RAL Advances in Land Surface Modeling Part I. Andrea Hahmann
|
|
|
- Brianne Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RAL Advances in Land Surface Modeling Part I Andrea Hahmann
2 Outline The ATEC real-time high-resolution land data assimilation (HRLDAS) system - Fei Chen, Kevin Manning, and Yubao Liu (RAL) The fine-mesh model and its parameterizations - Gordon Bonan, Mariana Vertenstein (CGD) and David Gochis
3 A land surface model numerically represents the water and energy exchanges that take place between the atmosphere and the land surface It includes processes such as the calculation of: rainfall interception by the canopy, drip, plant transpiration surface albedo, absorption and emission of radiation by the soil and the vegetation movement of water trough the soil column, surface runoff, snow processes ground temperatures and surface fluxes of latent, sensible and momentum (output back to atmos)
4 Land Data Assimilation System: Provides a continuous record of the state of the land surface The land surface model is run uncoupled (off-line) from its host mesoscale model (i.e., MM5 or WRF)
5 Domain-averaged soil moisture over Dugway Proving Grounds (Utah) Volumetric soil moisture content, D2 since Aug 21, 2005 layer 2 layer 3 layer 1 surface Land-use categories domains 1 and 2 12-hour precipitation
6 HRLDAS implementation HRLDAS uses the same land surface model as in coupled mesoscale model: same soil moisture climatology No mismatch of terrain, land use type, soil texture, or physical parameters No interpolation or soil moisture conversion Uses atmospheric forcing (temp, wind, etc.) from mesoscale model; observed precipitation, solar incident radiation, and water equivalent snow depth (available in real time)
7 MM5 RTFDDA for Aberdeen Test Center (ATC), Maryland domain 2 ( x=10 km) In the standard real-time fourdimensional data assimilation (RTFDDA) surface fields are initialized from interpolated NAM (previously known as ETA) fields HRLDAS example New system will use HRLDAS fields to initialize model fields Volumetric soil moisture surface layer
8 Real-time MM5 experiments Three parallel RTFDDA experiments for three ranges:dpg, WSMR, and ATC New runs (after bug fix) since Sept 17, 2005 Verification statistics compiled in real time
9
10 The characteristics of the land surface are spatially heterogeneous
11 But, general circulation models usually have horizontal grid spacings of ~100 km!
12 The answer: the fine-mesh model!
13 The fine-mesh model The fine-mesh model represents sub-grid scale processes by a land sub-mesh imposed on each atmospheric model grid; Advantages: cheap (compared to high resolution runs or limited-area models), defined geographic location, sub-grid parameterizations are easy to implement;
14 surface temperature (K) precipitation (mm/day) Changes in temperature and precipitation introduced by the fine-mesh model (Hahmann and Dickinson, 2001) Significant changes in precipitation over Africa, where climate is sensitive to the location of the boundary between vegetated and non-vegetated land.
15 Sub-grid disaggregation parameterizations Introduce sub-grid scale parameterizations for a non-uniform distribution of atmospheric forcings. Precipitation Elevation Topographic Slope/Aspect
16 Precipitation disaggregation scheme The probability distribution of rainfall within the rain-covered area, µ, based on the method by Eagleson (1978) is given by QuickTime and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. f ( P ) ij P ij µ µ P = exp ij P P The amount of rainfall received at a randomly selected grid point (i,j) is given by P = ln( 1 µ x) where 0<x<1 is an additionally produced random number. The process is repeated until a fraction µ of the large-scale grid square is covered with rainfall.
17 Disaggregation according to sub-grid elevation The temperature, pressure, density and humidity at a subgrid point are adjusted from the GCM value using a standard atmosphere lapse rate and the sub-grid point elevation. height temperature GCM elevation and temperature 1 1/2 1/4 surface elevation over the western US
18 Differences in water equivalent snow cover using elevationbased disaggregation
19 Disaggregation of solar insolation according to sub-grid slope and azimuth Geometry of the solar angle incidence on an inclined surface Slope and azimuth at 1km resolution over the western US
20 Insolation and snow depth differences during the melting season introduced by the sub-grid slope and aspect Water equivalent snow depth Insolation (W/m2)
21 Summary, conclusions, etc. The climate simulated using the precipitation disaggregation scheme is considerably different from that simulated using rainfall which is homogeneously distributed within the GCM grid square. Precipitation disaggregation scheme suffers from many drawbacks: unable to reproduce the spatial structure of the precipitation field; unable to reproduce the temporal and spatial memory of the precipitation processes; Drawbacks could be corrected by enhancements to the current scheme. Use observations to determine characteristic of the precipitation field and it relationship to the large-scale environment. The introduction of the effects of topography (elevation, slope and azimuth) in the fine-mesh model produces differences in snow cover in mid-latitude mountainous terrain. Changes are also seen in the atmospheric circulation near regions of steep terrain.
22 After 10 years of work... Fine-mesh model will finally be coupled to the Community Climate System Model!
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting
 Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM
 1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
Effects of sub-grid variability of precipitation and canopy water storage on climate model simulations of water cycle in Europe
 Adv. Geosci., 17, 49 53, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Effects of sub-grid variability of precipitation and canopy
Adv. Geosci., 17, 49 53, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Effects of sub-grid variability of precipitation and canopy
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Atmospheric Processes
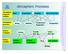 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
ONE DIMENSIONAL CLIMATE MODEL
 JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS
 A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
Lecture 3A: Interception
 3-1 GEOG415 Lecture 3A: Interception What is interception? Canopy interception (C) Litter interception (L) Interception ( I = C + L ) Precipitation (P) Throughfall (T) Stemflow (S) Net precipitation (R)
3-1 GEOG415 Lecture 3A: Interception What is interception? Canopy interception (C) Litter interception (L) Interception ( I = C + L ) Precipitation (P) Throughfall (T) Stemflow (S) Net precipitation (R)
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis
 What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
Climate FDDA. Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL/NSAP February 26, 2008
 Climate FDDA Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL/NSAP hahmann@ucar.edu February 26, 2008 Outline Climate downscaling - the basics Method (ATEC ranges) - Climo-FDDA Possible application of Climo-FDDA data at the ranges
Climate FDDA Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL/NSAP hahmann@ucar.edu February 26, 2008 Outline Climate downscaling - the basics Method (ATEC ranges) - Climo-FDDA Possible application of Climo-FDDA data at the ranges
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS
 P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
Factors That Affect Climate
 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude (horizontal lines) increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The tropical zone is between the tropic of Cancer and
Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude (horizontal lines) increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The tropical zone is between the tropic of Cancer and
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Zachary Holden - US Forest Service Region 1, Missoula MT Alan Swanson University of Montana Dept. of Geography David Affleck University of Montana
 Progress modeling topographic variation in temperature and moisture for inland Northwest forest management Zachary Holden - US Forest Service Region 1, Missoula MT Alan Swanson University of Montana Dept.
Progress modeling topographic variation in temperature and moisture for inland Northwest forest management Zachary Holden - US Forest Service Region 1, Missoula MT Alan Swanson University of Montana Dept.
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ
 Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2. Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei
 Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2 Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei 1 Outline NCEP CFSRR Land component CFSv1 vs CFSv2 Land
Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2 Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei 1 Outline NCEP CFSRR Land component CFSv1 vs CFSv2 Land
- continental vs. marine regimes
 (1 of 14) Further Reading: Chapter 05 of the text book Outline - continental vs. marine regimes - temperature structure of the atmosphere - seasonal variations - urban heat island (2 of 14) Introduction
(1 of 14) Further Reading: Chapter 05 of the text book Outline - continental vs. marine regimes - temperature structure of the atmosphere - seasonal variations - urban heat island (2 of 14) Introduction
Arctic System Reanalysis *
 Arctic System Reanalysis * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1 and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center 2 Atmospheric Sciences Program, Dept. of Geography The Ohio State
Arctic System Reanalysis * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1 and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center 2 Atmospheric Sciences Program, Dept. of Geography The Ohio State
GEO1010 tirsdag
 GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004
 Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes
 1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale heterogeneity in a GCM
 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003
 GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
way and atmospheric models
 Scale-consistent consistent two-way way coupling of land-surface and atmospheric models COSMO-User-Seminar 9-11 March 2009 Annika Schomburg, Victor Venema, Felix Ament, Clemens Simmer TR / SFB 32 Objective
Scale-consistent consistent two-way way coupling of land-surface and atmospheric models COSMO-User-Seminar 9-11 March 2009 Annika Schomburg, Victor Venema, Felix Ament, Clemens Simmer TR / SFB 32 Objective
Climate Modelling: Basics
 Climate Modelling: Basics Lecture at APN-TERI Student Seminar Teri University, 16 th Feb 2015 Saurabh Bhardwaj Associate Fellow Earth Science & Climate Change Division TERI saurabh.bhardwaj@teri.res.in
Climate Modelling: Basics Lecture at APN-TERI Student Seminar Teri University, 16 th Feb 2015 Saurabh Bhardwaj Associate Fellow Earth Science & Climate Change Division TERI saurabh.bhardwaj@teri.res.in
Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004
 Dag.Lohmann@noaa.gov, Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004 Land Data Assimilation at NCEP: Strategic Lessons Learned from the North American Land Data Assimilation System
Dag.Lohmann@noaa.gov, Land Data Assimilation at NCEP NLDAS Project Overview, ECMWF HEPEX 2004 Land Data Assimilation at NCEP: Strategic Lessons Learned from the North American Land Data Assimilation System
Climate and the Atmosphere
 Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki March 17, 2014 Lecture 08: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
Manoa Watershed Water Balance Study: Potential ET
 Manoa Watershed Water Balance Study: Potential ET Wyatt Blair, Josh Donovan, Max Irion, Jordan Muratsuchi, and David Heir Geography 405 Fall 2016 Overview Introduction Objectives Methodology Results Summary/Conclusion
Manoa Watershed Water Balance Study: Potential ET Wyatt Blair, Josh Donovan, Max Irion, Jordan Muratsuchi, and David Heir Geography 405 Fall 2016 Overview Introduction Objectives Methodology Results Summary/Conclusion
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation
 Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Sensitivity Analysis of WRF Forecasts in Arizona During the Monsoon Season Case Study: August 2, 2005 to August 3, 2005
 Sensitivity Analysis of WRF Forecasts in Arizona During the Monsoon Season Case Study: August 2, 2005 to August 3, 2005 Christopher L. Castro and Stephen Bieda III University of Arizona Susanne Grossman-Clarke
Sensitivity Analysis of WRF Forecasts in Arizona During the Monsoon Season Case Study: August 2, 2005 to August 3, 2005 Christopher L. Castro and Stephen Bieda III University of Arizona Susanne Grossman-Clarke
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department
 Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Near-surface weather prediction and surface data assimilation: challenges, development, and potential data needs
 Near-surface weather prediction and surface data assimilation: challenges, development, and potential data needs Zhaoxia Pu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah,
Near-surface weather prediction and surface data assimilation: challenges, development, and potential data needs Zhaoxia Pu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah,
Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling
 st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
Regional dry-season climate changes due to three decades of Amazonian deforestation
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:./NCLIMATE Regional dry-season climate changes due to three decades of Amazonian deforestation Jaya problemkhanna by using
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:./NCLIMATE Regional dry-season climate changes due to three decades of Amazonian deforestation Jaya problemkhanna by using
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
8-km Historical Datasets for FPA
 Program for Climate, Ecosystem and Fire Applications 8-km Historical Datasets for FPA Project Report John T. Abatzoglou Timothy J. Brown Division of Atmospheric Sciences. CEFA Report 09-04 June 2009 8-km
Program for Climate, Ecosystem and Fire Applications 8-km Historical Datasets for FPA Project Report John T. Abatzoglou Timothy J. Brown Division of Atmospheric Sciences. CEFA Report 09-04 June 2009 8-km
NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models
 NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models D.T. Mihailović and B. Lalić Faculty of Agriculture, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad,
NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models D.T. Mihailović and B. Lalić Faculty of Agriculture, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad,
The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy
 Energy Balance The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic
Energy Balance The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic
Why modelling? Glacier mass balance modelling
 Why modelling? Glacier mass balance modelling GEO 4420 Glaciology 12.10.2006 Thomas V. Schuler t.v.schuler@geo.uio.no global mean temperature Background Glaciers have retreated world-wide during the last
Why modelling? Glacier mass balance modelling GEO 4420 Glaciology 12.10.2006 Thomas V. Schuler t.v.schuler@geo.uio.no global mean temperature Background Glaciers have retreated world-wide during the last
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki November 17, 2017 Lecture 11: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki November 17, 2017 Lecture 11: Terrain Analysis Outline: Terrain Analysis Earth Surface Representation Contour TIN Mass Points Digital Elevation Models Slope
NCEP Land-Surface Modeling
 NCEP Land-Surface Modeling Michael Ek and the EMC Land-Hydrology Team Environmental Modeling Center (EMC) National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) 5200 Auth Road, Room 207 Suitland, Maryland
NCEP Land-Surface Modeling Michael Ek and the EMC Land-Hydrology Team Environmental Modeling Center (EMC) National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) 5200 Auth Road, Room 207 Suitland, Maryland
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES. Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski #
 P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
A Description and Example Output of the WRF-NMM land surface and radiation packages used at NCEP
 A Description and Example Output of the WRF-NMM land surface and radiation packages used at NCEP Ken Mitchell and Michael Ek NCEP/EMC NOAA/NWS WRF-NMM Tutorial 8-11 August 2006 Boulder, CO Noah Land Surface
A Description and Example Output of the WRF-NMM land surface and radiation packages used at NCEP Ken Mitchell and Michael Ek NCEP/EMC NOAA/NWS WRF-NMM Tutorial 8-11 August 2006 Boulder, CO Noah Land Surface
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
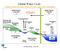 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Components of the Climate System. Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System. Pop Quiz. Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes out
 Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System Components of the Climate System terrestrial radiation Atmosphere Ocean solar radiation Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System Components of the Climate System terrestrial radiation Atmosphere Ocean solar radiation Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What
Use of Satellite-Based Precipitation Observation in Improving the Parameterization of Canopy Hydrological Processes in Land Surface Models
 OCTOBER 2005 W A N G E T A L. 745 Use of Satellite-Based Precipitation Observation in Improving the Parameterization of Canopy Hydrological Processes in Land Surface Models DAGANG WANG, GUILING WANG, AND
OCTOBER 2005 W A N G E T A L. 745 Use of Satellite-Based Precipitation Observation in Improving the Parameterization of Canopy Hydrological Processes in Land Surface Models DAGANG WANG, GUILING WANG, AND
Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range
 Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range Kyle R. Knipper 1, Alicia M. Kinoshita 2, and Terri S. Hogue 1 January 5 th, 2015
Evaluation of a MODIS Triangle-based Algorithm for Improving ET Estimates in the Northern Sierra Nevada Mountain Range Kyle R. Knipper 1, Alicia M. Kinoshita 2, and Terri S. Hogue 1 January 5 th, 2015
Joseph M. Shea 1, R. Dan Moore, Faron S. Anslow University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada. 1 Introduction
 17th Conference on Applied Climatology, American Meteorological Society, 11-1 August, 28, Whistler, BC, Canada P2. - Estimating meteorological variables within glacier boundary layers, Southern Coast Mountains,
17th Conference on Applied Climatology, American Meteorological Society, 11-1 August, 28, Whistler, BC, Canada P2. - Estimating meteorological variables within glacier boundary layers, Southern Coast Mountains,
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System
 Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System terrestrial radiation solar radiation Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System terrestrial radiation solar radiation Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes
Glacier meteorology Surface energy balance. How does ice and snow melt? Where does the energy come from? How to model melt?
 Glacier meteorology Surface energy balance How does ice and snow melt? Where does the energy come from? How to model melt? Melting of snow and ice Ice and snow melt at 0 C (but not necessarily at air temperature
Glacier meteorology Surface energy balance How does ice and snow melt? Where does the energy come from? How to model melt? Melting of snow and ice Ice and snow melt at 0 C (but not necessarily at air temperature
Observation: predictable patterns of ecosystem distribution across Earth. Observation: predictable patterns of ecosystem distribution across Earth 1.
 Climate Chap. 2 Introduction I. Forces that drive climate and their global patterns A. Solar Input Earth s energy budget B. Seasonal cycles C. Atmospheric circulation D. Oceanic circulation E. Landform
Climate Chap. 2 Introduction I. Forces that drive climate and their global patterns A. Solar Input Earth s energy budget B. Seasonal cycles C. Atmospheric circulation D. Oceanic circulation E. Landform
Air Pollution Meteorology
 Air Pollution Meteorology Government Pilots Utilities Public Farmers Severe Weather Storm / Hurricane Frost / Freeze Significant Weather Fog / Haze / Cloud Precipitation High Resolution Weather & Dispersion
Air Pollution Meteorology Government Pilots Utilities Public Farmers Severe Weather Storm / Hurricane Frost / Freeze Significant Weather Fog / Haze / Cloud Precipitation High Resolution Weather & Dispersion
- matter-energy interactions. - global radiation balance. Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book. Outline. - shortwave radiation balance
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature
 Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
Chapter 3- Energy Balance and Temperature Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Influences on Insolation Absorption Reflection/Scattering Transmission 1 Absorption An absorber gains energy
Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale
 Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste, Italy ESA summer school on Earth System Monitoring and Modeling Frascati, Italy, 31 July 11 August 2006
Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste, Italy ESA summer school on Earth System Monitoring and Modeling Frascati, Italy, 31 July 11 August 2006
Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps
 Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps L. Laiti*, L. Giovannini and D. Zardi Atmospheric Physics Group University of Trento - Italy outline of the talk Introduction
Characterization of the solar irradiation field for the Trentino region in the Alps L. Laiti*, L. Giovannini and D. Zardi Atmospheric Physics Group University of Trento - Italy outline of the talk Introduction
A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 6, 325 329 A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model YU En-Tao 1,2,3, WANG Hui-Jun 1,2, and SUN Jian-Qi
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 6, 325 329 A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model YU En-Tao 1,2,3, WANG Hui-Jun 1,2, and SUN Jian-Qi
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model
 New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array
 Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array R.M. Randall, C.M Hocut, D.K. Knapp, B.T. MacCall, & J.A. Smith MSA Program Overview Army Challenge Research gaps exist which challenge
Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array R.M. Randall, C.M Hocut, D.K. Knapp, B.T. MacCall, & J.A. Smith MSA Program Overview Army Challenge Research gaps exist which challenge
MATERHORN Field Campaign
 High Resolution Modeling for MATERHORN Field Campaign Applications to Synoptically Driven Flow Zachariah Silver, Reneta Dimitrova, and Tamás Zsedrovits Overview Adjusted WRF model setup Application to
High Resolution Modeling for MATERHORN Field Campaign Applications to Synoptically Driven Flow Zachariah Silver, Reneta Dimitrova, and Tamás Zsedrovits Overview Adjusted WRF model setup Application to
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
 The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
THE LAND SURFACE SCHEME OF THE UNIFIED MODEL AND RELATED CONSIDERATIONS
 CHAPTER 7: THE LAND SURFACE SCHEME OF THE UNIFIED MODEL AND RELATED CONSIDERATIONS 7.1: Introduction The atmosphere is sensitive to variations in processes at the land surface. This was shown in the earlier
CHAPTER 7: THE LAND SURFACE SCHEME OF THE UNIFIED MODEL AND RELATED CONSIDERATIONS 7.1: Introduction The atmosphere is sensitive to variations in processes at the land surface. This was shown in the earlier
Melting of snow and ice
 Glacier meteorology Surface energy balance How does ice and snow melt? Where does the energy come from? How to model melt? Melting of snow and ice Ice and snow melt at 0 C (but not necessarily at air temperature
Glacier meteorology Surface energy balance How does ice and snow melt? Where does the energy come from? How to model melt? Melting of snow and ice Ice and snow melt at 0 C (but not necessarily at air temperature
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL. 1. Introduction
 DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
Earth s Climate Patterns
 Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
Earth s Climate Patterns Reading: Chapter 17, GSF 10/2/09 Also Jackson (linked on course web site) 1 What aspects of climate affect plant distributions? Climate: long-term distribution of weather in an
The Atmosphere. Importance of our. 4 Layers of the Atmosphere. Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate. What makes up the atmosphere?
 The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions
 Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions Jialun Li, X. Gao, K.-L. Hsu, B. Imam, and S. Sorooshian Department of Civil and Environmental
Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions Jialun Li, X. Gao, K.-L. Hsu, B. Imam, and S. Sorooshian Department of Civil and Environmental
Temperature and rainfall changes over East Africa from multi-gcm forced RegCM projections
 Temperature and rainfall changes over East Africa from multi-gcm forced RegCM projections Gulilat Tefera Diro and Adrian Tompkins - Earth System Physics Section International Centre for Theoretical Physics
Temperature and rainfall changes over East Africa from multi-gcm forced RegCM projections Gulilat Tefera Diro and Adrian Tompkins - Earth System Physics Section International Centre for Theoretical Physics
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Model resolution impact on Precipitation: Comparison to SNOTEL observations
 Model resolution impact on Precipitation: Comparison to SNOTEL observations 5/7/2012 40 proj. updates Sensitivity to model grid resolution: Precipitation from the 8-year Current Climate Simulation Percent
Model resolution impact on Precipitation: Comparison to SNOTEL observations 5/7/2012 40 proj. updates Sensitivity to model grid resolution: Precipitation from the 8-year Current Climate Simulation Percent
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems
 Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems 6 Chapter Overview The atmosphere is a complex system, sometimes described as chaotic in nature. In this chapter we examine one of the principal
Atmospheric Moisture, Precipitation, and Weather Systems 6 Chapter Overview The atmosphere is a complex system, sometimes described as chaotic in nature. In this chapter we examine one of the principal
Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice. (from Our Changing Planet)
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Earth s s Climate System Solar forcing Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry
Earth s Climate System. Surface Albedo. Climate Roles of Land Surface. Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Earth s Climate System Solar forcing Land Surface Sea Ice Land Ice Atmosphere Ocean Land Solid Earth Energy, Water, and Biochemistry Cycles (from Our Changing
J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul
 J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul Hae-Jung Koo *, Kyu Rang Kim, Young-Jean Choi, Tae Heon Kwon, Yeon-Hee Kim, and Chee-Young Choi
J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul Hae-Jung Koo *, Kyu Rang Kim, Young-Jean Choi, Tae Heon Kwon, Yeon-Hee Kim, and Chee-Young Choi
T Bias ( C) T Bias ( C)
 P.7 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF A REAL-TIME MESOSCALE FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM UNDER DIFFERENT SYNOPTIC SITUATIONS RONG-SHYANG SHEU*, JENNIFER CRAM, YUBAO LIU, AND SIMON LOW-NAM
P.7 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF A REAL-TIME MESOSCALE FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM UNDER DIFFERENT SYNOPTIC SITUATIONS RONG-SHYANG SHEU*, JENNIFER CRAM, YUBAO LIU, AND SIMON LOW-NAM
Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon the Baiu Front
 Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 101 109. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon
Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 101 109. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY
 P2.17 PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY Jeffrey E. Passner U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION The Army Research Laboratory
P2.17 PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY Jeffrey E. Passner U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION The Army Research Laboratory
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
PART II. Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 CLIMATE CLIMATE STUDYING CLIMATE R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their Physical Environment 10/19/2017
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
Using Multivariate Adaptive Constructed Analogs (MACA) data product for climate projections
 Using Multivariate Adaptive Constructed Analogs (MACA) data product for climate projections Maria Herrmann and Ray Najjar Chesapeake Hypoxia Analysis and Modeling Program (CHAMP) Conference Call 2017-04-21
Using Multivariate Adaptive Constructed Analogs (MACA) data product for climate projections Maria Herrmann and Ray Najjar Chesapeake Hypoxia Analysis and Modeling Program (CHAMP) Conference Call 2017-04-21
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS)
 Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States
 The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States Michael Barlage, Fei Chen, Changhai Liu NCAR/RAL Gonzalo Miguez-Macho U. Santiago de Compostela
The Scale-dependence of Groundwater Effects on Precipitation and Temperature in the Central United States Michael Barlage, Fei Chen, Changhai Liu NCAR/RAL Gonzalo Miguez-Macho U. Santiago de Compostela
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Meteorology Course(s): Meteorology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period (average minutes): 42 Periods per cycle: 6 Length
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Meteorology Course(s): Meteorology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period (average minutes): 42 Periods per cycle: 6 Length
17 March Good luck!
 ! Midterm Exam 17 March 2005 Name:! SID:!! The mid-term has a maximum of 120 points: 60 points for a section with short essays, and 60 points for a section with qualitative/quantitative problems. Remember
! Midterm Exam 17 March 2005 Name:! SID:!! The mid-term has a maximum of 120 points: 60 points for a section with short essays, and 60 points for a section with qualitative/quantitative problems. Remember
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives
 Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
PART II. Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 CLIMATE CLIMATE STUDYING CLIMATE R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their Physical Environment 10/26/2017
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
BIOGEOGRAPHY GEO 4300/5107C. The Environmental Setting (Geographic Template) Lecture 3: 8 January 2015
 BIOGEOGRAPHY GEO 4300/5107C The Environmental Setting (Geographic Template) Lecture 3: 8 January 2015 Last Time Topics and Subdisciplines of Biogeography History of Biogeography Western biogeography first
BIOGEOGRAPHY GEO 4300/5107C The Environmental Setting (Geographic Template) Lecture 3: 8 January 2015 Last Time Topics and Subdisciplines of Biogeography History of Biogeography Western biogeography first
Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest
 Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest Jimmy O. Adegoke 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro 2, Roger
Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest Jimmy O. Adegoke 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro 2, Roger
May 3, :41 AOGS - AS 9in x 6in b951-v16-ch13 LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING DATA
 Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Inter- Annual Land Surface Variation NAGS 9329
 Annual Report on NASA Grant 1 Inter- Annual Land Surface Variation NAGS 9329 PI Stephen D. Prince Co-I Yongkang Xue April 2001 Introduction This first period of operations has concentrated on establishing
Annual Report on NASA Grant 1 Inter- Annual Land Surface Variation NAGS 9329 PI Stephen D. Prince Co-I Yongkang Xue April 2001 Introduction This first period of operations has concentrated on establishing
