26 Robustness in a model for calcium signal transduction dynamics
 26 Robustness in a model for calcium signal transduction dynamics U. Kummer 1,G.Baier 2 and L.F. Olsen 3 1 European Media Laboratory, Villa Bosch, Schloss-Wolfsbrunnenweg 33, 69118 Heidelberg, Germany
26 Robustness in a model for calcium signal transduction dynamics U. Kummer 1,G.Baier 2 and L.F. Olsen 3 1 European Media Laboratory, Villa Bosch, Schloss-Wolfsbrunnenweg 33, 69118 Heidelberg, Germany
Src Family Kinases and Receptors: Analysis of Three Activation Mechanisms by Dynamic Systems Modeling
 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 March 2008 1995 2006 1995 Src Family Kinases and Receptors: Analysis of Three Activation Mechanisms by Dynamic Systems Modeling Hendrik Fuß, Werner Dubitzky, C. Stephen Downes,
Biophysical Journal Volume 94 March 2008 1995 2006 1995 Src Family Kinases and Receptors: Analysis of Three Activation Mechanisms by Dynamic Systems Modeling Hendrik Fuß, Werner Dubitzky, C. Stephen Downes,
Cell Memory in the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Eugenia Lyashenko
 Cell Memory in the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Eugenia Lyashenko Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy under the Executive Committee
Cell Memory in the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Eugenia Lyashenko Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy under the Executive Committee
PROBABILISTIC SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTION SYSTEMS. Hongxuan Zhang
 PROBABILISTIC SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTION SYSTEMS by Hongxuan Zhang A dissertation submitted to The Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor
PROBABILISTIC SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTION SYSTEMS by Hongxuan Zhang A dissertation submitted to The Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Effect of Cardiac Phases and Conductivity Inhomogeneities of the Thorax Models on ECG Lead Selection and Reconstruction
 Effect of Cardiac Phases and Conductivity Inhomogeneities of the Thorax Models on ECG Lead Selection and Reconstruction Noriyuki Takano, Hanna-Greta Puurtinen, Pasi Kauppinen, Jari Hyttinen, Jaakko Malmivuo
Effect of Cardiac Phases and Conductivity Inhomogeneities of the Thorax Models on ECG Lead Selection and Reconstruction Noriyuki Takano, Hanna-Greta Puurtinen, Pasi Kauppinen, Jari Hyttinen, Jaakko Malmivuo
SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes
 1/ 223 SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes Jane Hillston LFCS, School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Scotland 7th March 2013 Outline 2/ 223 1 Introduction
1/ 223 SPA for quantitative analysis: Lecture 6 Modelling Biological Processes Jane Hillston LFCS, School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Scotland 7th March 2013 Outline 2/ 223 1 Introduction
Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model
 Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model D.Y. Geng, G. Hu, L. Wang, N. Jia and F.X. Wang Province-Ministry Joint Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic
Mechanism underlying the bio-effects of an electromagnetic field based on the Huang-Ferrell model D.Y. Geng, G. Hu, L. Wang, N. Jia and F.X. Wang Province-Ministry Joint Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic
Signal Transduction: Ethylene PSI AP Biology
 Signal Transduction: Ethylene PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will analyze the role ethylene plays as a plant hormone in the signal transduction pathway of fruit ripening. Students will use their
Signal Transduction: Ethylene PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will analyze the role ethylene plays as a plant hormone in the signal transduction pathway of fruit ripening. Students will use their
ADAM FAMILY. ephrin A INTERAZIONE. Eph ADESIONE? PROTEOLISI ENDOCITOSI B A RISULTATO REPULSIONE. reverse. forward
 ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
The Logic of EGFR/ErbB Signaling: Theoretical Properties and Analysis of High-Throughput Data
 The Logic of EGFR/ErbB Signaling: Theoretical Properties and Analysis of High-Throughput Data The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
The Logic of EGFR/ErbB Signaling: Theoretical Properties and Analysis of High-Throughput Data The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins
 13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
return in class, or Rm B
 Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Last lectures: Genetic Switches and Oscillators PS #2 due today bf before 3PM return in class, or Rm. 68 371B Naturally occurring: lambda lysis-lysogeny decision lactose operon in E. coli Engineered: genetic
Rapid and sustained nuclear cytoplasmic ERK oscillations induced by epidermal growth factor
 Molecular Systems Biology 5; Article number 332; doi:1.138/msb.29.9 Citation: Molecular Systems Biology 5:332 & 29 EMBO and Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1744-4292/9 www.molecularsystemsbiology.com
Molecular Systems Biology 5; Article number 332; doi:1.138/msb.29.9 Citation: Molecular Systems Biology 5:332 & 29 EMBO and Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1744-4292/9 www.molecularsystemsbiology.com
Supplement to: How Robust are Switches in Intracellular Signaling Cascades?
 Supplement to: How Robust are Switches in Intracellular Signaling Cascades? Nils Blüthgen and Hanspeter Herzel Institute for Theoretical Biology, Invalidenstrasse 43, D-10115 Berlin, Germany (Dated: January
Supplement to: How Robust are Switches in Intracellular Signaling Cascades? Nils Blüthgen and Hanspeter Herzel Institute for Theoretical Biology, Invalidenstrasse 43, D-10115 Berlin, Germany (Dated: January
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
THE EFFECT OF POROUS BLOWING AND SUCTION ON AERODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER IN SEPARATED LAMINAR FLOW IN DUCT BEHIND OF BACKWARD-FACING STEP S.R.
 THE EFFECT OF POROUS BLOWING AND SUCTION ON AERODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER IN SEPARATED LAMINAR FLOW IN DUCT BEHIND OF BACKWARD-FACING STEP S.R. Batenko,A.P.Grechanova, and V.I. Terekhov S.S. Kutateladze
THE EFFECT OF POROUS BLOWING AND SUCTION ON AERODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER IN SEPARATED LAMINAR FLOW IN DUCT BEHIND OF BACKWARD-FACING STEP S.R. Batenko,A.P.Grechanova, and V.I. Terekhov S.S. Kutateladze
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
DNA DAMAGE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS: INHIBITION BY CALMODULIN ANTAGONIST, FAS RECEPTOR ANTIBODY AND CASPASE INHIBITORS
 DNA DAMAGE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS: INHIBITION BY CALMODULIN ANTAGONIST, FAS RECEPTOR ANTIBODY AND CASPASE INHIBITORS R. Ray, B. J. Benton, M. E. Burke, T. Rockwood, K. R. Bhat, D. R. Anderson, J. P. Petrali,
DNA DAMAGE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS: INHIBITION BY CALMODULIN ANTAGONIST, FAS RECEPTOR ANTIBODY AND CASPASE INHIBITORS R. Ray, B. J. Benton, M. E. Burke, T. Rockwood, K. R. Bhat, D. R. Anderson, J. P. Petrali,
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
From cell biology to Petri nets. Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE
 From cell biology to Petri nets Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE Biology = Concentrations Breitling / 2 The simplest chemical reaction A B irreversible,
From cell biology to Petri nets Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE Biology = Concentrations Breitling / 2 The simplest chemical reaction A B irreversible,
P. Kestener and A. Arneodo. Laboratoire de Physique Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon 46, allée d Italie Lyon cedex 07, FRANCE
 A wavelet-based generalization of the multifractal formalism from scalar to vector valued d- dimensional random fields : from theoretical concepts to experimental applications P. Kestener and A. Arneodo
A wavelet-based generalization of the multifractal formalism from scalar to vector valued d- dimensional random fields : from theoretical concepts to experimental applications P. Kestener and A. Arneodo
ON A MECHANISM OF INTRAPHASE INTERACTION IN NON-RELAXING TWO-PHASE FLOW V.M.
 ON A MECHANISM OF INTRAPHASE INTERACTION IN NON-RELAXING TWO-PHASE FLOW V.M. Boiko, K.V. Klinkov, and S.V. Poplavski Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics SB RAS, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia 1.
ON A MECHANISM OF INTRAPHASE INTERACTION IN NON-RELAXING TWO-PHASE FLOW V.M. Boiko, K.V. Klinkov, and S.V. Poplavski Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics SB RAS, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia 1.
Report Documentation Page
 Inhibition of blood cholinesterase activity is a poor predictor of acetylcholinesterase inhibition in brain regions of guinea pigs exposed to repeated doses of low levels of soman. Sally M. Anderson Report
Inhibition of blood cholinesterase activity is a poor predictor of acetylcholinesterase inhibition in brain regions of guinea pigs exposed to repeated doses of low levels of soman. Sally M. Anderson Report
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 2 November 8, 2016 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms
 References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
References on Kinetics and Mechanisms Excellent reference for all aspects of enzyme kinetics including important elements of Metabolic Control Analysis of relevance to systems analysis of enzyme function
targets. clustering show that different complex pathway
 Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Integrating Bayesian variable selection with Modular Response Analysis to infer biochemical network topology
 Santra et al. BMC Systems Biology 2013, 7:57 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Integrating Bayesian variable selection with Modular Response Analysis to infer biochemical network topology Tapesh Santra 1*,
Santra et al. BMC Systems Biology 2013, 7:57 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Integrating Bayesian variable selection with Modular Response Analysis to infer biochemical network topology Tapesh Santra 1*,
Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases
 Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases The TGFβ (transforming growth factorβ) family of growth factors TGFβ1 was first identified as a transforming factor; however, it is a member of a family of structurally
Biol403 - Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases The TGFβ (transforming growth factorβ) family of growth factors TGFβ1 was first identified as a transforming factor; however, it is a member of a family of structurally
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts
 Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
Signal transduction by Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix contacts - Integrins as central adhesion receptors - - Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) as a central signal molecule - Structure of Cell/Cell and Cell/Matrix
A Database of human biological pathways
 A Database of human biological pathways Steve Jupe - sjupe@ebi.ac.uk 1 Rationale Journal information Nature 407(6805):770-6.The Biochemistry of Apoptosis. Caspase-8 is the key initiator caspase in the
A Database of human biological pathways Steve Jupe - sjupe@ebi.ac.uk 1 Rationale Journal information Nature 407(6805):770-6.The Biochemistry of Apoptosis. Caspase-8 is the key initiator caspase in the
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Molecular Characterization and Proposed Taxonomic Placement of the Biosimulant 'BG'
 Molecular Characterization and Proposed Taxonomic Placement of the Biosimulant 'BG' S.A. Burke 1, J.W. Wright 2, M.K. Robinson, B. Bronk 3, and R.L. Warren 1 1 Battelle Dugway Operations 2 U.S. Army Soldier
Molecular Characterization and Proposed Taxonomic Placement of the Biosimulant 'BG' S.A. Burke 1, J.W. Wright 2, M.K. Robinson, B. Bronk 3, and R.L. Warren 1 1 Battelle Dugway Operations 2 U.S. Army Soldier
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Domain 6: Communication
 Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Domain 6: Communication 6.1: Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. (EK3.D.1) 1. Introduction to Communication Communication requires the generation,
Biological Pathways Representation by Petri Nets and extension
 Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
schematic diagram; EGF binding, dimerization, phosphorylation, Grb2 binding, etc.
 Lecture 1: Noncovalent Biomolecular Interactions Bioengineering and Modeling of biological processes -e.g. tissue engineering, cancer, autoimmune disease Example: RTK signaling, e.g. EGFR Growth responses
Lecture 1: Noncovalent Biomolecular Interactions Bioengineering and Modeling of biological processes -e.g. tissue engineering, cancer, autoimmune disease Example: RTK signaling, e.g. EGFR Growth responses
Generating executable models from signaling network connectivity and semi-quantitative proteomic measurements
 Generating executable models from signaling network connectivity and semi-quantitative proteomic measurements Derek Ruths 1 Luay Nakhleh 2 1 School of Computer Science, McGill University, Quebec, Montreal
Generating executable models from signaling network connectivity and semi-quantitative proteomic measurements Derek Ruths 1 Luay Nakhleh 2 1 School of Computer Science, McGill University, Quebec, Montreal
6 Mechanotransduction
 6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
6.1 Motivation The process of converting physical forces into biochemical signals and integrating these signals into the cellular response is referred to as mechnotransduction [11, 20]. To fully understand
Host-Pathogen Interaction. PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur
 Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Bacterial chemotaxis and the question of high gain in signal transduction. Réka Albert Department of Physics
 Bacterial chemotaxis and the question of high gain in signal transduction Réka Albert Department of Physics E. coli lives in the gut and takes up nutrients through its pores E. coli moves by rotating its
Bacterial chemotaxis and the question of high gain in signal transduction Réka Albert Department of Physics E. coli lives in the gut and takes up nutrients through its pores E. coli moves by rotating its
No oscillations in the Michaelis-Menten approximation of the dual futile cycle under a sequential and distributive mechanism
 No oscillations in the Michaelis-Menten approximation of the dual futile cycle under a sequential and distributive mechanism Luna Bozeman 1 and Adriana Morales 2 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson
No oscillations in the Michaelis-Menten approximation of the dual futile cycle under a sequential and distributive mechanism Luna Bozeman 1 and Adriana Morales 2 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson
International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews
 Jain Shruti et al., IJSRR 08, 7(), 5-63 Research article Available online www.ijsrr.org ISSN: 79 0543 International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews Computational Model Using Anderson Darling
Jain Shruti et al., IJSRR 08, 7(), 5-63 Research article Available online www.ijsrr.org ISSN: 79 0543 International Journal of Scientific Research and Reviews Computational Model Using Anderson Darling
Introduction to Cellular Communication *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Simulation of Signal Transduction Pathways
 Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum Heidelberg Abteilung Theoretische Bioinformatik Simulation of Signal Transduction Pathways DKFZ, Heidelberg Universität Ulm Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades
Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum Heidelberg Abteilung Theoretische Bioinformatik Simulation of Signal Transduction Pathways DKFZ, Heidelberg Universität Ulm Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades
Essentials of Cell Signaling
 Essentials of Cell Signaling MUDr. Jan láten teník, hd. Bioengineered tooth in mice Ikeda e. et al.: Fully functional bioengineered tooth replacement as an organ replacement therapy, NAS 106, 2009, 13475-13480.
Essentials of Cell Signaling MUDr. Jan láten teník, hd. Bioengineered tooth in mice Ikeda e. et al.: Fully functional bioengineered tooth replacement as an organ replacement therapy, NAS 106, 2009, 13475-13480.
arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.bio-ph] 16 Sep 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.bio-ph] 16 Sep 2003 arxiv:physics/ v3 [physics.bio-ph] 16 Sep 2003](/thumbs/92/110902603.jpg) Accepted for publication in Biophysical Chemistry Special Issue for Walter Kauzmann arxiv:physics/0207049v3 [physics.bio-ph] 16 Sep 2003 Thermodynamic and Kinetic Analysis of Sensitivity Amplification
Accepted for publication in Biophysical Chemistry Special Issue for Walter Kauzmann arxiv:physics/0207049v3 [physics.bio-ph] 16 Sep 2003 Thermodynamic and Kinetic Analysis of Sensitivity Amplification
A MULTI-LAYER FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF THE SURFACE EMG SIGNAL
 A MULTI-LAYER FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF THE SURFACE EMG SIGNAL M. Lowery,2, N. Stoykov,2, A. Taflove 3 and T. Kuiken,2,3 Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago, IL, USA 2 Department of Physical Medicine and
A MULTI-LAYER FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF THE SURFACE EMG SIGNAL M. Lowery,2, N. Stoykov,2, A. Taflove 3 and T. Kuiken,2,3 Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago, IL, USA 2 Department of Physical Medicine and
COURSE NUMBER: EH 590R SECTION: 1 SEMESTER: Fall COURSE TITLE: Computational Systems Biology: Modeling Biological Responses
 DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health COURSE NUMBER: EH 590R SECTION: 1 SEMESTER: Fall 2017 CREDIT HOURS: 2 COURSE TITLE: Computational Systems Biology: Modeling Biological Responses COURSE LOCATION: TBD PREREQUISITE:
DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health COURSE NUMBER: EH 590R SECTION: 1 SEMESTER: Fall 2017 CREDIT HOURS: 2 COURSE TITLE: Computational Systems Biology: Modeling Biological Responses COURSE LOCATION: TBD PREREQUISITE:
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective
 Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
Enabling Technologies from the Biology Perspective H. Steven Wiley January 22nd, 2002 What is a Systems Approach in the Context of Biological Organisms? Looking at cells as integrated systems and not as
1
 http://photos1.blogger.com/img/13/2627/640/screenhunter_047.jpg 1 The Nose Knows http://graphics.jsonline.com/graphics/owlive/img/mar05/sideways.one0308_big.jpg 2 http://www.stlmoviereviewweekly.com/sitebuilder/images/sideways-253x364.jpg
http://photos1.blogger.com/img/13/2627/640/screenhunter_047.jpg 1 The Nose Knows http://graphics.jsonline.com/graphics/owlive/img/mar05/sideways.one0308_big.jpg 2 http://www.stlmoviereviewweekly.com/sitebuilder/images/sideways-253x364.jpg
Systems biology 9 Signal Transduction
 Humbol- Sommersemester 2 Systems biology 9 Signal Transuction Ea Klipp Humbol- Institut für Biologie Theoretische Biophysi Moeling of Signal Transuction Humbol- Before: Metabolismus - Mass transfer Now:
Humbol- Sommersemester 2 Systems biology 9 Signal Transuction Ea Klipp Humbol- Institut für Biologie Theoretische Biophysi Moeling of Signal Transuction Humbol- Before: Metabolismus - Mass transfer Now:
Rule-based modeling. NIMBioS tutorial, April 8-10 th, 2013 Michael Blinov
 Rule-based modeling NIMBioS tutorial, April 8-10 th, 2013 Michael Blinov Vcell BioNetGen version: http://vcell.org/bionetgen Stand-alone BioNetGen version: http://bionetgen.org References used in the slides:
Rule-based modeling NIMBioS tutorial, April 8-10 th, 2013 Michael Blinov Vcell BioNetGen version: http://vcell.org/bionetgen Stand-alone BioNetGen version: http://bionetgen.org References used in the slides:
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam
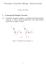 Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
