Model Exam. 6 th Primary. 2 nd term. Name:. Class:..
|
|
|
- Briana McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Model Exam 6 th Primary 2 nd term Name:. Class:.. 1
2 Model (1) Answer the following questions : 1- [A] Complete the following sentences : 1) The fluorescent lamps contain...gas and a little of... 2) One of the dangers of the electricity which is causing the damage of the tissues of the body is called... 3) The sweet holder is from the.. class lever. 4) The electric lamps in houses are not connected in... [B] Mention the name of scientist who : 1) Invented the light bulb? (...) 2) Was the first one made an astronomical telescope in 1609?(...) 2- [A] Choose the correct answer: 1) The electric lamp converts electric energy into...energy. a. kinetic b. light c. sound 2) The biggest and the oldest source of light is... a. candle. b. glowing lamp. c. the sun. 3) The lunar eclipse phenomenon occurs in the.of the lunar month. a. end b. middle c. first 4) Force arm is always longer than resistance arm in the...class lever. a. first b. second c. third [B] A force of 100 Newton affected a lever, its force arm 10 cm. and its resistance is 20 Newton and resistance arm 50 cm. 1) Is this lever balanced or not. 2) Why? 3- [A] Write the scientific term for each of the following sentences : 1) Materials that allow the flow of electricity through them. (...) 2) The closed route through which electric current passes. (...) 2
3 3) Phenomenon occurs when a part of the moon enters the shadow area of the earth. (...) 4) A rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called fulcrum, and is affected by force and resistance. (...) [B] Mention one function for each of the following : 1) The base of the light bulb. 4- [A] Put ( ) in front of the correct statements and ( ) in front of the wrong statements in each of the following: 1) The solar eclipse is a phenomenon that does not last more than seven hours. ( ) 2) Third class levers do not conserve the effort. ( ) 3) The filament of the light bulb is made of aluminum. ( ) [B] What happen in each case of the following: 1) Putting off fires that resulting from electricity with water.. 2) Observation of the solar eclipse directly without using special glasses.. 3
4 Model (2) Answer the following questions : 1- [A] Complete the following sentences : 1) The type of lever in which the force arm equals the resistance arm is... 2) The fluorescent lamp contains the inert...gas. 3) When the moon comes in an orbit higher from earth,... solar eclipse is formed. 4) The sun glow in the solar eclipse is... [B] What would happen if...? 1) Putting of the electric fires with water. 2) Someone looks to the sun directly with the naked eye for a long time. 2- [A] Choose the correct answer : 1) All the following are possible to be functions of levers except... a. increasing force. b. decreasing speed. c. increasing distance. d. avoid dangers. 2) Lunar eclipse occurs when the earth is on straight line with the moon and the sun, and the... a. earth is between the moon and the sun. b. moon is between the earth and the sun. c. sun is between the earth and the moon. d. stars are between the earth and the moon. [B] A third class lever has force arm of length 5 cm, and the length of resistance arm is 15 cm. if the resistance is 300 Newton. Calculate the affecting force [A] Put ( ) in front of the correct statements and ( ) in front of the wrong statements: 1) The duration of solar eclipse doesn't exceed seven minutes and few seconds. ( ) 2) If the resistance arm is longer than the force arm, the lever saves effort. ( ) 3) The spiral base of the light bulb glows due to passing the electric current through it. ( ) 4) The moon revolves around the earth in an oval orbit. ( ) 4
5 [B] Complete the following tables : 1. Point of First class lever comparison Mid point Second class lever Third class lever 2. Points of comparison Light intensity of the lamps Removing one of the lamps from the connection Connecting in series Connecting in parallel 4- [A] Write the scientific term for each of the following : 1) It occurs when a part of the moon enters the shadow of the earth. (...) 2) The fixed point of a rigid bar. ( ) 3) A force that is exerted by a person to equilibrate the resistance force. (.) 4) The most popular type of lever in our daily life. ( ) 5) The type of lever where the mid-point is the effort force.( ) [B] The drawing represents : (1)... (2)... (3)... (4)... 5
6 Answer the following questions : Model (3) 1- [A] Complete the following sentences : 1) The type of levers that always conserves effort is...while the type of levers that always doesn't conserve effort is... 2) Lunar eclipse phenomenon occurs when...is located between... and... 3)...is an example of the first class levers. [B] Give reasons for the following : 1) Avoiding the usage of water in putting off fires resulted from electricity [A] Choose the correct answer: 1) From the examples of bad electric conductors substances is... a. iron. b. plastic. c. copper. 2) The 1 st class lever differs from the 2 nd class lever in... a. the absence of the acted force. b. the presence of fixed point to rest on. c. the position of the fulcrum 3) Which of the following gases is found in the florescent lamp but not in the electric bulb... a. neon. b. argon. c. mercury vapour. [B] What is meant by: 1) Partial solar eclipse :... 2) The lever: [A] Write the scientific term for the following: 1) A phenomenon occurs when a part of the moon enters the shadow area of the earth. [ ] 2) A way in which the light bulbs is connected one after one and the light intensity of the bulbs decreases with the increase in their number. [ ] 6
7 [B] The exerted force of a first class lever equal 250 Newton and the length of its arm is 10 cm. and it is affected by a resistance of 100 Newton. Find the value of the resistance arm length [C] What happens if: 1) There is air inside the light bulb... 2) Someone looks to the sun directly with the naked eye for a long time [A] Correct the underlined part : 1) There are two points of connection from inside on both tips of the lamp. (...) 2) The simple electric circuit consists of battery, lamp and an insulator to connect the battery with lamp. (...) 3) Some levers allow the increase in the speed of objects as in the manual broom. (...) [B] The figure represents the solar eclipse phenomenon write the labels from 1-4 7
8 Model (4) Answer the following questions : 1- Complete the following sentences : 1) The scissors are an example of the...levers. 2) The type of the levers where the arm of the force and the arm of resistance are equal is... 3) In case of connecting the lamps in...the lighting of the lamps decreases with the increase in their number. 4)...solar eclipse occurs when the moon is located in a higher orbit than the Earth. 5) The electric shock occurs as a result of passing...through the human body. 6) The filament of the light bulb is made of [A] Write the scientific term for each of the following : 1) A tool converts the electric energy to light energy. (...) 2) One of the dangers of the electricity causing the damage of the tissues of the body. (...) [B] Give reason for each of the following: 1) We should not look directly at the sun with the naked eye. 2) The electric wires are made of copper. 3- [A] The force affecting a second class lever equals 200 Newton and the length of its arm is 50 cm, and has a resistance with value 1000 Newton. Calculate the value of the arm of the resistance. [B] Compare between each of the following in a table : 1) Second class levers and third class levers according to... a. The arm of force and the arm of resistance. b. Saving effort. 2) Series connection and parallel connection of the electric lamps according to... a. The light intensity of the electric lamps with the increase of their number. b. The route of the electric current. 8
9 3) The conducting materials of electricity and the non-conducting materials of electricity according to... a. Definition. b. One example. 4- [A] What happens if: 1) There is air inside the light bulb.... 2) You insert a metallic bar in an electric socket.... 3) The earth comes between the sun and the moon and they are all in one straight line.... 4) Burning an electric bulb in an electric circuit contains many electric bulbs connected in series.... [B] Choose the correct answer from a, b or c: 1) All the following are functions of levers except... a. increasing force. b. increasing speed. c. increasing size. 2) All the following are the types of lunar eclipse except... a. annular eclipse. b. total eclipse. c. partial eclipse. 3) Which of the following is found in the fluorescent lamps and is not found in the electric lamps... a. neon gas. b. argon gas. c. mercury vapour. 9
10 Model (5) Answer the following questions: 1- [A] Write the scientific term for each of the following : 1) The fixed point of a rigid bar. (...) 2) One of the dangerous of the electricity occurs as a result of the passage of electric current to the human body. (...) [B] Give reasons: 1) The lunar eclipse occurs in the middle of the lunar month. 2- Complete the following statements : 1) The fish hook is a.. class lever. 2) arm of resistance.. arm of resistance =... 3) There are.types of solar eclipses, which are., and.. 4) The. is formed when a dark object blocks a part of the incoming light. 3- [A] Correct the underlined in the following sentences : 1) The partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes in an orbit higher to earth. (.) 2) Wood is considered a good conductor of electricity. (.) 3) The nutcracker is a first class lever. (.) 4) The plant converts electric energy to light energy. (. ) [B] What is meant by: 1) lever.. 2) Insulators of electricity Complete the following table: Points of comparison Series connection Parallel connection 1- Light intensity of the electric lamp. 2- Damage or turning off any of the lamps. 10
Science Primary /2018. Teacher's Name:... Name :. Work Sheets SE C O N D T E R M
 The Vision of the School :Distinct Environment for Refined Education Work Sheets SE C O N D Science Primary 6 2017 /2018 Teacher's Name:... Name :. Class : T E R M -0- Unit 1 : Force and Motion Lesson
The Vision of the School :Distinct Environment for Refined Education Work Sheets SE C O N D Science Primary 6 2017 /2018 Teacher's Name:... Name :. Class : T E R M -0- Unit 1 : Force and Motion Lesson
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch. Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers
 Governorate Department: Science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch A- Complete: Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers 1- is a rigid bar that
Governorate Department: Science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 6 th primary Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch A- Complete: Unit One Lesson (1) Types of levers 1- is a rigid bar that
Sixth primary science
 Sixth primary science Complete the following : 1 ) Levers are three types.& & 2 ) The craw bar is considered a class lever, but the manual broom is a...class lever 3 ) &..are example of the first class
Sixth primary science Complete the following : 1 ) Levers are three types.& & 2 ) The craw bar is considered a class lever, but the manual broom is a...class lever 3 ) &..are example of the first class
1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance
![1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance](/thumbs/85/92584639.jpg) 1)Write the scientific term: 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance [ ] 3. Levers that have the fixed point between the force &
1)Write the scientific term: 1. The fixed point of a rigid bar. [ ] 2. A rigid bar rotates on a fixed point & affects by a force & resistance [ ] 3. Levers that have the fixed point between the force &
First exercise p.90 to Choose: 1- c 2-b 3-b 4-c 5-a 6-c 7-b 8-c 9-c 10-b 11-a 12-a
 First exercise p.90 to 93 1-Choose: 1- c 2-b 3-b 4-c 5-a 6-c 7-b 8-c 9-c 10-b 11-a 12-a 2- x=2 y=10 3-Give reasons for: 1- Because they may increase the distance, move force from one place to another,
First exercise p.90 to 93 1-Choose: 1- c 2-b 3-b 4-c 5-a 6-c 7-b 8-c 9-c 10-b 11-a 12-a 2- x=2 y=10 3-Give reasons for: 1- Because they may increase the distance, move force from one place to another,
Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch Department: Science Form : 6 th Primary Unit ( 1 ) Lesson ( 1 ) : Type of levers A- Complete: 1- is a rigid
Cairo Governorate Nozha Directorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch Department: Science Form : 6 th Primary Unit ( 1 ) Lesson ( 1 ) : Type of levers A- Complete: 1- is a rigid
The lever is: a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point called fulcrum and is affected by force and resistance.
 1-Types of Levers All of the simple machines have common properties such as: 1- Different in shape and size. 2- Consist of rigid bar. 3- Made of different materials. 4- A person must inflict force on the
1-Types of Levers All of the simple machines have common properties such as: 1- Different in shape and size. 2- Consist of rigid bar. 3- Made of different materials. 4- A person must inflict force on the
Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction
 RECORD SHEET Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction Name Date Class Key Questions 1. 2. Explore Your Ideas Experiment 1: When does an electric-circuit interaction occur? 1. Draw a picture of the
RECORD SHEET Activity 4: The Electric-Circuit Interaction Name Date Class Key Questions 1. 2. Explore Your Ideas Experiment 1: When does an electric-circuit interaction occur? 1. Draw a picture of the
The Ever-Changing Sky. By Megan McGibney
 The Ever-Changing Sky The Ever-Changing Sky By Megan McGibney Look up at the sky. You will see the sun. It is bright and shiny, warming everything in the world. Look up at the sky again at night. You may
The Ever-Changing Sky The Ever-Changing Sky By Megan McGibney Look up at the sky. You will see the sun. It is bright and shiny, warming everything in the world. Look up at the sky again at night. You may
Science subject progression and skills
 Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
Science subject progression and skills Year 1 : Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and mammals Identify and name a variety of common animals that are
An eclipse is when light from a moon or sun gets blocked. People can see two kinds of eclipses from Earth.
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 584 Level 570L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 584 Level 570L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Skills and Knowledge Progression. Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
 Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants Animals, including humans Rocks Light Forces and magnets
 Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Science Curriculum Year 3 programme of study Plants identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers explore the requirements of plants
Madinaty Language School Science Department Class: Revision Sheet
 Madinaty Language School Science Department Name: Class: Grade Four Revision Sheet 1)Choose the correct answer : 1) The amount of matter in an object is called a-length b-matter c-mass 2) The space occupied
Madinaty Language School Science Department Name: Class: Grade Four Revision Sheet 1)Choose the correct answer : 1) The amount of matter in an object is called a-length b-matter c-mass 2) The space occupied
The Ever-Changing Sky
 The Ever Changing Sky The Ever-Changing Sky By Megan McGibney Look up at the sky. You will see the sun. It is bright and shiny, warming everything in the world. Look up at the sky again at night. You may
The Ever Changing Sky The Ever-Changing Sky By Megan McGibney Look up at the sky. You will see the sun. It is bright and shiny, warming everything in the world. Look up at the sky again at night. You may
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
f Static Electricity:
 ELECTRICITV VOCflB WORDS Electricity: f Static Electricity: Current Electricity: Electron: Neutron: Proton: Attraction: Repulsion: / ^ Source: Conductor: Insulator: Load: Switch: Series Circuit: Parallel
ELECTRICITV VOCflB WORDS Electricity: f Static Electricity: Current Electricity: Electron: Neutron: Proton: Attraction: Repulsion: / ^ Source: Conductor: Insulator: Load: Switch: Series Circuit: Parallel
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview
 Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Year 3 - Science Curriculum Overview Forces and Magnets Light Rocks * compare how things move on different surfaces * notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act
Year 1 Science overview
 Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Year 1 Science overview asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways observing closely, using simple equipment performing simple tests identifying and classifying
Fairlawn Primary School Science Curriculum
 Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Materials Plants Animals and Humans At Fairlawn, we follow the curriculum set out in the Science Bug resource Year 1 SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians,
Primary Science Curriculum Pupil Assessment Record
 Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
Year 1 Plants Can identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees, and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. Can describe the basic structure of a variety
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Science Curriculum Map: KS1 & KS
 Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6. Herts for Learning Ltd.
 HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
HfL Science Topic Maps for Years 1-6 Year 1 Science Map Working scientifically Everyday materials Different animals asking simple questions and recognising that they can be answered in different ways distinguish
Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc humans
 Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Science - Whole School Coverage of the National Curriculum 2018-19 Year/Cycle Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Y1 Animals, inc Everyday Plants identify and name a animals including
Electricity. Prepared by Juan Blázquez, Alissa Gildemann. Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena.
 Unit 11 Electricity 1. Electric charge Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena. Electrical phenomena are caused by the forces of attraction and repulsion.
Unit 11 Electricity 1. Electric charge Electric charge is a property of all objects. It is responsible for electrical phenomena. Electrical phenomena are caused by the forces of attraction and repulsion.
Essential Characteristics of Scientists
 SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
 GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DISTRICT SCHOOL NAME EMIS NUMBER CLASS (e.g. 6A) SURNAME NAME EKURHULENI NORTH TOM NEWBY SCHOOL
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DISTRICT SCHOOL NAME EMIS NUMBER CLASS (e.g. 6A) SURNAME NAME EKURHULENI NORTH TOM NEWBY SCHOOL
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary. Ismailia Road Branch
 Governorate Department : science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary Nozha Language Schools Revision sheet Ismailia Road Branch Question on Lesson ( 1 ) I ) Complete the following statements
Governorate Department : science Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 4 th primary Nozha Language Schools Revision sheet Ismailia Road Branch Question on Lesson ( 1 ) I ) Complete the following statements
Science Curriculum Map Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2
 The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
produce sugar, which contains stored chemical energy. Most of the energy that we use on Earth originally came from the Sun.
 Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Light. An Introduction
 Light An Introduction What is light? Light is a form of energy it can make things move What other form of energy have we dealt with? Heat is also a form of energy Quite often light energy and heat energy
Light An Introduction What is light? Light is a form of energy it can make things move What other form of energy have we dealt with? Heat is also a form of energy Quite often light energy and heat energy
National Curriculum 2014: Progression in Science
 Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Evaluating Concluding Working Scientifically Measuring and Recording Asking Questions Year 1/2 Year 3/4 Year 5/6 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways ask relevant
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2. Science. Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC
 Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
Mapping progression across KS1 to KS2 Science Adapted from Mapping Progression in the Primary Science Curriculum written by Sue Atkinson CYC Sc1 Working Scientifically Asking simple questions and recognising
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P ) What Is Light? What Is Light?
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
The Spectroscope: New Meanings in Light
 TOPIC 3 The Spectroscope: New Meanings in Light Now that astronomers could gaze deeper into the universe using simple telescopes, they faced a new challenge the stars. Galileo had seen the stars through
TOPIC 3 The Spectroscope: New Meanings in Light Now that astronomers could gaze deeper into the universe using simple telescopes, they faced a new challenge the stars. Galileo had seen the stars through
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance
 Paper Reference(s) 5PH1F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Paper Reference(s) 5PH1F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Introduction To Modern Astronomy II
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document. September 2014
 Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
Stamford Green Primary School Science Progression Document September 2014 Early Years Early Learning Goals Area of EYFS curriculum Early Learning Goals The World Children know about the similarities and
General Physics II (PHYS 104) Exam 2: March 21, 2002
 General Physics II (PHYS 104) Exam 2: March 21, 2002 Name: Multiple Choice (3 points each): Answer the following multiple choice questions. Clearly circle the response (or responses) that provides the
General Physics II (PHYS 104) Exam 2: March 21, 2002 Name: Multiple Choice (3 points each): Answer the following multiple choice questions. Clearly circle the response (or responses) that provides the
DOSTHILL PRIMARY SCHOOL I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science
 I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
I am working towards Building Block A1 in Science 1 I can observe things closely using some simple equipment 2 I can carry out investigations 3 With some help, I can test out some ideas suggested to me
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage
 National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
National Curriculum 2014 Science Coverage Aims: The national curriculum for science aims to ensure that all pupils: FCCE Primary School - National Curriculum 2014 develop scientific knowledge and conceptual
13 + Entrance Examination
 13 + Entrance Examination Paper 1 Physics - Level 2 Total marks: 60 Time allowed: 40 minutes Calculators may be used Full name. 1. Circle the correct answer for each of the following questions: a. On Earth
13 + Entrance Examination Paper 1 Physics - Level 2 Total marks: 60 Time allowed: 40 minutes Calculators may be used Full name. 1. Circle the correct answer for each of the following questions: a. On Earth
Key Skills (to be covered during the year) (from CQ Milestones)
 Science Whole School Unit Overview and Key Skills Checklist Essential Learning Objectives (Chris Quigley): Year 3 National Curriculum Unit To work scientifically Ask relevant questions. Key Skills (to
Science Whole School Unit Overview and Key Skills Checklist Essential Learning Objectives (Chris Quigley): Year 3 National Curriculum Unit To work scientifically Ask relevant questions. Key Skills (to
Band 1 - Science All. Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans Materials. Plants. Seasonal Changes
 Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
Band 1 - Science All Working Scientifically Materials Ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 focus). I can ask questions and know they can be answered in
Parkstone Primary School Science Long Term Plan Updated January 2017
 Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
Year 1 of cycle Key Stage 1 Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term Investigation Seasonal Changes (1) Observing over time observe changes across the four seasons observe and describe weather associated with
SCI-4 Pemberton_Malecky_4.3Electricity_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-4 Pemberton_Malecky_4.3Electricity_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:8W50FV 1 What contribution did Benjamin Franklin make toward the study of electricity? A He invented the
SCI-4 Pemberton_Malecky_4.3Electricity_Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:8W50FV 1 What contribution did Benjamin Franklin make toward the study of electricity? A He invented the
Science Revision Paper- Final Exam May-June Write the scientific terms for the following statements/definitions: Part A
 Name Grade 4 Date : Science Revision Paper- Final Exam May-June 2018 Write the scientific terms for the following statements/definitions: Part A 1. An imaginary line that goes through an object s center:
Name Grade 4 Date : Science Revision Paper- Final Exam May-June 2018 Write the scientific terms for the following statements/definitions: Part A 1. An imaginary line that goes through an object s center:
Have a look at the following video which shows an invention developed in the High-Low Tech Lab at MIT.
 Have a look at the following video which shows an invention developed in the High-Low Tech Lab at MIT. What is the special property of the ink the researchers have invented? We will investigate which materials
Have a look at the following video which shows an invention developed in the High-Low Tech Lab at MIT. What is the special property of the ink the researchers have invented? We will investigate which materials
What is an eclipse? Lunar Eclipses. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 866 Level 940L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.17.17 Word Count 866 Level 940L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
gear gravity heat inclined plane
 Equal and opposite forces which occur in pairs Upward force acting on objects when they are placed in water Substance which allows electric current to pass through it Force applied at one point of a machine
Equal and opposite forces which occur in pairs Upward force acting on objects when they are placed in water Substance which allows electric current to pass through it Force applied at one point of a machine
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at January 2016
 Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
1. Which of the following appliances makes use of the heating effect of electricity?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: ASSIGNMENT Chapter 15: Practical Electricity 25 Multiple-Choice Questions (10 marks) 1. Which of the following appliances makes use of the heating effect of electricity? A Electric
Name: ( ) Class: Date: ASSIGNMENT Chapter 15: Practical Electricity 25 Multiple-Choice Questions (10 marks) 1. Which of the following appliances makes use of the heating effect of electricity? A Electric
Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 N/A N/A N/A
 Non Negotiables Science Plants Biology Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Know some names of plants Begin to say how they are different from each other Start to describe the features
Non Negotiables Science Plants Biology Nursery Reception Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Know some names of plants Begin to say how they are different from each other Start to describe the features
igcse Physics Specification Questions 2. State the equation linking average speed, distance moved and time.
 igcse Physics Specification Questions Forces and Motion 1. What does the gradient of a distance-time graph represent? 2. State the equation linking average speed, distance moved and time. 3. State the
igcse Physics Specification Questions Forces and Motion 1. What does the gradient of a distance-time graph represent? 2. State the equation linking average speed, distance moved and time. 3. State the
Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Kings and Queens Rocks
 Curriculum Overview Science Years 3/4 Cycle A 2016/17 Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Rocks living Identify and describe the together different things can be grouped functions of different
Curriculum Overview Science Years 3/4 Cycle A 2016/17 Aut1 Aut 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Rocks living Identify and describe the together different things can be grouped functions of different
PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL
 PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 9 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three questions
PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2010 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 9 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three questions
Name: Grade 6 Date: REVISION BOOKLET
 REVISION BOOKLET science 1 Chapter # 16 MACHINES QA: Read each question and choose the best answer. Then fill in the circle next to the correct answer. 1. Dan and Paul push a box 4 meters with a force
REVISION BOOKLET science 1 Chapter # 16 MACHINES QA: Read each question and choose the best answer. Then fill in the circle next to the correct answer. 1. Dan and Paul push a box 4 meters with a force
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 786 Level 870L
 What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
What is an eclipse? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.16.17 Word Count 786 Level 870L This image of the moon crossing in front of the sun was captured on January 30, 2014, by NASA's Solar Dynamics
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1. Two Year rolling programme KS1
 Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
Mowbray School Long Term Science Plan KS1 Two Year rolling programme KS1 Pupils should be taught to; Ø develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding through the specific disciplines of biology,
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Symbol Meaning unit. 2. k 3. q. 4. r. 5. E 6. R Total 7. 1/R Total 8. P 9. V 10. I 11. R. 12. Q 13. N 14. e 15. F magnetic 16. v 17.
 Name period 3 rd 9 weeks test PEOPLE and SYMBOLS practice Instructions: Work in groups following Quiz-Quiz-Trade activity Date: Monday 2/25/13 Write what each symbol means, including the unit Symbol Meaning
Name period 3 rd 9 weeks test PEOPLE and SYMBOLS practice Instructions: Work in groups following Quiz-Quiz-Trade activity Date: Monday 2/25/13 Write what each symbol means, including the unit Symbol Meaning
Creating eclipses in the classroom
 Creating eclipses in the classroom During an eclipse, the Sun or the Moon seems to disappear, these are called solar or lunar eclipses, respectively. These astronomical phenomena have been shrouded in
Creating eclipses in the classroom During an eclipse, the Sun or the Moon seems to disappear, these are called solar or lunar eclipses, respectively. These astronomical phenomena have been shrouded in
SAM Teachers Guide Electricity
 SAM Teachers Guide Electricity Overview Students explore the role of electron voltage and density on electric current. They compare the movement of electrons in a conductor and an insulator. They derive
SAM Teachers Guide Electricity Overview Students explore the role of electron voltage and density on electric current. They compare the movement of electrons in a conductor and an insulator. They derive
Explain how Earth's movement and the moon's orbit cause the phases of the moon. Explain the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse.
 Explain how Earth's movement and the moon's orbit cause the phases of the moon. Explain the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. The Earth- Moon System Have you ever wondered why the
Explain how Earth's movement and the moon's orbit cause the phases of the moon. Explain the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. The Earth- Moon System Have you ever wondered why the
Heat: the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another. Electrons: the small particles inside an atom that have negative charge.
 GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
1.3 Most domestic appliances are connected to the mains electricity with a plug. Explain why a plug needs a live and a neutral wire.
 4-2 Electricity Physics.0 Most domestic appliances are connected to the mains electricity.. What is the frequency of mains electricity? Tick one box [ mark].05 A 50 Hz 230 V.2 What is the potential difference
4-2 Electricity Physics.0 Most domestic appliances are connected to the mains electricity.. What is the frequency of mains electricity? Tick one box [ mark].05 A 50 Hz 230 V.2 What is the potential difference
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Curriculum Standard One: The student will understand that energy and matter have multiple forms and can be changed from one form to another.
 Physical Sciences SCIENCE 3 Curriculum Standard One: The student will understand that energy and matter have multiple forms and can be changed from one form to another. *1A. The student will demonstrate
Physical Sciences SCIENCE 3 Curriculum Standard One: The student will understand that energy and matter have multiple forms and can be changed from one form to another. *1A. The student will demonstrate
The Sun and the Stars
 Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
Science homework booklet Energy
 Merrylands High School Science homework booklet Energy Due date: Thursday November 14 Name: How to complete this homework booklet This homework booklet is divided into lessons. There are 5 lessons altogether.
Merrylands High School Science homework booklet Energy Due date: Thursday November 14 Name: How to complete this homework booklet This homework booklet is divided into lessons. There are 5 lessons altogether.
6th Standard Physics
 1 PHYSICS: 2 6th Standard Physics Term I Physics is the branch of science that deals with measurement, motion, sound light, electricity, electronics etc. Measurement and motion: Measurement is a process
1 PHYSICS: 2 6th Standard Physics Term I Physics is the branch of science that deals with measurement, motion, sound light, electricity, electronics etc. Measurement and motion: Measurement is a process
Electricity. What is electricity?
 Words attract = pull towards an object back and forth = to go in one direction and then in the other balanced = the same as stable carbon = a chemical material that is in coal or petrol. It is in its purest
Words attract = pull towards an object back and forth = to go in one direction and then in the other balanced = the same as stable carbon = a chemical material that is in coal or petrol. It is in its purest
An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits
 An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits Materials prepared by Daniel Duke 4 th Sept 2013. This document may be copied and edited freely with attribution. This course has been designed to introduce
An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits Materials prepared by Daniel Duke 4 th Sept 2013. This document may be copied and edited freely with attribution. This course has been designed to introduce
Q2: What is meant by energy transfer? Energy is converted from one form into others. The total amount will be the same.
 Q1: What is a Sankey diagram used to show? A diagram that represents energy transfers by arrows. The width of each arrow depends upon the amount of energy it represents. Q2: What is meant by energy transfer?
Q1: What is a Sankey diagram used to show? A diagram that represents energy transfers by arrows. The width of each arrow depends upon the amount of energy it represents. Q2: What is meant by energy transfer?
NEW GCSE 4463/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER PHYSICS 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number NEW GCSE 4463/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER PHYSICS 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require a calculator. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number NEW GCSE 4463/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER PHYSICS 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require a calculator. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
St Olave s Physics Department. Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist
 St Olave s Physics Department Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 11 Mock exam. Students should use the tickboxes to check
St Olave s Physics Department Year 11 Mock Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 11 Mock exam. Students should use the tickboxes to check
Homework Questions: Geometrical Optics & Angular Momentum
 2017 Eclipse: Research-Based Teaching Resources Homework Questions: Geometrical Optics & Angular Momentum Description: These open-ended homework prompts encourage students to reveal their thinking about
2017 Eclipse: Research-Based Teaching Resources Homework Questions: Geometrical Optics & Angular Momentum Description: These open-ended homework prompts encourage students to reveal their thinking about
PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL
 *P16* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2011 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 9 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three
*P16* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2011 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from section A and five questions from section B. Page 1 of 9 SECTION A (120 marks) Answer three
The equation which links current, potential difference and resistance is:
 An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current that
An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current that
1. The type of energy described by Energy C is which type of energy?
 Energy A Energy B Energy C Energy D Energy E Energy stores within a particle (measured by the particle s temperature). Energy generated by the sun. Energy released when particles react to form a new substance.
Energy A Energy B Energy C Energy D Energy E Energy stores within a particle (measured by the particle s temperature). Energy generated by the sun. Energy released when particles react to form a new substance.
is energy in particles of matter. Chemical energy can be released, for example in or, when these particles react to form new substances.
 TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide
 Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Year 7 Recall Booklet. Name: Class:
 Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Preliminary Course Physics Module 8.3 Electrical Energy in the Home Summative Test. Student Name:
 Summative Test Student Name: Date: / / IMPORTANT FORMULAE I = Q/t V = I.R R S = R 1 + R 2 +.. 1/R P = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 + P = V.I = I 2.R = V 2 /R Energy = V.I.t E = F/q Part A. Multiple Choice Questions 1-20.
Summative Test Student Name: Date: / / IMPORTANT FORMULAE I = Q/t V = I.R R S = R 1 + R 2 +.. 1/R P = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 + P = V.I = I 2.R = V 2 /R Energy = V.I.t E = F/q Part A. Multiple Choice Questions 1-20.
What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017
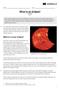 Name: Class: What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017 Solar and lunar eclipses are some of the beautiful, outerspace events that we are able to witness from Earth. This text details how solar and lunar eclipses
Name: Class: What is an Eclipse? By NASA 2017 Solar and lunar eclipses are some of the beautiful, outerspace events that we are able to witness from Earth. This text details how solar and lunar eclipses
Which of the following is the SI unit of gravitational field strength?
 T5-2 [122 marks] 1. A cell is connected in series with a 2.0Ω resistor and a switch. The voltmeter is connected across the cell and reads 12V when the switch is open and 8.0V when the switch is closed.
T5-2 [122 marks] 1. A cell is connected in series with a 2.0Ω resistor and a switch. The voltmeter is connected across the cell and reads 12V when the switch is open and 8.0V when the switch is closed.
LIGHT. A beam is made up of several rays. It maybe parallel, diverging (spreading out) or converging (getting narrower). Parallel Diverging Converging
 LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
Comparing the Mechanical Advantage of Levers
 Chapter 14 Work, Power, and Machines Investigation 14A Comparing the Mechanical Advantage of Levers Background Information A lever consists of a rigid bar that is free to rotate around a fixed point. The
Chapter 14 Work, Power, and Machines Investigation 14A Comparing the Mechanical Advantage of Levers Background Information A lever consists of a rigid bar that is free to rotate around a fixed point. The
Question Bank. Electric Energy, Power and Household Circuits
 Electric Energy, Power and Household Circuits 1. (a) What do you understand by the term electric work? (b) State the SI unit of electric work and define it. (c) Name two bigger units of electric work.
Electric Energy, Power and Household Circuits 1. (a) What do you understand by the term electric work? (b) State the SI unit of electric work and define it. (c) Name two bigger units of electric work.
Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2
 Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2 Basic Electronics What is electricity? Voltage, Current, Resistance DC/AC Ohm s Law Capacitors & Inductors Conductor & Insulator What is Electricity? Everything
Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2 Basic Electronics What is electricity? Voltage, Current, Resistance DC/AC Ohm s Law Capacitors & Inductors Conductor & Insulator What is Electricity? Everything
9. Which of the following is the correct relationship among power, current, and voltage?. a. P = I/V c. P = I x V b. V = P x I d.
 Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
12.2. The Earth Moon System KNOW? The Phases of the Moon. Did You
 12.2 The Earth Moon System Did You KNOW? The Moon is Earth s closest neighbour. It is highly influential in our lives because it causes the oceans tides. The Moon is also responsible for eclipses. waxing
12.2 The Earth Moon System Did You KNOW? The Moon is Earth s closest neighbour. It is highly influential in our lives because it causes the oceans tides. The Moon is also responsible for eclipses. waxing
KS3 Science. Heat and Energy
 KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
1.4 recall and use the relationship between acceleration, velocity and time: 1.6 determine acceleration from the gradient of a velocity-time graph
 Physics Section 1: Forces and motion b) Movement and position c) Forces, movement and shape d) Astronomy 1.1 use the following units: kilogram (kg), metre (m), metre/second (m/s), metre/second 2 (m/s 2
Physics Section 1: Forces and motion b) Movement and position c) Forces, movement and shape d) Astronomy 1.1 use the following units: kilogram (kg), metre (m), metre/second (m/s), metre/second 2 (m/s 2
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
