The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
|
|
|
- Franklin Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
2 Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization & Boundary Conditions MM5 Physics Data Assimilation Model Verification
3 X,Y, σ Coordinate System p = p o + p`(x,y, σ,t) ρ = ρ o + ρ`(x,y, σ,t) T = T o + T`(x,y, σ,t) σ = (p o p t ) / p* where p*(x,y) = (p s p t ) p* is a function of only topography
4 Nonhydrostatic Momentum Equations U: Sloped σ terms Subgrid scale eddy terms V: W:
5 Nonhydrostatic Pressure and Temperature Equations Pressure: Temperature: V V Ideal gas Law: p = ρ R d T v Diabatic Heating
6 Horizontal Spacing 500 m through 200 km Arakawa B Grid U,V (dot) staggered with P,T,q (cross) Vertical Velocity Staggered Grid
7 Equation Solution Spatial Differencing Centered In Space Precipitation Fall terms Use Forward Upstream Prevent Negative Values Time Split Method Long Time Step Uses Leap Frog Advection, Coriolis, Diffusion Short Time Step Uses Forward In Time U,V Advanced First Explicitly W,P` Advanced After Asselin Time Filter Applied every large time step T n-1 = T n *(T n-2 2T n-1 + T n )
8 Error in Finite Difference Scheme PGF: Forward in Time Advection: Leap Frog 10 dx 4 dx 10 dx 4 dx 2 dx Courant number Courant Number
9 1 and 2 Way Nesting 2 Way Nesting Requires a 3:1 ratio 3 Methods Nest Interpolation Nesting Initialized by interpolating coarse-mesh grid Nest Analysis Input Initialized with a fine resolution topographic and initial condition file Nest Terrain Input Interpolate IC from coarse-mesh grid Terrain input from fine-mesh input file
10 MM5 Initialization Objective analysis Dynamic initialization (Integrated divergence removal) Data Assimilation (FDDA or 3DVAR)
11 Lateral Boundary Condition Fixed Time-dependent/Nest Relaxation/inflow-outflow
12 Vertical Boundary Conditions Upper Boundary Condition Rigid lid: w = 0 at top Radiative: w is a function of p at top Lower Boundary Condition Dataset (SST, substrate temperature, snow cover, sea-ice) (Fixed or Time-dependent) Terrain-following flow conditions
13 MM5 Physics Cumulus Parameterizations Explicit Moisture/Microphysics Planetary Boundary Layer/Vertical Diffusion Radiation Land Surface Model
14 Cumulus Parameterizations None x 5-10 km Anthes-Kuo x > 30 km Moiusture Convergence Closure Arakawa-Schubert Grell Entrainment into updrafts Downdrafts x km Based on quasi equilibrium Single cloud closure scheme Shallow Cumulus Based on Grell Non-precipitating clouds Fritsch-Chappell x km Based on relaxation to a profile Fixed entrainment Kain-Fritsch Based on removal of buoyant energy over given time Variable entrainment Kain-Fritsch 2 Includes shallow convection Betts-Miller Relax to adjust to postconvective thermodynamic profile over given time No explicit downdrafts/updrafts
15 Illustration of Microphysics Processes
16 Explicit Moisture/Microphysics Dry No Moisture Stable Removal of supersaturation No explicit clouds Warm rain No Ice phases Simple Ice Immediately freeze/melt at 0 o C Look up table Reisner 1 Mixed Phase Supercooled Liquid Gradual Snow Melt Look up table Goddard Includes graupel and hail Reisner 2 Includes graupel Predicts cloud ice number concentration Schultz Simple tuneable equations Includes graupel
17 Illustration of PBL Processes
18 PBL Process Parameterization Represent sub-grid vertical fluxes due to turbulence. Mostly distinguished by treatment of the unstable boundary layer. Generally provide column tendencies of heat, moisture and momentum and may provide cloud tendencies Interacts with fluxes from surface scheme Provides frictional effects on momentum
19 PBL Schemes (Options) Bulk formula High-Resolution Blackadar scheme MRF scheme <OSU-LSM> Burk-Thompson (Mellor-Yamada 1.5-order/level- 2.5 scheme) Eta TKE scheme <OSU-LSM (v3.5)> Gayno-Seaman scheme Pleim-Chang scheme <Pleim-Xiu LSM> (Zhang and Anthes 1982; Hong and Pan 1996; Janjic,1990, 1994; Gayno 1994 )
20 Illustration of Radiation Processes
21 Radiation Schemes Represent radiative effects in atmosphere and at surface Provides surface downwelling longwave and shortwave fluxes for surface scheme Provides column temperature tendencies due to vertical radiative flux divergence May interact with model clouds or relative humidity
22 Radiation Schemes (Options) None (Surface radiation) Simple cooling (Surface radiation) Dudhia's long and short-wave radiation scheme (Cloud Radiation) NCAR/CCM2 radiation scheme RRTM long-wave radiation scheme (V3 only) (Dudhia 1989; Hack et al. 1993; Mlawer et al., 1997)
23 Illustration of Surface Processes
24 Land Surface Schemes Represent effects of land and water surfaces May also represent sub-soil temperature and moisture profiles Ground temperature based on heat budget using radiative fluxes and surface-layer atmospheric properties Provides sensible and latent heat flux May provide snow-cover tendencies and surface moisture availability variation
25 Land Surface Schemes (Options) Force-restore (Blackadar) Five-layer Soil Temperature Oregon State University/Eta LSM (V3.1 - V3.5) NOAH Land Surface Model (since V3.6) Pleim-Xiu LSM (V3 only) (Pan and Mahrt 1987; Chen and Dudhia 2001)
26 Four-Dimensional Data Assimilation (FDDA) Newtonian relaxation or nudging Three primary uses for FDDA: Dynamical initialization Four-dimensional dataset (e.g. for air quality model) Boundary conditions (outer domain nudged towards analysis) Two methods of data assimilation: Grid or analysis nudging Observation or station nudging (Stauffer and Seaman 1990)
27 Interactions of Parameterizations
28 Verification IC and BC from NCEP model analysis and forcast grid x = 27 km, with 27 σ levels (White et al 1998)
29 Verification Initialized from satellite measurements SST updated daily (Zhu et al. 2004)
30 MM5 model users website: White, B.G., J. Paegle, W.J. Steenburgh, J.D. Horel, R.T. Swanson, L.K. Cook, D.J. Onton, J.G. Miles, 1998: Short Term Forecast Validation of Six Models. Weather and Forecasting, 14, Zhu, T., D. Zhang, F. Weng, 2004: Numerical Simulation of Hurricane Bonnie (1998). Part 1: Eyewall Evolution and Intensity Changes. Monthly Weather Review, 132,
Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004
 Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Weather Research and Forecasting Model Melissa Goering Glen Sampson ATMO 595E November 18, 2004 Outline What does WRF model do? WRF Standard Initialization WRF Dynamics Conservation Equations Grid staggering
Chapter 3 DEVELOPING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS
 Chapter 3 DEVELOPING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS Tanya L. Otte * Atmospheric Modeling Division National Exposure Research Laboratory U. S. Environmental Protection Agency Research Triangle Park, NC 27711 ABSTRACT
Chapter 3 DEVELOPING METEOROLOGICAL FIELDS Tanya L. Otte * Atmospheric Modeling Division National Exposure Research Laboratory U. S. Environmental Protection Agency Research Triangle Park, NC 27711 ABSTRACT
Meteorological Modeling using Penn State/NCAR 5 th Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5)
 TSD-1a Meteorological Modeling using Penn State/NCAR 5 th Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5) Bureau of Air Quality Analysis and Research Division of Air Resources New York State Department of Environmental
TSD-1a Meteorological Modeling using Penn State/NCAR 5 th Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5) Bureau of Air Quality Analysis and Research Division of Air Resources New York State Department of Environmental
Simulating orographic precipitation: Sensitivity to physics parameterizations and model numerics
 Simulating orographic precipitation: Sensitivity to physics parameterizations and model numerics 2nd COPS-Meeting, 27 June 2005 Günther Zängl Overview A highly idealized test of numerical model errors
Simulating orographic precipitation: Sensitivity to physics parameterizations and model numerics 2nd COPS-Meeting, 27 June 2005 Günther Zängl Overview A highly idealized test of numerical model errors
Regional Scale Modeling and Numerical Weather Prediction
 Regional Scale Modeling and Numerical Weather Prediction Jimy Dudhia NCAR/MMM Mesoscale & Microscale Meteorological Division / NCAR Overview of talk WRF Modeling System Overview WRF Model Dynamics Physics
Regional Scale Modeling and Numerical Weather Prediction Jimy Dudhia NCAR/MMM Mesoscale & Microscale Meteorological Division / NCAR Overview of talk WRF Modeling System Overview WRF Model Dynamics Physics
Investigation of feedback mechanisms between soil moisture, land use and precipitation in West Africa
 Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02a held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280, 2003. 1 Investigation of feedback mechanisms
Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02a held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280, 2003. 1 Investigation of feedback mechanisms
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity
 The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
The Effect of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Jeffrey S. Gall, Young Kwon, and William Frank The Pennsylvania State University University Park, Pennsylvania 16802 1. Introduction Under high-wind
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016
 MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective
 Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective Ming-Jen Yang Institute of Hydrological Sciences, National Central University 1. Introduction Typhoon Nari (2001) struck
Precipitation Structure and Processes of Typhoon Nari (2001): A Modeling Propsective Ming-Jen Yang Institute of Hydrological Sciences, National Central University 1. Introduction Typhoon Nari (2001) struck
A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 170 175 A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF WANG Zi-Qian 1,2 and DUAN An-Min 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 170 175 A New Ocean Mixed-Layer Model Coupled into WRF WANG Zi-Qian 1,2 and DUAN An-Min 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ
 Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
WRF Modeling System Overview
 WRF Modeling System Overview Louisa Nance National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Developmental Testbed Center (DTC) 27 February 2007 1 Outline What is WRF? WRF Modeling System WRF Software Design
WRF Modeling System Overview Louisa Nance National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Developmental Testbed Center (DTC) 27 February 2007 1 Outline What is WRF? WRF Modeling System WRF Software Design
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
LARGE-SCALE WRF-SIMULATED PROXY ATMOSPHERIC PROFILE DATASETS USED TO SUPPORT GOES-R RESEARCH ACTIVITIES
 LARGE-SCALE WRF-SIMULATED PROXY ATMOSPHERIC PROFILE DATASETS USED TO SUPPORT GOES-R RESEARCH ACTIVITIES Jason Otkin, Hung-Lung Huang, Tom Greenwald, Erik Olson, and Justin Sieglaff Cooperative Institute
LARGE-SCALE WRF-SIMULATED PROXY ATMOSPHERIC PROFILE DATASETS USED TO SUPPORT GOES-R RESEARCH ACTIVITIES Jason Otkin, Hung-Lung Huang, Tom Greenwald, Erik Olson, and Justin Sieglaff Cooperative Institute
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China
 Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
P1.2 SENSITIVITY OF WRF MODEL FORECASTS TO DIFFERENT PHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS IN THE BEAUFORT SEA REGION
 P1.2 SENSITIVITY OF WRF MODEL FORECASTS TO DIFFERENT PHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS IN THE BEAUFORT SEA REGION Jeremy R. Krieger *, Jing Zhang Arctic Region Supercomputing Center, University of Alaska Fairbanks
P1.2 SENSITIVITY OF WRF MODEL FORECASTS TO DIFFERENT PHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS IN THE BEAUFORT SEA REGION Jeremy R. Krieger *, Jing Zhang Arctic Region Supercomputing Center, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
NCEP s "NAM" (North American Mesoscale) model WRF-NMM. NCEP =National Centers for Environmental Prediction
 NCEP s "NAM" (North American Mesoscale) model WRF-NMM NCEP =National Centers for Environmental Prediction Weather Research and Forecasting Non-hydrostatic Mesoscale Model (WRF-NMM)** model is run as the
NCEP s "NAM" (North American Mesoscale) model WRF-NMM NCEP =National Centers for Environmental Prediction Weather Research and Forecasting Non-hydrostatic Mesoscale Model (WRF-NMM)** model is run as the
THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST
 THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST Peter Childs, Sethu Raman, and Ryan Boyles State Climate Office of North Carolina and
THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST Peter Childs, Sethu Raman, and Ryan Boyles State Climate Office of North Carolina and
IMPROVING CLOUD PREDICTION IN WRF THROUGH THE USE OF GOES SATELLITE ASSIMILATION
 IMPROVING CLOUD PREDICTION IN WRF THROUGH THE USE OF GOES SATELLITE ASSIMILATION Andrew T. White*, Arastoo P. Biazar, Richard T. McNider, Kevin Doty, Maudood Khan Earth System Science Center, The University
IMPROVING CLOUD PREDICTION IN WRF THROUGH THE USE OF GOES SATELLITE ASSIMILATION Andrew T. White*, Arastoo P. Biazar, Richard T. McNider, Kevin Doty, Maudood Khan Earth System Science Center, The University
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
SIMULATION OF ATMOSPHERIC STATES FOR THE CASE OF YEONG-GWANG STORM SURGE ON 31 MARCH 2007 : MODEL COMPARISON BETWEEN MM5, WRF AND COAMPS
 SIMULATION OF ATMOSPHERIC STATES FOR THE CASE OF YEONG-GWANG STORM SURGE ON 31 MARCH 2007 : MODEL COMPARISON BETWEEN MM5, WRF AND COAMPS JEONG-WOOK LEE 1 ; KYUNG-JA HA 1* ; KI-YOUNG HEO 1 ; KWANG-SOON
SIMULATION OF ATMOSPHERIC STATES FOR THE CASE OF YEONG-GWANG STORM SURGE ON 31 MARCH 2007 : MODEL COMPARISON BETWEEN MM5, WRF AND COAMPS JEONG-WOOK LEE 1 ; KYUNG-JA HA 1* ; KI-YOUNG HEO 1 ; KWANG-SOON
Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over American, Yuba and Feather River Basins
 Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over merican, Yuba and Feather River Basins M. L. Kavvas 1, K. Ishida 1, S. Jang 1, N. Ohara 2, Z.Q.Chen 3, and M. nderson 3 1 University Of California,
Maximization of Historical Severe Precipitation Events over merican, Yuba and Feather River Basins M. L. Kavvas 1, K. Ishida 1, S. Jang 1, N. Ohara 2, Z.Q.Chen 3, and M. nderson 3 1 University Of California,
Development and Validation of Polar WRF
 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Department of Meteorology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT. Second revision. Submitted to Monthly Weather Review.
 Sensitivity of Numerical Simulation of Early Rapid Intensification of Hurricane Emily (2005) to Cloud Microphysical and Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations XUANLI LI and ZHAOXIA PU * Department
Sensitivity of Numerical Simulation of Early Rapid Intensification of Hurricane Emily (2005) to Cloud Microphysical and Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations XUANLI LI and ZHAOXIA PU * Department
Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL Physical Sciences Division
 The role of gray zone convective model physics in highresolution simulations of the 2013 Colorado Front Range Flood WRF model simulated precipitation over terrain in CO Front Range Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL
The role of gray zone convective model physics in highresolution simulations of the 2013 Colorado Front Range Flood WRF model simulated precipitation over terrain in CO Front Range Kelly Mahoney NOAA ESRL
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition. SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club
 Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
Model description of AGCM5 of GFD-Dennou-Club edition SWAMP project, GFD-Dennou-Club Mar 01, 2006 AGCM5 of the GFD-DENNOU CLUB edition is a three-dimensional primitive system on a sphere (Swamp Project,
INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS, NW GREECE), ON PRECIPITATION, DURING THE WARM PERIOD OF THE YEAR
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Davis
 Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model
 Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics
 Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics Tieh-Yong KOH 1 and Ricardo M. FONSECA 2 1 Singapore University of Social Sciences, Singapore 2
Improved rainfall and cloud-radiation interaction with Betts-Miller-Janjic cumulus scheme in the tropics Tieh-Yong KOH 1 and Ricardo M. FONSECA 2 1 Singapore University of Social Sciences, Singapore 2
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models
 Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models Natalie Perlin, Dudley Chelton, Simon de Szoeke College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
Use of Satellite Observations to Measure Air-Sea Coupling and to Validate Its Estimates from Numerical Atmospheric Models Natalie Perlin, Dudley Chelton, Simon de Szoeke College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric
A comparison of MM5 and meteo mast wind profiles at Cabauw, The Netherlands and Wilhelmshaven, Germany
 A comparison of MM and meteo mast wind profiles at Cabauw, The Netherlands and Wilhelmshaven, Germany Francesco Durante 1, Tim de Paus 2,3 1 DEWI, German Wind Energy Institute Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven,
A comparison of MM and meteo mast wind profiles at Cabauw, The Netherlands and Wilhelmshaven, Germany Francesco Durante 1, Tim de Paus 2,3 1 DEWI, German Wind Energy Institute Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven,
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM
 1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
1.5 HIGH-RESOLUTION LAND DATA ASSIMILATION IN THE NCAR/ATEC 1.5 REAL-TIME FDDA AND FORECASTING SYSTEM Andrea N. Hahmann, Yubao Liu, Fei Chen, Kevin W. Manning, Thomas T. Warner, and Laurie Carlson Research
Sensitivity of tropical cyclone Jal simulations to physics parameterizations
 Sensitivity of tropical cyclone Jal simulations to physics parameterizations R Chandrasekar and C Balaji Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Chennai 6 36, India.
Sensitivity of tropical cyclone Jal simulations to physics parameterizations R Chandrasekar and C Balaji Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Chennai 6 36, India.
Uncertainties in planetary boundary layer schemes and current status of urban boundary layer simulations at OU
 Uncertainties in planetary boundary layer schemes and current status of urban boundary layer simulations at OU Xiaoming Hu September 16 th @ 3:00 PM, NWC 5600 Contributors: Fuqing Zhang, Pennsylvania State
Uncertainties in planetary boundary layer schemes and current status of urban boundary layer simulations at OU Xiaoming Hu September 16 th @ 3:00 PM, NWC 5600 Contributors: Fuqing Zhang, Pennsylvania State
Using MM5 to Hindcast the Ocean Surface Forcing Fields over the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank Region*
 FEBRUARY 2005 C H E N E T A L. 131 Using MM5 to Hindcast the Ocean Surface Forcing Fields over the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank Region* CHANGSHENG CHEN School for Marine Science and Technology, University
FEBRUARY 2005 C H E N E T A L. 131 Using MM5 to Hindcast the Ocean Surface Forcing Fields over the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank Region* CHANGSHENG CHEN School for Marine Science and Technology, University
Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain)
 Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain) Jordi Mercader (1), Bernat Codina (1), Abdelmalik Sairouni (2), Jordi Cunillera (2) (1) Dept. of Astronomy and
Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain) Jordi Mercader (1), Bernat Codina (1), Abdelmalik Sairouni (2), Jordi Cunillera (2) (1) Dept. of Astronomy and
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS
 P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity
 3032 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity DA-LIN ZHANG AND ERIC ALTSHULER Department of Meteorology, University of Maryland, College
3032 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Effects of Dissipative Heating on Hurricane Intensity DA-LIN ZHANG AND ERIC ALTSHULER Department of Meteorology, University of Maryland, College
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics
 Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
Advanced Hurricane WRF (AHW) Physics Jimy Dudhia MMM Division, NCAR 1D Ocean Mixed-Layer Model 1d model based on Pollard, Rhines and Thompson (1973) was added for hurricane forecasts Purpose is to represent
5.6 IMPACT OF THREE DIMENSIONAL DATA ASSIMILATION ON HIGH RESOLUTION WEATHER AND POLLUTION FORECASTING IN THE LOS ANGELES BASIN
 5.6 IMPACT OF THREE DIMENSIONAL DATA ASSIMILATION ON HIGH RESOLUTION WEATHER AND POLLUTION FORECASTING IN THE LOS ANGELES BASIN Michael D. McAtee *, Leslie O. Belsma, James F. Drake, Arlene M. Kishi, and
5.6 IMPACT OF THREE DIMENSIONAL DATA ASSIMILATION ON HIGH RESOLUTION WEATHER AND POLLUTION FORECASTING IN THE LOS ANGELES BASIN Michael D. McAtee *, Leslie O. Belsma, James F. Drake, Arlene M. Kishi, and
Evaluation of nonlocal and local planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd017080, 2012 Evaluation of nonlocal and local planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model Bo Xie, 1 Jimmy C. H. Fung, 1,2 Allen Chan,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jd017080, 2012 Evaluation of nonlocal and local planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model Bo Xie, 1 Jimmy C. H. Fung, 1,2 Allen Chan,
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues
 PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
PBL and precipitation interaction and grey-zone issues Song-You Hong, Hyun-Joo Choi, Ji-Young Han, and Young-Cheol Kwon (Korea Institute of Atmospheric Prediction Systems: KIAPS) Overview of KIAPS (seminar
Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment. Ren Xia
 Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment Ren Xia 2017.05.12 1 Outline Background Experimental design Result and discussion Next work Background Taihu Lake is the largest
Simulation studies for Lake Taihu effect on local meteorological environment Ren Xia 2017.05.12 1 Outline Background Experimental design Result and discussion Next work Background Taihu Lake is the largest
The cientificworldjournal. Sujata Pattanayak, U. C. Mohanty, and Krishna K. Osuri. 1. Introduction
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 12, Article ID 671437, 18 pages doi:1.1/12/671437 The cientificworldjournal Research Article Impact of Parameterization of Physical Processes on Simulation of Track
The Scientific World Journal Volume 12, Article ID 671437, 18 pages doi:1.1/12/671437 The cientificworldjournal Research Article Impact of Parameterization of Physical Processes on Simulation of Track
The Global Weather Research and Forecasting (GWRF) Model: Model Evaluation, Sensitivity Study, and Future Year Simulation
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 231-253 doi:10.4236/acs.2012.23024 Published Online July 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) The Global Weather Research and Forecasting (GWRF) Model: Model
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 231-253 doi:10.4236/acs.2012.23024 Published Online July 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) The Global Weather Research and Forecasting (GWRF) Model: Model
Shu-Ya Chen 1, Tae-Kwon Wee 1, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1,2, and David H. Bromwich 3. University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado 2
 IMPACT OF GPS RADIO OCCULTATION DATA ON ANALYSIS AND PREDICTION OF AN INTENSE SYNOPTIC-SCALE STORM OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEAN NEAR THE ANTARCTIC PENINSULA Shu-Ya Chen 1, Tae-Kwon Wee 1, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1,2,
IMPACT OF GPS RADIO OCCULTATION DATA ON ANALYSIS AND PREDICTION OF AN INTENSE SYNOPTIC-SCALE STORM OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEAN NEAR THE ANTARCTIC PENINSULA Shu-Ya Chen 1, Tae-Kwon Wee 1, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1,2,
Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe convective storm
 Annales Geophysicae (2004) 22: 1861 1874 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2004-22-1861 European Geosciences Union 2004 Annales Geophysicae Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe
Annales Geophysicae (2004) 22: 1861 1874 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2004-22-1861 European Geosciences Union 2004 Annales Geophysicae Analysis of the role of the planetary boundary layer schemes during a severe
A New Method for Representing Mixed-phase Particle Fall Speeds in Bulk Microphysics Parameterizations
 November Journal of the 2008 Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. J. 86A, DUDHIA pp. 33 44, et al. 2008 33 A New Method for Representing Mixed-phase Particle Fall Speeds in Bulk Microphysics Parameterizations
November Journal of the 2008 Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. J. 86A, DUDHIA pp. 33 44, et al. 2008 33 A New Method for Representing Mixed-phase Particle Fall Speeds in Bulk Microphysics Parameterizations
Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17802, doi:10.1029/2009gl039100, 2009 Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization Akihiko Murata 1 Received 24 May 2009; revised 16 July 2009; accepted
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17802, doi:10.1029/2009gl039100, 2009 Errors caused by draft fraction in cumulus parameterization Akihiko Murata 1 Received 24 May 2009; revised 16 July 2009; accepted
Impacts of the Lowest Model Level Height on the Performance of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations
 664 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 140 Impacts of the Lowest Model Level Height on the Performance of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations HYEYUM HAILEY SHIN AND SONG-YOU HONG Department
664 M O N T H L Y W E A T H E R R E V I E W VOLUME 140 Impacts of the Lowest Model Level Height on the Performance of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations HYEYUM HAILEY SHIN AND SONG-YOU HONG Department
Air Quality Screening Modeling
 Air Quality Screening Modeling 2007 Meteorology Simulation with WRF OTC Modeling Committee Meeting September 16, 2010 Baltimore, MD Presentation is based upon the following technical reports available
Air Quality Screening Modeling 2007 Meteorology Simulation with WRF OTC Modeling Committee Meeting September 16, 2010 Baltimore, MD Presentation is based upon the following technical reports available
ANALYSIS OF THE MPAS CONVECTIVE-PERMITTING PHYSICS SUITE IN THE TROPICS WITH DIFFERENT PARAMETERIZATIONS OF CONVECTION REMARKS AND MOTIVATIONS
 ANALYSIS OF THE MPAS CONVECTIVE-PERMITTING PHYSICS SUITE IN THE TROPICS WITH DIFFERENT PARAMETERIZATIONS OF CONVECTION Laura D. Fowler 1, Mary C. Barth 1, K. Alapaty 2, M. Branson 3, and D. Dazlich 3 1
ANALYSIS OF THE MPAS CONVECTIVE-PERMITTING PHYSICS SUITE IN THE TROPICS WITH DIFFERENT PARAMETERIZATIONS OF CONVECTION Laura D. Fowler 1, Mary C. Barth 1, K. Alapaty 2, M. Branson 3, and D. Dazlich 3 1
WRF Modeling System Overview
 WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
WRF Modeling System Overview
 WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
Addressing Diurnal Temperature Biases in the WRF Model
 Addressing Diurnal Temperature Biases in the WRF Model Jeffrey Massey University of Utah Collaborators: Jim Steenburgh, Jason Knievel, Sebastian Hoch, Josh Hacker Long term 2-m temperature verification
Addressing Diurnal Temperature Biases in the WRF Model Jeffrey Massey University of Utah Collaborators: Jim Steenburgh, Jason Knievel, Sebastian Hoch, Josh Hacker Long term 2-m temperature verification
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection
 An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
An Intercomparison of Single-Column Model Simulations of Summertime Midlatitude Continental Convection S. J. Ghan Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington D. A. Randall, K.-M. Xu, and
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Toshi Matsui, Taka Iguchi, and Wei-Kuo Tao NASA GSFC Code 612 ESSIC UMD
 Precipitation Variability and Diurnal Cycle of Convection- Permitting Deterministic Simulations versus Mesoscale Multi-Physics Ensemble Simulations: A Preliminary Result from the NASA Downscaling Project
Precipitation Variability and Diurnal Cycle of Convection- Permitting Deterministic Simulations versus Mesoscale Multi-Physics Ensemble Simulations: A Preliminary Result from the NASA Downscaling Project
Developing Sub-Domain Verification Methods on GIS Tools
 Developing Sub-Domain Verification Methods on GIS Tools By Jeffrey A. Smith, Theresa A. Foley, John W. Raby, Brian Reen U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, NM Abstract The meteorological
Developing Sub-Domain Verification Methods on GIS Tools By Jeffrey A. Smith, Theresa A. Foley, John W. Raby, Brian Reen U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, NM Abstract The meteorological
Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities
 WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
Tue 2/16/2016. Wrap-up on some WRF PBL options Paper presentations (Hans, Pat, Dylan, Masih, Xia, James) Begin convective parameterization (if time)
 Tue 2/16/2016 Finish turbulence and PBL closure: Wrap-up on some WRF PBL options Paper presentations (Hans, Pat, Dylan, Masih, Xia, James) Begin convective parameterization (if time) Reminders/announcements:
Tue 2/16/2016 Finish turbulence and PBL closure: Wrap-up on some WRF PBL options Paper presentations (Hans, Pat, Dylan, Masih, Xia, James) Begin convective parameterization (if time) Reminders/announcements:
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases
 The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
The Total Energy Mass Flux PBL Scheme: Overview and Performance in Shallow-Cloud Cases Wayne M. Angevine CIRES, University of Colorado, and NOAA ESRL Thorsten Mauritsen Max Planck Institute for Meteorology,
Xuanli LI and Zhaoxia PU. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA
 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 87, No. 3, pp. 403--421, 2009. 403 DOI:10.2151/jmsj.87.403 Sensitivity of Numerical Simulations of the Early Rapid Intensification of Hurricane Emily
Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 87, No. 3, pp. 403--421, 2009. 403 DOI:10.2151/jmsj.87.403 Sensitivity of Numerical Simulations of the Early Rapid Intensification of Hurricane Emily
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting
 Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts
 Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts Chris Bretherton and Matt Wyant University of Washington Eric Grimit 3Tier NASA MODIS Image Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts PBL-related forecast
Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts Chris Bretherton and Matt Wyant University of Washington Eric Grimit 3Tier NASA MODIS Image Testing and Improving Pacific NW PBL forecasts PBL-related forecast
Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4)
 Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4) Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Nygård 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla
Towards the Fourth GEWEX Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model Inter-Comparison Study (GABLS4) Timo Vihma 1, Tiina Nygård 1, Albert A.M. Holtslag 2, Laura Rontu 1, Phil Anderson 3, Klara Finkele 4, and Gunilla
THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE
 JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
JP1.17 THE IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS SLANT-PATH WET DELAY MEASUREMENTS ON SHORT-RANGE PREDICTION OF A PREFRONTAL SQUALL LINE So-Young Ha *1,, Ying-Hwa Kuo 1, Gyu-Ho Lim 1 National Center for Atmospheric
TOVS and the MM5 analysis over Portugal
 TOVS and the MM5 analysis over Portugal YOSHIHIRO YAMAZAKI University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal MARIA DE LOS DOLORS MANSO ORGAZ University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal ABSTRACT TOVS data retrieved from
TOVS and the MM5 analysis over Portugal YOSHIHIRO YAMAZAKI University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal MARIA DE LOS DOLORS MANSO ORGAZ University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal ABSTRACT TOVS data retrieved from
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons)
 Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger Moist convec+on in models (and observa+ons) Cathy Hohenegger How do we parameterize convec+on? Precipita)on response to soil moisture Increase
An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation
 1 An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation Qifeng QIAN* 1, and Yanluan Lin 1 ABSTRACT The default SBU-YLIN scheme in Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) is
1 An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation Qifeng QIAN* 1, and Yanluan Lin 1 ABSTRACT The default SBU-YLIN scheme in Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) is
Tue 3/1/2016. Arakawa-Schubert, Grell, Tiedtke, Zhang-McFarlane Explicit convection Review for MT exam
 Tue 3/1/2016 Convective parameterization: Arakawa-Schubert, Grell, Tiedtke, Zhang-McFarlane Explicit convection Review for MT exam Reminders/announcements: - Midterm Thu 3/3 (2014 exam posted on www page)
Tue 3/1/2016 Convective parameterization: Arakawa-Schubert, Grell, Tiedtke, Zhang-McFarlane Explicit convection Review for MT exam Reminders/announcements: - Midterm Thu 3/3 (2014 exam posted on www page)
A Study of Sensitivity of WRF Simulation to Microphysics Parameterizations, Slope Option and Analysis Nudging in Haean Basin, South Korea
 A Study of Sensitivity of WRF Simulation to Microphysics Parameterizations, Slope Option and Analysis Nudging in Haean Basin, South Korea Kim, Jea-Chul (1); Lee, Chong Bum (1); Belorid, Miloslav (1); Zhao,
A Study of Sensitivity of WRF Simulation to Microphysics Parameterizations, Slope Option and Analysis Nudging in Haean Basin, South Korea Kim, Jea-Chul (1); Lee, Chong Bum (1); Belorid, Miloslav (1); Zhao,
Variational data assimilation of lightning with WRFDA system using nonlinear observation operators
 Variational data assimilation of lightning with WRFDA system using nonlinear observation operators Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida rstefane@vt.edu, inavon@fsu.edu
Variational data assimilation of lightning with WRFDA system using nonlinear observation operators Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida rstefane@vt.edu, inavon@fsu.edu
Tue 3/29/2016. Representation of clouds and precipitation:
 Tue 3/29/2016 Representation of clouds and precipitation: - Case study example of microphysics test - Bulk parameterizations: Process listing - WRF scheme options Convective parameterization paper summaries
Tue 3/29/2016 Representation of clouds and precipitation: - Case study example of microphysics test - Bulk parameterizations: Process listing - WRF scheme options Convective parameterization paper summaries
FORECASTING MESOSCALE PRECIPITATION USING THE MM5 MODEL WITH THE FOUR-DIMENSIONAL DATA ASSIMILATION (FDDA) TECHNIQUE
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 7, No 3, pp 258-263, 2005 Copyright 2005 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved FORECASTING MESOSCALE PRECIPITATION USING THE MM5 MODEL WITH THE FOUR-DIMENSIONAL DATA
Global NEST Journal, Vol 7, No 3, pp 258-263, 2005 Copyright 2005 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved FORECASTING MESOSCALE PRECIPITATION USING THE MM5 MODEL WITH THE FOUR-DIMENSIONAL DATA
A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004
 A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004 Jennifer M. Laflin Philip N. Schumacher NWS Sioux Falls, SD August 6 th, 2011 Introduction Forecasting challenge: strong forcing for ascent and large
A Study of Convective Initiation Failure on 22 Oct 2004 Jennifer M. Laflin Philip N. Schumacher NWS Sioux Falls, SD August 6 th, 2011 Introduction Forecasting challenge: strong forcing for ascent and large
Parameterization of effects of unresolved clouds and precipitation
 Parameterization of effects of unresolved clouds and precipitation eas471_cumparam.odp JDW, EAS, U. Alberta Last modified: 29 Mar. 2016 (from Physical Parameterizations in Canadian Operational Models,
Parameterization of effects of unresolved clouds and precipitation eas471_cumparam.odp JDW, EAS, U. Alberta Last modified: 29 Mar. 2016 (from Physical Parameterizations in Canadian Operational Models,
Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2. Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei
 Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2 Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei 1 Outline NCEP CFSRR Land component CFSv1 vs CFSv2 Land
Implementation of Land Information System in the NCEP Operational Climate Forecast System CFSv2 Jesse Meng, Michael Ek, Rongqian Yang, Helin Wei 1 Outline NCEP CFSRR Land component CFSv1 vs CFSv2 Land
ABSTRACT 2 DATA 1 INTRODUCTION
 16B.7 MODEL STUDY OF INTERMEDIATE-SCALE TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES AND COMPARISON TO TWP-ICE CAM- PAIGN OBSERVATIONS. S. Evan 1, M. J. Alexander 2 and J. Dudhia 3. 1 University of Colorado, Boulder,
16B.7 MODEL STUDY OF INTERMEDIATE-SCALE TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES AND COMPARISON TO TWP-ICE CAM- PAIGN OBSERVATIONS. S. Evan 1, M. J. Alexander 2 and J. Dudhia 3. 1 University of Colorado, Boulder,
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS
 A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting
 Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting Detlev Heinemann ForWind Center for Wind Energy Research Energy Meteorology Unit, Oldenburg University Contents Model Physics
Wind Flow Modeling The Basis for Resource Assessment and Wind Power Forecasting Detlev Heinemann ForWind Center for Wind Energy Research Energy Meteorology Unit, Oldenburg University Contents Model Physics
IMPACT OF ASSIMILATING COSMIC FORECASTS OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE CYCLONES OVER WEST ANTARCTICA
 IMPACT OF ASSIMILATING COSMIC REFRACTIVITY PROFILES ON POLAR WRF FORECASTS OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE CYCLONES OVER WEST ANTARCTICA David H. Bromwich 1, 2 and Francis O. Otieno 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd
IMPACT OF ASSIMILATING COSMIC REFRACTIVITY PROFILES ON POLAR WRF FORECASTS OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE CYCLONES OVER WEST ANTARCTICA David H. Bromwich 1, 2 and Francis O. Otieno 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd
WRF Modeling System Overview
 WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
WRF Modeling System Overview Jimy Dudhia What is WRF? WRF: Weather Research and Forecasting Model Used for both research and operational forecasting It is a supported community model, i.e. a free and shared
Interactions among Cloud, Water Vapor, Radiation and. Large-scale Circulation in the Tropical Climate. Department of Atmospheric Sciences
 Interactions among Cloud, Water Vapor, Radiation and Large-scale Circulation in the Tropical Climate Part 1: Sensitivity to Uniform Sea Surface Temperature Changes Kristin Larson * and Dennis L. Hartmann
Interactions among Cloud, Water Vapor, Radiation and Large-scale Circulation in the Tropical Climate Part 1: Sensitivity to Uniform Sea Surface Temperature Changes Kristin Larson * and Dennis L. Hartmann
Variable-Resoluiton Global Atmospheric Modeling Spanning Convective to Planetary Scales
 Variable-Resoluiton Global Atmospheric Modeling Spanning Convective to Planetary Scales Bill Skamarock, NCAR/MMM MPAS consists of geophysical fluid-flow solvers based on unstructured centroidal Voronoi
Variable-Resoluiton Global Atmospheric Modeling Spanning Convective to Planetary Scales Bill Skamarock, NCAR/MMM MPAS consists of geophysical fluid-flow solvers based on unstructured centroidal Voronoi
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development
 Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Using Cloud-Resolving Models for Parameterization Development Steven K. Krueger University of Utah! 16th CMMAP Team Meeting January 7-9, 2014 What is are CRMs and why do we need them? Range of scales diagram
Description of. Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill. Bill Skamarock. WPS d1 output. WPS d2 output Real and WRF. real.exe General Functions.
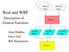 WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
Single-Column Modeling, General Circulation Model Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data
 Single-Column ing, General Circulation Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data S. F. Iacobellis, D. E. Lane and R. C. J. Somerville Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Single-Column ing, General Circulation Parameterizations, and Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Data S. F. Iacobellis, D. E. Lane and R. C. J. Somerville Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
RAMS - Regional Atmospheric Modeling System
 RAMS - Regional Atmospheric Modeling Sstem Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State Universit and ASTeR Division of Mission Research Corporation Rosie Polkinghorne ATOC 7500 - Meteorological Mesoscale
RAMS - Regional Atmospheric Modeling Sstem Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State Universit and ASTeR Division of Mission Research Corporation Rosie Polkinghorne ATOC 7500 - Meteorological Mesoscale
Jacobians of transformation 115, 343 calculation of 199. Klemp and Wilhelmson open boundary condition 159 Kuo scheme 190
 Index A acoustic modes 121 acoustically active terms 126 adaptive grid refinement (AGR) 206 Advanced Regional Prediction System 3 advection term 128 advective form 129 flux form 129 Allfiles.tar 26 alternating
Index A acoustic modes 121 acoustically active terms 126 adaptive grid refinement (AGR) 206 Advanced Regional Prediction System 3 advection term 128 advective form 129 flux form 129 Allfiles.tar 26 alternating
18.1 MODELING EXTREMELY COLD STABLE BOUNDARY LAYERS OVER INTERIOR ALASKA USING A WRF FDDA SYSTEM
 18.1 MODELING EXTREMELY COLD STABLE BOUNDARY LAYERS OVER INTERIOR ALASKA USING A WRF FDDA SYSTEM Brian Gaudet *, David Stauffer, Nelson Seaman, Aijun Deng Pennsylvania State University, University Park,
18.1 MODELING EXTREMELY COLD STABLE BOUNDARY LAYERS OVER INTERIOR ALASKA USING A WRF FDDA SYSTEM Brian Gaudet *, David Stauffer, Nelson Seaman, Aijun Deng Pennsylvania State University, University Park,
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
meso-sas, a modification of the SAS for meso-scale models Hua-Lu pan Qingfu Liu
 meso-sas, a modification of the SAS for meso-scale models Hua-Lu pan Qingfu Liu Problem with the conventional mass flux schemes Most of the mass-flux schemes are based on the original Arakawa-Schubert
meso-sas, a modification of the SAS for meso-scale models Hua-Lu pan Qingfu Liu Problem with the conventional mass flux schemes Most of the mass-flux schemes are based on the original Arakawa-Schubert
