A part of a line with two end points is called line segment and is denoted as AB
|
|
|
- Flora Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HTR 6 Lines and ngles Introduction In previous class we have studied that minimum two points are required to draw a line. line having one end point is called a ray. Now if two rays originate from a point, an angle is formed. If two lines intersect each other, different angles are formed. Here we will study different properties related to lines and angles. asic Terms and efinitions Line Segment part of a line with two end points is called line segment and is denoted as Ray part of a line with one end point is called ray and is denoted as point. It can be etended further from Line It can be etended from both sides (left and right) and is denoted as ollinear oints Three or more points are said to be collinear if a single straight line passes through them. Here,, are collinear. Non-ollinear oints Three or more points not lying on a single straight line are called non-collinear points.,, are not collinear. Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 99
2 ngle When two rays originates from the same end point they form an angle. Rays (arms of angle) nd point (Verte) ngle The rays are called arms of an angle and end point is called verte. Types of ngles Intersecting Lines and Non-Intersecting Lines In figure (i) and are intersecting lines. In figure (ii) and are non-intersecting lines (parallel lines). In parallel lines the lengths of the common perpendiculars at different points are equal. This equal length is called the distance between two parallel lines. airs of ngles z omplementary ngles If the sum of measure of two angles is 90, they are known as complementary angles. or eample : Q + = = 90 \ Q and are complementary angles and Q is called complement of and vice-versa. 70 Q 0 z Supplementary ngles If the sum of measure of two angles is 80, they are called supplementary angles. or eample : XY and QR are supplementary as XY + QR = = 80 and XY is called supplement of QR and vice-versa. z djacent ngles X 70 Y 0 Q R Two angles are said to be adjacent angles or adjacent to each other if (i) They have common arm. 00 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
3 (ii) They have common verte. (iii) Non-common arms lying on the different sides of the common arm. In the figure, and are adjacent angles. They have common verte, common arm and non-common arms and lying on the different sides of. z Linear air Two adjacent angles whose sum is 80 are said to form linear pair or in other words, supplementary adjacent angles are called linear pair. Here, + = 80, so they form linear pair. Linear air iom iom- If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of two adjacent angles so formed is 80. Ray stands on line, then and are adjacent angles. + = 80 iom- If the sum of two adjacent angles is 80, then the non-common arms of the angles form a straight line. Suppose and are two adjacent angles, with common arm, non common arms and. If + = 80, then would be a straight line. Vertically pposite ngles If two lines and intersects each other at point, then four angles are formed. is vertically opposite to. Similarly is vertically opposite to. These are called pairs of vertically opposite angles. Theorem Statement : If two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles are equal. Given : and are two lines intersecting each other at point. is vertically opposite to and is vertically opposite to. To rove : = = roof : + = 80...() [Linear pair] + = 80...() [Linear pair] rom () and (), we get + = + = Similarly, = Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 0
4 is a line such that = 5 and = 4. ind the value of and hence find and. 5 Soln.: Since is a line, \ and form a linear pair + = = 80 9 = 80 = 0 4 \ = 5 = 5 0 = 00 = 4 = 4 0 = 80 If the supplement of an angle is two-third of itself. etermine the angle and its supplement. Soln.: Let the angle be \ Its supplement = of = = 80 = = 80 = = \ The angle is 08 and its supplement = 08 = 36 = Lines, and intersect at. ind the measures of, and Soln.: and intersect at point. \ = [Vertically opposite angles] \ = 40 Similarly, = [Vertically opposite angles] = 35 lso, + + = 80 [Straight angle] = = 05 4 Lines l and l intersects at point forming angles a, b, c, d. l a d c If a = 45, find b, c, d, a + b, b + c and verify that a + d = b + c. Soln.: a = 45 c = 45 [Vertically opposite angles] a + d = 80 [Linear pair] d = 80 a = = 35 d = b [Vertically opposite angles] b = 35 Now, a + d = = 80 b + c = = 80 a + d = b + c b l Transversal line which intersects two or more lines at distinct points is called a transversal. l l q m q m ( q is a transversal of l and m) ( q is not a transversal of l and m) 0 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
5 ngles ormed by a Transversal Suppose l and m are two parallel lines intersected by a transversal n. Interior ngles, 4, 5, 6 terior ngles 3,, 7, 8 orresponding ngles : and 8, and 6, 3 and 5, 4 and 7 [Note that pairs of angles lie either above or below the lines.] lternate Interior ngles : 4 and 6, and 5 lternate terior ngles : 3 and 8, and 7 n o-interior ngles : (lso called consecutive interior angles or allied angles) 4 and 5, and 6. o-terior ngles : and 8, 3 and 7. l m Results when a Transveral Intersects Two arallel lines orresponding ngles iom (i) If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then each pair of corresponding angles are equal. (ii) If a transversal intersects two lines such that a pair of corresponding angles are equal, then the two lines are parallel to each other. lternate Interior ngles Theorem (i) If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then each pair of alternate interior angles are equal. (ii) If a transversal intersects two lines such that a pair of alternate interior angles are equal, then the two lines are parallel. o-interior ngles Theorem (i) If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then each pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal is supplementary. In other words, co-interior angles are supplementary. (ii) If a transversal intersects two lines such that a pair of co-interior angles are supplementary, then the two lines are parallel. o-eterior ngles Theorem (i) If a transversal intersects two parallel lines then each pair of co-eterior angles are supplementary. (ii) If a transversal intersects two lines such that a pair of co-eterior angles are supplementary, then two lines are parallel. arallel Lines Theorem Lines which are parallel to the same line are parallel to each other. This means if l n and m n l m. l m n Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 03
6 5 In the given figure if l m and t is a transversal, determine. ( + 6 ) l Q = 68 [rom (ii)] So, Q = = 68 and = 34 Soln.: l m t = 80 [o-eterior angles] = 80 6 = 64 = 3 6 and Q. etermine Q, and. 34 Soln.: and transveral intersects them at and respectively. \ = [orresponding angles] Q 78 = (i) Now ray stands on at \ + = 80 [Linear pair] + + = 80 m [ = + ] = 80 [rom (i)] = 80 = 68...(ii) Now Q and transversal intersects them at and respectively. \ = Q [orresponding angles] 7 If l m n and Q RS, find QRS. 70 Q R Soln.: tend Q to point and SR to point. l m = 5 [lternate interior angles] and = 70 lso, 3 = 3 = 70 S l m n [orresponding angles] [ S, corresponding angles] Now, = 80 [Linear pair] = 80 4 = 0 \ QRS = + 4 = = 35 8 In figure, if, G = 65 and = 80, then find and y y G Soln.: = [lternate interior angles] 65 + = 80 = = 5 Now, G = G [lternate interior angles] y = 65. roperties of Triangles z ngle Sum roperty of a Triangle Theorem Statement : The sum of the three angles of a triangle is 80. i.e., = LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
7 roof : raw a line XY through point parallel to. 3 = 4 [lternate interior angles] X 5 = [lternate interior angles] lso = 80 [Straight angle] Replacing 5 and 4 by and 3 respectively, we get = = 80 \ Sum of all angles of a triangle is Y z terior ngle roperty of a Triangle Theorem 3 Statement : If a side of a triangle is produced, then the eterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles. Given : In, side is etended to point. is an eterior angle. To rove : = + roof : + + = 80...() [ngle sum property of triangle] lso, + = 80...() [Linear pair] rom () and (), we get + + = + = + 9 If one angle of a triangle is 7 and the difference of the other two angles is, find the other two angles. Soln.: ne angle of the triangle = 7 Let other two angles be and + [Q The difference between the two angles is ] So, = 80 [ngle sum property of triangle] + 84 = 80 = = = = 48 \ The other angles are 48 and 48 + = 60 0 In the given figure show that l m l m n Soln.: + + = 80 [ngle sum property of triangle] = 80 = = 07 Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 05
8 + = 80 [Linear pair] = = 73 Since, = 73 and = 73 So, = l m [s corresponding angles are equal] The sides, and of, are produced in order, forming eterior angles, and. rove that + + = 360. Soln.: 3 rom eterior angle property of triangle, = (i) = (ii) = +...(iii) dding (i), (ii) and (iii), we get + + = = ( + + 3) = 80 [y angle sum property of triangle] + + = LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
9 ngle n angle is formed when two rays originate from the same point. Some ngle Relations z djacent ngles Two angles are called adjacent angles, if (i) they have same verte (ii) they have common arm (iii) uncommon arms are on different sides of the common arm z Linear air of nlges Two adjacent angles are said to form a linear pair of angles, if (i) their non-common arms are two opposite rays (ii) the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is 80 (iii) they are supplementary. z Vertically pposite ngles If two lines and intersects each other at point, then is vertically opposite to. Similarly is vertically opposite to. z Transversal line which intersects two or more given lines at distinct points, is called a transversal of the given lines. z The measures of vertical opposite angles are equal. z The measures of angles forming a linear pair has total 80. z ngle Relationships ormed by arallel Lines being cut by a Transversal. (i) The measures of alternate eterior angles are equal. (ii) The measures of alternate interior angles are equal. (iii) The measures of the same-side interior angles are supplementary (sum to 80 ) (iv) The measures of corresponding angles are equal z Lines which are parallel to a given line are parallel to each other. z Sum of three angles of a triangle is 80. z If a side of a triangle is produced, the eterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles. Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 07
10 SLV XMLS. rove that the sum of all angles formed on the same side of a line at a given point on the line is 80. Soln.: Given : is a straight line and rays, and stands on it, forming,, and. To rove : = 80. roof : Ray stands on line. \ + = 80 [Linear pair] + ( + + ) = = 80. Hence, the sum of all the angles formed on the same side of line at a point on it is 80.. rove that the bisectors of the angles of a linear pair are at right angle. Soln.: Given : and form a linear pair of angles. and are the bisectors of and respectively. To rove : = 90. roof : + = 80 [Linear pair] + = 90 + = 90 [Q and are the bisectors of and ] = 90. Hence, the bisectors of the angles of a linear pair are at right angle. 3. rove that the bisectors of a pair of vertically opposite angles are in the same straight line. Soln.: Given : Two lines and intersecting each other at a point. lso, and are the bisectors of and respectively. To rove : is a straight line. roof : Since, the sum of all angles around a point is 360, \ = = 360 [Q = (Vertically opposite angles). is bisector of, is bisector ] + + = 80 =80 Hence, is a straight line. 4. In the figure, lines and intersect at. If + = 80 and = 30, find and refle. Soln.: + = 80...(i) [Given] = 30...(ii) [Given] Lines and intersect at. \ = [Vertically opposite angles] = 30 [rom (ii)] Now, putting the value of in (i), we have 30 + = 80 = = 50. lso, + = 80 [Linear pair] = = 50 and refle = = LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
11 5. In the figure, lines XY and MN intersect at. If Y = 90 and a = b, find c. 7. If, then find the value of. M X b a c Y Soln.: onstruct a line l through parallel to. N Soln.: Given a = b Let a = then b = XM + M + Y = 80 [Linear pair] = = 80 = = = 45 \ XM = b = 45 and M = a = 45 Now, XN = c = MY [Vertically opposite angles] = M + Y = Hence, c = In the figure, if, and y : z = : 3, find. G Soln.: Let y = a and z = 3a HI + IH = 80 [, o-interior angles] y + z = 80 a + 3a = 80 5a = a = = 36 5 \ y = a = 36 = 7 and z = 3a = 3 36 = 08 lso, and GI is a transversal \ GI = HI [orresponding angles] = y = 7 H y I z l and = + Since, l = 0 [lternate interior angles] lso, l = 0 [lternate interior angles] Now, = + = = The side of a is produced such that is on ray. The bisector of meets in L as in figure. rove that + = L. L Soln.: In, we have = + [terior angle property of a triangle] = +...(i) [Q L is the bisector of \ = ] In L, we have L = + L [terior anlge property of a triangle] L = + L = +...(ii) Subtracting (i) from (ii), we get L = + = L + = L. 9. bisects and =, prove that. Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 09
12 Soln.: In, we have = + [terior angle property of a triangle] = [Given = ] = [Q is bisected by ] = = [s alternate interior angles are equal] 0. In figure, lines Q and RS intersect each other at point, ray and ray bisect R and S respectively. If : = : 7, then find SQ and Q. R Soln.: R + S = 80 [Linear pair] We are given that, ray and ray bisect R and S respectively. Therefore, = R and = S. + = R + S ( ) = 80 = 90 Now, if : = : 7, then, we have = 90 = 0 and 9 = 7 90 = R = = 0 = 40 SQ = R [Vertically opposite angles] \ SQ = 40 Q = S + SQ = + SQ = = 0 \ Q = 0. Q S = = S S. Ray bisects and is the ray opposite. Show that 3 = Soln.: Ray and are opposite. So, is a straight line. \ 3 + = 80 (Linear pair)...(i) and 4 + = 80 (Linear pair)...(ii) rom (i) and (ii), we have 3 + = = 4 + (Q bisect = ) 3 = 4. In the figure, line l and m intersect at, forming angles as shown in the figure. l m z y v (i) If = 45, what is z? (ii) If v = 5, what is y? Soln.: (i) z = = 45 (Vertically opposite angles) (ii) y = v = 5 (Vertically opposite angles) 3. In the given figure, and GH. ind the values of, y, z and t. 00 R 50 H Q z t S Soln.: GH and RQ is a transversal y = 50 (orresponding angles) Q and RQ interesect at R. = 50 (Vertically opposite angles) Now, GH and Q is a transversal 00 + z = 80 (o-eterior angles) z = z = 80 y G 0 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
13 Q and QS is a transversal t = z (lternate interior angles) t = In the figure,. If = 4 y 3 find the values of, y and z. y z and y z = = 36 = 48 3 and, z= 8 y 3 8 = 36 z = In the figure, prove that T QU. T U Soln.: and is a transversal ( + y) + z = 80 (co-interior angles) y = 36 Now, = 4 y = Q = y and y = z z = y = 80 = Soln.: In QRS 85 Q S = (terior angle property = 85 UQR = 85 So, TR = UQR T UQ R of a triangle) (s corresponding angles are equal) Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS
14 NRT STIN ercise 6.. In the given figure, lines and intersect at. If + = 70 and = 40, find and refle. Soln.: Since is a straight line, \ + + = 80 or ( + ) + = 80 or 70 + = 80 [Q + = 70 (Given)] or = = 0 \ Refle = = 50 lso, and intersect at. \ = [Vertically opposite angles] ut = 40 [Given] \ = 40 lso, + = 70 \ 40 + = 70 or = = 30 Thus, = 30 and refle = 50.. In the given figure, lines XY and MN intersect at. If Y = 90 and a : b = : 3, find c. 90 b = 3 = 54 5 Since XY and MN intersect at, \ c = [a + Y] [Vertically opposite angles] or c = = 6 Thus, the required measure of c = In the given figure, QR = RQ, then prove that QS = RT. S Q Soln.: ST is a straight line, \ QR + QS = 80...() [Linear pair] Similarly, RT + RQ = 80...() [Linear air] rom () and (), we have QS + QR = RT + RQ ut QR = RQ [Given] \ QS = RT 4. In the given figure, if + y = w + z, then prove that is a line. y z w R T Soln.: Since XY is a straight line. \ b + a + Y = 80 ut Y = 90 [Given] \ b + a = = 90 lso a : b = : 3 90 a = + = 90 = Soln.: Sum of all the angles at a point = 360 \ + y + z + w = 360 or, ( + y) + (z + w) = 360 ut ( + y) = (z + w) [Given] \( + y) + ( + y) = 360 or, ( + y) = or, ( + y) = = 80 \ is a straight line. LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
15 5. In the given figure, Q is a line. Ray R is perpendicular to line Q. S is another ray lying between rays and R. rove that RS = QS S ( ). Q Soln.: Q is a straight line. S \ S + RS + RQ = 80 ut R ^ Q \ RQ = 90 S + RS + 90 = 80 S + RS = 90 R [Given] RS = 90 S... () Now, we have RS + RQ = QS RS + 90 = QS RS = QS () dding () and (), we have RS = ( QS S) \ RS = QS S ( ). 6. It is given that XYZ = 64 and XY is produced to point. raw a figure from the given information. If ray YQ bisects ZY, find XYQ and refle QY. Soln.: XY is a straight line. Since XYQ = XYZ + ZYQ XYQ = 64 + QY [Q XYZ = 64 (Given) and ZYQ = QY] XYQ = = [ QY = 58 ] Thus, XYQ = and refle QY = 30. ercise 6.. In the given figure, find the values of and y and then show that y Q Soln.: In the figure, we have and Q intersect at. \ y = 30...() [Vertically opposite angles] gain, Q is a straight line and stands on it. \ + Q = 80 [Linear pair] or 50 + = 80 = = () rom () and (), = y s they are pair of alternate interior angles. \. In the given figure, if, and y : z = 3 : 7, find. y \ XYZ + ZYQ + QY = ZYQ + QY = 80 [Q XYZ = 64 (given)] 64 + QY = 80 [YQ bisects ZY so, QY = ZYQ] QY = = 6 6 QY = = 58 \ Refle QY = = 30 Mathematics lass 9 Soln.: and [Given] \ and Q is a transversal. \ = z... () [lternate interior angles] gain, + y = 80 [o-interior ngles] z + y = 80 [y ()] z Q LINS N NGLS 3
16 ut y : z = 3 : 7 80 \ z = + = = 6 ( 3 7) 0 rom () and (), we have = () 3. In the given figure, if, ^ and G = 6, find G, G and G. G Soln.: and G is a transversal. \ G = G [lternate interior angles] ut G = 6 [Given] \ G = 6 lso, G + = G or G + 90 = 6 [Q ^ (given)] G = 6 90 = 36 Now, and G is a transversal. \ G + G = 80 [o-interior angles] or G + 6 = 80 or G = 80 6 = 54 Thus, G = 6, G = 36 and G = In the given figure, if Q ST, QR = 0 and RST = 30, find QRS. [Hint: raw a line parallel to ST through point R.] Soln.: raw a line parallel to ST through R. 0 Q R S 30 Since Q ST [Given] and ST [onstruction] \ Q and QR is a transversal QR = QR [lternate Interior ngles] T ut QR = 0 [Given] \ QR = QRS + SR = 0...() gain ST and RS is a transversal \ RST + SR = 80 [o-interior angles] or 30 + SR = 80 SR = = 50 Now, from (), we have QRS + 50 = 0 QRS = 0 50 = 60 Thus, QRS = In the given figure, if, Q = 50 and R = 7, find and y. Soln.: We have and Q is a transversal. \ Q = QR [lternate interior angles] or 50 = [Q Q = 50 (Given)] gain, and R is a transversal. \ R = R [lternate interior angles] R = 7 [Q R = 7 (given)] Q + QR = y = 7 [Q Q = 50 (given)] y = 7 50 = 77 Thus, = 50 and y = In the given figure, Q and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. n incident ray strikes the mirror Q at, the reflected ray moves along the path and strikes the mirror RS at and again reflects back along. rove that. 4 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
17 Soln.: raw ray L ^ Q and M ^ RS X 6 54 Q Q RS L M [Q L ^ Q and M ^ RS] Now, L M and is a transversal. \ L = M...() [lternate interior angles] Since, angle of incidence = ngle of reflection L = L and M = M L = M...() \ dding () and (), we have L + L = M + M = i.e., a pair of alternate interior angles are equal, \. ercise 6.3. In the adjoining figure, sides Q and RQ of QR are produced to points S and T respectively. If SR = 35 and QT = 0, find RQ. Y Soln.: In XYZ, we have XYZ + YZX + ZXY = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] ut XYZ = 54 and ZXY = 6 \ 54 + YZX + 6 = 80 YZX = = 64 Y and Z are the bisectors of XYZ and XZY respectively, YZ= XYZ = 54 = 7 ( ) and ZY = YZX = 64 = 3 ( ) Now, in YZ, we have YZ + YZ + ZY = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] YZ = 80 YZ = = Thus, ZY = 3 and YZ = 3. In the given figure, if, = 35 and = 53, find. 35 Z Soln.: We have, TQ + QR = 80 [Linear pair] 0 + QR = 80 QR = 80 0 = 70 Since, the side Q of QR is produced to S. QR + RQ = 35 [terior angle property of a ] 70 + RQ = 35 [ QR = 70 ] RQ = RQ = 65. In the adjoining figure, X = 6, XYZ = 54. If Y and Z are the bisectors of XYZ and XZY respectively of XYZ, find ZY and YZ. Mathematics lass 9 53 Soln.: and is a transversal. So, = [lternate interior angles] and = 35 [Given] \ = 35 Now, in, we have + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] \ =80 [Q = = 35 and = 53 (Given)] = = 9 Thus, = 9 LINS N NGLS 5
18 4. In the adjoining figure, if lines Q and RS intersect at point T, such that RT = 40, RT = 95 and TSQ = 75, find SQT. R T 75 S Q Soln.: In RT, we have + R + TR = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] TR =80 [Q = 95, R = 40 (given)] TR = = 45 ut Q and RS intersect at T, \ TR = QTS [Vertically opposite angles] \ QTS = 45 [Q TR = 45 ] Now, in TQS, we have TSQ + STQ + SQT = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] \ SQT =80 [Q TSQ = 75 and STQ = 45 ] SQT = = 60 Thus, SQT = In the adjoining figure, if Q ^ S, Q SR, SQR = 8 and QRT = 65, then find the values of and y. Q 8 y 65 S R T Soln.: In QRS, the side SR is produced to T. \ QRT = RQS + RSQ [terior angle property of a triangle] ut RQS = 8 and QRT = 65 So, 8 + RSQ = 65 RSQ = 65 8 = 37 Since, Q SR and QS is a transversal. \ QS = RSQ = 37 [lternate interior angles] = 37 gain, Q ^ S = 90 Now, in QS, we have + QS + SQ = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] y = 80 y = = 53 Thus, = 37 and y = In the adjoining figure, the side QR of QR is produced to a point S. If the bisectors of QR and RS meet at point T, then prove that QTR = QR. Soln.: In QR, side QR is produced to S, so by eterior angle property, RS = + QR RS= + QR...() TRS= + TQR...() [Q QT and RT are bisectors of QR and RS respectively.] Now, in QRT, we have TRS = TQR + T...(3) [terior angle property of a triangle] rom () and (3), we have TQR+ = TQR+ T = T QR= QTR or QTR= QR 6 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
19 XRIS Multiple hoice Questions Level-. n angle is 8 less than its complementary angle. The measure of this angle is (a) 36 (b) 48 (c) 83 (d) 8. Supplement of an angle is one fourth of itself. The measure of the angle is (a) 8 (b) 36 (c) 44 (d) 7 3. Line and intersect to. If = (3 0 ) and = (0 ), then the value of, is (a) 6 (b) (c) 36 (d) If l m, then value of is 0 (a) 60 (b) 0 (c) 40 (d) annot be determined 5. The value of from the adjoining figure, if l m is (a) 5 (b) 0 (c) 9 (d) In, : : = : 3 : 5, then angle at is (a) 54 (b) 6 (c) 36 (d) In adjoining figure if = (3 + ), = ( 3 ), = 7, then = Mathematics lass 9 p l m (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 96 (d) The value of if is a straight line, is (a) 36 (b) 60 (c) 30 (d) If, what is the value of? 5 (a) 8 (b) 5 (c) 0 (d) 5 0. If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then each pair of corresponding angles so formed is (a) qual (b) omplementary (c) Supplementry (d) None of these. n angle is 4 more than its complementary angle, then angle is (a) 30 (b) 5 (c) 50 (d) None of these. If the supplement of an angle is three times its complement, then angle is (a) 40 (b) 35 (c) 50 (d) Which one of the following statement is not false? (a) If two angles forming a linear pair, then each of these angle is of measure 90. (b) ngles forming a linear pair can both be acute angles. (c) oth of the angles forming a linear pair can be obtuse angles. (d) isectors of the adjacent angles forming a linear pair form a right angle. LINS N NGLS 7
20 4. alculate the value of. 8 (a) 70 (b) 70 (c) 5 (d) alculate the value of. (a) 4 (b) 70 (c) 05 (d) In figure, if l m, then = (a) 45 (b) 5 (c) 5 (d) In Q.6, value of y = (a) 45 (b) 65 (c) 55 (d) 8 8. In figure, if l m, l n and : y = 3 :, then z = (a) 0 (b) 6 (c) 08 (d) In figure, if l m, then = (a) 30 (b) 40 (c) 0 (d) 54. ind the value of (a) 70 (b) 75 (c) 60 (d) 65. ind (a) 45 (b) 60 (c) 50 (d) If two interior angles on the same side of a transversal intersecting two parallel lines are in the ratio 5 : 4, then the greater of the two angles is (a) 54 (b) 00 (c) 0 (d) If is a straight line, then is (a) 60 (b) 30 (c) 90 (d) In the adjoining figure, if l m and n be the transversal, then the relation between and is n l m 70 (a) 0 (b) 0 (c) 90 (d) In figure, if l m, m n, then = 50 l m l m n (a) = (b) + = 80 (c) = 90 (d) + = 90 Level- 6. If angle with measure and y form a complementary pair, then angles with which of the following measures will form a supplementary pair? (a) ( + 47 ), (y + 43 ) (b) ( 3 ), (y + 3 ) (c) ( 43 ), (y 47 ) (d) No such pair is possible 8 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
21 7. If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then triangle is a/an (a) acute angled triangle (b) obtuse angled triangle (c) right angled triangle (d) none of these 8. In figure, if, and y : z = 4 : 5, = (a) 00 (b) 76 (c) 8 (d) 9. In figure, lines and intersect at. If + = 00 and = 60, find and refle respectively. 3. In figure, and transversal cuts them at G and H respectively. If G = 0, then GH = In figure, a transversal Q intersects two parallel lines and at L and M respectively. If = 95, then =.... L M 5. In figure, if is a straight line, then =.... Q 6. In figure, is a straight line and is greater than by 60, then =... (a) 40, 80 (b) 40, 60 (c) 30, 60 (d) 30, In figure, lines XY and MN intersect at. If Y = 70 and : y = 3 :, find z. 7. In figure, if = and = 3, the magnitude of which makes a straight line is.... (a) 70 (b) 95 (c) 36 (d) 0 ill in the lanks. If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the sum of the interior angles on the same side of the transversal is In figure, is a straight line, if =, then = In figure, =.... ( + 0) ( + 40). Lines which are parallel to the same line are... to each other. Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 9
22 0. In figure, =..., y =..., z =... True or alse. ngles forming a linear pair are supplementary.. If two adjacent angles are equal, then each angle measure ngles forming a linear pair can be both acute angles. 4. If angles forming a linear pair are equal, then each of these angles is of measure If two lines intersect each other and one pair of vertically opposite angles is formed by acute angles, then the other pair of vertically opposite angles will be formed by obtuse angles. 6. If two lines are intersected by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. 7. If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then alternate angles are equal. 8. If two lines are intersected by a transversal, then angles on the same side of transversal are supplementary. 9. Two angles are complementary if their sum is The supplementary angles have their sum equal to 360. Match the ollowing In this section each question has two matching lists. hoices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.. Use the given figure to match List-I with List-II. z y 55 () List-I ngles m and y are List-II () lternate interior pair of angles (Q) ngles a and d are () lternate eterior pair of angles (R) ngles d and u are (3) Vertically opposite angles (S) ngles u and g are (4) orresponding angles ode : Q R S (a) 3 4 (b) 4 3 (c) 4 3 (d) 4 3. Use the given figure to match List-I with List-II., List-I List-II () orresponding () = 7 angles (Q) lternate interior () = 80 angles (R) lternate eterior (3) = 5 angles (S) o-interior angles (4) 4 = 6 ode : Q R S (a) 4 3 (b) 3 4 (c) 4 3 (d) 3 4 ssertion & Reason Type irections : In each of the following questions, a statement of ssertion is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason just below it. f the statements, mark the correct answer as (a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct eplanation of assertion. (b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct eplanation of assertion. (c) If assertion is true but reason is false. (d) If assertion is false but reason is true. 0 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
23 . ssertion : Two adjacent angles always form a linear pair. Reason : In a linear pair of angles two noncommon arms are opposite rays.. ssertion : The bisectors of the angles of a linear pair are at right angles. Reason : If the sum of two adjacent angles is 80, then the non-common arms of the angles are in a straight line. 3. ssertion : If a line is perpendicular to one of the two given parallel lines then it is also perpendicular to the other line. Reason : If two lines are intersected by a transversal then the bisectors of any pair of alternate interior angles are parallel. 4. ssertion : In figure, if XY is parallel to Q, then the angles and y are 70 and 45 respectively. (ii) each pair of alternate interior angles are equal (iii) each pair of co-interior angles are supplementary.. In the given figure, Q. The values of and y respectively are 75 5 y 0 G (a) 50, 70 (b) 70, 50 (c) 75, 45 (d) 0, 75. In the figure,. Then the value of p + q r = Q (a) 80 (b) 80 (c) 00 (d) 360 Reason : Sum of angles of a triangle is ssertion : In the given figure, if and = 30, then is In the given figure, Q RS and QXN = 05, RYN = 45, find XNY. Reason : If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then co-interior angles are equal. (a) 45 (b) 30 (c) 60 (d) 0 SSG-II : The sum of all the angles formed on the same side of a line at a given point on the line is 80.. ind largest angle, if is a straight line. omprehension Type SSG-I : If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then (i) each pair of corresponding angles are equal y y 3y (a) 60 (b) 30 (c) 80 (d) 90 Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS
24 . If three straight lines, Q and RS intersect at. ind the value of from the given figure. (a) 0 (b) 7 (c) 7 (d) In the given figure and are two lines intersecting at. If and are in ratio : 3, find all angles. (a) 7, 08, 08, 7 (b) 45, 00, 00, 45 (c) 30, 0, 30, 0 (d) 50, 0, 50, 0 SSG-III : If a transversal intersects two lines in such a way that a pair of alternate interior angles are equal, or each pair of co-interior angles are supplementary then the two lines are parallel.. rom the given figure for what value of if l m. (a) 60 (b) 90 (c) 50 (d) 0 Subjective roblems Very Short nswer Type. In the figure, find the angles marked as and y.. In the figure,. ind the values of and y. 3. In the figure and, find a and b. 0 l m (a) 0 (b) 80 (c) 60 (d) 00. In the given figure, is an isosceles triangle with = and, = 50. ind 50 (a) 50 (b) 60 (c) 65 (d) In the figure, find the value of, if is bisector of angle in the triangle In figure, if QT ^ R, TQR = 40 and SR = 30, find. 30 T 3. In the given figure. If = 45 and = 75. ind. Q 40 S R LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
25 6. In figure,, = 70 and = 40, then find In figure, R and QR form a linear pair. If a b = 80, find the value of a and b. a R 40 Q 8. In the figure,. ind the value of. 00 b 0 9. rom the adjoining figure, find, y and z. 70 y z. In figure, and. lso ^. If = 55, find the values of, y and z. z 55 y 3. In the figure, and Q RS, find the value of angles,, 3, 4, 5, 6 and Q R S 4. The sides and of the parallelogram are produced as shown in figure. rove that a + b = + y. y a 0. In the given figure,, Q. ind value of and y. b 5. In the figure given, and G find and y. 65 y 5 G H Short nswer Type. In the given figure, divides in the ratio : 3 and =. etermine the value of QRST is a regular pentagon and bisector of TQ meets SR at L. If bisector of SRQ meets L at M, find RML. S L T R M Q Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 3
26 7. In figure, if, G,, = 55 and 4 = 60, then find and In the adjoining figure bisects, bisects and ^. Show that,, are collinear. 9. In figure,. rove that + = In the given figure,. ind the value of G Long nswer Type. In the given figure, S is the angle bisector of the QR. T ^ QR. rove that TS = Q T S 45 R. In the given figure, b a = 65 and = 90, find the measure of, and. 3. In a, = 90 and ^. rove that =. 4. In figure, the sides and of are produced to points and respectively. If bisectors and of and respectively meet at point, then find. 5. In the figure, l m n and. ind the value of angles,, 3, 4, 5 and Integer nswer Type 4 3 In this section, each question, when worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).. In the given figure,. ind the value of If an angle is supplement of itself. Then value of 60 is 6 6 l m n y 4 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
27 3. ngles of a triangle are in ratio : : 3, then the greatest angle is what times to the smallest angle. 4. If two interior angles on the same side of a transversal intersecting two parallel lines are in the ratio of : 4. Then what will be the result if difference of the angles is divided by smaller angle. irections (5 0) : In the given figure, l m and p q. 5. a = 6. ngle b when divided by is 7. What is the sum of digits of angle c? 8. What is the sum of digits of angle d? 9. Value of e + 5 is 0 0. alculate f 5. 5 Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS 5
28 HTR 6 Lines and ngles Multiple hoice Questions. (a) : Let the angle be. \ its complement = = 90 = 90 8 = 7 = 36. (c) : Let the angle be \ its supplement = of = = 80 = = = (a) : Since vertically opposite angles are always equal \ (3 0 ) = (0 ) 3 + = = 30 = (a) : + 0 = 80 [Linear pair] = 80 0 = 60 Since l m = = 60 M36 LINS N NGLS [orresponding ngles] 5. (a) : Since l m = 80 [o-interior angles] = 80 4 = 60 = 5 6. (a) : : : = : 3 : 5 =, = 3, = 5 \ + + = = 0 0 = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] = 8 = 3 8 = (d): In = + [y eterior angle property of a triangle] 7 = = 4 8 = 4 = 3 \ = (3 + ) = = 96 + = (b): = [Vertically opposite angles] Since is a straight line + + = 80 3 = 80 \ = (c) : Since = 80 [o-interior angles] 9 = 80 \ = 0 0. (a). (b): Let the angle be. omplement of = (90 ) Since the difference is 4, we have (90 ) = 4 = 04 = 5.. (d): Let the angle be. omplement of = 90 Supplement of = 80 Given that, 80 = 3 (90 ) 80 = 70 3 = = 90 = 45. lass 9 Mathematics
29 3. (d) 4. (c) : = 80 [Linear air] = 80 = (a) : = 360 [omplete ngle] = (b): Since l m, then y = 55 [orresponding ngles] Now, + y = 80 [Linear air] + 55 = 80 = 5 7. (c) 8. (c) : We have, l m, l n m n. Now, : y = 3 : = 3 y Mathematics lass 9... (i) lso + y = 80 [o-interior ngles] 3 + = 80 = 7 lso, = z...(ii) [lternate Interior ngles] rom (i) and (ii), we have 3 3 z= y z = 7 = (b) : Since l m, 70 + = 80 [o-interior ngles] = 0 0. (a) : Since l m and m n, then l n + 50 = 80 [o-interior ngles] = 30.. (b) : + (80 30 ) + (80 5 ) = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] = 80 = 75.. (d) : = 80 ( ) = 55 [ngle sum property of a triangle] \ = = 55 [Vertically opposite angles] 3. (b): Let the angle be 5 and 4. Since, these two angles are co-interior angles. So, we have = 80 9 = 80 = 0. Hence, greater angle = 5 = 5 0 = (d): Since, is a straight line \ ( + 40 ) + ( 0 ) + = = 80 4 = 60 = (b): Since l m and n is a transversal line. \ = (lternate interior angles) and + = 80 (Linear pair) + = (a) : and y forms a complementary pair + y = 90 Now, y + 43 = + y = + y + 90 = = 80 \ ( + 47 ) and (y + 43 ) form a supplementary pair. 7. (c) : Let,, be the three angles of a triangle. = + [Given] lso, + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] + = 80 = 80 = 90 \ Triangle is a right angled triangle. 8. (a) : Given that and \ + y = 80...(i) [o-interior ngles] y + z = 80...(ii) [ HI = y, (Vertically pposite ngles)] Given that y : z = 4 : 5 y = 4 z 5 Substituting in (ii), we get = 80 = 80 5 z = 80 5 z = 00 9 Substituting value of z in (ii), we get y + 00 = 80 y = 80 rom (i), we have + 80 = 80 = 00. LINS N NGLS M37
30 9. (a) : and intersect at. = (vertically opposite angles) = 60 Now, + = 00 (given) = = 40 is a straight line. + + = = 80 = = 80 Refle = = (c) : : y = 3 : Let = 3a and y = a Now, XY is a straight line. \ + y + Y = 80 3a + a + 70 = 80 5a = 0 a = Hence, = 3a = 3 = 66 and y = a = = 44 Now, XY and MN intersect at. \ z = + Y (vertically opposite angles) z = z = 36 ill in the lanks. 80. arallel : and G = 0 GH = G = 0 [Vertically pposite ngles] nd, GH + GH = 80 [o-interior ngles] GH = 80 0 = : = LM [Vertically pposite ngles] LM = 95 \ = 95 [orresponding ngles] : is straight line () + ( + 3) + ( + 5) = 80 4 = = 7 = : = + 60 is a straight line \ + = 80 = = 60 So, = : or to be a straight line 8. + = = 80 0 = 60 \ = 6 80 : is a straight line = 80 ( + 40) + ( + 0) + ( + 40) = = 80 3 = 80 \ = : = 80 [Linear air] = 80 3 = 77 = , 5, 5 : = 55 lso, + y = 80 [Vertically pposite ngles] y = = 5 [Linear air] Now, z = y = 5 [Vertically pposite \ = 55, y = 5, z = 5. True or alse. True ngles]. alse : The measure of each adjacent angle that are equal may not be equal to alse : ngles forming a linear pair cannot be both acute angles because then their sum cannot be True : + = 80 [Linear pair] = 80 = 90 \ If each angle forming a linear pair are equal then each angle is of measure 90. M38 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
31 5. True : + = 80 [Linear pair] If < 90 > cute ngle a (acute) (obtuse) and 3 are acute and and 4 are obtuse. 6. alse : If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. 7. True 8. alse : Two lines must be parallel. 9. True 0. alse : Sum of supplementary angles is 80. Match the ollowing. (b): ; Q ; R 4; S 3 () ngles m and y lternate eterior pair of angles (Q) ngles a and d lternate interior pair of angles (R) ngles d and u orresponding angles (S) ngles u and g Vertically opposite angles.. (d): 3; Q 4 ; R ; S () orresponding angles = 5 (Q) lternate interior angles 4 = 6 (R) ltenate eterior angles = 7 (S) o-interior angles = 80 ssertion & Reason Type. (d): Two adjacent angles do not always form a linear pair. In a linear pair of angles two non-common arms are opposite rays. ssertion: alse; Reason: True. (b): + = 80 [Linear air] 80 ( + ) = + = 90 + = 90. \ The bisectors of the angles of a linear pair are at right angles. ssertion: True; Reason: True but is not the correct eplanation of assertion. 3. (c) : l m and n ^ l = 90 [orresponding angles] n ^ m Reason is false. It can be stated in case of parallel lines. ssertion: True; Reason : alse. 4. (d): XY Q and is a transversal Q = Y (orresponding angles) 0 + y = 60 y = 60 0 y = 40 Now, in, + 0 = (ternal angle property) + 0 = = 95 0 = 75 ssertion: alse; Reason: True n 90 l m Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS M39
32 5. (c) : In, by pythagoras theorem. + + = = 80 = 80 0 = 60 and intersect at \ = (vertically opposite angles) = 60 Now, and is a transversal + = 80 (o-interior angles) = = 0 ssertion: True; Reason: alse. omprehension Type SSG-I. (b): = Q [orresponding angles] 5 + y = 75 y = 50 M40 LINS N NGLS 75 5 y 0 G lso, + Q = 80 [o-interior angles] ( G + G) + (5 + y ) = 80 G = 80 G = 85 In G, G + G + = = 80 = 70.. (b): raw HK parallel to, let H be and H p G HG be y such that + y = q. p + = 80 [o-interior ngles] y = r [lternate Interior ngles] dding both equations, we get p + + y = 80 + r p + q = 80 + r p + q r = 80 r y Q K 3. (d) : onstruction : raw l Q + QXN = 80 [o-interior ngles] \ = = 75 nd, \ = RYN [lternate Interior ngles] = 45 XNY = + = = 0 SSG-II. (d): y + y + 3y = 80 [Linear air] 6y = 80 y = 30 \ largest angle = 3y = 3 30 = 90. (c) : R =, = 4 and = RQ = 45 Q is a straight line R + + RQ = 80 [Linear air] = 80 5 = = 35 = 7 3. (a) : + = 80 [Linear air] Let = and = 3 \ + 3 = 80 = 36 Thus, = 7, = 08, = 08, = 7. SSG-III. (c) : = 0 [Vertically pposite ngles] or l m, co-interior angles must be supplementary, so + = = 80 \ = 60. (c) : Since is an isosceles triangle. \ = = Now, in, + + = 80 [ngle sum property of ] = = 30 = 65 Since = [lternate Interior ngles] \ = = 80 [Linear air] \ = = 65. lass 9 Mathematics
33 3. (d): [Given] = [lternate Interior ngles] = 45 Now, in, is eterior angle So, = + [terior angle property of a ] = = 0 Subjective roblems Very Short nswer Type. + 5 = 80 [o-interior ngles] \ = 80 5 = 55 Now y + 5 = 75 [lternate Interior ngles] \ y = 75 5 = 50. Hence, = 55, y = 50.. G = [orresponding ngles] \ y + 0 = 58 y = 58 0 y = 38 gain, y + = [terior angle of G] \ 38 + = 58 + = = 4 Hence, = 4, y = = 55 and = b b = 55 [orresponding ngles] In, = 80 (60 + b ) [ngle sum property of a triangle] = 80 ( ) = 80 5 = 65 \ a = = 65 [orresponding ngles] 4. In, = 80 ( ) = 00 [ngle sum property of a triangle] In, = 80 ( ) = and = = = 50 Now, = = = = 0 Hence, = 0 5. In TQR, we have TQR + QRT + RTQ = 80 [ngle sum property of ] = = 80 = 50 6., = 70, = 40 Since = [lternate interior angles] = 70 lso from = + [terior angle property of a ] = = R and QR form a linear pair \ R + QR = 80 or a + b = 80...() ut a b = 80...() [Given] dding eq. () and (), we get 60 a = 60 = = 30 Substituting the value of a in (), we get 30 + b = 80 b = = 50 \ a = 30, b = raw Q parallel to and. a + 00 = 80 [o-interior angles] a = 80 Now, b + 0 = 80 [o-interior ngles] b = a b Q Since, Q is a straight line a + + b = = 80 = Here = = 70 [orresponding angles as ] and = 90 Now, = = 70 [ = ] In, = 80 = = 40 nd = = 40 [lternate angles] y = 40 Since, z + = 80 [o-interior angles] z = = 90 z = Q = 70 [orresponding angles] lso S = Q = 00 [Vertically opposite angles] s Q + Q = 80 [o-interior angles] y = 80 y = = 0 \ = 70 and y = 0 Mathematics lass 9 LINS N NGLS M4
34 M4 LINS N NGLS Short nswer Type. = (80 08 ) = 7 ivide 7 in the ratio : 3 we get 8 and 54. \ = 8 and = 54 lso, = = = 8, etc. Now, in + = 8 + = 08 = 90. y + 55 = 80 [o-interior ngles] y = = 5 gain = y [, orresponding ngles] Therefore = 5 Now, since and, therefore,. So, + = 80 [o-interior ngle] Therefore, 90 + z + 55 = 80 z = = 90 [o-interior ngles, Q RS] 3 = 36 [Vertically pposite ngles] + 3 = 90 [, and 3 from a linear pair] = = 54 7 = 90 [Linear air] = + 36 [lternate Interior ngles] 4 = 36 5 = [Linear air] 5 = 44 6 = 4 = 36 [Vertically pposite ngles] Hence, = 90 = 7, = 54, 3 = 4 = 6 = 36, 5 = Since, \ a =...() [lternate interior angles] and b = y...() [lternate interior angles] dding () and (), we get a + b = + y. 5. = = 65...(i) [lternate Interior ngles] y = 80 5 [Linear air] \ y = 55 = y = 55 [orresponding ngles] In, we have + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] \ = 80 ( ) \ = 60 and = = 60 [orresponding ngles] Hence, = 60, y = QRST is a regular pentagon \ = Q = R = S = T = 540 = 08..(i) 5 L is the bisector of TQ QL = 08 = 54...(ii) In quadrilateral QRL, QL + QR + QRL + RL = 360 [ngle sum property of a quadrilateral] RL = 360 RL = = 90 In LMR, MRL + RLM + RML = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] RML = 80 [MR is the bisector of SRQ] RML = = ; G; = 55, 4 = 60 Now, 4 = 3 [lternate Interior ngles] 3 = 60 and G + 4 = 80 [o-interior ngles] = = 0 = 0, 3 = Given : Ray bisects, i.e., =, Ray bisects. i.e., 3 = 4. lso ^ To rove : oints, and are collinear. roof : ^ = = 90 Multiplying both sides by + 3 = 80 ( + ) + ( 3 + 3) = 80 ( + ) + ( 3 + 4) = 80 [ =, 4 = 3] + = 80 y the converse of Linear air iom Ray and Ray are opposite rays. is a line. Hence, the points, and are collinear. lass 9 Mathematics
35 9. Through, draw parallel to and. Now + = 80...() [o-interior angles] lso, =...() [lternate interior angles] dding () and (), we get \ + + = = 80 + [... + = ] Hence proved. 0. rom, draw. 05 So, a a + b b = 360 [omplete angle] or, 3a + 3b + 05 = 360 or, 3a + 3b = or, 3a + 3b = 55 or, a + b = 85...() dding () and (), we get 3b = 50 b = 50 rom (), we have 00 a = 65 a = = 35 So, = a = 35 = b = 50 = 00 and = a + b + 5 = = = Given : with = 90 and ^. To rove : = roof : In, + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] 5 Now, and is the transversal. \ + = 80 [o-interior angles] + = 80 = (80 ) gain, and is the transversal. \ + = 80 [o-interior angles] (80 ) = 80 = 30. Hence, = 30. Mathematics lass 9 Long nswer Type. In QR, Q = 60, R = 45 \ QR = 80 ( Q + R) = 80 ( ) = = 75 s S is angle bisector of QR = QR 75 QS = = lso, TQ is a right angled triangle. So, QT = 80 ( ) = = 30 \ TS = QS QT = = Here, we have b a = 65...() and = 90 + = 90...() [Q = 90 ] lso, in, ^ So, = 90 and + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] + = 90...() [Q = 90 ] rom () and (), we get + = + =. 4. In, + + y = () [ngle sum property of a triangle] lso, 6 + y = [terior angle property of a triangle] + = 6 ( y) y 3 + =...() Similarly, 3 + =... (3) In, + + = 80 [ngle sum property of a triangle] LINS N NGLS M43
36 y = 80 [Using () and (3)] y = = 80 [using angle sum property of ] = = 90 3 = 59 \ = = 80 [Linear air] \ 6 = = = 80 [o-interior ngles] 5 = 80 8 = 6 = 8 [lternate Interior ngle] = + 6 [lternate angles as ] = \ 4 = = 80 [Linear air] 3 = 80 8 = = 80 [Linear air] = 80 8 = 5 Hence, = 8, = 5, 3 = 6, 4 = 8, 5 = 6, 6 = 8. Integer nswer Type. () : onstruction : Through draw a line GH. Now, G and is a transversal. \ G = = 50 [lternate interior angles] gain, H and is a transversal. \ H + = 80 [o-interior angles] H + 00 = 80 H = 80 Now, GH is a straight line. \ G + + H = = 80 = So, 5 = 5 =.. (5) : = 80 = = = (3) : Let angles be, and 3. So, = 80 [ngle sum property of triangle] = 30 Smallest angle = 30 ; Greatest angle = 90 So, the greatest angle is 3 times to the smallest angle. 4. (3) : Let angles be and = 80 5 = 80 = 36. ngles are 36 and 44 ifference ofangles = = 3. Smaller angle (9) : a = 360 [omplete angle] a = 45 a 45 = 5 5 = 9 6. (5) : b = 80 (30 + a) [s l m, co-interior angles] = 80 ( ) b = 05 b 05 = = 5 7. (9) : Since a and c are alternate interior angles c = 45. [s p q] \ Sum of digits = = 9 8. (3) : c + b + d = 80 [Linear pair] d = 80 d = 30 \ Sum of digits of d = = (5) : c and e are vertically opposite angles. \ e = 45. So, e + 5 = = 5 0. (4) : b and f are vertically opposite angles. \ f = 05 So, f 5 00 = 5 5 = 4. M44 LINS N NGLS lass 9 Mathematics
Class IX Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Maths. Exercise 6.1. In the given figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If
 Question 1: Exercise 6.1 In the given figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If and find BOE and reflex COE. Question 2: In the given figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If POY = and a:b = 2 : 3,
Question 1: Exercise 6.1 In the given figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If and find BOE and reflex COE. Question 2: In the given figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If POY = and a:b = 2 : 3,
Class IX Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Maths
 Class IX Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Maths Exercise 6.1 Question 1: In the given figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If and find BOE and reflex COE. Question 2: 2 In the given figure, lines XY and MN
Class IX Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Maths Exercise 6.1 Question 1: In the given figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If and find BOE and reflex COE. Question 2: 2 In the given figure, lines XY and MN
Int. Geometry Units 1-6 Review 1
 Int. Geometry Units 1-6 Review 1 Things to note about this review and the Unit 1-6 Test: 1. This review packet covers major ideas of the first six units, but it does not show examples of all types of problems..
Int. Geometry Units 1-6 Review 1 Things to note about this review and the Unit 1-6 Test: 1. This review packet covers major ideas of the first six units, but it does not show examples of all types of problems..
B C. You try: What is the definition of an angle bisector?
 US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? The midpoint of a line segment is the point that divides the segment into two congruent segments. That is, M is the midpoint of if M is on and M M. 1
US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? The midpoint of a line segment is the point that divides the segment into two congruent segments. That is, M is the midpoint of if M is on and M M. 1
GEOMETRY. Similar Triangles
 GOMTRY Similar Triangles SIMILR TRINGLS N THIR PROPRTIS efinition Two triangles are said to be similar if: (i) Their corresponding angles are equal, and (ii) Their corresponding sides are proportional.
GOMTRY Similar Triangles SIMILR TRINGLS N THIR PROPRTIS efinition Two triangles are said to be similar if: (i) Their corresponding angles are equal, and (ii) Their corresponding sides are proportional.
Triangles. Exercise 4.1
 4 Question. xercise 4. Fill in the blanks using the correct word given in brackets. (i) ll circles are....(congruent, similar) (ii) ll squares are....(similar, congruent) (iii) ll... triangles are similar.
4 Question. xercise 4. Fill in the blanks using the correct word given in brackets. (i) ll circles are....(congruent, similar) (ii) ll squares are....(similar, congruent) (iii) ll... triangles are similar.
MT EDUCARE LTD. MATHEMATICS SUBJECT : Q L M ICSE X. Geometry STEP UP ANSWERSHEET
 IS X MT UR LT. SUJT : MTHMTIS Geometry ST U NSWRSHT 003 1. In QL and RM, LQ MR [Given] LQ RM [Given] QL ~ RM [y axiom of similarity] (i) Since, QL ~ RM QL M L RM QL RM L M (ii) In QL and RQ, we have Q
IS X MT UR LT. SUJT : MTHMTIS Geometry ST U NSWRSHT 003 1. In QL and RM, LQ MR [Given] LQ RM [Given] QL ~ RM [y axiom of similarity] (i) Since, QL ~ RM QL M L RM QL RM L M (ii) In QL and RQ, we have Q
Prove that a + b = x + y. Join BD. In ABD, we have AOB = 180º AOB = 180º ( 1 + 2) AOB = 180º A
 bhilasha lasses lass- IX ate: 03- -7 SLUTIN (hap 8,9,0) 50 ob no.-947967444. The sides and of a quadrilateral are produced as shown in fig. rove that a + b = x + y. Join. In, we have y a + + = 80º = 80º
bhilasha lasses lass- IX ate: 03- -7 SLUTIN (hap 8,9,0) 50 ob no.-947967444. The sides and of a quadrilateral are produced as shown in fig. rove that a + b = x + y. Join. In, we have y a + + = 80º = 80º
6 LINES AND ANGLES EXERCISE 6.1. Q.1. In the figure lines AB and CD intersect at O. If AOC + BOE = 70 and BOD = 40, find BOE and reflex COE.
 6 LINES AND ANGLES EXERCISE 6.1 Q.1. In the figure lines AB and CD intersect at O. If AOC + BOE = 70 and BOD = 40, find BOE and reflex COE. Sol. Lines AB and CD intersect at O. AOC + BOE = 70 (Given) (1)
6 LINES AND ANGLES EXERCISE 6.1 Q.1. In the figure lines AB and CD intersect at O. If AOC + BOE = 70 and BOD = 40, find BOE and reflex COE. Sol. Lines AB and CD intersect at O. AOC + BOE = 70 (Given) (1)
Int. Geometry Unit 2 Test Review 1
 Int. Geometry Unit Test Review irections -: Use the diagram to determine if the angles are vertical, adjacent, supplementary, complementary, or a linear pair. Write all that apply.. and. and 6 0. 8 and
Int. Geometry Unit Test Review irections -: Use the diagram to determine if the angles are vertical, adjacent, supplementary, complementary, or a linear pair. Write all that apply.. and. and 6 0. 8 and
Geometry: A Complete Course
 Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas E. lark Larry E. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module Student Worktext opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas E. lark Larry E. ollins Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module Student Worktext opyright 2014 by VideotextInteractive
MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 4
 017 1100 MT.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) In STR, line l side TR S SQ T = RQ x 4.5 = 1.3 3.9 x = MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI RELIM - II : ER - 4 Time : Hours Model nswer aper Max. Marks : 40 4.5 1.3
017 1100 MT.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) In STR, line l side TR S SQ T = RQ x 4.5 = 1.3 3.9 x = MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI RELIM - II : ER - 4 Time : Hours Model nswer aper Max. Marks : 40 4.5 1.3
TOPIC-1 Rational Numbers
 TOPI- Rational Numbers Unit -I : Number System hapter - : Real Numbers Rational Number : number r is called a rational number, if it can be written in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0,
TOPI- Rational Numbers Unit -I : Number System hapter - : Real Numbers Rational Number : number r is called a rational number, if it can be written in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0,
Theorems on Area. Introduction Axioms of Area. Congruence area axiom. Addition area axiom
 3 Theorems on rea Introduction We know that Geometry originated from the need of measuring land or recasting/refixing its boundaries in the process of distribution of certain land or field among different
3 Theorems on rea Introduction We know that Geometry originated from the need of measuring land or recasting/refixing its boundaries in the process of distribution of certain land or field among different
Geometry Midterm Review Packet
 Name: ate: lock: 2012 2013 Geometry Midterm Review Packet ue: 1/7/13 (for +5 on packet) 1/8/13 (for +3 on packet) 1/9/13 (for +2 on packet) 1/10/13 ( ay lasses) 1/11/13 ( ay lasses) The midterm will be
Name: ate: lock: 2012 2013 Geometry Midterm Review Packet ue: 1/7/13 (for +5 on packet) 1/8/13 (for +3 on packet) 1/9/13 (for +2 on packet) 1/10/13 ( ay lasses) 1/11/13 ( ay lasses) The midterm will be
Alg. Exercise (1) Department : Math Form : 1 st prep. Sheet. [1] Complete : 1) Rational number is 2) The set of integer is.. 3) If. is rational if x.
![Alg. Exercise (1) Department : Math Form : 1 st prep. Sheet. [1] Complete : 1) Rational number is 2) The set of integer is.. 3) If. is rational if x. Alg. Exercise (1) Department : Math Form : 1 st prep. Sheet. [1] Complete : 1) Rational number is 2) The set of integer is.. 3) If. is rational if x.](/thumbs/88/117810047.jpg) airo Governorate Nozha irectorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road epartment : Math Form : 1 st prep. Sheet [1] omplete : lg. Exercise (1) 1) Rational number is ) The set of integer is..
airo Governorate Nozha irectorate of Education Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road epartment : Math Form : 1 st prep. Sheet [1] omplete : lg. Exercise (1) 1) Rational number is ) The set of integer is..
NAME DATE PERIOD. 4. If m ABC x and m BAC m BCA 2x 10, is B F an altitude? Explain. 7. Find x if EH 16 and FH 6x 5. G
 5- NM IO ractice isectors, Medians, and ltitudes LG In, is the angle bisector of,,, and are medians, and is the centroid.. ind x if 4x and 0.. ind y if y and 8.. ind z if 5z 0 and 4. 4. If m x and m m
5- NM IO ractice isectors, Medians, and ltitudes LG In, is the angle bisector of,,, and are medians, and is the centroid.. ind x if 4x and 0.. ind y if y and 8.. ind z if 5z 0 and 4. 4. If m x and m m
Questions. Exercise (1)
 Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
Circles-Tangent Properties
 15 ircles-tangent roperties onstruction of tangent at a point on the circle. onstruction of tangents when the angle between radii is given. Tangents from an external point - construction and proof Touching
15 ircles-tangent roperties onstruction of tangent at a point on the circle. onstruction of tangents when the angle between radii is given. Tangents from an external point - construction and proof Touching
1 st Preparatory. Part (1)
 Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Part (1) (1) omplete: 1) The square is a rectangle in which. 2) in a parallelogram in which m ( ) = 60, then m ( ) =. 3) The sum of measures of the angles of the quadrilateral equals. 4) The ray drawn
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday October Problem Set 1
 Intermediate Math ircles Wednesda October 10 2018 Problem Set 1 1. In the diagram, is parallel to. etermine the values of and. b 3 50 F a G 13 Let a = GF, b = F G. Since, we know that alternate interior
Intermediate Math ircles Wednesda October 10 2018 Problem Set 1 1. In the diagram, is parallel to. etermine the values of and. b 3 50 F a G 13 Let a = GF, b = F G. Since, we know that alternate interior
Geometry: A Complete Course
 Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas. lark Larry. ollins RRT 4/2010 6. In the figure below, and share the common segment. Prove the following conditional
Geometry: omplete ourse (with Trigonometry) Module - Student WorkText Written by: Thomas. lark Larry. ollins RRT 4/2010 6. In the figure below, and share the common segment. Prove the following conditional
1 = 1, b d and c d. Chapter 7. Worked-Out Solutions Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 357) Slope of line b:
 hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
hapter 7 aintaining athematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 = 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 = 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) 7 = 1 7 1 x = 3 1 = 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5)
Name: GEOMETRY: EXAM (A) A B C D E F G H D E. 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane?
 GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
Common Core Readiness Assessment 4
 ommon ore Readiness ssessment 4 1. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing element of the two-column proof. 2. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing
ommon ore Readiness ssessment 4 1. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing element of the two-column proof. 2. Use the diagram and the information given to complete the missing
Exercise. and 13x. We know that, sum of angles of a quadrilateral = x = 360 x = (Common in both triangles) and AC = BD
 9 Exercise 9.1 Question 1. The angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral. Solution Given, the ratio of the angles of quadrilateral are 3 : 5 : 9
9 Exercise 9.1 Question 1. The angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral. Solution Given, the ratio of the angles of quadrilateral are 3 : 5 : 9
2. A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 5. Diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other and are equal and vice-versa.
 QURILTERLS 1. Sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360. 2. diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 3. In a parallelogram, (i) opposite sides are equal (ii) opposite angles
QURILTERLS 1. Sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360. 2. diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. 3. In a parallelogram, (i) opposite sides are equal (ii) opposite angles
Definitions. (V.1). A magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures
 hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
Chapter 19 Exercise 19.1
 hapter 9 xercise 9... (i) n axiom is a statement that is accepted but cannot be proven, e.g. x + 0 = x. (ii) statement that can be proven logically: for example, ythagoras Theorem. (iii) The logical steps
hapter 9 xercise 9... (i) n axiom is a statement that is accepted but cannot be proven, e.g. x + 0 = x. (ii) statement that can be proven logically: for example, ythagoras Theorem. (iii) The logical steps
7. m JHI = ( ) and m GHI = ( ) and m JHG = 65. Find m JHI and m GHI.
 1. Name three points in the diagram that are not collinear. 2. If RS = 44 and QS = 68, find QR. 3. R, S, and T are collinear. S is between R and T. RS = 2w + 1, ST = w 1, and RT = 18. Use the Segment Addition
1. Name three points in the diagram that are not collinear. 2. If RS = 44 and QS = 68, find QR. 3. R, S, and T are collinear. S is between R and T. RS = 2w + 1, ST = w 1, and RT = 18. Use the Segment Addition
Theorem 1.2 (Converse of Pythagoras theorem). If the lengths of the sides of ABC satisfy a 2 + b 2 = c 2, then the triangle has a right angle at C.
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided.
 1 st Semester Final xam Review Name: Geometry ate: lock: You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided. Topic #1 (Foundations of Geometry) 1) Multiple hoice:
1 st Semester Final xam Review Name: Geometry ate: lock: You must show your work to receive full credit! Write your final answer on the blank provided. Topic #1 (Foundations of Geometry) 1) Multiple hoice:
Intermediate Math Circles for Wednesday 13 October 2010
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for ducation in Mathematics and omputing Intermediate Math ircles for Wednesday 13 October 2010 2. Intermediate Week 1 roblem Set 1: Solving More roblems
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics entre for ducation in Mathematics and omputing Intermediate Math ircles for Wednesday 13 October 2010 2. Intermediate Week 1 roblem Set 1: Solving More roblems
Introduction Circle Some terms related with a circle
 141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question.
 Geometry Homework Worksheets: Chapter 2 HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question. 1. Which of the following statements is/are always true? I. adjacent
Geometry Homework Worksheets: Chapter 2 HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question. 1. Which of the following statements is/are always true? I. adjacent
Review for Geometry Midterm 2015: Chapters 1-5
 Name Period Review for Geometry Midterm 2015: Chapters 1-5 Short Answer 1. What is the length of AC? 2. Tell whether a triangle can have sides with lengths 1, 2, and 3. 3. Danny and Dana start hiking from
Name Period Review for Geometry Midterm 2015: Chapters 1-5 Short Answer 1. What is the length of AC? 2. Tell whether a triangle can have sides with lengths 1, 2, and 3. 3. Danny and Dana start hiking from
Honors Geometry Mid-Term Exam Review
 Class: Date: Honors Geometry Mid-Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Classify the triangle by its sides. The
Class: Date: Honors Geometry Mid-Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Classify the triangle by its sides. The
Chapter 1. Some Basic Theorems. 1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
EC and AB because AIA are congruent Substituting into the first equation above
 4.1 Triangles Sum onjectures uxillary line: an extra line or segment that helps you with your proof. Page 202 Paragraph proof explaining why the Triangle Sum onjecture is true. onjecture: The sum of the
4.1 Triangles Sum onjectures uxillary line: an extra line or segment that helps you with your proof. Page 202 Paragraph proof explaining why the Triangle Sum onjecture is true. onjecture: The sum of the
Geometry Final exam Review First Semester
 Name: lass: ate: Geometry Final exam Review First Semester Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measure of O. Then, classify the angle
Name: lass: ate: Geometry Final exam Review First Semester Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measure of O. Then, classify the angle
Circles. Exercise 9.1
 9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Triangles 1. In the given figure, find the values of x and y. Since, AB = AC C = B [angles opposite to the equal sides are equal] x = 50 Also, the sum of all angles of a triangle
Revision Question Bank Triangles 1. In the given figure, find the values of x and y. Since, AB = AC C = B [angles opposite to the equal sides are equal] x = 50 Also, the sum of all angles of a triangle
Objectives To find the measure of an inscribed angle To find the measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a chord
 1-3 Inscribed ngles ommon ore State Standards G-.. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. lso G-..3, G-..4 M 1, M 3, M 4, M 6 bjectives To find the measure of an
1-3 Inscribed ngles ommon ore State Standards G-.. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. lso G-..3, G-..4 M 1, M 3, M 4, M 6 bjectives To find the measure of an
Name: Jan 2016 Semester1 Review Block: Date:
 GOMTRY Name: Jan 2016 Semester1 Review lock: ate: To be prepared for your midterm, you will need to PRTI PROLMS and STUY TRMS from the following chapters. Use this guide to help you practice. Unit 1 (1.1
GOMTRY Name: Jan 2016 Semester1 Review lock: ate: To be prepared for your midterm, you will need to PRTI PROLMS and STUY TRMS from the following chapters. Use this guide to help you practice. Unit 1 (1.1
Geometry Essentials ( ) Midterm Review. Chapter 1 For numbers 1 4, use the diagram below. 1. Classify as acute, obtuse, right or straight.
 Geometry Essentials (2015-2016) Midterm Review Name: Chapter 1 For numbers 1 4, use the diagram below. 1. Classify as acute, obtuse, right or straight. 2. is a linear pair with what other angle? 3. Name
Geometry Essentials (2015-2016) Midterm Review Name: Chapter 1 For numbers 1 4, use the diagram below. 1. Classify as acute, obtuse, right or straight. 2. is a linear pair with what other angle? 3. Name
2013 ACTM Regional Geometry Exam
 2013 TM Regional Geometry Exam In each of the following choose the EST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To insure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures completely. The
2013 TM Regional Geometry Exam In each of the following choose the EST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To insure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures completely. The
CLASS IX : CHAPTER - 1 NUMBER SYSTEM
 MCQ WORKSHEET-I CLASS IX : CHAPTER - 1 NUMBER SYSTEM 1. Rational number 3 40 is equal to: (a) 0.75 (b) 0.1 (c) 0.01 (d) 0.075. A rational number between 3 and 4 is: (a) 3 (b) 4 3 (c) 7 (d) 7 4 3. A rational
MCQ WORKSHEET-I CLASS IX : CHAPTER - 1 NUMBER SYSTEM 1. Rational number 3 40 is equal to: (a) 0.75 (b) 0.1 (c) 0.01 (d) 0.075. A rational number between 3 and 4 is: (a) 3 (b) 4 3 (c) 7 (d) 7 4 3. A rational
REAL NUMBERS. Rational Numbers P-1 TOPIC-1 SECTION. Solutions S O L U T I O N S CHAPTER. 7. x = 1 7
 SETION HPTER REL NUMERS TOPI- Rational Numbers.. 58 0.058 (Decimal point is shifted three places 000 to the left) 5 6 S O L U T I O N S.0.... It is non-repeating, so it is not a rational number. 0.60....
SETION HPTER REL NUMERS TOPI- Rational Numbers.. 58 0.058 (Decimal point is shifted three places 000 to the left) 5 6 S O L U T I O N S.0.... It is non-repeating, so it is not a rational number. 0.60....
UNIT 1 SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS Lesson 9: Proving Theorems About Triangles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: identifying and using vertical angles, supplementary angles, and complementary angles to find unknown angle measures recognizing
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: identifying and using vertical angles, supplementary angles, and complementary angles to find unknown angle measures recognizing
Chapter 6. Worked-Out Solutions. Chapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 299)
 hapter 6 hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 99) 1. Slope perpendicular to y = 1 x 5 is. y = x + b 1 = + b 1 = 9 + b 10 = b n equation of the line is y = x + 10.. Slope perpendicular to y
hapter 6 hapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 99) 1. Slope perpendicular to y = 1 x 5 is. y = x + b 1 = + b 1 = 9 + b 10 = b n equation of the line is y = x + 10.. Slope perpendicular to y
1.2 Perpendicular Lines
 Name lass ate 1.2 erpendicular Lines Essential Question: What are the key ideas about perpendicular bisectors of a segment? 1 Explore onstructing erpendicular isectors and erpendicular Lines You can construct
Name lass ate 1.2 erpendicular Lines Essential Question: What are the key ideas about perpendicular bisectors of a segment? 1 Explore onstructing erpendicular isectors and erpendicular Lines You can construct
Geo 10 Ch Angles of a Triangle. (A) A triangle is a figure formed by 3 joining 3
 Geo 0 h.4-.5-4..ngles of a Triangle () triangle is a figure formed b joining raw a picture and describe each of the following triangles.. Scalene 4. cute. Isoceles 5. Obtuse. Equilateral 6. Right () Given
Geo 0 h.4-.5-4..ngles of a Triangle () triangle is a figure formed b joining raw a picture and describe each of the following triangles.. Scalene 4. cute. Isoceles 5. Obtuse. Equilateral 6. Right () Given
GR 11 MATHS ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY
 GR MATHS ANALYTIAL GEMETRY Gr Maths Analtical Geometr hecklist: The Drawers of Tools onsider 'drawers' of tools - all BASI FATS. Use these to analse the sketches, to reason, calculate, prove.... Distance,
GR MATHS ANALYTIAL GEMETRY Gr Maths Analtical Geometr hecklist: The Drawers of Tools onsider 'drawers' of tools - all BASI FATS. Use these to analse the sketches, to reason, calculate, prove.... Distance,
Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018
 Name: Period: The midterm will cover Chapters 1-6. Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018 You WILL NOT receive a formula sheet, but you need to know the following formulas Make sure you memorize
Name: Period: The midterm will cover Chapters 1-6. Geometry Honors: Midterm Exam Review January 2018 You WILL NOT receive a formula sheet, but you need to know the following formulas Make sure you memorize
Unit 4. Algebraic and Geometric Proof. Math 2 Spring 2017
 1 Unit 4 lgebraic and Geometric Proof Math 2 Spring 2017 1 Table of ontents Introduction to lgebraic and Geometric Proof... 3 Properties of Equality for Real Numbers... 3 lgebra Proofs... 4 Introduction
1 Unit 4 lgebraic and Geometric Proof Math 2 Spring 2017 1 Table of ontents Introduction to lgebraic and Geometric Proof... 3 Properties of Equality for Real Numbers... 3 lgebra Proofs... 4 Introduction
Geometry Unit 1 Practice
 Lesson 1-1 1. Persevere in solving problems. Identify each figure. hen give all possible names for the figure. a. S Geometry Unit 1 Practice e. P S G Q. What is a correct name for this plane? W R Z X b..
Lesson 1-1 1. Persevere in solving problems. Identify each figure. hen give all possible names for the figure. a. S Geometry Unit 1 Practice e. P S G Q. What is a correct name for this plane? W R Z X b..
Geometry 1 st Semester review Name
 Geometry 1 st Semester review Name 1. What are the next three numbers in this sequence? 0, 3, 9, 18, For xercises 2 4, refer to the figure to the right. j k 2. Name the point(s) collinear to points H and
Geometry 1 st Semester review Name 1. What are the next three numbers in this sequence? 0, 3, 9, 18, For xercises 2 4, refer to the figure to the right. j k 2. Name the point(s) collinear to points H and
Time : 2 Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40. Q.1. Solve the following : (Any 5) 5 In PQR, m Q = 90º, m P = 30º, m R = 60º. If PR = 8 cm, find QR.
 Q.P. SET CODE Q.1. Solve the following : (ny 5) 5 (i) (ii) In PQR, m Q 90º, m P 0º, m R 60º. If PR 8 cm, find QR. O is the centre of the circle. If m C 80º, the find m (arc C) and m (arc C). Seat No. 01
Q.P. SET CODE Q.1. Solve the following : (ny 5) 5 (i) (ii) In PQR, m Q 90º, m P 0º, m R 60º. If PR 8 cm, find QR. O is the centre of the circle. If m C 80º, the find m (arc C) and m (arc C). Seat No. 01
Grade 7 Lines and Angles
 ID : ae-7-lines-and-angles [1] Grade 7 Lines and Angles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) If lines AC and BD intersects at point O such that AOB: BOC = 3:2, f ind
ID : ae-7-lines-and-angles [1] Grade 7 Lines and Angles For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) If lines AC and BD intersects at point O such that AOB: BOC = 3:2, f ind
Answers. Chapter10 A Start Thinking. and 4 2. Sample answer: no; It does not pass through the center.
 hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
Chapter 18 Exercise 18.1
 hapter 18 Eercise 18.1 Q. 1. (i) 180 37 = 143 ( = 143 ) (ii) 180 117 = 63 ( = 63 ) 180 90 = 90 (y = 90 ) (iii) + + 3 + 45 = 180 4.5 = 135 (iv) 180 90 = y 90 = y = 30 45 = y 66 + ( + y) + 47 = 180 + y =
hapter 18 Eercise 18.1 Q. 1. (i) 180 37 = 143 ( = 143 ) (ii) 180 117 = 63 ( = 63 ) 180 90 = 90 (y = 90 ) (iii) + + 3 + 45 = 180 4.5 = 135 (iv) 180 90 = y 90 = y = 30 45 = y 66 + ( + y) + 47 = 180 + y =
Plane geometry Circles: Problems with some Solutions
 The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
Solve problems involving tangents to a circle. Solve problems involving chords of a circle
 8UNIT ircle Geometry What You ll Learn How to Solve problems involving tangents to a circle Solve problems involving chords of a circle Solve problems involving the measures of angles in a circle Why Is
8UNIT ircle Geometry What You ll Learn How to Solve problems involving tangents to a circle Solve problems involving chords of a circle Solve problems involving the measures of angles in a circle Why Is
Which statement is true about parallelogram FGHJ and parallelogram F ''G''H''J ''?
 Unit 2 Review 1. Parallelogram FGHJ was translated 3 units down to form parallelogram F 'G'H'J '. Parallelogram F 'G'H'J ' was then rotated 90 counterclockwise about point G' to obtain parallelogram F
Unit 2 Review 1. Parallelogram FGHJ was translated 3 units down to form parallelogram F 'G'H'J '. Parallelogram F 'G'H'J ' was then rotated 90 counterclockwise about point G' to obtain parallelogram F
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3. Topic 1 : Equation of a circle
 Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Name Geometry Common Core Regents Review Packet - 3 Topic 1 : Equation of a circle Equation with center (0,0) and radius r Equation with center (h,k) and radius r ( ) ( ) 1. The endpoints of a diameter
Geometry. Midterm Review
 Geometry Midterm Review Class: Date: Geometry Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A plumber knows that if you shut off the water
Geometry Midterm Review Class: Date: Geometry Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A plumber knows that if you shut off the water
Unit 4-Review. Part 1- Triangle Theorems and Rules
 Unit 4-Review - Triangle Theorems and Rules Name of Theorem or relationship In words/ Symbols Diagrams/ Hints/ Techniques 1. Side angle relationship 2. Triangle inequality Theorem 3. Pythagorean Theorem
Unit 4-Review - Triangle Theorems and Rules Name of Theorem or relationship In words/ Symbols Diagrams/ Hints/ Techniques 1. Side angle relationship 2. Triangle inequality Theorem 3. Pythagorean Theorem
Practice. 8. Use inductive reasoning to determine the next two terms in the sequence. a. 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, b. 3, -6, 12, -24, 48,
 CTIC CTIVITY 1.1 1. Which is the correct name for this line? G M a. G c. MG b. GM d. M 2. Use the diagram to name each of the following. L M a. parallel lines b. perpendicular lines. In this diagram, m
CTIC CTIVITY 1.1 1. Which is the correct name for this line? G M a. G c. MG b. GM d. M 2. Use the diagram to name each of the following. L M a. parallel lines b. perpendicular lines. In this diagram, m
Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise Characterizations
 Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise haracterizations Theorem (The Scalene Inequality): If one side of a triangle has greater length than another side, then the angle opposite the longer side has the
Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise haracterizations Theorem (The Scalene Inequality): If one side of a triangle has greater length than another side, then the angle opposite the longer side has the
Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice Name Date Earth Measure Introduction to Geometry and Geometric Constructions Vocabulary Write the term that best completes the statement. 1. means to have the same size, shape,
Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice Name Date Earth Measure Introduction to Geometry and Geometric Constructions Vocabulary Write the term that best completes the statement. 1. means to have the same size, shape,
Given: You try: Given: Prove: ABC ADC. Prove: ABE DCE. 1. Given 1. AB AD BC DC. 2. AC AC 2. Reflexive Prop. of. 3. ABC ADC 3. SSS Post.
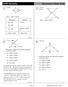 US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
US Geometr enchmark Stud Guide 1 Given: 1 Given: Prove: Statements 1. 1. Given Reasons.. Refleive Prop. of 3. 3. SSS Post Prove: G.O.1 etermine whether the following statements are rue or alse. ) ) ) )
MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 5
 017 1100 MT MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI PRELIM - II : PPER - 5 Time : Hours Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) X In XYZ, ray YM bisects XYZ XY YZ XM MZ Y Z [Property of
017 1100 MT MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI PRELIM - II : PPER - 5 Time : Hours Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) X In XYZ, ray YM bisects XYZ XY YZ XM MZ Y Z [Property of
3 = 1, a c, a d, b c, and b d.
 hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
hapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 357) 1. (7 x) = 16 (7 x) = 16 7 x = 7 7 x = 3 x 1 = 3 1 x = 3. 7(1 x) + = 19 7(1 x) = 1 7(1 x) = 1 7 7 1 x = 3 1 1 x = x 1 = 1 x = 3. 3(x 5) + 8(x 5) =
Chapter 7. Geometric Inequalities
 4. Let m S, then 3 2 m R. Since the angles are supplementary: 3 2580 4568 542 Therefore, m S 42 and m R 38. Part IV 5. Statements Reasons. ABC is not scalene.. Assumption. 2. ABC has at least 2. Definition
4. Let m S, then 3 2 m R. Since the angles are supplementary: 3 2580 4568 542 Therefore, m S 42 and m R 38. Part IV 5. Statements Reasons. ABC is not scalene.. Assumption. 2. ABC has at least 2. Definition
SEMESTER REVIEW 1: Chapters 1 and 2
 Geometry Fall emester Review (13-14) EEER REVIEW 1: hapters 1 and 2 1. What is Geometry? 2. What are the three undefined terms of geometry? 3. Find the definition of each of the following. a. Postulate
Geometry Fall emester Review (13-14) EEER REVIEW 1: hapters 1 and 2 1. What is Geometry? 2. What are the three undefined terms of geometry? 3. Find the definition of each of the following. a. Postulate
9. AD = 7; By the Parallelogram Opposite Sides Theorem (Thm. 7.3), AD = BC. 10. AE = 7; By the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem (Thm. 7.6), AE = EC.
 3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
3. Sample answer: Solve 5x = 3x + 1; opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent; es; You could start b setting the two parts of either diagonal equal to each other b the Parallelogram Diagonals Theorem
Geometry Unit 2 Review Show all work and follow the criteria for credit.
 Competency 1: Angles and Angle Bisectors 1. What is the classification of an angle that has a measure of less than 90 o? 4. Given the diagram below where BD is an angle bisector. A D 2. Given the following
Competency 1: Angles and Angle Bisectors 1. What is the classification of an angle that has a measure of less than 90 o? 4. Given the diagram below where BD is an angle bisector. A D 2. Given the following
SSC EXAMINATION GEOMETRY (SET-A)
 GRND TEST SS EXMINTION GEOMETRY (SET-) SOLUTION Q. Solve any five sub-questions: [5M] ns. ns. 60 & D have equal height ( ) ( D) D D ( ) ( D) Slope of the line ns. 60 cos D [/M] [/M] tan tan 60 cos cos
GRND TEST SS EXMINTION GEOMETRY (SET-) SOLUTION Q. Solve any five sub-questions: [5M] ns. ns. 60 & D have equal height ( ) ( D) D D ( ) ( D) Slope of the line ns. 60 cos D [/M] [/M] tan tan 60 cos cos
8.2 Investigate Parallelograms
 Investigating g Geometry TIVITY 8.2 Investigate arallelograms T E I graphing calculator or computer Use before esson 8.2 classzone.com Keystrokes Q U E T I O N What are some of the properties of a parallelogram?
Investigating g Geometry TIVITY 8.2 Investigate arallelograms T E I graphing calculator or computer Use before esson 8.2 classzone.com Keystrokes Q U E T I O N What are some of the properties of a parallelogram?
UNIT 1: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS. 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1).
 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
Semester 1 Cumulative Summative Review Teacher: Date: B
 GOMTRY Name: 2016-2017 Semester 1 umulative Summative Review Teacher: ate: To be prepared for your midterm, you will need to PRTI PROLMS and STUY TRMS from the following chapters. Use this guide to help
GOMTRY Name: 2016-2017 Semester 1 umulative Summative Review Teacher: ate: To be prepared for your midterm, you will need to PRTI PROLMS and STUY TRMS from the following chapters. Use this guide to help
LINES and ANGLES CLASS IX
 LINES and ANGLES CLASS IX Questions From CBSE Examination Papers 1. In the given figure, the value of x which makes POQ a straight line is: 6. The complementary angles are in the ratio 1 : 5. Find the
LINES and ANGLES CLASS IX Questions From CBSE Examination Papers 1. In the given figure, the value of x which makes POQ a straight line is: 6. The complementary angles are in the ratio 1 : 5. Find the
UNIT 1 VECTORS INTRODUCTION 1.1 OBJECTIVES. Stucture
 UNIT 1 VECTORS 1 Stucture 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Objectives 1.2 Vectors and Scalars 1.3 Components of a Vector 1.4 Section Formula 1.5 nswers to Check Your Progress 1.6 Summary 1.0 INTRODUCTION In this unit,
UNIT 1 VECTORS 1 Stucture 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Objectives 1.2 Vectors and Scalars 1.3 Components of a Vector 1.4 Section Formula 1.5 nswers to Check Your Progress 1.6 Summary 1.0 INTRODUCTION In this unit,
Geometry Chapter 3 & 4 Test
 Class: Date: Geometry Chapter 3 & 4 Test Use the diagram to find the following. 1. What are three pairs of corresponding angles? A. angles 1 & 2, 3 & 8, and 4 & 7 C. angles 1 & 7, 8 & 6, and 2 & 4 B. angles
Class: Date: Geometry Chapter 3 & 4 Test Use the diagram to find the following. 1. What are three pairs of corresponding angles? A. angles 1 & 2, 3 & 8, and 4 & 7 C. angles 1 & 7, 8 & 6, and 2 & 4 B. angles
XIV GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions
 XIV GEOMETRIL OLYMPI IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (L.Shteingarts, grade 8) Three circles lie inside a square. Each of them touches externally two remaining circles. lso
XIV GEOMETRIL OLYMPI IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (L.Shteingarts, grade 8) Three circles lie inside a square. Each of them touches externally two remaining circles. lso
Class : IX(CBSE) Worksheet - 1 Sub : Mathematics Topic : Number system
 Class : IX(CBSE) Worksheet - Sub : Mathematics Topic : Number system I. Solve the following:. Insert rational numbers between. Epress 57 65 in the decimal form. 8 and.. Epress. as a fraction in the simplest
Class : IX(CBSE) Worksheet - Sub : Mathematics Topic : Number system I. Solve the following:. Insert rational numbers between. Epress 57 65 in the decimal form. 8 and.. Epress. as a fraction in the simplest
Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER 1
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER 1 Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement(s)
Name: Class: Date: Geometry Advanced Fall Semester Exam Review Packet -- CHAPTER 1 Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement(s)
MAHESH TUTORIALS. Time : 1 hr. 15 min. Q.1. Solve the following : 3
 S.S.. MHESH TUTRILS Test - II atch : S Marks : 30 Date : GEMETRY hapter : 1,, 3 Time : 1 hr. 15 min..1. Solve the following : 3 The areas of two similar triangles are 18 cm and 3 cm respectively. What
S.S.. MHESH TUTRILS Test - II atch : S Marks : 30 Date : GEMETRY hapter : 1,, 3 Time : 1 hr. 15 min..1. Solve the following : 3 The areas of two similar triangles are 18 cm and 3 cm respectively. What
Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam
 Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam Format of Midterm Exam: Scantron Sheet: Always/Sometimes/Never and Multiple Choice 40 Questions @ 1 point each = 40 pts. Free Response: Show all work and write answers
Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam Format of Midterm Exam: Scantron Sheet: Always/Sometimes/Never and Multiple Choice 40 Questions @ 1 point each = 40 pts. Free Response: Show all work and write answers
EXERCISE Two angles of a quadrilateral are 70 and 130 and the other two angles are equal. Find the measure of these two angles.
 CHPTER 3 UNIT-5 EXERCISE 3.5.2 1. Two angles of a quadrilateral are 70 and 130 and the other two angles are equal. Find the measure of these two angles. ns: Let and be x, C=70 and D = 130 + + C + D = 360
CHPTER 3 UNIT-5 EXERCISE 3.5.2 1. Two angles of a quadrilateral are 70 and 130 and the other two angles are equal. Find the measure of these two angles. ns: Let and be x, C=70 and D = 130 + + C + D = 360
Math 1312 Sections 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 Informal Geometry and Measurement; Early Definitions and Postulates; Angles and Their Relationships
 Math 1312 Sections 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 Informal Geometry and Measurement; Early Definitions and Postulates; Angles and Their Relationships Undefined Terms (set, point, line, plane) A, which is represented
Math 1312 Sections 1.2, 1.3, and 1.4 Informal Geometry and Measurement; Early Definitions and Postulates; Angles and Their Relationships Undefined Terms (set, point, line, plane) A, which is represented
126 Holt McDougal Geometry
 test prep 51. m Q = m S 3x + 5 = 5x - 5 30 = x x = 15 5. J 53. 6.4 P = + + + = + + + = (5 + 8.) = 6.4 challenge and extend 54. Let given pts. be (0, 5), (4, 0), (8, 5), and possible 4th pts. be X, Y, Z.
test prep 51. m Q = m S 3x + 5 = 5x - 5 30 = x x = 15 5. J 53. 6.4 P = + + + = + + + = (5 + 8.) = 6.4 challenge and extend 54. Let given pts. be (0, 5), (4, 0), (8, 5), and possible 4th pts. be X, Y, Z.
REVIEW PACKET January 2012
 NME: REVIEW PKET January 2012 My PERIOD DTE of my EXM TIME of my EXM **THERE RE 10 PROBLEMS IN THIS REVIEW PKET THT RE IDENTIL TO 10 OF THE PROBLEMS ON THE MIDTERM EXM!!!** Your exam is on hapters 1 6
NME: REVIEW PKET January 2012 My PERIOD DTE of my EXM TIME of my EXM **THERE RE 10 PROBLEMS IN THIS REVIEW PKET THT RE IDENTIL TO 10 OF THE PROBLEMS ON THE MIDTERM EXM!!!** Your exam is on hapters 1 6
NAME DATE PER. 1. ; 1 and ; 6 and ; 10 and 11
 SECOND SIX WEEKS REVIEW PG. 1 NME DTE PER SECOND SIX WEEKS REVIEW Using the figure below, identify the special angle pair. Then write C for congruent, S for supplementary, or N for neither. d 1. ; 1 and
SECOND SIX WEEKS REVIEW PG. 1 NME DTE PER SECOND SIX WEEKS REVIEW Using the figure below, identify the special angle pair. Then write C for congruent, S for supplementary, or N for neither. d 1. ; 1 and
Mathematics. Sample Question Paper. Class 9th. (Detailed Solutions) 2. From the figure, ADB ACB We have [( 16) ] [( 2 ) ] 3.
![Mathematics. Sample Question Paper. Class 9th. (Detailed Solutions) 2. From the figure, ADB ACB We have [( 16) ] [( 2 ) ] 3. Mathematics. Sample Question Paper. Class 9th. (Detailed Solutions) 2. From the figure, ADB ACB We have [( 16) ] [( 2 ) ] 3.](/thumbs/85/92233599.jpg) 6 Sample Question Paper (etailed Solutions) Mathematics lass 9th. Given equation is ( k ) ( k ) y 0. t and y, ( k ) ( k ) 0 k 6k 9 0 4k 8 0 4k 8 k. From the figure, 40 [ angles in the same segment are
6 Sample Question Paper (etailed Solutions) Mathematics lass 9th. Given equation is ( k ) ( k ) y 0. t and y, ( k ) ( k ) 0 k 6k 9 0 4k 8 0 4k 8 k. From the figure, 40 [ angles in the same segment are
2010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
Pythagoras Theorem and Its Applications
 Lecture 10 Pythagoras Theorem and Its pplications Theorem I (Pythagoras Theorem) or a right-angled triangle with two legs a, b and hypotenuse c, the sum of squares of legs is equal to the square of its
Lecture 10 Pythagoras Theorem and Its pplications Theorem I (Pythagoras Theorem) or a right-angled triangle with two legs a, b and hypotenuse c, the sum of squares of legs is equal to the square of its
Geometry First Semester Exam Review
 Geometry First Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Name three points that are collinear. a. points T, Q, and R c. points
Geometry First Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Name three points that are collinear. a. points T, Q, and R c. points
ADARSHA VIDYALAYA HUNASHYAL P.B
 ADARSHA VIDYALAYA HUNASHYAL P.B SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FA 1 SL.N O CONTENTS TOPIC FA 1 PLYING WITH-NUMBERS ARITHMETIC FA - 1 2 SQUARE,SQUARE ROOTS CUBES AND CUBE ROOTS ARITHMETIC FA - 1 3 RATIONAL
ADARSHA VIDYALAYA HUNASHYAL P.B SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FA 1 SL.N O CONTENTS TOPIC FA 1 PLYING WITH-NUMBERS ARITHMETIC FA - 1 2 SQUARE,SQUARE ROOTS CUBES AND CUBE ROOTS ARITHMETIC FA - 1 3 RATIONAL
1.4 Reasoning and Proof
 Name Class Date 1.4 Reasoning and Proof Essential Question: How do you go about proving a statement? Explore Exploring Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Resource Locker A conjecture is a statement that
Name Class Date 1.4 Reasoning and Proof Essential Question: How do you go about proving a statement? Explore Exploring Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Resource Locker A conjecture is a statement that
