Incorporation of Non-Linear and Quasi-Linear Hydraulic Mount Formulations into a Vehicle Model
|
|
|
- Janis Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
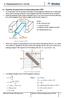
1 Incopoaion of Non-Linea and Quasi-Linea Hydaulic Moun Foulaions ino a Vehicle Mol Copyigh 007 SAE Inenaional Song He and Rajenda Singh Acousics and Dynaics Laboaoy The Ohio Sae Univesiy ABSTRACT This pape copaaively evaluaes easueen-based quasi-linea and ue non-linea (echanical and fluid ype) ols of hydaulic engine ouns and exaines hei dynaic effecs wihin he conex of a siplifd half-vehicle syse. A non-linea appoxiae ol is also veloped o povi ipoved insigh ino he coupling effecs. The poposed ol is validaed by copaing pedicions wih hose fo a ue non-linea fluid ol. When ebedd ino he vehicle syse, hydaulic oun efficnly povis high apliusensiive daping and unes he engine bounce o. Poposed ol conceps could be effecively uilized o exaine linea and non-linea vehicle esponses in boh ie and fequency doains. INTRODUCTION Ove he pas wo cas, significan eseach [-] has been conduced on he dynaics of non-linea hydaulic engine ouns. Much of he lieaue [4-9] focuses on is fequency- and exciaion apliusensiive popes on a vice level, which is necessay bu no sufficn fo he syse vwpoin. This pape ais o fill in his void by incopoaing linea, quasi-linea o non-linea oun ols ino a siplifd, ye easonable, half-vehicle ol. This will pei a copaaive evaluaion of he copeing oling ehods in he conex of vehicle dynaics. I is of couse assued ha he oun popes as easued by he elasoe es achines can be dcly ipoed ino vehicle ols even hough hee ae key diffeences beween he elasoe es ehod and insiu vehicle ouning syse. In fac, any paciiones use ad hoc ehods o bing in easued daa (o paaees) in a vehicle ol. Accodingly, he following objecives ae esablished: Fis, popose a siplifd half-vehicle ol ha would incopoae copeing oun ols (based on elasoe es daa). Modal sudy of he vehicle syse, based on he quasi-linea ol, will help o answe he key quesion ha ceain vehicle os could be effecively uned due o a coupling beween hydaulic oun and ohe vehicle coponens. Second, velop a non-linea appoxiae INCORORATION OF HYDRAULIC MOUNT FORMULATION(S) INTO HALF-VEHICLE MODEL Table Copaison of oun sub-syse ols Mol Type Moun (Fig.) Analysis Doain Moling Effos Need DOF of Fig. (a) Linea Rubbe (b) Tie & Modal ol fo he fee couple ype hydaulic oun o povi ipoved insigh ino he coupling effecs. The swiching echanis will be scibed in es of a cleaance ype non-lineaiy. Thid, esiae effecive paaees via he appoxiae ehod fo educed oling effos. The poposed ol will hen be validaed by copaing pedicions wih a ue fluid ype ol (based on ie doain soluions [5]). Finally, he ue non-linea fluid ol will be uilized o exaine non-linea dynaic vehicle esponses such as he supehaonics. Quasi- Linea Hydaulic (c) Tie & Modal Tue Non- Linea (Fluid) Hydaulic (d) Tie & Feq. (FFT) Non-Linea (Appoxiae ehod) Hydaulic (e) Tie & Feq. (FFT) Minial Minial High Moae 6 DOF 6+ DOF 6+ DOF 6+ DOF Fig. (a) shows a siplifd 6 DOF half-vehicle ol wih displaceens only in he veical dcion x i (i =,,6). Luped asses o 6 coespond o he ineia eleens of he engine, fon vehicle body, cenal body, ea body, fon wheel & axle and ea wheel & axle, especively. Coodinaes x 7 and x 8 epesen he igid bases a he fon and ea s. Siffness eleens inclu body flexue, suspensions and s; hese ae foulaed using he Voigh ol (siffness and daping eleens in paallel), as shown in Fig. (a). Alenae engine oun sub-syses could hen be incopoaed ino he vehicle ol. These ae suaized in Table including: (i) ubbe oun
2 scibed by he Voigh ol (esuling in a 6 DOF linea vehicle ol), as shown in Fig. (b); (ii) quasilinea hydaulic oun foulaion [3] (leading o a 7 DOF quasi-linea vehicle ol in Fig. (c)); and (iii) non-linea fluid o appoxiae oun foulaions (ylding 8 DOF non-linea vehicle ols), as shown by Figs. (d-e). Maheaical scipions of such nonlinea ols will be given lae in his pape. (a) 6 DOF half-vehicle ol incopoaing oun sub-syse; (b) ubbe oun sub-syse; (c) quasi-linea hydaulic oun sub-syse; # F x = x + x F x # k b q d C q i #d I i R i #i b k k b b k x x + x () I d R d # C k b F ( ) T (d) fluid ol of he non-linea hydaulic oun sub-syse; F ( ) T (e) appoxiae ol of he non-linea hydaulic oun sub-syse. Fig. Vehicle syse and sub-syse exaples. Also, see Table.
3 MODAL ANALYSIS BASED ON QUASI-LINEAR MODEL Fis, analyical odal analysis is conduced fo he ubbe oun of Fig. (b) as benchak. Given noinal ass, siffness and daping values of Table, he following six vehicle os ae obained: () vehicle bounce; () engine bounce; (3) ea wheel hop; (4) fon wheel hop; and (5) and (6) ae vehicle body pich and beaing (hough he discee ol does no have enough esoluion fo hese). The naual fequencs f n and esiaed odal daping aios ζ ae lised in Table 3. Hee, we ae os concened abou he engine bounce o of Fig., which shows soe coupling wih ea body and axle. Also, his o is found o be os sensiive o he paaees of he oun sub-syse. Table Paaees of half-vehicle ol of Fig. (a) Mass (kg) (Poweain) 5 (Fon Body) 0 3 (Wheel+Axle) 45 4 (Cene Body) 70 5 (Rea Body) 40 6 (Wheel+Axle) 75 Eleen k (N/) c (N-s/) PT oun k 300* b 50* Fon suspension k 3 c 3 00 Fon k 3 00 c 3 40 Body flexue k 4,000 c 4 75 Body flexue k 45,800 c Rea suspension k 56 6 c Rea k 6 00 c 6 40 *Baseline values fo he ubbe oun Table 3 Vibaion os of 6 DOF half-vehicle ol wih ubbe oun of Fig. (b) Inx Mo Type f n (Hz) ζ (%) Vehicle bounce..6 Engine bounce Rea wheel hop Fon wheel hop Vehicle pich Body bending Fig. Engine bounce o wih ubbe oun subsyse. Un ceain opeaional condiions, he quasi-linea foulaion [3] of Fig. (c) leads o a luped paaee epesenaion of he hydaulic oun sub-syse in es of equivalen sping, ass, dape eleens. Thus, odal analysis and fequency esponse suds could be cad ou in he conex of vehicle dynaics. This should povi alenae and apid evaluaion of he uning capabiliy of hydaulic oun. An exaple case is povid hee using he quasi-linea paaees esiaed fo one hydaulic oun (signaed as D) a X = wih k = 344 N/, k = 379 N/, b = 4 N/s, b = 300 N/s and = 37.6 kg. Table 4 liss he esuling naual fequencs f n and esiaed odal daping aios ζ. The engine bounce o of Fig. wih ubbe oun now sees o be ansfoed ino wo new coupled os as shown in Fig. 3. The es of vehicle os eain alos unaffeced. Table 4 Mos of half-vehicle ol wih hydaulic oun scibed by a quasi-linea ol of Fig (c) Inx Mo Type fn (Hz) ζ (%) Vehicle bounce..6 Coupled o I (in phase) Rea wheel hop Fon wheel hop Vehicle pich Coupled o II (ou of phase ) Body bending
4 Fig. 3 Coupled engine bounce os of half-vehicle ol wih hydaulic oun sub-syse of Fig. (c) foulaed using he quasi-linea ol. (a) In-phase o; (b) Ou-of-phase o. Obseve he following: Fis, and vibae in phase fo he o piced by Fig. 3(a), while and ae ou of phase fo he ohe coupled o of Fig. 3(b). Second, he axiu aplius of new os coespond o he effecive ineia ack ass insead of he engine ineia, so ha he ineia ack esonance o is doinan ove he engine bounce o fo boh cases. Thid, since ineia ack is inenionally signed o povi high fluid daping, he ineia ack esonance o is associaed wih high viscous daping, as clealy shown by he high odal daping aios fo hese wo coupled os. Fo his specific case, ζ inceases 4 and 0 ies fo he wo new engine bounce os. This eveals he supeioiy of a hydaulic oun ove he convenional ubbe oun in conolling engine bounce esonances. By coelaing he echanical eleens o fluid paaees [3], he quasilinea ol could be efficnly used by vehicle signes o quanify he oun specificaions. Fig. 4 Acceleance speca (a) Acceleance A /F a engine given foce exciaion fo engine; (b) Acceleance A /F 3 a fon body given foce exciaion fo fon wheel. Key:, ubbe oun;, hydaulic oun using quasi-linea foulaion;, hydaulic oun using dc invesion ehod. Nex, fequency esponse funcions (esponses of displaceen X(f), velociy V(f) o acceleaion A(f) given uni foce exciaion F(f)) ae ived by using he quasilinea foulaion. These ae hen copaed o hose yld by he dc invesion ehod given easued dynaic siffness daa (as benchak) o quanify he eos induced by he quasi-linea esiaion algoih. Fig. 4(a) shows he A /F engine acceleance given uniapliu engine foce exciaion. Likewise, Fig. 4(b) shows he A /F 3 fon body acceleance given uniapliu fon wheel foce exciaion. Copaed wih he ubbe oun, he hydaulic oun sufficnly conols he engine bounce esonance aound 8 Hz in Fig. 4(a), as well as he vehicle pich esonance aound 6 Hz in Fig. 4(b).
5 Copaison esuls of Fig. 4 iply ha hydaulic oun can be uilized o povi no only high daping fo engine oion conol, bu i also povis addiional coupling beween vehicle sub-syses. Such coupling could be useful in solving soe vehicle vibaion pobles (such as he pich esonance) ha ae encouneed in sub-syses away fo he engine ouns. Mino discepancs exis beween he quasilinea ol pedicions and he dc invesion ehod due o he appoxiaion pocess [3] and he assupion a in he pocess [3,8], i.e. F T () F(). FLUID VS. APPROXIMATE NON-LINEAR MODELS OF HYDRAULIC MOUNTS In a ecen pape [3], we poposed a quasi-linea appoxiae ol ha uilizes seady sae dynaic siffness easueens o consuc fequency- and exciaion apliu-sensiive oun ols un ceain opeaing condiions. Copaed wih a ue nonlinea fluid ol, i significanly educes he oling effecs and is capable of poviding a quick assessen of he augened daping and ineia effecs [3,4]. Ye, he quasi-linea ol is no sufficnly accuae o scibe he non-linea esponses especially fo he couple echanis. Theefoe, an ipoved nonlinea appoxiae ol is veloped as follows wih an ai o capue he on-off swiching acions of he couple. We will eploy a cleaance ype eleen, while inheiing effecive paaees fo he quasilinea ol fo educed oling effos. FLUID SYSTEM FORMULATION The non-linea fluid ol of Fig. 5 is bfly inoduced hee o ive he appoxiae ol as well as fo he sake of copaison. Refe o [5,6] fo ailed scipion of he ol and is expeienal validaion. k b # # q d I d R d C F x = x + x q i #d I i R i #i b k The viual diving poin foce F() could be fined as follows whee x() is he pison displaceen;, b and k ae he ass, daping and siffness of ubbe eleen; p () is he dynaic pessue of he op chabe and A is he effecive pison aea. F = ɺɺ x + b xɺ + k x + A p () Coninuiy equaions fo he op and boo chabes yld: A xɺ q q = C ( p ) pɺ, () i d i d q + q = C ( x ) pɺ. (3) Hee, C (p ) is he uli-sad op chabe copliance; C (x ) is he boo chabe copliance sensiive o ean displaceen x ; q i () and q d () ae he volueic flow aes hough he ineia ack (i) and couple (d), especively. Moenu equaions fo he couple and ineia ack yld he following, whee I d and I i ae he ineia of fluid coluns; R i (q i ) and R d (q d ) ae he nonlinea esisances: p p = I qɺ + R ( q ) q, (4) d d d d d p p = I qɺ + R ( q ) q (5) i i i i i Noe ha Eq. (4) dicaes he coupled sae when he couple gap is open, and Eq. (5) is doinan ove he coupled sae wih he couple gap closes. The dynaic coponen of foce F T () ansied o he igid base is ived and is elaed o F() as follows: F = k x + b xɺ + A p = F ɺɺ x (6) T NON-LINEAR APPROXIMATE METHOD An appoxiae echanical ol of Fig. 6 is veloped fo ipoved unsanding of he coupling effecs of a fee couple oun. k b F k x b x () x + x # C k b F ( ) T FT Fig. 5 Non-linea fluid ol of he hydaulic oun wih ineia ack and couple. Fig. 6 Non-linea appoxiae ol of he hydaulic oun wih ineia ack and couple
6 Noe ha all non-linea paaees such as C (p ) ae oled as a funcion of he noinal exciaion apliu X. The swiching echanis is scibed in es of a cleaance ype non-lineaiy and he effecive paaees as scibed in [3] could be dcly incopoaed ino he appoxiae ol. Given equaions (-6) and paaees of Table 5, he nonlinea appoxiae ol of Fig. 6 is ived as follows, whee x () is he (absolue) displaceen of he ineia ack fluid ass, and x () is he elaive displaceen beween he effecive asses and. The absolue displaceen of is heefoe x () + x (). Table 5 Physical and effecive paaees of he appoxiae ol of Fig. 6 Paaees Physical value Effecive value Ineia ack fluid ass Decouple ass Ineia ack daping Decouple daping Ineia ack displaceen Decouple displaceen Decouple gap lengh Top chabe fluid siffness Boo chabe fluid siffness b i = Ai I i = A I i d = Ad I d = A I d = A i = Ai Ri i b d = Ad Rd b = A Rd qi d xi = A qd d xd = A l g i d b R qi d x = A x l k k qd d = A = l g Ad A = A / C = A / C The effecive (bu viual) dynaic foce a he diving poin of Fig. 6 is ived as: [ x( ) x x ( )] F = ɺ x + k x( ) + b xɺ + k (7) In he coupled sae, he couple gap is open such ha 0 < x () < l. Fluid flows ainly hough he couple gap since R i >> R d (o b >> b ). Consequenly, q i ( ) << q d (), o xɺ << xɺ and ɺɺ x << ɺɺ x. Fluid equaions (-4) ae ewien in es of he echanical syse sybols of Table 5 as follows: [ ] [ ] ɺɺ x + bxɺ + k x + x x, + k x + x = 0 coupled sae ( 0 < x < l ) (8a) Since ɺɺ x ɺɺ x + ɺɺ x, Eq. (8a) is appoxiaed by Eq. (8b), which dicaes he dynaics of duing he coupled sae, when a elaive oion xɺ exiss beween and. [ ɺɺ ɺɺ ] ɺ x + x + b x + k [ x + x], + k [ x + x x] = 0 coupled sae ( 0 < x < l ) (8b) Eqs. (4-5) also lead o he syse equaion as follows: ɺɺ x + b xɺ = ɺɺ x + b xɺ, coupled sae ( 0 < x < l ) (9a) Ove he lowe fequency an, say up o 50 Hz, assue ha he couple viscous foce is doinan so ha b xɺ >> ɺɺ x. Eq. (9a) is hen appoxiaed by Eq. (9b) coesponding o he govening equaion of duing he coupled sae. ɺɺ x + b xɺ b xɺ = 0, coupled sae ( 0 < x < l ) (9b) Duing he coupled sae, he couple gap is closed so ha x = 0 o x = l. No fluid flows hough he couple gap, i.e. q d () = 0 o x ɺ = 0 and ɺɺ x = 0. This ipls no elaive oion exiss beween and. Eqs (, 3, 5) ae conveed ino: ɺɺ x + b xɺ + k [ x x] + k x = 0, coupled sae (x = 0 o l ) (0a) Since >>, Eq. (0a) is appoxiaed by Eq. (0b), which dicaes he dynaic oion of cobined asses + while oving ohe afe eaching eihe he op o boo sop. ( ) + ɺɺ x + b xɺ + k [ x x] + k x = 0, coupled sae (x = 0 o l ) (0b) Finally, fo boh saes, F T () is conveed fo Eq. (6) o he following: F = k x + b xɺ + k x x x () T [ ]
7 The swiching echanis beween he coupled and coupled saes is conveed ino a cleaance ype nonlineaiy in he appoxiae ol of Fig. 6: When he exciaion apliu of x() is sall enough so ha avels wihou eaching he op o boo sop ( 0 < x < l ), is coupled fo he oun syse. Thus he syse is in a sof sae dicaed by Eqs. (8b) and (9b) ylding educed siffness and daping. Un highe exciaion aplius, when eaches he op o boo sop (x = 0 o l ), oves along wih and he syse is scibed by Eq. (0b). The ineia ack is hus coupled ino he syse poviding high fluid esisance b. Noe ha ou quasilinea ol [3] is essenially a liiing case of his when b (o R d ) appoaches infiniy. The copessive conac foce F c () beween and is foulaed as: ɺɺ x + F F, x = l Fc = ɺɺ x F + F, x = 0 whee F k [ x x ] (a) = and F = kx ae he effecive elasic foces analogous o he op and boo chabe pessue foces p ( ) A and p ( ) A. Since he couple is ypically signed like a flow conol valve, is ineial foce ɺɺ x is negligible copaed wih he elasic foce. Hence, he swiching condiion fo he coupled o he coupled sae is conveed fo Eq. (a) o he following: F F < 0, x = l F F > 0, x = 0 (b) COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO NONLINEAR MODELS The non-linea appoxiae ol is nex copaed wih a validaed non-linea fluid ol [5,6] in boh ie and fequency doains. Assuing a sinusoidal displaceen x() wih f = 5 Hz and X = (p-p), Fig. 7(a) pics he dynaic chabe pessues p () and p () ha ae pediced by he fluid ol. And, Fig. 7(b) shows he conac foce F () and F () wavefos as pediced by he appoxiae ol. Obseve ha pediced wavefos shae essenially he sae chaaceisics. The spikes in p () o F () coespond o he ie insans when he couple is closed in he fluid syse o when is coupled wih in he appoxiae syse; he fla egions in p () o F () ae associaed wih he opeaion condiions such ha he couple is open o when loses conac wih in he coupled sae. The p () and F () wavefos ae copaaively soohe due o he fac ha C >> C in he fluid syse, o k >> k in he appoxiae ol. Fig. 7 Dynaic esponses given sinusoidal displaceen exciaion wih X =.0 and f = 5 Hz: (a) p () and p () pediced by he fluid ol; (b) elasic conac foces F () and F () pediced by he appoxiae ol. Key:, p () o F ();, p () o F (). In Fig. 8, siulaed dynaic siffness daa ae copaed. They ae fo he fluid and appoxiae ols un haonic exciaions wih aplius anging fo 0.3 o 3 (p-p) in up o 50 Hz. Nealy inical dynaic siffness speca ae obained, which confis ha he appoxiae ol wih cleaance non-lineaiy ined capues he couple swiching echanis of he fluid ol in Fig. 5.
8 ( + ) ɺɺ x + b [ xɺ xɺ ] + k [ x x ] A p = F sin ( π f + φ ) e e e (3) The coninuiy equaion fo he boo chabe eains he sae as Eq. (3), and he coninuiy equaion fo he op chabe now chans o: [ ] A xɺ xɺ q q = C ( p ) pɺ (4) i d Govening equaions fo he couple and ineia ack dynaics eain he sae as Eqs. (4) and (5), especively, while he ansied foce is now: [ ] [ ] F = k x x + b xɺ xɺ + A p (5) T Dynaics of he fon body is dicaed by: ( ) + [ ( ) ( )] + [ ɺ ( ) ɺ ( )] ( ) 3 [ ( ) 3( )] 4 [ ( ) 4( )] [ ɺ ( ) ɺ ( )] [ ɺ ( ) ɺ ( )] 0 ɺɺ x k x x b x x + A p + k x x + k x x + c x x + c x x = (6) The es of he govening equaions no dcly involved wih he hydaulic oun sub-syse could be easily ived. Fig. 8 Dynaic siffness pediced using (a) fluid ol wih fee couple; (b) appoxiae ol wih cleaance non-lineaiy. Key:, X = 0.3 (p-p);, X = 0.5 (p-p);, X = (p-p);, X = (p-p);, X = 3 (p-p). INCOPORATION OF NON-LINEAR MODELS INTO VEHICLE SYSTEM Nex, non-linea hydaulic oun ols ae incopoaed ino he vehicle syse and copaed wih linea and quasi-linea foulaions. Key govening equaions of he non-linea vehicle syse wih fluid ype oun ae given as follows; copaable vehicle foulaions including he non-linea appoxiae oun could also be ived by cobining Eqs. (8) o () wih ohe vehicle coponens in a siila anne. Wih efeence o Figs. (a) and (d), whee he posiive dcions of x i () ae aken o be upwad, he engine dynaics is scibed as: Vehicle esponses ae calculaed in boh ie and fequency doains given engine foce exciaions. Since highe haonics ae no easily disinguished fo he ie doain esponses, only he fequency speca ae pesened hee in o o copae linea and quasilinea vehicle ols. Figs. 9-0 copae esuls of vehicle ass displaceens o acceleaions given sinusoidal engine foce wih he apliu of 000 N a 0 Hz. In Fig. 9, he engine esponse is shown o be os sensiive o he ouning syse, and he engine bounce esonance a 8.4 Hz (wih ubbe oun) is educed up o 40 db by using he hydaulic oun. The vehicle pich esonance aound 5 Hz is also affeced due o a coupling beween hydaulic oun and ohe vehicle coponens. Given he sae sinusoidal exciaion wih apliu of 000 N a 0 Hz, Fig. 0 copaes he dynaic vehicle acceleaions pediced by using he quasi-linea foulaion and by using he non-linea fluid ol (wih fixed couple), especively. Obseve ha: (i) The slopes of he acceleaion speca pediced by boh ols ach well wih each ohe. (ii) Boh ols capue he basic vehicle esonances which wee pediced by he odal analysis. Recall Table 4 fo he naual fequencs and esiaed odal daping aios coesponding o hese esonances. (iii) The wheel hop esonance aound Hz is doinaing he dynaic esponses, and is supe-haonics a he uliples of he fundaenal fequency ae pediced only by he nonlinea fluid (o appoxiae) ol. This confis he necessiy of incopoaing non-linea hydaulic oun foulaion ino he vehicle syse fo exaining nonlinea phenoena such as he supe-haonics.
9 Fig. 9 Pediced vehicle displaceen speca (db e ) given sinusoidal engine foce exciaion wih an apliu of 000 N a 0 Hz. Key:, linea ol wih ubbe oun;, quasi-linea ol wih hydaulic oun. Fig. 0 Pediced vehicle acceleaion speca (db e /s ) given sinusoidal engine foce exciaion wih an apliu of 000 N a 0 Hz. Key:, quasi-linea ol wih hydaulic oun;, non-linea fluid ol wih fixed couple.
10 CONCLUSION This pape has copaaively evaluaed linea, quasilinea and ue non-linea (appoxiae and fluid ype) ols of hydaulic engine ouns and exained hei dynaic effecs in a siplifd half-vehicle syse. A non-linea appoxiae ol is veloped o povi ipoved insigh ino he coupling effecs. Hydaulic oun is shown o be highly efficn in poviding high daping and in uning vehicle dynaics. Poposed vehicle ols could be effecively uilized o exaine vehicle esponses in boh ie and fequency doains. Ou vehicle ols (in alenae fos) could seve as he plafo fo fuhe eseach ino ipoved esiaions of daping and siffness ols, bee pedicions in ie doain as well as efineens of he vehicle sign and inegaions issues. The fundaenal quesion of ipoing easued daa (given displaceen exciaion and blocked bounday in he elasoe es ehod) and incopoaing he in a syse wih ealisic boundas and foce exciaions is ye o be esolved. We ae exaining his issue and will povi soe guidance in fuue papes. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We acknowled he expeienal effos of M. Tiwai and J. Soenson fo 999 o 00. Those suds wee financially suppoed by he Fod Moo Copany. We hank D. J. H. Lee fo his coens and sugsions. REFERENCES. R. Singh, G. Ki and P. V. Ravinda, Linea analysis of auooive hydo-echanical oun wih ephasis on couple chaaceisics, J. Sound Vib. 58, 9-43 (99).. G. Ki and R. Singh, Sudy of Passive and Adapive Hydaulic Engine Moun Syses wih Ephasis on Nonlinea Chaaceisics, J. Sound Vib. 79, (995). 3. S. He and R. Singh, Esiaion of Apliu and Fequency Depenn Paaees of Hydaulic Engine Moun Given Liied Dynaic Siffness Measueens, Noise Conol Eng. J., 53(6), 7-85, (005). 4. J. E. Colgae, C. T. Chang, Y. C. Chiou, W. K. Liu and L. M. Kee, Moling of a Hydaulic Engine Moun Focusing on Response o Sinusoidal and Coposie Exciaions, J. Sound Vib., 84(3), (995). 5. M. Tiwai, H. Adiguna and R. Singh, Expeienal Chaaceizaion of a Nonlinea Hydaulic Engine Moun, Noise Conol Eng. J. 5(), (003). 6. H. Adiguna, M. Tiwai and R. Singh, Tansn Response of a Hydaulic Engine Moun, J. Sound Vib. 68, 7-48 (003). 7. Y. Yu, N. G. Naganahan and R. V. Dukkipai, A Lieaue Revw of Auooive Vehicle Engine Mouning Syses, J. Dynaic Sys, Measueen, and Conol, 3(), (00). 8. J. H. Lee, M. S. Bae and K. J. Ki, Liiaions of Mechanical Mol Wih Luped Mass in Repesening Dynaic Chaaceisics of Hydaulic Moun, SAE Pape (003). 9. N. Tsujiuchi, T. Koizui and K. Yaazaki. Vibaion Analysis of Engine Suppoed by Hydaulic Mouns, SAE Pape (003). 0. T. Jeong and R. Singh, Inclusion of Measued Fequency-and Apliu-Depenn Moun Popes in Vehicle o Machiney Mols, J. Sound Vib. 45, (00).. S. B. Choi and H. J. Song, Vibaion Conol of a Passen Vehicle Uilizing a Sei-Acive ER Engine Moun, J. Vehicle Sys. Dynaics, 37(3), 93-6, (00). CONTACT Pofesso Rajenda Singh Acousics and Dynaics Laboaoy Cene fo Auooive Reseach and NSF I/UCRC Sa Vehicle Conceps Cene The Ohio Sae Univesiy Eail: singh.3@osu.edu Phone: Websie:
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
In. J. Pue Appl. Sci. Technol., 4 (211, pp. 23-29 Inenaional Jounal of Pue and Applied Sciences and Technology ISS 2229-617 Available online a www.ijopaasa.in eseach Pape Opizaion of he Uiliy of a Sucual
Trajectory estimation based on extended state observer with Fal-filter
 The Aeonauical Jounal Augus 05 Volue 9 No 8 07 Tajecoy esiaion based on exended sae obseve wih Fal-file C- in chunlin@dagon.nchu.edu.w S- Hsieh and Y-P in Depaen of Elecical Engineeing Naional Chung Hsing
The Aeonauical Jounal Augus 05 Volue 9 No 8 07 Tajecoy esiaion based on exended sae obseve wih Fal-file C- in chunlin@dagon.nchu.edu.w S- Hsieh and Y-P in Depaen of Elecical Engineeing Naional Chung Hsing
Design Considerations for Achieving ZVS in a Half Bridge Inverter that Drives a Piezoelectric Transformer with No Series Inductor
 Design onsideaions fo Achievg ZS a Half Bidge Invee ha Dives a iezoelecic Tansfoe wih No Seies Induco Svelana Bonse and Sa Ben-Yaaov* owe Eleconics aboaoy Depaen of Elecical and opue Engeeg Ben-Guion Univesiy
Design onsideaions fo Achievg ZS a Half Bidge Invee ha Dives a iezoelecic Tansfoe wih No Seies Induco Svelana Bonse and Sa Ben-Yaaov* owe Eleconics aboaoy Depaen of Elecical and opue Engeeg Ben-Guion Univesiy
Stress Analysis of Infinite Plate with Elliptical Hole
 Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
Sess Analysis of Infinie Plae ih Ellipical Hole Mohansing R Padeshi*, D. P. K. Shaa* * ( P.G.Suden, Depaen of Mechanical Engg, NRI s Insiue of Infoaion Science & Technology, Bhopal, India) * ( Head of,
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
A FINITE-MEMORY DISCRETE-TIME CONVOLUTION APPROACH FOR THE NON-LINEAR DYNAMIC MODELLING OF S/H-ADC DEVICES
 FINITE-MEMORY DISCRETE-TIME CONVOLUTION PPROCH FOR THE NON-LINER DYNMIC MODELLING OF S/H-DC DEVICES D. Mii, G. Pasini, P.. Taveso 2, F. Filicoi 2, G. Iclano 3 Depaen of Elecical Engineeing, Univesiy of
FINITE-MEMORY DISCRETE-TIME CONVOLUTION PPROCH FOR THE NON-LINER DYNMIC MODELLING OF S/H-DC DEVICES D. Mii, G. Pasini, P.. Taveso 2, F. Filicoi 2, G. Iclano 3 Depaen of Elecical Engineeing, Univesiy of
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Sharif University of Technology - CEDRA By: Professor Ali Meghdari
 Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
Physics 207 Lecture 13
 Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Introduction to Numerical Analysis. In this lesson you will be taken through a pair of techniques that will be used to solve the equations of.
 Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Inroducion o Nuerical Analysis oion In his lesson you will be aen hrough a pair of echniques ha will be used o solve he equaions of and v dx d a F d for siuaions in which F is well nown, and he iniial
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Fundamental Vehicle Loads & Their Estimation
 Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Lecture 23 Damped Motion
 Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
Differenial Equaions (MTH40) Lecure Daped Moion In he previous lecure, we discussed he free haronic oion ha assues no rearding forces acing on he oving ass. However No rearding forces acing on he oving
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
Design Guideline for Buried Hume Pipe Subject to Coupling Forces
 Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
International Journal of Automotive Technology, Vol.?, No.?, pp.??(year) Serial#Given by KSAE TIRE LATERAL FORCE ESTIMATION USING KALMAN FILTER
 Inenaional Jounal o Auooive echnology, Vol.?, No.?, pp.??(yea) Copyigh 000 KSAE Seial#Given by KSAE IRE LAERAL FORCE ESIMAION USING KALMAN FILER Eun Jae Lee ), Ho Jin Jung ) and Sei Bu Choi )* ) Hanoo
Inenaional Jounal o Auooive echnology, Vol.?, No.?, pp.??(yea) Copyigh 000 KSAE Seial#Given by KSAE IRE LAERAL FORCE ESIMAION USING KALMAN FILER Eun Jae Lee ), Ho Jin Jung ) and Sei Bu Choi )* ) Hanoo
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
THE FINITE HAUSDORFF AND FRACTAL DIMENSIONS OF THE GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-TYPE EQUATIONS
 European Journal of Maheaics and Copuer Science Vol 4 No 7 ISSN 59-995 HE FINIE HAUSDORFF AND FRACAL DIMENSIONS OF HE GLOBAL ARACOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-YPE EQUAIONS Guoguang Lin & Xiangshuang Xia Deparen
European Journal of Maheaics and Copuer Science Vol 4 No 7 ISSN 59-995 HE FINIE HAUSDORFF AND FRACAL DIMENSIONS OF HE GLOBAL ARACOR FOR A CLASS KIRCHHOFF-YPE EQUAIONS Guoguang Lin & Xiangshuang Xia Deparen
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Monochromatic Wave over One and Two Bars
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
2.1 Harmonic excitation of undamped systems
 2.1 Haronic exciaion of undaped syses Sanaoja 2_1.1 2.1 Haronic exciaion of undaped syses (Vaienaaoan syseein haroninen heräe) The following syse is sudied: y x F() Free-body diagra f x g x() N F() In
2.1 Haronic exciaion of undaped syses Sanaoja 2_1.1 2.1 Haronic exciaion of undaped syses (Vaienaaoan syseein haroninen heräe) The following syse is sudied: y x F() Free-body diagra f x g x() N F() In
TIME DELAY BASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OBSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM
 TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
TIME DELAY ASEDUNKNOWN INPUT OSERVER DESIGN FOR NETWORK CONTROL SYSTEM Siddhan Chopra J.S. Laher Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India Elecrical Engineering Deparen NIT Kurukshera (India
Conservation of Momentum. The purpose of this experiment is to verify the conservation of momentum in two dimensions.
 Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Conseraion of Moenu Purose The urose of his exerien is o erify he conseraion of oenu in wo diensions. Inroducion and Theory The oenu of a body ( ) is defined as he roduc of is ass () and elociy ( ): When
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Robust Output Command Tracking for Linear Systems with Nonlinear Uncertain Structure with Application to Flight Control
 Poceedings of he 44h IEEE Confeence on Decision and Conol and he Euopean Conol Confeence 5 Seville Spain Decebe -5 5 hb5.6 Robus Oupu Coand acking fo Linea Syses wih Nonlinea Unceain Sucue wih Applicaion
Poceedings of he 44h IEEE Confeence on Decision and Conol and he Euopean Conol Confeence 5 Seville Spain Decebe -5 5 hb5.6 Robus Oupu Coand acking fo Linea Syses wih Nonlinea Unceain Sucue wih Applicaion
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Tidal forces. m r. m 1 m 2. x r 2. r 1
 Tidal foces Befoe we look at fee waves on the eath, let s fist exaine one class of otion that is diectly foced: astonoic tides. Hee we will biefly conside soe of the tidal geneating foces fo -body systes.
Tidal foces Befoe we look at fee waves on the eath, let s fist exaine one class of otion that is diectly foced: astonoic tides. Hee we will biefly conside soe of the tidal geneating foces fo -body systes.
Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform. Joseph Fourier, our hero. Lord Kelvin on Fourier s theorem. What do we want from the Fourier Transform?
 ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
ourier Series & The ourier Transfor Wha is he ourier Transfor? Wha do we wan fro he ourier Transfor? We desire a easure of he frequencies presen in a wave. This will lead o a definiion of he er, he specru.
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
x y θ = 31.8 = 48.0 N. a 3.00 m/s
 4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
1. Calibration factor
 Annex_C_MUBDandP_eng_.doc, p. of pages Annex C: Measureen uncerainy of he oal heigh of profile of a deph-seing sandard ih he sandard deviaion of he groove deph as opography er In his exaple, he uncerainy
Annex_C_MUBDandP_eng_.doc, p. of pages Annex C: Measureen uncerainy of he oal heigh of profile of a deph-seing sandard ih he sandard deviaion of he groove deph as opography er In his exaple, he uncerainy
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS AND CONTROL OF ACTIVE ENGINE MOUNT SYSTEM
 To be submied o Jounal of Auomobile Engineeing DYNAMIC ANALYSIS AND CONTROL OF ACTIVE ENGINE MOUNT SYSTEM by Yong-Wook Lee and Chong-Won Lee Cene fo Noise and Vibaion Conol (NOVIC) Depamen of Mechanical
To be submied o Jounal of Auomobile Engineeing DYNAMIC ANALYSIS AND CONTROL OF ACTIVE ENGINE MOUNT SYSTEM by Yong-Wook Lee and Chong-Won Lee Cene fo Noise and Vibaion Conol (NOVIC) Depamen of Mechanical
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
ANALYSIS OF RECORD LINKAGE DECISION RULES. William E. Winkler, Rm , Bureau of the Census, Washington, DC 20223
 COMPARATIV ANALYSIS OF RCORD LINKAG DCISION RULS Willia. Winkle, R 3000-4, Bueau of he Census, Washingon, DC 20223 Keywods: M Algoih, Log, linea, Dependence, Sing Copaao Meic This pape povides an epiical
COMPARATIV ANALYSIS OF RCORD LINKAG DCISION RULS Willia. Winkle, R 3000-4, Bueau of he Census, Washingon, DC 20223 Keywods: M Algoih, Log, linea, Dependence, Sing Copaao Meic This pape povides an epiical
Homework 2 Solutions
 Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Mah 308 Differenial Equaions Fall 2002 & 2. See he las page. Hoework 2 Soluions 3a). Newon s secon law of oion says ha a = F, an we know a =, so we have = F. One par of he force is graviy, g. However,
Viscous Damping Summary Sheet No Damping Case: Damped behaviour depends on the relative size of ω o and b/2m 3 Cases: 1.
 Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
Viscous Daping: && + & + ω Viscous Daping Suary Shee No Daping Case: & + ω solve A ( ω + α ) Daped ehaviour depends on he relaive size of ω o and / 3 Cases:. Criical Daping Wee 5 Lecure solve sae BC s
Eigenvalue problems of rotor system with uncertain parameters
 Jounal of Mechanical Science and echnology 6 () () ~ www.singelink.co/conen/738-494x DOI.7/s6--8-5 Eigenvalue obles of oo syse wih unceain aaees Bao-Guo Liu * Insiue of Mechaonic Engineeing, Henan Univesiy
Jounal of Mechanical Science and echnology 6 () () ~ www.singelink.co/conen/738-494x DOI.7/s6--8-5 Eigenvalue obles of oo syse wih unceain aaees Bao-Guo Liu * Insiue of Mechaonic Engineeing, Henan Univesiy
Thus the force is proportional but opposite to the displacement away from equilibrium.
 Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
Chaper 3 : Siple Haronic Moion Hooe s law saes ha he force (F) eered by an ideal spring is proporional o is elongaion l F= l where is he spring consan. Consider a ass hanging on a he spring. In equilibriu
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Q & Particle-Gas Multiphase Flow. Particle-Gas Interaction. Particle-Particle Interaction. Two-way coupling fluid particle. Mass. Momentum.
 Paicle-Gas Muliphase Flow Fluid Mass Momenum Enegy Paicles Q & m& F D Paicle-Gas Ineacion Concenaion highe dilue One-way coupling fluid paicle Two-way coupling fluid paicle Concenaion highe Paicle-Paicle
Paicle-Gas Muliphase Flow Fluid Mass Momenum Enegy Paicles Q & m& F D Paicle-Gas Ineacion Concenaion highe dilue One-way coupling fluid paicle Two-way coupling fluid paicle Concenaion highe Paicle-Paicle
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Chapter 9 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
Chaper 9 Sinusoidal Seady Sae Analysis 9.-9. The Sinusoidal Source and Response 9.3 The Phasor 9.4 pedances of Passive Eleens 9.5-9.9 Circui Analysis Techniques in he Frequency Doain 9.0-9. The Transforer
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
TP A.14 The effects of cut angle, speed, and spin on object ball throw
 echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
echnical proof echnical proof TP A.14 The effecs of cu angle, speed, and spin on objec ball hrow supporing: The Illusraed Principles of Pool and illiards hp://billiards.colosae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore,
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Chapter 5. Canopy Spectral Invariants
 Chape 5 Canopy Specal Invaians. Inoducion.... Physical Pinciples of Specal Invaians... 3. RT Theoy of Specal Invaians... 5 4. Scaling Popeies of Specal Invaians... 6 Poble Ses... 39 Refeences... 4. Inoducion
Chape 5 Canopy Specal Invaians. Inoducion.... Physical Pinciples of Specal Invaians... 3. RT Theoy of Specal Invaians... 5 4. Scaling Popeies of Specal Invaians... 6 Poble Ses... 39 Refeences... 4. Inoducion
Risk tolerance and optimal portfolio choice
 Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
Risk oleance and opimal pofolio choice Maek Musiela BNP Paibas London Copoae and Invesmen Join wok wih T. Zaiphopoulou (UT usin) Invesmens and fowad uiliies Pepin 6 Backwad and fowad dynamic uiliies and
A Mathematical study of Two Species Amensalism Model With a Cover for the first Species by Homotopy Analysis Method
 Available online a www.pelagiaeseachlibay.co Advances in Applied Science Reseach,, 3 (3):8-86 A Maheaical sudy of Two Species Aensalis Model Wih a Cove fo he fis Species by Hooopy Analysis Mehod B. Sia
Available online a www.pelagiaeseachlibay.co Advances in Applied Science Reseach,, 3 (3):8-86 A Maheaical sudy of Two Species Aensalis Model Wih a Cove fo he fis Species by Hooopy Analysis Mehod B. Sia
Research on the Algorithm of Evaluating and Analyzing Stationary Operational Availability Based on Mission Requirement
 Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
Reseach on he Algoihm of Evaluaing and Analyzing Saionay Opeaional Availabiliy Based on ission Requiemen Wang Naichao, Jia Zhiyu, Wang Yan, ao Yilan, Depamen of Sysem Engineeing of Engineeing Technology,
EFFECT OF PERMISSIBLE DELAY ON TWO-WAREHOUSE INVENTORY MODEL FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH SHORTAGES
 Volume, ssue 3, Mach 03 SSN 39-4847 EFFEC OF PERMSSBLE DELAY ON WO-WAREHOUSE NVENORY MODEL FOR DEERORANG EMS WH SHORAGES D. Ajay Singh Yadav, Ms. Anupam Swami Assisan Pofesso, Depamen of Mahemaics, SRM
Volume, ssue 3, Mach 03 SSN 39-4847 EFFEC OF PERMSSBLE DELAY ON WO-WAREHOUSE NVENORY MODEL FOR DEERORANG EMS WH SHORAGES D. Ajay Singh Yadav, Ms. Anupam Swami Assisan Pofesso, Depamen of Mahemaics, SRM
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Analysis of Pressure Transient Tests in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
 Oil & Gas Reseach ISSN: 47-0518 Oil & Gas Reseach Gaal Rezk, Oil Gas Res 016, :3 DOI: 10.417/47-0518.100011 Reseach Aicle Aicle Open Open Access Analysis o Pessue Tansien Tess in Naually Facued Resevois
Oil & Gas Reseach ISSN: 47-0518 Oil & Gas Reseach Gaal Rezk, Oil Gas Res 016, :3 DOI: 10.417/47-0518.100011 Reseach Aicle Aicle Open Open Access Analysis o Pessue Tansien Tess in Naually Facued Resevois
NUMERICAL SIMULATION FOR NONLINEAR STATIC & DYNAMIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
 Join Inenaional Confeence on Compuing and Decision Making in Civil and Building Engineeing June 14-16, 26 - Monéal, Canada NUMERICAL SIMULATION FOR NONLINEAR STATIC & DYNAMIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS ABSTRACT
Join Inenaional Confeence on Compuing and Decision Making in Civil and Building Engineeing June 14-16, 26 - Monéal, Canada NUMERICAL SIMULATION FOR NONLINEAR STATIC & DYNAMIC STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS ABSTRACT
Oscillations. Simple Harmonic Motion The most basic oscillation, with sinusoidal motion, is called simple harmonic motion.
 14 Oscillaions his loudspeae cone geneaes sound waes by oscillaing bac and foh a audio fequencies. Looing head he goal of Chape 14 is o undesand syses ha oscillae wih siple haonic oion. Siple Haonic Moion
14 Oscillaions his loudspeae cone geneaes sound waes by oscillaing bac and foh a audio fequencies. Looing head he goal of Chape 14 is o undesand syses ha oscillae wih siple haonic oion. Siple Haonic Moion
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
 Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Applications of force vibration. Rotating unbalance Base excitation Vibration measurement devices
 Applicaios of foce viaio Roaig ualace Base exciaio Viaio easuee devices Roaig ualace 1 Roaig ualace: Viaio caused y iegulaiies i he disiuio of he ass i he oaig copoe. Roaig ualace 0 FBD 1 FBD x x 0 e 0
Applicaios of foce viaio Roaig ualace Base exciaio Viaio easuee devices Roaig ualace 1 Roaig ualace: Viaio caused y iegulaiies i he disiuio of he ass i he oaig copoe. Roaig ualace 0 FBD 1 FBD x x 0 e 0
ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS
 Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
Mem. Fac. Inegaed As and Sci., Hioshima Univ., Se. IV, Vol. 8 9-33, Dec. 00 ON 3-DIMENSIONAL CONTACT METRIC MANIFOLDS YOSHIO AGAOKA *, BYUNG HAK KIM ** AND JIN HYUK CHOI ** *Depamen of Mahemaics, Faculy
ON THE BEAT PHENOMENON IN COUPLED SYSTEMS
 8 h ASCE Specialy Conference on Probabilisic Mechanics and Srucural Reliabiliy PMC-38 ON THE BEAT PHENOMENON IN COUPLED SYSTEMS S. K. Yalla, Suden Member ASCE and A. Kareem, M. ASCE NaHaz Modeling Laboraory,
8 h ASCE Specialy Conference on Probabilisic Mechanics and Srucural Reliabiliy PMC-38 ON THE BEAT PHENOMENON IN COUPLED SYSTEMS S. K. Yalla, Suden Member ASCE and A. Kareem, M. ASCE NaHaz Modeling Laboraory,
Practice Problems - Week #4 Higher-Order DEs, Applications Solutions
 Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Pracice Probles - Wee #4 Higher-Orer DEs, Applicaions Soluions 1. Solve he iniial value proble where y y = 0, y0 = 0, y 0 = 1, an y 0 =. r r = rr 1 = rr 1r + 1, so he general soluion is C 1 + C e x + C
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
A note on characterization related to distributional properties of random translation, contraction and dilation of generalized order statistics
 PobSa Foum, Volume 6, July 213, Pages 35 41 ISSN 974-3235 PobSa Foum is an e-jounal. Fo eails please visi www.pobsa.og.in A noe on chaaceizaion elae o isibuional popeies of anom anslaion, conacion an ilaion
PobSa Foum, Volume 6, July 213, Pages 35 41 ISSN 974-3235 PobSa Foum is an e-jounal. Fo eails please visi www.pobsa.og.in A noe on chaaceizaion elae o isibuional popeies of anom anslaion, conacion an ilaion
Pressure Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Stress Analysis
 Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Control Volume Derivation
 School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
Module 4: Time Response of discrete time systems Lecture Note 2
 Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
An Open cycle and Closed cycle Gas Turbine Engines. Methods to improve the performance of simple gas turbine plants
 An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION BİLGE BOZKURT
 B. BOZKURT METU 6 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION BİLGE BOZKURT JANUARY 6 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL
B. BOZKURT METU 6 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION BİLGE BOZKURT JANUARY 6 DYNAMIC ION BEHAVIOR IN PLASMA SOURCE ION IMPLANTATION A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF NATURAL
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
Second-Order Boundary Value Problems of Singular Type
 JOURNAL OF MATEMATICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS 226, 4443 998 ARTICLE NO. AY98688 Seond-Order Boundary Value Probles of Singular Type Ravi P. Agarwal Deparen of Maheais, Naional Uniersiy of Singapore,
JOURNAL OF MATEMATICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS 226, 4443 998 ARTICLE NO. AY98688 Seond-Order Boundary Value Probles of Singular Type Ravi P. Agarwal Deparen of Maheais, Naional Uniersiy of Singapore,
A GENERAL METHOD TO STUDY THE MOTION IN A NON-INERTIAL REFERENCE FRAME
 The Inenaional onfeence on opuaional Mechanics an Viual Engineeing OME 9 9 OTOBER 9, Basov, Roania A GENERAL METHOD TO STUDY THE MOTION IN A NON-INERTIAL REFERENE FRAME Daniel onuache, Vlaii Mainusi Technical
The Inenaional onfeence on opuaional Mechanics an Viual Engineeing OME 9 9 OTOBER 9, Basov, Roania A GENERAL METHOD TO STUDY THE MOTION IN A NON-INERTIAL REFERENE FRAME Daniel onuache, Vlaii Mainusi Technical
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Technical Vibration - text 2 - forced vibration, rotational vibration
 Technicl Viion - e - foced viion, oionl viion 4. oced viion, viion unde he consn eenl foce The viion unde he eenl foce. eenl The quesion is if he eenl foce e is consn o vying. If vying, wh is he foce funcion.
Technicl Viion - e - foced viion, oionl viion 4. oced viion, viion unde he consn eenl foce The viion unde he eenl foce. eenl The quesion is if he eenl foce e is consn o vying. If vying, wh is he foce funcion.
Multivariate Auto-Regressive Model for Groundwater Flow Around Dam Site
 Mulivariae uo-regressive Model for Groundwaer Flow round Da Sie Yoshiada Mio ), Shinya Yaaoo ), akashi Kodaa ) and oshifui Masuoka ) ) Dep. of Earh Resources Engineering, Kyoo Universiy, Kyoo, 66-85, Japan.
Mulivariae uo-regressive Model for Groundwaer Flow round Da Sie Yoshiada Mio ), Shinya Yaaoo ), akashi Kodaa ) and oshifui Masuoka ) ) Dep. of Earh Resources Engineering, Kyoo Universiy, Kyoo, 66-85, Japan.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Probabilistic Models
 CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
Research Article Strategic Conditions for Opening an Internet Store and Pricing Policies in a Retailer-Dominant Supply Chain
 aheaical Pobles in Engineeing Volue 2015, Aicle ID 640719, 15 pages hp://dx.doi.og/10.1155/2015/640719 Reseach Aicle Saegic Condiions fo Opening an Inene Soe and Picing Policies in a Reaile-Doinan Supply
aheaical Pobles in Engineeing Volue 2015, Aicle ID 640719, 15 pages hp://dx.doi.og/10.1155/2015/640719 Reseach Aicle Saegic Condiions fo Opening an Inene Soe and Picing Policies in a Reaile-Doinan Supply
Equations to Calculate Characteristic Frequencies of Multiple Chamber Aligned in Parallel Cavity Resonator (MCAP-CR)
 MCAPE Equations to Calculate Chaacteistic Fequencies of Multiple Chabe Aligne in Paallel Cavity Resonato (MCAP-CR) Shigeu Suzui Mach, (Revise in ovebe, ). Peface It is necessay to solve the equations of
MCAPE Equations to Calculate Chaacteistic Fequencies of Multiple Chabe Aligne in Paallel Cavity Resonato (MCAP-CR) Shigeu Suzui Mach, (Revise in ovebe, ). Peface It is necessay to solve the equations of
M x t = K x F t x t = A x M 1 F t. M x t = K x cos t G 0. x t = A x cos t F 0
 Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
Forced oscillaions (sill undaped): If he forcing is sinusoidal, M = K F = A M F M = K cos G wih F = M G = A cos F Fro he fundaenal heore for linear ransforaions we now ha he general soluion o his inhoogeneous
AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M. KAMESWAR RAO AND K.P. RAVINDRAN Depamen of Mechanical Engineeing, Calicu Regional Engineeing College, Keala-67 6, INDIA. Absac:- We eploe
AN EVOLUTIONARY APPROACH FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS M. KAMESWAR RAO AND K.P. RAVINDRAN Depamen of Mechanical Engineeing, Calicu Regional Engineeing College, Keala-67 6, INDIA. Absac:- We eploe
Time-Space Model of Business Fluctuations
 Time-Sace Moel of Business Flucuaions Aleei Kouglov*, Mahemaical Cene 9 Cown Hill Place, Suie 3, Eobicoke, Onaio M8Y 4C5, Canaa Email: Aleei.Kouglov@SiconVieo.com * This aicle eesens he esonal view of
Time-Sace Moel of Business Flucuaions Aleei Kouglov*, Mahemaical Cene 9 Cown Hill Place, Suie 3, Eobicoke, Onaio M8Y 4C5, Canaa Email: Aleei.Kouglov@SiconVieo.com * This aicle eesens he esonal view of
