First exercise p.90 to Choose: 1- c 2-b 3-b 4-c 5-a 6-c 7-b 8-c 9-c 10-b 11-a 12-a
|
|
|
- Marylou Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First exercise p.90 to 93 1-Choose: 1- c 2-b 3-b 4-c 5-a 6-c 7-b 8-c 9-c 10-b 11-a 12-a 2- x=2 y=10 3-Give reasons for: 1- Because they may increase the distance, move force from one place to another, increase the speed, avoid dangers, be accurate in performance. 2- Because the force arm is longer than the resistance arm as resistance lies between fulcrum and force. 3- Because the increase force, increase distance, move force from one place to another, increase the speed, avoid dangers, be accurate in performance. 4- Because it has high melting point and it emits light when it is heated as electric current passes through. 5- When one lamp is damaged the other lamps will not turned off and the intensity of the lamps will not be affected by the increase of their number. 6- To connect the filament with the electric current and to keep positions of the lamp in upright position. 7- To help the root penetration through soil particles and to facilitate water absorption. 8- Because it contains a large vacuole that contains concentrated salt solution to help water transmission from the soil to the root hair by osmosis. 9- To enables the plant to lose water in the form of water vapor through stomata. 10- Because the epidermal cells are lost from time to time during root growth through the soil particles. 11- Their shapes change to open or close the stoma. 12- It has selective permeability to allow some salts to pass through according to the plant s need. 13- To prevent electric shock as wood doesn t allow electric current to flow though. 4-What is meant by: 1- They don t allow electricity to pass through such as wood, rubber and glass. 2- It is the fire produced as a result of placing electrical machines that produce heat near flammable materials such as curtains or rugs, not disconnecting these machines after use or operating many electrical machines using the same socket and it can be put off using sand instead of water. 3- It is composed of: dry cell (battery), lamp, electric wire and a switch. All must be connected to close the circuit and lighten the lamp. Page 1 of 12
2 4- It allows only some mineral salts to pass through the root hair s cell membrane according to the plant s need and it needs energy which is produced by respiration. 5-see fig(3-7) book page Force x force arm = resistance x resistance arm 100 x 25 = 500 x resistance arm Resistance arm = 100 x 25 / 500 = 5 cm Second ex. Page 94, 95 First Q. : 1- Electric conductors. 2- levers. 3- galaxies. 4- transpiration. Second Q. : 1- b 2- c 3-a Third Q.: 1- when one lamp is damaged the other lamps will turn off and the intensity of lamps will decrease by increasing the number of lamps. 2- Total lunar eclipse occurs. 3- Partial lunar eclipse occurs. Forth Q. : 1-2-x 3-x 4-5-x Fifth Q.: 1- High melting point and emits light when it is heated. 2- Inert gas to increase the life time of the filament. 3- Their shapes change to open and close the stoma 4- Water is electric conductor which increases the fire and harm the rescuer. Sixth Q.; 1- It is the result of a current passing through the human body, the harms resulted depend on the strength of the electric current and the time taken by the current to flow through the body. Page 2 of 12
3 2- It happens when the moon, the sun and the earth are on a straight line with the moon in the middle and it is found in a higher orbit from the earth so the shadow area will not reach the earth and the sun appears as a ring. 3- They are flying astronomical observatories that are provided with cameras and telescopes to study stars and galaxies from their locations outside the earth s atmosphere. The first on launched in an orbit is Sputnik. 4- They re groups of millions of stars forming beams of light in the dark space. They are different in shape. 5- It is the process by which the plant loses water in the form of water vapor from the leaves through stomata. 6- It is the property by which the cell membrane of the root hair allows some salts to pass according to the plant s need. First Q.; Third ex. p.96 1-Lever 2-rigid bar 3-first third 4-Edison 5-parallel 6-argon 7- coductors- insulators 8-electric shock 9-earth-sun-moon 10-spiral-four 11-sticky 12-slective permeability Second Q.: 1- second class of levers 2- law lever 3-filament 4-levers 5- series connection 6-electric insulators 7-partial lunar eclipse 8-galaxies 9-telescope 10-stomata 11- transpiration Third Q.: 1- If one lamp turns off, the others keep working and light intensity doesn t change 2- As the sun emits harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiations the harm the retina of the eye leading to temporarily blindness. 3- Because the resistance arm is always longer than the force arm so force is larger than the resistance. 4- To allow the flow of electricity. 5- To prevent electric shock as insulators don t allow electricity to pass through. 6- To prevent electric fires. 7- When the moon, the sun and the earth are on a straight line with the moon in the middle. 8- See q.3 p To expose and direct the telescopes towards any part of the sky. 10- To find reasons for the astronomical phenomena happen in the sky. Page 3 of 12
4 Forth Q.: 1-x 2-x 3-4-x 5-x 6-x x Fifth Q.: 1-c 2-b 3-a 4-c 5-b 6-b 7-c 8-b 9-d 10-c 11-c 12-b Sixth Q.: 1-second 2-inert 3-electric conductor copper wire 4-second 5-filaments 6- light 7-iron 8-18 years 9-annular 10-Galilleo 11-root hair 12-two guard cells 13- transpiration Seventh Q.: Points of comparison First class Second class Third class Definition Levers in which the fulcrum lies between the resistance and the force and they may conserve effort. Levers in which the resistance lies between the fulcrum and the force and they always conserve effort. Levers in which the force lies between the resistance and the fulcrum and they never conserve effort. Save effort Sometimes save effort Always save effort Never save effort. Points of comparison Series connection Parallel connection Light intensity Decreases by increasing the number of lamps Remains constant and is not affected by increasing or decreasing the number of lamps. Removing one lamp The other lamps will turn off The other lamps will keep working Electric conductors Materials that allow electricity to flow through. Ex: all metals, water, graphite, human body Electric insulators Materials that don t allow electricity to flow through. Ex: rubber, glass, wood, paper Total solar eclipse Formed in the shadow area (umbra) of the moon in which we cannot see the sun completely only sun corona appears. Total lunar eclipse Occurs when the whole moon enters the shadow area (umbra) of the earth. Page 4 of 12
5 Light bulb Structure: glass bulb filled with argon gas, tungsten filament, metal base connected to one or two pieces of lead. Fluorescent lamp Structure: glass tube filled with argon gas and little mercury and lined from inside with phosphoric material, two tungsten filaments one at each tip,two points of connection on each tip Direct injuries They are injuries that result from direct dealing with electricity such as electric fire, electric shock and electric burn Indirect injuries Injuries that result from falling from the ladder due to electric shock. Umbra area The real shadow area (cone shadow) formed when an opaque object totally blocks the light. Penumbra area The semi-shadow area where some light falls on it. Eighth Q.: 1) 1-b 2-c 3-a 4-g 5-d 2) 1-c 2-b 3-e 3) 1-c 2-b Ninth Question: What happens if: 1- We will not be able to perform many tasks such as saving effort or avoiding danger or increasing speed. 2- Astronomers will not be able to monitor movements of planets and moon, also they will not be able to study locations of stars. 3- The moon appears red and it is a total lunar eclipse. 4- Wrong question. 5- The lever will save effort. 6- It will not glow when heated. 7- The filament will burn. 8- It will cause many dangers such as electric shock or fire or burn. 9- Electricity will not flow and the lamp will not light. 10- They can cause electric shock. 11- It can cause blindness to him and affects his retina. Page 5 of 12
6 12- No transpiration process. 13- It creates a pulling force that raises water to the top of the plant. 14- The opening and closure of stoma will not be controlled and will not be able to control the water loss. 15- Water will not enter the root hair and epidermis. 16- Root hair will not be able to penetrate easily through soil particles. 17- Water will not enter by osmosis process. 18- The ball is close to the light source, the shadow area behind it is bigger than far from the Light source. 19- The fire will increase as water is an electric conductor. Tenth Question: First: 1- Light bulb. 2- Electric wire. 3- Positive pole. 4- Battery. Second: 1- Epidermis. 2- Cortex. 3- Endodermis. 4- Xylem. Third: 1- Penumbra. 2- Moon. 3- Sun. 4- Earth. Eleventh Question: Problems: 1- Resistance arm= force its arm resistance= 8 2 4= 4cm. 2- Resistance= force its arm resistance arm= = 100 N. 3- Resistance= force its arm resistance arm= = 320 N. 4- Force arm= resistance its arm force = = 10 cm. Page 6 of 12
7 1- Write the scientific term: a- Fulcrum. b- Electric fire. c- Root hairs. d- Wrong question. 2- Put ( ) or ( ) and correct: a- ( ), it doesn t affect life on earth. Test (1) p. 111 b- ( ), aren t extinguished by water or are extinguished by sand. c- ( ) The leaves in plants are responsible for photosynthesis process. d- ( ) e- (X) if the force arm is longer. 3- Complete: a- Second. b- Electricity. c- Stoma. d- Resistance its arm. 4- Compare: a- Check p.64 and revision sheets. b- Good conductors of electricity: are materials that allow electricity to pass through.(water iron copper ) Electric insulators: are materials that don t allow electricity to pass through( rubber plastic wood ). 5- Give reason: 1- Because solar eclipse occurs when the umbra region of the moon falls on the earth s surface while lunar eclipse occurs when the moon enters the umbra region of the earth. 2- Because this can cause an electric fire. 3- As the fulcrum is in the middle. 4- Because the earth and moon are moving in fixed orbits with constant speed. 5- Resistance arm= force its arm resistance= = 50cm. 6- Solar eclipse. Page 7 of 12
8 Q(1): a- 1 b- 1 c- 3 d- 4 e- 1 Q(2): Test (2) 1- To allow the penetration of water and salts through them. 2- Because sometimes the force arm can be longer than resistance arm in first class levers. 3- To protect the filament from burning as it is an inert gas. 4- Because water is an electric conductor. 5- To protect our eyes from the harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays that affects the retina. Q(3): A) What happens if: 1- It will not glow when heated. 2- He will have an electric shock. 3- Nothing will control the penetration of water and salts to the root hairs. B) Mention one function: 1- Changes electric energy to light energy. 2- Helps us to monitor movements of planets and moon, also it helps us to study locations of stars. Q4: a) What is the difference: 1- Total solar eclipse: all the sun is covered and we can see only the corona and you are in the umbra of the moon. Partial solar eclipse: part of the sun only is covered by the moon and you are in the penumbra of the moon. 2-3 rd class levers: never save effort while 2 nd class levers: always save effort. b) What s meant by: 1- Rigid bar that rotates around fixed point and affected by force and resistance. 2- The loss of water from the plants in the form of water vapour. 3- The type of injury happens when electricity pass through a human body. Q(5); 1- Human body is a good conductor of electricity. 2- We cannot see the sun completely in the partial eclipse. 3- The root hair absorb water and salts from the soil. 4- Galaxies are groups of millions of stars. 5- Stomata spread on the lower surface of the plants leaves. Page 8 of 12
9 Q(1): a- 2 b- 2 c- 1 Test (3) d- 2 e- 2 Q(2): 1- Because force arm is always longer than resistance arm. 2- To conduct electricity from the circuit to the lamp. 3- Because they are lost from time to time by the resistance of soil particles during root expansion. 4- Because the sun produces ultraviolet and infrared rays which harm the eye. 5- To allow the water to move from the soil to the root hair and epidermis by osmosis process. Q(3): A) What happens : 1- The transpiration process will not happen and water will not rise from the root to the top of the plant. 2- Filament will burn. 3- See Q2 P107. Q(4): B) What s meant by: 1- The fixed point that the lever rotates around. 2- Check Q4 p The movement of water molecules from the higher water concentration to the lower water concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Q(5): 1- ( ) first class. 2- ( ) 3- ( ) has spiral shape and four arms. 4- ( ) collecting light. 5- ( ) Page 9 of 12
10 1) Choose: a- 1 b- 1 c- 2 d- 2 2) Write the scientific term: 1- Series connection. 2- Transpiration. 3- Galaxies. 4- Total lunar eclipse. 3) Put( ) or ( ): 1- ( ) thin. 2- ( ) lower surface. 3- ( ) Jupiter. 4- ( ) solar eclipse. 5- ( ) argon gas. 6- ( ) 4) Give reason: Test (4) 1- To help in the root penetration through soil particles. 2- So light intensity of lamps will not be affected by increasing number of lamps and if one lamp is burned the others are not affected. 3- As the arm of force is smaller than the arm of resistance and the force is greater than the resistance. 4- To protect the filament from burning. 5) See p43. 6) Resistance= force its arm resistance arm= = 200N. Page 10 of 12
11 Test (5) First question: 1- Force resistance. 2- Effort force resistance force. 3- Direct- indirect. 4- Moon- earth. Second question: A) Write the scientific term: 1- Third class. 2- Total lunar eclipse. 3- Parallel connection. B)1- Lead piece. 2- base. 3- copper and lead wires. 4- glass bulb. 5- tungsten filament. Third question: A) Give reason: 1- To get rid of water in the form of water vapor by transpiration. 2- Because the earth is bigger than the sun so even if the moon is in a higher orbit, the earth s shadow will cover it. 3- Because force arm is longer than resistance arm. b) What s meant by: 1- Materials that allow electricity to pass through. 2- When sun, earth and moon are in one straight line with the earth in the middle and part of the moon enters the shadow area of the earth. Fourth question: A) Put( ) or ( ): 1- ( ) 2- ( ) 3- ( ) 4- ( ) 5- ( ) c) force its arm= = resistance its arm = = as they are equal so this lever is balanced. Page 11 of 12
12 First question: 1- force fulcrum. 2- Moon-sun. 3- Galileo telescope. 4- Stomata- transpiration. Second question: 1- First class. 2- Galaxies. 3- Root. 4- Electric lamp. Third question: a) Give reason: Test(6) 1- Because force arm is shorter than resistance arm. 2- Because it is surrounded by thin membrane and contains concentrated salt solution that allow the osmosis process to happen. 3- To avoid having an electric shock as they don t allow electricity to pass through. b) What is meant by: 1- When the sun, earth and moon are in one straight line with the earth in the middle. 2- See q4 (b) P114 Fourth question: A) Put( ) or ( ): 1- ( ) 2- ( ) 3- ( ) short age. 4- ( ) Jupiter. c) force its arm = = 5000 resistance its arm= = 4000 as they are not equal so this lever is not balanced. Page 12 of 12
Sixth primary science
 Sixth primary science Complete the following : 1 ) Levers are three types.& & 2 ) The craw bar is considered a class lever, but the manual broom is a...class lever 3 ) &..are example of the first class
Sixth primary science Complete the following : 1 ) Levers are three types.& & 2 ) The craw bar is considered a class lever, but the manual broom is a...class lever 3 ) &..are example of the first class
Science Primary /2018. Teacher's Name:... Name :. Work Sheets SE C O N D T E R M
 The Vision of the School :Distinct Environment for Refined Education Work Sheets SE C O N D Science Primary 6 2017 /2018 Teacher's Name:... Name :. Class : T E R M -0- Unit 1 : Force and Motion Lesson
The Vision of the School :Distinct Environment for Refined Education Work Sheets SE C O N D Science Primary 6 2017 /2018 Teacher's Name:... Name :. Class : T E R M -0- Unit 1 : Force and Motion Lesson
1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance
![1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance](/thumbs/85/92584639.jpg) 1)Write the scientific term: 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance [ ] 3. Levers that have the fixed point between the force &
1)Write the scientific term: 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance [ ] 3. Levers that have the fixed point between the force &
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch. Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers
 Governorate Department: Science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch A- Complete: Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers 1- is a rigid bar that
Governorate Department: Science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch A- Complete: Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers 1- is a rigid bar that
The lever is: a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called fulcrum and is affected by force and resistance.
 1-Types of Levers All of the simple machines have common properties such as: 1- Different in shape and size. 2- Consist of rigid bar. 3- Made of different materials. 4- A person must inflict force on the
1-Types of Levers All of the simple machines have common properties such as: 1- Different in shape and size. 2- Consist of rigid bar. 3- Made of different materials. 4- A person must inflict force on the
Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch Department: Science Form : 6 th Primary Unit ( 1 ) Lesson ( 1 ) : Type of levers A- Complete: 1- is a rigid
Cairo Governorate Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch Department: Science Form : 6 th Primary Unit ( 1 ) Lesson ( 1 ) : Type of levers A- Complete: 1- is a rigid
Model Exam. 6 th Primary. 2 nd term. Name:. Class:..
 Model Exam 6 th Primary 2 nd term Name:. Class:.. 1 Model (1) Answer the following questions : 1- [A] Complete the following sentences : 1) The fluorescent lamps contain...gas and a little of... 2) One
Model Exam 6 th Primary 2 nd term Name:. Class:.. 1 Model (1) Answer the following questions : 1- [A] Complete the following sentences : 1) The fluorescent lamps contain...gas and a little of... 2) One
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Station 1 - Applicability Reading Total Solar Eclipse
 Station 1 - Applicability Reading Total Solar Eclipse Instructions : Read the following information article and answer the associated questions found below. Total solar eclipses occur when the Moon comes
Station 1 - Applicability Reading Total Solar Eclipse Instructions : Read the following information article and answer the associated questions found below. Total solar eclipses occur when the Moon comes
Wave - Particle Duality of Light
 Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Electricity. What is electricity?
 Words attract = pull towards an object back and forth = to go in one direction and then in the other balanced = the same as stable carbon = a chemical material that is in coal or petrol. It is in its purest
Words attract = pull towards an object back and forth = to go in one direction and then in the other balanced = the same as stable carbon = a chemical material that is in coal or petrol. It is in its purest
Creating eclipses in the classroom
 Creating eclipses in the classroom During an eclipse, the Sun or the Moon seems to disappear, these are called solar or lunar eclipses, respectively. These astronomical phenomena have been shrouded in
Creating eclipses in the classroom During an eclipse, the Sun or the Moon seems to disappear, these are called solar or lunar eclipses, respectively. These astronomical phenomena have been shrouded in
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P ) What Is Light? What Is Light?
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
Chapter 26: Properties of Light
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at January 2016
 Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
Name: Grade 6 Date: REVISION BOOKLET
 REVISION BOOKLET science 1 Chapter # 16 MACHINES QA: Read each question and choose the best answer. Then fill in the circle next to the correct answer. 1. Dan and Paul push a box 4 meters with a force
REVISION BOOKLET science 1 Chapter # 16 MACHINES QA: Read each question and choose the best answer. Then fill in the circle next to the correct answer. 1. Dan and Paul push a box 4 meters with a force
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced)
 The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary. Ismailia Road Branch
 Governorate Department : science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary Nozha Language Schools Revision sheet Ismailia Road Branch Question on Lesson ( 1 ) I ) Complete the following statements
Governorate Department : science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary Nozha Language Schools Revision sheet Ismailia Road Branch Question on Lesson ( 1 ) I ) Complete the following statements
Light is an important form of energy for all of us
 What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview
 Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Topic 5 Practice Test
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere 1. The Earth surface that best absorbs short-wave
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which represents the greenhouse effect in which heat energy is trapped in Earth's atmosphere 1. The Earth surface that best absorbs short-wave
Investigating Planets Name: Block: E1:R6
 FYI: Planetary Temperatures and Atmospheres Read FYI: A Planet s Temperature, The Importance of an Atmosphere, and The Greenhouse Effect As you read answer the following questions about the readings: Word/Term
FYI: Planetary Temperatures and Atmospheres Read FYI: A Planet s Temperature, The Importance of an Atmosphere, and The Greenhouse Effect As you read answer the following questions about the readings: Word/Term
CHAPTER TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants Animals, including humans Rocks Light Forces and magnets
 Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Introduction To Modern Astronomy II
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 786 Level 870L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 20 of 34
 Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
Page 20 of 34 (i) The role of haemoglobin in transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide To include the reversible binding of oxygen molecules, carbonic anhydrase, haemoglobinic acid, HCO3- and the chloride
of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does not cross the
 Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
Uptake of water The through Casparian Strip blocks root epidermis by passage osmosis of water unless it is moving via the symplast Water moves into the xylem for transport up the plant Water that does
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer
![L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer](/thumbs/78/76842080.jpg) L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
Science subject progression and skills
 Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Primary Science Curriculum Pupil Assessment Record
 Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Transport in Vascular Plants
 Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Vascular tissue Transports nutrients throughout a plant; such
Static Electricity. Electric Field. the net accumulation of electric charges on an object
 Static Electricity the net accumulation of electric charges on an object Electric Field force exerted by an e - on anything that has an electric charge opposite charges attract like charges repel Static
Static Electricity the net accumulation of electric charges on an object Electric Field force exerted by an e - on anything that has an electric charge opposite charges attract like charges repel Static
Skills and Knowledge Progression. Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
 Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
SHORT DISCOVERY-BASED STEM EXPERIENCES STEM. Brought to you by the NATIONAL AFTERSCHOOL ASSOCIATION
 SHORT DISCOVERY-BASED STEM EXPERIENCES STEM gems Brought to you by the NATIONAL AFTERSCHOOL ASSOCIATION SOLAR ECLIPSE big IDEAS ON MONDAY AUGUST 21, 2017 NORTH AMERICA WILL BE TREATED TO A RARE CELESTIAL
SHORT DISCOVERY-BASED STEM EXPERIENCES STEM gems Brought to you by the NATIONAL AFTERSCHOOL ASSOCIATION SOLAR ECLIPSE big IDEAS ON MONDAY AUGUST 21, 2017 NORTH AMERICA WILL BE TREATED TO A RARE CELESTIAL
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Science Curriculum Map Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2
 The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
Electromagnetic Waves
 4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
 Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
Question 1: What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion of
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
In class quiz - nature of light. Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel)
 In class quiz - nature of light Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel) Nature of light - review Light travels at very high but finite speed. Light is electromagnetic wave characterized by wavelength (or
In class quiz - nature of light Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel) Nature of light - review Light travels at very high but finite speed. Light is electromagnetic wave characterized by wavelength (or
Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc humans
 Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Year 1 Science overview
 Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
McKinley Presidential Library & Museum Planetarium Show Ohio Science Standards Fifth Grade
 Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
Fairlawn Primary School Science Curriculum
 Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
LIGHT. A beam is made up of several rays. It maybe parallel, diverging (spreading out) or converging (getting narrower). Parallel Diverging Converging
 LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
Science Curriculum Map: KS1 & KS
 Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Announcements. Astronomical perspective. The Greek Model of the Solar System Geocentric model (because the Earth is at the center)
 Astronomy 101: 9/25/2008 Announcements Exam study materials will be posted on the course web page tomorrow. Homework 2 is now available on the OWL Due 10/01/08 before midnight 1st midterm: 10/2/08 Midterms
Astronomy 101: 9/25/2008 Announcements Exam study materials will be posted on the course web page tomorrow. Homework 2 is now available on the OWL Due 10/01/08 before midnight 1st midterm: 10/2/08 Midterms
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2. Science. Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC
 Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6. Herts for Learning Ltd.
 HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
Parkstone Primary School Science Long Term Plan Updated January 2017
 Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
Answer Key for Exam C
 Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B
 Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Obtain an optical "bench" setup (there should be three sliding mounts on the calibrated horizontal bar. The setup is shown in the diagram below.
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 4: Telescopes and spectroscopy Once the various focal issues are resolved, magnification of a small image is a significant consideration for a telescope. Though a planet
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 4: Telescopes and spectroscopy Once the various focal issues are resolved, magnification of a small image is a significant consideration for a telescope. Though a planet
Chapter 26. Properties of Light
 Chapter 26 Properties of Light James Clerk Maxwell discovered that light is composed of a. electromagnetic waves. b. ultrasonic waves. c. infrasonic waves. d. electron vibrations. James Clerk Maxwell discovered
Chapter 26 Properties of Light James Clerk Maxwell discovered that light is composed of a. electromagnetic waves. b. ultrasonic waves. c. infrasonic waves. d. electron vibrations. James Clerk Maxwell discovered
Madinaty Language School Science Department Class: Revision Sheet
 Madinaty Language School Science Department Name: Class: Grade Four Revision Sheet 1)Choose the correct answer : 1) The amount of matter in an object is called a-length b-matter c-mass 2) The space occupied
Madinaty Language School Science Department Name: Class: Grade Four Revision Sheet 1)Choose the correct answer : 1) The amount of matter in an object is called a-length b-matter c-mass 2) The space occupied
National Curriculum 2014: Progression in Science
 Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
The Moon -Around the Earth and in the Sky
 The Moon -Around the Earth and in the Sky Our goals for learning: Why do we see phases of the Moon? When do we see the phases of the Moon? What causes eclipses? Why do we see phases of the Moon? Lunar
The Moon -Around the Earth and in the Sky Our goals for learning: Why do we see phases of the Moon? When do we see the phases of the Moon? What causes eclipses? Why do we see phases of the Moon? Lunar
St Olave s Physics Department. Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist
 St Olave s Physics Department Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 11 Mock exam. Students should use the tickboxes to check
St Olave s Physics Department Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 11 Mock exam. Students should use the tickboxes to check
Solution 3: A glass prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
 EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
solar system outer planets Planets located beyond the asteroid belt; these are known as the gas giants. CELESTIAL BODIES
 solar system Region of our galaxy under the influence of the ; includes eight planets and their natural satellites as well as one dwarf planet, two plutoids, asteroids and comets. outer planets Planets
solar system Region of our galaxy under the influence of the ; includes eight planets and their natural satellites as well as one dwarf planet, two plutoids, asteroids and comets. outer planets Planets
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 3.3: Transport in plants Notes Plants require a transport system to ensure that all the cells of a plant receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is achieved through
Band 1 - Science All. Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans Materials. Plants. Seasonal Changes
 Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves.
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
Electricity. Prepared by Juan Blázquez, Alissa Gildemann. Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena.
 Unit 11 Electricity 1. Electric charge Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena. Electrical phenomena are caused by the forces of attraction and repulsion.
Unit 11 Electricity 1. Electric charge Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena. Electrical phenomena are caused by the forces of attraction and repulsion.
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
The greenhouse effect
 16 Waves of amplitude of 1 m roll onto a beach at a rate of one every 12 s. If the wavelength of the waves is 120 m, calculate (a) the velocity of the waves (b) how much power there is per metre along
16 Waves of amplitude of 1 m roll onto a beach at a rate of one every 12 s. If the wavelength of the waves is 120 m, calculate (a) the velocity of the waves (b) how much power there is per metre along
An eclipse is when light from a moon or sun gets blocked. People can see two kinds of eclipses from Earth.
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 584 Level 570L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 584 Level 570L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
 Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Light. An Introduction
 Light An Introduction What is light? Light is a form of energy it can make things move What other form of energy have we dealt with? Heat is also a form of energy Quite often light energy and heat energy
Light An Introduction What is light? Light is a form of energy it can make things move What other form of energy have we dealt with? Heat is also a form of energy Quite often light energy and heat energy
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves
 Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
Plant Anatomy: roots, stems and leaves The plant body has a hierarchy of organs, tissues and cells Plants, like animals, have organs composed of different tissues, which are composed of cells. Tissue is
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document. September 2014
 Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Chapter 17, Electromagnetic Waves Physical Science, McDougal-Littell, 2008
 SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
ELECTRICITY. Chapter ELECTRIC CHARGE & FORCE
 ELECTRICITY Chapter 17 17.1 ELECTRIC CHARGE & FORCE Essential Questions: What are the different kinds of electric charge? How do materials become charged when rubbed together? What force is responsible
ELECTRICITY Chapter 17 17.1 ELECTRIC CHARGE & FORCE Essential Questions: What are the different kinds of electric charge? How do materials become charged when rubbed together? What force is responsible
Name Class Date. a. Light is a wave. 2. Empedocles. b. Light consists of tiny 3. Euclid
 Exercises 27.1 Early Concepts of (page 533) Scientist Idea About 1. Einstein a. is a wave. 2. Empedocles b. consists of tiny 3. Euclid particles. 4. Huygens c. Vision results from streamers or filaments
Exercises 27.1 Early Concepts of (page 533) Scientist Idea About 1. Einstein a. is a wave. 2. Empedocles b. consists of tiny 3. Euclid particles. 4. Huygens c. Vision results from streamers or filaments
What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017
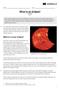 Name: Class: What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017 Solar and lunar eclipses are some of the beautiful, outerspace events that we are able to witness from Earth. This text details how solar and lunar eclipses
Name: Class: What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017 Solar and lunar eclipses are some of the beautiful, outerspace events that we are able to witness from Earth. This text details how solar and lunar eclipses
F = ma P 2 = a 3 (M + m) P 2 = a 3. max T = 2900 K m
 Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 1 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Summer 2013 Astronomy - Test 1 Test form A Name Do not forget to write your name and fill in the bubbles with your student number, and fill in test form A on the answer sheet. Write your name above as
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky
 Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold?
 Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Essential Characteristics of Scientists
 SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
DOSTHILL PRIMARY SCHOOL I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science
 I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
Transport of substances in plants
 Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
5thscience physical (5thscience_physical)
 5thscience physical (5thscience_physical) Name: Date: 1. Which circuit would turn the light bulb on? A. B. C. D. 2. Which item would conduct electricity? A. a glass cup B. a chicken feather C. a plastic
5thscience physical (5thscience_physical) Name: Date: 1. Which circuit would turn the light bulb on? A. B. C. D. 2. Which item would conduct electricity? A. a glass cup B. a chicken feather C. a plastic
fr>uafcji *> \E % jw r"'''f^,""'i;- ~^H^^
 NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
Electric Charges & Current. Chapter 12. Types of electric charge
 Electric Charges & Current Chapter 12 Types of electric charge Protons w/ + charge stuck in the nucleus Electrons w/ - charge freely moving around the nucleus in orbits 1 Conductors Allow the easy flow
Electric Charges & Current Chapter 12 Types of electric charge Protons w/ + charge stuck in the nucleus Electrons w/ - charge freely moving around the nucleus in orbits 1 Conductors Allow the easy flow
2 sentences. Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct
 2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it. 3. Electrons in the outer electron shells have greater potential energy.
 30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
Investigating Stomata
 Investigating Stomata Learning Objectives: To be able to identify stomata and compare stomata on leaves of a plant To understand the function of stomata and the role they play in a plant To understand
Investigating Stomata Learning Objectives: To be able to identify stomata and compare stomata on leaves of a plant To understand the function of stomata and the role they play in a plant To understand
12.2. The Earth Moon System KNOW? The Phases of the Moon. Did You
 12.2 The Earth Moon System Did You KNOW? The Moon is Earth s closest neighbour. It is highly influential in our lives because it causes the oceans tides. The Moon is also responsible for eclipses. waxing
12.2 The Earth Moon System Did You KNOW? The Moon is Earth s closest neighbour. It is highly influential in our lives because it causes the oceans tides. The Moon is also responsible for eclipses. waxing
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM PART I Multiple Choice Answer all questions in this part [60 pts] Directions (1-30): For each statement of question, select the word or expression that best completes the statement
