Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert
|
|
|
- Emerald Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
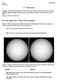
1 Stone circles on the harraat of Syrian desert Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Department of Applied Science and Technology Politecnico di Torino, C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy Recently some stone structures covering the harraat of the Syrian desert had been investigated using satellite imagery (arxiv: ). Dispersed in an arid landscape, they were probably made during the Neolithic period. Some of these structures are here discussed, which display a possible use as ancient sun observatories. For the analysis, a freely available software is used which can be quite suitable for evaluating the effect of solar radiation on physical features of natural structures too. An arid land, characterized by huge lava fields, the harraat, is covering a large part of the Middle East. It is the Syrian Desert, extending from the northern Arabian Peninsula to the eastern Jordan, southern Syria and western Iraq, and in the past considered as a barrier between Levant and Mesopotamia. This desert has two volcanic regions. One is the Jabal al-druze, in the As-Suwayda Governorate, consisting of several basaltic volcanoes active from the lower-pleistocene to the Holocene [1]. The other field is that of the Harrat Ash Shaam. In Arabic, the lava fields are the harraat (sing. harrah; before a name, harrat). Harrat Ash Shaam includes the Es-Safa volcano, in the South of Syria, south-east of Damascus [2]. A survey of this desert with satellite imagery, for instance with the Google Maps, shows the lava fields and the extent of harraat, with different colors of magma extruded in past epochs [3]. We see also that this region is crossed by some huge stone structures, the desert kites, which were kiteshaped Neolithic stone fences, probably used as animal traps [3-5]. Besides the kites, there are also abundant archaeological evidence of Neolithic communities because thousands of tumuli, stone fences, circular structures are covering large areas [6]. Sometimes we can see some structures superimposed to older ones (see for instance the Fig.1). Fig.1 Desert kites. Several stone circles are visible too, as many Stonehenge sites dispersed in the desert landscape. Referred to by archaeologists as "wheels," these stone structures have a wide variety of designs, with a common one being a circle with spokes radiating inside. [7]. These structures range from 25 meters to 70 meters across. Proposed as Stonehenges of the Middle East [8], and compared
2 with the Nazca lines as possible geoglyphs with astronomical alignments [7], we can investigate whether the hypothesis of being ancient rudimental sun observatories is possible or not. The prototypes of ancient solar observatories in Europe are the sites of Stonehenge and Goseck and, in Peru, the complex of Chankillo [9-11]. The European sites have generally a circular structure, but Chankillo is a more or less straight line of towers on a low hill. Therefore, a structure connected with the observation of sunrise, sunset and zenith (if any) position of the sun, can have quite different shapes according to its location relative to the Equator, that is, to its latitude. Recently I have discussed the orientation of ancient temples and roman towns in some paper using the angles of the horizontal and equatorial systems [12-14]. Since the Syrian wheels have clear radial structures, let us use a different approach and compare them with directions of sunset, noon, and sunrise, as given according to their latitude. Some software, developed for solar energy applications, is available for our purpose. Among the many sites providing solar information, we can choose that proposed a model of sunlight direction into a Google map on any day of the year. Figure 1-3 show some of the stone circles of Syrian desert already displayed in Ref.4, analysed according to the solar directions. It seems that there is a good agreement between sunrises and sunsets at equinoxes as given by the model and stone circle features. There is also a site, that shows a certain alignment of a line of stones with the sunrise on the winter solstice as given by the model of sollumis.com (see Fig.4). At a first glance then, the proposal of Ref. 8 of some Stonehenges in the Middle East seems to be reliable. Of course, it is necessary to tell that some hills on the horizon can alter the direction of apparent sunrise and sunset and therefore an on-site evaluation is required. Moreover, the original alignment of stones could had been different from the observed one, that is, it could had been altered during time by the local population, to have an agreement with sunrise and sunset at equinoxes, creating their own rudimental solar observatory. It is therefore difficult to give any conclusion on the age of the stone circle layout by their simple observation from satellites [15]. Fig.1 This is one of the stone structure of Syrian Desert. The image shows directions of sun during the day. The lines on the drawing show the direction and height (altitude) of the sun throughout the day. Thicker and shorter lines mean the sun is higher in the sky. Longer and thinner lines mean the sun is closer to the horizon, according to Sollumis.com On the left, the site as it appears in the Google Maps. In the middle, the direction of the sun on the summer solstice, choosing the center of the circle for observation. We see that, at sunrise, the sun is passing near the dot. At the sunset the direction is that of a line. In the image on the right, we see the direction of the sun on winter solstice. At sunrise, the lines is passing between dots. The sunset has the direction of a radius (images have been obtained from original provided by Google Maps and sollumis.com).
3 Fig.2 Other two stone circles analysed as in Fig.1, and having, more or less, the same features. Fig.3 A complex structure in the Syrian desert, with its analysis with sollumis.com
4 Fig.4 This site has a line of stones which seems aligned with the sunrise of the winter solstice. Of course, the comparison of structures, natural or human, observed by satellites with models drawing the solar directions, is fundamental for all the solar energy applications. For this reason, it is quite easy to find freely available software on the web. Here we used the software to investigate the orientation of ancient stone circles. But this and other similar software can be applied for modelling the solar radiation on natural structures (lakes, marshes, dunes, etc.) to evaluate their evolution during cycles of years. References 1. Jabal al-druze Volcanic Field in Southern Syria May 16th, 2010, / 2. Global Volcanic Program, Es-Safa, 3. A.C. Sparavigna, Arabia: from craters to stone circles, arxiv, Geophysics, 2011, 4. A.C. Sparavigna, Stone structures in the Syrian Desert, Archaeogate, July 14, 2011; arxiv, Geophysics, 2011, 5. Mysterious desert lines were animal traps, Larry O'Hanlon, Apr 20, 2010, 6. Desert Kites, Ancient Hunting Technique Desert Kites, K. Kris Hirst, About.com Guide, 7. Owen Jarus, Visible only from above, 8. Owen Jarus, Syria's Stonehenge: Neolithic stone circles, alignments and possible tombs discovered, 1 March 2010, The Independent, I. Ghezzi and C. L.N. Ruggles, The social and ritual context of horizon astronomical observations at Chankillo, Oxford IX International Symposium on Archaeoastronomy, Proceedings, IAU Symposium No. 278, 2011, The_social_and_ritual_context_of_horizon_astronomical_observations_at_Chankillo
5 12. A.C. Sparavigna, The orientation of Julia Augusta Taurinorum (Torino), arxiv, 2012, A.C. Sparavigna, The sunrise amplitude equation applied to an Egyptian temple, arxiv, 2012, A.C. Sparavigna, The orientation of Trayans town of Timagd, arxiv, 2012, A web site, date 27 March 2011, published the news of a 11,000- year-old settlement unearthed in Syria.
For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern
 632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
632 CHAPTER 25: EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS WHAT IS THE SUN S APPARENT PATH ACROSS THE SKY? For most observers on Earth, the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky. The sun reaches its greatest angular altitude
WAS LEPENSKI VIR AN ANCIENT SUN OR PLEIADES OBSERVATORY? Vladan Panković, Milan Mrdjen, Miodrag Krmar
 WAS LEPENSKI VIR AN ANCIENT SUN OR PLEIADES OBSERVATORY? Vladan Panković, Milan Mrdjen, Miodrag Krmar Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, 21000 Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 4., Serbia, vladan.pankovic@df.uns.ac.rs
WAS LEPENSKI VIR AN ANCIENT SUN OR PLEIADES OBSERVATORY? Vladan Panković, Milan Mrdjen, Miodrag Krmar Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, 21000 Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 4., Serbia, vladan.pankovic@df.uns.ac.rs
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018
 Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR
 STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR One of the most impressive megalithic structures in the world is Stonehenge just north of Salisbury, England. I first visited the monument during my post-doctorate year
STONEHENGE AS A SOLSTICE INDICATOR One of the most impressive megalithic structures in the world is Stonehenge just north of Salisbury, England. I first visited the monument during my post-doctorate year
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why?
 (1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
(1) Over the course of a day, the sun angle at any particular place varies. Why? (Note: Although all responses below are true statements, only one of them actually explains the observation!) (A)The sun
Discovering the Night Sky
 Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Ancient astronomical observatories
 FUTURE OF THE PAST: ICTS Mini Workshop, Mangalore, 22-26, 2011 Ancient astronomical observatories Srikumar M. Menon Manipal University, Manipal Stonehenge Nilaskal The Fascinating Heavens the sky as a
FUTURE OF THE PAST: ICTS Mini Workshop, Mangalore, 22-26, 2011 Ancient astronomical observatories Srikumar M. Menon Manipal University, Manipal Stonehenge Nilaskal The Fascinating Heavens the sky as a
Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons: Earth, Moon, and Sun Vocabulary: altitude, axis, azimuth, equinox, horizon, latitude, revolution, rotation, solstice Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE
Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D Vocabulary: axis, equinox, latitude, Northern Hemisphere, revolve, rotate, solar energy, solar intensity, Southern Hemisphere, summer solstice, winter solstice
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Seasons in 3D Vocabulary: axis, equinox, latitude, Northern Hemisphere, revolve, rotate, solar energy, solar intensity, Southern Hemisphere, summer solstice, winter solstice
Knowing the Heavens. Chapter Two. Guiding Questions. Naked-eye (unaided-eye) astronomy had an important place in ancient civilizations
 Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Exercises in Archaeoastronomy -2 -The passage mound of Newgrange
 Exercises in Archaeoastronomy -2 -The passage mound of Newgrange Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Exercises in Archaeoastronomy -2 -The passage mound of Newgrange.
Exercises in Archaeoastronomy -2 -The passage mound of Newgrange Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Exercises in Archaeoastronomy -2 -The passage mound of Newgrange.
Craters and ring complexes of the North-East Sudanese country
 Craters and ring complexes of the North-East Sudanese country Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Dipartimento di Fisica, Politecnico di Torino C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy Abstract We propose a survey
Craters and ring complexes of the North-East Sudanese country Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Dipartimento di Fisica, Politecnico di Torino C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy Abstract We propose a survey
A possible role of Alpha Crucis in the astronomical landscape of Silbury Hill
 A possible role of Alpha Crucis in the astronomical landscape of Silbury Hill Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Politecnico di Torino The paper is discussing a possible link between the construction of Silbury
A possible role of Alpha Crucis in the astronomical landscape of Silbury Hill Amelia Carolina Sparavigna Politecnico di Torino The paper is discussing a possible link between the construction of Silbury
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION
 ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
ME 476 Solar Energy UNIT THREE SOLAR RADIATION Unit Outline 2 What is the sun? Radiation from the sun Factors affecting solar radiation Atmospheric effects Solar radiation intensity Air mass Seasonal variations
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Seasons. What causes the seasons?
 Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
Questions: Seasons What causes the seasons? How do we mark the progression of the seasons? What is the seasonal motion of the sun in the sky? What could cause the seasonal motion of the sun to change over
The Celestial Sphere. Chapter 1. Constellations. Models and Science. Constellations. Diurnal vs. Annular Motion 9/16/2010
 The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
The Celestial Sphere Chapter 1 Cycles of the Sky Vast distances to stars prevent us from sensing their true 3-D arrangement Naked eye observations treat all stars at the same distance, on a giant celestial
Solar Alignments of the Planning of Angkor Wat Temple Complex
 Solar Alignments of the Planning of Angkor Wat Temple Complex Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Solar Alignments of the Planning of Angkor Wat Temple Complex.
Solar Alignments of the Planning of Angkor Wat Temple Complex Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Solar Alignments of the Planning of Angkor Wat Temple Complex.
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
Name: Partner(s): 5 - Seasons ASTR110L Purpose: To measure the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. Answer all questions
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY
 CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
CHAPTER 2 A USER'S GUIDE TO THE SKY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In one way of naming stars, a letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation. a. English b. Arabic c. Greek d. Cyrillic
Daily Motions. Daily Motions. Solar and Sidereal Days. Annual Motions of the Sun. Coordinate system on Earth. Annual Motion of the Stars.
 Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
CA1 2.11: Designing an Equatorial Sundial Activity
 Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Purpose: To design an equatorial sundial and learn about motions of the sun and earth that have a bearing on its design. Materials: poster board, length of stiff wire or dowel rod, tape, protractor, ruler,
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 7. The Seasons
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 7 The Seasons The Importance of Seasons The seasons govern both natural and human patterns of behavior. Some big and small examples: Planting and harvesting of crops Migratory
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 7 The Seasons The Importance of Seasons The seasons govern both natural and human patterns of behavior. Some big and small examples: Planting and harvesting of crops Migratory
StoneHenge. (Neolithic-Period)
 StoneHenge (Neolithic-Period) Stonehenge, England Stonehenge, the most visited and well known of the British stone rings, is a composite structure built during three distinct periods. In Period I (radiocarbon-dated
StoneHenge (Neolithic-Period) Stonehenge, England Stonehenge, the most visited and well known of the British stone rings, is a composite structure built during three distinct periods. In Period I (radiocarbon-dated
Physics 312 Introduction to Astrophysics Lecture 3
 Physics 312 Introduction to Astrophysics Lecture 3 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lecture 3 Celestial Coordinates the Planets and more History Reason for the Seasons Summer Solstice: Northern Hemisphere
Physics 312 Introduction to Astrophysics Lecture 3 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lecture 3 Celestial Coordinates the Planets and more History Reason for the Seasons Summer Solstice: Northern Hemisphere
Before you Sit. Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium
 Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
Before you Sit Please Pick-up: Blue Information Sheet for Evening Observing. 1 Red and 1 Blue ticket for Observing/ Planetarium Evening Observing Observing at the Brooks Observatory: Three different weeks
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME. a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system.
 UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
NAME; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle
 NAME; PERIOD; DATE; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle 1 OBJECTIVE Explain how latitude affects the seasonal path of the Sun. I) Path of the Sun and Latitude.
NAME; PERIOD; DATE; LAB # SEASONAL PATH OF THE SUN AND LATITUDE Hemisphere Model #3 at the Arctic Circle 1 OBJECTIVE Explain how latitude affects the seasonal path of the Sun. I) Path of the Sun and Latitude.
Space. Universe - everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere
 Space Universe - everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere Astronomy - study of what is beyond the Earth Constellations - groups of stars that form shapes or patterns in the sky.
Space Universe - everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere Astronomy - study of what is beyond the Earth Constellations - groups of stars that form shapes or patterns in the sky.
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
November 20, NOTES ES Rotation, Rev, Tilt.notebook. vertically. night. night. counterclockwise. counterclockwise. East. Foucault.
 NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
NOTES ES, Rev,.notebook, and Rotates on an imaginary axis that runs from the to the South North Pole Pole vertically North The of the axis points to a point in space near day Pole Polaris night Responsible
How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? Where is the Sun at noon today? What about the path of the Sun?
 The changing position of the Sun during the year! How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? X Zenith or overhead How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? Where is the Sun at noon
The changing position of the Sun during the year! How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? X Zenith or overhead How can we describe the motion of the sun in the sky? Where is the Sun at noon
FOR DISCUSSION TODAY: THE ANNUAL MOTION OF THE SUN
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework #1 due today at end of class. HW #2 due next Thursday. Homework #1 question #1 and Homework #2 meridian slice questions will be discussed in the course of the lecture today. Observing
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008
 Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World
 Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Days & Nights 1 Name Daylight Data: Days and Nights Around the World Purpose: To investigate the number of hours of daylight received by countries at different latitudes. Materials: Daylight data sheet
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Motions of the Sun Model Exploration
 Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
Name Date Bell Motions of the Sun Model Exploration 1. Go to the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Motions of the Sun Simulator: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion3/animations/sunmotions.swf 2. This is what
3 - Celestial Sphere
 3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
3 - Celestial Sphere Purpose: To construct and use a celestial sphere to show the motion of the Sun and stars in the sky. There are six questions, Q1 Q6, to answer on a separate piece of paper. Due: in
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Seasons Pre-Lab Assignment: In class, we've talked about the cause of the seasons. In this lab, you will use globes to study the relative positions of Earth and the Sun during
Geography Class 6 Chapters 3 and
 CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
CHAPTER 3 MOTIONS OF THE EARTH The Earth is always travelling in Space. That makes each person on Earth, a Space Traveller. No one feels the movement of the Earth because humans are too tiny when compared
Astro 101 Lab #2. Start up the Stellarium program. If you do not remember how to use the user interface, please refer to Lab#1 or the user s guide.
 Name: Astro 101 Lab #2 Lab objectives 1) Learn about how the Sun s path, through the sky, changes with the changing seasons. 2) Learn about how the Sun s path changes while viewing it at different locations
Name: Astro 101 Lab #2 Lab objectives 1) Learn about how the Sun s path, through the sky, changes with the changing seasons. 2) Learn about how the Sun s path changes while viewing it at different locations
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?)
 Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Today Appearance of the Sky Orientation Motion of sky Seasons Precession (?) The Celestial Sphere Stars at different distances all appear to lie on the celestial sphere. The ecliptic is the Sun s apparent
Earth s Orbit. Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology
 1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
1 ESCI-61 Introduction to Photovoltaic Technology Sun Earth Relationships Ridha Hamidi, Ph.D. Spring (sun aims directly at equator) Winter (northern hemisphere 23.5 tilts away from sun) 2 Solar radiation
Benefit of astronomy to ancient cultures
 Benefit of astronomy to ancient cultures Usefulness as a tool to predict the weather (seasons) Usefulness as a tool to tell time (sundials) Central Africa (6500 B.C.) Alignments Many ancient cultures built
Benefit of astronomy to ancient cultures Usefulness as a tool to predict the weather (seasons) Usefulness as a tool to tell time (sundials) Central Africa (6500 B.C.) Alignments Many ancient cultures built
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2017 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 30 September 2017 Time limit: 50 min
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2017 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2017 Number of pages: 10 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 30 September 2017 Time limit: 50 min
C) wavelength C) eastern horizon B) the angle of insolation is high B) increases, only D) thermosphere D) receive low-angle insolation
 1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
1. What is the basic difference between ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation? A) half-life B) temperature C) wavelength D) wave velocity 2. In New York State, the risk of sunburn is greatest between
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
Sun Inclinometer. Curriculum Levels 3-4 Maths. Activity Description
 Sun Inclinometer Curriculum Levels 3-4 Maths Activity Description Students will transform a protractor into an accurate and reliable instrument that measures the angle of the sun and by taking multiple
Sun Inclinometer Curriculum Levels 3-4 Maths Activity Description Students will transform a protractor into an accurate and reliable instrument that measures the angle of the sun and by taking multiple
Upon Whose Shoulders We Stand: A History of Astronomy Up to 200 A.D. Dick Mallot 3/17/2005
 Upon Whose Shoulders We Stand: A History of Astronomy Up to 200 A.D. Dick Mallot 3/17/2005 Who were these ancient astronomers? Where did real astronomy begin? What did we know about astronomy 2000+ years
Upon Whose Shoulders We Stand: A History of Astronomy Up to 200 A.D. Dick Mallot 3/17/2005 Who were these ancient astronomers? Where did real astronomy begin? What did we know about astronomy 2000+ years
1. Which continents are experiencing daytime? 2. Which continents are experiencing nighttime?
 Name: Section: Astronomy 101: Seasons Lab Objective: When you have completed this lab, you will be able to describe the seasons of the year and explain the reasons for those seasons. Answer the questions
Name: Section: Astronomy 101: Seasons Lab Objective: When you have completed this lab, you will be able to describe the seasons of the year and explain the reasons for those seasons. Answer the questions
Planet Earth. Part 2
 Planet Earth Part 2 Sun, Earth and Moon Motions The Solar System revolves around the Milky Way galaxy center. The Sun rotates on its own axis. Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year) and rotates on its
Planet Earth Part 2 Sun, Earth and Moon Motions The Solar System revolves around the Milky Way galaxy center. The Sun rotates on its own axis. Earth revolves around the Sun (1 year) and rotates on its
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Phys Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations
 Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
Phys 10293 Lab #1: The Sun and the Constellations Introduction Astronomers use a coordinate system that is fixed to Earth s latitude and longitude. This way, the coordinates of a star or planet are the
What Is the Relationship Between Earth s Tilt and the Seasons?
 Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
Learning Set 2 Why Are There Differences in Temperature? Review Images and Graphics While reading about Earth s tilt and the seasons, pay particular attention to the graphics included. How do they help
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Heat Transfer. Energy from the Sun. Introduction
 Heat Transfer Energy from the Sun Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun
Heat Transfer Energy from the Sun Introduction The sun rises in the east and sets in the west, but its exact path changes over the course of the year, which causes the seasons. In order to use the sun
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2
 MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
MiSP Astronomy - Seasons Worksheet #1 L2 Name Date Changing Hours of Daylight on Long Island (L 1, 2, 3) Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter.
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 1 February 3, 2003
 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 1 February 3, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional space,
Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 1 February 3, 2003 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. If you need additional space,
Name and Student ID Section Day/Time:
 AY2 - Overview of the Universe - Midterm #1 - Instructor: Maria F. Duran Name and Student ID Section Day/Time: 1) Imagine we ve discovered a planet orbiting another star at 1 AU every 6 months. The planet
AY2 - Overview of the Universe - Midterm #1 - Instructor: Maria F. Duran Name and Student ID Section Day/Time: 1) Imagine we ve discovered a planet orbiting another star at 1 AU every 6 months. The planet
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Earth is tilted (oblique) on its Axis!
 MONDAY AM Radiation, Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Earth's orbit around the Sun is slightly elliptical (not circular) Seasons & Days Why do we have seasons? Why aren't seasonal temperatures highest at
MONDAY AM Radiation, Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Earth's orbit around the Sun is slightly elliptical (not circular) Seasons & Days Why do we have seasons? Why aren't seasonal temperatures highest at
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude
 Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
Seasonal Path of the Sun and Latitude Overview This lesson is a modification of what Dave Hess and I, Stan Skotnicki, use in our Earth Science classes at Cheektowaga Central High School. It is an extension
a. 0.5 AU b. 5 AU c. 50 AU d.* AU e AU
 1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Earth is rotating on its own axis
 Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Earth is rotating on its own axis 1 rotation every day (24 hours) Earth is rotating counterclockwise if you are looking at its North pole from other space. Earth is rotating clockwise if you are looking
Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures?
 Light Power and seasons Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures? 1 Lab Activity: Lab Activity Obtain a Styrofoam ball. This will represent the earth. Stick a push pin into the
Light Power and seasons Exploration Phase What are the differences between these pictures? 1 Lab Activity: Lab Activity Obtain a Styrofoam ball. This will represent the earth. Stick a push pin into the
Practice Questions: Seasons #1
 1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
1. Seasonal changes on Earth are primarily caused by the A) parallelism of the Sun's axis as the Sun revolves around Earth B) changes in distance between Earth and the Sun C) elliptical shape of Earth's
A. the spinning of Earth on its axis B. the path of the Sun around Earth
 stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
stronomy 1 Packet Write answers on your own paper 1. The Sun appears to move across the sky each day. What causes this?. the spinning of Earth on its axis. the path of the Sun around Earth. the production
Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator
![Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator Celestial Sphere. Altitude [of a celestial object] Zenith. Meridian. Celestial Equator](/thumbs/83/88077665.jpg) Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
Earth Science Regents Interactive Path of the Sun University of Nebraska Resources Copyright 2011 by Z. Miller Name Period COMPANION WEBSITES: http://www.analemma.com/ http://www.stellarium.org/ INTRODUCTION:
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107
 Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
Chapter 4 Earth, Moon, and Sky 107 planetariums around the world. Figure 4.4 Foucault s Pendulum. As Earth turns, the plane of oscillation of the Foucault pendulum shifts gradually so that over the course
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Motion of the Sun. View Comments
 Login 2017 Survey to Improve Photovoltaic Education Christiana Honsberg and Stuart Bowden View Comments Instructions 1. Introduction 2. Properties of Sunlight 2.1. Basics of Light Properties of Light Energy
Login 2017 Survey to Improve Photovoltaic Education Christiana Honsberg and Stuart Bowden View Comments Instructions 1. Introduction 2. Properties of Sunlight 2.1. Basics of Light Properties of Light Energy
Astronomy 120 Winter 2005 Highlights of Astronomy. First Midterm Examination
 Astronomy 120 Winter 2005 Highlights of Astronomy First Midterm Examination Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE: Choose the one best answer from among the five choices for each of the following 6 questions. Each correct
Astronomy 120 Winter 2005 Highlights of Astronomy First Midterm Examination Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE: Choose the one best answer from among the five choices for each of the following 6 questions. Each correct
SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6
 NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
NJCCCS: 5.1, 5.2, 5.4 SOLAR ENERGY: THAT S HOT Grades 4-6 Field Trip Overview: This program illuminates the various ways in which our nearest star affects life on Earth. Students will learn about the apparent
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations
 Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
Sky, Celestial Sphere and Constellations Last lecture Galaxies are the main building blocks of the universe. Consists of few billions to hundreds of billions of stars, gas clouds (nebulae), star clusters,
Answer Key for Exam C
 Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam C 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B
 Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B 1 point each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy
 Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
Tools of Astronomy Tools of Astronomy The light that comes to Earth from distant objects is the best tool that astronomers can use to learn about the universe. In most cases, there is no other way to study
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
2.2 The Reason for Seasons
 2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
2.2 The Reason for Seasons Our goals for learning: What causes the seasons? How does the orientation of Earth's axis change with time? Thought Question TRUE OR FALSE? Earth is closer to the Sun in summer
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1
 Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season?
 Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
Name: Date: LAB: What Events Mark the Beginning of Each Season? The relationship between the Sun and Earth have been used since antiquity to measure time. The day is measured by the passage of the Sun
HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY, PART 1. How our understanding of the Universe has changed
 HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY, PART 1 How our understanding of the Universe has changed Focus Question: How and why has our understanding of the universe changed over time? The oldest science? As far back as the
HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY, PART 1 How our understanding of the Universe has changed Focus Question: How and why has our understanding of the universe changed over time? The oldest science? As far back as the
Astronomy: Universe at a Glance, Ch. 1a
 1 Astronomy: Universe at a Glance, Ch. 1a What you see depends on from where you observe: Ancients lived in a very dark world at night compared to us today, and the sky was magnificent and enticing. Sometimes
1 Astronomy: Universe at a Glance, Ch. 1a What you see depends on from where you observe: Ancients lived in a very dark world at night compared to us today, and the sky was magnificent and enticing. Sometimes
Objectives. Duration: one week
 Objectives At the conclusion of the lesson, students will be able to: 1. Analyze data to describe the motion of the sun including equinox and solstice paths in the sky for an Ancient Culture 2. Use alt-azimuth
Objectives At the conclusion of the lesson, students will be able to: 1. Analyze data to describe the motion of the sun including equinox and solstice paths in the sky for an Ancient Culture 2. Use alt-azimuth
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
function get_style23731 () { return "none"; } function end23731_ () { document.getelementbyid('elastomer23731').style.display = get_style23731(); }
 function get_style23731 () { return "none"; } function end23731_ () { document.getelementbyid('elastomer23731').style.display = get_style23731(); } EarthSky Late dawn. Early sunset. Short day. Long night.
function get_style23731 () { return "none"; } function end23731_ () { document.getelementbyid('elastomer23731').style.display = get_style23731(); } EarthSky Late dawn. Early sunset. Short day. Long night.
Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images
 Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images. Philica, Philica,
Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images Amelia Carolina Sparavigna To cite this version: Amelia Carolina Sparavigna. Peruvian Transverse Dunes in the Google Earth Images. Philica, Philica,
Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics
 SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride The Year Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Celestial Coordinates Right Ascension RA or From prime meridian (0 h ) to 23 h
SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride The Year Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Celestial Coordinates Right Ascension RA or From prime meridian (0 h ) to 23 h
Parowan Gap Nature s Perfect Observatory by V.Garth Norman
 Parowan Gap Nature s Perfect Observatory by V.Garth Norman CFI, Inc. Publication Available @ www.amazon.com Archaeological Research Consultants ARCON Inc. 2006 No part of this presentation may be reproduced
Parowan Gap Nature s Perfect Observatory by V.Garth Norman CFI, Inc. Publication Available @ www.amazon.com Archaeological Research Consultants ARCON Inc. 2006 No part of this presentation may be reproduced
Sunlight and its Properties Part I. EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz
 Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
Sunlight and its Properties Part I EE 446/646 Y. Baghzouz The Sun a Thermonuclear Furnace The sun is a hot sphere of gas whose internal temperatures reach over 20 million deg. K. Nuclear fusion reaction
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
MiSP Astronomy Seasons Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date CHANGING HOURS OF DAYLIGHT ON LONG ISLAND Introduction You sometimes hear people say, Days are longer in the summer and shorter in the winter. That is a
