1 Temperature And Super Conductivity. 1.1 Defining Temperature
|
|
|
- Blaze Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Tempeaue And Supe Conduiviy 1.1 Defining Tempeaue In ode o fully undesand his wok on empeaue and he elaed effes i helps o have ead he Quanum Theoy and he Advaned Quanum Theoy piees of he Pi-Spae Theoy as i builds upon hese seions. I will assume he eade is familia wih he Wave Wihin Wave (WaWiW) design paen. Also I will assume he eade is familia wih he Pi-Spae Hamilonian noaion used o develop he Navie-Sokes fomulas. Tempeaue and Pessue ae elaed. Using he WaWiW noaion hese ae seen as vibaions on he Nx(0) laye aleing (loweing/aising) he wave ampliude. Reall ha hese Nx(0) onsideed o be he loal waves. Tha is o say hese ae he waves whih ae easie o measue in ou ealiy (e.g. empeaue and pessue fo example). Fo example we have wo waves ou of phase onibuing o Eleiiy and he Gaviy field on he Nx(0) laye (see he Advaned Quanum Theoy). The espeive ohogonal waves ae he Magnei waves and he Tubulene waves. Fo he puposes of his seion on empeaue we ll fous on hee disin Nx(0) wave disubanes. Ng(0) = Gaviy Mass wave whih aies empeaue Ne(0) = Elei Chage wave whih aies empeaue Addiionally empeaue is aied hough he ehe by means of he Sandad Model Bozons whih wee evese engineeed ino he WaWiW noaion. This empeaue vibaion is also a he Nb(0) laye whee b is any abiay Bozon. Tempeaue is seen as a vibaion whih is a sign of empeaue. How an we model his Pi-Spae empeaue vibaion using he WaWiW noaion? Le s ake any abiay Nx(0) wave onaining one o moe hild-waves. Fo simpliiy he diagams I ll show jus assume one paen and one hild wave bu in ealiy he nesed waves go deepe. Howeve hese ae suffiien o show he piniple of empeaue in aion. Fo now we don ae if i s an elei wave a Bozon aying empeaue a Femion o whaeve. We jus wan o show Lowe Tempeaue and Highe Tempeaue and Zeo Tempeaue. Lae I ll dive ino he deail of he Classial Laws Bose-Einsein Condensae Supe Fluidiy and Supe Conduiviy e; based on hese simple Pi-Spae empeaue diagams. All of he uen behavio we an see and measue exend fom hese simple oneps wih some addiional deail. 1. Highe Tempeaue (Highe Ampliude Wave size.0 Nx(0) Ampliude)
2 . Lowe Tempeaue (Lowe Ampliude Wave size 0.5 Nx(0) Ampliude) 3. Absolue Zeo (Zeo Ampliude Wave size 0.0 Nx(0) Ampliude)
3 Noe how he las empeaue example looks quie diffeen. As a onsequene I ll show how exeme empeaue hange ales he vey behavio of subsanes in ou ealiy.` 1. Aveage Moleula Kinei Enegy In Pi-Spae Le s map he aveage moleula kinei enegy o Pi-Spae and solve a sample poblem. Le s do i lassially and using Pi-Spae Tansvese Kinei Enegy KE 3 kt 1 mv Solving fo veloiy v KE m Solving fo Veloiy in Pi-Spae we have he fom 3 kt v Cos ASin 1 m * Le s solve a poblem Find Tansvese KE and Aveage Veloiy T = 7 Degees Celsius = 300 Kelvin Mass Helium = 6.65*10^-7 Kg Solve fo Classi KE = (3/) ( ^ 3) (300)= Solving fo Veloiy Sq[(.0*(6.*10^-1))/(6.65*10^-7)] V = = 1.37*10^3 m/j
4 Solve fo Pi-Spae V = (Cos[ASin[ 1 - (((6.1*10^-1)/(6.65*10^-7))/( ^))]])*( ) Gives us V = = 1.37*10^3 m/j 1.3 Tempeaue and Pessue In Pi-Spae In Pi-Spae hea in a fluid is on he loal plane whee he pailes ae. In ode o map o Pi- Spae we need o deemine wha he effe of Tempeaue on he wave funion is. The ideal gas law shows us he elaionship. pv nrt Volume says he same so we see ha ineased pessue auses ineased empeaue. A lage pessue maps o a lage poenial whih in his ase means lage wave ampliude. Addiionally a lage Tempeaue also means lage wave ampliude. Noe: When hese lage ampliudes a on one o moe pailes hey make hem smalle and give hem ineased Kinei Enegy. I have aleady solved he veloiy fomulas fo hese ases. We onside he use of Bolzmann s Consan k pv nkt Le s onside he loal plane one moe. We add he pessue Poenial. Nex we add he empeaue. v Cos ASin p Loal
5 Loal T k p v ASin Cos The wave funion is expessed diely hee. In he wave-wihin-wave design paen we an daw his as follows 1. Highe Tempeaue/Pessue Poenial (Highe Ampliude Wave size.0 Nx(0) Ampliude) Tempeaue and Pessue ae a he Nx(0) laye. If we dop he Kinei Componen (we have aleady solved his fo he Aveage Tansvese Kinei Enegy and Pio Pessue) and fous on he poenial fo a losed sysem we ae lef wih he wo values equal o one anohe. The eason fo his is ha hey shae he same undelying wave funion wihin he losed sysem wih a fixed volume. T k p T k p This is he same as nkt pv
6 1.4 Chales Law Tempeaue And Volume In Pi-Spae Tempeaue and Volume ae elaed in Chales Law. The pessue says onsan. We end up wih he following expession. Also his an be expessed as V T V1 V T1 T So fa we have no expessed Volume in he Pi-Spae fomula. How does his law elae o Pi-Spae? v Cos ASin p T k We know pessue is onsan so we an dop he Pessue Loal v Cos ASin T k Loal Nex we need o show he elaionship beween empeaue and volume. In Pi-Spae empeaue ales he aea of a Pi-Shell/aom. Also in ealie seions I also showed ha a Gaviaional poenial o Pessue ales he aea of a Pi-Shell. In my Gaviy wok I showed ha Gauss Law fo Gaviy showed ha Gaviy ales he Volume of a Sphee. This is foundaional. D s D. da Theefoe any aea hange o an aom auses a Volume hange. Wha Gauss Divegene heoem saes is ha an aea hange o a Sphee also ales is volume. If you ae unsue of his please ead he Quanum Theoy do o Gauss Theoem. Theefoe empeaue hange ales he volume of a Pi-Shell o Mole of aoms.
7 volume T k v ASin Cos Loal This is how we desibe Chales Law in Pi-Spae. 1.5 Boyles Law Pessue And Volume In Pi-Spae Pessue and Volume ae elaed in Boyles Law. The wo values ae invesely popoional o one anohe when empeaue is onsan in a losed sysem. 1 1 v p v p Fom his we an see ha pessue and volume ae invesely popoional o one anohe. How an we epesen his in Pi-Spae? This is easonably easy. Le s ake a look a he Pi- Spae equaion. Loal T k p v ASin Cos We know empeaue is onsan so we an dop he empeaue. Loal p v ASin Cos We know densiy is mass divided by volume. Loal v m p v ASin Cos Whih give us
8 v Cos ASin pv m Loal Theefoe we an see pv is a onsan. This is how we see Boyle s Law in Pi-Spae. Please noe ha he expession on he lef is he Kinei Componen elaed o any paiula pessue. I ve aleady solved his in he Quanum Theoy do elaing o Pio. 1.6 Fis Law of Themodynamis In Pi-Spae This is a onsevaion of enegy fo Themodynami sysems. I is usually fomulaed by saing ha he hange in he inenal enegy of a losed sysem is equal o he amoun of hea supplied o he sysem minus he wok done by he sysem on is suoundings. The law of onsevaion of enegy an be saed: The enegy of an isolaed sysem is onsan. In Chemisy we have du dq dw du dq dw Le s map his o he Pi-Spae fomula. U is he oal enegy of he sysem. Q is he hea of he sysem and W is he wok done. In Pi-Spae we use a Hamilonian o expess he oal enegy of a sysem whih is zeo v Cos ASin p T Loal 0 k The expession on he lef is he Kinei Componen. The expessions on he igh ae he Themodynami omponens. These ae empeaue and PV (pessue volume). So we an lose he pas we don need and show ha hey epesen a onsan enegy value U in a losed sysem. p T k U In he ase of a losed sysem whee hee is being wok done by i we an expess a gain in one pa o he hea as a loss on he ohe. Theefoe we an say
9 This is analogous o T k p U du dq dw Also if an ouside empeaue gain due o heaing is added hen he oal enegy of he oveall sysem ineases. This is analogous o T k p U du dq dw In ase one is wondeing whee Pessue and Volume is I aleady showed This gives us pv m p This mahes T k pv m U du dq pdv Noe: The wave funion an be dopped if fo example he obje is symmei. Please ake a look a how he shape of he onaine affes he wave funion fo Venui and so on in he Quanum Theoy do. 1.7 Seond Law of Themodynamis in Pi-Spae Hea moves fom ho o old. This indiaes he pefeed veo omponen of he waves whih ay he hea. Theefoe lage ampliude waves move o smalle ampliude waves. 1. Highe Tempeaue (Highe Ampliude Wave size.0 Nx(0) Ampliude)
10 . Lowe Tempeaue (Lowe Ampliude Wave size 0.5 Nx(0) Ampliude)
11 In paie his is simila o he Piniple of Leas Aion exep we ae dealing wih wave lengh as opposed o wave ampliude. Waves move owads a plae whee he smalles waves ae. When an obje falls unde Gaviy i moves owads he ene of Gaviy. This is whee he waves ae he shoes. High pessue moves o low pessue. This is whee he aoms have he leas vibaions. Eihe he shoe wave lengh o he shoe wave ampliude is he pefeed veo omponen. Theefoe we an say ha minimizing Nx(0) is he pefeed veo omponen. 1.8 Dawing of Ho/Cold Paile in Pi-Spae Hee is a ough hand dawn piue of a ho and old paile.
12 One an see fom he piue ha ineased empeaue means lage wave ampliudes on he paile in quesion. This in un ineases he vibaional naue of he paile. I also anslaes ino an aea hange on he paile whih an be mapped o an aea/volume hange. Remembe in Pi-Spae ha aea hange anslaes o Classial Enegy so we an hen use his in he Tanslaional Kinei Enegy fomula I deived ealie.
13 1.9 Radiaion and Lases in Pi-Spae Now ha we have esablished he idea of empeaue in Pi-Spae being ampliude elaed we an apply his piniple o Eleomagnei Radiaion. We fous on he Elei wave whih is Ne(0). In he Advaned Quanum Seion we defined he Elei pa of he wave as follows. The Phoon is a gauge Bozon. This is pey saighfowad o model. We define jus he Ne(x) Elei wave fo now. The Nm(x) Magnei wave is he same jus ohogonal. I s Ne(0). In his ase he ampliude is 1. This is analogous o a empeaue. The lage he ampliude he lage he empeaue i aies. Phoons an be plaed on op of one anohe so ha hei ampliude ineases and heefoe hei empeaue ineases. This is how lases wok. Phoons ae plaed on op of one anohe and he ampliude keeps geing lage; fo example if you plaed wo one op of one anohe you would have ampliude. Phoons ae heefoe seen as adiaion. Visually hey fom a beam of ligh. The wavelengh deemined he olo. The ampliude deemines he bighness and sengh of he beam. Now in ode o undesand he meaning of he Waage of a lase hee is how i woks in Pi- Spae. Le s imagine one has a lase whih has powe of 1Was wha does his mean? Tanslaed ino a Pi-Spae undesanding his means ha he ampliude of he adiaion beam while ineaing wih a mass of one kilogam ove one seond auses he mass o lose aea of 1/^. This is analogous o one Newon pe seond. The aleed ampliude hange auses an aea hange and he obje appeas o bun/mel if suffiienly song.
14 1.10 Bose Einsein Condensae Bose and Einsein woked on a saisial model fo low empeaues and ealized ha Bozons ondensae a ula low empeaues. In his piee I will no evese enginee he mah bu I will explain puely in Pi-Spae a a onepual level wha is happening. Cold aom physis is pobably he mos ineesing aea of he Pi-Spae Theoy in ems of wha one an do wih mae in his sae. Reall ha empeaue equaes o an ampliude a he Nx(0) laye. This is he Loal wave. By his I mean hese ae he waves ha ae mos eadily measuable in ou ealiy. Fo example we have he Ne(0) wave whih is he elei wave and i an ay hea. Le s daw his one moe fo an aom wih he Ng(x) waves. Reall ha Ng(0) is he gaviy wave whih auses he aom o have diamee d. Inside ha is he Ng(1) whih is he Mass wave. Theefoe Mass geneaes a Gaviy field. I ve explained his in he Advaned Quanum Theoy do. Le s lowe he empeaue of he aom. 1. Lowe Tempeaue (Lowe Ampliude Wave size 0.5 Ng(0) Ampliude Mass Ng(1) is 10 ampliude 1)
15 Wha happens if we lowe he empeaue of he Ng(0) o absolue zeo?. Absolue Zeo (Zeo Ampliude Wave size 0.0 Ng(0) Ampliude jus mass 10 Ng(1)) We now only have he Ng(1) mass waves whih is wha emains in he ondensae. We no longe have a paile bu lumps of Non-Loal Ng(1) waves. The aom sill exiss and has mass and a diamee d. I sill exiss in ou ealiy bu has eneed a new sae. The aoms lump ogehe and fom a ondensae. In Pi-Spae he way we desibe his is ha we have eaed a Non-Loal Wave Pool. Namely we ae dealing wih mae whih has no Ng(0) waves. When we look a i i should appea dak as Ne(0) aies phoons. Also beause i has no Ng(0) waves is has only he popeies of Ng(1) whih is he mass waves and deepe. I will explain he moe ineesing popeies lae like why ligh sops in Bose Einsein ondensae and so on lae. Impoanly fom a Quanum Mehanial view poin no infomaion is los inside a ondensae. I is meely soed in he lowe Ng(1) and deepe waves o simply held in plae unil anspo is available (e.g. eheaing). The ondensaes ae he way o undesand wha happens in a Blak Hole fo example. The diffeene of ouse is ha he wavelengh is no shoened in a ondensae.
16 All we ae essenially doing wih a Condensae is emoving o dampening down he wave ampliude and effeing wave loss a a paiula laye. This is all I wan o explain hee fo now. Moe mah will ome lae. All a Bose Einsein ondensae does is lowe he Nx(0) ampliudes. This may no seem like suh a big deal bu in Pi-Spae i opens up a whole new way o do hings Non-Loally whih may seem o defy ou inuiion of wha ou ealiy is. Howeve all one is eally doing is ansfeing eihe mae o infomaion on Non-Loal waves; namely Nx(1++) waves. Wha i looks like (Non-Loal wave pool) The Loal waves Ng(0) fom aound he ondensae and we ge a lage wave lengh aound he ondensae. I gows as he empeaue dops. To a eain exen i has dopped ou of ou ealiy bu in Pi-Spae he pefeed em is a Non-Loal wave pool. (diagams espefully boowed fom Keele do) Bose Einsein Mah Bose Einsein ondensae uses a saisial disibuion model. Hee I ll show how he uen mah ies in wih Pi-Spae. The saisial model uses he Exponen
17 f ( E) Ae 1 E kt 1 Also we know fom Eule ha e ix os x isin x Reall fom he advaned quanum seion ha Ne(x) and Ng(x) wee modeled as ou of phase wih one anohe. This is anohe wave of saying osine x and sine x. Theefoe he exponen in his fom epesens Ne(x) and Ng(x). Now I also saed ha empeaue is based on he wave ampliude whih maps o he value A in Bose Einsein disibuion. I an be aied by eihe he Elei Wave Ne(x) o Ng(x). Theefoe we an ewie he Bose Einsein disibuion so i is ompaible wih Pi-Spae f ( E) A os E kt 1 isin E kt 1 This fomula epesens boh he Ne(x) and Ng(x) whih ae ou of Phase wih one anohe. Also i only epesens he loal Ne(0) and Ng(0) waves. Ampliude A is 0 when absolue empeaue is 0. Reall fom he pevious diagams ha Ng(0) is modeled as a Sin wave heefoe Nx( 0) Ai sin E kt We an dop he imaginay axis i as his maps o he uni ile whih is he pah of he wave aound he paile. Nx( 0) Asin E kt The Pi-Spae inepeaion of his is ha Ampliude A size maps o he empeaue. A zeo empeaue maps o a zeo ampliude size. This fomula only oves he Nx(0) laye and Pi-Spae models he deepe inne waves. 1.1 Slowing Ligh In a Condensae In Pi-Spae
18 I will disuss he high level heoeial way ha ligh an be fozen in a Condensae in Pi- Spae. Please ead he Advaned Quanum do if you ae unsue of Ne(x) and Ng(x). Ligh is a gauge bozon and so exiss puely on Ne(0) I is a massless wave and a so-alled Loal wave on Laye 0 In ode fo ligh o move hough a medium hee needs o be anspo waves on he espeive Ne(0) laye in he medium he waves ae moving hough. This an be povided fo example by an aom a oom empeaue whih onains Ne(0) waves. I an heefoe absob and hen e-emi Ne(0) waves. I an also pass hough a anspaen maeial whih onains Ne(0) waves. Le s desibe he well known EIT expeimen (Eleomagneially indued anspaeny) whee ligh is fozen. The maeial (ould be sodium aoms o silion) is ooled o nea absolue zeo Kelvin. Theefoe he aoms povide no anspo suppo fo ligh Ne(0). A oupling beam is shone on he old aoms whih allows hem o vibae whih maps o a paiula pobabiliy ampliude A. In Pi-Spae his maps o Ne(0) waves on he old aoms o have a speifi ampliude. In Quanum Mehanis his is he n > noaion bu is essenially a pobabiliy ampliude. Nex he pobe pulse is sen hough he old aoms. This is a guage bozon wih a paiula ampliude on he Ne(0) laye. The ampliudes of he oupling beam and pobe ae oheen o hey pass hough he Ne(0) oupling waves on he old aoms and he aoms beome anspaen.
19 Howeve nex he oupling beam is uned off. The old aom no longe has suffiien ampliude suppo fo ligh. Theefoe he pobe pules Ne(0) ligh waves have no anspo waves on he Ne(0) layes of he aom so he pobe ligh wais unil Ne(0) anspo is available in he medium. Theefoe we have fozen ligh. Also he less Ne(0) waves hee ae on he old aoms he slowe he Ne(0) ligh waves move. Imagine a high speed highway whee ula old holes in he oad oasionally open up and he as (ligh waves) have o wai unil hey fill bak in. Ne(0) ligh waves need o move hough Ne(0) anspo waves povided by he medium. I hee ae no anspo waves you have augh hem. Typially we do his by feezing aoms. Noe: If one undesand his piniple hee is no eason why one anno go a level deepe and ale/dampen he ampliude of waves whih ay mass waves. I will desibe moe on he heoeial impliaions of his lae and heoeial ool suff hee. Clealy in his ase ligh does no ay mass so i is a moo poin fo now a leas.
Lecture 9. Transport Properties in Mesoscopic Systems. Over the last 1-2 decades, various techniques have been developed to synthesize
 eue 9. anspo Popeies in Mesosopi Sysems Ove he las - deades, vaious ehniques have been developed o synhesize nanosuued maeials and o fabiae nanosale devies ha exhibi popeies midway beween he puely quanum
eue 9. anspo Popeies in Mesosopi Sysems Ove he las - deades, vaious ehniques have been developed o synhesize nanosuued maeials and o fabiae nanosale devies ha exhibi popeies midway beween he puely quanum
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Physics 442. Electro-Magneto-Dynamics. M. Berrondo. Physics BYU
 Physis 44 Eleo-Magneo-Dynamis M. Beondo Physis BYU Paaveos Φ= V + Α Φ= V Α = = + J = + ρ J J ρ = J S = u + em S S = u em S Physis BYU Poenials Genealize E = V o he ime dependen E & B ase Podu of paaveos:
Physis 44 Eleo-Magneo-Dynamis M. Beondo Physis BYU Paaveos Φ= V + Α Φ= V Α = = + J = + ρ J J ρ = J S = u + em S S = u em S Physis BYU Poenials Genealize E = V o he ime dependen E & B ase Podu of paaveos:
4/3/2017. PHY 712 Electrodynamics 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 103
 PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
PHY 7 Eleodnais 9-9:50 AM MWF Olin 0 Plan fo Leue 0: Coninue eading Chap Snhoon adiaion adiaion fo eleon snhoon deies adiaion fo asonoial objes in iula obis 0/05/07 PHY 7 Sping 07 -- Leue 0 0/05/07 PHY
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Millennium Theory Equations Original Copyright 2002 Joseph A. Rybczyk Updated Copyright 2003 Joseph A. Rybczyk Updated March 16, 2006
 Millennim heoy Eqaions Oiginal Copyigh 00 Joseph A. Rybzyk Updaed Copyigh 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Updaed Mah 6, 006 Following is a omplee lis o he Millennim heoy o Relaiviy eqaions: Fo easy eeene, all eqaions
Millennim heoy Eqaions Oiginal Copyigh 00 Joseph A. Rybzyk Updaed Copyigh 003 Joseph A. Rybzyk Updaed Mah 6, 006 Following is a omplee lis o he Millennim heoy o Relaiviy eqaions: Fo easy eeene, all eqaions
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
KINGS UNIT- I LAPLACE TRANSFORMS
 MA5-MATHEMATICS-II KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS ACADEMIC YEAR - ( Even Semese ) QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: MA5 SUBJECT NAME: MATHEMATICS - II YEAR / SEM: I / II UNIT-
MA5-MATHEMATICS-II KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Punalkulam DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS ACADEMIC YEAR - ( Even Semese ) QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: MA5 SUBJECT NAME: MATHEMATICS - II YEAR / SEM: I / II UNIT-
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Engineering Accreditation. Heat Transfer Basics. Assessment Results II. Assessment Results. Review Definitions. Outline
 Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
Hea ansfe asis Febua 7, 7 Hea ansfe asis a Caeo Mehanial Engineeing 375 Hea ansfe Febua 7, 7 Engineeing ediaion CSUN has aedied pogams in Civil, Eleial, Manufauing and Mehanial Engineeing Naional aediing
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
An Open cycle and Closed cycle Gas Turbine Engines. Methods to improve the performance of simple gas turbine plants
 An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Representing Knowledge. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Properties of BNs. Independence? Reachability (the Bayes Ball) Example
 C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
C 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 epesening Knowledge ecue 17: ayes Nes III 10/25/2007 an Klein UC ekeley Popeies of Ns Independence? ayes nes: pecify complex join disibuions using simple local condiional
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Probabilistic Models
 CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
CS 188: Aificial Inelligence Fall 2007 Lecue 15: Bayes Nes 10/18/2007 Dan Klein UC Bekeley Pobabilisic Models A pobabilisic model is a join disibuion ove a se of vaiables Given a join disibuion, we can
Final Exam. Tuesday, December hours, 30 minutes
 an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
an Faniso ae Univesi Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 04 Final Exam Tuesda, Deembe 6 hous, 30 minues Name: Insuions. This is losed book, losed noes exam.. No alulaos of an kind ae allowed. 3. how all he alulaions.
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
Control Volume Derivation
 School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
School of eospace Engineeing Conol Volume -1 Copyigh 1 by Jey M. Seizman. ll ighs esee. Conol Volume Deiaion How o cone ou elaionships fo a close sysem (conol mass) o an open sysem (conol olume) Fo mass
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
Ferent equation of the Universe
 Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
PHYS-3301 Lecture 5. Chapter 2. Announcement. Sep. 12, Special Relativity. What about y and z coordinates? (x - direction of motion)
 Announemen Course webpage hp://www.phys.u.edu/~slee/33/ Tebook PHYS-33 Leure 5 HW (due 9/4) Chaper, 6, 36, 4, 45, 5, 5, 55, 58 Sep., 7 Chaper Speial Relaiiy. Basi Ideas. Consequenes of Einsein s Posulaes
Announemen Course webpage hp://www.phys.u.edu/~slee/33/ Tebook PHYS-33 Leure 5 HW (due 9/4) Chaper, 6, 36, 4, 45, 5, 5, 55, 58 Sep., 7 Chaper Speial Relaiiy. Basi Ideas. Consequenes of Einsein s Posulaes
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
5-1. We apply Newton s second law (specifically, Eq. 5-2). F = ma = ma sin 20.0 = 1.0 kg 2.00 m/s sin 20.0 = 0.684N. ( ) ( )
 5-1. We apply Newon s second law (specfcally, Eq. 5-). (a) We fnd he componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma cos 0.0 = 1.00kg.00m/s cos 0.0 = 1.88N. (b) The y componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma
5-1. We apply Newon s second law (specfcally, Eq. 5-). (a) We fnd he componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma cos 0.0 = 1.00kg.00m/s cos 0.0 = 1.88N. (b) The y componen of he foce s ( ) ( ) F = ma = ma
Mass Transfer Coefficients (MTC) and Correlations I
 Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Number of modes per unit volume of the cavity per unit frequency interval is given by: Mode Density, N
 SMES404 - LASER PHYSCS (LECTURE 5 on /07/07) Number of modes per uni volume of he aviy per uni frequeny inerval is given by: 8 Mode Densiy, N (.) Therefore, energy densiy (per uni freq. inerval); U 8h
SMES404 - LASER PHYSCS (LECTURE 5 on /07/07) Number of modes per uni volume of he aviy per uni frequeny inerval is given by: 8 Mode Densiy, N (.) Therefore, energy densiy (per uni freq. inerval); U 8h
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
The Wrong EHT Black Holes image and money; the Ferent image. Einstein and all the scientists did not understand Gravitation
 The Wong EHT Black Holes image and money; he Feen image. Einsein and all he scieniss did no undesand Gaviaion I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize -
The Wong EHT Black Holes image and money; he Feen image. Einsein and all he scieniss did no undesand Gaviaion I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize -
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Problem Set 9 Due December, 7
 EE226: Random Proesses in Sysems Leurer: Jean C. Walrand Problem Se 9 Due Deember, 7 Fall 6 GSI: Assane Gueye his problem se essenially reviews Convergene and Renewal proesses. No all exerises are o be
EE226: Random Proesses in Sysems Leurer: Jean C. Walrand Problem Se 9 Due Deember, 7 Fall 6 GSI: Assane Gueye his problem se essenially reviews Convergene and Renewal proesses. No all exerises are o be
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Pressure Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Stress Analysis
 Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
(Radiation Dominated) Last Update: 21 June 2006
 Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
P h y s i c s F a c t s h e e t
 P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Derivation of longitudinal Doppler shift equation between two moving bodies in reference frame at rest
 Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
AP Physics - Coulomb's Law
 AP Physics - oulomb's Law We ve leaned that electons have a minus one chage and potons have a positive one chage. This plus and minus one business doesn t wok vey well when we go in and ty to do the old
AP Physics - oulomb's Law We ve leaned that electons have a minus one chage and potons have a positive one chage. This plus and minus one business doesn t wok vey well when we go in and ty to do the old
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
8.5 Circles and Lengths of Segments
 LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
LenghofSegmen20052006.nb 1 8.5 Cicle and Lengh of Segmen In hi ecion we will how (and in ome cae pove) ha lengh of chod, ecan, and angen ae elaed in ome nal way. We will look a hee heoem ha ae hee elaionhip
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Chapter Q1. We need to understand Classical wave first. 3/28/2004 H133 Spring
 Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
Chaper Q1 Inroducion o Quanum Mechanics End of 19 h Cenury only a few loose ends o wrap up. Led o Relaiviy which you learned abou las quarer Led o Quanum Mechanics (1920 s-30 s and beyond) Behavior of
A Cosmological Model and Modifications to Einstein s Theory of Relativity
 Open Aess Liay Jounal A osmologial odel and odifiaions o Einsein s Theoy of Relaiiy Jianheng Liu Dongfang Boile o, Ld, Zigong, hina Reeied 6 Januay 6; aeped Feuay 6; pulished 5 Feuay 6 opyigh 6 y auho
Open Aess Liay Jounal A osmologial odel and odifiaions o Einsein s Theoy of Relaiiy Jianheng Liu Dongfang Boile o, Ld, Zigong, hina Reeied 6 Januay 6; aeped Feuay 6; pulished 5 Feuay 6 opyigh 6 y auho
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
2-d Motion: Constant Acceleration
 -d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
-d Moion: Consan Acceleaion Kinemaic Equaions o Moion (eco Fom Acceleaion eco (consan eloci eco (uncion o Posiion eco (uncion o The eloci eco and posiion eco ae a uncion o he ime. eloci eco a ime. Posiion
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 1 bis. Photo courtesy of Malene Thyssen,
 3.012 Fund of Ma Sci: Bonding Lecue 1 bis WAVE MECHANICS Phoo couesy of Malene Thyssen, www.mfoo.dk/malene/ 3.012 Fundamenals of Maeials Science: Bonding - Nicola Mazai (MIT, Fall 2005) Las Time 1. Playes:
3.012 Fund of Ma Sci: Bonding Lecue 1 bis WAVE MECHANICS Phoo couesy of Malene Thyssen, www.mfoo.dk/malene/ 3.012 Fundamenals of Maeials Science: Bonding - Nicola Mazai (MIT, Fall 2005) Las Time 1. Playes:
Add the transfer payments and subtract the total taxes from (1): Using these definitions, the above becomes: The Saving and Investment Equation:
 San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
San Fanio Sae Univei Mihael Ba ECON 30 Fall 06 Poblem e 5 Conumpion-Saving Deiion and Riadian Equivalene. (0 poin. Saving and Invemen equaion. a. Deive he aving and invemen equaion. The fomula fo GDP uing
Variance and Covariance Processes
 Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Vaiance and Covaiance Pocesses Pakash Balachandan Depamen of Mahemaics Duke Univesiy May 26, 2008 These noes ae based on Due s Sochasic Calculus, Revuz and Yo s Coninuous Maingales and Bownian Moion, Kaazas
Generalized The General Relativity Using Generalized Lorentz Transformation
 P P P P IJISET - Inernaional Journal of Innoaie Siene, Engineering & Tehnology, Vol. 3 Issue 4, April 6. www.ijise.om ISSN 348 7968 Generalized The General Relaiiy Using Generalized Lorenz Transformaion
P P P P IJISET - Inernaional Journal of Innoaie Siene, Engineering & Tehnology, Vol. 3 Issue 4, April 6. www.ijise.om ISSN 348 7968 Generalized The General Relaiiy Using Generalized Lorenz Transformaion
Consider a Binary antipodal system which produces data of δ (t)
 Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Problem 1. Part b. Part a. Wayne Witzke ProblemSet #1 PHY 361. Calculate x, the expected value of x, defined by
 Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
Poblem Pat a The nomal distibution Gaussian distibution o bell cuve has the fom f Ce µ Calculate the nomalization facto C by equiing the distibution to be nomalized f Substituting in f, defined above,
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - State Feedback Design
 Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Part I. Labor- Leisure Decision (15 pts)
 Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
Eon 509 Sping 204 Final Exam S. Paene Pa I. Labo- Leisue Deision (5 ps. Conside he following sai eonom given b he following equaions. Uili ln( H ln( l whee H sands fo he househ f f Poduion: Ah whee f sands
(a) Unde zeo-bias conditions, thee ae no lled states on one side of the junction which ae at the same enegy as the empty allowed states on the othe si
 1 Esaki Diode hen the concentation of impuity atoms in a pn-diode is vey high, the depletion laye width is educed to about 1 nm. Classically, a caie must have an enegy at least equal to the potential-baie
1 Esaki Diode hen the concentation of impuity atoms in a pn-diode is vey high, the depletion laye width is educed to about 1 nm. Classically, a caie must have an enegy at least equal to the potential-baie
2. v = 3 4 c. 3. v = 4c. 5. v = 2 3 c. 6. v = 9. v = 4 3 c
 Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Properties of Logarithms. Properties. Properties. log. Exponential. Logarithmic.
 Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
Eponenial and Logaihmic Equaions and Popeies of Logaihms Popeies Eponenial a a s = a +s a /a s = a -s (a ) s = a s a b = (ab) Logaihmic log s = log + logs log/s = log - logs log s = s log log a b = loga
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
The k-filtering Applied to Wave Electric and Magnetic Field Measurements from Cluster
 The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
Scholars Research Library. Archives of Applied Science Research, 2014, 6 (5):36-41 (
 Available online a wwwsholaseseahlibayom Ahives o Applied Siene Reseah 4 6 5:6-4 hp://sholaseseahlibayom/ahivehml ISSN 975-58X CODEN USA AASRC9 Einsein s equaions o moion o es pailes exeio o spheial disibuions
Available online a wwwsholaseseahlibayom Ahives o Applied Siene Reseah 4 6 5:6-4 hp://sholaseseahlibayom/ahivehml ISSN 975-58X CODEN USA AASRC9 Einsein s equaions o moion o es pailes exeio o spheial disibuions
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
( ) is the stretch factor, and x the
 (Lecures 7-8) Liddle, Chaper 5 Simple cosmological models (i) Hubble s Law revisied Self-similar srech of he universe All universe models have his characerisic v r ; v = Hr since only his conserves homogeneiy
(Lecures 7-8) Liddle, Chaper 5 Simple cosmological models (i) Hubble s Law revisied Self-similar srech of he universe All universe models have his characerisic v r ; v = Hr since only his conserves homogeneiy
Chapter Finite Difference Method for Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Chape 8.7 Finie Diffeence Mehod fo Odinay Diffeenial Eqaions Afe eading his chape, yo shold be able o. Undesand wha he finie diffeence mehod is and how o se i o solve poblems. Wha is he finie diffeence
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Algebra-based Physics II
 lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
lgebabased Physics II Chapte 19 Electic potential enegy & The Electic potential Why enegy is stoed in an electic field? How to descibe an field fom enegetic point of view? Class Website: Natual way of
Field due to a collection of N discrete point charges: r is in the direction from
 Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
PHYS 2135 Exam I February 13, 2018
 Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
Amit Mehra. Indian School of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA Vijay Mookerjee
 RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY
 Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
PHYSICS 4E FINAL EXAM SPRING QUARTER 2010 PROF. HIRSCH JUNE 11 Formulas and constants: hc =12,400 ev A ; k B. = hf " #, # $ work function.
 PHYSICS 4E FINAL EXAM SPRING QUARTER 1 Fomulas and constants: hc =1,4 ev A ; k B =1/11,6 ev/k ; ke =14.4eVA ; m e c =.511"1 6 ev ; m p /m e =1836 Relativistic enegy - momentum elation E = m c 4 + p c ;
PHYSICS 4E FINAL EXAM SPRING QUARTER 1 Fomulas and constants: hc =1,4 ev A ; k B =1/11,6 ev/k ; ke =14.4eVA ; m e c =.511"1 6 ev ; m p /m e =1836 Relativistic enegy - momentum elation E = m c 4 + p c ;
s = rθ Chapter 10: Rotation 10.1: What is physics?
 Chape : oaon Angula poson, velocy, acceleaon Consan angula acceleaon Angula and lnea quanes oaonal knec enegy oaonal nea Toque Newon s nd law o oaon Wok and oaonal knec enegy.: Wha s physcs? In pevous
Chape : oaon Angula poson, velocy, acceleaon Consan angula acceleaon Angula and lnea quanes oaonal knec enegy oaonal nea Toque Newon s nd law o oaon Wok and oaonal knec enegy.: Wha s physcs? In pevous
Traveling Waves. Chapter Introduction
 Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
Chaper 4 Traveling Waves 4.1 Inroducion To dae, we have considered oscillaions, i.e., periodic, ofen harmonic, variaions of a physical characerisic of a sysem. The sysem a one ime is indisinguishable from
- If one knows that a magnetic field has a symmetry, one may calculate the magnitude of B by use of Ampere s law: The integral of scalar product
 11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
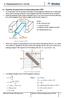 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
Math 333 Problem Set #2 Solution 14 February 2003
 Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
AP Physics Electric Potential Energy
 AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
AP Physics lectic Potential negy Review of some vital peviously coveed mateial. The impotance of the ealie concepts will be made clea as we poceed. Wok takes place when a foce acts ove a distance. W F
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
